Dropwise Condensation Mechanism on Smooth Hydrophilic Surfaces
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
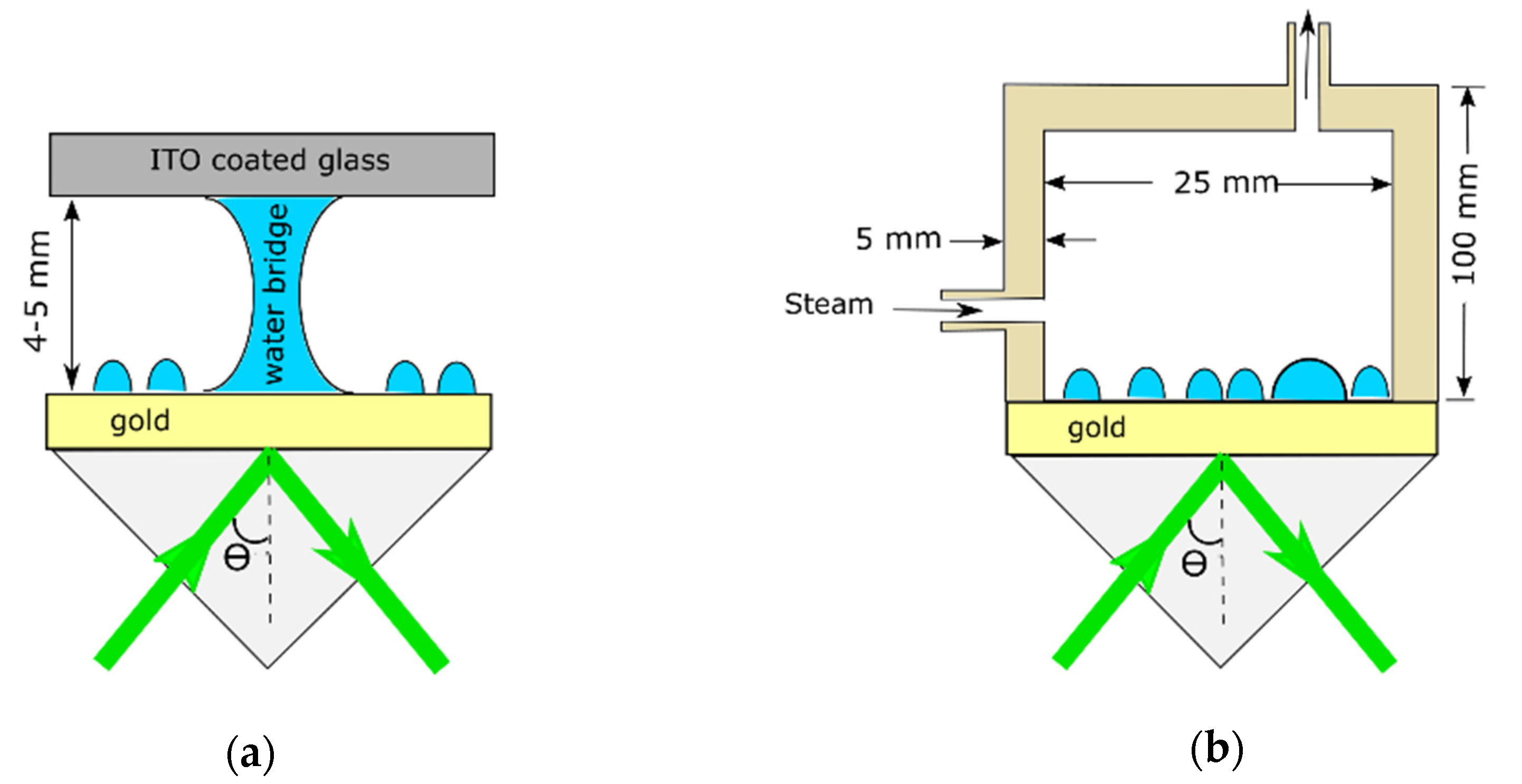
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
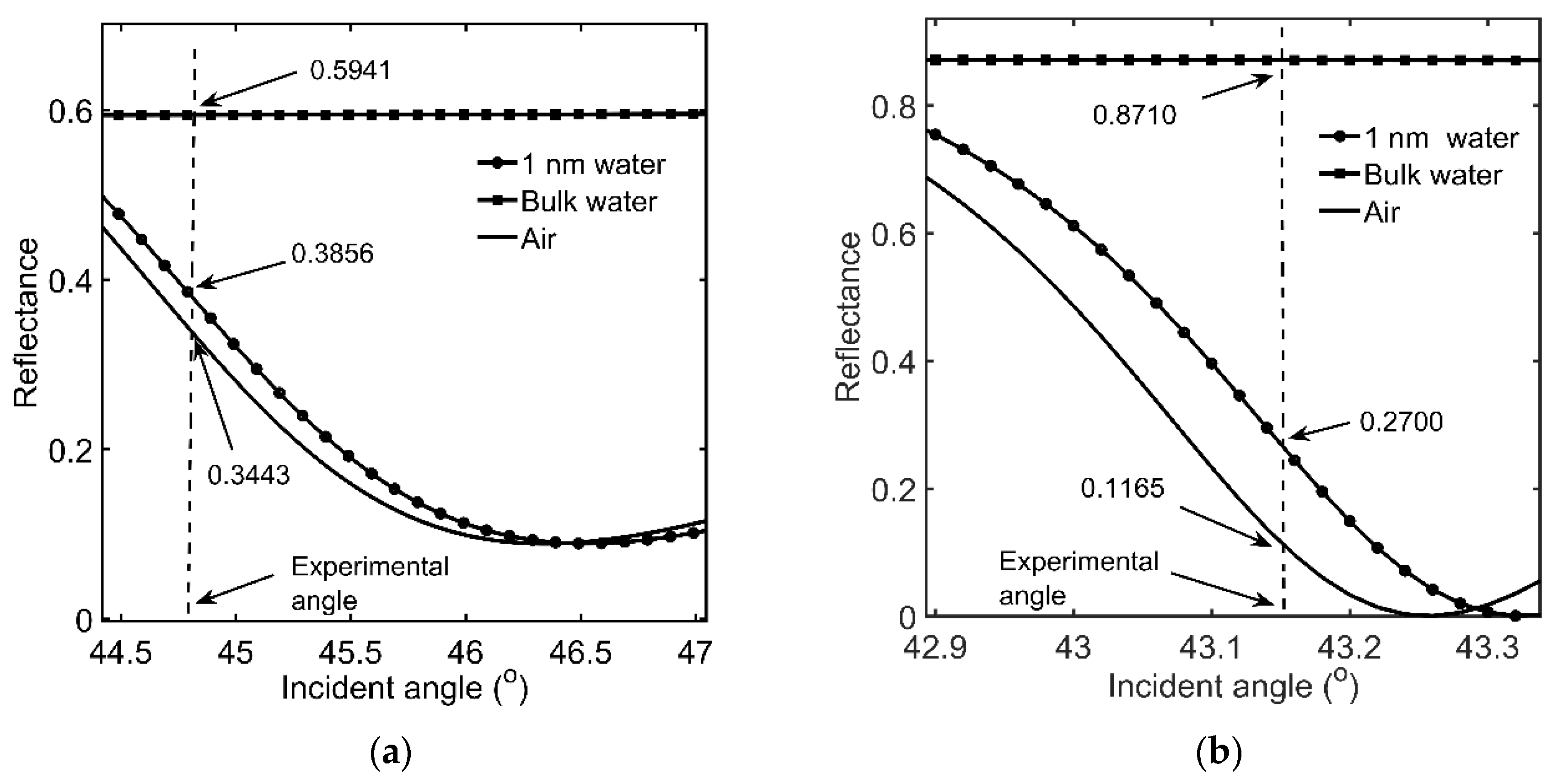
3.1. Onset of SDC
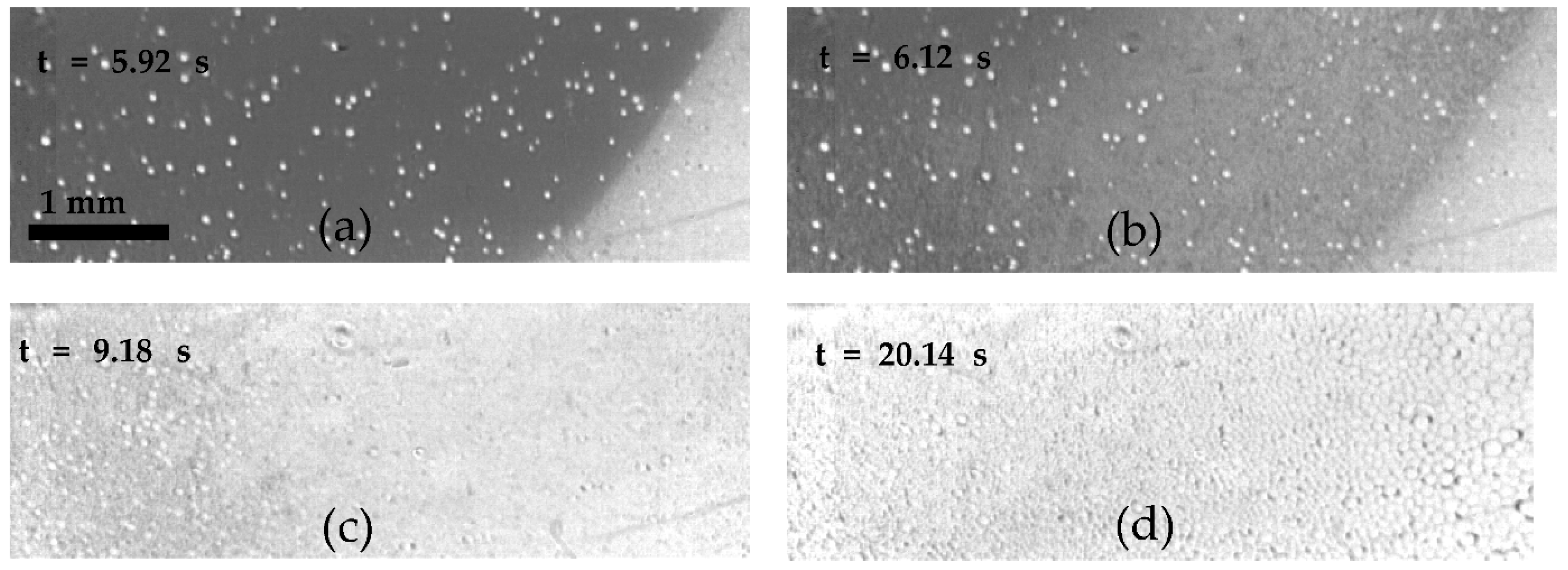
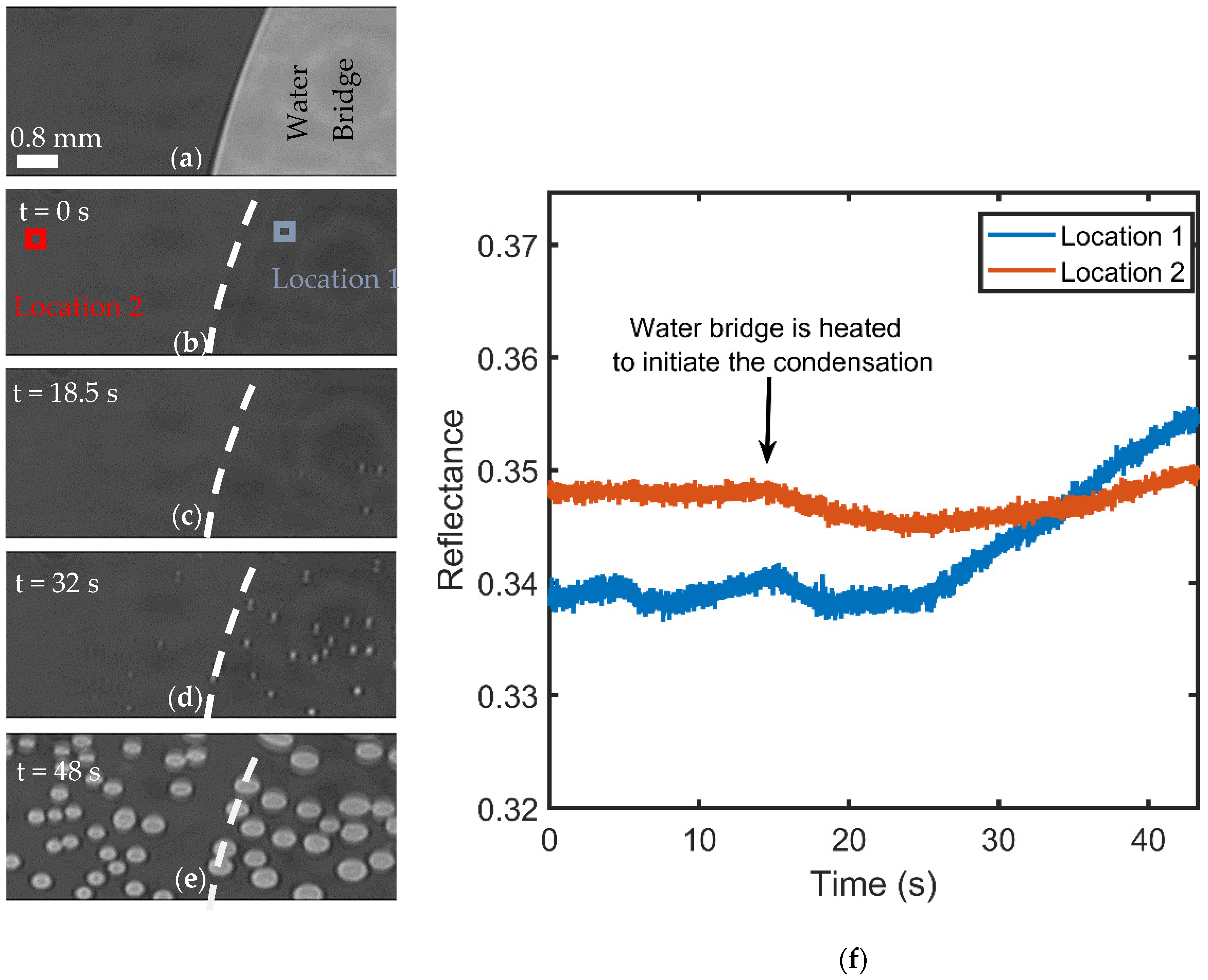
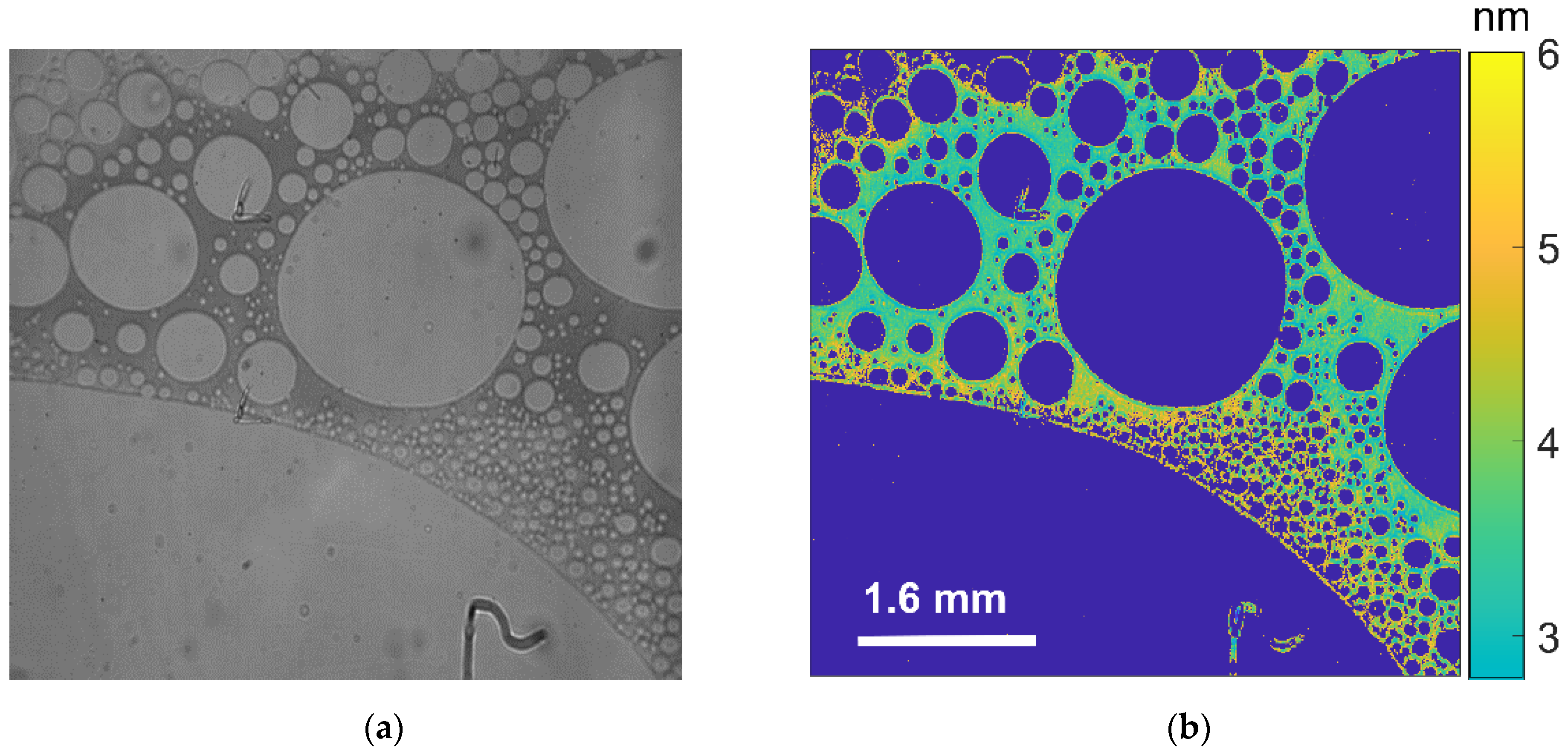
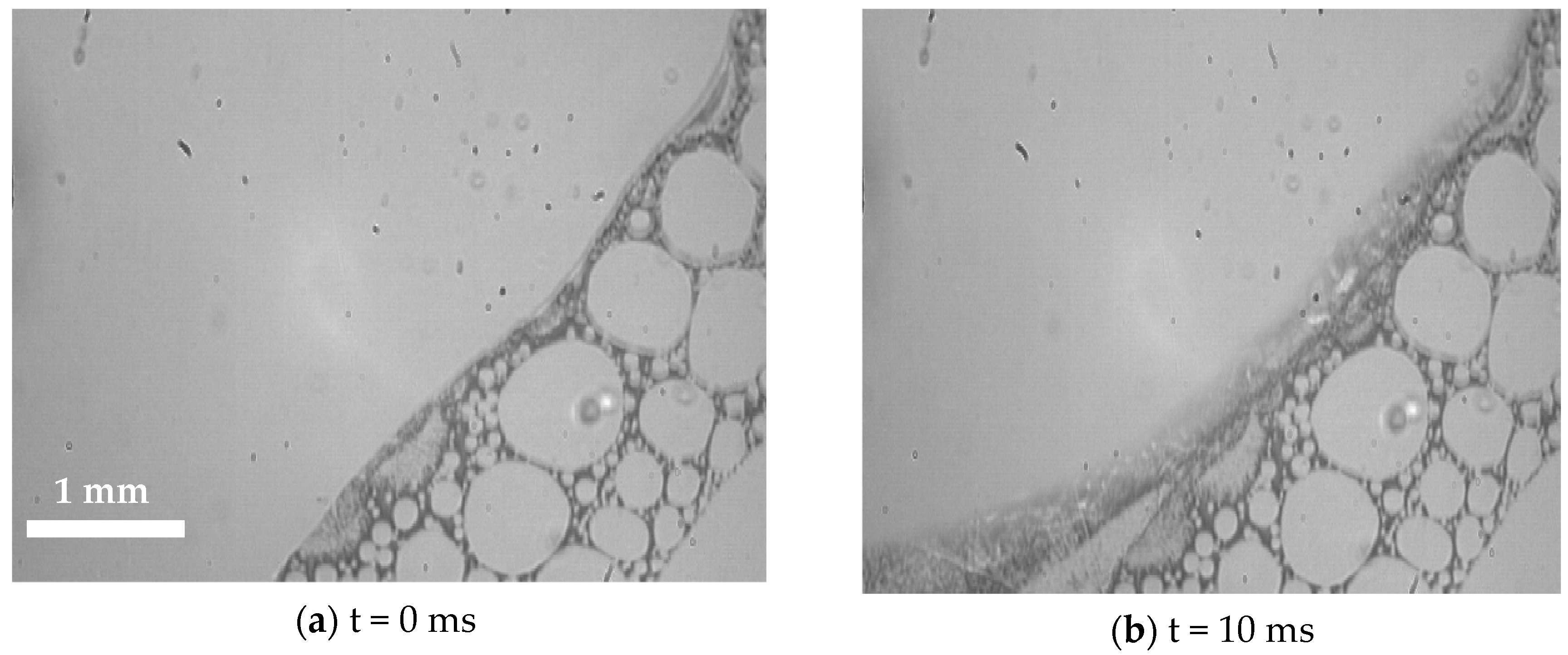
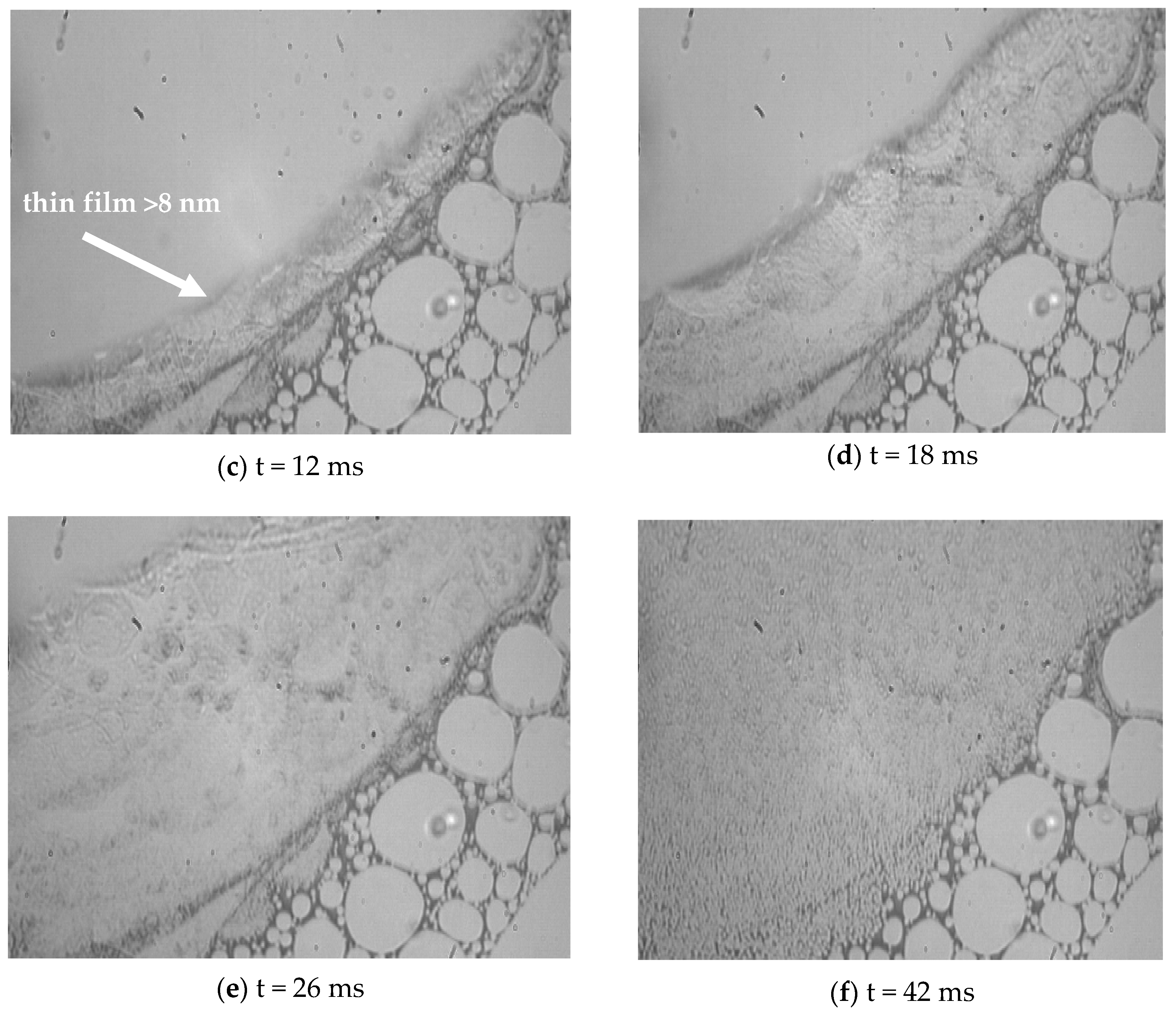
3.2. Visualization of USDC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahlers, M.; Buck-Emden, A.; Bart, H.-J. Is dropwise condensation feasible? A review on surface modifications for continuous dropwise condensation and a profitability analysis. