Abstract
Our research examined the nest-building characteristics of two mouse species native to Hungary, the mound-building mouse (Mus spicilegus) and the house mouse (Mus musculus), under laboratory housing conditions. In indoor housing, the nest-building material plays a very important role in the welfare of the animals. The present study examined how wild mouse species choose from natural nest material. In a three-way test, mice were able to choose whether to make their nest from long blades of hay, nonfibrous cotton, or paper strips. In addition, the effect of nest composition on its quality was also investigated. The test was run at the standard laboratory (21 °C) and lower (10 °C) temperatures, assuming that temperature influences the choice. Based on the results of the three-way selection tests, both species of wild mice chose hay nest material in the highest proportion, and it was also found that the increasing the hay proportion coincided with better nest quality. Mice kept in colder places used more hay nest material for their nests and built better quality nests. Our results show that wild mouse species prefer natural nest-building materials that meet their ecological needs even under laboratory conditions, resulting in a good quality nest. This finding is worth considering in designing appropriate enclosures for wild rodent species.
1. Introduction
1.1. Nest Building in Small Mammals
For rodents, the nest is important for heat retention and progeny care and as a refuge from predators [1,2,3]. Because of their small size, mice are sensitive to heat loss. Both male and female mice build nests [4], so nest building in mice is not limited to reproductive and offspring care [5], as in wild rabbits. Nest building in mice increases lifetime reproductive success [6,7].
1.2. Benefits of the Nest in Laboratory Mice
Nest-building behavior was also maintained in inbred laboratory mouse strains [8]. Both male and female mice build nests of similar size if the appropriate nest-building material is provided [4,9]. In the laboratory environment, the nest allows animals to hide from their companions as well as from humans and other external stimuli, such as light [10]. In most standard animal facilities, the ambient temperature is below the thermoneutral temperature [11], so it is also very important for mice kept in the laboratory to be able to build a nest for thermoregulation [12]. Appropriate nest material reduces heat loss and feed intake [13]. Heat preference studies have shown that mice prefer temperatures close to 30 °C [14,15,16]. However, research has shown that warmer temperatures increase aggression [17], so increasing the laboratory temperature is not a viable option. Wild mice build a nest against extreme temperature conditions [3,18], making it an ideal solution to the problem of cold stress even in laboratory conditions [14].
1.3. Nest Material as Environmental Enrichment
In laboratory animals, enrichment may improve animal welfare, test reliability, and even the opinion of the general public on animal experiments [19,20,21]. Many researchers favor biologically relevant environmental enrichment, which allows animals to adopt natural behaviors, reducing chronic stress resulting from indoor confinement [20,21,22,23]. The provision of nest-building material as an enriching element is paramount in reducing stress levels in laboratory rodent housing. Mice strongly prefer a cage containing nest material [24]. The choice mice make is more influenced by the nest material than the nesting box, even if the nest material was located on a lattice floor and the nesting box was placed on a solid floor or wood chip [5].
1.4. Evaluation of Nest-Building Performance
Because maternal and nonmaternal nesting performance has been studied and used as a monitoring tool in many disciplines for decades, different protocols are available to evaluate nesting. For example, the assessment can focus on the finished nest or the nest-building behavior itself or on the nest-building materials. Nest quality is often determined by a complexity score of 4–6 [25,26], from the absence of the nest to the entire nest sphere [27,28]. Studies on the quantity and quality of the nest material used are also typical [29,30], as the quality of the nest is strongly influenced by the nest-building material used [2]. Currently, mice kept in the laboratory are often given strips of paper as nest-building material [31]. When mice receive nest material, both sexes begin to assemble the nest material within one hour [9,32]. Mice usually build and repair their nests before dawn [32,33,34], so the nest quality or other properties should be evaluated after the dark phase [1].
Our model animals used for the study were two species belonging to the genus Mus native to Hungary, the mound-building mouse (Mus spicilegus) and the house mouse (Mus musculus). The house mouse is a species that lives with humans; it spends its vegetation period in agricultural areas bordering human settlements and then moves into human structures during the colder season. In contrast, the mound-building mouse occurs in abandoned agricultural areas [35]; it avoids human settlements based on observations [36]. The mound-building mouse makes a huge pile of soil and plant material in the fall; its function is to protect mice from moisture and eliminate temperature fluctuations [37]. The material of these nests consists of long strands of homogeneous, monocotyledonous plant species [37].
