Behavior of Primary Human Oral Keratinocytes Grown on Invisalign® SmartTrack® Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aligner Preparation and Cell Culture Stimulation Protocol
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3. Bright Field Microscopy
2.4. Cell Proliferation/Viability
2.5. Live/Dead Staining
2.6. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
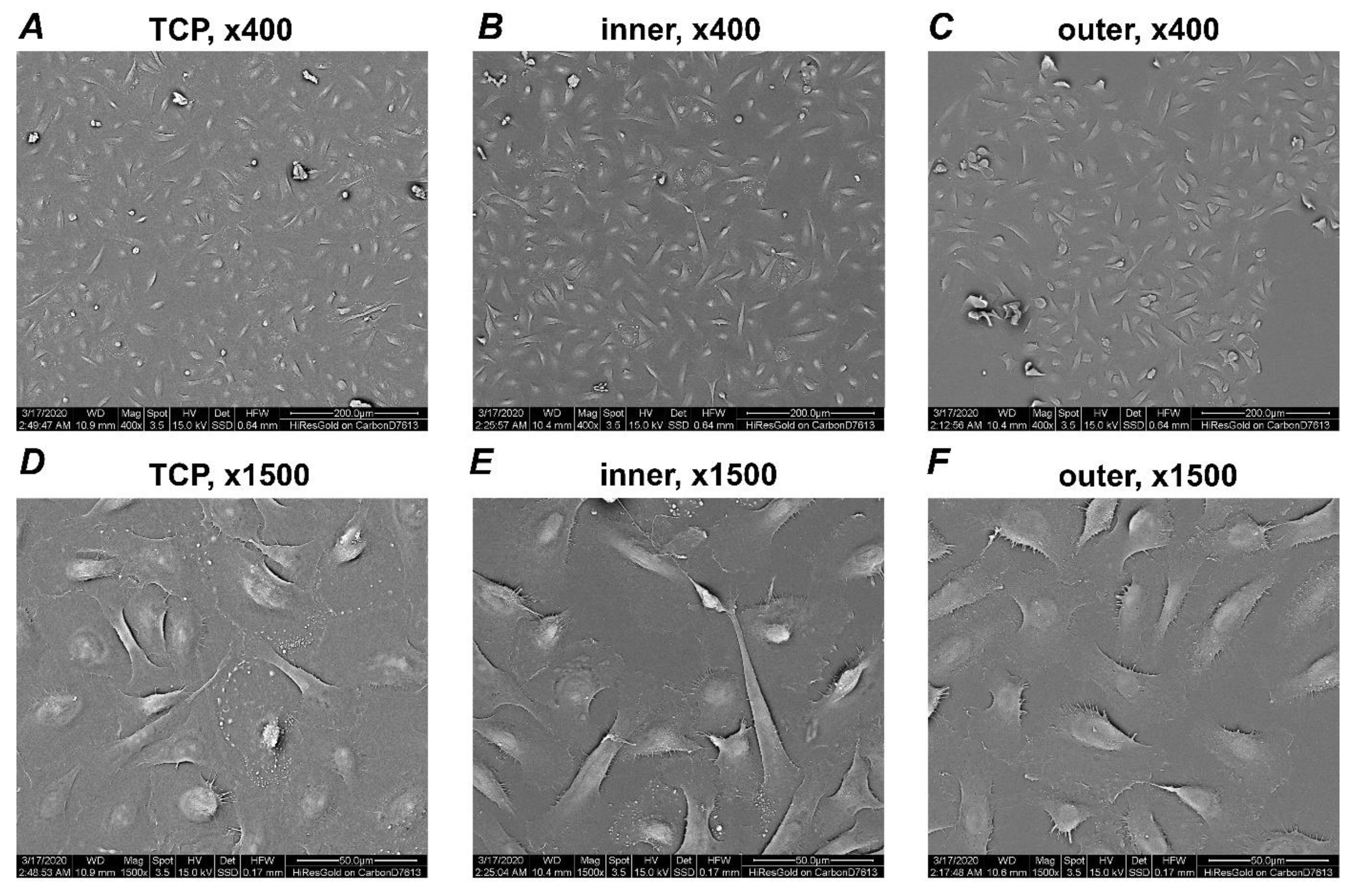
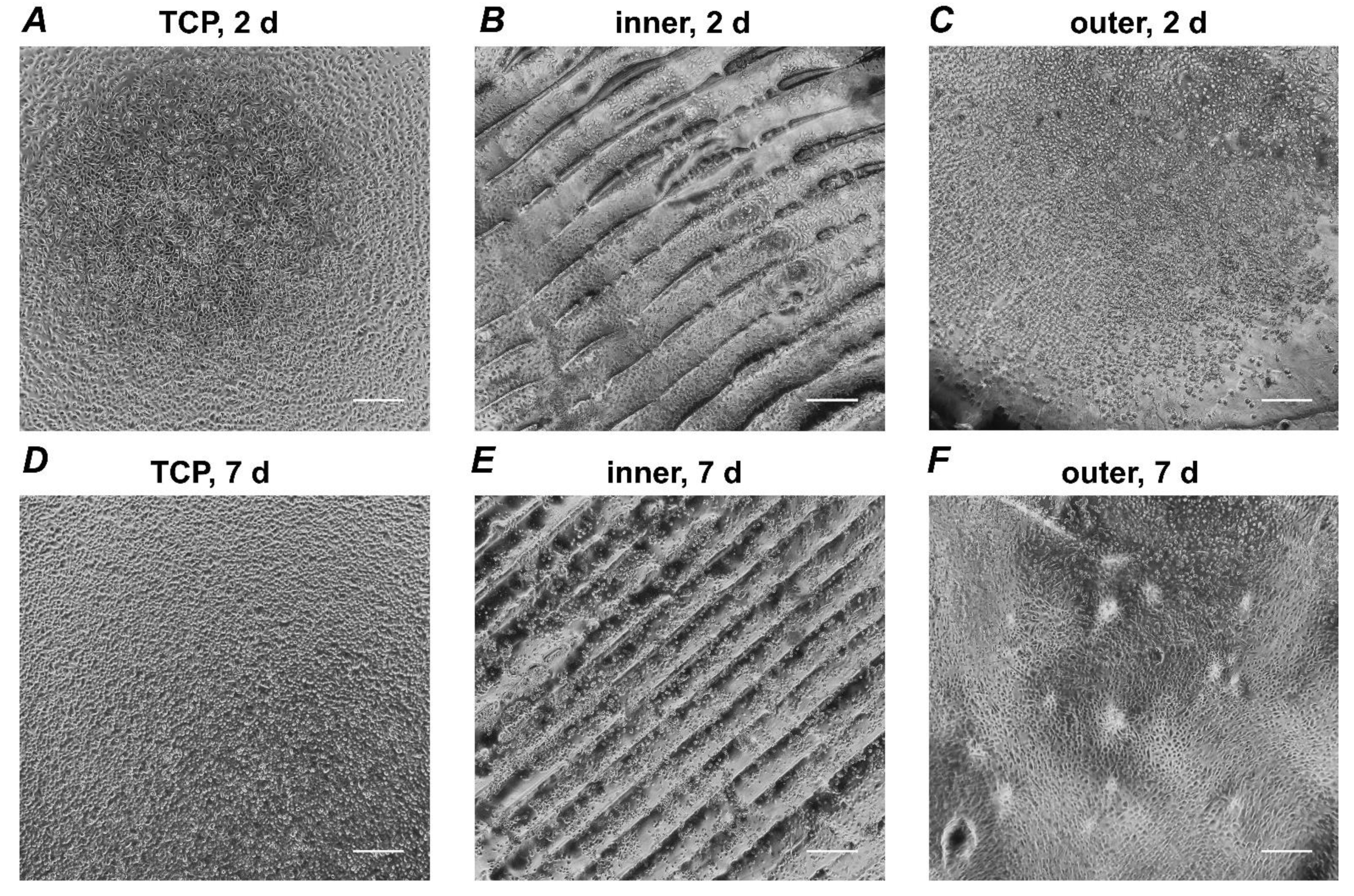
3.1. Microscopic Analysis
3.2. Proliferation/Viability of HOKs
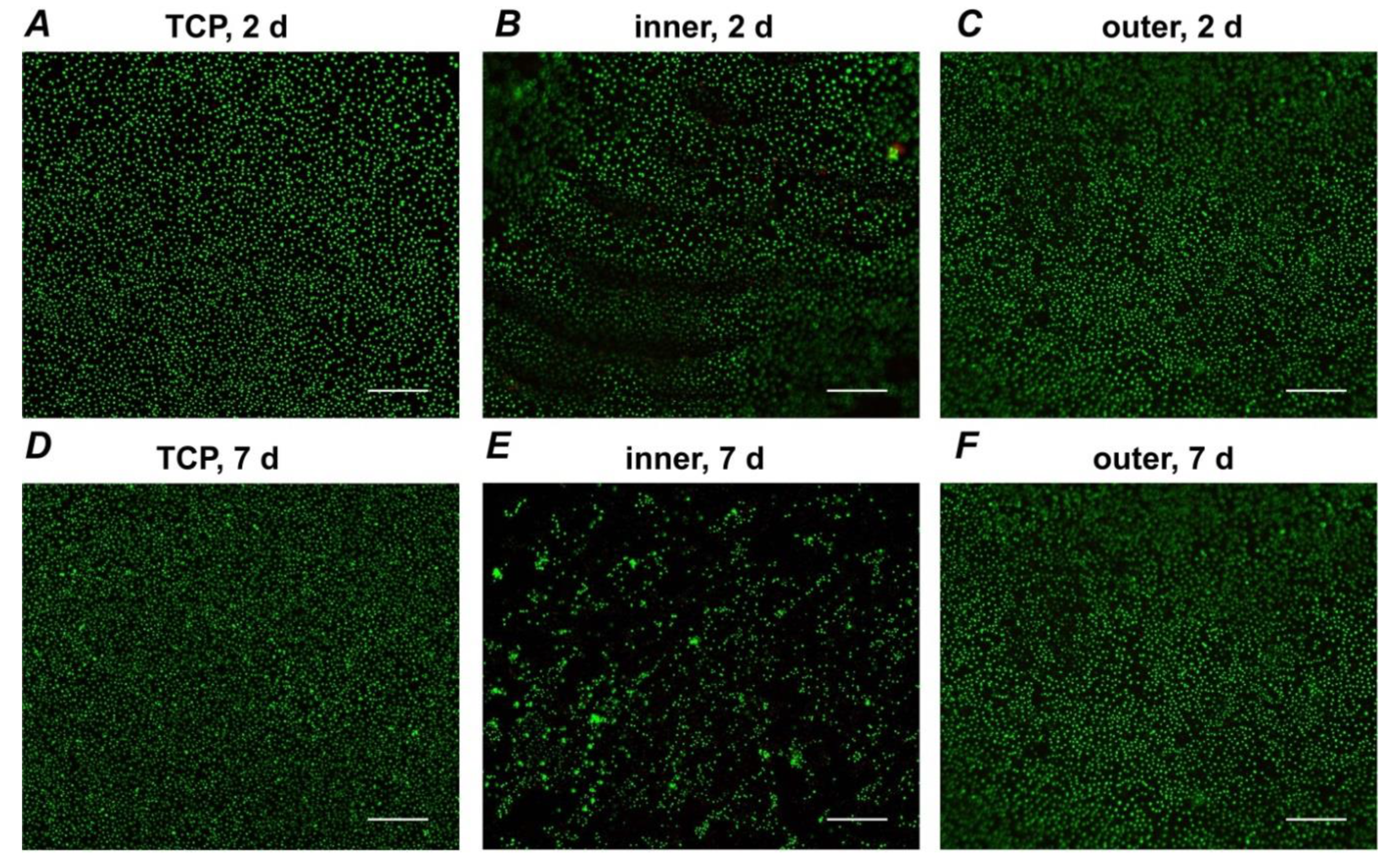
3.3. Live/Dead Staining
3.4. Gene Expressions of Inflammatory Markers
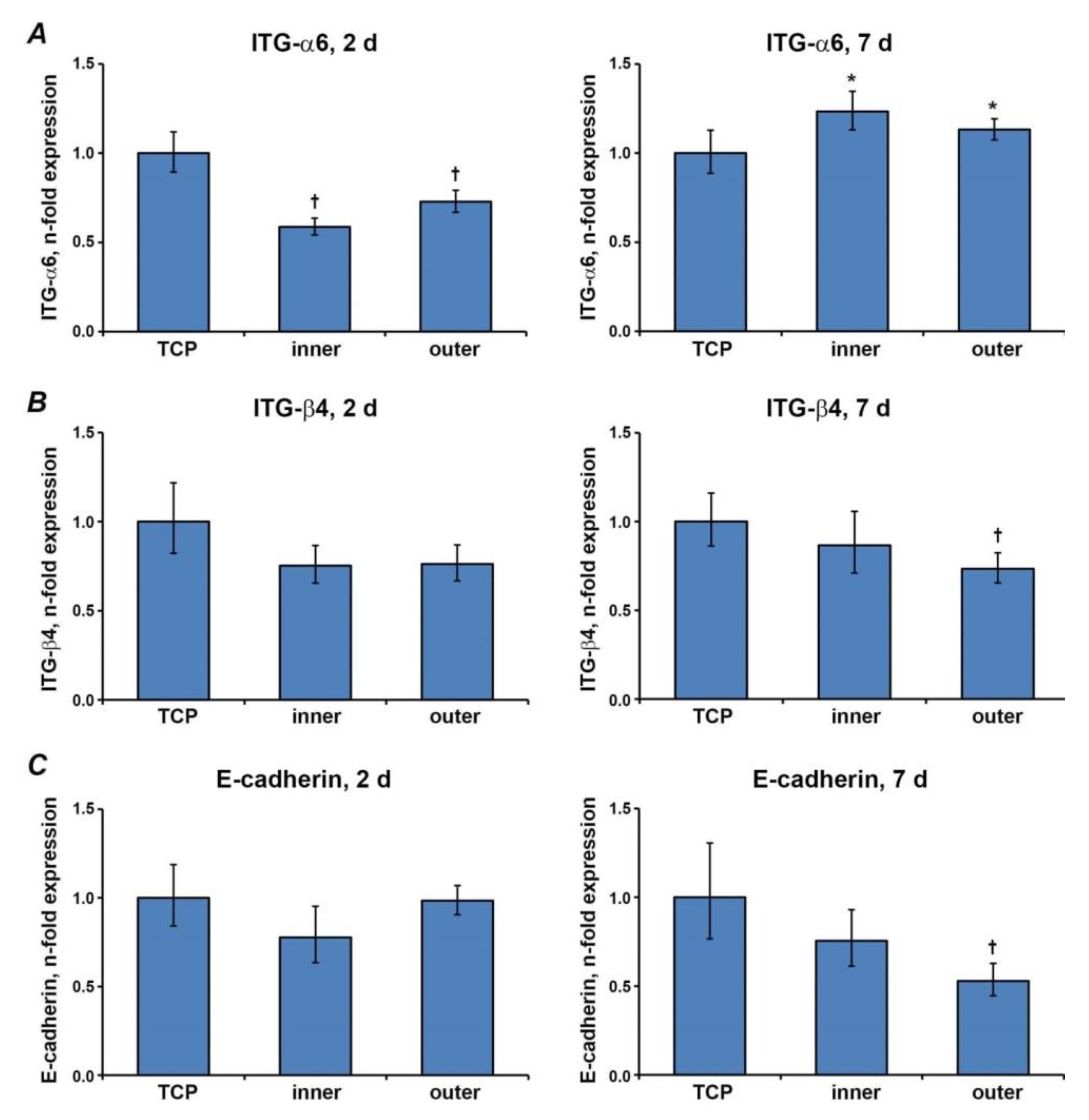
3.5. Gene Expression Levels of Proteins Involved in the Barrier Function
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosvall, M.D.; Fields, H.W.; Ziuchkovski, J.; Rosenstiel, S.F.; Johnston, W.M. Attractiveness, acceptability, and value of orthodontic appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 276.e1–276.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C.L. Efficacy of clear aligners in controlling orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iliadi, A.; Koletsi, D.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Eliades, T. Safety Considerations for Thermoplastic-Type Appliances Used as Orthodontic Aligners or Retainers. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical and In-Vitro Research. Materials 2020, 13, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keim, R.G.; Gottlieb, E.L.; Vogels, D.S.; Vogels, P.B. 2014 JCO study of orthodontic diagnosis and treatment procedures, Part 1: Results and trends. J. Clin. Orthod. 2014, 48, 607–630. [Google Scholar]
- Tamer, I.; Oztas, E.; Marsan, G. Orthodontic Treatment with Clear Aligners and the Scientific Reality Behind Their Marketing: A Literature Review. Turk. J. Orthod. 