Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Kampo Medicine, BO
2.3. KOA Induction by Destabilization of the Medial Meniscus (DMM)
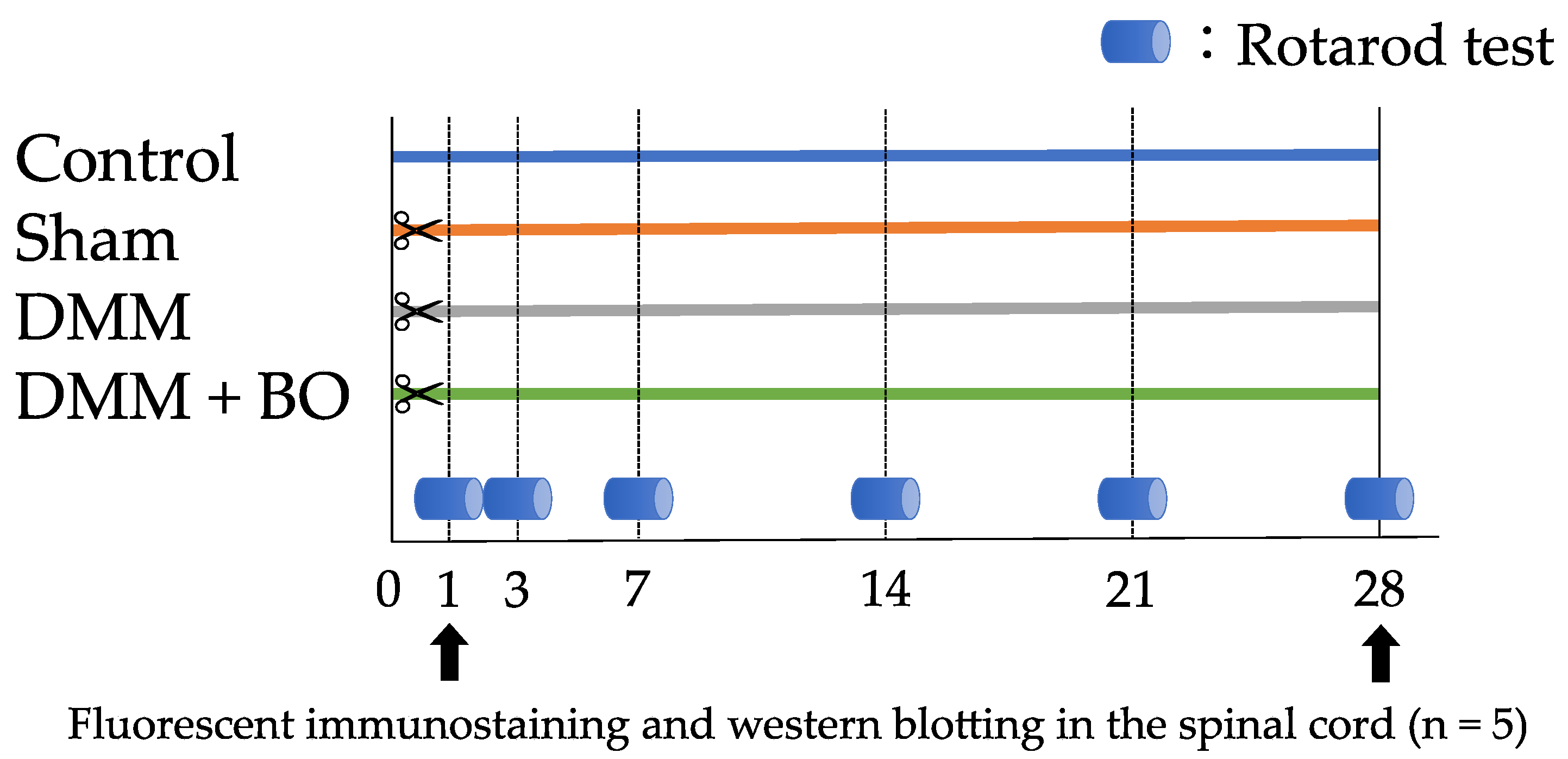
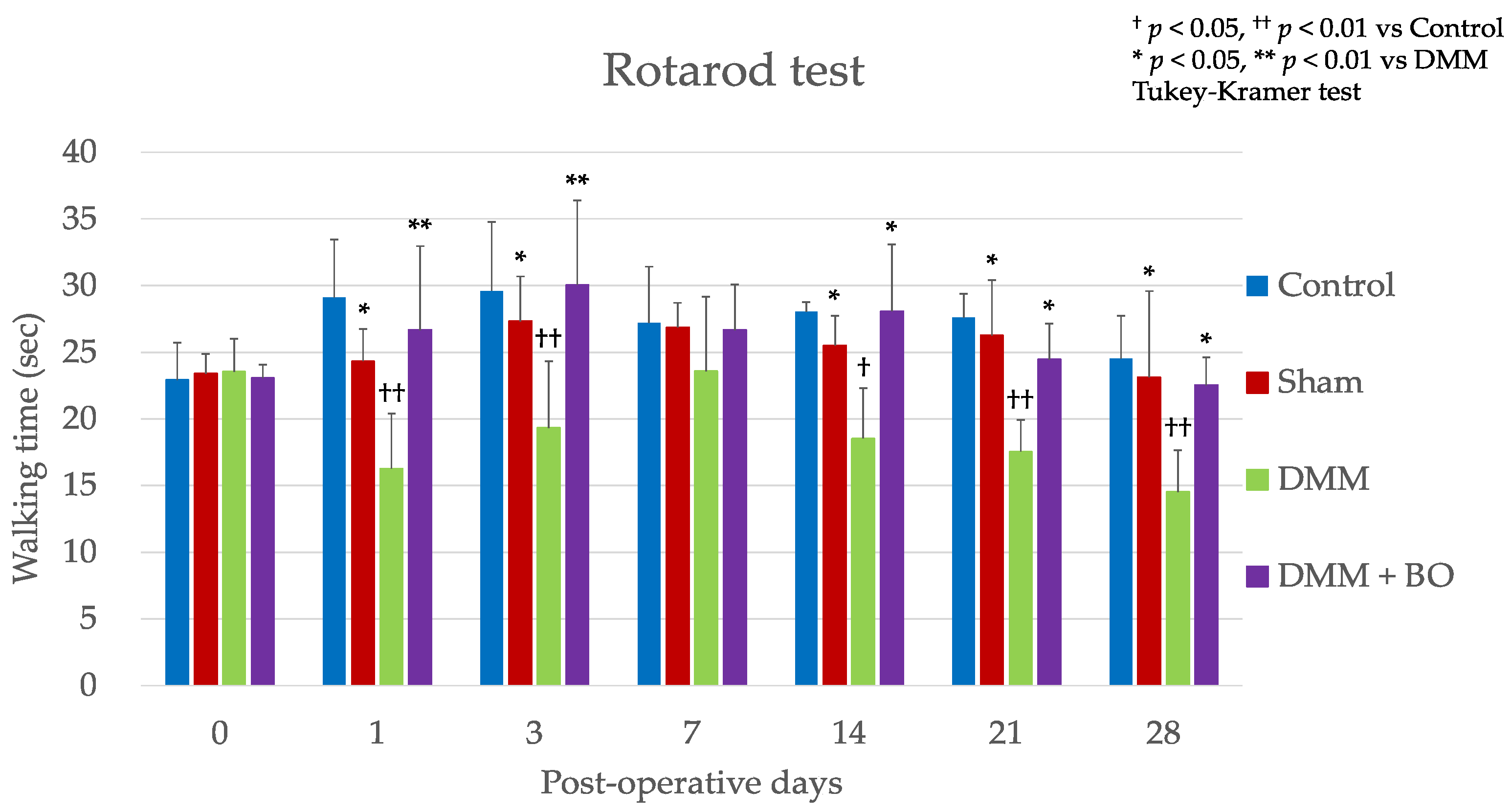
2.4. Rotarod Test
2.5. Experiment 1: Investigation of the Analgesic Effect of BO
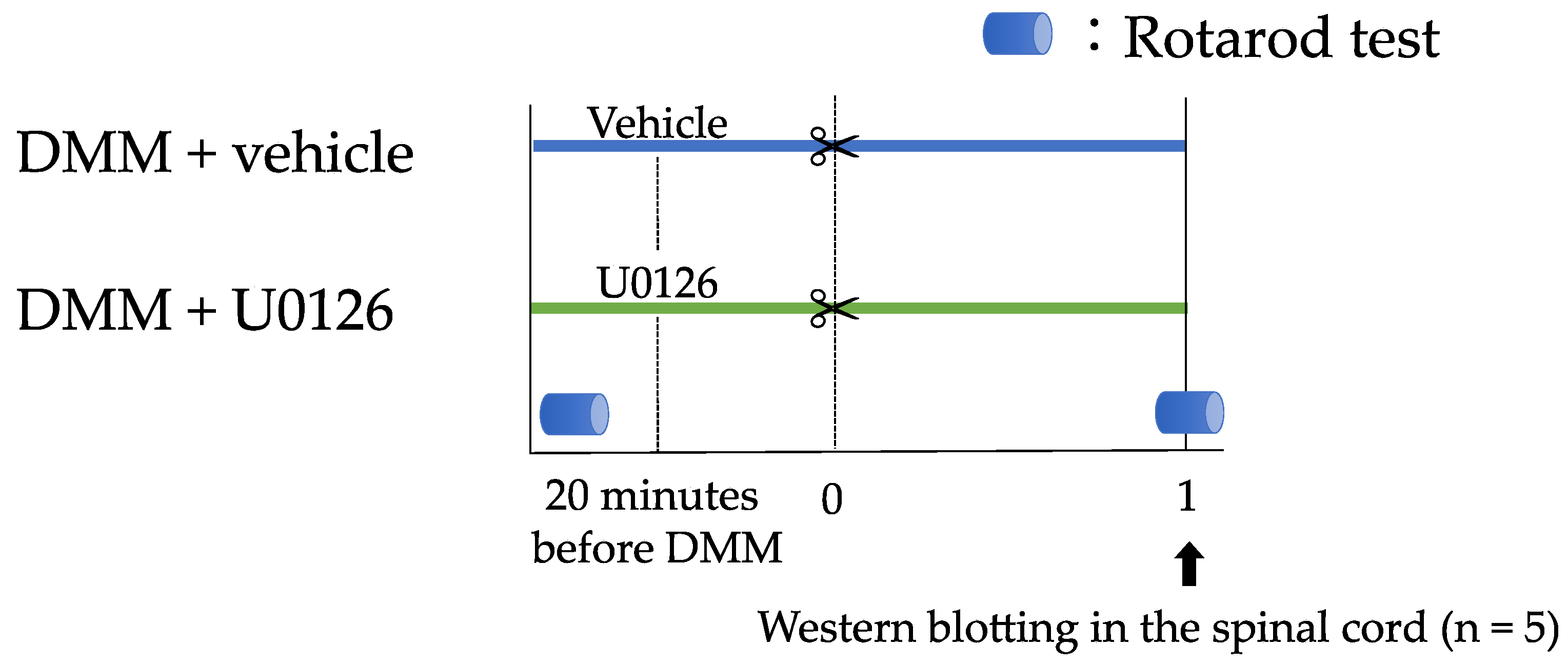
2.6. Experiment 2: Contribution of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation to Pain-Related Locomotive Dysfunction with DMM Surgery
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1: Analgesic Effect of BO
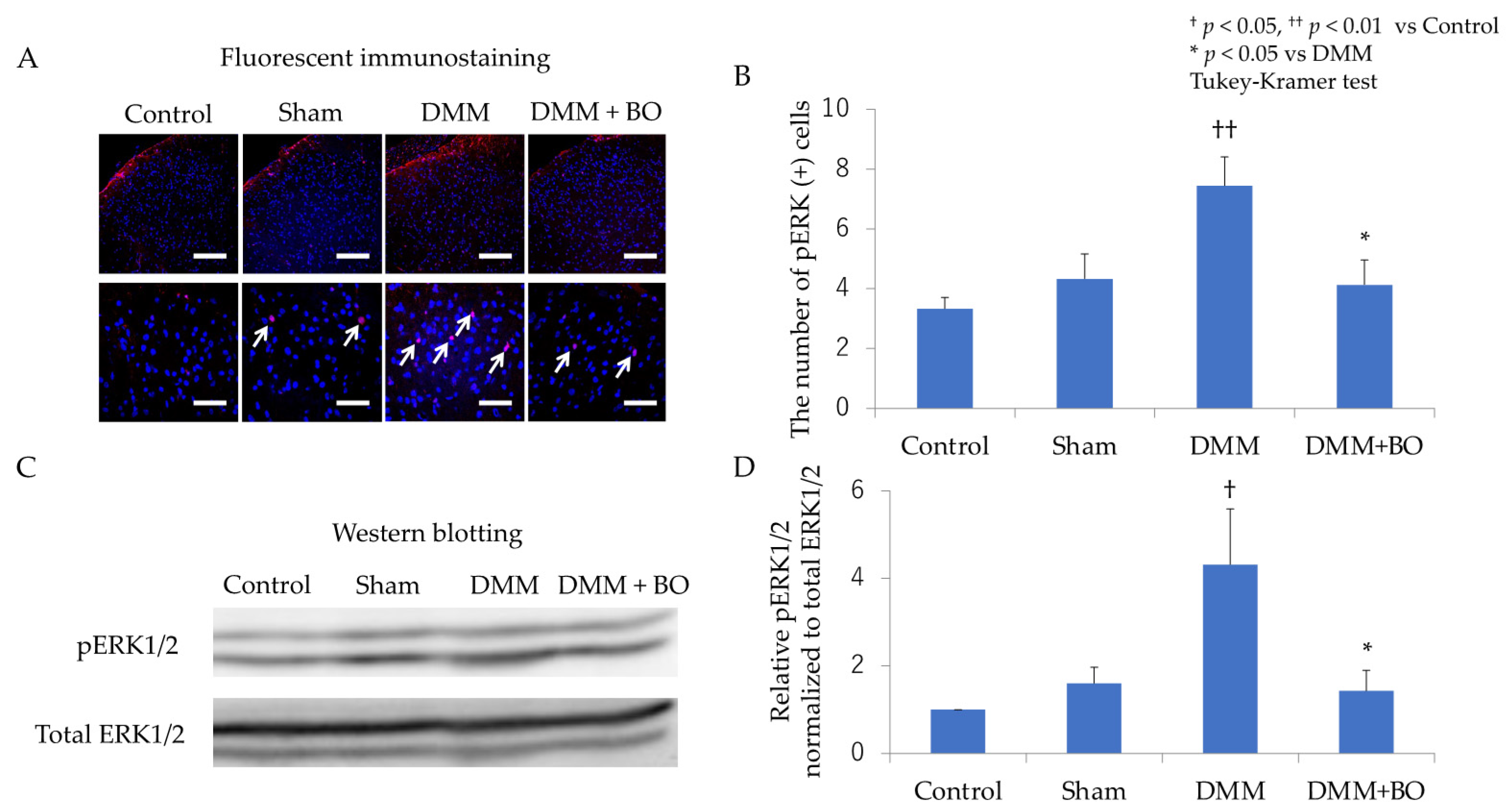
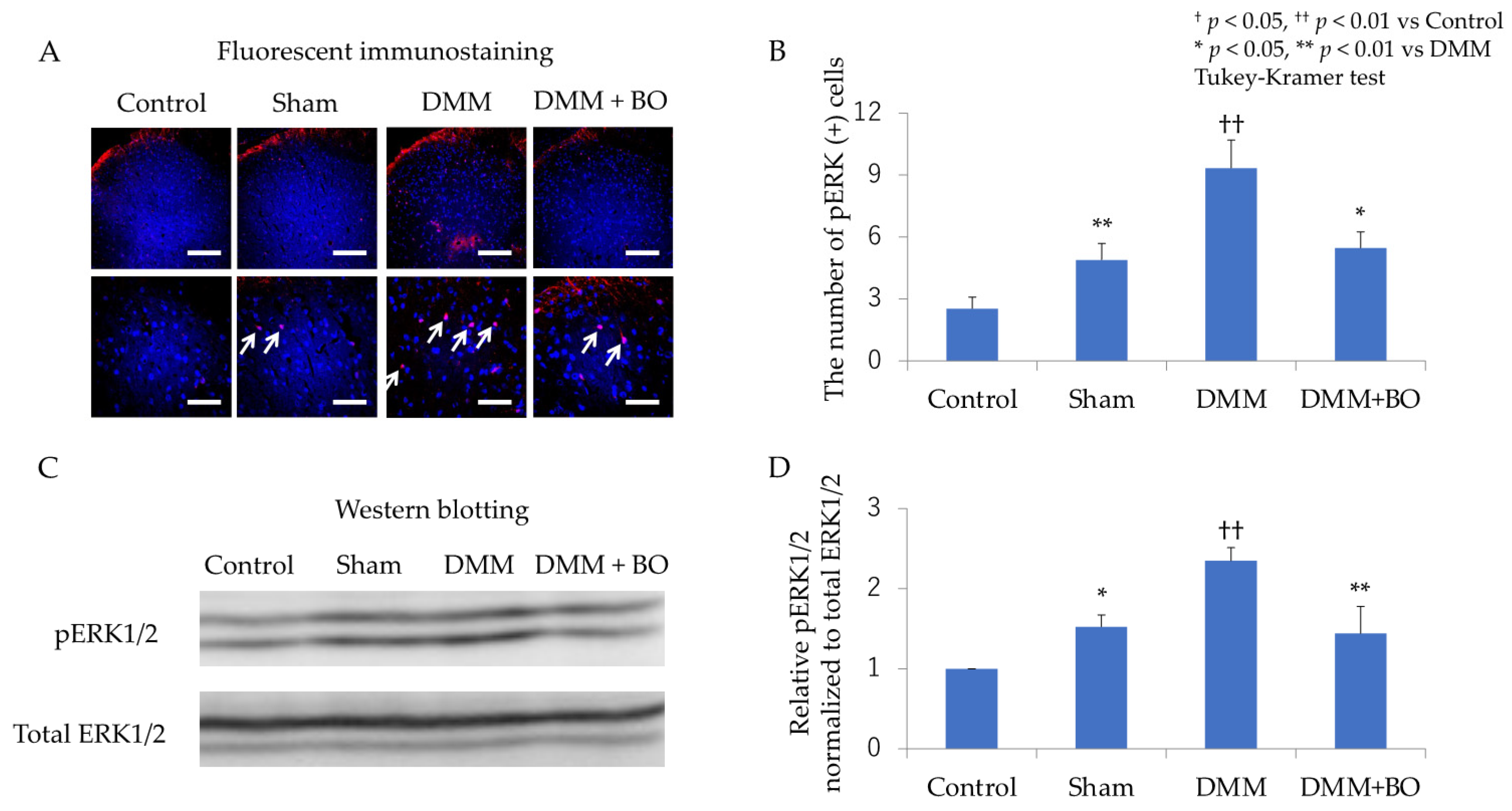
3.2. Suppressive Effect of BO on ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord in the Acute Phase after DMM Surgery
3.3. Suppressive Effect of BO on ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord in the Chronic Phase after DMM Surgery
