Optimizing Power and Thermal Efficiency of an Irreversible Variable-Temperature Heat Reservoir Lenoir Cycle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cycle Model and Thermodynamic Performance
3. Numerical Examples and Discussions
3.1. Cycle Performance Analysis When the HTC of Hot- and Cold-Side HEXs Is Constant
3.2. Cycle Performance Optimization When the HTC Distributions of the Two HEXs Can Be Optimized
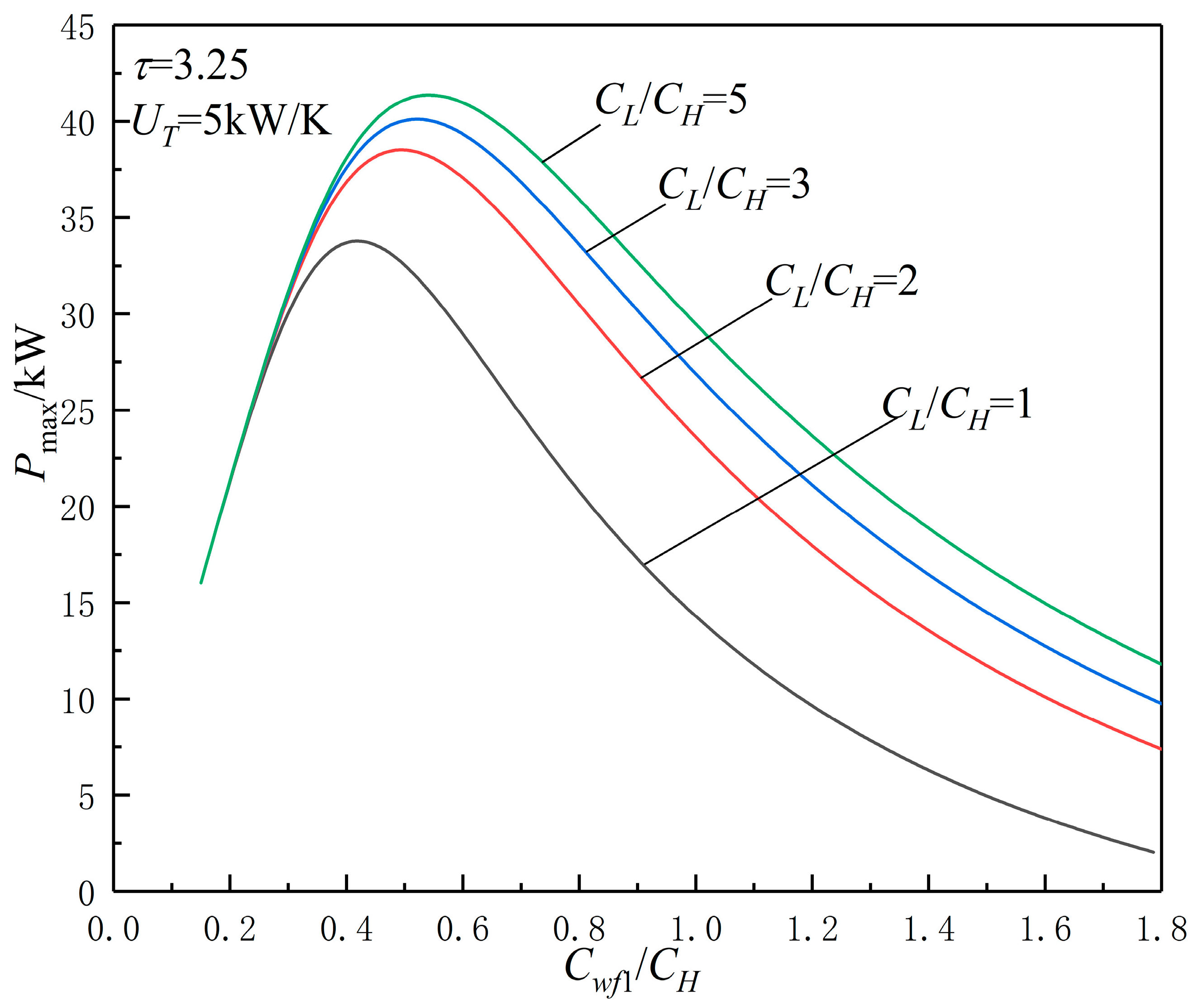
3.3. TCR Matching Optimization
4. Conclusions
| (1) | When and are constants, is a certain “point”, and with the increases in , , , and , and increase. When can be optimized, and versus characteristics are parabolic-like ones, there are and which makes the cycle reach and . |
| (2) | With the increase of , show a parabolic-like change, there is an , which makes the cycle reach . With the increases in , , and , and increase. With the increases in , increases, and is unchanged. |
| (3) | Internal irreversibility and variable temperature HR are two general properties of practical cycles. It is necessary to study their influences on the cycle performance. FTT is a powerful theoretical tool for thermodynamic cycles with those properties. |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| specific heat at constant pressure () | |
| specific heat at constant volume () | |
| effectiveness of heat exchanger | |
| specific heat ratio (-) | |
| mass flow rate of the working fluid () | |
| number of heat transfer units | |
| cycle power () | |
| quantity of heat transfer rate () | |
| temperature () | |
| heat conductance () | |
| total heat conductance () | |
| heat conductance distribution | |
| Greek symbols | |
| heat reservoirs inlet temperature ratio | |
| cycle thermal efficiency | |
| Subscripts | |
| hot-side | |
| cold-side | |
| maximum value | |
| optimal | |
| maximum power point | |
| maximum thermal efficiency point | |
| , | cycle state points |
Abbreviations
| FTT | finite-time thermodynamic |
| HEG | heat engine |
| HEX | heat exchanger |
| HR | heat reservoirs |
| HTC | heat conductance |
| LC | Lenoir cycle |
| SFLC | steady flow Lenoir cycle |
| TCR | thermal capacity rate |
References
- Andresen, B. Finite-Time Thermodynamics; Physics Laboratory II, University of Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Danmark, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, K.H.; Burzler, J.M.; Schubert, S. Endoreversible thermodynamics. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 1997, 22, 311–355. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.G.; Wu, C.; Sun, F.R. Finite time thermodynamic optimization or entropy generation minimization of energy systems. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 1999, 24, 327–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, B. Current trends in finite-time thermodynamics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2690–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.L.; Chen, L.G.; Sun, F.R. Progress in finite time thermodynamic studies for internal combustion engine cycles. Entropy 2016, 18, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feidt, M. The history and perspectives of efficiency at maximum power of the Carnot engine. Entropy 2017, 19, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidt, M.; Costea, M. Progress in Carnot and Chambadal modeling of thermomechnical engine by considering entropy and heat transfer entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diskin, D.; Tartakovsky, L. Efficiency at maximum power of the low-dissipation hybrid electrochemical-Otto cycle. Energies 2020, 13, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, U.; Grisolia, G.; Kuzemsky, A.L. Time, irreversibility and entropy production in nonequilibrium systems. Entropy 2020, 22, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costea, M.; Petrescu, S.; Feidt, M.; Dobre, C.; Borcila, B. Optimization modeling of irreversible Carnot engine from the perspective of combining finite speed and finite time analysis. Entropy 2021, 23, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.S.; Salamon, P.; Andresen, B. How it all began. Entropy 2020, 22, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.W.; Chen, L.G. Theoretical maximum efficiency and higher power output in triboelectric nanogenerators. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 2463–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Meng, Z.W.; Ge, Y.L.; Wu, F. Performance analysis and optimization for irreversible combined quantum Carnot heat engine working with ideal quantum gases. Entropy 2021, 23, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.Z.; Ding, Z.M.; Chen, L.G.; Ge, Y.L.; Feng, H.J. Modeling and performance optimization of an irreversible two-stage combined thermal Brownian heat engine. Entropy 2021, 23, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.Z.; Ding, Z.M.; Chen, L.G.; Ge, Y.L.; Feng, H.J. Modelling of irreversible two-stage combined thermal Brownian refrigerators and their optimal performance. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2021, 46, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourkiaei, S.M.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Sadeghzadeh, M.; Moosavi, S.; Pourfayaz, F.; Chen, L.G.; Yazdi, M.A.; Kumar, R. Thermoelectric cooler and thermoelectric generator devices: A review of present and potential applications, modeling and materials. Energy 2019, 186, 115849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Meng, F.K.; Ge, Y.L.; Feng, H.J.; Xia, S.J. Performance optimization of a class of combined thermoelectric heating devices. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.S.; Ding, Z.M.; Chen, L.G.; Ge, Y.L. Performance optimization of thermionic refrigerators based on van der Waals heterostructures. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.S.; Ding, Z.M.; Chen, L.G. Performance evaluation and parametric optimum design of irreversible thermionic generators based on van der Waals heterostructures. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 225, 113360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Q.; Feng, H.J.; Chen, L.G.; Wang, W.H. Power density analysis and multi-objective optimization for a modified endoreversible simple closed Brayton cycle with one isothermal heat process. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Shen, J.F.; Ge, Y.L.; Wu, Z.X.; Wang, W.H.; Zhu, F.L.; Feng, H.J. Power and efficiency optimization of open Maisotsenko-Brayton cycle and performance comparison with traditional open regenerated Brayton cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 217, 113001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Tang, C.Q.; Feng, H.J.; Ge, Y.L. Power, efficiency, power density and ecological function optimizations for an irreversible modified closed variable-temperature reservoir regenerative Brayton cycle with one isothermal heating process. Energies 2020, 13, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Ge, Y.L.; Liu, C.; Feng, H.J.; Lorenzini, G. Performance of universal reciprocating heat-engine cycle with variable specific heats ratio of working fluid. Entropy 2020, 22, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.S.; Ge, Y.L.; Chen, L.G.; Feng, H.J. Performance optimizations with single-, bi-, tri- and quadru-objective for irreversible Atkinson cycle with nonlinear variation of working fluid’s specific heat. Energies 2021, 14, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.J.; Tao, G.S.; Tang, C.Q.; Ge, Y.L.; Chen, L.G.; Xia, S.J. Exergoeconomic performance optimization for a regenerative gas turbine closed-cycle heat and power cogeneration plant. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Yang, B.; Feng, H.J.; Ge, Y.L.; Xia, S.J. Performance optimization of an open simple-cycle gas turbine combined cooling, heating and power plant driven by basic oxygen furnace gas in China’s steelmaking plants. Energy 2020, 203, 117791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.G. Exergoeconomic performance optimization of space thermoradiative cell. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, L.G.; Xia, S.J.; Ge, Y.L.; Wang, C.; Feng, H.J. Multi-objective optimization for helium-heated reverse water gas shift reactor by using NSGA-II. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 148, 119025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, R.; Chen, L.G.; Xia, S.J.; Li, P.L.; Ge, Y.L. Performance analysis of hydrogen iodide decomposition membrane reactor under different sweep modes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 244, 114436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R. Maximum profit configurations of commercial engines. Entropy 2011, 13, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirlin, A.; Gagarina, L. Finite-time thermodynamics in economics. Entropy 2020, 22, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, B.; Walker, S.; Ng, B.; Tam, I.C.K. Finite time analysis of a tri-generation cycle. Energies 2015, 8, 6215–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumitrascu, G.; Feidt, M.; Popescu, A.; Grigorean, S. Endoreversible trigeneration cycle design based on finite physical dimensions thermodynamics. Energies 2019, 12, 3165. [Google Scholar]
- Yasunaga, T.; Fontaine, K.; Ikegami, Y. Performance evaluation concept for ocean thermal energy conversion toward standardization and intelligent design. Energies 2021, 14, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrașcu, G.; Feidt, M.; Grigorean, S. Finite physical dimensions thermodynamics analysis and design of closed irreversible cycles. Energies 2021, 14, 3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ayala, J.; Roco, J.M.M.; Medina, A.; Calvo, H.A. Optimization, stability, and entropy in endoreversible heat engines. Entropy 2020, 22, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levario-Medina, S.; Valencia-Ortega, G.; Barranco-Jimenez, M.A. Energetic optimization considering a generalization of the ecological criterion in traditional simple-cycle and combined cycle power plants. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2020, 45, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.K.; Sahoo, R.R. Effective power and effective power density analysis for water in diesel emulsion as fuel in diesel engine performance. Energy 2019, 180, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinnezhad, S.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Pourkiaei, S.M.; Pourfayaz, F.; Mosavi, A.; Feidt, M.; Shamshirband, S. Thermodynamic assessment and multi-objective optimization of performance of irreversible Dual-Miller cycle. Energies 2019, 12, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masser, R.; Hoffmann, K.H. Endoreversible modeling of a hydraulic recuperation system. Entropy 2020, 22, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwalbe, K.; Fischer, A.; Wagner, K.; Schmidt, K.; Hoffmann, K.H. Recuperation gain for a hydraulic energy storage in automotive applications. Appl. Thermal Eng. 2020, 175, 115275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheunert, M.; Masser, R.; Khodja, A.; Paul, R.; Schwalbe, K.; Fischer, A.; Hoffmann, K.H. Power-optimized sinusoidal piston motion and its performance gain for an Alpha-type Stirling engine with limited regeneration. Energies 2020, 13, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonca, G.; Sahin, B.; Cakir, M. Performance assessment of a modified power generating cycle based on effective ecological power density and performance coefficient. Int. J. Exergy 2020, 33, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.S.; Chen, L.G.; Ge, Y.L.; Feng, H.J. Performance optimizations with single-, bi-, tri- and quadru-objective for irreversible Diesel cycle. Entropy 2021, 23, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.L.; Chen, L.G.; Feng, H.J. Ecological optimization of an irreversible Diesel cycle. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Chan, Y.H. Efficiency enhancement on hybrid power system composed of irreversible solid oxide fuel cell and Stirling engine by finite time thermodynamics. Energies 2021, 14, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masser, R.; Hoffmann, K.H. Optimal control for a hydraulic recuperation system using endoreversible thermodynamics. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Hoffmann, K.H. Cyclic control optimization algorithm for Stirling engines. Symmetry 2021, 13, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, G.; Mehta, A.; Chaudhary, S.; Somani, S.K. Performance comparison of an irreversible closed variable temperature heat reservoir Carnot engine under maximum power density and maximum power conditions. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2006, 27, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ust, Y.; Sogut, O.S.; Sahin, B.; Durmayaz, A. Ecological coefficient of performance (ECOP) optimization for an irreversible Brayton heat engine with variable-temperature thermal reservoirs. J. Energy Inst. 2006, 79, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidt, M.; Costea, M.; Feidt, R.; Danel, Q.; Périlhon, C. New criteria to characterize the waste heat recovery. Energies 2020, 13, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasunaga, T.; Noguchi, T.; Morisaki, T.; Ikegami, Y. Basic heat exchanger performance evaluation method on OTEC. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.Q.; Chen, L.G.; Feng, H.J.; Wang, W.H.; Ge, Y.L. Power optimization of a closed binary Brayton cycle with isothermal heating processesand coupled to variable-temperature reservoirs. Energies 2020, 13, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichty, C. Combustion Engine Processes; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, D.P. Useful work and the thermal efficiency in the ideal Lenoir with regenerative preheating. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 88, 5981–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, B.; Salamon, P.; Berry, R.S. Thermodynamics in finite time. Phys. Today 1987, 37, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.S.; Kazakov, V.A.; Sieniutycz, S.; Szwast, Z.; Tsirlin, A.M. Thermodynamic Optimization of Finite Time Processes; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Feidt, M. Thermodynamics applied to reverse cycle machines, a review. Int. J. Refrig. 2010, 33, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, T.N.F.; Salamon, P.; Nulton, J.; Andresen, B.; Felts, B.; Haas, A.; Calhoun, S.; Robinett, N.; Rohwer, F. Application of finite-time and control thermodynamics to biological processes at multiple scales. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2018, 43, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Chen, L.G.; Ge, Y.L.; Sun, F.R. Finite-time thermodynamic analysis for endoreversible Lenoir cycle coupled to constant-temperature heat reservoirs. Int. J. Energy Environ. 2017, 8, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Nazari, M.A.; Feidt, M. Thermodynamic analysis and multi-objective optimisation of endoreversible Lenoir heat engine cycle based on the thermo-economic performance criterion. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2019, 40, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.B.; Ge, Y.L.; Chen, L.G.; Feng, H.J.; Wu, Z.X. Power and thermal efficiency optimization of an irreversible steady-flow Lenoir cycle. Entropy 2021, 23, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Chen, L.; Ge, Y.; Feng, H. Optimizing Power and Thermal Efficiency of an Irreversible Variable-Temperature Heat Reservoir Lenoir Cycle. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7171. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11157171
Wang R, Chen L, Ge Y, Feng H. Optimizing Power and Thermal Efficiency of an Irreversible Variable-Temperature Heat Reservoir Lenoir Cycle. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(15):7171. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11157171
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruibo, Lingen Chen, Yanlin Ge, and Huijun Feng. 2021. "Optimizing Power and Thermal Efficiency of an Irreversible Variable-Temperature Heat Reservoir Lenoir Cycle" Applied Sciences 11, no. 15: 7171. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11157171
APA StyleWang, R., Chen, L., Ge, Y., & Feng, H. (2021). Optimizing Power and Thermal Efficiency of an Irreversible Variable-Temperature Heat Reservoir Lenoir Cycle. Applied Sciences, 11(15), 7171. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11157171






