Numerical and Experimental Studies of the ŁK Type Shaped Charge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
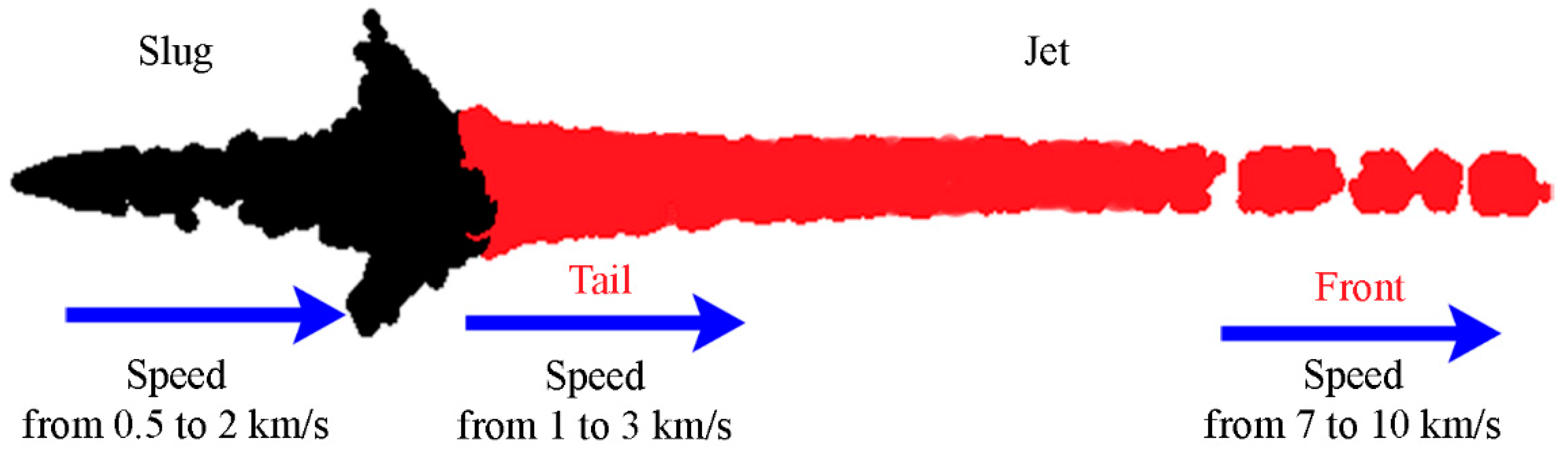
2. Theory
3. Experimental Method and Results
3.1. Assumptions
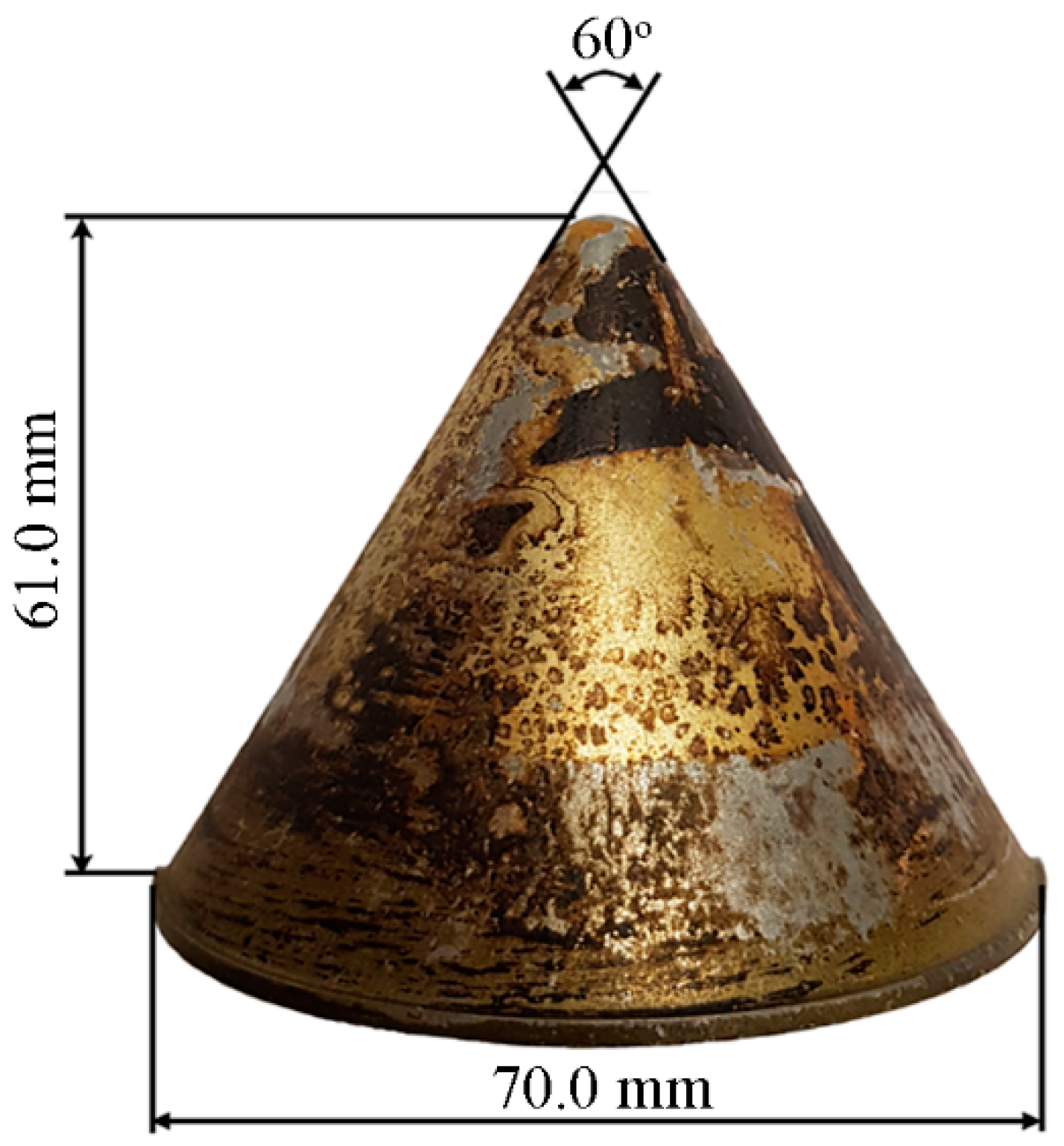
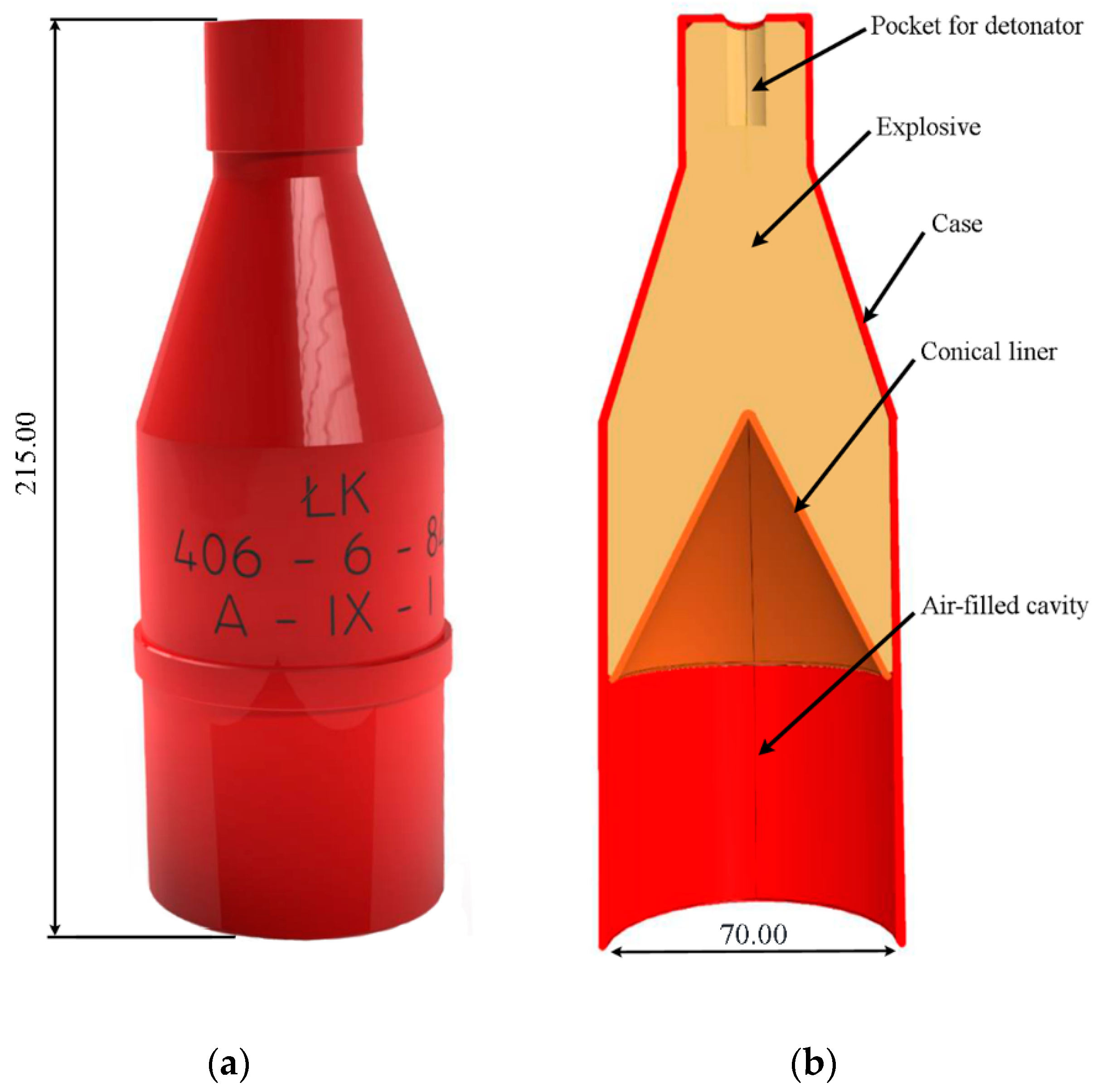
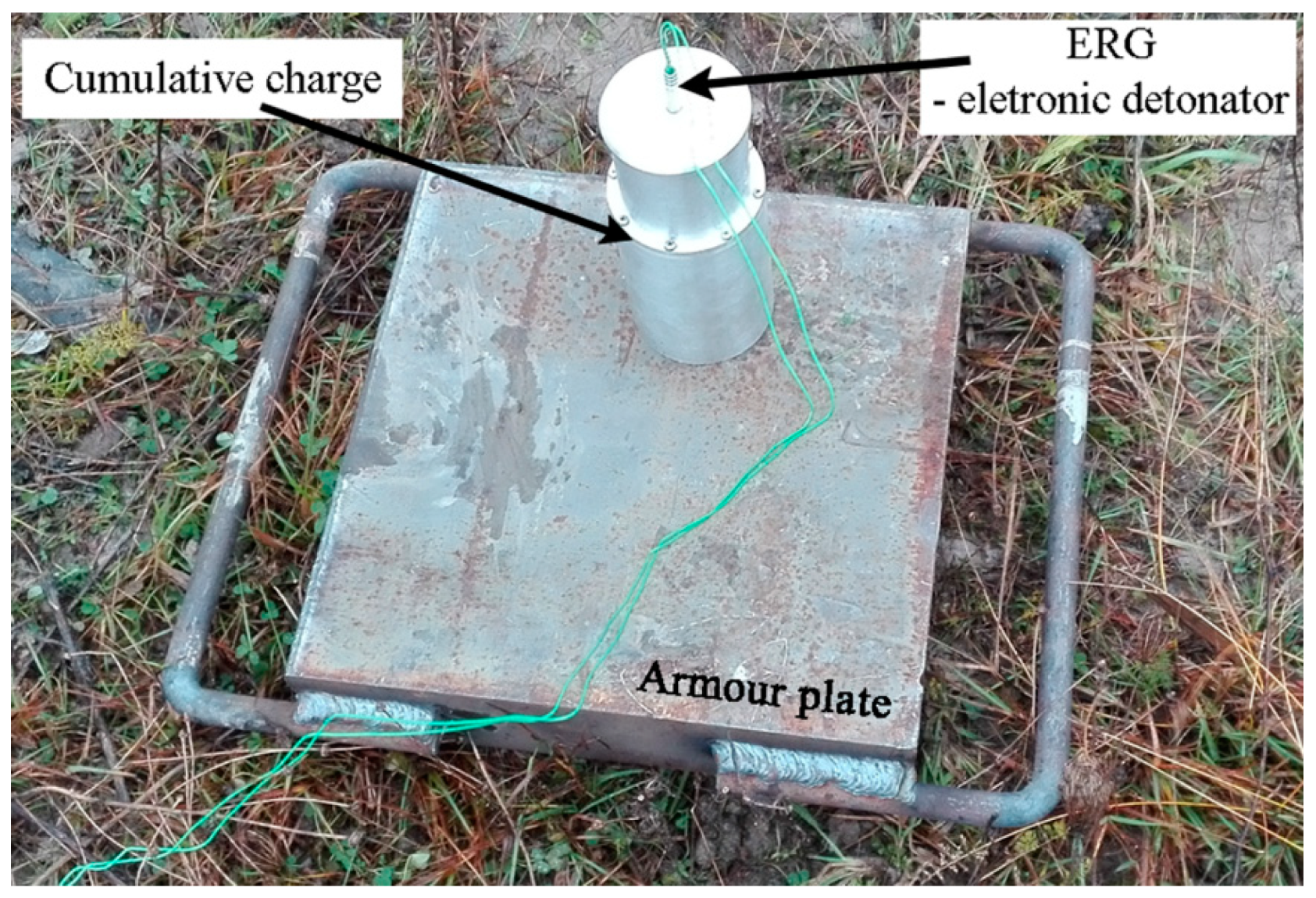
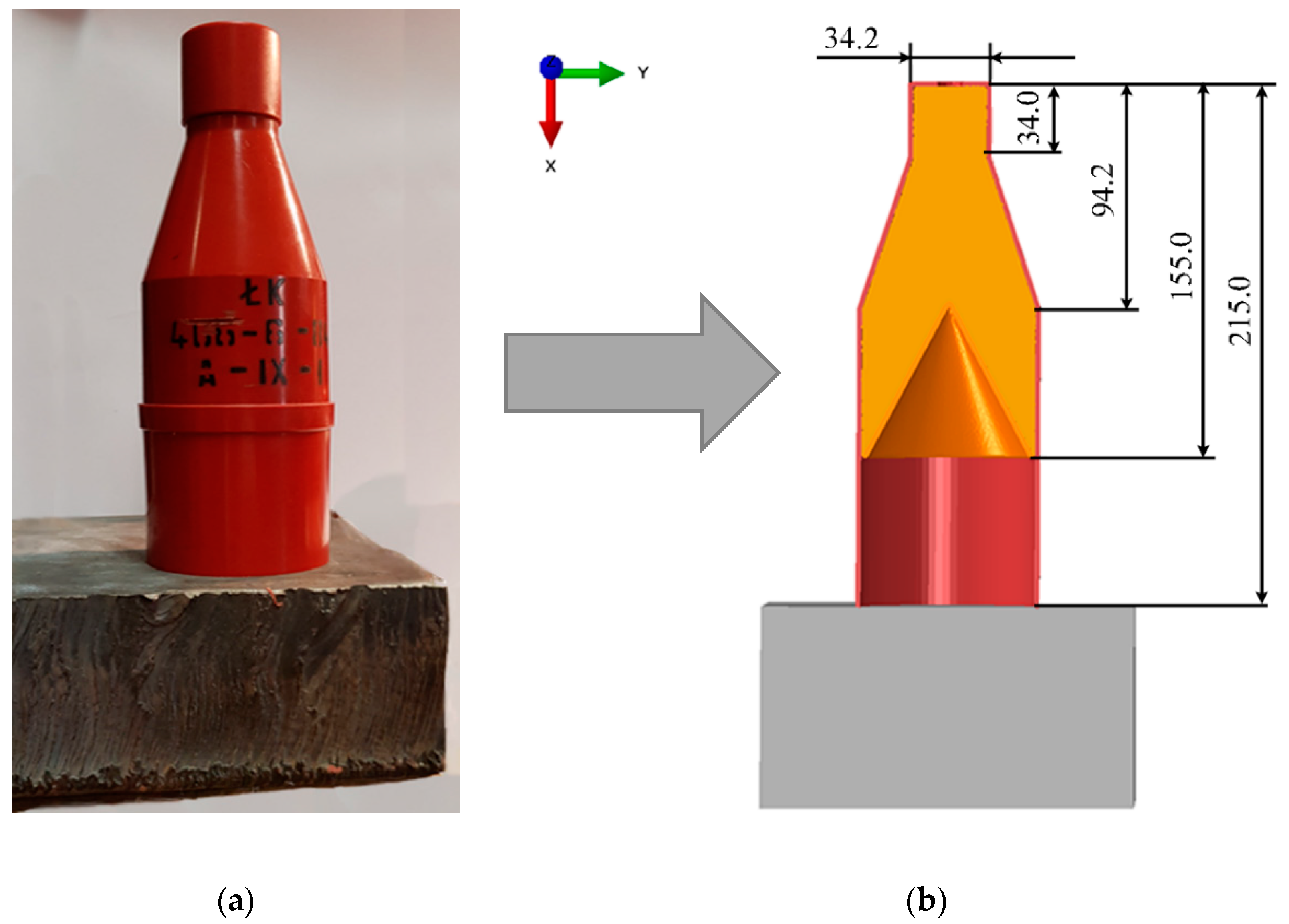
3.2. The Structure of Shaped Charge Tests
3.3. Experimental Results
4. Numerical Analysis
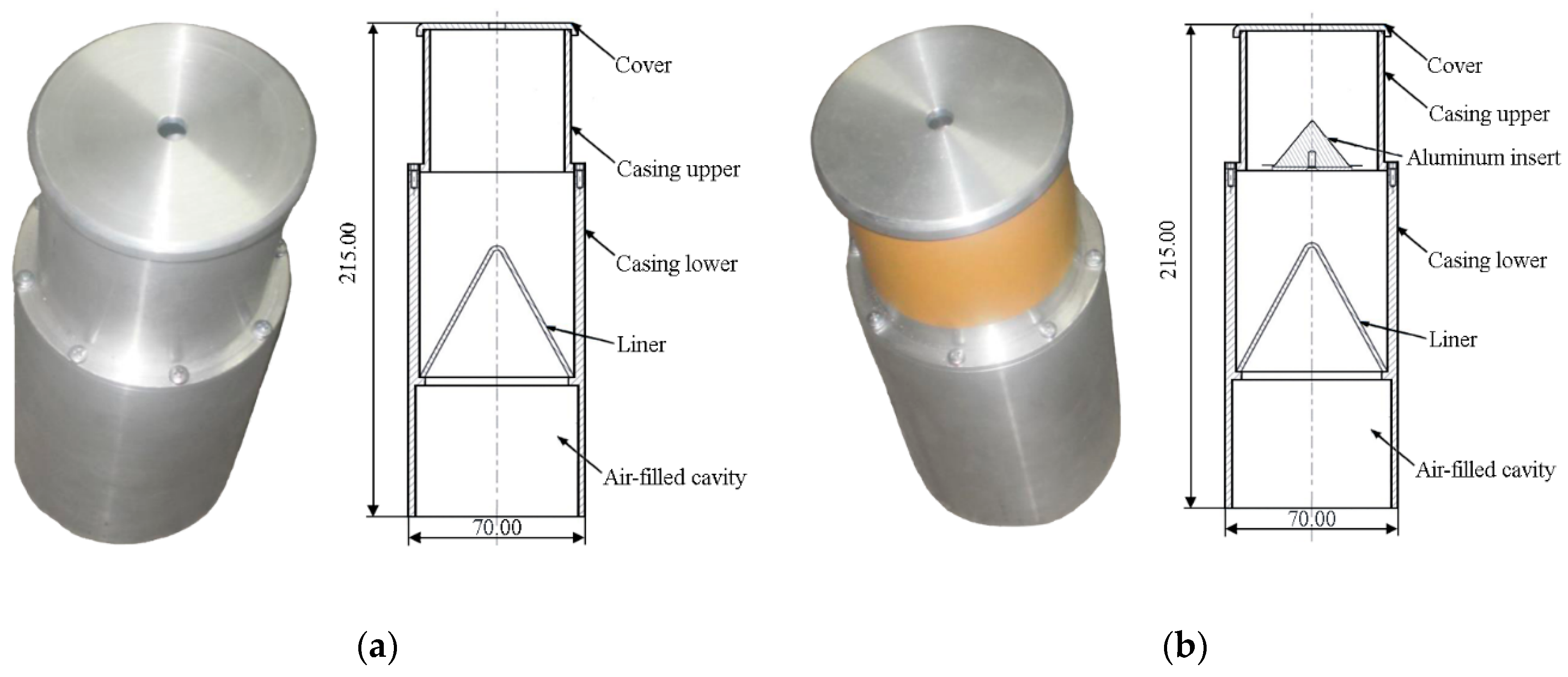
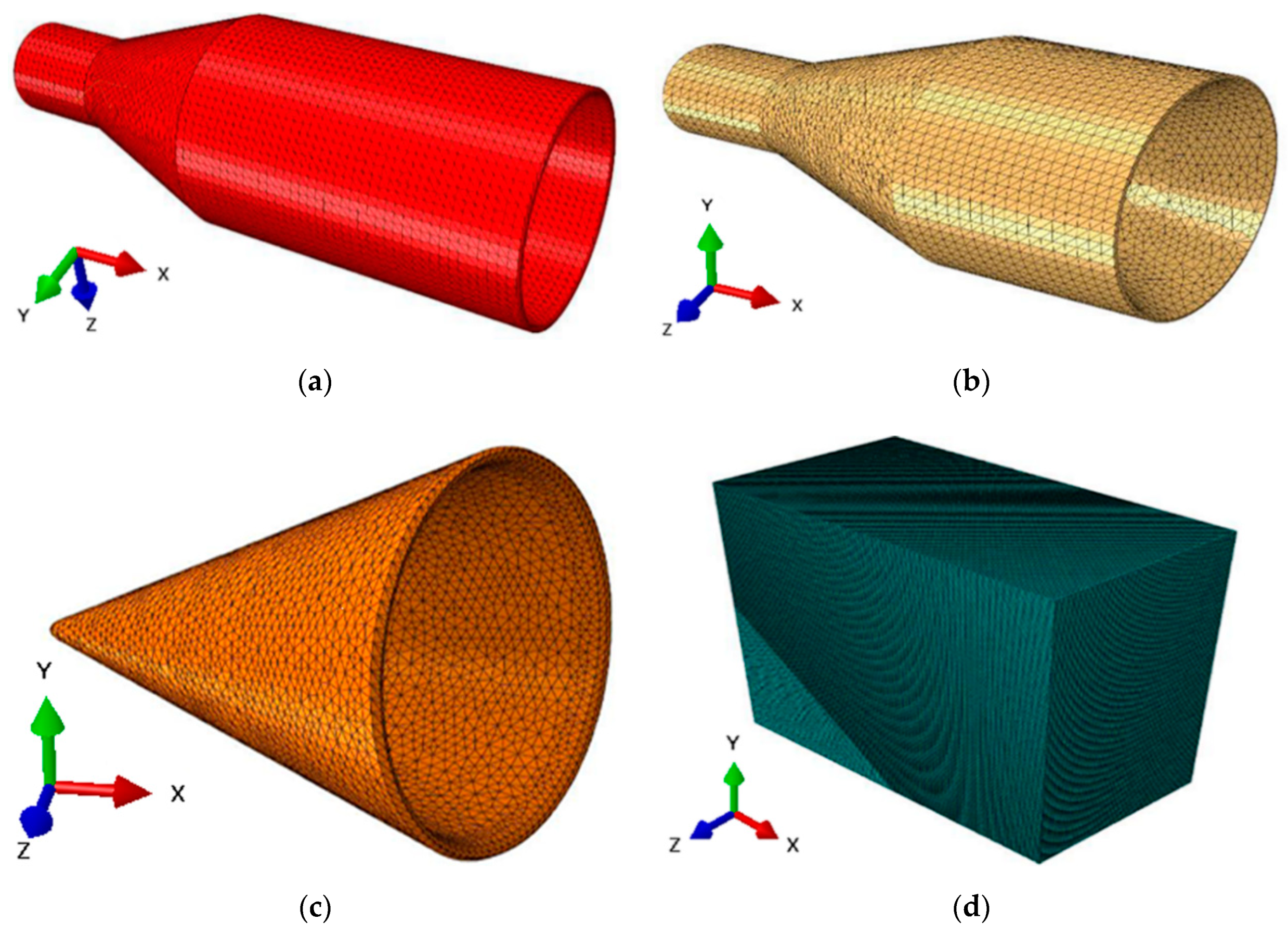
4.1. Assumptions for Modelling
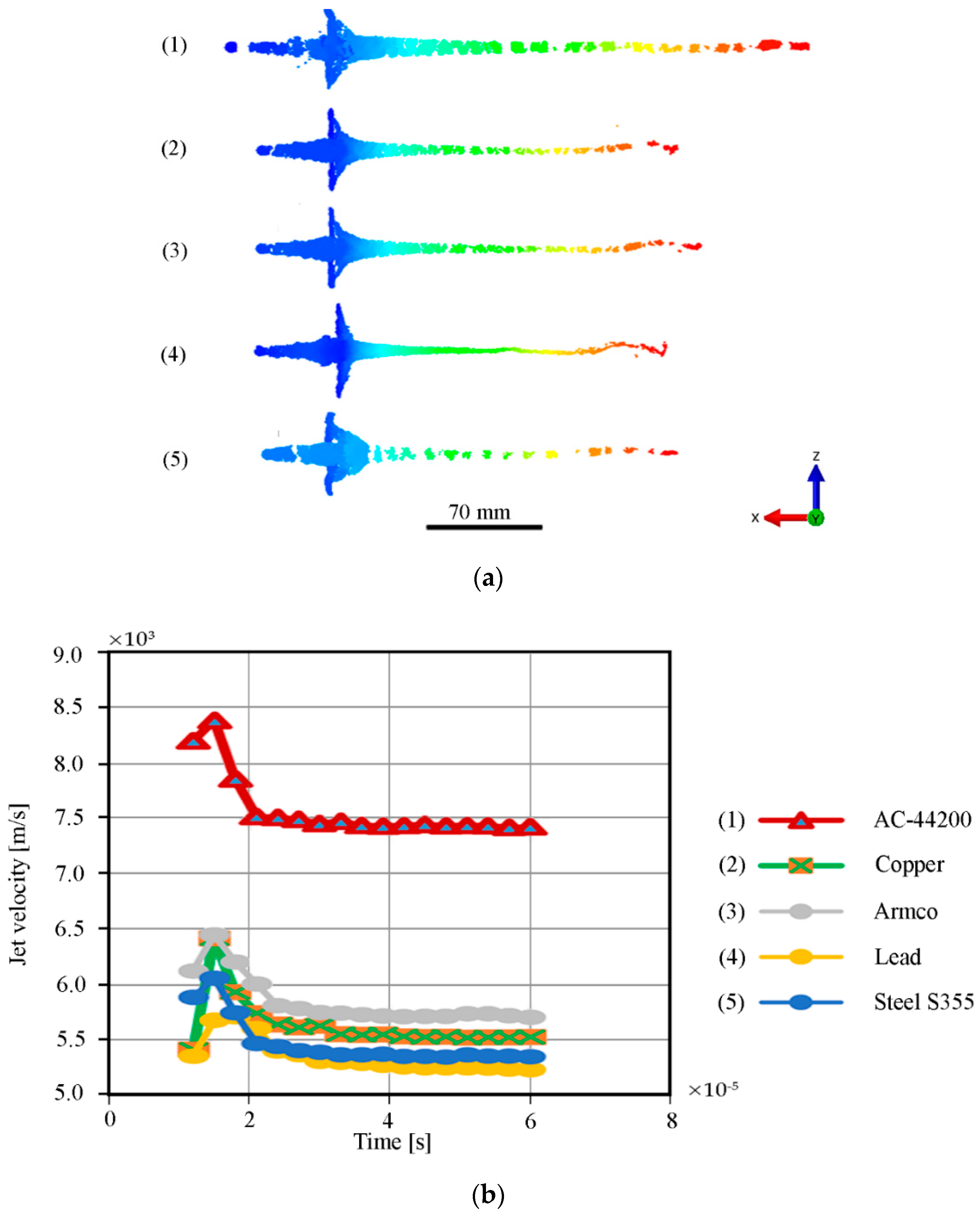
4.2. Description of Materials
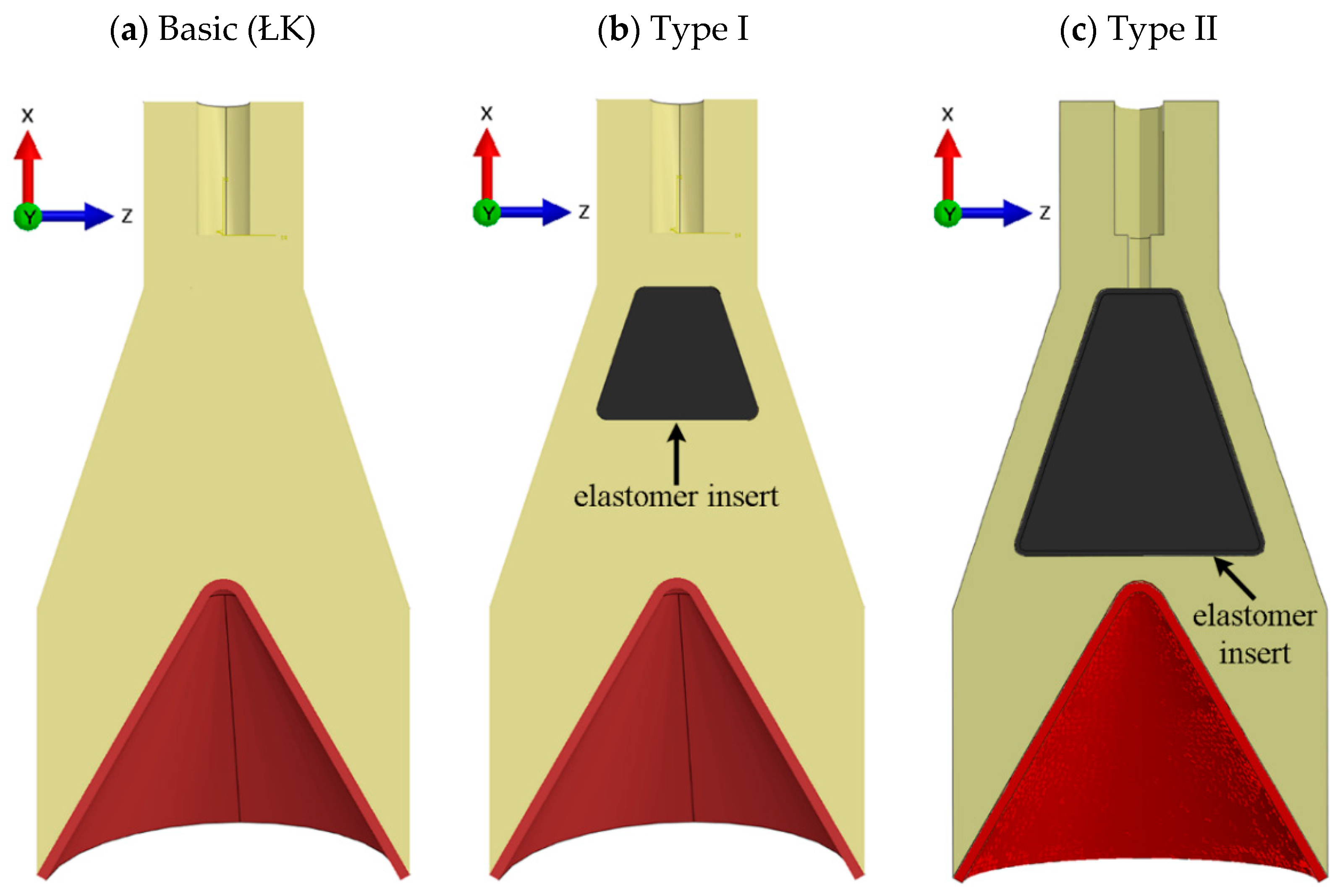
4.3. ŁK Charge Options
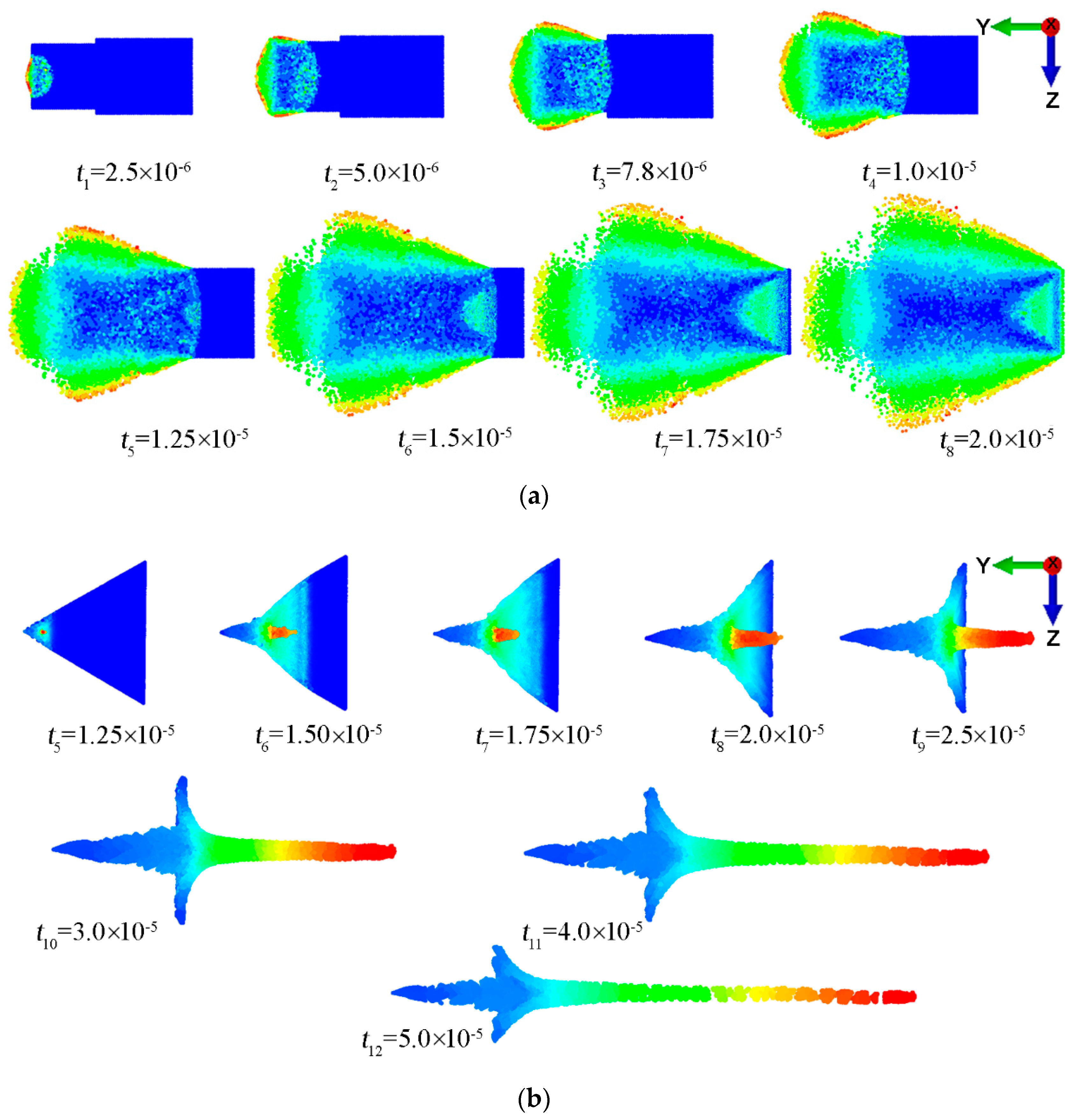
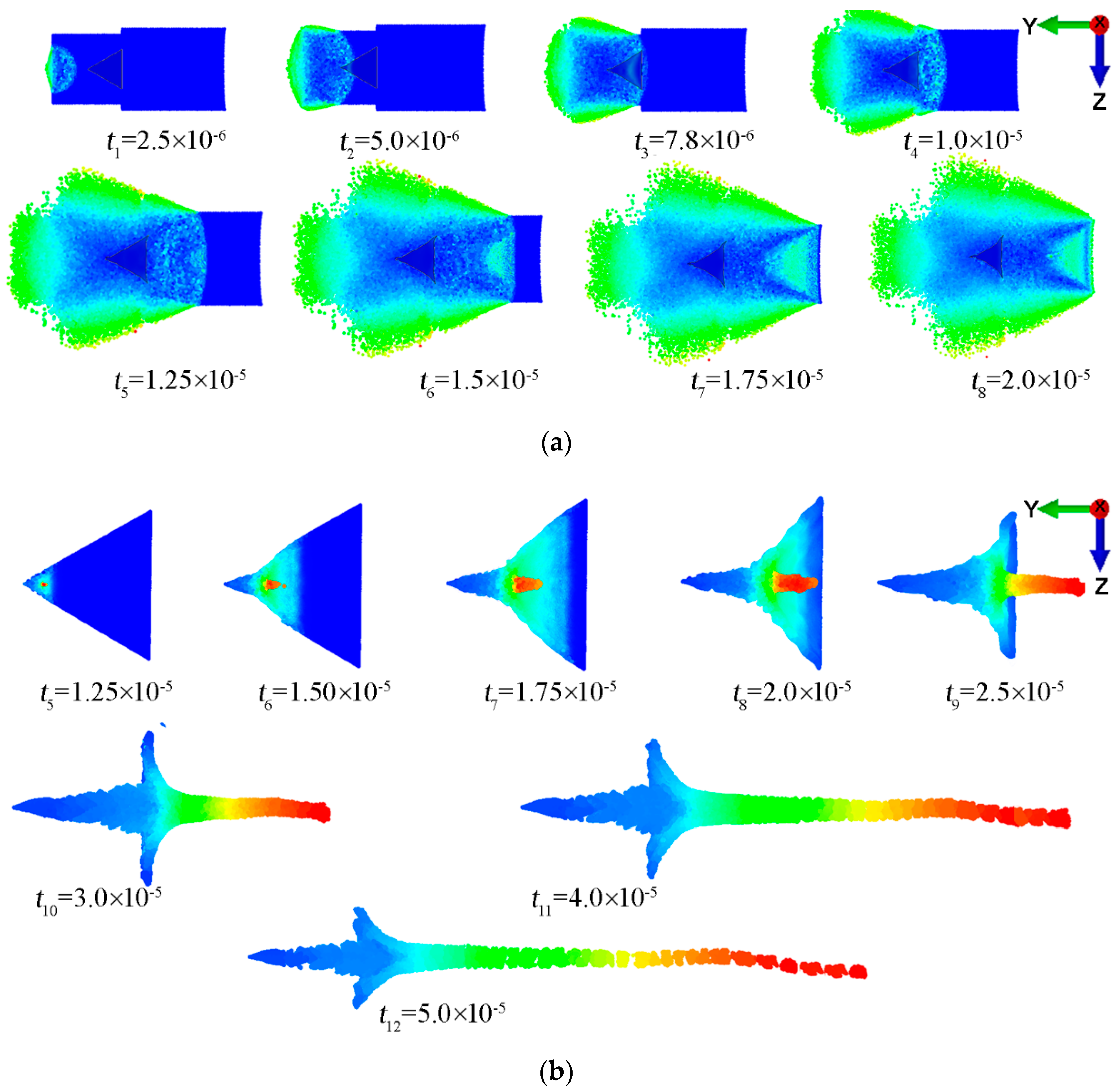
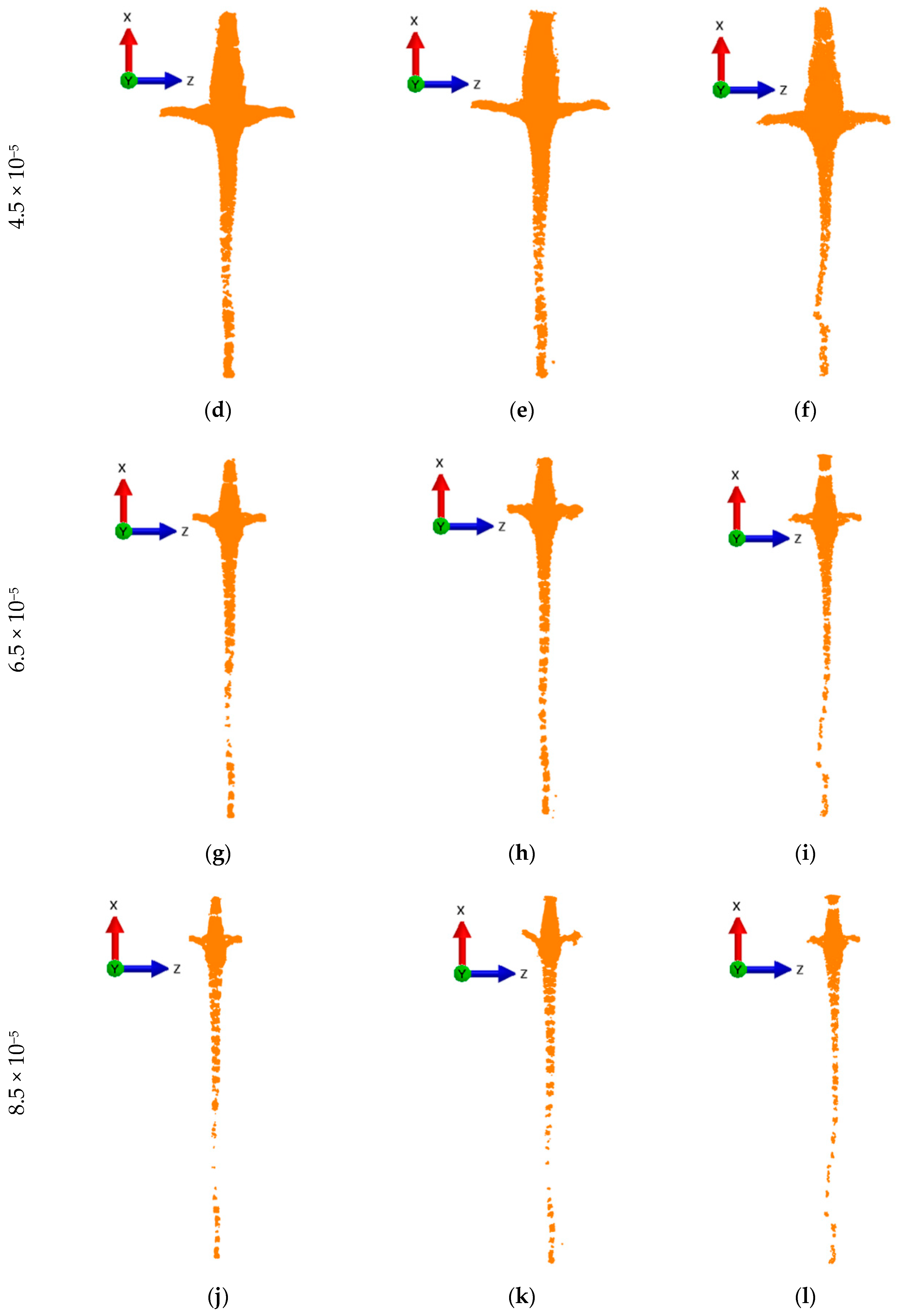
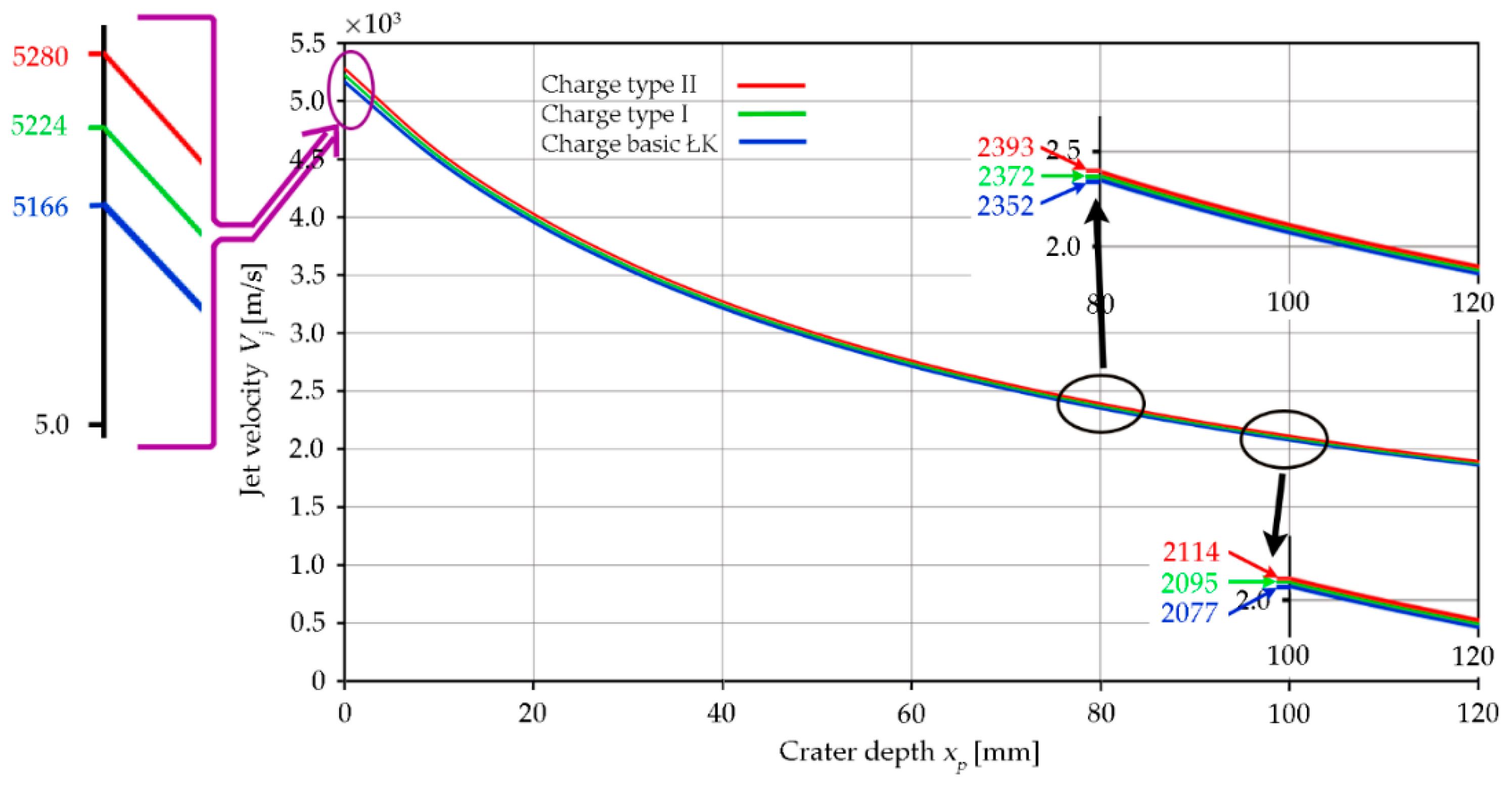
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Austin, C.F. Lined-Cavity Shaped Charges and Their Use in Rock and Earth Materials; Bulletin 59; New Mexico Institute Mining and Technology, State Bureau of Mines and Mineral Research: Socorro, NM, USA, 1959; Available online: https://geoinfo.nmt.edu/publications/monographs/bulletins/downloads/69/Bulletin69.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Cheng, X.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Feng, S. Design of a novel linear shaped charge and factors. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohanek, V.; Dobrilović, M.; Škrlec, V. The efficiency of linear shaped charges. Tehnički Vjesnik 2014, 21, 525–531. [Google Scholar]
- Magier, M.; Burian, W.; Rotkegel, M.; Szymala, J. Experimental analysis of the concrete penetration by using warheads from demobilized ammunition. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 715, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.R. History of the Shaped Charge Effect, the First 100 Years; AD-A220 095; U. S. Department of Commerce: Washingdon, DC, USA, 1983.
