Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dental Extraction of Patients at Risk of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Entry and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Clinical and Surgical Procedures
2.3.1. First Evaluation
2.3.2. Second Evaluation
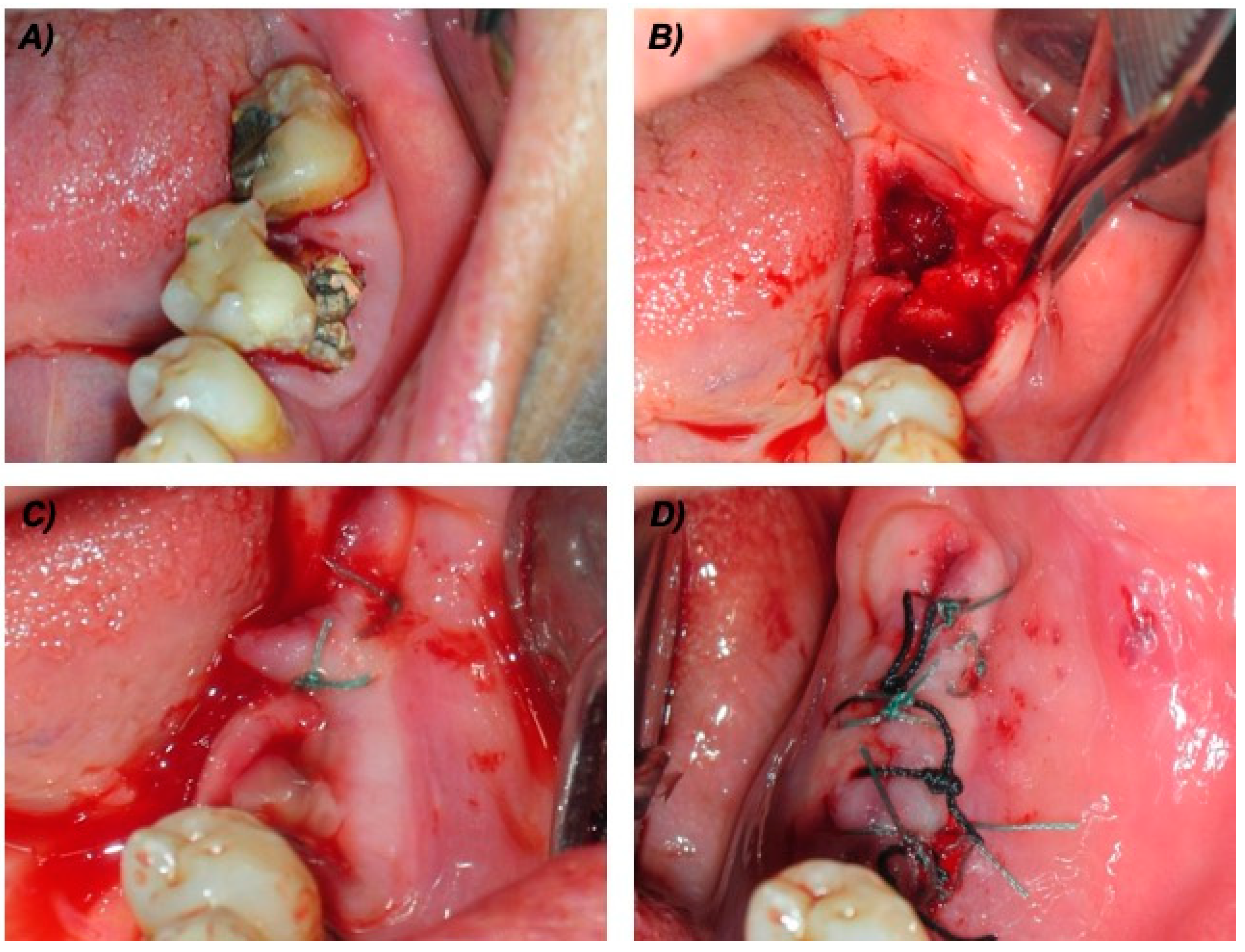
2.3.3. Surgical Dental Extraction
2.3.4. Follow-Up
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Historical Controls
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bedogni, A.; Campisi, G.; Fusco, V. Medication Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ); Qeios: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Campisi, G.; Fedele, S.; Fusco, V.; Pizzo, G.; Di Fede, O.; Bedogni, A. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, risk reduction and treatment strategies of jaw osteonecrosis in cancer patients exposed to antiresorptive agents. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E. Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: A growing epidemic. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, V.; Santini, D.; Armento, G.; Tonini, G.; Campisi, G. Osteonecrosis of jaw beyond antiresorptive (bone-targeted) agents: New horizons in oncology. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauceri, R.; Panzarella, V.; Morreale, I.; Campisi, G. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in a cancer patient receiving lenvatinib. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 1530–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolatou-Galitis, O.; Kouri, M.; Papadopoulou, E.; Vardas, E.; Galiti, D.; Epstein, J.B.; Elad, S.; Campisi, G.; Tsoukalas, N.; Bektas-Kayhan, K.; et al. Osteonecrosis of the jaw related to non-antiresorptive medications: A systematic review. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Fantasia, J.; Goodday, R.; Aghaloo, T.; Mehrotra, B.; O’Ryan, F. American association of oral and maxillofacial surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw—2014 update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1938–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisi, M.; La Ferla, F.; Karapetsa, D.; Gennai, S.; Miccoli, M.; Baggiani, A.; Graziani, F.; Gabriele, M. Risk factors influencing BRONJ staging in patients receiving intravenous bisphosphonates: A multivariate analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fede, O.; Panzarella, V.; Mauceri, R.; Fusco, V.; Bedogni, A.; Lo Muzio, L.; Board, S.O.; Campisi, G. The dental management of patients at risk of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: New paradigm of primary prevention. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2684924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Hiraga, T.; Ueda, A.; Wang, L.; Matsumoto-Nakano, M.; Hata, K.; Yatani, H.; Yoneda, T. Zoledronic acid delays wound healing of the tooth extraction socket, inhibits oral epithelial cell migration, and promotes proliferation and adhesion to hydroxyapatite of oral bacteria, without causing osteonecrosis of the jaw, in mice. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2010, 28, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milstein, D.M.J.; Lindeboom, J.A.H.; Ince, C. The influence of zoledronic acid and cyclophosphamide on microcirculation regeneration in healing oral mucosal flaps. Arch. Oral Biol. 2011, 56, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.; Schreyer, C.; Hafner, S.; Mast, G.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Stürzenbaum, S.; Pautke, C. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws—Characteristics, risk factors, clinical features, localization and impact on oncological treatment. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, P.L.; Nicoletti, P.; Shen, Y.; Porter, S.; Fedele, S. Pharmacogenetics of Bisphosphonate-associated Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 27, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodem, J.P.; Kargus, S.; Eckstein, S.; Saure, D.; Engel, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Freudlsperger, C. Incidence of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in high-risk patients undergoing surgical tooth extraction. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.; Troltzsch, M.; Jambrovic, V.; Panya, S.; Probst, F.; Ristow, O.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Pautke, C. Tooth extraction in patients receiving oral or intravenous bisphosphonate administration: A trigger for BRONJ development? J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beth-Tasdogan, N.H.; Mayer, B.; Hussein, H.; Zolk, O. Interventions for managing medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 10, CD012432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz-Freitas, M.; Limeres, J. Prevention of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws secondary to tooth extractions. A systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2016, 21, e250–e259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Gallesio, G.; Mozzati, M. Autologous platelet concentrates for bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw treatment and prevention. A systematic review of the literature. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Licata, M.E.; Polizzi, B.; Campisi, G. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in dental and oral surgery: From the wound healing to bone regeneration. Immun. Ageing 2013, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Bucchi, C.; Lolato, A.; Corbella, S.; Testori, T.; Taschieri, S. Healing of Postextraction Sockets Preserved With Autologous Platelet Concentrates. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1601–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Andia, I.; Zumstein, M.A.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Pinto, N.R.; Bielecki, T. Classification of platelet concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF) for topical and infiltrative use in orthopedic and sports medicine: Current consensus, clinical implications and perspectives. Muscles. Ligaments Tendons J. 2014, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Corso, M.; Vervelle, A.; Simonpieri, A.; Jimbo, R.; Inchingolo, F.; Sammartino, G.; Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M. Current knowledge and perspectives for the use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) in oral and maxillofacial surgery part 1: Periodontal and dentoalveolar surgery. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1207–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saia, G.; Blandamura, S.; Bettini, G.; Tronchet, A.; Totola, A.; Bedogni, G.; Ferronato, G.; Nocini, P.F.; Bedogni, A. Occurrence of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw After Surgical Tooth Extraction. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlito, S.; Puzzo, S.; Liardo, C. Preventive protocol for tooth extractions in patients treated with zoledronate: A case series. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heufelder, M.J.; Hendricks, J.; Remmerbach, T.; Frerich, B.; Hemprich, A.; Wilde, F. Principles of oral surgery for prevention of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2014, 117, e429–e435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Bielsa, J.M.; Bagán, J.V.; Murillo, J.; Díaz, J.M.; Asensio, L. Risk of developing BRONJ among patients exposed to intravenous bisphosphonates following tooth extraction. Quintessence Int. (Berlin) 2014, 45, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzati, M.; Arata, V.; Gallesio, G. Tooth extraction in osteoporotic patients taking oral bisphosphonates. Osteoporos. Int. 2013, 24, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, A.; Campisi, G.; Fusco, V.; Agrillo, A. Raccomandazioni Clinico-Terapeutiche Sull’osteonecrosi Delle Ossa Mascellari Associata A Bisfosfonati E Sua Prevenzione; Cleup: Padova, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bedogni, A.; Fusco, V.; Agrillo, A.; Campisi, G. Learning from experience. Proposal of a refined definition and staging system for bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ). Oral Dis. 2012, 18, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarom, N.; Shapiro, C.L.; Peterson, D.E.; Van Poznak, C.H.; Bohlke, K.; Ruggiero, S.L.; Migliorati, C.A.; Khan, A.; Morrison, A.; Anderson, H.; et al. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: MASCC/ISOO/ASCO clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2270–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolatou-Galitis, O.; Papadopoulou, E.; Vardas, E.; Kouri, M.; Galiti, D.; Galitis, E.; Alexiou, K.; Tsiklakis, K.; Ardavanis, A.; Razis, E.; et al. Alveolar bone histological necrosis observed prior to extractions in patients, who received bone targeting agents. Oral Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolatou-Galitis, O.; Razis, E.; Galiti, D.; Galitis, E.; Labropoulos, S.; Tsimpidakis, A.; Sgouros, J.; Karampeazis, A.; Migliorati, C. Periodontal disease preceding osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) in cancer patients receiving antiresorptives alone or combined with targeted therapies: Report of 5 cases and literature review. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 120, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutome, S.; Hayashida, S.; Funahara, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Yanamoto, S.; Umeda, M. Factors affecting development of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer patients receiving high-dose bisphosphonate or denosumab therapy: Is tooth extraction a risk factor? PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Hayashida, S.; Kondo, E.; Takeda, Y.; Miyamoto, H.; Kawaoka, Y.; Ueda, N.; Iwata, E.; Nakahara, H.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw afte tooth extraction in cancer patients: A multicenter retrospective study. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, E.L.; Lin, Y.-L.; Saunders, M.M. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A mechanobiology perspective. Bone Rep. 2018, 8, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozzati, M.; Arata, V.; Gallesio, G. Tooth extraction in patients on zoledronic acid therapy. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.-G.; Hwang, J.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.H.; Na, J.Y.; Han, S.-S. Risk factors of osteonecrosis of the jaw after tooth extraction in osteoporotic patients on oral bisphosphonates. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2017, 47, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, A.; Saia, G.; Bettini, G.; Tronchet, A.; Totola, A.; Bedogni, G.; Ferronato, G.; Nocini, P.F.; Blandamura, S. Long-term outcomes of surgical resection of the jaws in cancer patients with bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrgidis, A.; Koloutsos, G.; Vahtsevanos, K. Treatment protocols of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. Head Neck 2009, 1112–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzati, M.; Gallesio, G.; Arata, V.; Pol, R.; Scoletta, M. Platelet-rich therapies in the treatment of intravenous bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A report of 32 cases. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, F.; Guida, A.; Aversa, C.; Pavone, E.; Di Costanzo, G.; Ramaglia, L.; Ionna, F.; Di Costanzo, G.; Ramaglia, L.; Ionna, F. Platelet Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: Personal Experience and Review of the Literature. Int. J. Dent. 2014, 2014, 298945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauceri, R.; Panzarella, V.; Maniscalco, L.; Bedogni, A.; Licata, M.E.; Albanese, A.; Toia, F.; Cumbo, E.M.G.; Mazzola, G.; Di Fede, O.; et al. Conservative Surgical Treatment of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw with Er, Cr: YSGG Laser and Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Longitudinal Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaka, T.; Ohga, N.; Yamazaki, Y.; Sato, J.; Satoh, C.; Kitagawa, Y. Platelet-rich fibrin may reduce the risk of delayed recovery in tooth-extracted patients undergoing oral bisphosphonate therapy: A trial study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoletta, M.; Arduino, P.G.; Pol, R.; Arata, V.; Silvestri, S.; Chiecchio, A.; Mozzati, M. Initial experience on the outcome of teeth extractions in intravenous bisphosphonate-treated patients: A cautionary report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoletta, M.; Arata, V.; Arduino, P.G.; Lerda, E.; Chiecchio, A.; Gallesio, G.; Scully, C.; Mozzati, M. Tooth extractions in intravenous bisphosphonate-treated patients: A refined protocol. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Step | Procedure |
