Increasing the Reliability of an Electrical Power System in a Big European Hospital through the Petri Nets and Fuzzy Inference System Mamdani Modelling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. State of the Art
2.1. The Maintenance Concept
2.2. The Electrical Maintenance Activity in Hospitals
2.3. Maintenance, Reliability, and Availability
2.4. Petri Nets Systems
- (1)
- P = {P1, P2, …, Pm} is a limited set of places;
- (2)
- T = {t1, t2, …, tn} is a limited set of transitions, P U T ≠ ∅, and P ∩ T = ∅;
- (3)
- I (P, T) → N is an Input function that defines an arc directed from a Place to a Transition, where N is a set of negative integers;
- (4)
- (T, P) → N is the Output function that defines the arc directed from Transition to Place; and
- (5)
- Mo: P → N is the initial marking.
- P = {p1, p2, …, p7};
- T = {t1, t2, …, t5};
- I (t1, p1) = 2, I(t1, pi) = 0 for i = 2, 3, …, 7;
- I (t2, p2) = 1, I(t2, p7) = 1, I(t2, pi) = 0 for i = 1, 3, 4, 5, 6;
- O (t1, p2) = 1, O(t1, p3) = 2, O(t1, pi) = 0 for i = 1, 4, 5, 6, 7;
- O (t2, p4) = 1, O(t2, pi) = 0 for i = 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7;
- Mo = (2 0 0 0 0 0 1).
2.5. Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) and Fuzzy Petri Nets
2.6. The HiPS Software Simulator Description
3. Electrical Power System of a Big European Hospital
3.1. Characterization of the Hospital
3.2. Modelling of the Hospital’s Electrical System Using Block Diagrams
3.3. The Group of Generators, Automatic Transfer Switch, and UPS
4. Modelling the Hospital’s Electrical System Using Petri Nets
4.1. Modelling the Hospital’s Electrical System by Petri Nets
4.2. The Hospital Electrical System Block Diagrams
4.3. Modelling and Analysing with a Fuzzy Inference System
4.3.1. Fuzzification Data Processing
- Fuzzy Low set: µLow (420) = 0
- Fuzzy Normal set: µNormal (420) = 0.8
- Fuzzy High set: µHigh (420) = 0.215
- Fuzzy set On: µOn (700) = 0.7
- Fuzzy set Off: µOff (700) = 0.3
- Fuzzy Function set: µFunction (140) = 0.7
- Fuzzy Not Function set: µOff (700) = 0.3
- Fuzzy On set: µOn (220) = 0.73
- Fuzzy Off set: µOff (220) = 0.27
- Fuzzy Low set: µLow (420) = 0
- Fuzzy Normal set: µNormal (420) = 0.8
- Fuzzy High set: µHigh (420) = 0.215
- Fuzzy set On: µOn (700) = 0.7
- Fuzzy set Off: µOff (700) = 0.3 × 2 (the value of two Genset)
- Fuzzy Function set: µFunction (140) = 0.7
- Fuzzy Not Function set: µOff (700) = 0.3
- Fuzzy set On: µOn (220) = 0.73
- Fuzzy set Off: µOff (220) = 0.27 × 2 (the value of two UPS)
- Maximum Value:;;; ; ; and
- Minimum Value:;;; ; ; and .