- Walters, W.P.; Zukas, J.A. Fundamentals of Shaped Charges; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Balagansky, I.A.; Bataev, A.A.; Bataev, I.A. Explosion Systems with Inert High-Modulus Components; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wojewodka, A.; Belzowski, J.; Witkowski, T. Shaped charge and numerical modeling of their detonation. Chemik 2010, 64, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lavrent’ev, M.A. Cumulative charge and the principles of its operation. Math Net. Ru 1957, 12, 41–56. Available online: http://www.mathnet.ru/links/644214662b2c98a79b446b5f0cc6a666/rm7663.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Birkhoff, G.; MacDougall, D.; Pugh, E.; Taylor, G. Explosive with lined cavities. J. Appl. Phys. 1948, 19, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkhoff, G.; Zarantonello, E.H. Jets, Wakes and Cavities; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Minin, I.V.; Minin, O.V. Physics of hypercumulation: Jet formation in shaped charge and ablatively-driven implosion of hollow cones. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2014, 22, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, P.C.; Carleone, J.; Karpp, R.R. Criteria for jet formation from impinging shells and plates. J. Appl. Phys. 1976, 47, 2975–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariman-Zadeh, N.; Darvizeh, A.; Darvizeh, M.; Gharababaei, H. Modelling of explosive cutting process of plates using GMDH-type neural network and singular value decomposition. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2002, 128, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Zhu, X.; Chen, C. Theoretical calculation of the fragment initial velocity following aerial explosion of the cylindrical warhead with two terminals. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 274, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.-W.