2019, 32, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, T. Clear aligners in orthodontic treatment. Aust. Dent. J. 2017, 62, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, H.; Wu, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Jian, F.; Liao, L.; Li, X.; Lai, W. An objective system for appraising clear aligner treatment difficulty: Clear aligner treatment complexity assessment tool (CAT–CAT). BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, A.D.; Shroff, B.; Carrico, C.K.; Lindauer, S.J. Treatment management between orthodontists and general practitioners performing clear aligner therapy. Angle Orthod. 2016, 87, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hennessy, J.; Al-Awadhi, E.A. Clear Aligners Generations and Orthodontic Tooth Movement. J. Orthod. 2016, 43, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, G.; Rompré, P.; Tavares, J.R.; Montpetit, A. Colorimetric and spectrophotometric measurements of orthodontic thermoplastic aligners exposed to various staining sources and cleaning methods. Head Face Med. 2020, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, M.; Eckhart, J.; McShane, P.; German, D.S. Consequences of poor oral hygiene during aligner therapy. J. Clin. Orthod. 2013, 47, 494–498. [Google Scholar]
- Minamikawa, H.; Yamada, M.; Iwasa, F.; Ueno, T.; Deyama, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Yawaka, Y.; Ogawa, T. Amino acid derivative-mediated detoxification and functionalization of dual cure dental restora-tive material for dental pulp cell mineralization. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7213–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, S.; Rongo, R.; Bucci, R.; Razionale, A.V.; Valletta, R.; D’Antò, V. In vitro cytotoxicity of different thermoplastic materials for clear aligners. Angle Orthod. 2019, 89, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Premaraj, T.; Simet, S.; Beatty, M.; Premaraj, S. Oral epithelial cell reaction after exposure to Invisalign plastic material. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2014, 145, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliades, T.; Pratsinis, H.; Athanasiou, A.E.; Eliades, G.; Kletsas, D. Cytotoxicity and estrogenicity of Invisalign appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 136, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squier, C.A.; Kremer, M.J. Biology of Oral Mucosa and Esophagus. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2001, 2001, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhatt, A.P.; Redinbo, M.R.; Bultman, S.J. The role of the microbiome in cancer development and therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gartner, L.P. Oral anatomy and tissue types. Semin. Dermatol. 1994, 13, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nemec, M.; Bartholomaeus, H.M.; Bertl, M.; Behm, C.; Ali Shokoohi-Tabrizi, H.; Jonke, E.; Andrukhov, O.; Rausch-Fan, X. Behaviour of Human Oral Epithelial Cells Grown on Invisalign(®) SmartTrack(®) Material. Materials 2020, 13, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, M.M.; Pantano, D.M.; Flanders, J.A.; Augustin-Voss, H.G.; Dougherty, E.P.; Varvayanis, M. Comparison of Growth and Differentiation of Normal and Neoplastic Canine Keratinocyte Cultures. Vet. Pathol. 1991, 28, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakelius, M.; Koskela, A.; Ivarsson, M.; Grenman, R.; Rubin, K.; Gerdin, B.; Nowinski, D. Keratinocytes and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells regulate urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in fibroblasts. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 3113–3118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Contreras, R.; Scougall-Vilchis, R.J.; Contreras-Bulnes, R.; Kanda, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Sakagami, H. Cytotoxicity and pro-inflammatory action of chemo-mechanical caries-removal agents against oral cells. In Vivo 2014, 28, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García-Contreras, R.; Vilchis, R.J.S.; Contreras-Bulnes, R.; Kanda, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Sakagami, H. Effects of TiO2 nano glass ionomer cements against normal and cancer oral cells. In Vivo 2014, 28, 895–907. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, C.; Venegas, B. Histological and molecular aspects of oral squamous cell carcinoma (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negi, A.; Puri, A.; Gupta, R.; Nangia, R.; Sachdeva, A.; Mittal, M. Comparison of Immunohistochemical Expression of Antiapoptotic Protein Survivin in Normal Oral Mu-cosa, Oral Leukoplakia, and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Patholog. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 840739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolós, V.; Peinado, H.; Pérez-Moreno, M.A.; Fraga, M.F.; Esteller, M.; Cano, A. The transcription factor Slug represses E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal tran-sitions: A comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, H.E.; Listgarten, M.A. The gingival tissues: The architecture of periodontal protection. Periodontology 1997, 13, 91–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.; Lim, I.J.; Tan, E.K.; Bay, B.H.; Lee, S.T. Evaluation of cell culture on the polyurethane-based membrane (Tegaderm): Implication for tissue engi-neering of skin. Cell Tissue Bank. 2005, 6, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeger, S.; Meyle, J. Oral Mucosal Epithelial Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Imboden, M.; Gerber, L.; Lang, N.P.; Laissue, J.; Mueller, C. Localized expression of mRNA for phagocyte-specific chemotactic cytokines in human periodontal infections. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asai, Y.; Ohyama, Y.; Gen, K.; Ogawa, T. Bacterial Fimbriae and Their Peptides Activate Human Gingival Epithelial Cells through Toll-Like Receptor. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 7387–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyauchi, M.; Sato, S.; Kitagawa, S.; Hiraoka, M.; Kudo, Y.; Ogawa, I.; Zhao, M.; Takata, T. Cytokine expression in rat molar gingival periodontal tissues after topical application of lipopoly-saccharide. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 116, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azaripour, A.; Weusmann, J.; Mahmoodi, B.K.; Peppas, D.; Gerhold-Ay, A.; Van Noorden, C.J.F.; Willershausen, B. Braces versus Invisalign®: Gingival parameters and patients’ satisfaction during treatment: A cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levrini, L.; Mangano, A.; Montanari, P.; Margherini, S.; Caprioglio, A.; Abbate, G.M. Periodontal health status in patients treated with the Invisalign(®) system and fixed orthodontic appli-ances: A 3 months clinical and microbiological evaluation. Eur. J. Dent. 2015, 9, 404–410. [Google Scholar]
- Sandros, J.; Karlsson, C.; Lappin, D.; Madianos, P.; Kinane, D.; Papapanou, P. Cytokine Responses of Oral Epithelial Cells to Porphyromonas gingivalis Infection. J. Dent. Res. 2000, 79, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nibali, L.; Fedele, S.; D’Aiuto, F.; Donos, N. Interleukin-6 in oral diseases: A review. Oral Dis. 2011, 18, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Imboden, M.A.; Lang, N.P. Neutrophil migration into the gingival sulcus is associated with transepi-thelial gradients of interleukin-8 and ICAM-1. J. Periodontol. 1998, 69, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, I.; Hajishengallis, G. Major neutrophil functions subverted by Porphyromonas gingivalis. J. Oral Microbiol. 2016, 8, 30936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamont, R.J.; Hajishengallis, G. Polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis in inflammatory disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misawa, M.Y.O.; Silvério Ruiz, K.G.; Nociti, F.H., Jr.; Albiero, M.L.; Saito, M.T.; Nóbrega Stipp, R.; Condino-Neto, A.; Holzhausen, M.; Palombo, H.; Villar, C.C. Periodontal ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells modulate neutrophil responses via para-crine mechanisms. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfakianakis, A.; Barr, C.E.; Kreutzer, D.L. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans-induced expression of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta in human gingival epithelial cells: Role in IL-8 expression. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2001, 109, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukandu, O.M.; Bredholt, T.; Neppelberg, E.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Johannessen, A.C.; Vintermyr, O.K.; Costea, D.E. Early loss of mitochondrial inner transmembrane potential in khat-induced cell death of primary normal human oral cells. Toxicology 2009, 263, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presland, R.B.; Jurevic, R.J. Making sense of the epithelial barrier: What molecular biology and genetics tell us about the functions of oral mucosal and epidermal tissues. J. Dent. Educ. 2002, 66, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, L.; Broad, S.; Diekmann, D.; Evans, R.D.; Watt, F.M. beta1 integrins regulate keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation by distinct mechanisms. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nemec, M.; Bartholomaeus, H.M.; Wehner, C.; Behm, C.; Shokoohi-Tabrizi, H.A.; Rausch-Fan, X.; Andrukhov, O.; Jonke, E. Behavior of Primary Human Oral Keratinocytes Grown on Invisalign® SmartTrack® Material. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062826
Nemec M, Bartholomaeus HM, Wehner C, Behm C, Shokoohi-Tabrizi HA, Rausch-Fan X, Andrukhov O, Jonke E. Behavior of Primary Human Oral Keratinocytes Grown on Invisalign® SmartTrack® Material. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(6):2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062826
Chicago/Turabian StyleNemec, Michael, Hans Magnus Bartholomaeus, Christian Wehner, Christian Behm, Hassan Ali Shokoohi-Tabrizi, Xiaohui Rausch-Fan, Oleh Andrukhov, and Erwin Jonke. 2021. "Behavior of Primary Human Oral Keratinocytes Grown on Invisalign® SmartTrack® Material" Applied Sciences 11, no. 6: 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062826