3.4. Experiment 2: Contribution of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation to Pain-Related Locomotive Dysfunction with DMM Surgery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kloppenburg, M.; Berenbaum, F. Osteoarthritis years. 2019: Epidemiology and therapy. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Jordan, J.M. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2010, 26, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vina, E.R.; Kwoh, C.K. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Literature update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.D.; Johnston, R.C.; Saltzman, C.L.; Marsh, J.L.; Buckwalter, J.A. Posttraumatic osteoarthritis: A first estimate of incidence, prevalence, and burden of disease. J. Orthop. Trauma 2006, 20, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, E.L.; Paul, I.L.; Rose, R.M. Role of mechanical factors in pathogenesis of primary osteoarthritis. Lancet 1972, 1, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.P.C.; Hunter, D.J. Emerging drugs for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2015, 20, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijimatsu, R.; Kunugiza, Y.; Taniyama, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Tomita, T.; Yoshikawa, H. Expression and pathological effects of periostin in human osteoarthritis cartilage. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015, 16, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burns, L.C.; Ritvo, S.E.; Ferguson, M.K.; Clarke, H.; Seltzer, Z.; Katz, J. Pain catastrophizing as a risk factor for chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review. J. Pain Res. 2015, 8, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bannuru, R.R.; Osani, M.C.; Vaysbrot, E.E.; Arden, N.K.; Bennell, K.