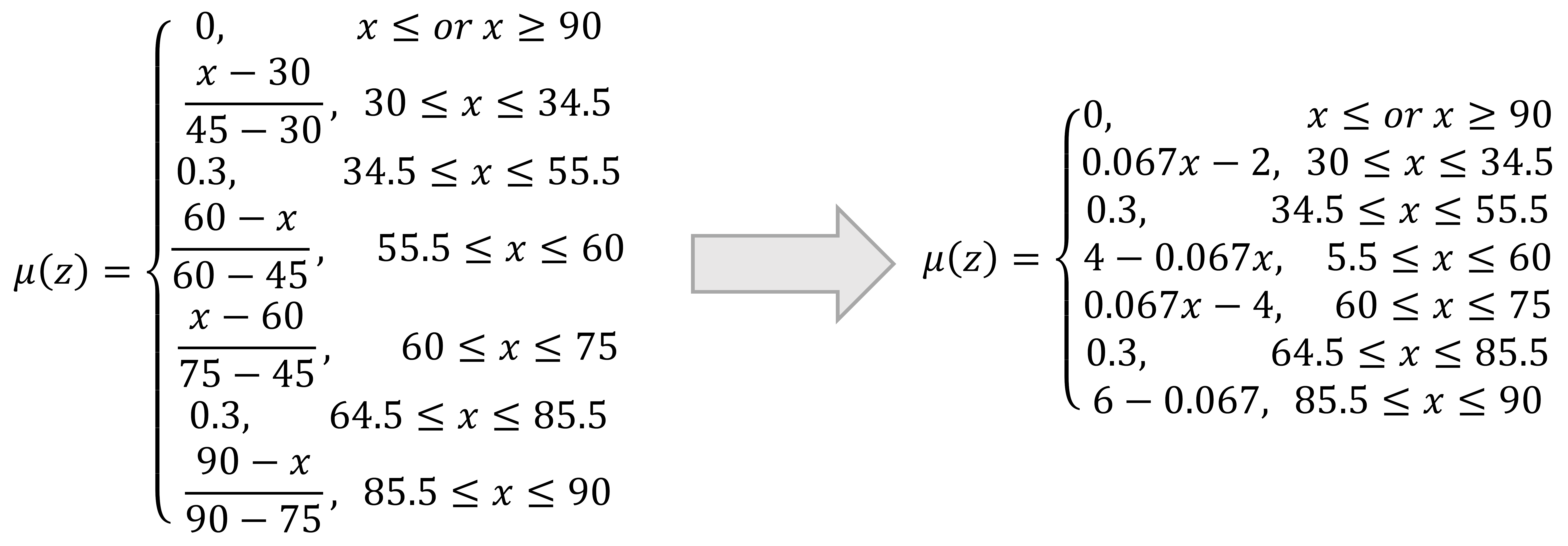
4.3.2. Fuzzy Logic Designer
4.3.3. Membership Function Editor
4.3.4. Rules of Editor
4.3.5. Rules Viewer
4.3.6. Surface Viewer
4.4. Synthesis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Hospital Association (AHA). Hospital Engineering Handbook; American Hospital Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 1980; ISBN 0-939450-74-7. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson Ronald, T.; Lewis, N. Reliability Centred Maintenance Management and Engineering Methods; Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1990; ISBN 1-85166-470-X. [Google Scholar]
- Department of the Army. TM 5-698-2 Reliability-Centred Maintenance (RCM) for Command, Control, Communications, Computer, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (C4ISR) Facilities; Headquarters Department of the Army: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Available online: https://www.wbdg.org/FFC/ARMYCOE/COETM/tm_5_698_2.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2015).
- Farinha, J. Manutenção A Terologia e as Novas Ferramentas de Gestão; Edição, Monitor, Lda: Lisboa, Portugal, 2011; ISBN 9789729413827. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, R.; Smith, R. Maintenance and Reliability Best Practices; Industrial Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-8311-3311-5. [Google Scholar]
- Moubray, J. Reliability-Centred Maintenance; Industrial Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-8311-3078-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. An overview of the recent advances in delay-time-based maintenance modelling. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2012, 106, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwanza, B.G.; Mbohwa, C. An Assessment of the Effectiveness of Equipment Maintenance Practices in Public Hospitals. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 4, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The “IEEE C2: National Electrical Safety Code, 2007”; The Instituto of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 0-7381-4893-8.
