Aging Affects Multi-Objective Optimal Control Strategies during Obstacle Crossing
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Protocol
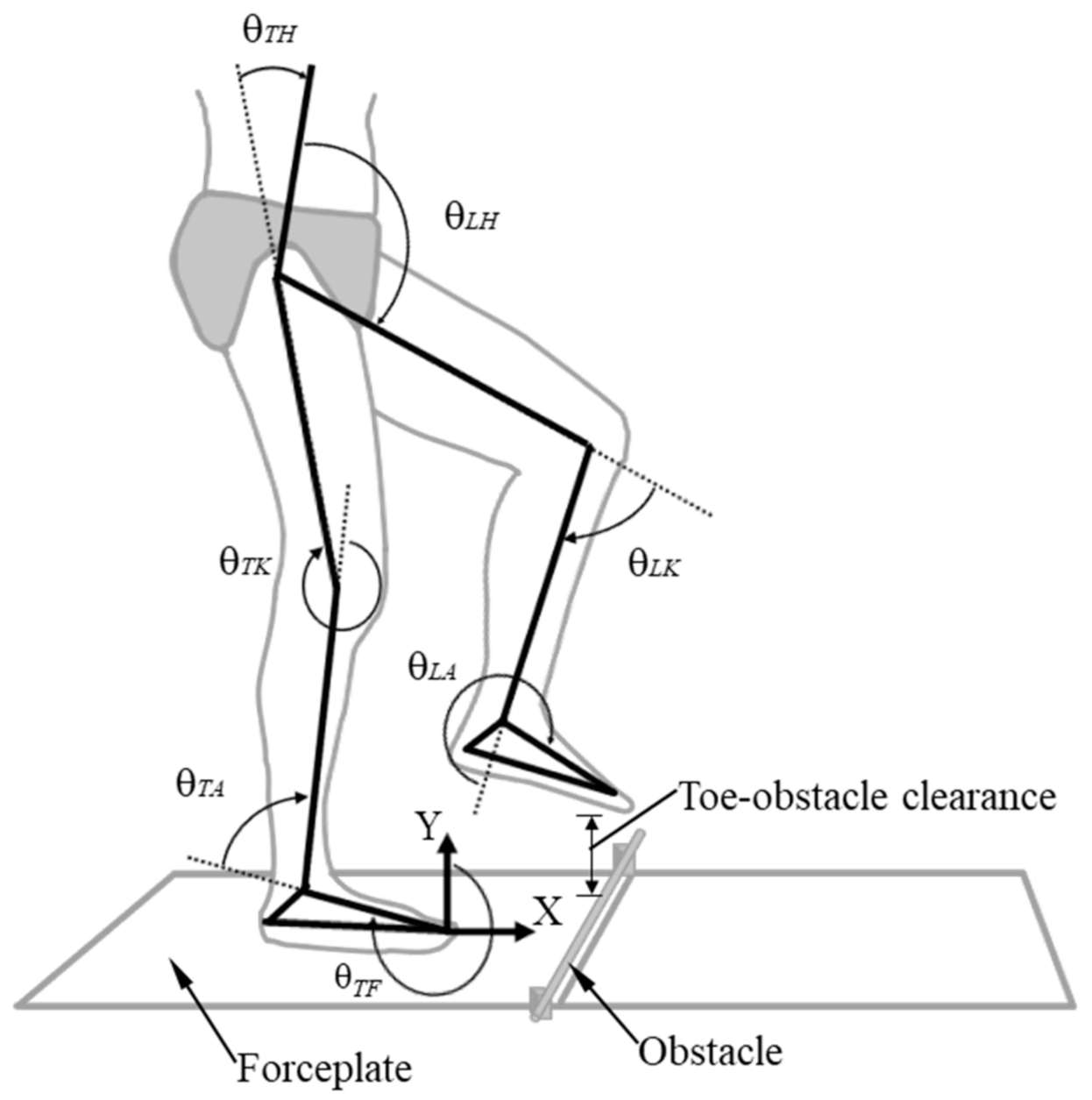
2.3. Mathematical Model of the Body
2.4. Multi-Objective Optimal Control (MOOC) of Obstacle Crossing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
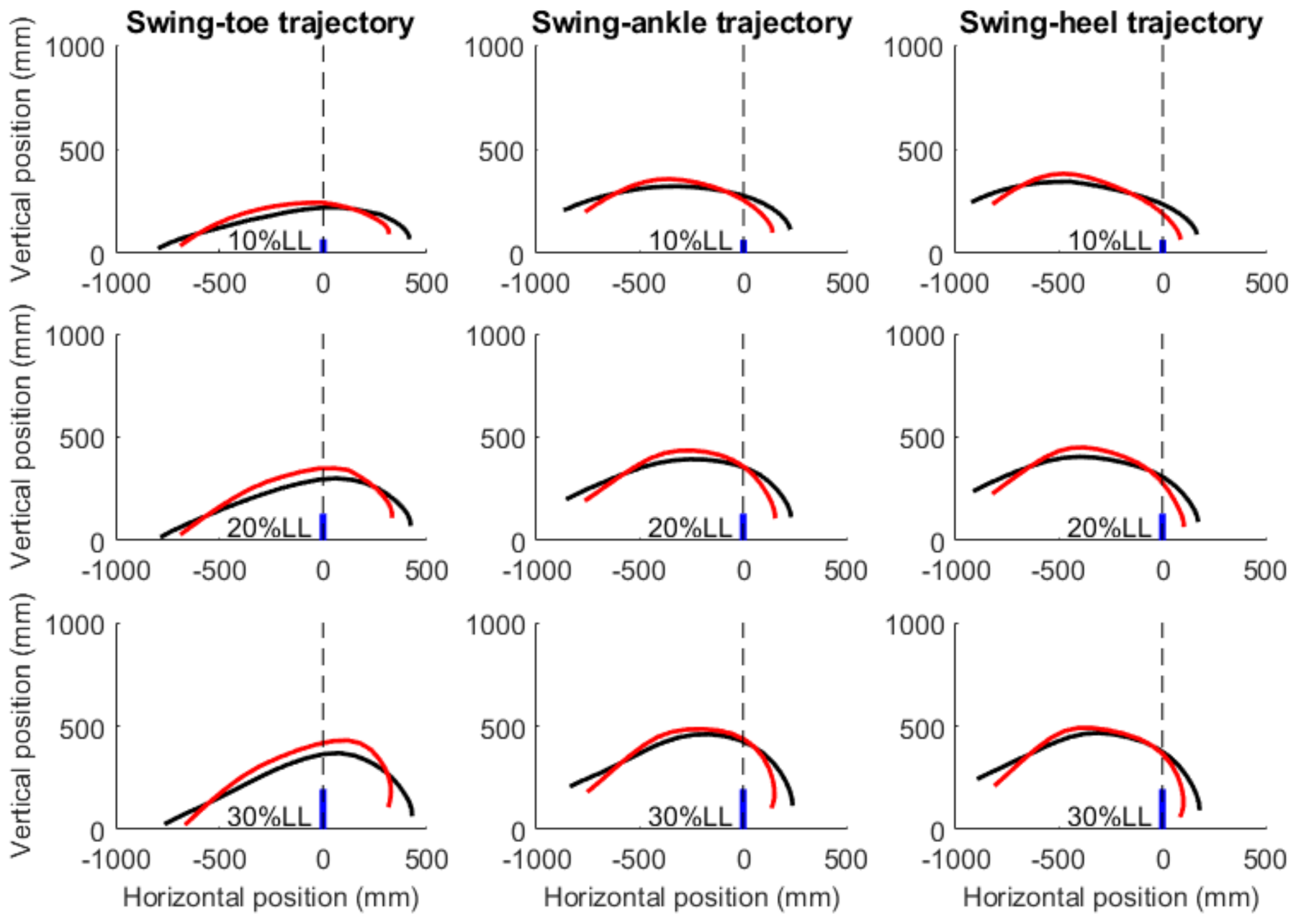
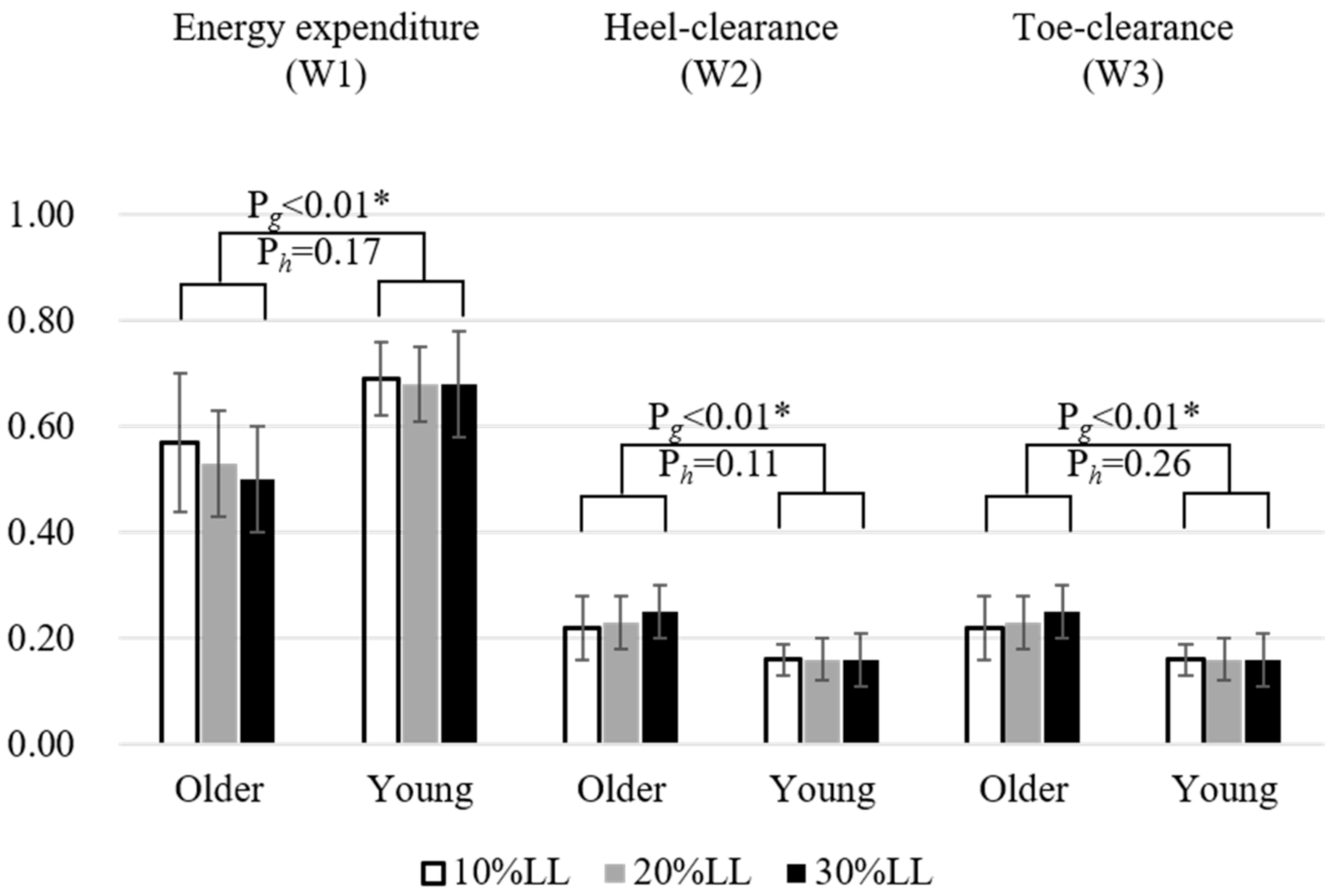
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tinetti, M.E.; Speechley, M.; Ginter, S.F. Risk-Factors for Falls among Elderly Persons Living in the Community. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fabio, R.P.; Kurszewski, W.M.; Jorgenson, E.E.; Kunz, R.C. Footlift asymmetry during obstacle avoidance in high-risk elderly. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 2088–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, A.C.; Deshpande, N. Effects of aging on whole body and segmental control while obstacle crossing under impaired sensory conditions. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 35, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.G.; Hwangbo, G. The effect of obstacle gait training on the plantar pressure and contact time of elderly women. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 60, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.L.; Lu, T.W. Comparisons of the joint moments between leading and trailing limb in young adults when stepping over obstacles. Gait Posture 2006, 23, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overstall, P.; Exton-Smith, A.; Imms, F.; Johnson, A. Falls in the elderly related to postural imbalance. Br. Med. J. 1977, 1, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blake, A.J.; Morgan, K.; Bendall, M.J.; Dallosso, H.; Ebrahim, S.B.; Arie, T.H.; Fentem, P.H.; Bassey, E.J. Falls by elderly people at home: Prevalence and associated factors. Age Ageing 1988, 17, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinetti, M.E.; Speechley, M. Prevention of falls among the elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, L.S.; Draganich, L.F. Stepping over an obstacle increases the motions and moments of the joints of the trailing limb in young adults. J. Biomech. 1997, 30, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patla, A.; Rietdyk, S. Visual control of limb trajectory over obstacles during locomotion: Effect of obstacle height and width. Gait Posture 1993, 1, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Ashton-Miller, J.A.; Alexander, N.B.; Schultz, A.B. Stepping over obstacles: Gait patterns of healthy young and old adults. J. Gerontol. 