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liu, H. Jet formation and penetration study of double-layer shaped charge. J. Energetic Mater. 2018, 36, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, A.; Podgórzak, P. Research results on precursor of the tandem shaped charge projectile model. Probl. Tech. Uzbroj. 2005, 94, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kurzawa, A.; Pyka, D.; Bocian, M.; Jamroziak, K.; Sliwinski, J. Metallographic analysis of piercing armor plate by explosively formed projectiles. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 8, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotney, D.; Mallery, M. Historical development of linear shaped charge. AIAA 2007, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayisit, O. The influence of asymmetries in shaped charge performance. Int. J. Impact. Eng. 2008, 35, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokamoto, K.; Raghukandan, K. Explosion Shock Waves and High Strain Rate Phenomena; Materials Research Forum LLC: Millersville, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Geng, B.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, Y. Application of PTFE/Al reactive materials for double-layered liner shaped charge. Materials 2019, 12, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saran, S.; Ayisit, O.; Yavuz, M.S. Experimental investigations on aluminum shaped charge liners. Proc. Eng. 2013, 58, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naeem, K.; Hussain, A.; Abbas, S. A review of shaped charge variables for its optimum performance. Eng. Tech. Appl. Sci. Res. 2019, 9, 4917–4924. [Google Scholar]
- Abdo, G.M.; Elshenawy, T. Density effect of the compacted copper-tungsten shaped charge powder liners on its penetration performance. J. Powder. Metall. Min. 2017, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenlong, X.; Cheng, W.; Dongping, C. Formation of a bore-center annular shaped charge and its penetration into steel targets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2019, 127, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, D. The jet formation and penetration capability of hyperveloci-ty shaped charges. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2019, 132, 103337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Jeong, J.; Lee, C. Performance comparison of double-layer liner for shaped charge fabricated using kinetic spray. J. Therm. Spray. Tech. 2019, 28, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ding, J.; Zhao, H. Numerical Simulation on jet formation of shaped charge with different liner materials. Def. Sci. J. 2015, 65, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshenawya, T.; Elbeihb, A.; Klapötkec, T.M. A numerical method for the determination of the virtual origin point of shaped charge jets instead of using flash X-ray radiography. J. Energetic Mater. 2018, 36, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Hameed, A.; Hetherington, J.G.; Barton, P.C.; Malik, A.Q. Hydrocode simulation with modified Johnson-Cook model and experimental analysis of explosively formed projectiles. J. Energetic Mater. 2013, 31, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.H.; Ou, J.B.; Jhu, Y.J. The design and analysis for shaped charge liner using Taguchi method. Int. J. Mech. 2014, 8, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, D.J.; Lund, C.M. A constitutive model for strain rates from 10-4 to 106 s-1. J. Appl. Phys. 1989, 65, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, G.; Serradeill, R. Review of Jones-Wilkins-Lee equation of state. EPJ Web Conf. 2010, 10, 00021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downes, D.; Bouamoul, A.; Ensan, M.N.; Baillargeon, Y. Development of an efficient numerical model for shaped charge analysis. J. Def. Mod. Simul. Appl. Met. Tech. 2016, 13, 355362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, W.