- Christiansen, N.; Kaltschmitt, M.; Dzukowski, F.; Isensee, F. Electricity consumption of medical plug loads in hospital laboratories: Identification, evaluation, prediction and verification. Energy Build. 2015, 107, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenSaleh, M.S.; Hermache, A.S. Planning, optimizing and analyzing of safety and maintenance for the critical role of emergency power plant in saudi healthcare facilities. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Region 8 International Conference on Computational Technologies in Electrical and Electronics Engineering (SIBIRCON), Irkutsk, Russia, 11–15 July 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; Rahimi, S.A.; Ait-Kadi, D.; Ruiz, A. A comprehensive fuzzy risk-based maintenance framework for prioritization of medical devices. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 32, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The WHO (World Health Organization and Pan American Health Organization); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-92-4-154898-4.
- Hameed, A.; Khan, F.; Ahmed, S. A risk-based shutdown inspection and maintenance interval estimation considering human error. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 100, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Qyyum, M.A.; Khan, M.S.; Duong, P.L.T.; Lee, M. Knowledge-inspired operational reliability for optimal LNG production at the offshore site. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 150, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, R.M.A.; Lara, J.V.M.; Melgar, A. Reliability model for switchgear failure analysis applied to ageing. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 101, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, E. Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability (RAM Analysis). In Gas and Oil Reliability Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 269–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çekyay, B.; Özekici, S. Reliability, MTTF and steady-state availability analysis of systems with exponential lifetimes. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvaro, F.; Giacchetta, G.; Marchetti, B.; Recanati, M. Reliability, Availability, Maintainability (RAM) study, on reciprocating compressors API 618. Petroleum 2017, 3, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, C. An Introduction to Reliability and Maintainability Engineering; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Zhu, C.; Sun, B.; Liu, L. Process reengineering method for synthesis design of reliability maintainability supportability and performance. In Proceedings of the 2011 9th International Conference on Reliability, Maintainability, and Safety, Guiyang, China, 12–15 June 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, Z.; Vatn, J.; Heggset, J. Challenges in the reliability and maintainability data collection for offshore wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 2154–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikos, L.; Klemeš, J. Reliability, availability and maintenance optimisation of heat exchanger networks. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Wang, B. Survey on Reliability of Power Electronic Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, I. Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability. In Process Risk and Reliability Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 667–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Fu, C.; Yang, K.; Zhang, X.-T.; Shi, G.-H.; Zhai, J. Reliability and availability analysis of redundant BCHP (building cooling, heating and power) system. Energy 2013, 61, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zio, E.; Fan, M.; Zeng, Z.; Kang, R. Application of reliability technologies in civil aviation: Lessons learnt and perspectives. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Cui, L.; Ma, Y. Availability and optimal maintenance policy for systems degrading in dynamic environments. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 276, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.; Vu, H.C.; Barros, A.; Bérenguer, C. Maintenance grouping for multi-component systems with availability constraints and limited maintenance teams. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 142, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto, C.A.; Farinha, J.T.; Singh, S. Contributions of Petri Nets to the Reliability and Availability of an Electrical Power System in a Big European Hospital-A Case Study. WSEAS Trans. Syst. Control. 2021, 16, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Timed Petri Nets: Theory and Application; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-1-4615-5537-7. [Google Scholar]
