Protective Action of Betulinic Acid on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Inflammation and Energy Metabolic Homeostasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagent
2.2. Animals
2.3. Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion (MCAO)
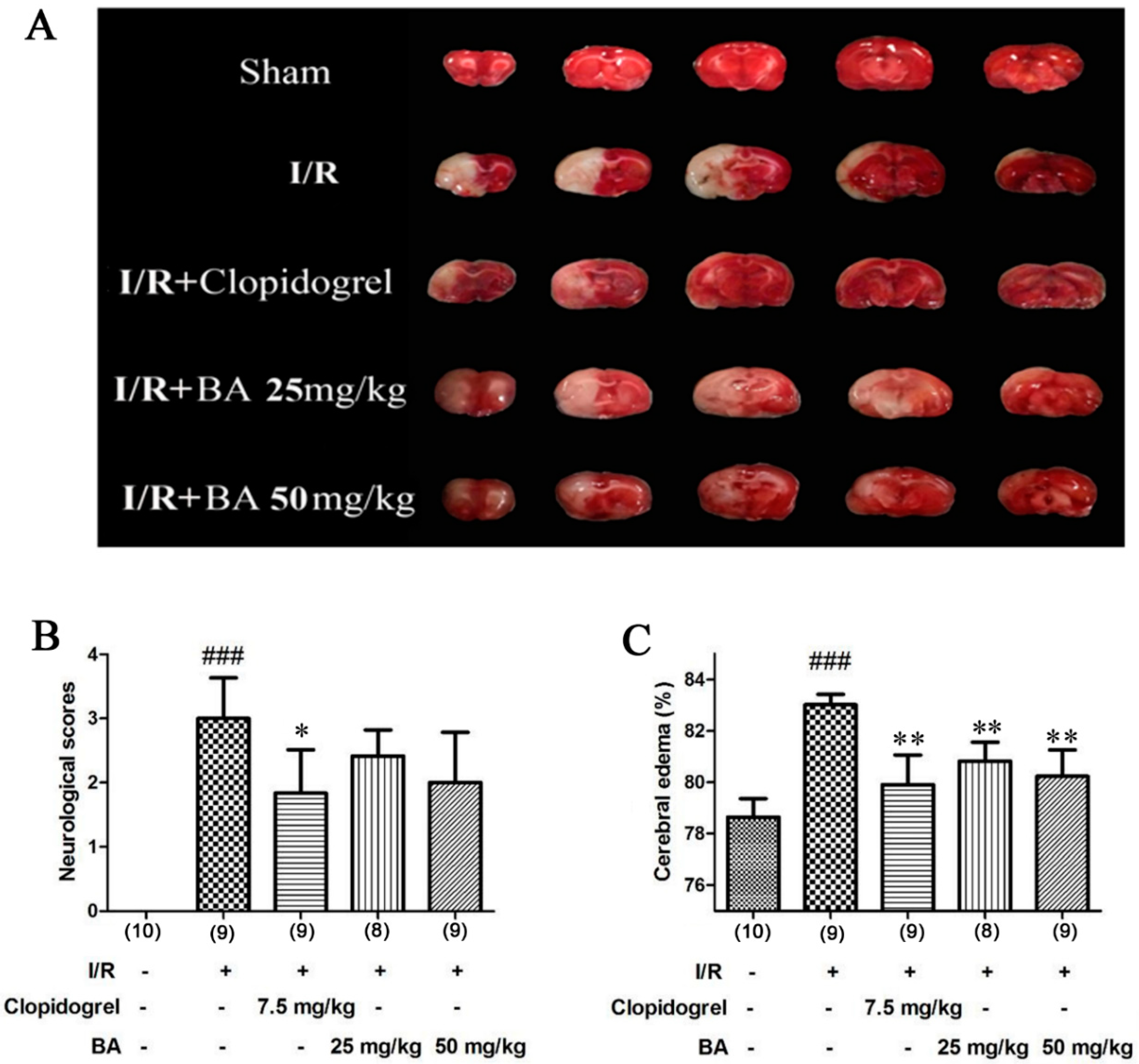
2.4. Neurological Scores
2.5. Measurement of Brain Infarction and Cerebral Edema
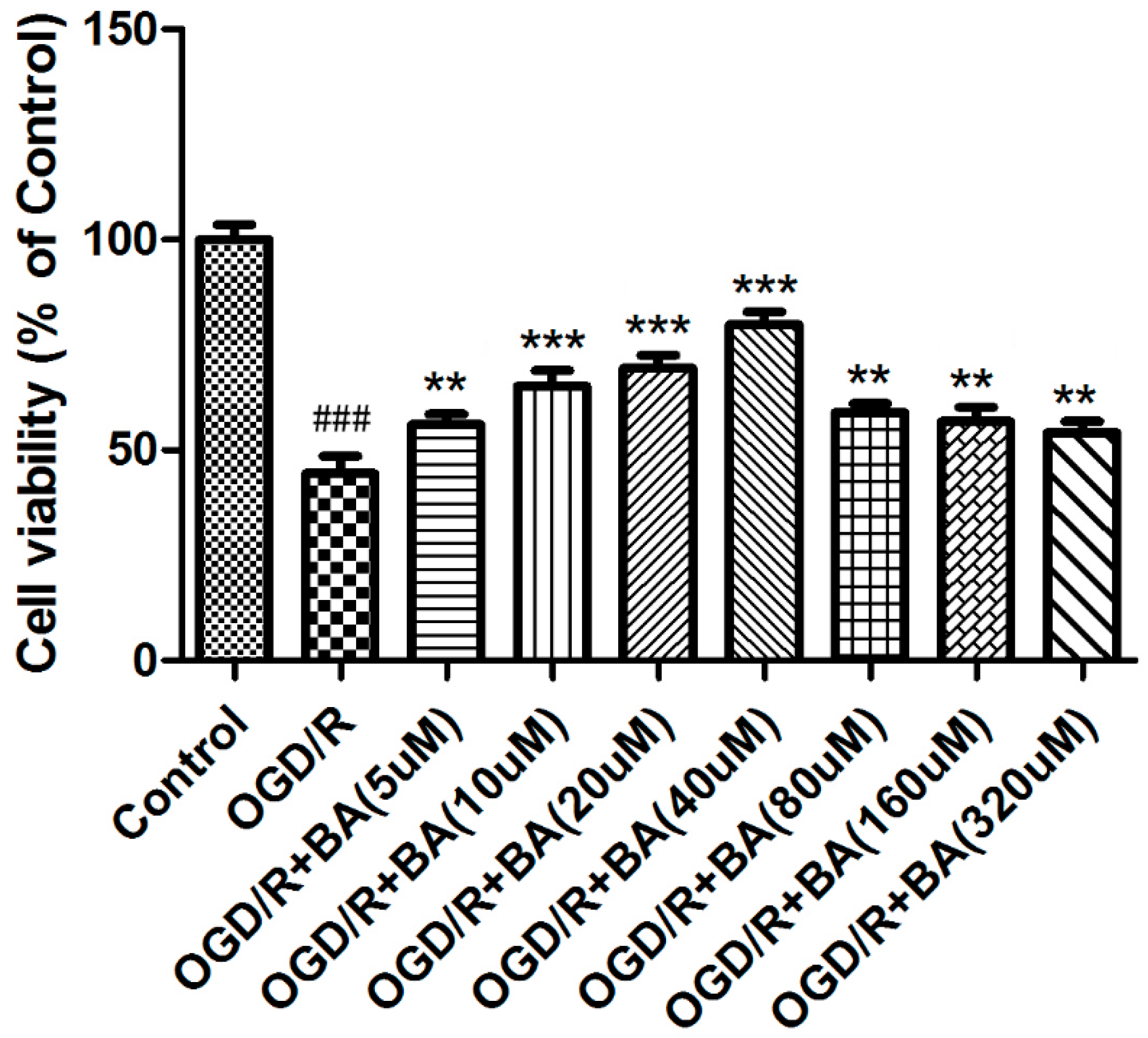
