Abstract
(1) Background: The purpose of this study was to develop an image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery (IGESS) system, named Medigator®, based on the leave-one-out registration strategy and three-dimensional (3D) volumetric visualization of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. (2) Methods: A phantom was designed and fabricated using a 3D printer. We then performed a phantom-based accuracy evaluation to validate the performance of the developed registration method. We included 11 patients who underwent IGESS for clinical study to compare the performance of the developed IGESS system with that of a commercialized system. (3) Results: The fiducial registration error (FRE) was 0.14 mm, and the target registration error (TRE) was 0.82 ± 0.50 mm by the phantom-based evaluation. As a result of the clinical comparative study, the average registration times were 36.04 ± 4.7 and 89.35 ± 26.1 s for the developed and commercialized systems, respectively (p < 0.05). The image loading time of the developed system was also shorter than that of the commercialized system (p < 0.05). The average accuracy score of the developed system was not significantly different from that of the commercialized system (p > 0.05). (4) Conclusions: The developed system provided an accurate point-to-point registration method based on the leave-one-out strategy. According to the results of the clinical comparative study, we demonstrated that the developed system showed reliable potential for clinical application.
1. Introduction
Nearly half of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis undergo surgery within 6 months of their diagnosis [1]. Endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) is the most common surgery in the treatment of chronic sinusitis patients. ESS requires precise dissection of the tissue adjacent to the orbit or the skull base in a spatially restricted surgical field and has a high risk of complications, such as cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea, visual disturbance, and injury to the ocular muscle [2]. Therefore, surgeons need a more accurate, technically advanced method to prevent such complications during surgery.
Image-guided surgery (IGS) systems have been introduced to provide intuitive perception of the surgical target and adjacent anatomical structures for surgeons. Three-dimensionally rendered virtual models are continuously visualized on the screen of the system to provide visual perceptions of the internal anatomy of the patients during surgery [3,4,5,6,7]. IGS systems require accurate positioning of the surgical instruments or target anatomical structures [2]. Accuracy of the IGS systems is closely related to registration between the patient’s physical space and the image space [6,7,8]. Point-to-point registration using a corresponding pair of fiducial markers, such as non-invasive adhesive markers, invasively implanted markers, or anatomical landmarks, is commonly used for IGS systems [9,10,11,12,13,14]. In ESS using an IGS system, point-to-point registration methods use anatomical fiducials on the facial skin of patient [8]. To date, since there are no systematic criteria for evaluating registration accuracy, researchers have used non-standardized methods to evaluate it.
An electromagnetic (EM) tracking-based IGS system has no line-of-sight problem, so it can be used in minimally invasive surgeries and especially in ESS [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. By using the transmitted information, the position and orientation of the tracking tool are calculated to visualize their locations during surgery. In ESS, the current position of the pointing tool is visualized on the screen of the IGS system.