Currently, few studies deal with the ecological enrichment of laboratory animals. However, as early as 2009, Carenzi and Verga [38] promoted the concept of animal welfare as ensuring the natural lifestyle of animals. We must strive to meet the ecological and ethological needs of animal species under natural conditions. Such studies and efforts are characteristic of zoos and game parks, and this kind of approach has not yet appeared in laboratory animal husbandry.
In the present study, we examined the environmental enrichment of the species in relation to the ecological needs of the species to determine whether the preference for nest material of the wild house mouse and mound-building mouse bred in the laboratory for 25 generations reflects the ecological needs of the wild mouse species under laboratory conditions. Furthermore, it was also evaluated how these materials affect nest quality and how temperature affects nest material selection and nest quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
The study was performed in the Rodent House of the Kaposvár Campus of the Hungarian University of Agricultural and Life Sciences. The rodent house has its own population where individuals of known age, sex, and origin are found.
The current herd consists of laboratory-born offspring of wild mice captured from several parts of the country. All the animals were born in the lab, and the population has been bred for 25 generations.
During the study, mice were individually housed in a T4 laboratory mouse box (600 × 200 × 380 mm) with ad libitum feed (Ssniff S8106-SO11 Spezialdiäten GmbH, Soest, Germany) and water supply (using nipple drinkers). The test lasted seven days, and it was performed simultaneously at 10 and 21 °C in two separate test rooms with similar lighting.
In the present study, 104 mice were randomly selected, with the restriction that species and sexes were represented in equal proportions. The age of the animals used in this study ranged between 100 and 120 days. In both rooms, 52 animals were individually housed. In the colder room (10 °C) and standard room (21 °C), 26–26 house mice and mound-building mice were kept with an equal sex ratio (13 males and 13 females, respectively).
Mice could choose from 3 nest material types (paper: Enviro-Dri rodent bedding 20 kg, cotton: MultiFit small rodent cotton bedding 30 L, and hay: Versele-laga mountain hay 50 L) placed in hay pockets attached to mouse boxes. On the first day of the study, between 100 and 150 g of nest material per type was measured to provide all substrates in the same volume, and on the seventh day, the completed nests were evaluated. An examination of the composition of nests was performed according to Szenczi et al., 2011 [37] and Bilko et al., 2022 [30]. After evaluating the quality of the finished nests, they were placed on a tray, and then every nest was homogenized, and subsequently 20 samples were taken blindly using forceps.
Prior to the nest composition analysis, we determined the quality of the nests based on the study of Gaskill et al., 2013 [13], where the completed nests received scores ranging from 2 to 5 (Figure 1).
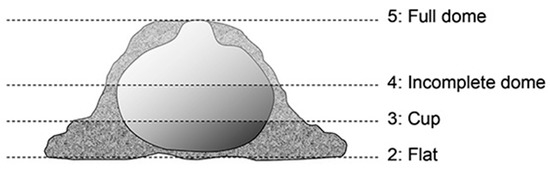
Figure 1.
Scores characterizing nest quality.
2.2. Statistical Analyses
To determine whe ther the choice rates of different nesting materials were the same, a Chi-square test was used, assuming equal contribution.
Afterwards, the effects of species, sexes, and temperature on the nest composition were evaluated with Generalized Linear Mixed Model. In case of the latter analysis, the distribution was multinomial, and the generalized logit link function was set. The association between the nest composition (percentages of the paper, cotton, and hay) and the nest quality was examined using polyserial correlation. The SAS 9.4 software (Cary, NC, USA) was used for all types of analysis applying the PROC FREQ, the PROC GLIMMIX, and the PROC CORR procedures, respectively.
3. Results
We found a significant difference in the choice of the three nest material types based on the Chi-square test (p < 0.005).