2.6. Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation and Recovery (OGD/R)
2.7. MTT Assay
2.8. Biochemical Assay
2.9. Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of BA on Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury In Vivo
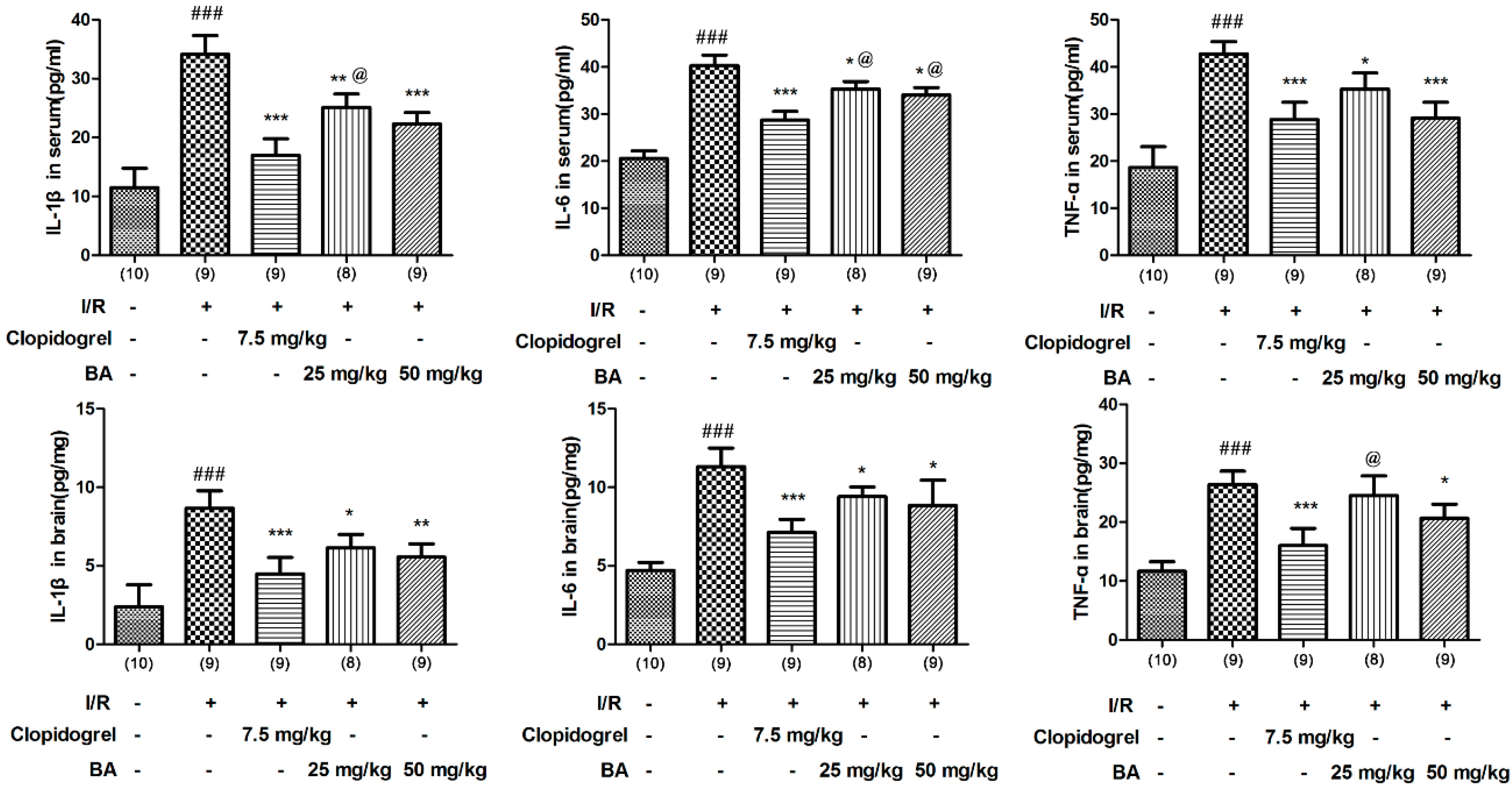
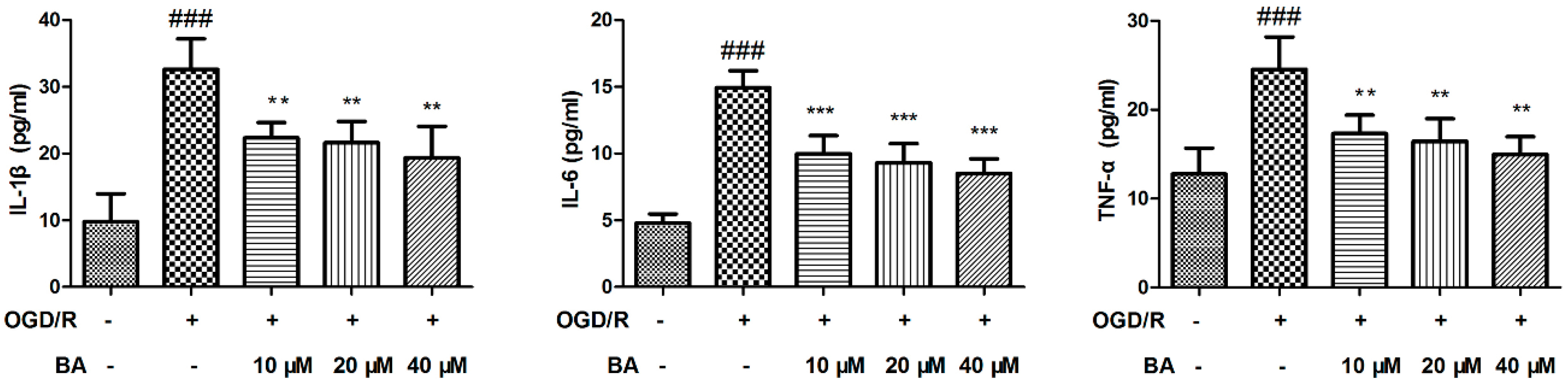
3.2. Effects of BA on Pro-inflammatory Cytokine
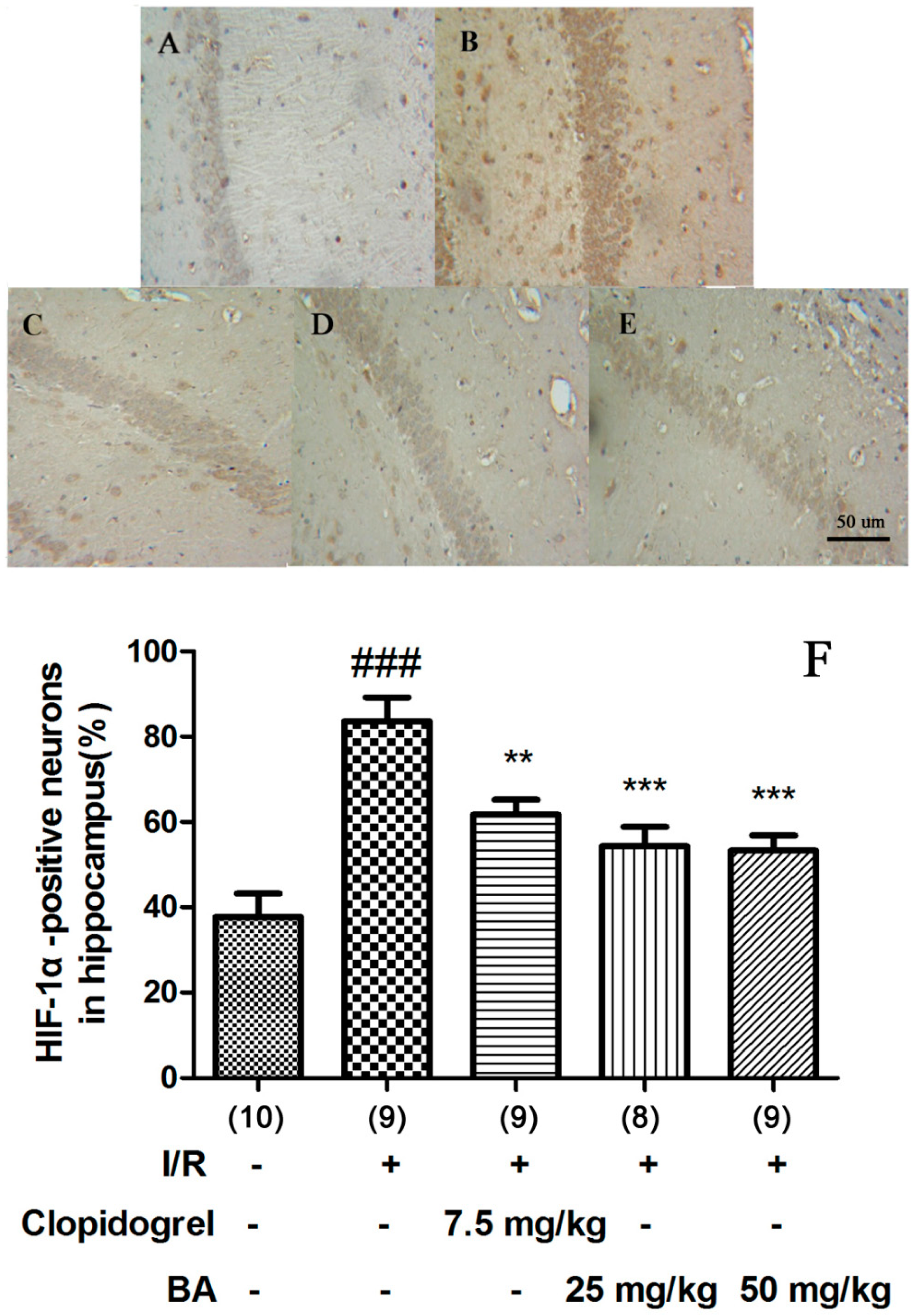
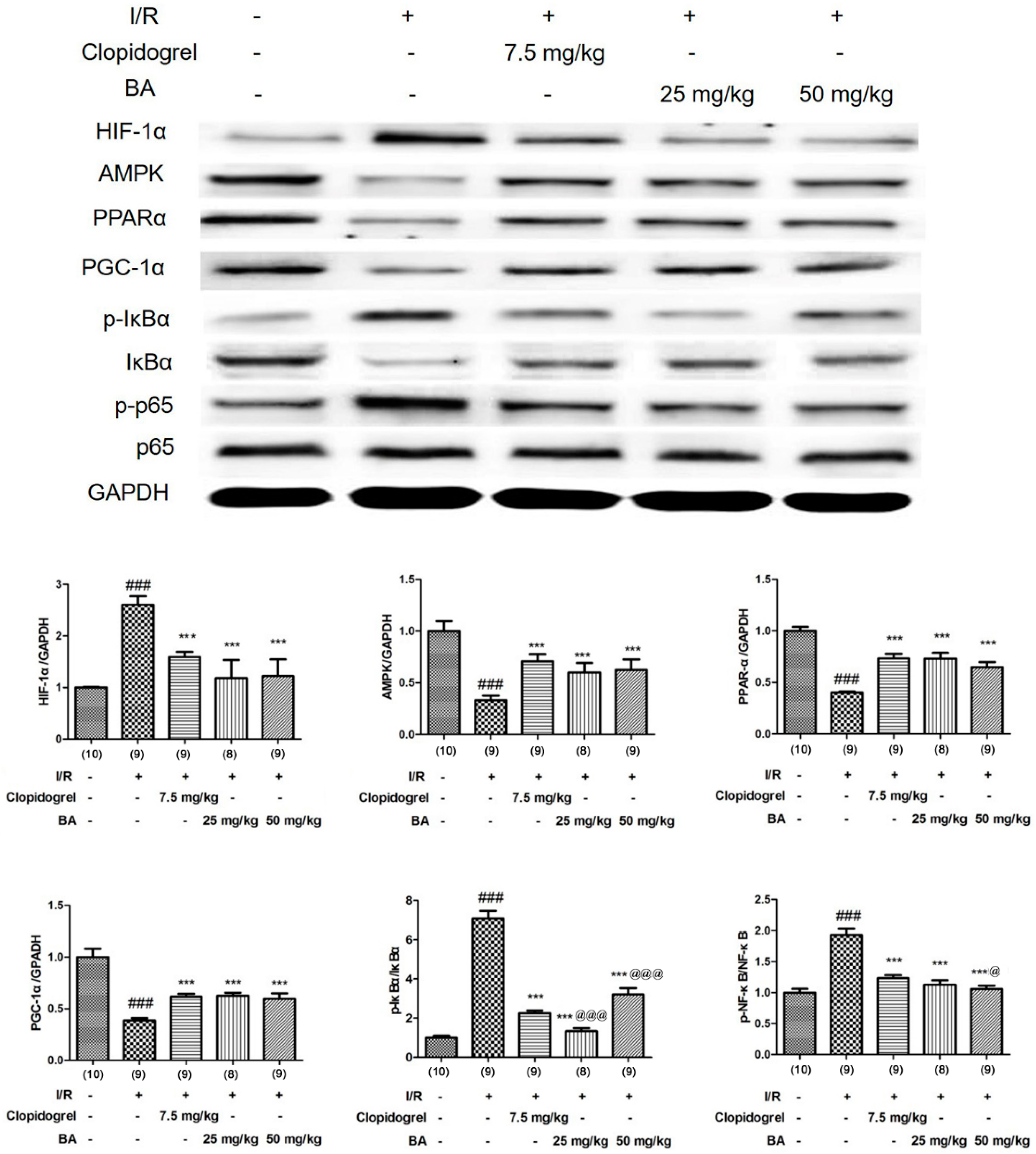