-W. Finite element modeling of the shaped charge jet and design of the reusable perforating gun. Pet. Sci. 2020, 17, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Wang, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Z. Simulation study on expansive jet formation characteristics of polymer liner. Materials 2019, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, D.L.; Liu, M.B.; Li, H.Q. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics modeling of linear shaped charge with jet formation and penetration effects. Comput. Fluids. 2013, 86, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Damage response of steel plate to underwater explosion: Effect of shaped charge liner. Int. J. Impact. Eng. 2017, 103, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Held, M. Time distance diagram of the jet initiation of covered high explosive charges. Int. J. Impact. Eng. 2007, 34, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Tang, W.; Ran, X. Simulation study on jet formability and damage characteristics of a low-density material liner. Materials 2018, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Industry standard: BN-72/6096-01. Open type directional cumulative hexogen charges HT/P-26 Z and HT/P-32. (In Polish). Available online: http://bc.pollub.pl/Content/3037/PDF/BN_72_6096_01.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Data Sheet. Armox 370T, ARMOX® Protection Plate; SAAB: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.R.; Liu, M.B. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics; A Meshfree Particle Method; World Scientific: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Hu, H. Penetration of annular and general jets into underwater plates. Comp. Partical Mech. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panowicz, R.; Konarzewski, M.; Trypolin, M. Analysis of criteria for determining a TNT equivalent. Stroj. Vestn. J. Mech. E. 2017, 63, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, C.A.; Lambourn, B.D.; Whitworth, N.J.; James, H.R.; Belfield, W.J. Under-standing the shock and detonation response of high explosives at the continuum and meso scales. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2018, 5, 011303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Andrae, M.; Gebbeken, N. Air blast TNT equivalence concept for blast-resistant design. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 185, 105871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucewicz, M.; Baranowski, P.; Malachowski, J.; Trzcinski, W.; Szymanczyk, L. Numerical modelling of cylindrical test for determining Jones–Wilkins-Lee equation parameters. In Proceedings of the 14th International Scientific Conference: Computer Aided Engineering. CAE 2018. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Rusiński, E., Pietrusiak, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 338–394. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.S.; Lee, M.; Lam, K.Y.; Yeo, K.S. Modeling mitigation effects of watershield on shock waves. Shock Vib. 1998, 5, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malachowski, J.; Mazurkiewicz, P. Elastic-plastic Half Cylidrical Surface Response under Blast Loading. CMM-2011–Computer Methods in Mechanics. 2011. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/1a60/2fd261123bb1f40f4d3ba6f92b49e42c5977.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Kurzawa, A.; Pyka, D.; Jamroziak, K.; Bocian, M.; Sliwinski, J. Experimental and metallographic analysis of the energy absorbing shield subjected to the EFP impact. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2078, 020035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jach, K. Computer Modeling of Dynamic Body Interactions Using a Smoothed Particles Hydrodynamics; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 2001. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sliwinski, J.; Ludas, M.; Kosnik, S.; Pyka, D.; Jamroziak, K. Investigations of the Detonation Wave Propagation Process in the ŁK Cumulative Charge; Research report; Ammunition Testing Laboratory: Wroclaw, Poland, 2016; Unpublished materials. [Google Scholar]