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Kraus, V.B.; Lohmander, L.S.; Abbott, J.H.; Bhandari, M.; et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henrotin, Y.; Clutterbuck, A.L.; Allaway, D.; Lodwig, E.M.; Harris, P.; Mathy-Hartert, M.; Shakibaei, M.; Mobasheri, A. Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, R.; Bartels, E.M.; Altman, R.D.; Astrup, A.; Bliddal, H. Does the hip powder of Rosa canina (rosehip) reduce pain in osteoarthritis patients? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arai, Y.C.; Makino, I.; Ikemoto, T.; Saisu, H.; Terajima, Y.; Owari, K. Kampo for the treatment of pain in Japan: A review. Pain Ther. 2020, 9, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majima, T.; Inoue, M.; Kasahara, Y.; Onodera, T.; Takahashi, D.; Minami, A. Effect of the Japanese herbal medicine, Boiogito, on the osteoarthritis of the knee with joint effusion. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rehabil. Ther. Technol. 2012, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujitsuka, N.; Tamai, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Iizuka, S.; Tsuchiya, N.; Makino, B.; Hattori, T.; Kase, Y.; Isohama, Y. Boiogito, a Kampo medicine, improves hydrarthrosis in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takenaga, M.; Niimi, J.; Hamaguchi, A.; Asano, T.; Tsuchiya, R.; Ohta, Y.; Yudoh, K.; Inoue, H. Protective effect of boiogito extract with glucosamine HCL against adjuvant–induced arthritis in rats. Tradit. Kampo Med. 2018, 5, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oike, J.; Okumo, T.; Ikemoto, H.; Kunieda, Y.; Nakai, S.; Takemura, H.; Takagi, H.; Kanzaki, K.; Sunagawa, M. Preventive effect of the Japanese traditional herbal medicine Boiogito on posttraumatic osteoarthritis in rats. Medicines 2020, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaible, H.G. Mechanisms of chronic pain in osteoarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2012, 14, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.A.; Nie, H.; Laursen, M.B.; Laursen, B.S.; Madeleine, P.; Simonsen, O.H.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Sensitization in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis. Pain 2010, 149, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.J.; Ji, R.R. c-Fos and pERK, which is a better marker for neuronal activation and central sensitization after noxious stimulation and tissue injury? Open Pain J. 2009, 2, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.D.; Fu, D.; Xu, J.M.; Zhang, Y.L.; Dai, R.P. Activation of spinal ERK1/2 contributes to mechanical allodynia in a rat model of postoperative pain. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Regulatory Science Society of Japan, Japanese Pharmacopoeia, 17th ed.English Version; Yakuji Nippo: Tokyo, Japan, 2016.