The contribution of this work is four-fold: (1) We developed a point-to-point registration method based on the leave-one-out strategy. (2) We fabricated a phantom for evaluating the accuracy of the image registration method according to ASTM F2554-10 [26]. (3) We developed an image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery (IGESS) system named Medigator® (Gmeditec, Incheon, Korea) by providing 3D volumetric visual perception of patient internal anatomy. (4) We performed clinical studies to compare the developed IGESS system with a commercialized system (Scopis® Hybrid Navigation System, Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI, USA).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Phantom and Acquisition of Phantom’s CT Data
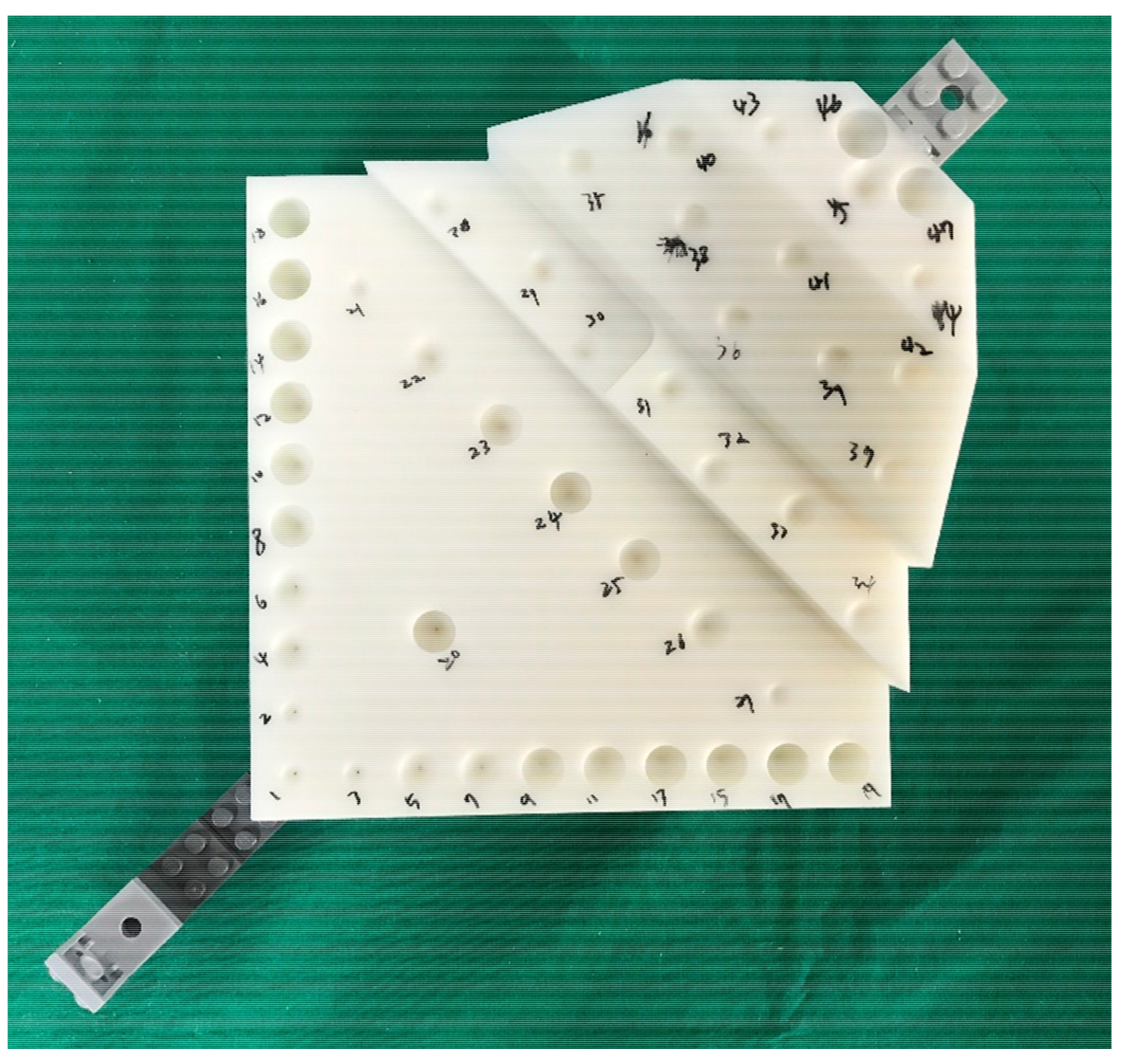
A phantom was fabricated with ABS-like material using a 3D printer (RSPro600, Shanghai 3D Union Technology, Shanghai, China) according to ASTM F2554-10 [26] (Figure 1). The phantom contained forty-seven cone-shaped divots, each 8 mm in diameter, 4 mm in depth, and having a semi-vertical angle of 22.5°. Eight of them were oriented at an angle of 45°, and the remaining 39 divots were oriented at an angle of 90°. The positions of the divots were the same as those specified in ASTM F2554-10 [26]. A three-dimensional coordinate measuring machine (global advantage silver model, hexagon metrology, Stockholm, Sweden) was used to measure the positions of all holes on the phantom. Then, we acquired a CT image of the phantom with MDCT (SOMATOM Sensation 10, Siemens, Munich, Germany) under 120 kVp and 80 mAs with a slice thickness of 0.75 mm.
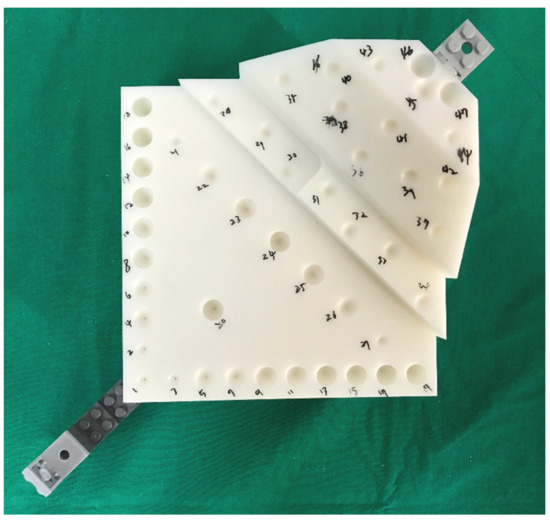
Figure 1.
A phantom for evaluating registration accuracy with forty-seven cone-shaped divots.
2.2. Point-to-Point Registration Method Based on Leave-One-Out Strategy
To define the optimal rotation matrix and translation vector between a pair of corresponding 3D point sets, we developed a novel point-to-point registration method using a singular value decomposition (SVD) according to the concept of the conventional iterative closest point algorithm [27]. We used six pairs of corresponding points for registration, and the overall registration procedure was as follows. (1) The centroids of the point sets were calculated by averaging the positions of the six points in each set. (2) The centroids of the point sets were moved to the origin for removing the translation components. (3) We generated the accumulating matrix and applied SVD to find the rotation (Equations (1)–(3)). (4) We calculated the translation vector (Equation (4)) and determined the rigid transformation for registration.
where M (moving points) and F (fixed points) are sets of 3D points with correspondence, R is a 3 × 3 rotation matrix, t is a translation vector (technically a 1 × 3 matrix), H is an accumulated matrix, U is an unitary matrix, S is a rectangular diagonal matrix with non-negative real numbers on the diagonal, and V is an unitary matrix [28].
To improve the accuracy of the point-to-point registration, we established a leave-one-out registration strategy. An initial registration was performed using the corresponding point sets using six points, and the fiducial registration error (FRE) was then calculated using the points used for the registration. After the initial registration, we found and excluded the point with the highest error. Then, we performed the fine registration using the remaining five points. As a result, the rigid transformation between the patient’s physical and image spaces was determined by the registration.