- Panowicz, R.; Konarzewski, M. Influence of imperfect position of a striker and input bar on wave propagation in a Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar (SHPB) Setup with a pulse-shape technique. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Wu, G.D.; Yin, J.P.; Dong, F.D.; Jin, Y.X. Density effect of PTFE-copper powder metallurgy liner material on the perforation performance of shaped charge jets. Strength Mater. 2019, 51, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzawa, A.; Pyka, D.; Jamroziak, K.; Bocian, M.; Kotowski, P.; Widomski, P. Analysis of ballistic resistance of composites based on EN AC-44200 aluminum alloy reinforced with Al2O3 particles. Compos. Struct. 2018, 201, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.P.; Kelly, R.J. Circular streamline model of shaped-charge jet and slug formation with asymmetry. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 75, 7700–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


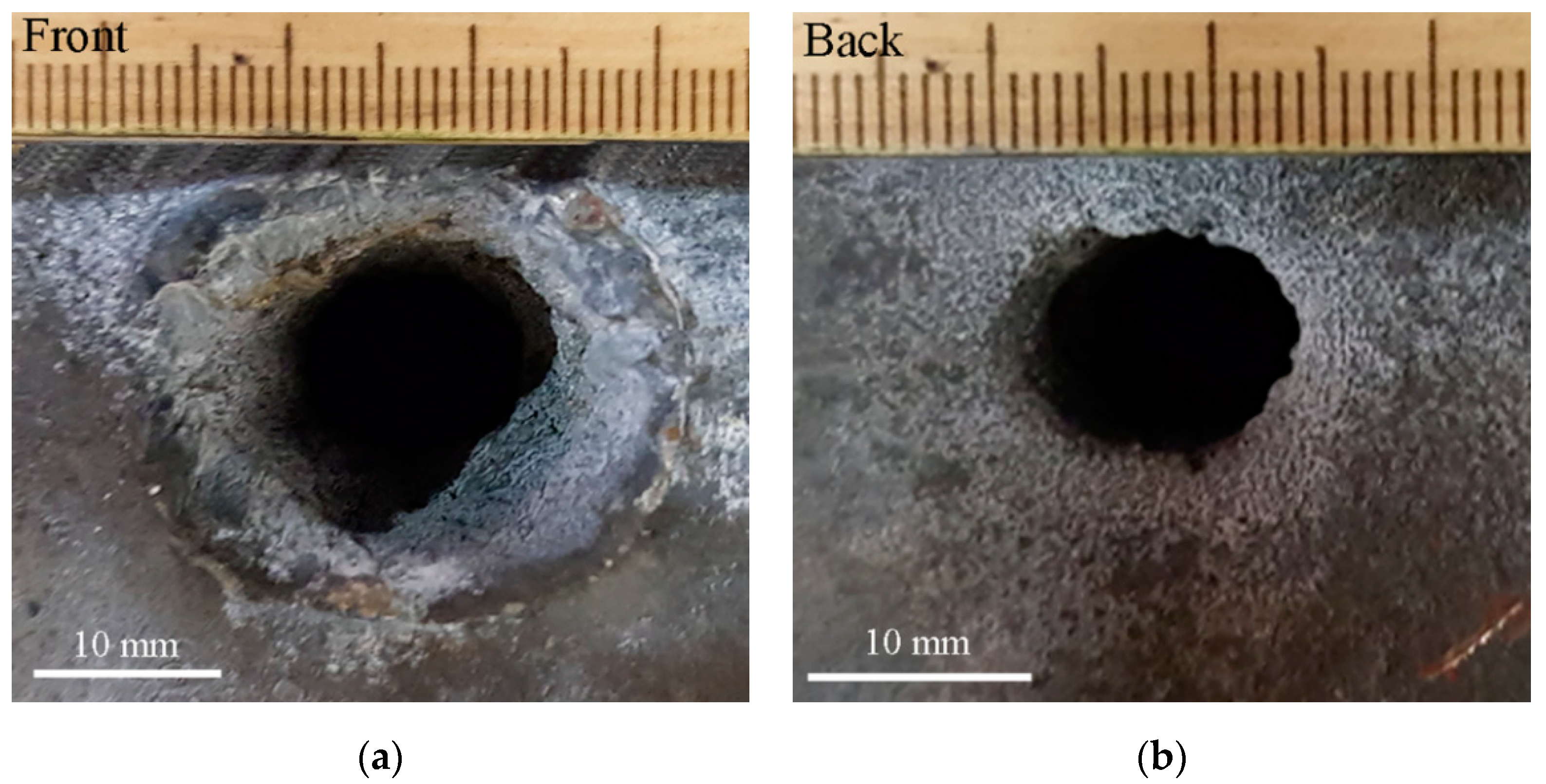
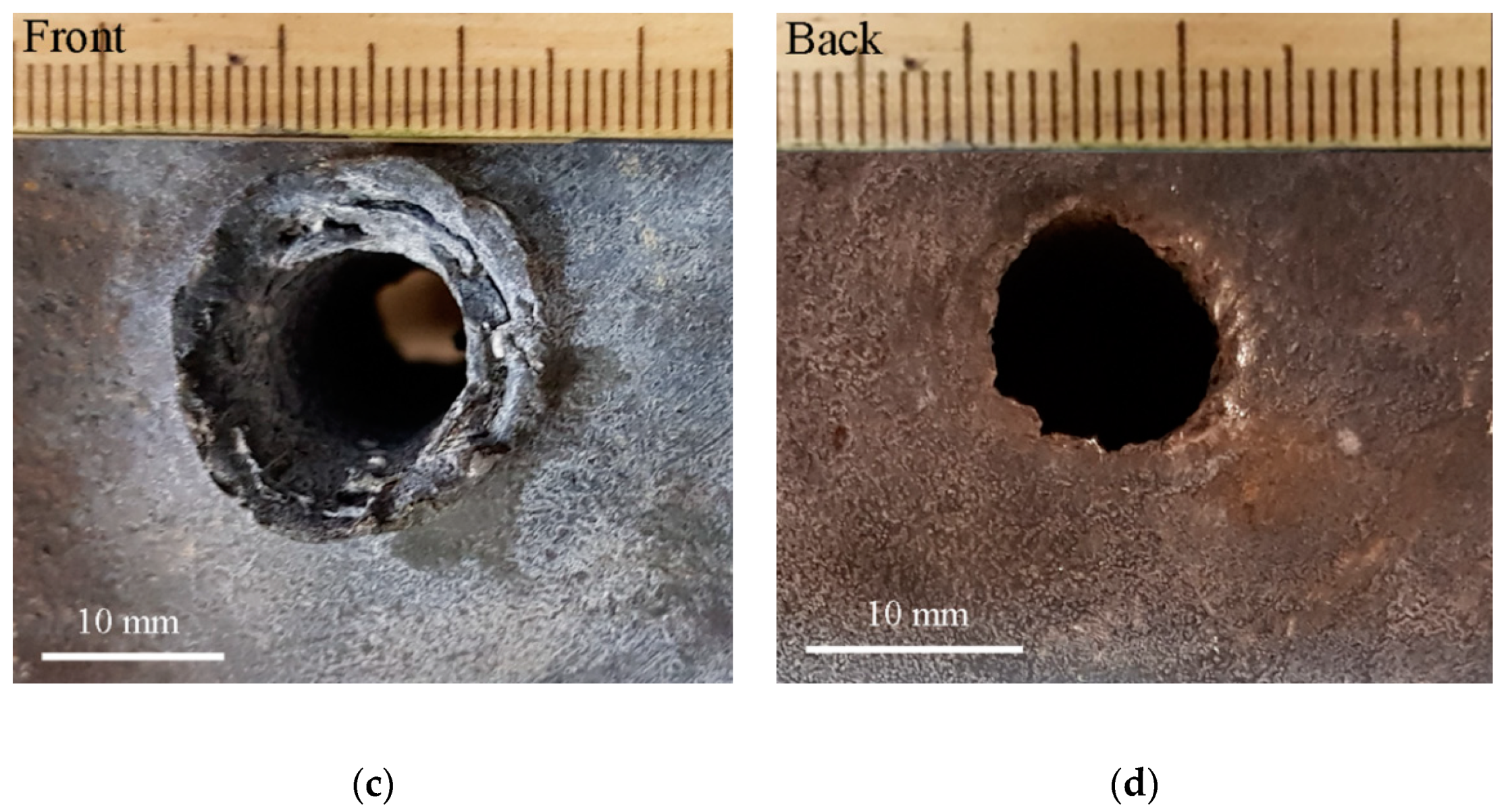



| Specimens Thickness (mm) | Yield Strength Rp02 (MPa) | Tensile Strength Rm (MPa) | Hardness (HBW) | Charpy-V (J) | Elongation A5 (min %) | Elongation A50 (min %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plate 80 | 800 | 900–1100 | 280–330 | 60 J/−40 °C | 13 | 15 |
| plate 100 | - | - | 300–350 | 40 J/−40 °C | - | - |
| Specimens [mm] | Axial Charges | Peripheral Charges | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 2A | 3A | 1P | 2P | 3P | ||
| plate 100 | front | 21.2 | 22.7 | 23.0 | 12.9 | 14.1 | 13.2 |
| back | None | None | 14.8 | 12.0 | 13.4 | 12.9 | |
| plate 80 | front | 22.0 | 23.0 | 24.0 | 12.0 | 12.5 | 13.0 |
| back | 15.3 | 16.0 | 15.0 | 11.7 | 12.3 | 12.8 | |
| Explosive | |||||||||||||||||
| ρ* | D | PCJ | A* | B* | R1 | R2 | ω | κpd | Sources | ||||||||
| (kg/m3) | (m/s) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (-) | (-) | (-) | (GPa) | |||||||||