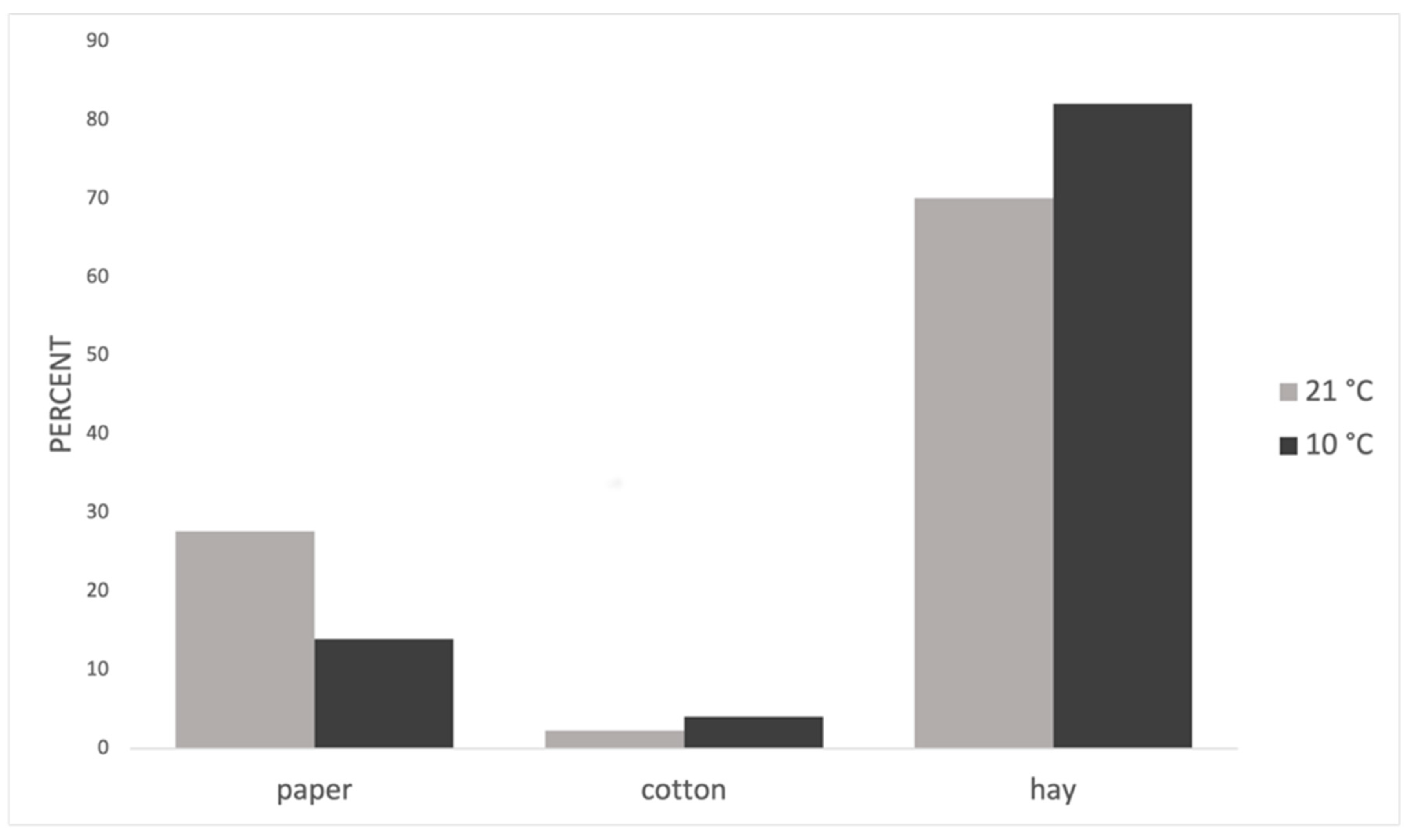
The mice chose 76% hay from the three nest material types, 21% paper, and only 3% cotton for nest building.
Based on the Generalized Linear Mixed Model, no significant difference was found between the predicted probabilities of choosing different nest material types between the two mouse species (p = 0.272). No significant difference was found in the choice of cotton nest material between the two species (p = 0.54) or in the choice of paper (p = 0.54) or hay (p = 0.94).
Based on the estimated probabilities, both mound-building mice and house mice also chose hay in the highest proportion (Table 1).

Table 1.
The predicted probability of nest selection estimated by species.