2.3. Image-Guided Endoscopic Sinus Surgery System with 3D Volumetric Visualization
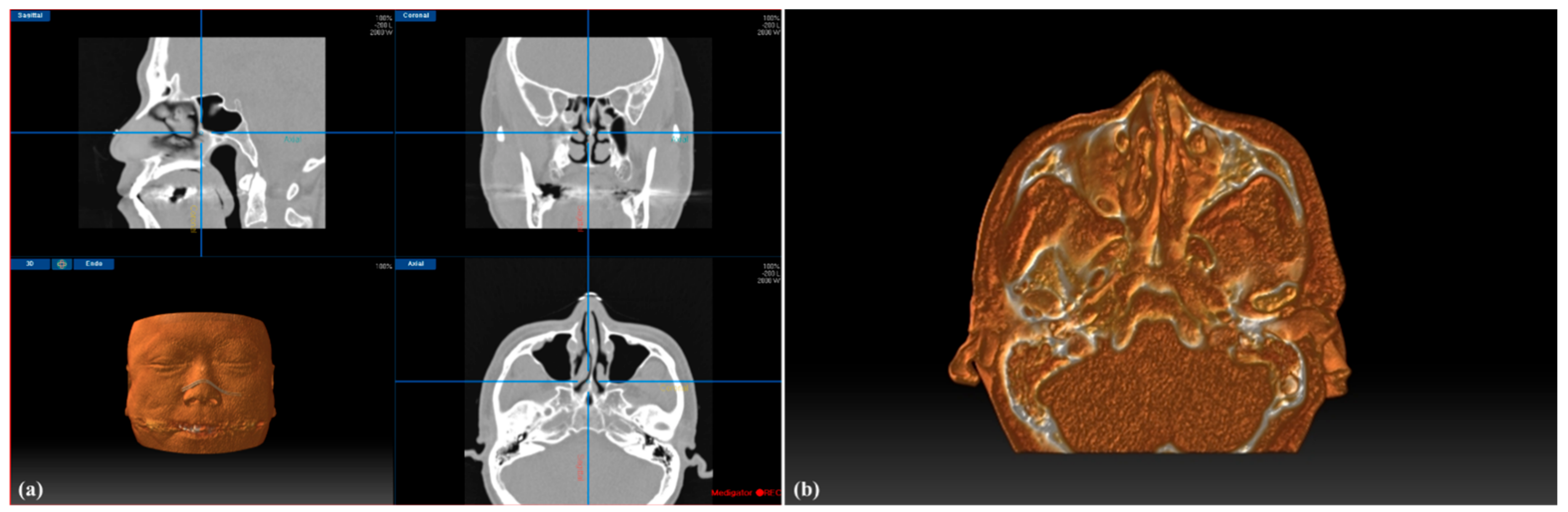
We developed a novel image-guided system named Medigator® (Gmeditec, Incheon, Korea) for endoscopic sinus surgery based on 3D volumetric visualization of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. The developed system consisted of patient CT imaging, registration, and intraoperative visualization. First, the patient’s CT image was loaded in DICOM format and virtually visualized in real-time as a multi-planar view and 3D-rendered volumetric image of the patient during surgery (Figure 2a). Then, registration was performed to match the patient’s physical space with the image space by applying the SVD-based point-to-point matching. Intraoperatively, the physical position of the pointing tool tip was transformed into position in the CT image space and visualized on the screen of the system in real time. To provide visual information of the patient’s internal anatomy for the surgeons, we extracted the slab volume of the region of interest around the position of the pointing tool tip from the patient volumetric image. By cutting the patient’s volumetric image into a virtual plane parallel to the sagittal plane, the operator could more intuitively identify the three-dimensional position of the pointing tool tip inside the patient (Figure 2b).
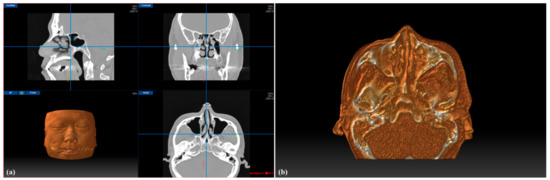
Figure 2.
Graphical user interface (GUI) of the developed image-guided system for endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) (a), and visualization of the slab volumetric model (b).
The visualization and manipulation functions of the multi-planar images and volumetric model were implemented using DirectX (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA) based on the C++ language. We implemented an electromagnetic (EM) tracking system (Aurora, Northern Digital Inc., Waterloo, ON, Canada) to track the 3D position of the pointing tool tip and the dynamic reference tracking tools.
2.4. In-Vitro Accuracy Evaluation of the IGESS System Using the Phantom
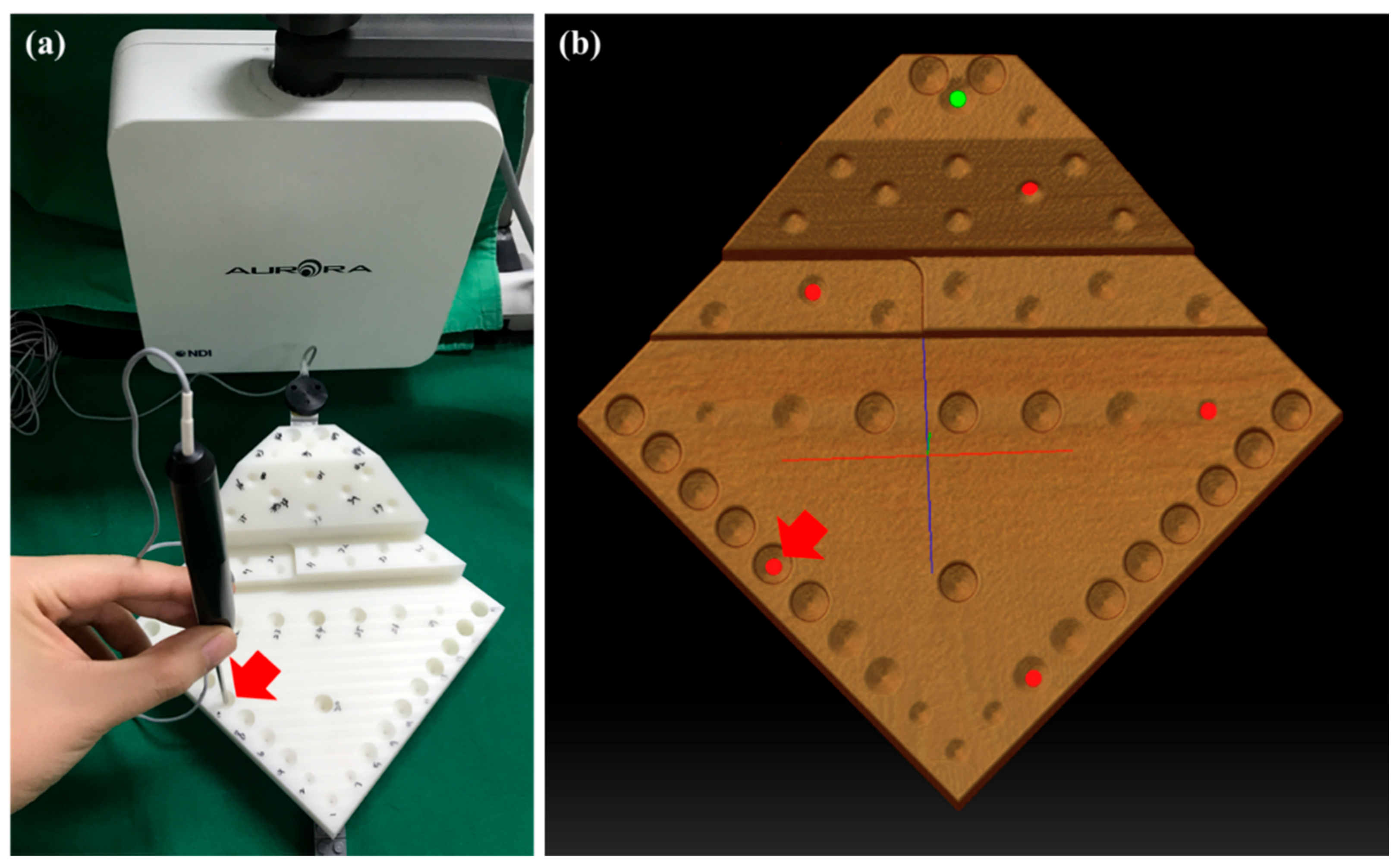
We performed the point-to-point registration between the CT image and the physical spaces using six fiducial points (divots) on the measuring part of the phantom. The physical positions of the divots on the phantom were measured using a tracked pointing tool with respect to the EM tracking tool on the installing part (Figure 3). Immediately after the registration, the system computed and provided the FRE. Then, we measured the positions of forty-one points (divots) on the measuring part with respect to the EM tracking tool on the installing part. Then, the physical positions of the points were transformed into positions in the CT image space using the transformation. The true positions of the points were measured in the phantom’s CT image space before the evaluation. To quantify the target registration errors (TRE), we calculated the root mean square (RMS) differences between the measured and true positions of the points on the phantom. We measured the positions of all points on the phantom five times and calculated the final TRE by averaging the repeatedly measured positions.