- Volovoi, V. Modeling of system reliability Petri nets with aging tokens. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2004, 84, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.; Dunnett, S.; Andrews, J. Phased mission modelling of systems with maintenance-free operating periods using simulated Petri nets. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2008, 93, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, H. Reliability analysis of repairable systems using Petri nets and vague Lambda-Tau methodology. ISA Trans. 2013, 52, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, J.M.; Dunnett, S.J. Use of Petri Nets to Model the Maintenance of Wind Turbines. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2014, 32, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Z.; Wu, Y. Modeling the Performance of Aircraft Utilizing Maintenance Free Operating Periods. Procedia Eng. 2015, 99, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadou, N.; Demmou, H. Reliability analysis of discrete event dynamic systems with Petri nets. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2009, 94, 1848–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberger, D.; Fink, O. Assessment of maintenance strategies for railway vehicles using Petri-nets. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 27, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinha, J. Asset Maintenance Engineering Methodologies; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cannarile, F.; Compare, M.; Rossi, E.; Zio, E. A fuzzy expectation maximization based method for estimating the parameters of a multi-state degradation model from imprecise maintenance outcomes. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2017, 110, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladj, A.; Tayeb, F.B.-S.; Varnier, C.; Dridi, A.A.; Selmane, N. A Hybrid of Variable Neighbor Search and Fuzzy Logic for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem with predictive maintenance. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 112, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touat, M.; Bouzidi-Hassini, S.; Benbouzid-Sitayeb, F.; Benhamou, B. A hybridization of genetic algorithms and fuzzy logic for the single-machine scheduling with flexible maintenance problem under human resource constraints. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 59, 556–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaderi, F.; Ibrahim, Z.Z.; Zahiri, M.R. Criticality analysis of petrochemical assets using risk based maintenance and the fuzzy inference system. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 121, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, R.C.; Antosz, K. Development of a Risk Matrix and Extending the Risk-based Maintenance Analysis with Fuzzy Logic. Procedia Eng. 2017, 182, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiti, H.; Hafezalkotob, A.; Fattahi, R. Extending a pessimistic–optimistic fuzzy information axiom based approach considering acceptable risk: Application in the selection of maintenance strategy. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 67, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babashamsi, P.; Golzadfar, A.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Ceylan, H.; Nor, N.G.M. Integrated fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and VIKOR method in the prioritization of pavement maintenance activities. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2016, 9, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordón, O. A historical review of evolutionary learning methods for Mamdani-type fuzzy rule-based systems: Designing interpretable genetic fuzzy systems. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2011, 52, 894–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahabi, M.; Kaber, D. A fuzzy system hazard analysis approach for human-in-the-loop systems. Saf. Sci. 2019, 120, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgun, A.; Sezer, E.; Nefeslioglu, H.; Gokceoglu, C.; Pradhan, B. An easy-to-use MATLAB program (MamLand) for the assessment of landslide susceptibility using a Mamdani fuzzy algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 38, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacimi, M.A.; Guenounou, O.; Brikh, L.; Yahiaoui, F.; Hadid, N. New mixed-coding PSO algorithm for a self-adaptive and automatic learning of Mamdani fuzzy rules. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 89, 103417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-Y.; Sy, C.-C. A real-time decision-making of maintenance using fuzzy agent. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 2691–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhimish, M.; Holmes, V.; Mehrdadi, B.; Dales, M. Comparing Mamdani Sugeno fuzzy logic and RBF ANN network for PV fault detection. Renew. Energy 2018, 117, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraidi, L.; Shah, R.; Matipa, W.; Borthwick, F. Using stakeholders’ judgement and fuzzy logic theory to analyze the risk influencing factors in oil and gas pipeline projects: Case study in Iraq, Stage II. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2020, 28, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravanian, R.; Sabah, M.; Wood, D.A.; Shahryari, A. Weight on drill bit prediction models: Sugeno-type and Mamdani-type fuzzy inference systems compared. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 36, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, T.T.; Logenthiran, T.; Woo, W.L.; Abidi, K.; John, T.; Wade, N.S.; Greenwood, D.M.; Patsios, C.; Taylor, P.C. Optimization of Fuzzy Energy-Management System for Grid-Connected Microgrid Using NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, T.T.; Thillainathan, L.; Woo, W.L.; Abidi, K. Intelligent Controller for Energy Storage System in Grid-Connected Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, T.T.; Logenthiran, T.; Woo, W.L.; Abidi, K. Fuzzy logic control of energy storage system in microgrid operation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies-Asia (ISGT-Asia), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 28 November–1 December 2016; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- HiPS: Hierarchical Petri Net Simulator. Available online: http://sourceforge.net/projects/hips-tools/ (accessed on 27 December 2015).

























