Inhibitory Effects of 4-Hexylresorcinol on Root Resorption Induced by Orthodontic Tooth Movement
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
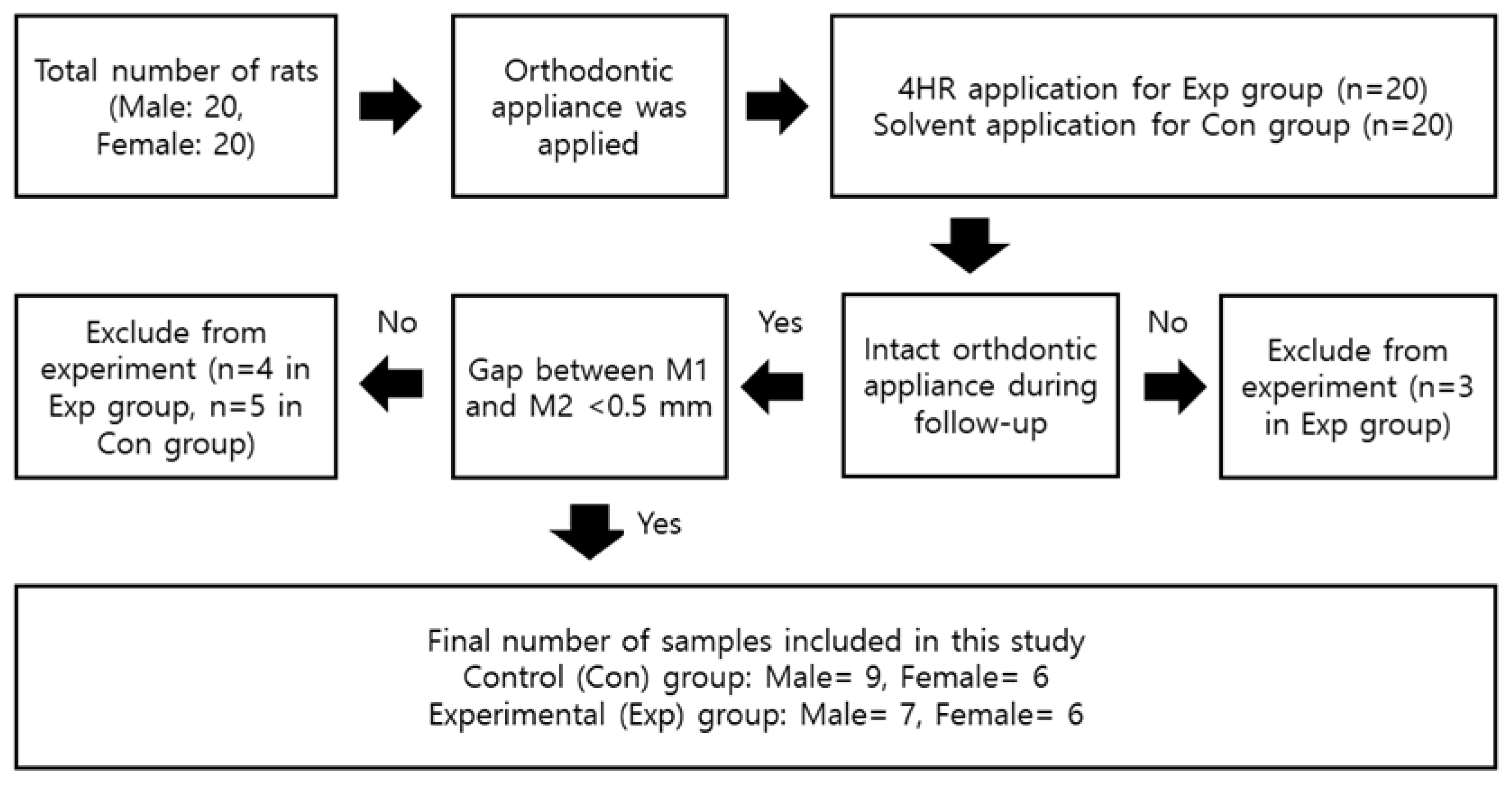
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Plain X-ray and Micro-Computerized Tomography (mCT)
2.3. Immunohistochemical Determination and Western Blot Analysis in Mandible Samples
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
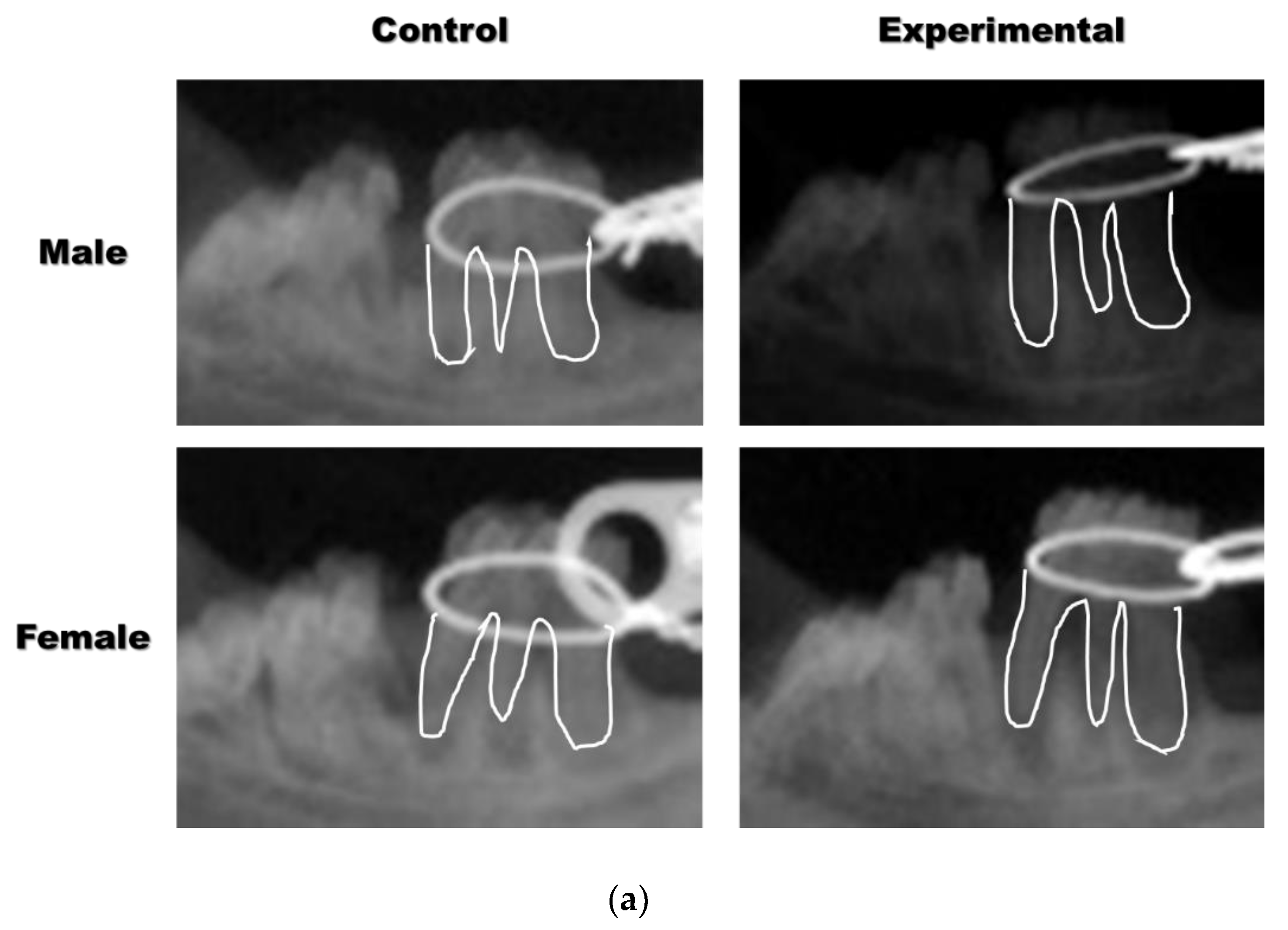
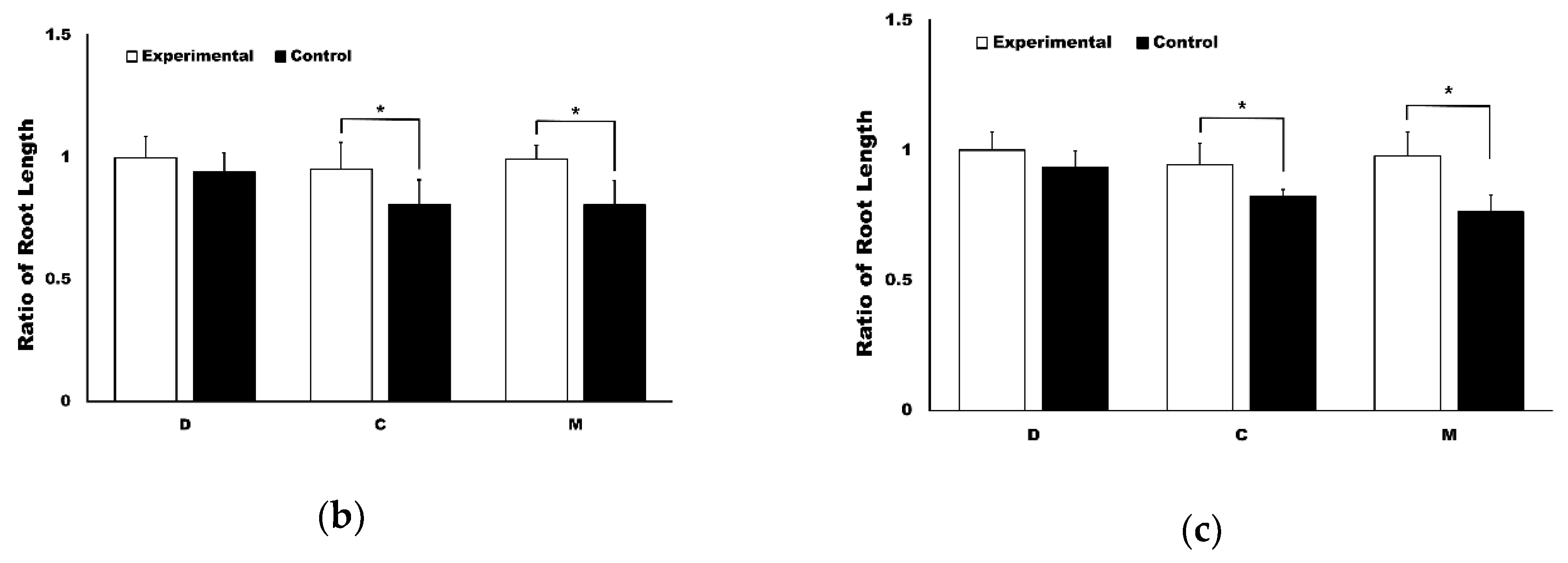
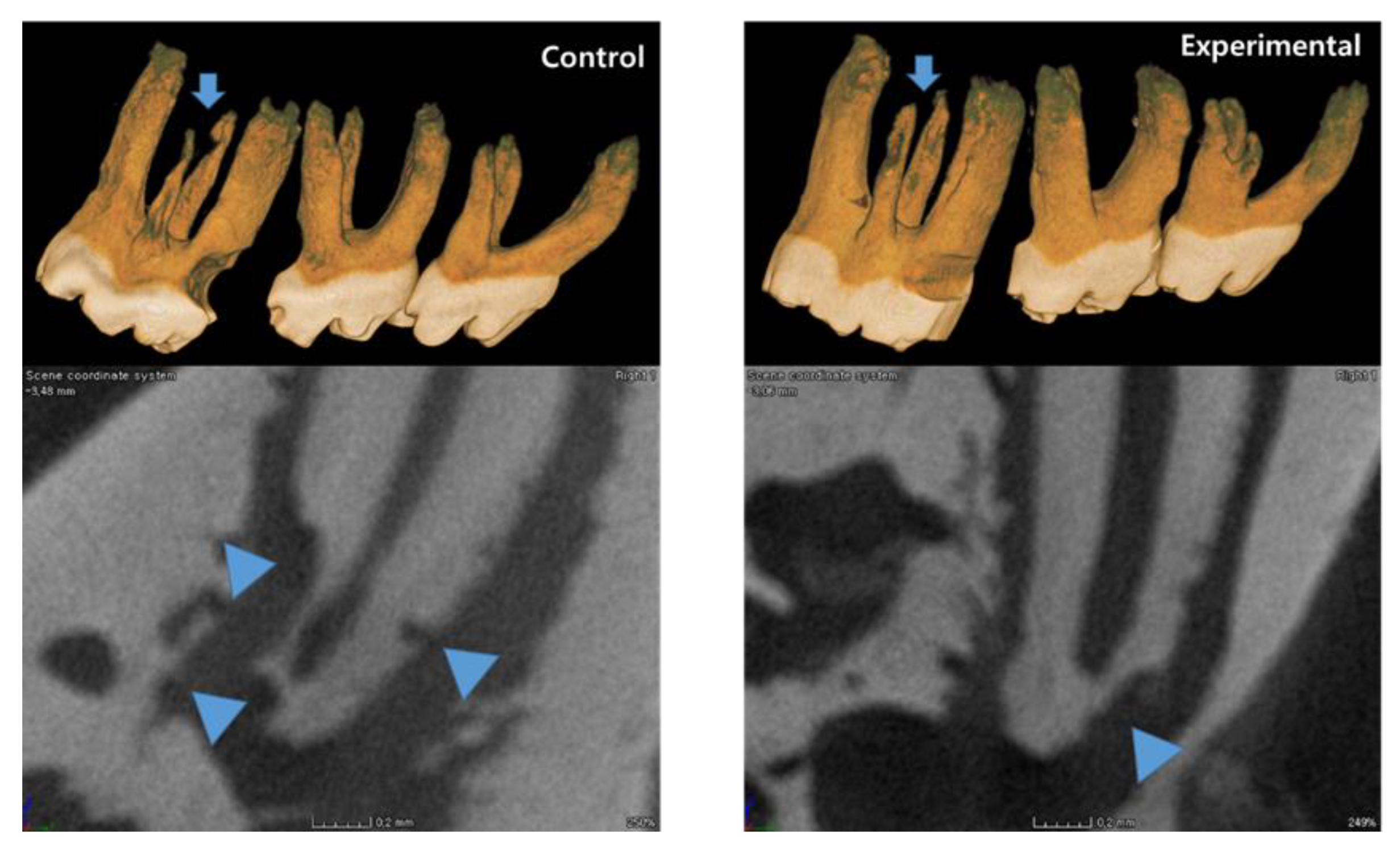
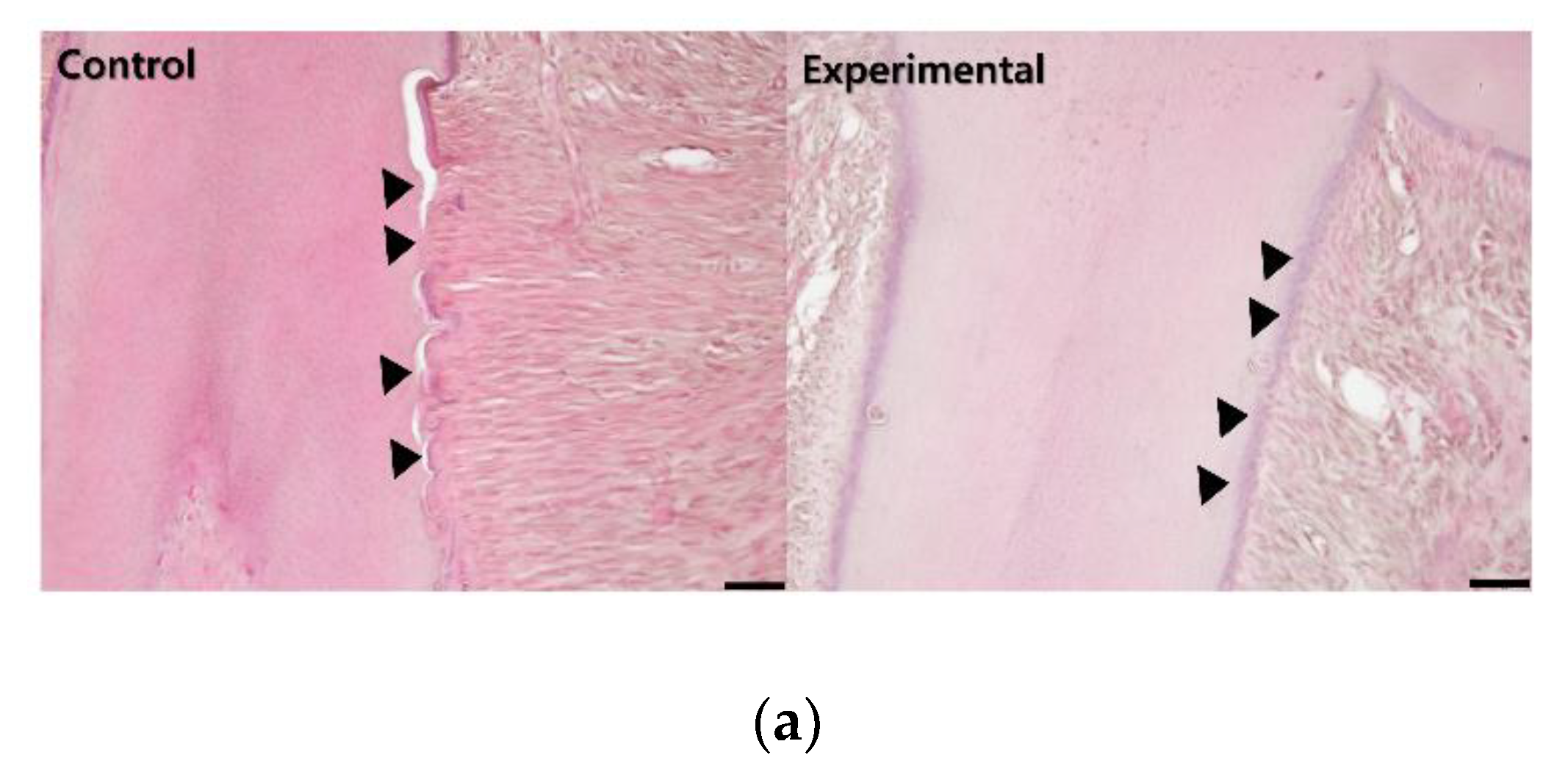
3.1. The Application of 4HR Inhibited Root Resorption during OTM
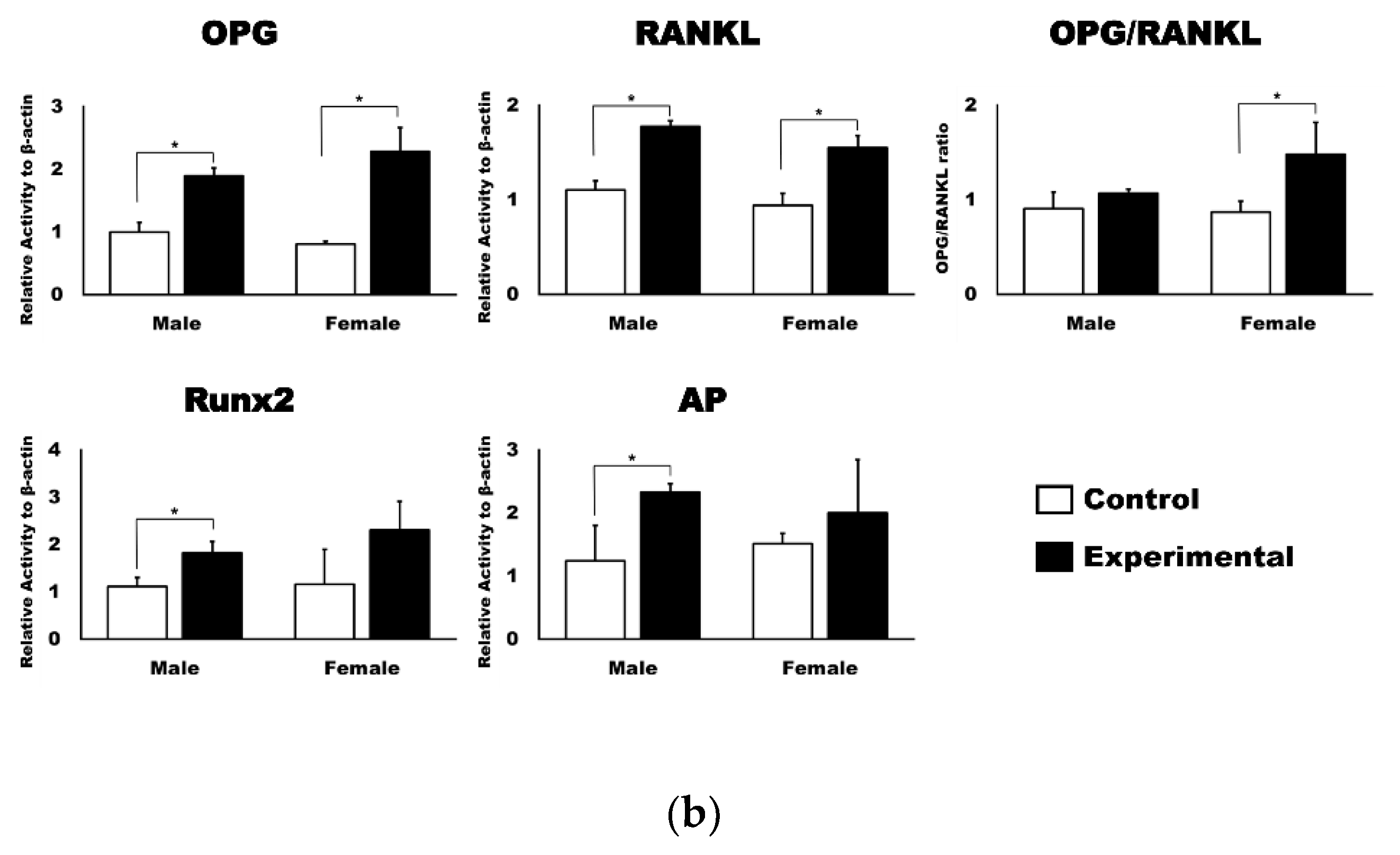
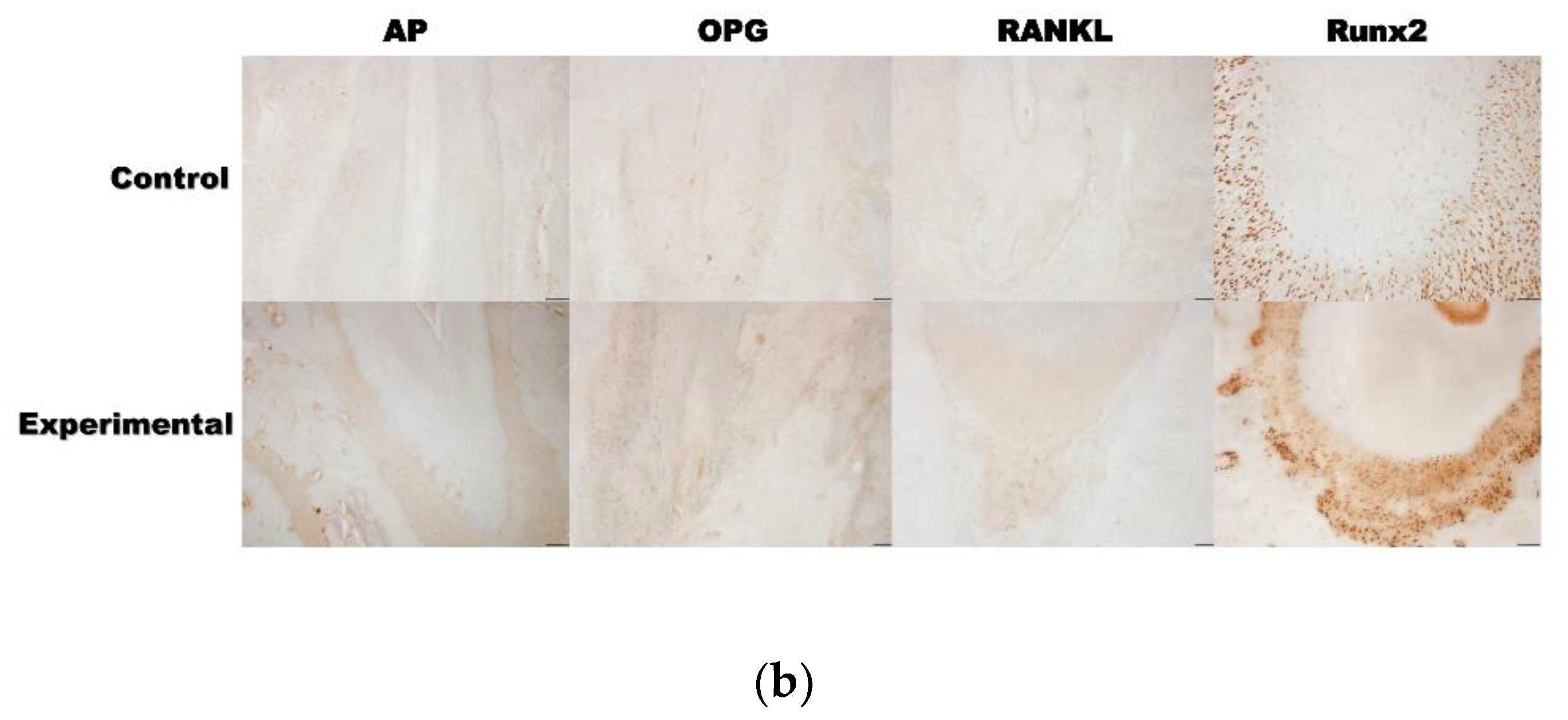
3.2. 4HR Increased OPG, RANKL, AP, and Runx2 Expression in Tissue
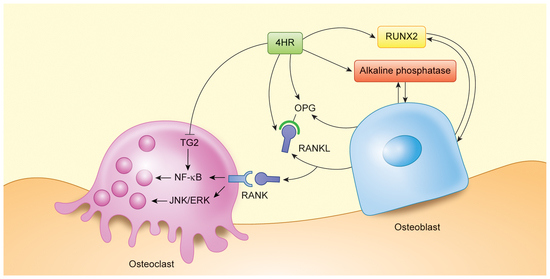
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, G.J.; Keeling, S.D.; Wronski, T.J. Histomorphometric study of alveolar bone turnover in orthodontic tooth movement. Bone 1991, 12, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.E.; Huja, S.; Roberts, J.A. Bone modeling: Biomechanics, molecular mechanisms, and clinical perspectives. Semin. Orthod. 2004, 10, 123–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrovola, J.B.; Spyropoulos, M.N. Effects of drugs and systemic factors on orthodontic treatment. Quintessence Int. 2001, 32, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamashita-Mikami, E.; Tanaka, M.; Sakurai, N.; Arai, Y.; Matsuo, A.; Ohshima, H.; Nomura, S.; Ejiri, S. Correlations between alveolar bone microstructure and bone turnover markers in pre- and post-menopausal women. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 115, e12–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, Y.; Kageyama, T.; Moriyama, K.; Kurihara, S.; Yagasaki, H.; Deguchi, T.; Ozawa, H.; Sahara, N. Effect of age on alveolar bone turnover adjacent to maxillary molar roots in male rats: A histomorphometric study. Arch. Oral Biol. 2007, 52, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiropoulou-Chatzigiannis, S.; Kourtidou, M.; Tsalikis, L. The effect of osteoporosis on periodontal status, alveolar bone and orthodontic tooth movement. A literature review. J. Int. Acad. Periodontol. 2007, 9, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Li, G.; Hu, H.; Liu, R.; Chen, J.; Zou, S. Effect of parathyroid hormone on experimental tooth movement in rats. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 144, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, A.C.; Boers, M.; te Koppele, J.M.; van der Laan, W.H.; Markusse, H.M.; Geusens, P.; van der Linden, S. Bone turnover, joint damage and bone mineral density in early rheumatoid arthritis treated with combination therapy including high-dose prednisolone. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shoji, S.; Tabuchi, M.; Miyazawa, K.; Yabumoto, T.; Tanaka, M.; Kadota, M.; Maeda, H.; Goto, S. Bisphosphonate inhibits bone turnover in OPG(-/-) mice via a depressive effect on both osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2010, 87, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgett, R.J.; Shaye, R.; Fruge, J.F.J. The effect of altered bone metabolism on orthodontic tooth movement. Am. J. Orthod. 1981, 80, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltman, B.; Vig, K.W.; Fields, H.W.; Shanker, S.; Kaizar, E.E. Root resorption associated with orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qawasmi, R.A.; Hartsfield, J.K.J.; Everett, E.T.; Flury, L.; Liu, L.; Foroud, T.M.; Macri, J.V.; Roberts, W.E. Genetic predisposition to external apical root resorption. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 123, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, G.R.; Schiffman, P.H.; Tuncay, O.C. Meta analysis of the treatment-related factors of external apical root resorption. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2004, 7, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehr, K.; Bock, N.C.; Serbesis, C.; Honemann, M.; Ruf, S. Severe external apical root resorption--local cause or genetic predisposition? J. Orofac. Orthop. 2011, 72, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrovola, J.B.; Spyropoulos, M.N.; Makou, M.; Perrea, D. Root resorption and the OPG/RANKL/RANK system: A mini review. J. Oral Sci. 2008, 50, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, T.; Seiryu, M.; Daimaruya, T.; Garetto, L.P.; Takano-Yamamoto, T.; Roberts, W.E. Decreased alveolar bone turnover is related to the occurrence of root resorption during experimental tooth movement in dogs. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Chiba, M.; Ohashi, T.; Sato, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Mitani, H. Periodontal tissue activation by vibration: Intermittent stimulation by resonance vibration accelerates experimental tooth movement in rats. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.S.; Garcez, A.S.; Suzuki, H.; Ervolino, E.; Moon, W.; Ribeiro, M.S. Low-level laser therapy stimulates bone metabolism and inhibits root resorption during tooth movement in a rodent model. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 1222–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaro, E.R.S.; Ortiz, F.R.; Dorneles, L.S.; Santos, M.S.; Barrioni, B.R.; Miranda, R.M.; Garlet, G.P.; Teixeira, M.M.; Szawka, R.E.; Silva, T.A.; et al. Estrogen protects dental roots from orthodontic-induced inflammatory resorption. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 117, 104820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.C.; Wang, X.X.; Zhang, L.N.; Yang, F.; Nie, F.J.; Zhang, J. Inhibitory effects of resveratrol on orthodontic tooth movement and associated root resorption in rats. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 111, 104642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Seok, H. Role of 4-hexylresorcinol in the field of tissue engineering. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Seok, H.; Choi, J.Y. Topical delivery of 4-hexylresorcinol promotes wound healing via tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppression. Burns 2016, 42, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.G.; Lee, S.W.; Park, Y.W.; Jeong, J.H.; Choi, J.Y. 4-hexylresorcinol inhibits NF-kappaB phosphorylation and has a synergistic effect with cisplatin in KB cells. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.G. 4-Hexylresorcinol and silk sericin increase the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor via different pathways. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, H.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, J.Y. Inhibition of foreign body giant cell formation by 4- hexylresorcinol through suppression of diacylglycerol kinase delta gene expression. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8576–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Park, N.R.; Choi, J.Y. Porcine Bone Incorporated With 4-Hexylresorcinol Increases New Bone Formation by Suppression of the Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2018, 29, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Yoon, C.S.; Kim, S.G.; Park, Y.W.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, S.K. Effects of 4-Hexylresorcinol on Protein Expressions in RAW 264.7 Cells as Determined by Immunoprecipitation High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, S.K. 4-Hexylresorcinol induced angiogenesis potential in human endothelial cells. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 42, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.-G.; Kim, T.-W. The administration of 4-Hexylresorcinol accelerates orthodontic tooth movement and increases the expression level of bone turnover markers in ovariectomized rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, T.W. 4-Hexylresorcinol administration increases dental hard tissue formation and incisor eruption rate in rats. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrygiannakis, M.A.; Kaklamanos, E.G.; Athanasiou, A.E. Effects of systemic medication on root resorption associated with orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review of animal studies. Eur. J. Orthod. 2019, 41, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodan, G.A.; Fleisch, H.A. Bisphosphonates: Mechanisms of action. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2692–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, Y.; Kitaura, H.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Eguchi, T.; Kohara, H.; Morita, Y.; Yoshida, N. Influence of bisphosphonates on orthodontic tooth movement in mice. Eur. J. Orthod. 2009, 31, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Igarashi, K.; Haruyama, N.; Saeki, S.; Shinoda, H.; Mitani, H. Effects of local administration of clodronate on orthodontic tooth movement and root resorption in rats. Eur. J. Orthod. 2004, 26, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bartzela, T.; Turp, J.C.; Motschall, E.; Maltha, J.C. Medication effects on the rate of orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic literature review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, C.; Hotokezaka, H.; Matsuo, K.; Shibazaki, T.; Yozgatian, J.H.; Darendeliler, M.A.; Yoshida, N. Effects of steroidal and nonsteroidal drugs on tooth movement and root resorption in the rat molar. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arioka, M.; Takahashi-Yanaga, F.; Sasaki, M.; Yoshihara, T.; Morimoto, S.; Hirata, M.; Mori, Y.; Sasaguri, T. Acceleration of bone regeneration by local application of lithium: Wnt signal-mediated osteoblastogenesis and Wnt signal-independent suppression of osteoclastogenesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 90, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ino-Kondo, A.; Hotokezaka, H.; Kondo, T.; Arizono, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Hotokezaka, Y.; Kurohama, T.; Morita, Y.; Yoshida, N. Lithium chloride reduces orthodontically induced root resorption and affects tooth root movement in rats. Angle Orthod. 2018, 88, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locklin, R.M.; Khosla, S.; Turner, R.T.; Riggs, B.L. Mediators of the biphasic responses of bone to intermittent and continuously administered parathyroid hormone. J. Cell Biochem. 2003, 89, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossdorfer, S.; Yildiz, F.; Gotz, W.; Kheralla, Y.; Jager, A. Anabolic effect of intermittent PTH(1-34) on the local microenvironment during the late phase of periodontal repair in a rat model of tooth root resorption. Clin. Oral Investig. 2010, 14, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakdach, W.M.M.; Hadad, R. Effectiveness of low-level laser therapy in accelerating the orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dent. Med. Probl. 2020, 57, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altan, B.A.; Sokucu, O.; Ozkut, M.M.; Inan, S. Metrical and histological investigation of the effects of low-level laser therapy on orthodontic tooth movement. Lasers Med. Sci. 2012, 27, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Williams, R.C.; Kyrkanides, S. Accelerated orthodontic tooth movement: Molecular mechanisms. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2014, 146, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, Y.; Motokawa, M.; Kaku, M.; Sumi, H.; Tanne, K.; Tanimoto, K. RANKL and OPG expression: Jiggling force affects root resorption in rats. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Aihara, N.; Kojima, T.; Kasai, K. RANKL increase in compressed periodontal ligament cells from root resorption. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Maltha, J.C.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. The rat as a model for orthodontic tooth movement—A critical review and a proposed solution. Eur. J. Orthod. 2004, 26, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sameshima, G.T.; Sinclair, P.M. Predicting and preventing root resorption: Part I. Diagnostic factors. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2001, 119, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, C.; Hotokezaka, H.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Yozgatian, J.H.; Darendeliler, M.A.; Yoshida, N. Force magnitude and duration effects on amount of tooth movement and root resorption in the rat molar. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Iida, J.; Kurihara, S. A histological study of the periodontal tissue changes during molar depression in rats. Nihon Kyosei Shika Gakkai Zasshi 1984, 43, 361–372. [Google Scholar]
- Le, M.H.; Warotayanont, R.; Stahl, J.; Den Besten, P.K.; Nakano, Y. Amelogenin exon4 forms a novel miRNA that directs ameloblast and osteoblast differentiation. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, Z.; Lohmann, C.H.; Wieland, M.; Cochran, D.L.; Dean, D.D.; Textor, M.; Bonewald, L.F.; Boyan, B.D. Osteoblast proliferation and differentiation on dentin slices are modulated by pretreatment of the surface with tetracycline or osteoclasts. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, R.; Bohmont, C.W.; Mcevily, A.J. 4-Hexylresorcinol and prevention of shrimp blackspot: Residual analyses. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1991, 4, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadasi, A.; Mozzarelli, A.; Meda, C.; Maggi, A.; Cozzini, P. Identification of xenoestrogens in food additives by an integrated in silico and in vitro approach. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Oh, J.; Seok, H.; Jo, Y.; Kim, D.; Garagiola, U.; Choi, J.; Kim, S. 4-Hexylresorcinol exhibits different characteristics to estrogen. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Linares, A.; Hartsfield, J.K.J. Cellular and molecular pathways leading to external root resorption. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G. Immunomodulation for maxillofacial reconstructive surgery. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 42, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Control group | 69.25 ± 1.51% | 68.68 ± 0.79% |
| Experimental group | 71.69 ± 0.88% * | 71.52 ± 1.85% * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, J.-K.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, S.-G.; Kim, T.-W. Inhibitory Effects of 4-Hexylresorcinol on Root Resorption Induced by Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186313
Jang J-K, Kim D-W, Kim S-G, Kim T-W. Inhibitory Effects of 4-Hexylresorcinol on Root Resorption Induced by Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(18):6313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186313
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Jun-Kyu, Dae-Won Kim, Seong-Gon Kim, and Tae-Woo Kim. 2020. "Inhibitory Effects of 4-Hexylresorcinol on Root Resorption Induced by Orthodontic Tooth Movement" Applied Sciences 10, no. 18: 6313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186313
APA StyleJang, J.-K., Kim, D.-W., Kim, S.-G., & Kim, T.-W. (2020). Inhibitory Effects of 4-Hexylresorcinol on Root Resorption Induced by Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Applied Sciences, 10(18), 6313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186313