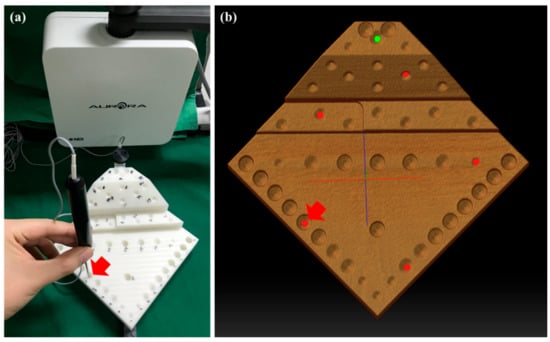
Figure 3.
The fiducial position measurement using a tracked pointing tool with respect to the dynamic reference tracking tool in the phantom’s physical space (a), and the corresponding positions in the CT image space (b).
2.5. Image-Guided Endoscopic Sinus Surgery System with 3D Volumetric Visualization
We performed a prospective cohort study by enrolling eleven chronic sinusitis patients who needed the ESS with an IGS system from 14 May 2019 to 23 July 2019. The CT images of the patients were acquired using a CT scanner (SOMATOM definition flash, Siemens, Berlin, Germany) under 120 kVp and 80 mAs with a slice thickness of 1 mm. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Gachon University Gil Medical Center (GCIRB2018-428)
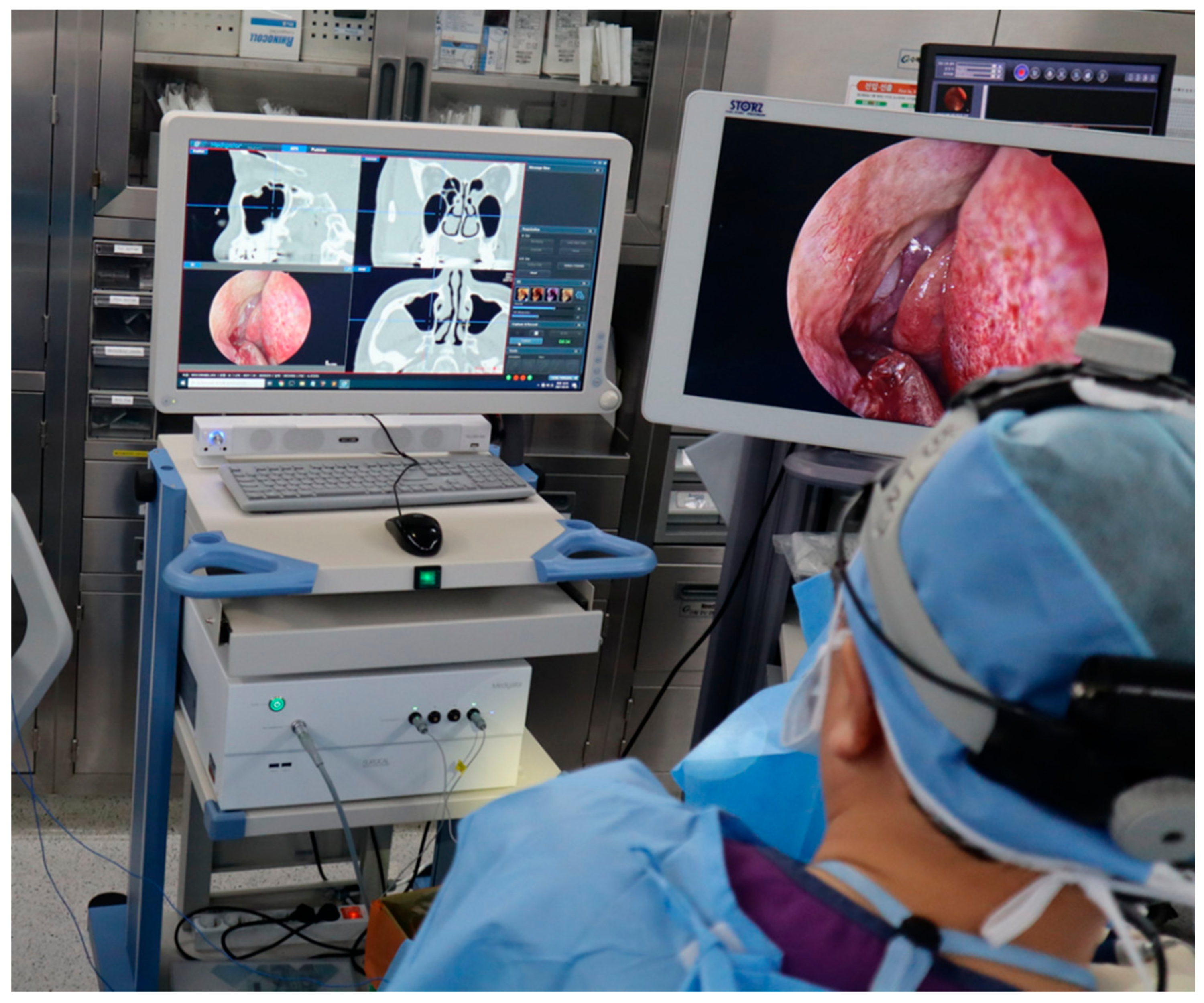
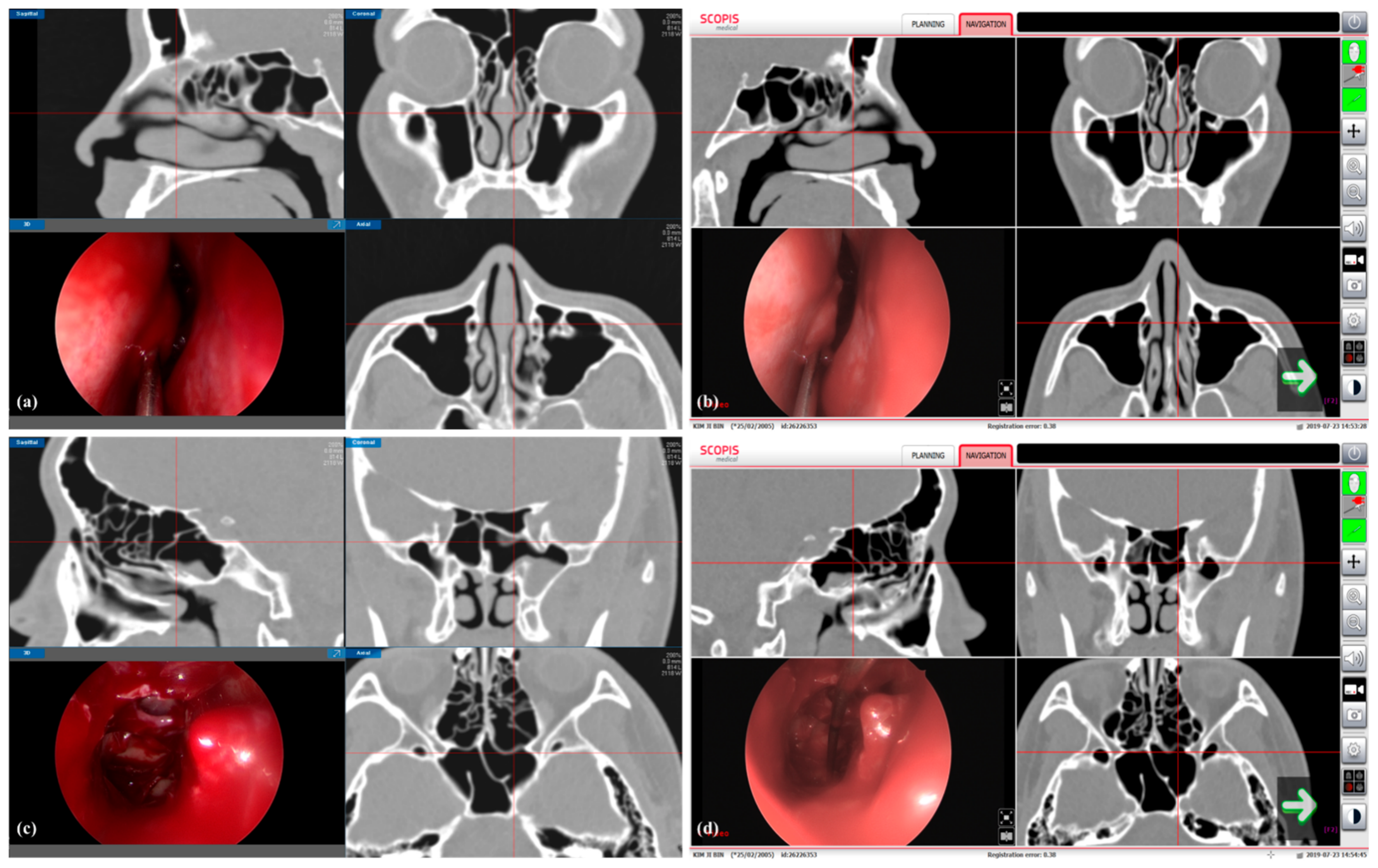
The overall intraoperative procedures were as follows. (1) Two IGESS systems were installed side by side for comparative evaluation (Figure 4). A field generator of the EM tracking system was installed on the back of the patient’s head. The reference tracking tool