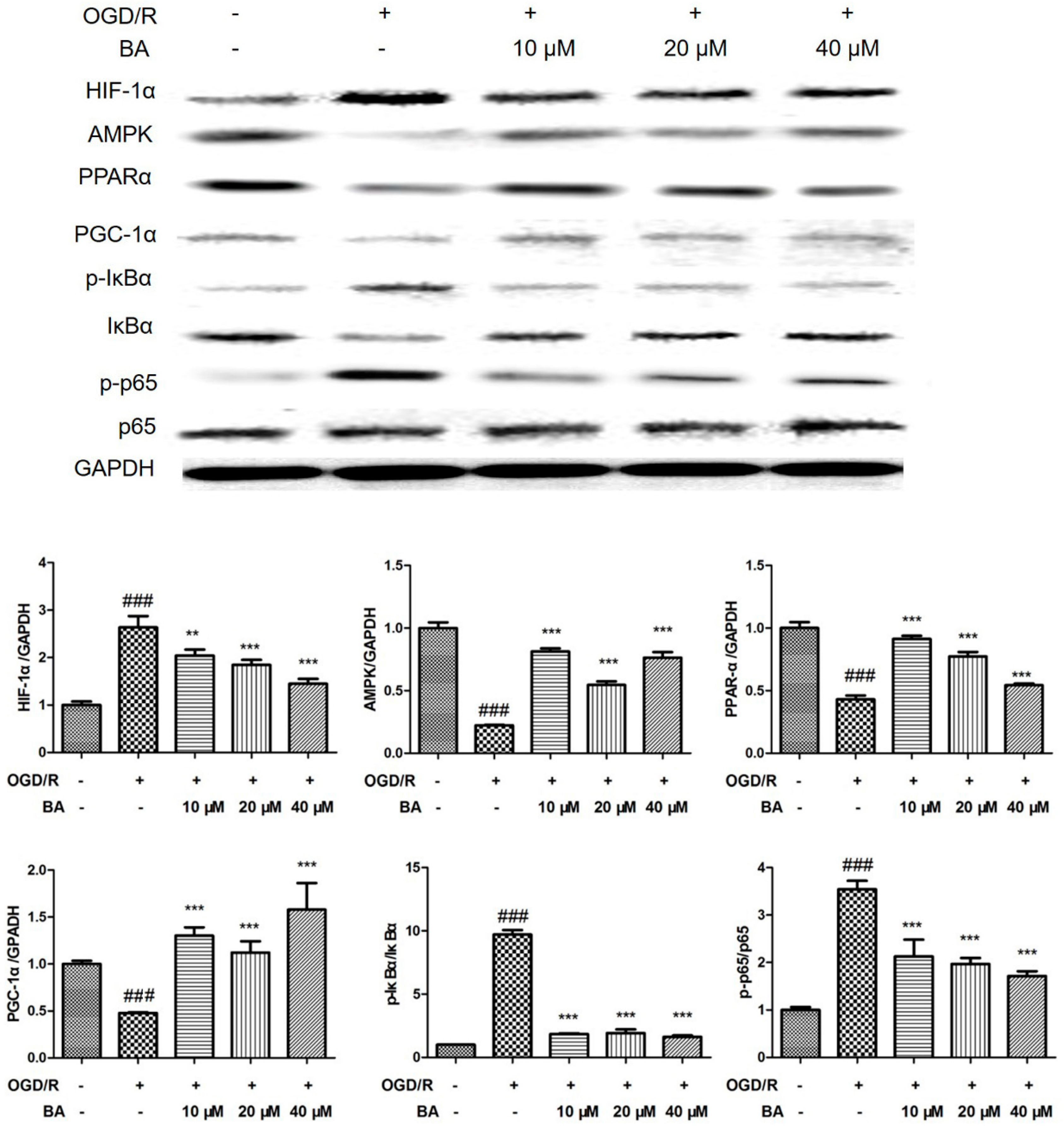
3.3. Effects of BA on HIF-1α Signaling
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turelson, T.; Begg, S.; Mathers, C. The global burden of cerebrovascular disease. Global Burden of Disease. 2006. Available online: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/statistics/bod_cerebrovasculardiseasestroke.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2020).
