A Fast Point Clouds Registration Algorithm for Laser Scanners
Abstract
1. Introduction
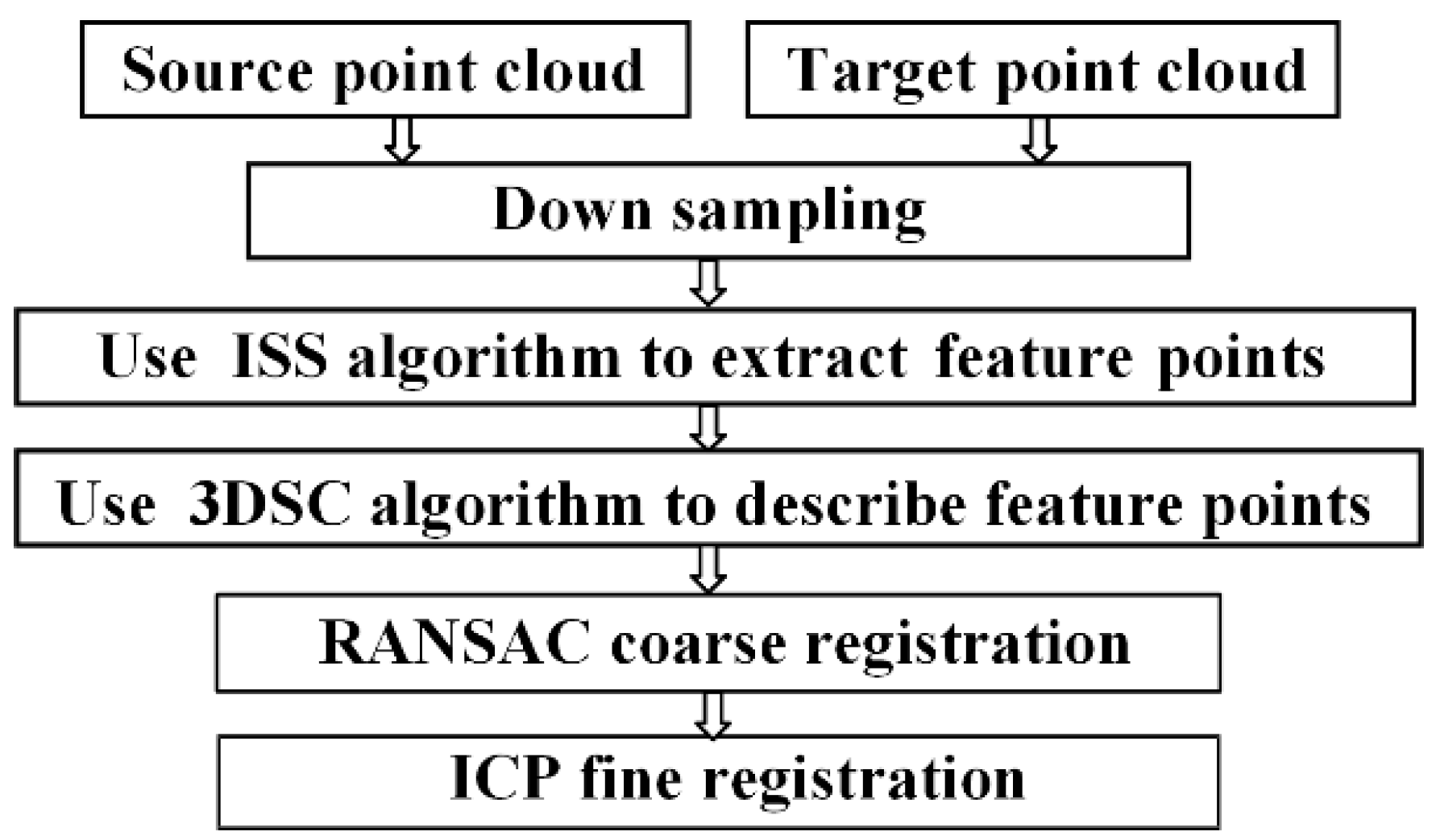
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Down Sampling
2.2. Intrinsic Shape Signatures Algorithm
2.3. 3D Shape Context
2.4. RANSAC Coarse Registration
2.5. ICP Fine Registration
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Selection of Main Parameters
3.2. Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Ko, H.; Kim, J. VICP: Velocity updating iterative closest point algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 1893–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, A.; Haehnel, D.; Thrun, S. Generalized-ICP. In Robotics: Science and Systems V; University of Washington: Seattle, DC, USA, 2009; Volume 2, p. 435. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Li, H.; Jia, Y. Go-ICP: Solving 3D registration efficiently and globally optimally. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1457–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Censi, A. An ICP variant using a point-to-line metric. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson, M.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Duckett, T. Scan registration for autonomous mining vehicles using 3D-NDT. J. Field Robot. 2007, 24, 803–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Ahn, C.; Lee, M.; Oh, S. Graph-matching-based correspondence search for nonrigid point cloud registration. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2020, 192, 102899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, W.; Zhou, M. An approach for model reconstruction based on multi-view scans registration. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Audio, Language and Image Processing, Shanghai, China, 23–25 November 2010; pp. 601–606. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Qian, F.; Chen, X. Point cloud registration algorithm based on overlapping region extraction. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1634, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, M.; Ahmed, M.T.; Rappaport, D.; Greenspan, M. Super generalized 4PCS for 3D registration. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on 3D Vision, Lyon, France, 19–22 October 2015; pp. 598–606. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Lee, C.-H. An improved ICP registration algorithm by combining PointNet++ and ICP algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics (ICCAR), Singapore, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 741–745. [Google Scholar]