- Ozeki, N.; Muneta, T.; Kawabata, K.; Koga, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Saito, R.; Udo, M.; Yanagisawa, K.; Ohara, T.; Mochizuki, T.; et al. Centralization of extruded medial meniscus delays cartilage degeneration in rats. J. Orthop. Sci. 2017, 22, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaire, R.; Muriuki, M.; Gilbertson, L.; Harner, C.D. Biomechanical consequences of a tear of the posterior root of the medial meniscus: Similar to total meniscectomy. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terada, T.; Hara, K.; Haranishi, Y.; Sata, T. Antinociceptive effect of intrathecal administration of taurine in rat models of neuropathic pain. Can. J. Anaesth. 2011, 58, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osmon, K.J.; Vyas, M.; Woodley, E.; Thompson, P.; Walia, J.S. Battery of behavioral tests assessing general locomotion, muscular strength, and coordination in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 131, e55491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Akase, T.; Kosugi, M.; Aburada, M. Preventive effect of boiogito on metabolic disorders in the TSOD mouse, a model of spontaneous obese type II diabetes mellitus. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2011, 2011, 931073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, Y.J. Crosstalk between Cdk5/p35 and ERK1/2 signaling mediates spinal astrocyte activity via the PPARγ pathway in a rat model of chronic constriction injury. J. Neurochem. 2019, 151, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, H.; Aoyama, T.; Ito, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nagai, M.; Tajino, J.; Zhang, X.; Kuroki, H. Effects of short-term gentle treadmill walking on subchondral bone in a rat model of instability-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.W.; Li, T.T.; Zhao, J.; Mao-Ying, Q.L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, S.; Li, Q.; Mi, W.L.; Wu, G.C.; Zhang, Y.Q.; et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in spinal astrocytes and microglia contributes to cancer-induced bone pain in rats. Neuroscience 2012, 217, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Shen, J.; Qiu, J.; Yin, X.; Yin, H.; Jiang, S. Inhibitory effects of astragaloside IV on diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 84, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.T.; Wang, B.; Jia, Y.N.; Liu, N.; Ma, P.S.; Gong, S.S.; Niu, Y.; Sun, T.; Li, Y.X.; Yu, J.Q. Neuroprotective effect of liquiritin against neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Paz, M.-D.S.; Garcia-Gimenez, M.D.; Quilez, A.M.; De la Puerta, R.; Fernandez-Arche, A. Ginger rhizome enhances the anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects of paracetamol in an experimental mouse model of fibromyalgia. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Takayama, Y.; Sunagawa, M. The calcium-activated chloride channel TMEM16A is Inhibitied by liquiritigenin. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 628968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamura, Y.; Hitomi, S.; Omiya, Y.; Ujihara, I.; Kokabu, S.; Morimoto, Y.; Ono, K. Isoliquiritigenin, an active ingredient of Glycyrrhiza, elicits antinociceptive effects via inhibition of Nav channels. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, Z.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. Isoliquiritigenin is a novel NMDA receptor antagonist in Kampo medicine yokukansan. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Z.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. Glycyrrhizin and its metabolite 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid in glycyrrhiza, a constituent herb of yokukansan, ameliorate thiamine deficiency-induced dysfunction of glutamate transport in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 626, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunieda, Y.; Okumo, T.; Ikemoto, H.; Adachi, N.; Tanaka, M.; Kimura, T.; Yusa, K.; Kanzaki, K.; Sunagawa, M. Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188421
Kunieda Y, Okumo T, Ikemoto H, Adachi N, Tanaka M, Kimura T, Yusa K, Kanzaki K, Sunagawa M. Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188421
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunieda, Yusuke, Takayuki Okumo, Hideshi Ikemoto, Naoki Adachi, Midori Tanaka, Taro Kimura, Kanako Yusa, Koji Kanzaki, and Masataka Sunagawa. 2021. "Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188421
APA StyleKunieda, Y., Okumo, T., Ikemoto, H., Adachi, N., Tanaka, M., Kimura, T., Yusa, K., Kanzaki, K., & Sunagawa, M. (2021). Analgesic Effect of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis through Inhibition of ERK1/2 Phosphorylation in the Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188421