Overall, we did not find a significant difference (p = 0.051) in the choice of nest material between the two sexes. However, there was a significant difference in the choice of cotton between the two sexes (p = 0.01), but no difference was found between the choice of paper (p = 0.54) and hay (p = 0.38). The males and females equally preferred the hay nest material (Table 2).

Table 2.
The predicted probability of nest selection estimated by sexes.
We found a significant difference between the predicted probabilities of nest material choices (p = 0.001) in different temperatures. At the two different temperatures, we found a significant difference in the choice of cotton nest material (p < 0.001), as well as in the case of paper (p < 0.001) and hay (p < 0.001).
At 10 °C, the probability of choosing hay for nests increased and that of paper decreased, while the use of cotton also increased (Table 3, Figure 2).

Table 3.
The predicted probability of nest selection estimated by temperatures.
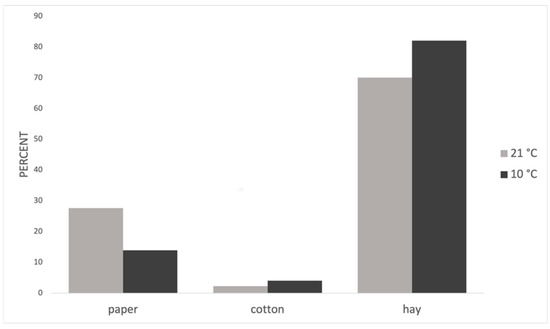
Figure 2.
Use of nesting material (%) at 21 °C and 10 °C.
Regarding the relationship between the nest material composition of the finished nests and the quality of the nest, we found that the amount of hay (p < 0.001) and paper (p < 0.001) influences the quality of the nest, but not the cotton (p = 0.161). The higher amount of hay improves the quality of the nest (r = 0.537), while the presence of paper worsens it (r = −0.482). On the contrary, the increased proportion of paper in the nest coincided with a lower nest quality (r = −0.482). At the two different temperatures, we found a significant difference in the quality of the nests (p = 0.008); the quality of the nests increased minimally (r = −0.258). At the warmer temperature (21 °C), the quality of the nests was on average 4 points, while at the colder temperature (10 °C), the finished nests received an average of 4.5 points.
4. Discussion
Under laboratory housing conditions, nest selection was examined for two species of wild mice at different temperatures. Based on our results, we can state that the offspring of wild mouse species kept in the laboratory for generations also choose hay for nest building, which is the same as the nests of their wild-type conspecifics observed in nature [37]. Hay is structurally better suited for nest building and is likely to be easier to form a suitable nest shape. Research on laboratory mice has shown that when it comes to synthetic fiber nest-building material and paper nest-building material, paper is preferred, which is a more natural material than synthetic fiber nesting material [9]. Others compared the nesting material of paper strips with the nesting material of cotton or cotton wool and found that paper strips were preferred by mice over other nonfibrous nesting materials [39]. These results are consistent with our results, as their animals also chose paper strips more than cotton after the hay nest material. These studies also show that longer, fibrous materials are more suitable for nesting.
Our studies have shown that wild mouse species have less preference for cotton nesting material over hay, even though it is also a natural material. The limited use of cotton was also supported by Estep et al. [8]. It was found that nesting between wild and domestic mice did not differ significantly, except those wild mice used less cotton for nesting than laboratory mice [8]. Van der Weerd et al. [40,41] offered different materials to mice, which usually used a combination of two materials to build a nest, a trend that is well observed in our work because we found few nests that were made of only one material, and most commonly the finished nests consisted of a mixture of hay and paper.
Our results show that mice can build better quality nests using hay, probably due to the long, fibrous structure of the material. Nest selection studies in rabbits also show that rabbits prefer long dry grass fibers to short ones [30]. Our findings are consistent with Hess’s [2] study, who found that the long, fibrous nest-building material allowed mice to build better quality nests than other materials that did not have a fibrous structure. Nests built with fabrics were of medium quality, and nests built with pressed cotton squares were of poor quality [2]. Similar results were obtained by Gedeon et al. [42], who found a dry grass preference and favorable insulation properties in nests made by ground squirrels.