- Kamencay, P.; Sinko, M.; Hudec, R.; Benco, M.; Radil, R. Improved feature point algorithm for 3D point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the 2019 42nd International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Budapest, Hungary, 1–3 July 2019; pp. 517–520. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, F.; Dong, B.; Huo, W.; Pang, M.; Kuang, L.; Han, X. A local feature descriptor based on rotational volume for pairwise registration of point clouds. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 100120–100134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Hoang, D.C.; Lin, H.I.; Nguyen, T.H. Innovative methodology for multi-view point cloud registration in robotic 3D object scanning and reconstruction. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.; González-Jorge, H.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.; Lorenzo, H. Automatic point cloud coarse registration using geometric keypoint descriptors for indoor scenes. Autom. Constr. 2017, 81, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y. Intrinsic shape signatures: A shape descriptor for 3D object recognition. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, ICCV Workshops, Kyoto, Japan, 27 September–4 October 2009; pp. 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Frome, A.; Huber, D.; Kolluri, R.; Bülow, T.; Malik, J. Recognizing objects in range data using regional point descriptors. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Read. Comput. Vis. 1987, 24, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, A.G.; Kraft, D.; Kämäräinen, J.-K.; Petersen, H.G.; Krüger, N. Pose estimation using local structure-specific shape and appearance context. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 2080–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.; Liang, Z.; Su, L. Tree point clouds registration using an improved ICP algorithm based on kd-tree. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 4545–4548. [Google Scholar]
- Prakhya, S.M.; Lin, J.; Chandrasekhar, V.; Lin, W.; Liu, B. 3DHoPD: A fast low-dimensional 3-D descriptor. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Dian, S.Y. Dynamic differential evolution algorithm applied in point cloud registration. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 428, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Grid Size/m | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Sample points (P) | 36,415 | 11,174 | 5425 | 3190 | 2173 |
| ISS feature points (P) | 769 | 220 | 120 | 48 | 32 |
| Sample points (Q) | 38,213 | 11,727 | 5661 | 3394 | 2239 |
| ISS feature points (Q) | 879 | 252 | 112 | 54 | 34 |
| /m | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Time/s | 0.926 | 0.844 | 0.801 | 0.812 | 0.815 | 0.812 | 0.812 |
| RMSE/m | 0.35 | 0.166 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.079 | 0.078 |
| /m | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Time/s | 0.812 | 0.8 | 0.813 | 0.801 | 0.819 | 0.803 | 0.802 | 0.806 | 0.809 |
| RMSE/m | 0.091 | 0.091 | 0.081 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| Parameter | Value | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Grid size | 0.03 m | The voxel grid of leaf size |
| 0.0043 m | Point cloud resolution | |
| Support radius for intrinsic frame | ||