1991, 46, M196–M203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.-W.; Chen, S.-C.; Chiu, H.-C. Best-compromise between mechanical energy expenditure and foot clearance predicts leading limb motion during obstacle-crossing. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.W.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, S.C. Comparisons of the lower limb kinematics between young and older adults when crossing obstacles of different heights. Gait Posture 2006, 23, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.W.; Chen, H.L.; Wang, T.M. Obstacle crossing in older adults with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture 2007, 26, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.C.; Chen, H.L.; Liu, M.W.; Liu, H.C.; Lu, T.W. Age effects on the inter-joint coordination during obstacle-crossing. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2501–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, G.P.; Garrett, G.E.; Bohannon, R.W. Kinematic analysis of obstacle clearance during locomotion. Gait Posture 1999, 10, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, W.; Shinkfield, A.J.; Chow, S.; Begg, R. Characteristics of gait in stepping over obstacles. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1996, 15, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyen, B. Anticipatory locomotor adjustments during obstructed human walking. Neurosci. Res. Commun. 1991, 9, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.M.; Yen, H.C.; Lu, T.W.; Chen, H.L.; Chang, C.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Tsai, W.C. Bilateral knee osteoarthritis does not affect inter-joint coordination in older adults with gait deviations during obstacle-crossing. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.W.; Yen, H.C.; Chen, H.L. Comparisons of the inter-joint coordination between leading and trailing limbs when crossing obstacles of different heights. Gait Posture 2008, 27, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.; Lu, T. Minimax multiobjective optimization in structural design. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1990, 30, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, L.S.; Song, S.M.; Draganich, L.F. Predicting the kinematics and kinetics of gait based on the optimum trajectory of the swing limb. J. Biomech. 