|---|---|
| 1th | First evaluation: • Clinical Evaluation • Computer Tomography (CT) prescription (when ONJ was suspected) |
| 2nd | Second evaluation: • Pre-operatory medical therapy prescription • Ultrasonic periodontal debridement (when required) and oral hygiene instructions • Platelet rich-plasma (PRP) preparation |
| 3rd | Surgical procedures • Dental extraction • PRP application • Flap suture |
| 4th | Suture removal and clinical control |
| 5th | Follow-ups at 15 days and at one-three-six-twelve-eighteen-twenty-four months |
| Pre- | Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium *: 1 gr per os 3x daily starting 1 day before. Metronidazole: 250 mg per os 2x daily starting 1 day before. Chlorhexidine 0.2% mouthwashes 30 mL swished up to 60 s, 3x daily 7 days before. |
| Post- | Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium: 1 gr per os 3x daily for 7 days. Metronidazole: 250 mg per os 2x daily for 7 days. Chlorhexidine 0.2% mouthwashes 30 mL swished up to 60 s, 3x daily 15 days post-operatively. Local application of sodium-hyaluronate 3x daily 10 days post-operatively. |
| Age (yr) | 72.35 (±7.19) |
| Gender (male/female) | 4/16 |
| ONC patients assuming zoledronic acid | 6 |
| Zoledronic acid cumulative dose (mg) | 142 (±80.85) |
| Systemic corticosteroid therapy (yes/no) | 3/6 |
| OST patients assuming BPs | 14 |
| Alendronic acid (yes/no) | 6/14 |
| Alendronic acid cumulative dose (mg) | 46,040 (±17.13) |
| Clodronic acid (yes/no) | 4/14 |
| Clodronic acid cumulative dose (mg) | 37,800 (±9.39) |
| Ibandronic acid (yes/no) | 2/14 |
| Ibandronic acid cumulative dose (mg) | 1 pt) 5500 2 pt) 18,000 |
| Risedronic acid (yes/no) | 2/14 |
| Risedronic acid cumulative dose (mg) | 1 pt) 5850 2 pt) 10,800 |
| N Extraction (%) | Maxilla/Mandible | Site | N (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONC group | 24 (38.09%) | Maxilla | Anterior | 3 (4.8%) |
| Posterior | 10 (15.9) | |||
| Mandible | Anterior | 2 (3.2%) | ||
| Posterior | 9 (14.3%) | |||
| OST group | 39 (61.9%) | Maxilla | Anterior | 5 (7.9%) |
| Posterior | 15 (23.8%) | |||
| Mandible | Anterior | 7 (11.1%) | ||
| Posterior | 12 (19%) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mauceri, R.; Panzarella, V.; Pizzo, G.; Oteri, G.; Cervino, G.; Mazzola, G.; Di Fede, O.; Campisi, G. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dental Extraction of Patients at Risk of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4487. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134487
Mauceri R, Panzarella V, Pizzo G, Oteri G, Cervino G, Mazzola G, Di Fede O, Campisi G. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dental Extraction of Patients at Risk of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(13):4487. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134487
Chicago/Turabian StyleMauceri, Rodolfo, Vera Panzarella, Giuseppe Pizzo, Giacomo Oteri, Gabriele Cervino, Giuseppina Mazzola, Olga Di Fede, and Giuseppina Campisi. 2020. "Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dental Extraction of Patients at Risk of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study" Applied Sciences 10, no. 13: 4487. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134487
APA StyleMauceri, R., Panzarella, V., Pizzo, G., Oteri, G., Cervino, G., Mazzola, G., Di Fede, O., & Campisi, G. (2020). Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dental Extraction of Patients at Risk of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study. Applied Sciences, 10(13), 4487. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134487