- Sudlow, C.L.M.; Warlow, C.P. Comparable studies of the incidence of stroke and its pathological types. Results from an international collaboration. Stroke 1997, 28, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G.; Scott, J.W.; Pan, D.A. Management of Cellular Energy by the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase System. FEBS Lett. 2003, 546, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.P.; Shi, Y.W.; Tang, M.; Zhang, X.C.; Gu, Y.; Liang, X.M.; Wang, Z.W.; Ding, F. Isoquercetin Ameliorates Cerebral Impairment in Focal Ischemia Through Anti-Oxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Effects in Primary Culture of Rat Hippocampal Neurons and Hippocampal CA1 Region of Rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2126–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, C.; Woods, A.; Ceballos, M.L.; Carling, D.; Guzman, M. The AMP-Activated Protein Kinase is Involved in the Regulation of Ketone Body Production by Astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, H.S.; Chang, C.Y.; Jeon, S.B.; Yoon, H.J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, I.H.; Jeon, S.H.; Johnson, R.S.; Park, E.J. The HIF-1/glial TIM-3 Axis Controls Inflammation-Associated Brain Damage under Hypoxia. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, R.; Paola, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion by an Intraluminal Suture Method. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1727, 393–401. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Holmes, S.S.; Baker, G.A.; Challa, S.; Bose, H.S.; Song, Z. Ionic derivatives of betulinic acid as novel HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Zhu, Z.F.; Tang, J.; Lin, Q.H.; Chen, L.; Sun, J.B. Design and Synthesis of NO-Releasing Betulinic Acid Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, A.; Xue, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Xia, J.; Wei, T.; Cao, J.; Zhou, W. Cardioprotective Effect of Betulinic Acid on Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 573745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekşioğlu-Demiralp, E.; Kardaş, E.R.; Özgül, S.; Yağci, T.; Bilgin, H.; Sehirli, O.; Ercan, F.; Sener, G. Betulinic Acid Protects against Ischemia/Reperfusion- Induced Renal Damage and Inhibits Leukocyte Apoptosis. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, X.H.; Zhang, J.D.; Li, R.B.; Jia, M.; Cui, X.R. Compared Efficacy of Clopidogrel and Tcagrelor in Treating Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 8, 217. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Gu, J.; Gao, M.; Du, N.; Liu, P.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.J.; Cao, X. Study on Antiplatelet Effect of A New Thiophenopyridine Platelets P2Y12 Receptor Antagonist DV-127. Thromb. Res. 2018, 170, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajsic, S.; Gothe, H.; Borba, H.H.; Sroczynski, G.; Vujicic, J.; Toell, T.; Siebert, U. Economic burden of stroke: A systematic review on post-stroke care. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2019, 20, 107–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2015 Neurological Disorders Collaborator Group. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 877–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, R.; Fernández-Gajardo, R.; Gutiérrez, R.; Matamala, J.M.; Carrasco, R.; Miranda-Merchak, A.; Feuerhake, W. Oxidative Stress and Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke: Novel Therapeutic Opportunities. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grysiewicz, R.A.; Thomas, K.; Pandey, D.K. Epidemiology of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke: Incidence, Prevalence, Mortality, and Risk Factors. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 871–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Sharma, S.; Hassan, K.M. Pathophysiologic Mechanisms of Acute Ischemic Stroke: An Overview with Emphasis on Therapeutic Significance beyond Thrombolysis. Pathophysiology 2010, 17, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.; Matei, C. Benefits and Risks of Anticoagulation in Acute Coronary Syndrome. Am. J. Ther. 2019, 26, e198–e207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Eckle, T. Ischemia and Reperfusion from Mechanism to Translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.; Chang, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.E. Inflammation after Ischemic Stroke: The Role of Leukocytes and Glial Cells. Exp. Neurobiol. 2016, 25, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wei, T.; Gao, J.; Chang, X.; He, H.; Luo, F.; Zhou, R.; Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Yan, T.H. The Cardioprotective Effect of Ssalidroside against Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Inhibiting Apoptosis and Inflammation. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delerive, P.; Fruchart, J.C.; Staels, B. Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors in Inflammation Control. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 169, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Drori, S.; Uldry, M.; Silvaggi, J.M.; Rhee, J.; Jäger, S.; Handschin, C.; Zheng, K.; Lin, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Suppression of Reactive Oxygen Species and Neurodegeneration by the PGC-1 Transcriptional Coactivators. Cell 2006, 127, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisele, P.S.; Furrer, R.; Beer, M.; Handschin, C. The PGC-1 Coactivators Promote an Anti-inflammatory Environment in Skeletal Muscle In Vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndubuizu, O.I.; Tsipis, C.P.; Li, A.; LaManna, J.C. Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1)- Independent Microvascular Angiogenesis in the Aged Rat Brain. Brain Res. 2010, 1366, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arany, Z.; Foo, S.Y.; Ma, Y.; Ruas, J.L.; Bommi-Reddy, A.; Girnun, G.; Cooper, M.; Laznik, D.; Chinsomboon, J.; Rangwala, S.M.; et al. HIF-Independent Regulation of VEGF and Angiogenesis by the Transcriptional Coactivator PGC-1alpha. Nature 2008, 451, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.H.; Mu, Y. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Activation as a Strategy for Protecting Vascular Endothelial Function. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 35, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnley, A.M.; Stapleton, D.; Mann, R.J.; Witters, L.A.; Kemp, B.E.; Bartlett, P.F. Cellular Distribution and Developmental Expression of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Isoforms in Mouse Central Nervous System. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.H.; Hou, X.Y.; Shi, C.M.; Nagata, D.; Walsh, K.; Cohen, R.A. Modulation by Peroxynitrite of Akt- and AMP-Activated Kinase-Dependent Ser1179 Phosphorylation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32552–32557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Chun, Y.S.; Chen, J.; Kim, J.E.; Park, J.W. Sirtuin 1 Modulates Cellular Responses to Hypoxia by Deacetylating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Guarente, L. Sirtuins at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, E.D.; Kang, L.; Lee-Young, R.S.; Hasenour, C.M.; Lustig, D.G.; Lynes, S.E.; Donahue, E.P.; Swift, L.L.; Charron, M.J.; Wasserman, D.H. Glucagon and Lipid Interactions in the Regulation of Hepatic AMPK Signaling and Expression of PPARalpha and FGF21 Transcripts In Vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E607–E614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Liu, W.; Shi, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gong, P. Docosahexaenoic Acid Attenuates LPS-Stimulated Inflammatory Response by Regulating the PPARγ/NF-κB Pathways in Primary Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 112, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Guardia, D.; Palomer, X.; Coll, T.; Davidson, M.M.; Chan, T.O.; Feldman, A.M.; Laguna, J.C.; Vázquez-Carrera, M. The P65 Subunit of NF-kappaB Binds to PGC-Lalpha, Linking Inflammation and Metabolic Disturbances in Cardiac Cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogeeswari, P.; Sriram, D. Betulinic Acid and Its Derivatives: A Review on Their Biological Properties. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperczyk, H.; La Ferla-Brühl, K.; Westhoff, M.A.; Behrend, L.; Zwacka, R.M.; Debatin, K.M.; Fulda, S. Betulinic Acid as New Activator of NF-κB: Molecular Nechanisms and Implications for Cancer Therapy. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6945–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; del Carmen Recio, M.; Maez, S.; Giner, R.; Ríos, J. Effect of Triterpenoids on the Inflammation Induced by Protein Kinase C Activators, Neuronally Acting Irritants and Other Agents. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 410, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.F.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Maia, G.L.; Guimarães, E.T.; Meira, C.S.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, R.; de Carvalho, L.C.; Soares, M.B. Potent Anti-Inflammatory Sctivity of Betulinic Scid Yreatment in A Model of Lethal Endotoxemia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasso, D.M.; Camporesi, E.M.; Mangar, D.; Saporta, S. Effects of Isoflurane or Propofol on Postnatal Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Young and Aged Rats. Brain Res. 2013, 1530, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, W.; Hao, K. Protective Action of Betulinic Acid on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Inflammation and Energy Metabolic Homeostasis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072578
Jiang W, Hao K. Protective Action of Betulinic Acid on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Inflammation and Energy Metabolic Homeostasis. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(7):2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072578
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Wenjiao, and Kun Hao. 2020. "Protective Action of Betulinic Acid on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Inflammation and Energy Metabolic Homeostasis" Applied Sciences 10, no. 7: 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072578
APA StyleJiang, W., & Hao, K. (2020). Protective Action of Betulinic Acid on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Inflammation and Energy Metabolic Homeostasis. Applied Sciences, 10(7), 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072578