1995, 28, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrugh, M. Power requirements and mechanical efficiency of treadmill walking. J. Biomech. 1981, 14, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckett, R.; Chang, K. An evaluation of the kinematics of gait by minimum energy. J. Biomech. 1968, 1, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, G. An analysis of the energy expenditure in level and grade walking. Ergonomics 1965, 8, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nubar, Y.; Contini, R. A minimal principle in biomechanics. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1961, 23, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefeli, J.; Vogeli, S.; Michel, J.; Dietz, V. Preparation and performance of obstacle steps: Interaction between brain and spinal neuronal activity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclellan, M.J.; McFadyen, B.J. Segmental control for adaptive locomotor adjustments during obstacle clearance in healthy young adults. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 202, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLellan, M.J. Modular organization of muscle activity patterns in the leading and trailing limbs during obstacle clearance in healthy adults. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 2011–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdfelder, E.; Faul, F.; Buchner, A. GPOWER: A general power analysis program. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1996, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Hsieh, H.J.; Lu, T.W.; Tseng, C.H. A method for estimating subject-specific body segment inertial parameters in human movement analysis. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.W.; Leu, T.H.; Wang, T.M.; Li, J.D.; Ho, W.P.; Lu, T.W. Control of body’s center of mass motion relative to center of pressure during uphill walking in the elderly. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, H.J.; Lu, T.W.; Chen, S.C.; Chang, C.M.; Hung, C. A new device for in situ static and dynamic calibration of force platforms. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-L.; Lu, T.-W.; Lin, H.-C. Three-dimensional kinematic analysis of stepping over obstacles in young subjects. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2004, 16, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.-W.; O’Connor, J. A three-dimensional computer graphics-based animated model of the human locomotor system with anatomical joint constraints. J. Biomech. 