| Imput Fuction “EMP” | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Situation | Low | Normal | High |
| Range | (0 600) | (0 600) | (0 600) |
| Parameters | (−300 0 200 319) | (200 320 400 500) | (401 550 699 799) |
| (a) | |||
| Imput Fuction “Genset 1 = Genset 2” | |||
| Situation | Off | On | |
| Range | (0 1000) | (0 1000) | |
| Parameters | (−512 0 1000) | (0 1000 1578) | |
| (b–c) | |||
| Imput Fuction “ATS” | |||
| Situation | Not Function | Function | |
| Range | (0 200) | (0 200) | |
| Parameters | (−80 0 200) | (0 200 280) | |
| (d) | |||
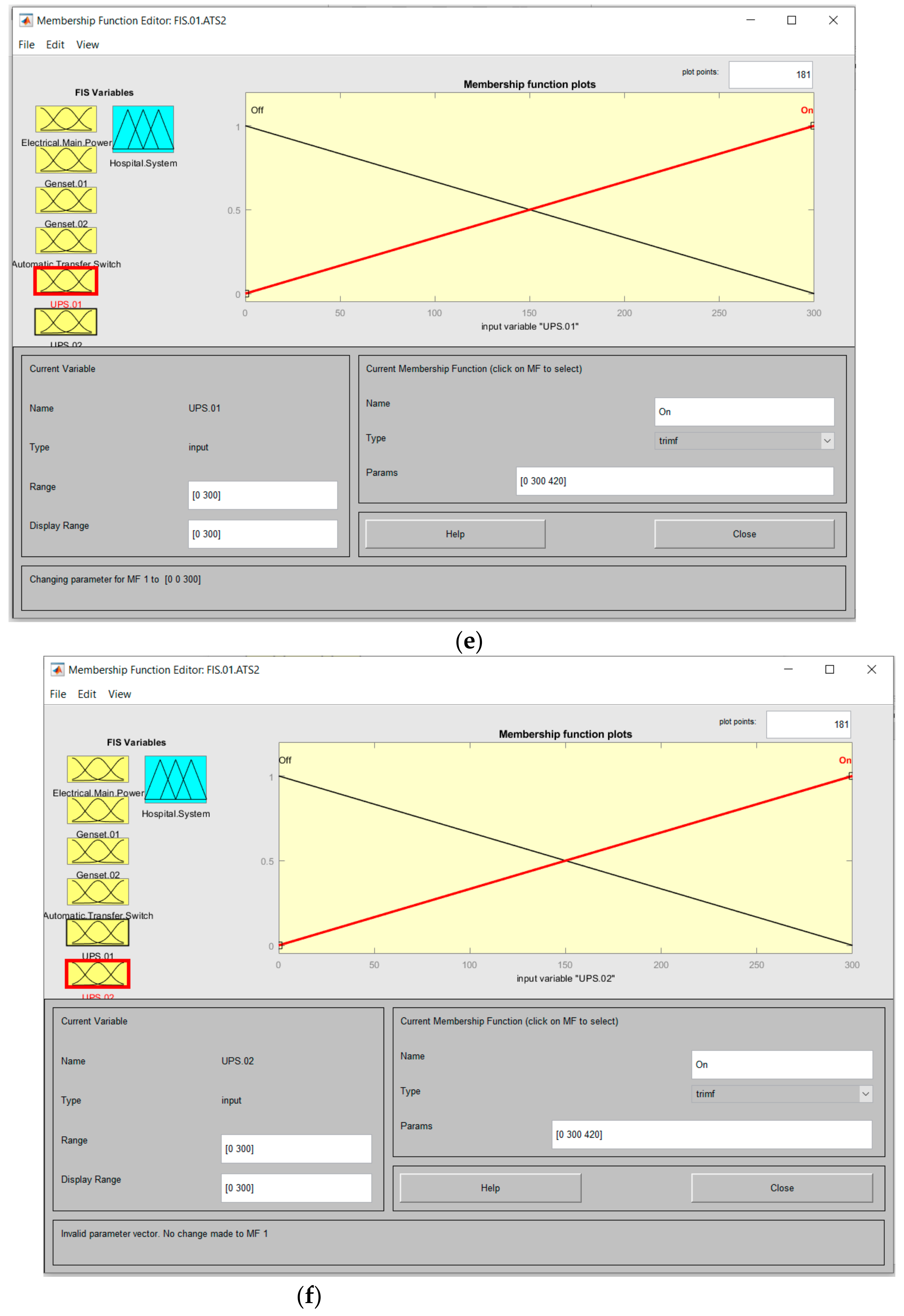
| Imput Fuction “UPS 1 = UPS 2” | |||
| Situation | Off | On | |
| Range | (0 300) | (0 300) | |
| Parameters | (−120 0 300) | (0 300 420) | |
| (e–f) | |||
| Output Function “EMP” | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Situation | Fail Load | Under Load | Normal Load |
| Range | (0 90) | (0 90) | (0 90) |
| Parameters | (0 15 30) | (30 45 60) | (60 75 90) |
| Rules Editor in Terms of Numerical in the Fuzzy Inference System | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIS Membership Fuctions Inputs | FIS Membership Outputs | |||||||
| No. | EMP | Genset 1 | Genset 2 | ATS | UPS 1 | UPS 2 | Hospital System | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | Fail |
| 2 | 0 | 1000 | 0 | 200 | 300 | 300 | 45 | Under Load |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 1000 | 200 | 300 | 300 | 45 | Under Load |
| 4 | 0 | 1000 | 1000 | 200 | 300 | 0 | 45 | Under Load |
| 5 | 0 | 1000 | 1000 | 200 | 0 | 300 | 45 | Under Load |
| 6 | 0 | 1000 | 1000 | 0 | 300 | 300 | 45 | Under Load |
| 7 | 0 | 1000 | 1000 | 200 | 300 | 300 | 75 | Normal Load |
| 8 | 360 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | Fail |
| 9 | 360 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 300 | 300 | 45 | Under Load |