was tightly fixed onto the patient’s forehead to prevent head movement during surgery. (2) The patient’s CT image was loaded into the two systems and virtually visualized on the screen using a volume-rendering technique. We then selected six landmarks for registration on the patient’s virtual face surface. (3) The physical positions of the corresponding landmarks on the patient’s face were measured with a tracked pointing tool with respect to the reference tracking tool, and these were sequentially registered by point-to-point matching with corresponding positions selected on the patient’s 3D volume rendered face. (4) We calculated the image loading time, registration time, and registration error (FRE) for comparison. (5) After performing the surgery, the surgeon indicated five anatomical landmarks (middle turbinate, maxillary sinus, posterior ethmoid, sphenoid sinus, and frontal sinus) using the pointing tools of the two systems (Figure 5). (6) Finally, the degree of accuracy was evaluated by two surgeons using a visual analogue scale ranging from 1 to 10 points.
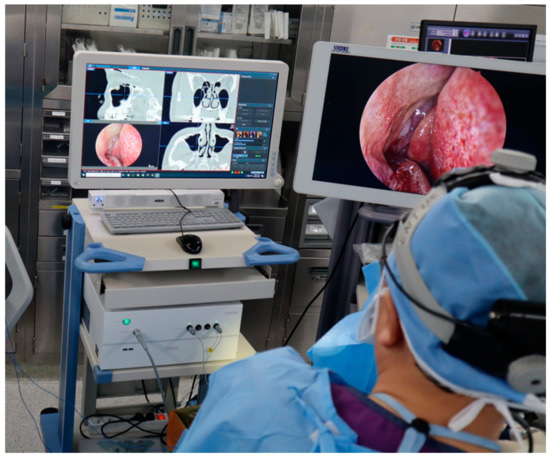
Figure 4.