| TNT | 1730 | 8193 | 28.00 | 609.00 | 13.00 | 4.50 | 1.40 | 0.25 | 9.00 | [48,53] | |||||||
| Liner Material | |||||||||||||||||
| ρ | E | ν | A | B | C | n | m | Sources | |||||||||
| (kg/m3) | (GPa) | (-) | (MPa) | (MPa) | (-) | (-) | (-) | ||||||||||
| Zn5Al | 7010 | 98 | 0.30 | 180 | 200 | 0.008 | 0.100 | 1.0 | [53,54] | ||||||||
| Cooper | 8960 | 1.28 | 0.36 | 80 | 500 | - | 0.605 | 1.00 | [55,56] | ||||||||
| AC-44200 | 2730 | 70 | 0.33 | 110 | 330 | 0.008 | 0.100 | 1.00 | [57] | ||||||||
| Steel S355 | 7820 | 210 | 0.35 | 807 | 1660 | 0.008 | 0.100 | 1.00 | [26,53] | ||||||||
| Armco | 7870 | 210 | 0.37 | 233 | 460 | 0.047 | 0.320 | 0.55 | [53] | ||||||||
| Lead | 11,300 | 115 | 0.42 | 24 | 40 | 0.010 | 0.500 | 1.00 | [53] | ||||||||
| Elastomer | 1.200 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 10 | 20 | - | - | - | [53,54] | ||||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pyka, D.; Kurzawa, A.; Bocian, M.; Bajkowski, M.; Magier, M.; Sliwinski, J.; Jamroziak, K. Numerical and Experimental Studies of the ŁK Type Shaped Charge. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196742
Pyka D, Kurzawa A, Bocian M, Bajkowski M, Magier M, Sliwinski J, Jamroziak K. Numerical and Experimental Studies of the ŁK Type Shaped Charge. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(19):6742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196742
Chicago/Turabian StylePyka, Dariusz, Adam Kurzawa, Miroslaw Bocian, Marcin Bajkowski, Mariusz Magier, Janusz Sliwinski, and Krzysztof Jamroziak. 2020. "Numerical and Experimental Studies of the ŁK Type Shaped Charge" Applied Sciences 10, no. 19: 6742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196742
APA StylePyka, D., Kurzawa, A., Bocian, M., Bajkowski, M., Magier, M., Sliwinski, J., & Jamroziak, K. (2020). Numerical and Experimental Studies of the ŁK Type Shaped Charge. Applied Sciences, 10(19), 6742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196742








