Quasi-Yagi Slotted Array Antenna with Fan-Beam Characteristics for 28 GHz 5G Mobile Terminals
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Antenna Design and Performance
2.1. Single Slot Radiator Design and Performance
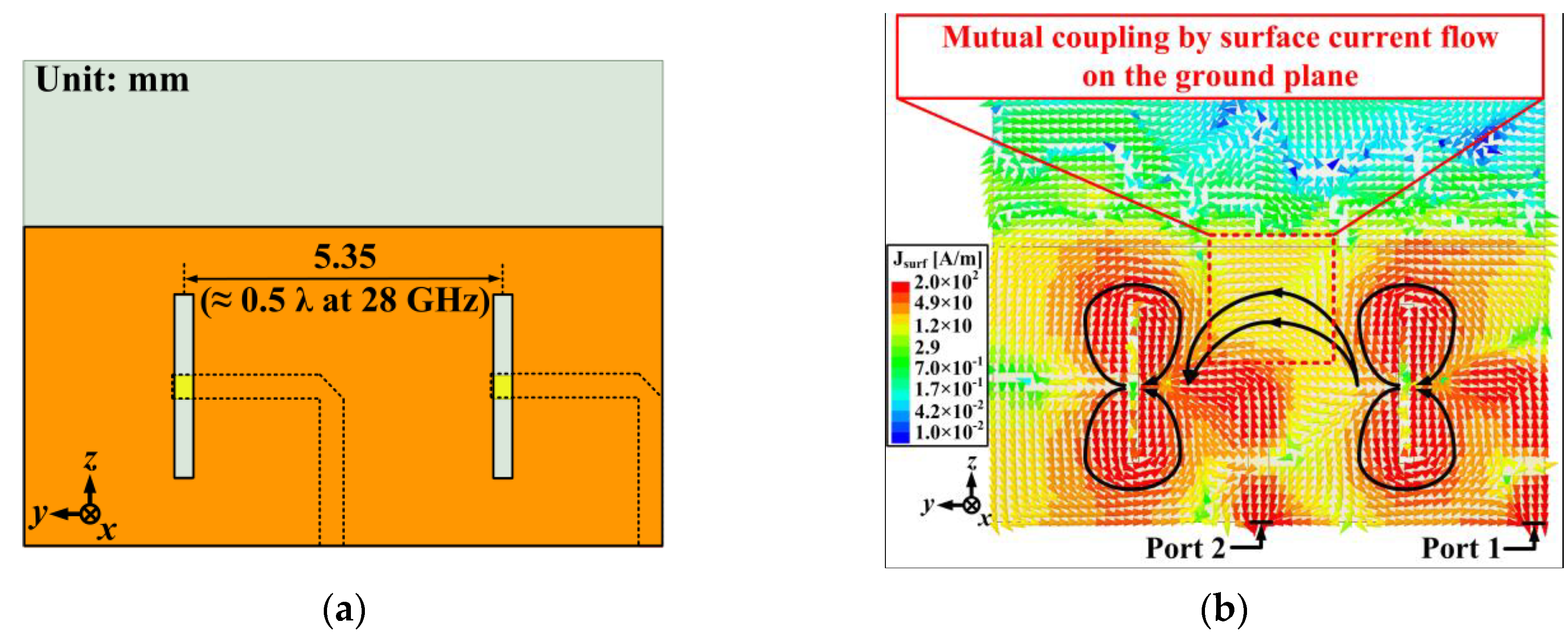
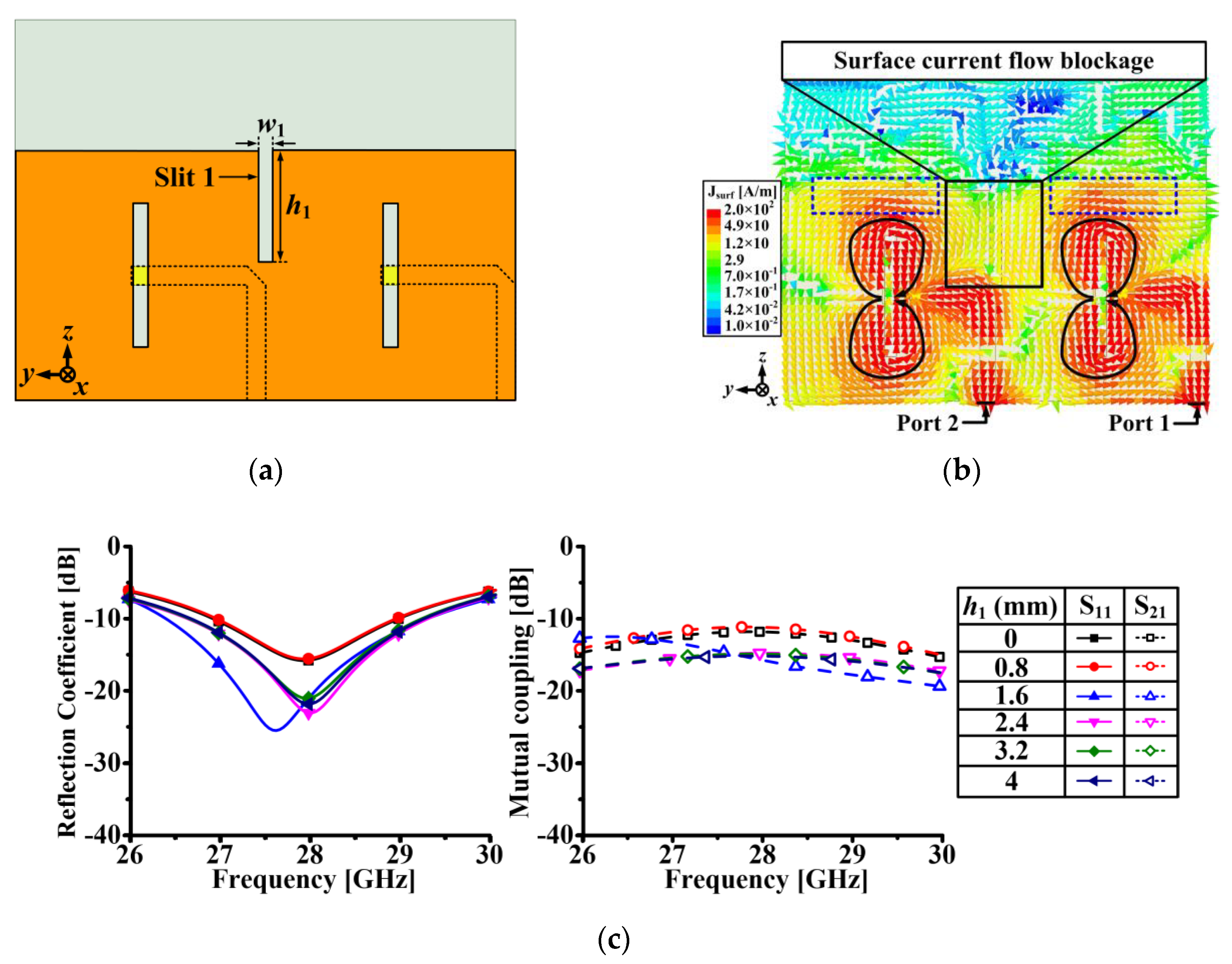
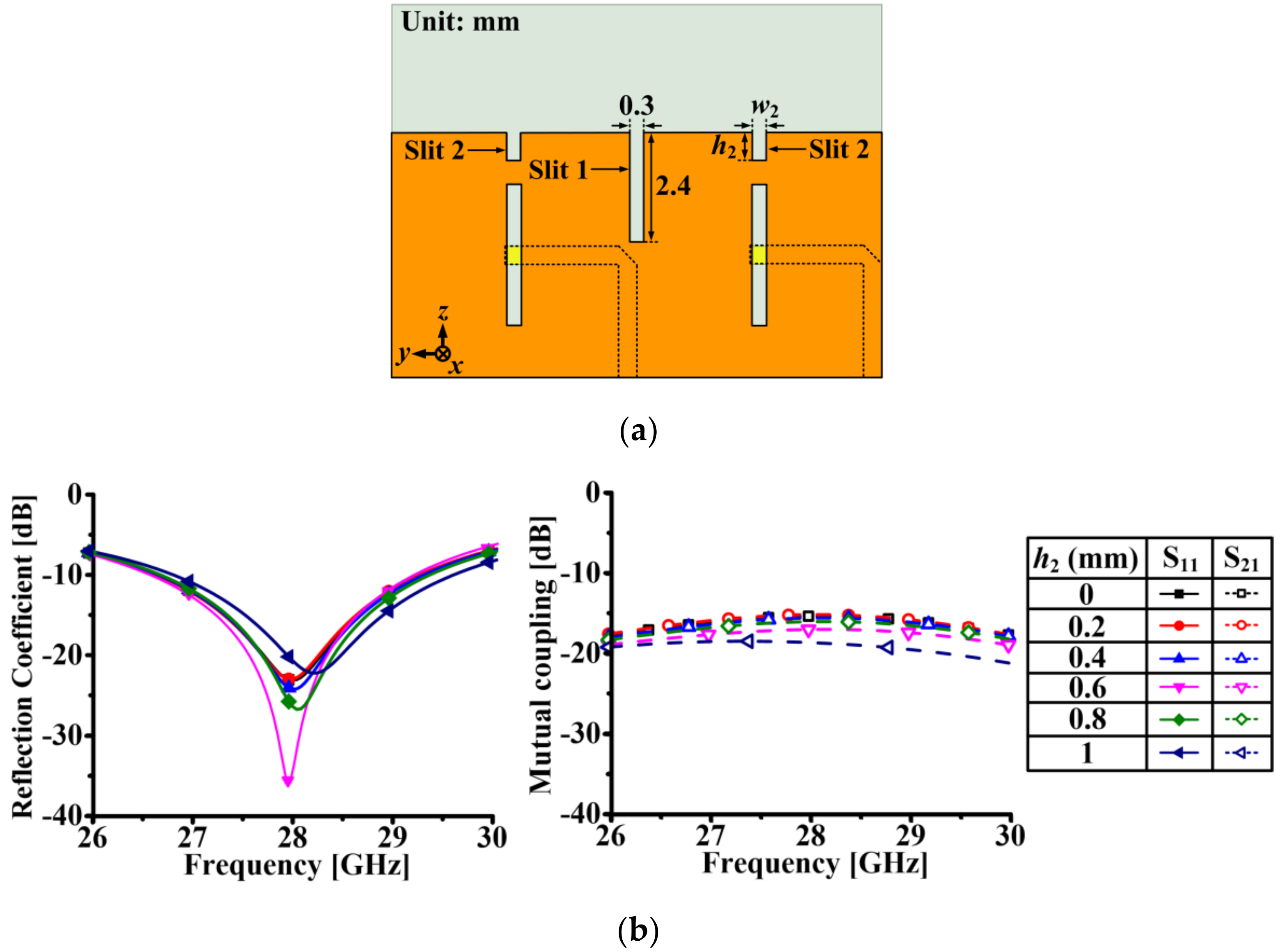
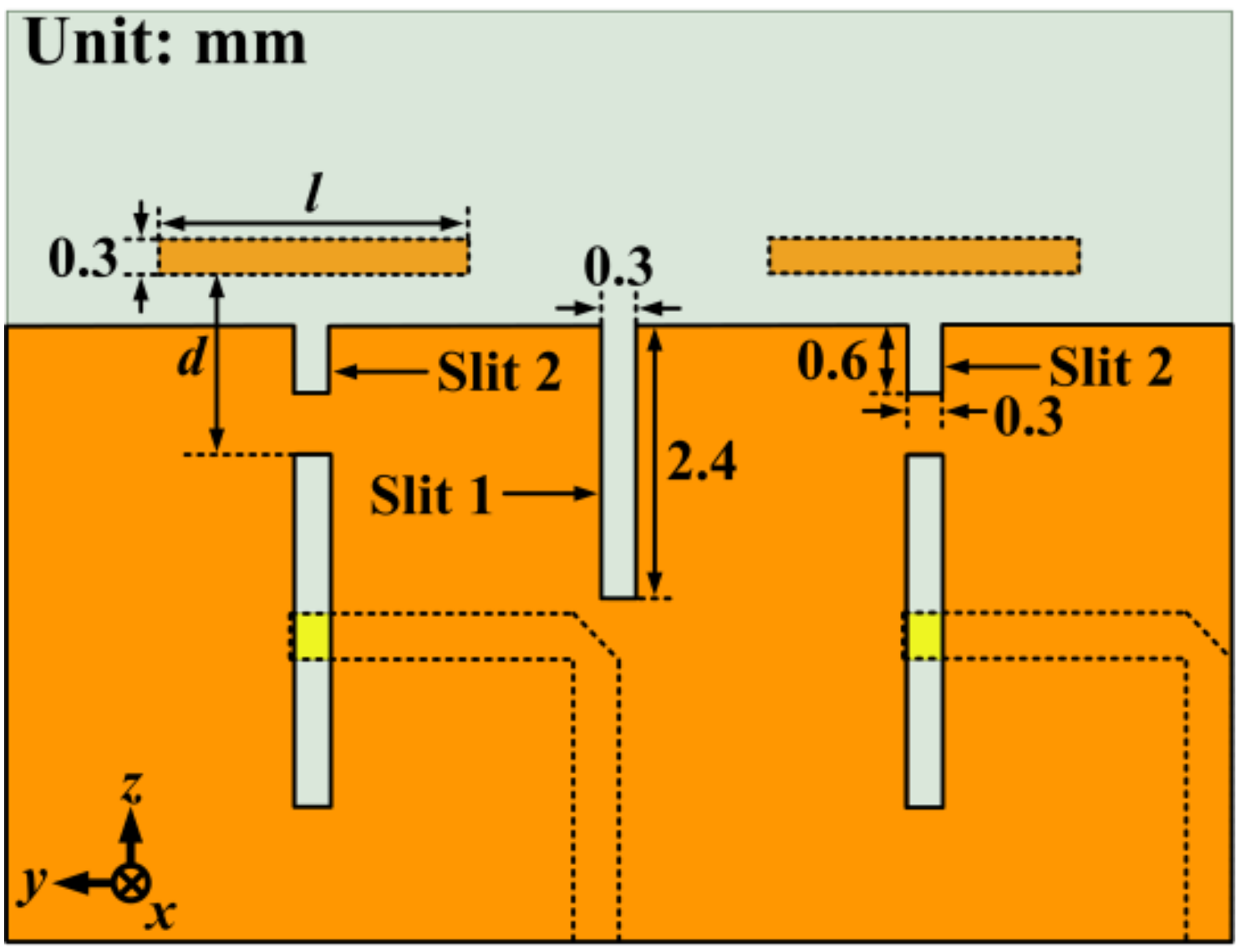
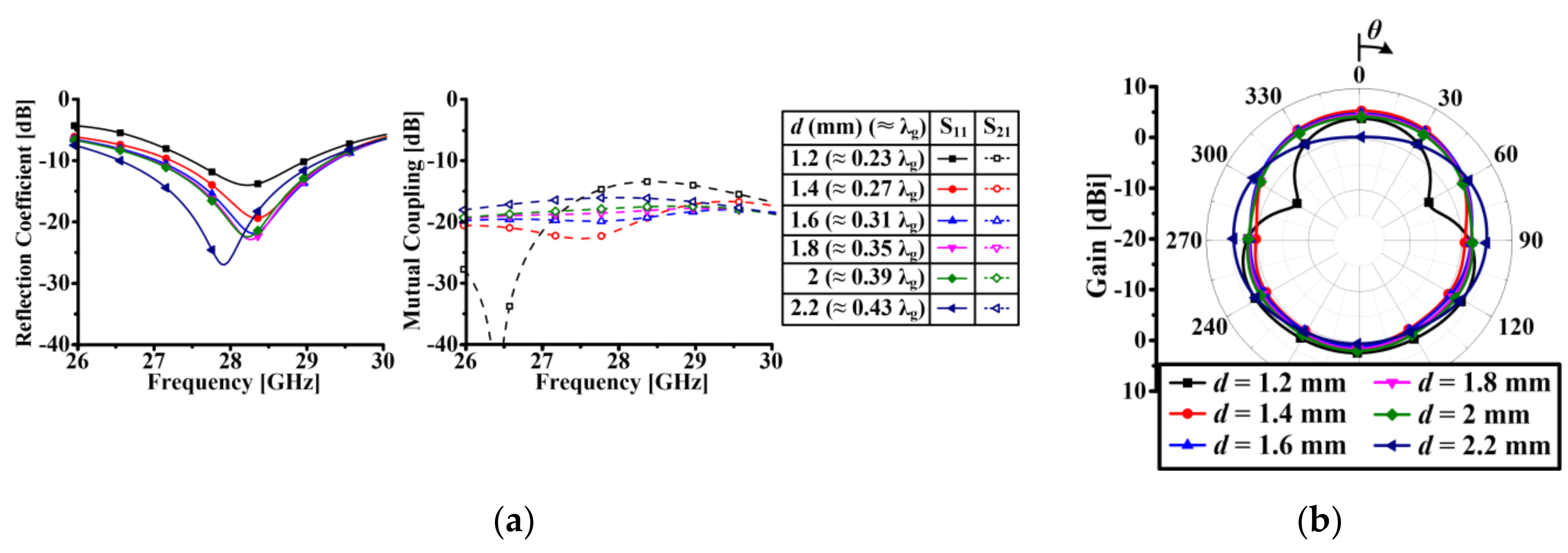
2.2. 1 × 2 Array Antenna Design and Performance
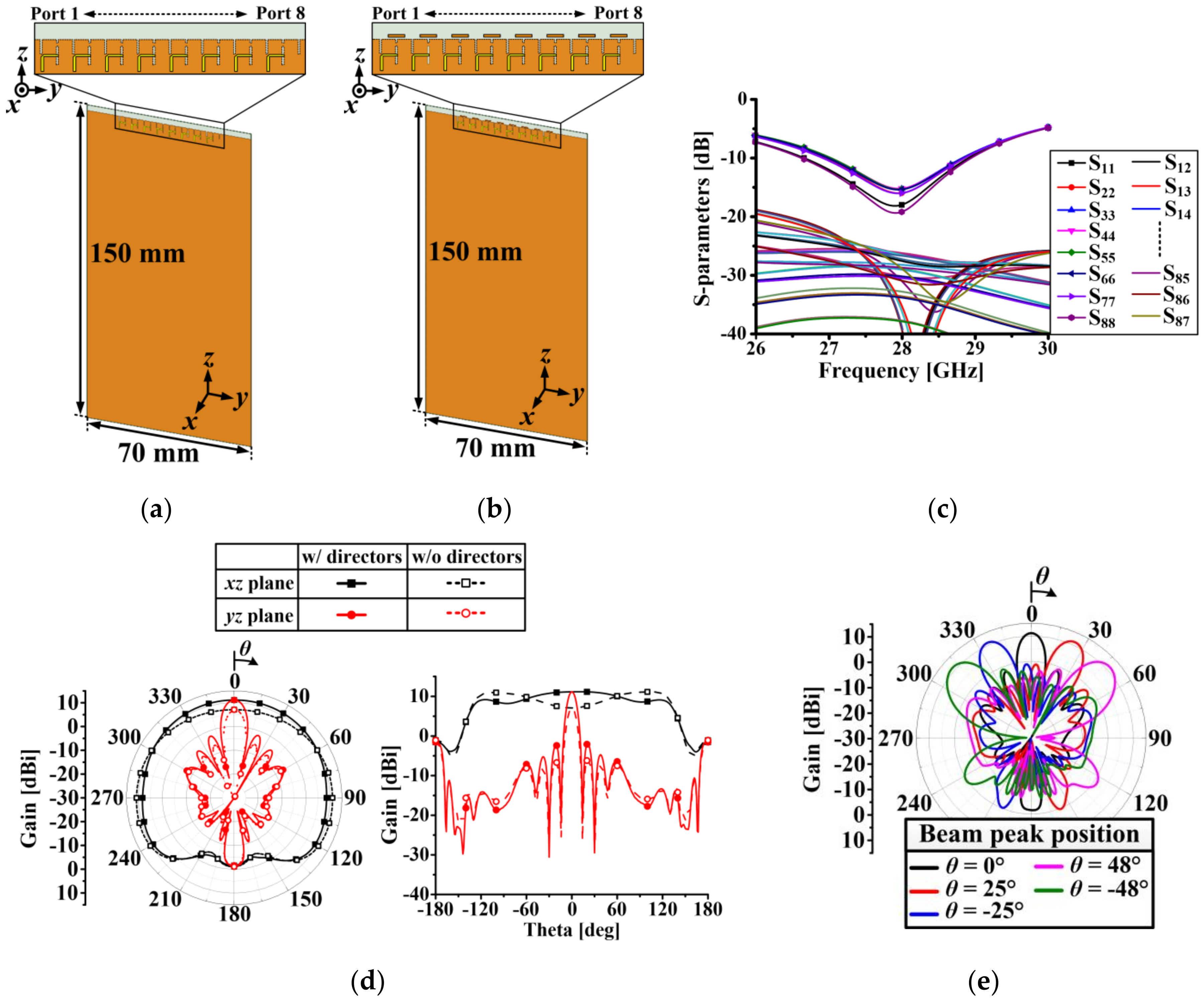
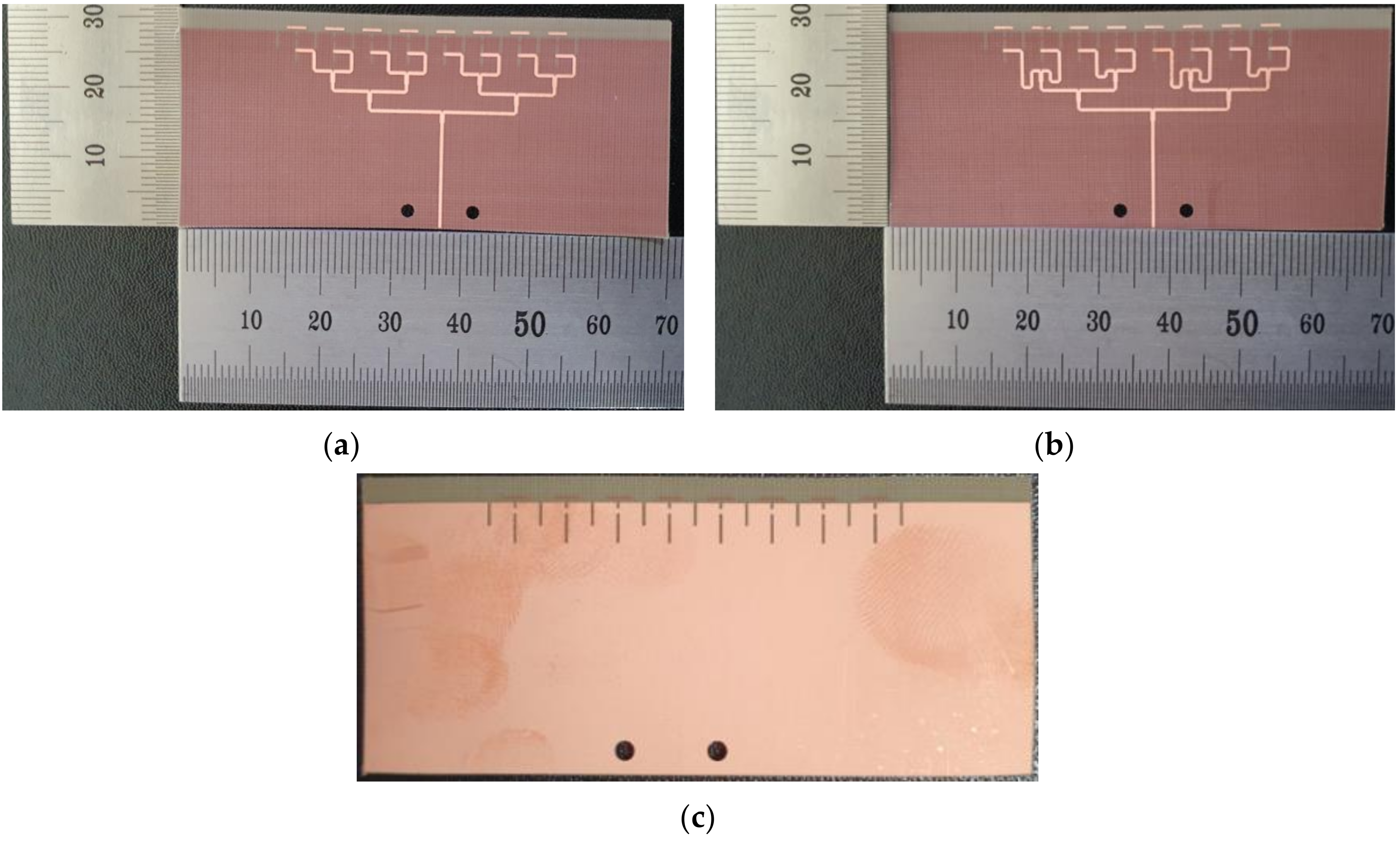
2.3. 1 × 8 Array Antenna Design and Performance
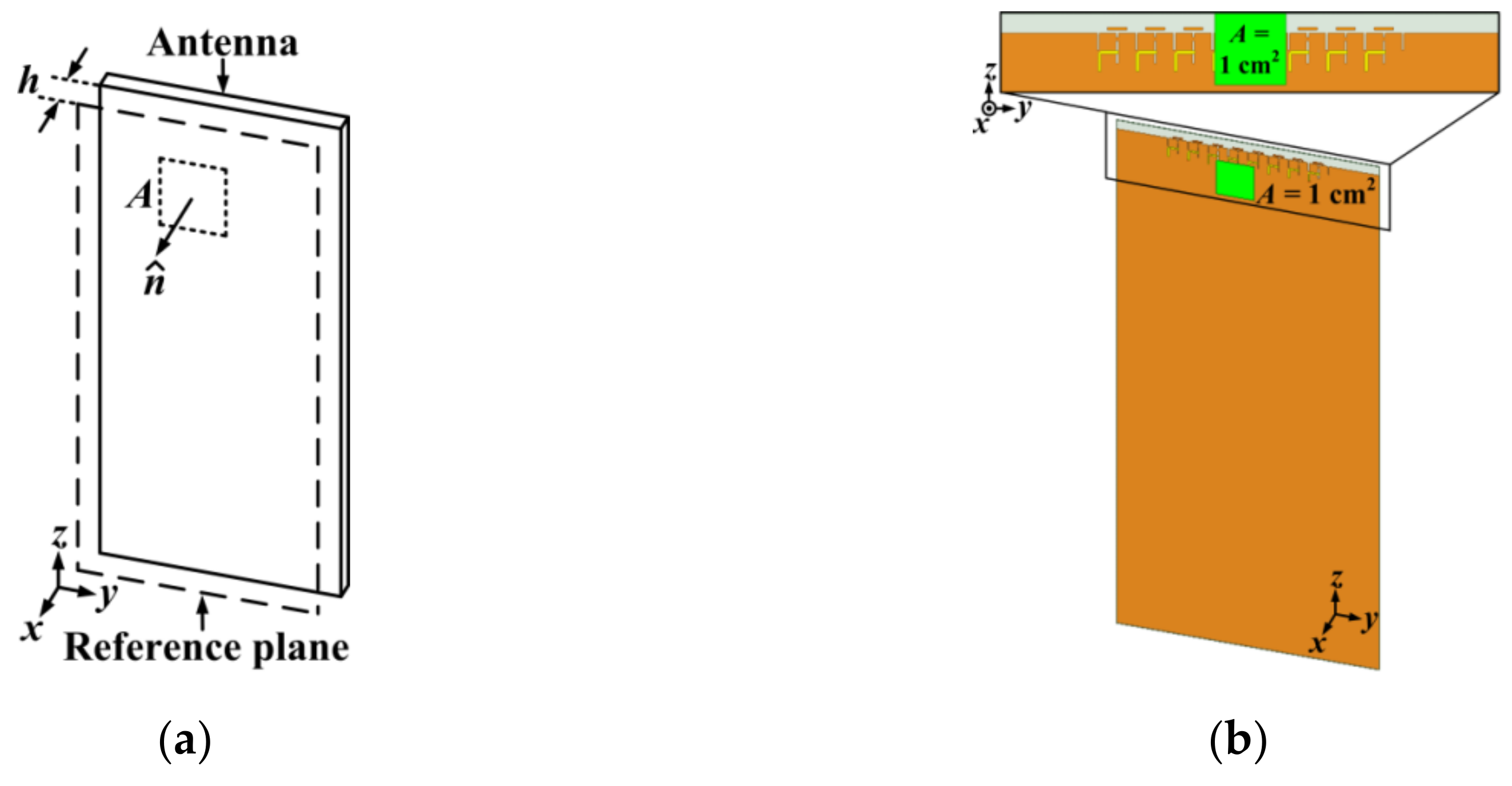
2.4. Analysis of Human Body Effect
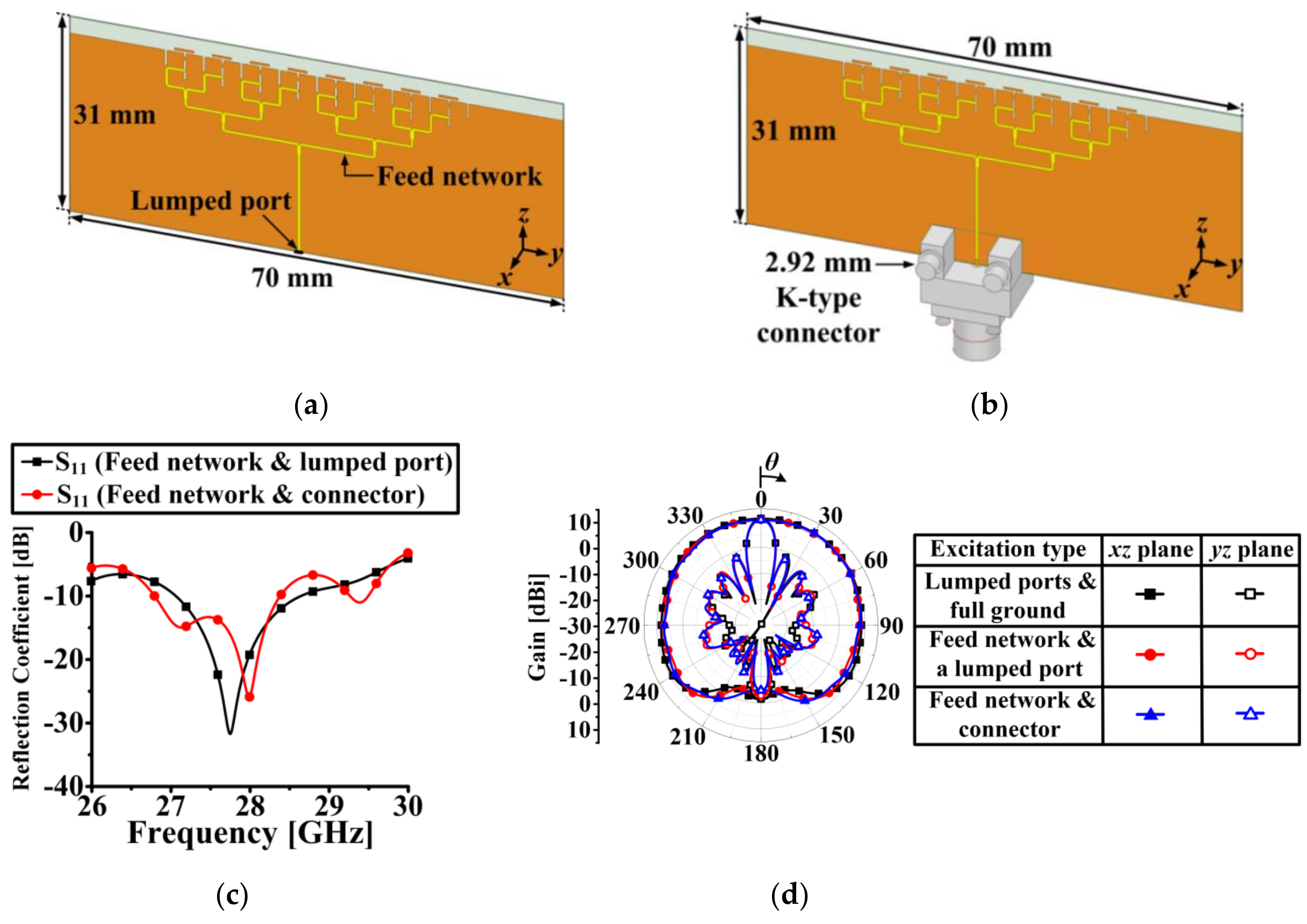
2.5. Effect of an RF Connector and a Feeding Network
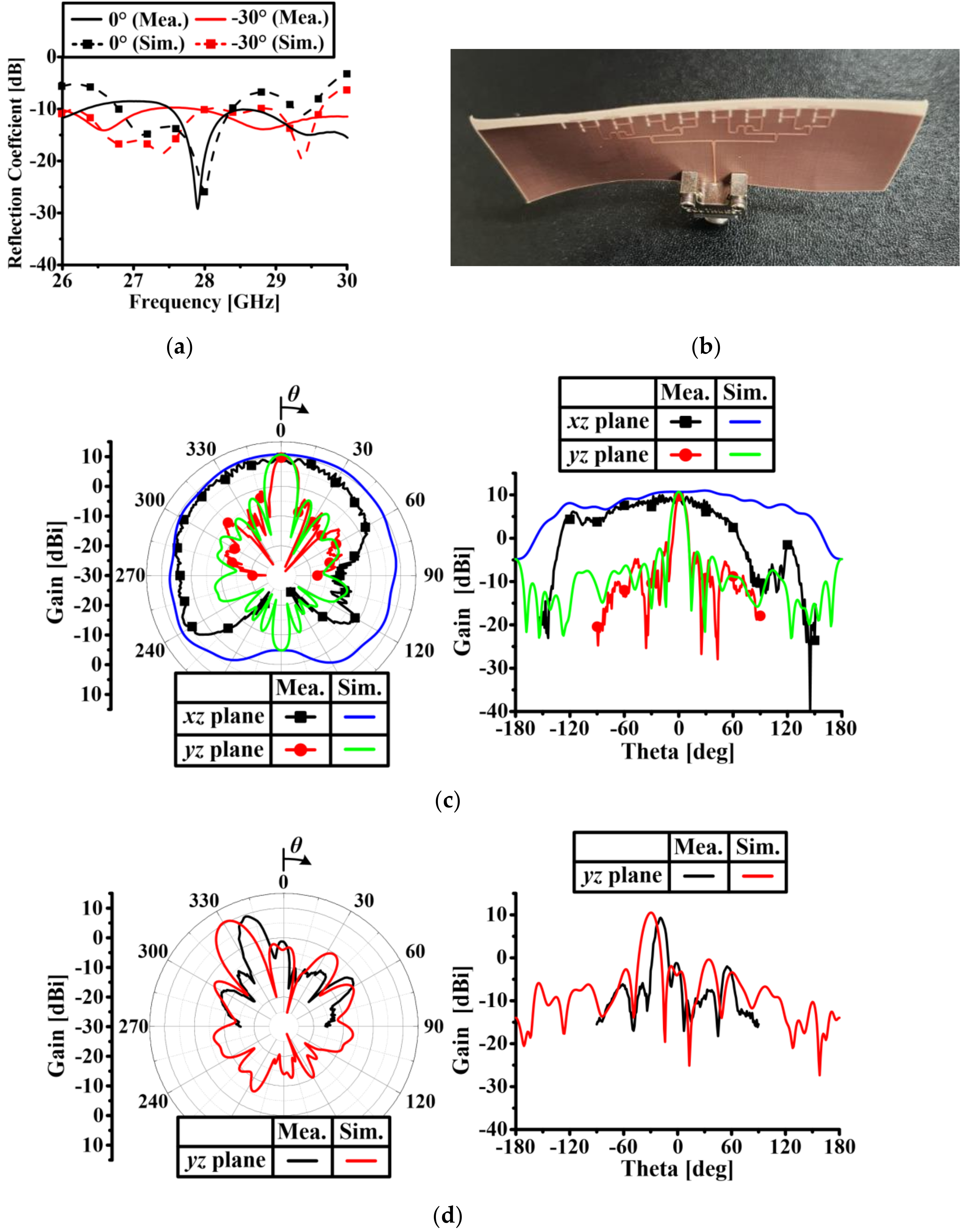
3. Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.; Choi, J. Array antenna with linear and circular polarization characteristics for 28 GHz band 5G mobile handset applications. J. Korean Inst. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2020, 31, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Choi, J. A SAR reduced mm-wave beam-steerable array antenna with dual-mode operation for fully metal-covered 5G cellular handsets. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Choi, J. A 28 GHz 5G phased array antenna with air-hole slots for beam width enhancement. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Ge, X.; Li, Q.; Guizani, M.; Zhang, Y. 5G millimeter-wave antenna array: Design and challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 24, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulyman, A.I.; Nassar, A.T.; Samimi, M.K.; MacCartney, G.R., Jr.; Rappaport, T.S.; Alsanie, A. Radio propagation path loss models for 5G cellular networks in the 28 GHz and 38 GHz millimeter-wave bands. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, W.; Seol, J.; Park, J.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Cho, J.; Cheun, K. Millimeter-wave beamforming as an enabling technology for 5G cellular communications: Theoretical feasibility and prototype results. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Halwagy, W.; Mirzavand, R.; Melzer, J.; Hossain, M.; Mousavi, P. Fence shaping of substrate integrated fan-beam electric dipole for high-band 5G. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Aryanfar, F. Millimeter-wave open ended SIW antenna with wide beam coverage. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 7–13 July 2013; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.; Beak, K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.G. Design and analysis of a low-profile 28 GHz beam steering antenna solution for future 5G cellular applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Tampa, FL, USA, 1–6 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, J.; Choi, J. A compact hemispherical beam-coverage phased array antenna unit