1998, 1001, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Zamora, F.J.; Lajoie, K.; Miller, A.B.; Marigold, D.S. Age-related changes in gaze sampling strategies during obstacle navigation. Gait Posture 2020, 76, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, L.S.; Draganich, L.F. Increasing obstacle height and decreasing toe-obstacle distance affect the joint moments of the stance limb differently when stepping over an obstacle. Gait Posture 1998, 8, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patla, A.E.; Prentice, S.; Gobbi, T. Visual Control of Obstacle Avoidance during Locomotion: Strategies in Young Children, Young and Older Adults. In Changes in Sensory-Motor Behavior in Aging; Ferandez, A.M., Teasdale, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 257–277. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.C.; Lu, T.W.; Chen, H.L.; Wang, T.M.; Chou, L.S. Age and height effects on the center of mass and center of pressure inclination angles during obstacle-crossing. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillner, S.; Wallen, P. Central pattern generators for locomotion, with special reference to vertebrates. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1985, 8, 233–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyen, B.J.; Prince, F. Avoidance and accommodation of surface height changes by healthy, community-dwelling, young, and elderly men. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2002, 57, B166–B174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamoureux, E.; Sparrow, W.A.; Murphy, A.; Newton, R.U. The effects of improved strength on obstacle negotiation in community-living older adults. Gait Posture 2003, 17, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, E.L.; Sparrow, W.A.; Murphy, A.; Newton, R.U. The Relationship Between Lower Body Strength and Obstructed Gait in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, B.C.; Haddad, J.M.; van Emmerik, R.E.A.; Rietdyk, S. Changes in the control of obstacle crossing in middle age become evident as gait task difficulty increases. Gait Posture 2019, 70, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.F.; Hsu, H.C.; Chang, W.N.; Renn, J.H.; Wu, H.W. Strategies for obstacle crossing in older adults with high and low risk of falling. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hass, C.J.; Gregor, R.J.; Waddell, D.E.; Oliver, A.; Smith, D.W.; Fleming, R.P.; Wolf, S.L.; Hass, C.J.; Gregor, R.J.; Waddell, D.E.; et al. The influence of Tai Chi training on the center of pressure trajectory during gait initiation in older adults. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.L.; Barnhart, H.X.; Ellison, G.L.; Coogler, C.E. The effect of Tai Chi Quan and computerized balance training on postural stability in older subjects. Phys. Ther. 1997, 77, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfson, L.; Whipple, R.; Derby, C.; Judge, J.; King, M.; Amerman, P.; Schmidt, J.; Smyers, D. Balance and strength training in older adults: Intervention gains and Tai Chi maintenance. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1996, 44, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, S.K.; Bailey, D.M. T’ai chi and postural control in the well elderly. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1992, 46, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, K.; Miyakawa, T. Gait Analysis during Stepping over the Different Height of Obstacles in Aged Persons. In Vestibular and Neural Front, Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Posture and Gait, Matsumoto, Japan, 3–7 October 1994; Taguchi, K., Igarashi, M., Mori, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, N.B. Postural control in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1994, 42, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiatarone, M.A.; Evans, W.J. 11 The etiology and reversibility of muscle dysfunction in the aged. J. Gerontol. 1993, 48, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Older | Young | Group Effect (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 72 ± 6 | 23 ± 3 | - - |
| Gender, no. of females/males | 4/13 | 4/13 | - - |
| BMI | 22.6 ± 3.5 | 22.2 ± 2.1 | 0.66 |
| Height, cm | 160 ± 6 | 175 ± 5 | 0.01 |
| Mass, kg | 58.7 ± 8.5 | 69.0 ± 7.4 | 0.01 |
| Obstacle Height (% Leg Length) | Group Effect | Height Effect | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | p-Value | ||
| Leading heel-obstacle distance (% Leg length) | |||||
| Older | 17.8 (4.9) | 17.3 (3.5) | 16.9 (3.9) | 0.01 * | 0.23 |
| Young | 20.3 (2.6) | 20.2 (2.4) | 19.5 (2.2) | ||
| Trailing toe-obstacle distance (% Leg length) | |||||
| Older | 24.9 (4.4) | 24.6 (4.2) | 24.2 (4.8) | 0.01 * | 0.18 |
| Young | 21.0 (2.7) | 20.4 (3.1) | 20.6 (2.9) | ||
| Leading-toe clearance (mm) | |||||
| Older | 156 (34) | 169 (33) | 176 (40) | 0.04 * | 0.57 |
| Young | 149 (25) | 144 (26) | 128 (20) | ||
| Leading-heel clearance (mm) | |||||