The present investigation performed at two different temperatures revealed that mice built more complex, spherical, and better quality nests under the influence of colder environments, with an increased use of hay nest-building material. Nest-building behavior as a thermoregulatory adaptation may increase due to cold ambient temperature [43], and more complex nests are created to avoid cold stress [7]. Our results are similar to those of Wolfe [44] and Barnett [43], where wild and laboratory mice nesting and nest quality were studied at different temperatures. In addition to good quality nesting material, wild and laboratory mice also built good quality nests, which showed minimal improvement in nest quality in colder environments. Further studies also show that rodents build better quality nests at lower ambient temperatures using wool [45], paper [46], and hay [47].
Overall, M. musculus and M. spicilegus prefer nesting materials made of natural hay under laboratory conditions, which can be used to build better quality nests and whose quality improves with decreasing temperature, thereby also promoting heat retention. The provision of nest-building material as an enriching element is of paramount importance when keeping rodents indoors. For animals kept in the laboratory, enrichment can significantly improve animal welfare. [19]. Based on the studies of Bailoo et al. [48], we know that even small-scale environmental enrichment can significantly reduce stress hormone levels [49], mainly when nest-building material is used as environmental enrichment [22]. The nest material allows the expression of species-specific nest-building behavior, thereby reducing stress, and the nest also helps with thermoregulation and serves as a hiding place for the animal [12,14,15,22]. Nest material is essential for thermoregulation, as rodents need a higher temperature (about 30 °C) to rest, which is not the same as 20–25 °C in conventional animal rooms, which causes cold heat stress in animals kept on litter only. [11].
The results of our research can promote the enclosure technology of wild rodent species in terms of the provision of nest-building material, where the use of dry grasses or hay that meet the natural, ecological needs of the species is strongly recommended.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.A.; methodology, V.A.; software, I.N.; validation, B.B., I.N. and V.A.; formal analysis, I.N. and Z.G.; investigation, B.B.; resources, B.B.; data curation, Z.G. and B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, B.B.; writing—review and editing, B.B. and I.N.; visualization, B.B. and Z.G.; supervision, V.A.; project administration, B.B.; funding acquisition, B.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work/publication is supported by the EFOP-3.6.3-VEKOP-16-2017-00005. The project was cofinanced by the European Union and the European Social Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences Kaposvár Campus (permit number: MATE KC MÁB/10-4/2021). The authors declare that all experiments were performed in accordance with approved guidelines and regulations.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Deacon, R.M. Assessing hoarding in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2828–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, S.E.; Rohr, S.; Dufour, B.D.; Gaskill, B.N.; Pajor, E.A.; Garner, J.P. Home improvement: C57BL/6J mice given more naturalistic nesting materials build better nests. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2008, 47, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Latham, N.; Mason, G. From house mouse to mouse house: The behavioural biology of free-living Mus musculus and its implications in the laboratory. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2004, 86, 261–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisk, R.D.; Pretlow, R.A.; Friedman, S.M. Hormonal stimulation necessary for elicitation of maternal nest-buliding in the mouse (Mus musculus). Anim. Behav. 1969, 17, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Weerd, H.A.; van Loo, P.L.P.; van Zutphen, L.F.M.; Koolhaas, J.M.; Baumans, V. Strength of preference for nesting material as environmental enrichment for laboratory mice. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1998, 55, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.J. The natural history of the house mouse. Field Stud. 1970, 3, 219–262. [Google Scholar]