for 5G mm-wave applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 139715–139726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-W.; Hwang, I.-J.; Jang, B. End-fire Vivaldi antenna array with wide fan-beam for 5G mobile handsets. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 118299–118304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, R.M.; Kellomäki, T. Body effects on thin single-layer slot, self-complementary, and wire antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, H.G. Slot aerials and their relation to complementary wire aerials (Babinet’s principle). J. IET Part ⅢA Radiol. 1946, 93, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5G Americas. Spectrum above 24 GHz. In 5G Americas White Paper—5G Spectrum Vision; 5G Americas: Washington, WA, USA, 2019; pp. 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Khalily, M.; Tafazolli, R.; Rahman, T.A.; Kamarudin, M.R. Design of phased arrays of series-fed patch antennas with reduced number of the controllers for 28-GHz mm-wave applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.; Rappaport, T.S.; Collins, C.M. Safe for generations to come: Considerations of safety for millimeter waves in wireless communications. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2015, 16, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.D.; Kim, N. 5G electromagnetic waves and analysis of impacts of EMF exposure. Proc. Korea Electromag. Eng. Soc. 2018, 29, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- ICNIRP. Guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 1998, 74, 494–522. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Zhao, K.; Ying, Z.; Sjoberg, D.; He, W.; He, S. Analysis of impacts of expected RF EMF exposure restrictions on peak EIRP of 5G user equipment at 28 GHz and 39 GHz bands. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 20996–21005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Cano, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, K.; Pedersen, G.F. User