| Older | 130 (31) | 137 (34) | 142 (39) | 0.96 | 0.24 |
| Young | 135 (27) | 137 (35) | 135 (33) | ||
| Energy expenditure (% body weight×leg length×total time) | |||||
| Older | 174.4 (41.7) | 172.8 (30.1) | 183.2 (35.9) | 0.03 * | 0.03 ↑ |
| Young | 149.3 (22.6) | 145.4 (20.8) | 156.3 (19.3) | ||
| Obstacle Height (% Leg Length) | Group Effect | Height Effect | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | p-Value | ||
| Ankle trajectory (mm) | |||||
| Older | 7.1 (3.1) | 7.1 (2.9) | 7.8 (1.7) | 0.4 | 0.63 |
| Young | 6.7 (1.9) | 6.7 (2.3) | 7.3 (2.3) | ||
| Swing hip angle (°) | |||||
| Older | 0.84 (0.22) | 0.81 (0.36) | 0.98 (0.29) | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| Young | 0.64 (0.19) | 0.66 (0.28) | 0.74 (0.23) | ||
| Swing knee angle (°) | |||||
| Older | 1.71 (0.49) | 1.39 (0.62) | 1.40 (0.33) | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| Young | 1.41 (0.39) | 1.29 (0.43) | 1.26 (0.38) | ||
| Trailing ankle moment (Nm) | |||||
| Older | 3.13 (0.72) | 3.77 (1.64) | 3.90 (0.81) | 0.73 | 0.11 |
| Young | 3.44 (0.76) | 3.71 (1.18) | 4.00 (0.97) | ||
| Trailing knee moment (Nm) | |||||
| Older | 3.08 (0.84) | 3.05 (1.68) | 2.99 (0.80) | 0.59 | 0.37 |
| Young | 2.75 (0.50) | 3.39 (0.85) | 3.53 (0.88) | ||
| Trailing hip moment (Nm) | |||||
| Older | 3.63 (0.90) | 4.02 (1.96) | 3.98 (1.11) | 0.11 | 0.68 |
| Young | 4.35 (0.74) | 4.59 (1.08) | 4.46 (1.02) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, C.-C.; Wang, J.-Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Lu, T.-W.; Hsu, H.-C. Aging Affects Multi-Objective Optimal Control Strategies during Obstacle Crossing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11178040
Kuo C-C, Wang J-Y, Chen S-C, Lu T-W, Hsu H-C. Aging Affects Multi-Objective Optimal Control Strategies during Obstacle Crossing. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(17):8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11178040
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Chien-Chung, Jr-Yi Wang, Sheng-Chang Chen, Tung-Wu Lu, and Horng-Chaung Hsu. 2021. "Aging Affects Multi-Objective Optimal Control Strategies during Obstacle Crossing" Applied Sciences 11, no. 17: 8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11178040
APA StyleKuo, C.-C., Wang, J.-Y., Chen, S.-C., Lu, T.-W., & Hsu, H.-C. (2021). Aging Affects Multi-Objective Optimal Control Strategies during Obstacle Crossing. Applied Sciences, 11(17), 8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11178040