| 10 | 360 | 0 | 0 | 200 | 300 | 300 | 75 | Normal Load |
| 11 | 600 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | Fail |
| 12 | 600 | 1000 | 1000 | 200 | 300 | 300 | 45 | Under Load |
| 13 | 600 | 0 | 1000 | 200 | 300 | 300 | 45 | Under Load |
| 14 | 600 | 1000 | 1000 | 200 | 300 | 0 | 45 | Under Load |
| 15 | 600 | 1000 | 1000 | 200 | 0 | 300 | 45 | Under Load |
| 16 | 600 | 1000 | 1000 | 0 | 300 | 300 | 45 | Under Load |
| 17 | 600 | 1000 | 1000 | 200 | 300 | 300 | 75 | Normal Load |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, C.A.; Farinha, J.T.; Singh, S.; Raposo, H. Increasing the Reliability of an Electrical Power System in a Big European Hospital through the Petri Nets and Fuzzy Inference System Mamdani Modelling. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062604
Pinto CA, Farinha JT, Singh S, Raposo H. Increasing the Reliability of an Electrical Power System in a Big European Hospital through the Petri Nets and Fuzzy Inference System Mamdani Modelling. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(6):2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062604
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Constâncio António, José Torres Farinha, Sarbjeet Singh, and Hugo Raposo. 2021. "Increasing the Reliability of an Electrical Power System in a Big European Hospital through the Petri Nets and Fuzzy Inference System Mamdani Modelling" Applied Sciences 11, no. 6: 2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062604
APA StylePinto, C. A., Farinha, J. T., Singh, S., & Raposo, H. (2021). Increasing the Reliability of an Electrical Power System in a Big European Hospital through the Petri Nets and Fuzzy Inference System Mamdani Modelling. Applied Sciences, 11(6), 2604. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062604