Performing image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery (IGESS) using a developed navigation system.
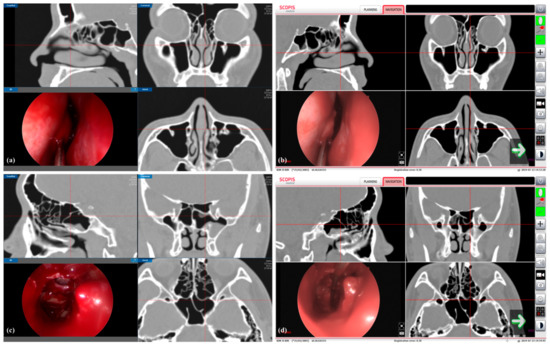
Figure 5.
Clinical comparative study using developed and commercialized image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery (IGESS) systems. Measurement of the positions of the anatomical landmarks (middle turbinate (a,b) and posterior ethmoid (c,d) in the nasal cavity with the developed (a,c) and the commercialized (b,d) systems.
We used SPSS ver. 20 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) for all statistical analyses. We used a Mann–Whitney test to compare the values of the two systems. All data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and the p-value < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3. Results
Before the clinical study, we calculated the FRE and TRE to evaluate the accuracy of the developed point-to-point registration method at the points (divots) on the phantom. We used six of the points for registration and the other forty-one points for evaluation. As a result, the mean FRE value of 0.25 mm at the initial registration was decreased to 0.14 mm by applying the fine registration after excluding the point with the highest FRE. Then, we calculated the TRE value of 0.82 ± 0.50 mm for the developed registration method (Table 1).

Table 1.
Absolute difference in x-, y-, and z-axes, and root mean square (RMS) difference between the true and measured positions of the points on the phantom after registration.
During endoscopic sinus surgery, the intraoperative position of the pointing tool tip was tracked continuously by the electromagnetic tracking system and visualized simultaneously on the multi-planar and 3D volumetric views. Our method also provided the slab volume view to the surgeon to accurately recognize the positional relationship between the pointing tool tip and the adjacent anatomical structures of the patient during the surgery (Figure 2). As a result, the 3D position of the pointing tool tip was visualized with respect to the nasal cavity and sinuses in real time (Figure 5).
We compared the two types of navigation systems, which were the developed system and the commercialized system, by clinical study. The average registration times were 36.04 ± 4.7 and 89.35 ± 26.1 s for the developed and commercialized systems, respectively (p < 0.05). The image loading time of the developed system was also shorter than that of the commercialized system (p < 0.05) (Table 2). Although the average FRE value of the developed system was higher than that of the commercialized system (p < 0.05) (Table 2), the average accuracy score of the developed system was not significantly different from that of the commercialized system (p > 0.05) (Table 3).

Table 2.
Comparison of registration time, image loading time, and fiducial registration errors (FREs) between the developed (Medigator®, Gmeditec, Incheon, Korea) and the commercialized (Scopis® Hybrid Navigation System, Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI, USA) systems.

Table 3.
Visual analogue scale accuracies when surgeon pointed out important structures in the nasal cavity using the developed (Medigator®, Gmeditec, Incheon, Korea) and the commercialized (Scopis® Hybrid Navigation System, Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI, USA) systems.
4. Discussion
In endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) in chronic sinusitis patients, an image-guided surgery (IGS) system is considered to be a valuable tool for surgeons to make important decisions during surgery [29]. The IGS system has been commonly used for ESS because it provides important topological information about the paranasal sinuses during surgery. The IGS system provides spatial and visual information to the surgeons by visualizing the patient’s preoperative medical images, such as from CT and MRI, on the screen of the system during surgery [30,31]. In addition, the IGS system relieves the operator’s mental and physical stress during ESS surgery, which leads to reduction of surgical risk to the patient [32,33]. IGS technology has improved dramatically over the last few decades, with smaller and more portable platforms, quick setup time, and user-friendly interfaces.
One of the most important elements of the IGS system is meeting clinically acceptable accuracy levels by performing accurate matching between the patient’s physical space and the image space. In general, the error of the IGS system for use in ESS surgery is less than 2 mm [34,35]. Previous studies have shown that the accuracy of registration is highly correlated with the surgical accuracy of IGS [36,37]. Some researchers proposed three metrics to evaluate the accuracy of the registration: (1) fiducial localization error (FLE), which is error in the location of the fiducials; (2) fiducial registration error (FRE), which is the root mean squared (RMS) distance between corresponding fiducials used in registration; and (3) target registration error (TRE), which is the RMS distance corresponding fiducials which are not used in registration [38,39]. To date, there is no standardized criterion for evaluating the accuracy of the registration. Therefore, previous studies evaluated the accuracy of registration with their own customized methods [8,40,41]. In a previous study, a skin-attached skull phantom with 26 titanium screws was fabricated to evaluate the TREs of five registration methods [8]. The TRE values (mean ± standard deviation) were 0.94 ± 0.06 mm for point-to-point registration using invasive fiducials, 1.41 ± 0.04 mm for non-invasive point-to-point registration using the metal balls on a headset, 1.59 ± 0.14 mm for the surface registration, and 5.15 ± 0.66 mm and 4.37 ± 0.73 mm for point-to-point registration using four and five anatomic landmarks, respectively [8]. Another study reported TRE values in the range of 0.71 to 3.51 mm for point-to-point registration using a customized plastic phantom [41]. Ecke et al. measured an accuracy of 1.82 ± 1.42 mm after performing the point-to-point registration using fiducials [42]. In addition, when measuring the registration accuracy using anatomical landmarks on the patient’s skin surface with the pointing tool, the lack of consistency was caused by the softness of the skin and the deformation due to pressure [43]. In this study, we designed and fabricated the phantom for evaluating our point-to-point registration method based on the standard phantom in ASTM F2554-10 for the first time [26]. Immediately after performing the registration using the developed point-to-point method, the FRE value was 0.14 mm. As a result of the accuracy evaluation using the phantom, the mean values of the absolute differences between the true and measured positions were 0.48 ± 0.50, 0.34 ± 0.23, and 0.41 ± 0.33 mm on the x-, y-, and z-axes, respectively, and the TRE was 0.82 ± 0.50 mm. Our method showed a higher accuracy than previous methods based on point-to-point registration using customized phantoms. We also demonstrated that our method showed a clinically acceptable level of accuracy (under 2 mm) [34,35].