body interaction of 5G switchable antenna system for mobile terminals at 28 GHz. In Proceedings of the 2019 13th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Krakow, Poland, 1–4 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Gustafsson, M.; Shi, S.; Zhao, K.; Ying, Z.; He, S. Radio frequency exposure compliance of multiple antennas for cellular equipment based on semidefinite relaxation. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2019, 61, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys. Available online: www.ansys.com/products/electonics/ansys-hfss (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Yazdandoost, K.Y.; Laakso, I. EMF exposure analysis for a compact multi-band 5G antenna. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2018, 68, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Ying, Z.; Scialacqua, L.; Scannavini, A.; Foged, L.J.; Bolin, T.; Zhao, K.; He, S.; Gustafsson, M. Radiation performance analysis of 28 GHz antennas integrated in 5G mobile terminal housing. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 48088–48101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory Analysis and Design, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Southwest Microwave. Available online: https://mpd.southwestmicrowave.com/product/1092-03a-6-end-launch-2-92mm-k-40-ghz-jack-female-standard-block/ (accessed on 4 September 2020).











| Structure | Target Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | HPBW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [2] | 1 × 8 slotted array | 28 | 16.92 | 116° |
| [3] | 1 × 8 dipole array with air hole slots | 28 | 11.15 | 219° |
| [7] | 4 × 1 SIW cavity array | 28 | 12.6 | 133° |
| [9] | 16 × 1 mesh grid array | 28 | 10.9 | 109° |
| [10] | 1 × 8 slotted array with AMC reflector | 28 | 11.8 | 142° |
| [11] | 4 × 1 Vivaldi antenna array | 28 | 9.46 | 165° |
| This work | 1 × 8 quasi-Yagi slotted array | 28 | 11.16 | 256.72° |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Choi, J. Quasi-Yagi Slotted Array Antenna with Fan-Beam Characteristics for 28 GHz 5G Mobile Terminals. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217686
Kim S, Choi J. Quasi-Yagi Slotted Array Antenna with Fan-Beam Characteristics for 28 GHz 5G Mobile Terminals. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(21):7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217686
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sungpeel, and Jaehoon Choi. 2020. "Quasi-Yagi Slotted Array Antenna with Fan-Beam Characteristics for 28 GHz 5G Mobile Terminals" Applied Sciences 10, no. 21: 7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217686
APA StyleKim, S., & Choi, J. (2020). Quasi-Yagi Slotted Array Antenna with Fan-Beam Characteristics for 28 GHz 5G Mobile Terminals. Applied Sciences, 10(21), 7686. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217686