| Weighted neighbors within the radius | ||
| 0.975 | Ratio of the second eigenvalue to the first | |
| 0.975 | Ratio of the third eigenvalue to the second | |
| 0.3 m | Support radius for 3DSC | |
| 0.02 m | Minimum radius of radial division to avoid noise | |
| 0.002 | Density of the corresponding local point | |
| 3 | Sample points in surface | |
| 0.01 | Edge length similarity threshold | |
| 0.01 | Inlier fraction | |
| 0.3 m | Max-distance threshold of corresponding points for RANSAC | |
| 3000 | Max-iteration number for RANSAC | |
| 0.3 m | Max-distance threshold of corresponding points for ICP | |
| 30 | Max-iteration number for ICP |
| Model | ICP | SAC-IA+ICP | 3DHoPD+ICP | Ours | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | β/% | ERMSE | RMSE | β/% | ERMSE | RMSE | β/% | ERMSE | RMSE | β/% | ERMSE | |
| Bed | 2.381 | 0.002 | 2.381 | 0.0763 | 75.2 | 0.0089 | 0.078 | 77.7 | 0.009 | 0.078 | 75.5 | 0.0079 |
| Motorbike | 0.6145 | 0.008 | 0.6145 | 0.0207 | 92.3 | 0.0117 | 0.021 | 92.3 | 0.0124 | 0.0221 | 91.3 | 0.0134 |
| Piano | 0.5435 | 0 | 0.5435 | 0.0007 | 100 | 0.0007 | 0.0009 | 100 | 0.0009 | 0.0058 | 100 | 0.0058 |
| Dragon1 | 0.1573 | 0 | 0.1573 | 0.002 | 91.1 | 0.0005 | 0.0022 | 95.9 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 91.9 | 0.0007 |
| Dragon2 | 0.0011 | 92.6 | 0.0005 | 0.0011 | 92.7 | 0.0005 | 0.002 | 95.8 | 0.0012 | 0.0011 | 92.4 | 0.0005 |
| Bunny | 0.0023 | 92.9 | 0.001 | 0.0026 | 91.5 | 0.0013 | 0.0024 | 91.1 | 0.0013 | 0.0026 | 94.6 | 0.0099 |
| Model | ICP | SAC-IA+ICP | 3DHoPD+ICP | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bed | 30.208 | 14.266 | 1.043 | 0.662 |
| Motorbike | 3.099 | 7.191 | 0.689 | 0.56 |
| Piano | 22.33 | 13.16 | 0.732 | 0.583 |
| Dragon1 | 4.776 | 17.426 | 1.385 | 0.38 |
| Dragon2 | 1.014 | 18.538 | 1.751 | 0.696 |
| Bunny | 1.745 | 19.342 | 1.462 | 0.613 |
| Total | 63.172 | 89.923 | 7.062 | 3.494 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, G.; Pang, Y.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z. A Fast Point Clouds Registration Algorithm for Laser Scanners. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3426. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083426
Xu G, Pang Y, Bai Z, Wang Y, Lu Z. A Fast Point Clouds Registration Algorithm for Laser Scanners. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(8):3426. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083426
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Guangxuan, Yajun Pang, Zhenxu Bai, Yulei Wang, and Zhiwei Lu. 2021. "A Fast Point Clouds Registration Algorithm for Laser Scanners" Applied Sciences 11, no. 8: 3426. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083426
APA StyleXu, G., Pang, Y., Bai, Z., Wang, Y., & Lu, Z. (2021). A Fast Point Clouds Registration Algorithm for Laser Scanners. Applied Sciences, 11(8), 3426. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083426