Intraoperatively, the IGS systems should accurately and intuitively provide the surgeons with the 3D position of the pointing tool tip in real-time. Conventional IGS systems visualized the intraoperative position of the pointing tool tip in two-dimensional multi-planar (axial, sagittal, and coronal) views, and it was difficult for surgeons to easily recognize 3D spatial information with the 2D positional information provided [42]. In addition, even if the position of the tool tip was displayed on the 3D virtual model of the patient, it was still difficult for the surgeon to intuitively identify the position of the tool tip occluded by the skin or bone tissue models [30]. To overcome the limitations of the conventional methods, our system provided 3D slab volumetric view for the surgeons to intuitively identify the real-time position of the pointing tool tip inside the patients’ nasal cavity (Figure 2).
We performed the clinical comparative study to validate the performance of our developed system by enrolling eleven chronic sinusitis patients who needed the ESS with an IGS system. As a result of the study, we demonstrated that the registration time and image loading time of the developed system were significantly shorter than those of the commercialized system. This showed that it was more efficient to use the developed system than to use the commercially available system in the surgical preparation process. Although the average FRE value of the commercialized system was significantly lower than that of the developed system, there was no statistically significant difference between the average accuracy scores of the two systems when digitizing five anatomical landmarks, as evaluated by the surgeons. A previous study demonstrated that the FRE and TRE were not correlated to each other [44].
In conclusion, we developed an image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery system with 3D volumetric visualization of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. The developed system provided an accurate point-to-point registration method based on the SVD algorithm and the leave-one-out strategy. According to the results of the clinical comparative study on eleven patients, we demonstrated that the developed system showed reliable potential for clinical application. However, the developed system could not perform the surface-based registration method. For future investigations, we will develop a surface-based registration method by modifying the conventional algorithms, such as iterative closest point (ICP) [27] and coherent point drift (CPD) [45]. In addition, we plan to recruit more patients to conduct clinical comparative studies, and to apply the developed system to additional cases of revision surgery or advanced skull base surgery.
Author Contributions
S.-J.L.: Contributed to conception and design, development of the system used in the work, in-vitro accuracy evaluation, data interpretation, and critically revised the manuscript.; J.-Y.Y.: Contributed to conception and design, in-vitro accuracy evaluation, and data interpretation.; S.K.Y.: Contributed to conception and design, design, and fabrication of the phantom for accuracy evaluation.; R.H.: Contributed to patient recruitment, conducted the clinical study, and revised the manuscript.; D.-H.L.: Contributed to data interpretation and revised the manuscript.; S.-T.K.: Contributed to patient recruitment and data interpretation, conducted the clinical study, and drafted and critically revised the manuscript.; W.-J.Y.: Contributed to conception and design, data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation, and drafted and critically revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Technology Innovation Program (10063389) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE), Korea, and by the Korea Medical Device Development Fund grant funded by the Korean government (the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the Ministry of Health and Welfare, and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety) (No. 202012E09).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Gachon University Gil Medical Center (GCIRB2018-428).
Informed Consent Statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Gachon University Gil Medical Center (GCIRB2018-428) with a waiver of informed consent. The data collection and all experiments were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated during the current study are not publicly available due to the restriction by the institutional review board (IRB) of Gachon University Gil Medical Center in order to protect patients’ privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Orlandi, R.R.; Grebner, J.; Martinson, M. Cost burden of chronic rhinosinusitis: A claims-based study. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 144, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliashar, R.; Sichel, J.Y.; Gross, M.; Hocwald, E.; Dano, I.; Biron, A.; Ben-Yaacov, A.; Goldfarb, A.; Elidan, J. Image guided navigation system-a new technology for complex endoscopic endonasal surgery. Postgrad. Med. J. 2003, 79, 686–690. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Woo, S.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Huh, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Heo, M.S.; Choi, S.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Yi, W.J. An integrated orthognathic surgery system for virtual planning and image-guided transfer without intermediate splint. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 2010–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linxweiler, M.; Pillong, L.; Kopanja, D.; Kuhn, J.P.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Radosa, J.C.; Wang, J.; Morris, L.G.T.; Al Kadah, B.; Bochen, F.; et al. Augmented reality-enhanced navigation in endoscopic sinus surgery: A prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2020, 5, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapeer, R.; Chen, M.S.; Gonzalez, G.; Linney, A.; Alusi, G. Image-enhanced surgical navigation for endoscopic sinus surgery: Evaluating calibration, registration and tracking. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2008, 4, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Woo, S.Y.; Huh, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Heo, M.S.; Choi, S.C.; Han, J.J.; Yang, H.J.; Hwang, S.J.; Yi, W.J. Virtual skeletal complex model- and landmark-guided orthognathic surgery system. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Yang, H.J.; Choi, M.H.; Woo, S.Y.; Huh, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Heo, M.S.; Choi, S.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Yi, W.J. Real-time augmented model guidance for mandibular proximal segment repositioning in orthognathic surgery, using electromagnetic tracking. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soteriou, E.; Grauvogel, J.; Laszig, R.; Grauvogel, T.D. Prospects and limitations of different registration modalities in electromagnetic ENT navigation. Eur Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 3979–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, C.R.; Fitzpatrick, J.M. A review of medical image registration. Interact. Image-Guided Neurosurg. 1993, 17, 17–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, J.M.; West, J.B.; Maurer, C.R. Predicting error in rigid-body point-based registration. Ieee T Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, C.R.; Maciunas, R.J.; Fitzpatrick, J.M. Registration of head CT images to physical space using a weighted combination of points and surfaces. Ieee T Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audette, M.A.; Ferrie, F.P.; Peters, T.M. An algorithmic overview of surface registration techniques for medical imaging. Med. Image Anal. 2000, 4, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, S.M.; Melroy, C.; White, D.R.; Dubin, M.; Senior, B. A comparison of computer-aided surgery registration methods for endoscopic sinus surgery. Am. J. Rhinol. 