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Yi, Q.; Kong, X.; Wang, J. A Review of Research on Dropwise Condensation Heat Transfer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandekar, S.; Muralidhar, K. Modeling dropwise condensation. In Dropwise Condensation on Inclined Textured Surfaces; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 17–72. [Google Scholar]
- Leipertz, A. J3 dropwise condensation. In VDI Heat Atlas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 933–938. [Google Scholar]
- Tammann, G.; Boehme, W. Die zahl der wassertröpfchen bei der kondensation auf verschiedenen festen etoffen. Ann. Phys. 1935, 414, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umur, A.; Griffith, P. Mechanism of Dropwise Condensation. J. Heat Transf. 1965, 87, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sikarwar, B.S.; Khandekar, S.; Agrawal, S.; Kumar, S.; Muralidhar, K. Dropwise Condensation Studies on Multiple Scales. Heat Transf. Eng. 2012, 33, 301–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikanto, J.; Vehkamäki, H.; Zapadinsky, E. Monte Carlo simulations of critical cluster sizes and nucleation rates of water. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diemand, J.; Angélil, R.; Tanaka, K.K.; Tanaka, H. Large scale molecular dynamics simulations of homogeneous nucleation. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 074309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.S. On the onset of surface condensation: Formation and transition mechanisms of condensation mode. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jakob, M. Heat Transfer in Evaporation and Condensation; University of Illinois: Urbana, IL, USA, 1937. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Xu, D.; Lin, J.; Tsian, S. A study on the mechanism of dropwise condensation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1991, 34, 2827–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umur, A.; Griffith, P. Mechanism of Dropwise Condensation; MIT Dept. of Mechanical Engineering: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Ahangar, S.B.; Konduru, V.; Allen, J.S.; Miljkovic, N.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, C.K. Development of automated angle-scanning, high-speed surface plasmon resonance imaging and SPRi visualization for the study of dropwise condensation. Exp. Fluids 2019, 61, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahangar, S.B.; Jeong, C.H.; Long, F.; Allen, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, C.K. The Effect of Adsorbed Volatile Organic Compounds on an Ultrathin Water Film Measurement. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayani, S.; Tabe, Y.; Kang, Y.T.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, C.K. Surface plasmon resonance imaging of drop coalescence at high-temporal resolution. J. Flow Vis. Image Process. 2018, 25, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangar, S.B.; Allen, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, C.K. Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging: A Technique to Reveal the Dropwise Condensation Mechanism. J. Heat Transf. 2020, 142, 030903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, C.; Shi, P.; Yan, W.; Chen, L.; Qian, L.; Kim, S.H. Thickness and structure of adsorbed water layer and effects on adhesion and friction at nanoasperity contact. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kochsiek, M. Measurement of water adsorption layers on metal surfaces. Metrologia 1982, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayani Ahangar, S.; Lee, K.-B.; Choi, C.K. Dropwise Condensation Mechanism on Smooth Hydrophilic Surfaces. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199184
Bayani Ahangar S, Lee K-B, Choi CK. Dropwise Condensation Mechanism on Smooth Hydrophilic Surfaces. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(19):9184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199184
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayani Ahangar, Shahab, Kyung-Bon Lee, and Chang Kyoung Choi. 2021. "Dropwise Condensation Mechanism on Smooth Hydrophilic Surfaces" Applied Sciences 11, no. 19: 9184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199184
APA StyleBayani Ahangar, S., Lee, K.-B., & Choi, C. K. (2021). Dropwise Condensation Mechanism on Smooth Hydrophilic Surfaces. Applied Sciences, 11(19), 9184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199184