2006, 20, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Z.; Wang, J.; Pan, J.; Meng, M.Q.-H. Generalized 3-D Point Set Registration With Hybrid Mixture Models for Computer-Assisted Orthopedic Surgery: From Isotropic to Anisotropic Positional Error. IEEE T Autom Sci Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, R.W.; Zhang, R.X.; Yu, H.Z.; SiTu, H.R.; Liu, C.H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L.L.; Zhuang, W.J.; Jin, Z.C.; et al. Application of image-guided system in endoscopic sinus and skull base surgery. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 32, 1856–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, T.; Nakamura, R.; Kuboki, A.; Honda, O.; Yamamoto, M.; Ohtori, N. Comparative analysis of surgical processes for image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, M.P.; Kleefield, J.; Gopal, H.; Reardon, E.; Ho, B.T.; Kuhn, F.A. Image-guided endoscopic surgery: Results of accuracy and performance in a multicenter clinical study using an electromagnetic tracking system. 1997. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.S.; Liang, K.L. Image-guided sphenoidotomy in revision functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 5, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seno, S.; Suzuki, M.; Sakurai, H.; Kitanishi, T.; Nakajima, D.; Sonoda, S.; Owaki, S.; Fukui, J.; Hoshi, J.; Hanamitsu, M.; et al. Image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery: A comparison of two navigation systems. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho 2005, 108, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Anand, V.K.; Hiltzik, D.H.; Kacker, A.; Honrado, C. Osteoplastic flap for frontal sinus obliteration in the era of image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery. Am. J. Rhinol. 2005, 19, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reittner, P.; Tillich, M.; Luxenberger, W.; Weinke, R.; Preidler, K.; Kole, W.; Stammberger, H.; Szolar, D. Multislice CT-image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery using an electromagnetic tracking system. Eur Radiol. 2002, 12, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C.R. Image-guided endoscopic sinus surgery. J. Miss State Med. Assoc. 2000, 41, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olson, G.; Citardi, M.J. Image-guided functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000, 123, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, E.; Christmas, D.A. The value of computer-aided (image-guided) systems for endoscopic sinus surgery. Ear Nose Throat J. 1999, 78, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freysinger, W.; Gunkel, A.R.; Thumfart, W.F. Image-guided endoscopic ENT surgery. Eur Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1997, 254, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard, A.J.A.I.W.C. F2554-10 Standard Practice for Measurement of Positional Accuracy of Computer Assisted Surgical Systems; STM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Besl, P.J.; Mckay, N.D. A Method for Registration of 3-D Shapes. IEEE T Pattern Anal. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W. A solution for the best rotation to relate two sets of vectors. Acta Crystallogr. 1976, 32, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosges, R.; Klimek, L. Computer-Assisted Surgery of the Paranasal Sinuses. J. Otolaryngol. 1993, 22, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stelter, K.; Andratschke, M.; Leunig, A.; Hagedorn, H. Computer-assisted surgery of the paranasal sinuses: Technical and clinical experience with 368 patients, using the Vector Vision Compact (R) system. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2006, 120, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelter, K.; Ertl-Wagner, B.; Luz, M.; Muller, S.; Ledderose, G.; Siedek, V.; Berghaus, A.; Arpe, S.; Leunig, A. Evaluation of an image-guided navigation system in the training of functional endoscopic sinus surgeons. A prospective, randomised clinical study. Rhinology 2011, 49, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzey, D.; Rottger, S.; Bahner-Heyne, J.E.; Schulze-Kissing, D.; Dietz, A.; Meixensberger, J.; Strauss, G. Image-guided navigation: The surgeon’s perspective on performance consequences and human factors issues. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comp. 2009, 5, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgorf, D.M.; Sacks, R.; Wormald, P.J.; Naidoo, Y.; Panizza, B.; Uren, B.; Brown, C.; Curotta, J.; Snidvongs, K.; Harvey, R.J. Image-Guided Surgery Influences Perioperative Morbidity from Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Otolaryng Head Neck 2013, 149, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartellieri, M.; Vorbeck, F. Endoscopic sinus surgery using intraoperative computed tomography imaging for updating a three-dimensional navigation system. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citardi, M.J.; Batra, P.S. Intraoperative surgical navigation for endoscopic sinus surgery: Rationale and indications. Curr Opin Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 15, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, G.; Muhling, J.; Marmulla, R. Image-to-patient registration techniques in head surgery. Int. J. Oral Max Surg. 2006, 35, 1081–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knott, P.D.; Batra, P.S.; Butler, R.S.; Citardi, M.J. Contour and paired-point registration in a model for image-guided surgery. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 1877–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, C.R.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Wang, M.Y.; Galloway, R.L.; Maciunas, R.J.; Allen, G.S. Registration of head volume images using implantable fiducial markers. IEEE T Med. Imaging 1997, 16, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Z.; Ren, H.L.; Meng, M.Q.H. Statistical Model of Total Target Registration Error in Image-Guided Surgery. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Choi, M.H.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, J.E.; Huh, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Heo, M.S.; Hwang, S.J.; Yi, W.J. Quantitative Augmented Reality-Assisted Free-Hand Orthognathic Surgery Using Electromagnetic Tracking and Skin-Attached Dynamic Reference. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenow, J.M.; Sootsman, W.K. Application accuracy of an electromagnetic field-based image-guided navigation system. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2007, 85, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecke, U.; Luebben, B.; Maurer, J.; Boor, S.; Mann, W.J. Comparison of different computer-aided surgery systems in skull base surgery. Skull Base-Interd Ap 2003, 13, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glicksman, J.T.; Reger, C.; Parasher, A.K.; Kennedy, D.W. Accuracy of computer-assisted navigation: Significant augmentation by facial recognition software. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2017, 7, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, J.M. Fiducial registration error and target registration error are uncorrelated. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2009: Visualization, Image-Guided Procedures, and Modeling, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 8 February 2009; p. 726102. [Google Scholar]
- Myronenko, A.; Song, X.B. Point Set Registration: Coherent Point Drift. IEEE T Pattern Anal. 2010, 32, 2262–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).