- Bult, A.; Lynch, C.B. Nesting and fitness: Lifetime reproductive success in house mice bidirectionally selected for thermoregulatory nest-building behavior. Behav. Genet. 1997, 27, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estep, D.Q.; Lanier, D.L.; Dewsbury, D.A. Copulatory behavior and nest building behavior of wild house mice (Mus musculus). Anim. Learn. Behav. 1975, 3, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, C.M. Observations on the prevalence of nest-building in non-breeding TO strain mice and their use of two nesting materials. Lab. Anim. 1997, 31, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clough, G. Environmental effects on animals used in biomedical research. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1982, 57, 487–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.S.; Taylor, D.J.; Green, A.R.; Gaskill, B.N. Effects of nesting material on energy homeostasis in BALB/cAnNCrl, C57BL/6NCrl, and Crl:CD1(ICR) mice housed at 20 °C. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2017, 56, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaskill, B.N.; Gordon, C.J.; Pajor, E.A.; Lucas, J.R.; Davis, J.K.; Garner, J.P. Heat or insulation: Behavioral titration of mouse preference for warmth or access to a nest. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskill, B.N.; Gordon, C.J.; Pajor, E.A.; Lucas, J.R.; Davis, J.K.; Garner, J.P. Impact of nesting material on mouse body temperature and physiology. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 110–111, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskill, B.N.; Rohr, S.A.; Pajor, E.A.; Lucas, J.R.; Garner, J.P. Some like it hot: Mouse temperature preferences in laboratory housing. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 116, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskill, B.N.; Rohr, S.A.; Pajor, E.A.; Lucas, J.R.; Garner, J.P. Working with what you’ve got: Changes in thermal preference and behavior in mice with or without nesting material. J. Therm. Biol. 2011, 36, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.J.; Becker, P.; Ali, J.S. Behavioral thermoregulatory responses of single- and group-housed mice. Physiol. Behav. 1998, 65, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, G. The effects of ambient temperature and population density on aggression in two inbred strains of mice. Mus musculus. Behaviour 1972, 42, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowcroft, P. Mice All Over; Chicago Zoological Society: Brookfield, IL, USA, 1966; 121p. [Google Scholar]
- Baumans, V. Environmental enrichment for laboratory rodents and rabbits: Requirements of rodents, rabbits, and research. ILAR J. 2005, 46, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, J.P. Stereotypies and other abnormal repetitive behaviors: Potential impact on validity, reliability, and replicability of scientific outcomes. ILAR J. 2005, 46, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Würbel, H.; Garner, J.P. Refinement of rodent research through environmental enrichment and systematic randomization. Nat. C. Rep. Ref. Red. Anim. Res. 2007, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, I.A.; Dahlborn, K. Improving housing conditions for laboratory mice: A review of environmental enrichment. Lab. Anim. 2002, 36, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurfein, B.T.; Stamm, A.W.; Bacchetti, P.; Dallman, M.F.; Nadkarni, N.A.; Milush, J.M.; Touma, C.; Palme, R.; Di Borgo, C.P.; Fromentin, G.; et al. The calm mouse: An animal model of stress reduction. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heizmann, V.; Jonas, I.; Hirschenauer, K.; Havelec, L. Choice tests with groups of mice: Nestbox, nesting material, and tubes as enrichment items for laboratory mice. J. Exp. Anim. Sci. 1998, 39, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, R.M.; Penny, C.; Rawlins, J.N. Effects of medial prefrontal cortex cytotoxic lesions in mice. Behav. Brain. Res. 2003, 139, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paumier, K.L.; Sukoff Rizzo, S.J.; Berger, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gonzales, C.; Kaftan, E.; Li, L.; Lotarski, S.; Monaghan, M.; Shen, W.; et al. Behavioral characterization of A53T mice reveals early and late stage deficits related to Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijam, N.; Paylor, R.; McDonald, M.P.; Crawley, J.N.; Deng, C.X.; Herrup, K.; Stevens, K.E.; Maccaferri, G.; McBain, C.J.; Sussman, D.J.; et al. Social interaction and sensorimotor gating abnormalities in mice lacking Dvl1. Cell 1997, 90, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, P.; Bouwknecht, J.A.; Teague, R.; Paylor, R.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Abnormalities of social interactions and home-cage behavior in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, R.M. Assessing nest building in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilkó, Á.; Petróczi, I.; Bárdos, B.; Nagy, I.; Altbacker, V. Composition of the Wild Rabbit Nest and Its Implication for Domestic Rabbit Breeding. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, X.M.; Zhou, J.N.; Liu, R.Y. Effect of aging on species-typical behaviors in senescence-accelerated mouse. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 85, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirkof, P.; Fleischmann, T.; Cesarovic, N.; Rettich, A.; Vogel, J.; Arras, M. Assessment of post- surgical distress and pain in laboratory mice by nest complexity scoring. Lab. Anim. 2013, 47, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, T.J. Nesting material as a reinforcer for female mice. Anim. Behav. 1973, 21, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oortmerssen, G.A. Biological significance, genetics and evolutionary origin of variability in behaviour of inbred strains of mice. Behaviour 1970, 38, 1–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, V.E.; Kotenkova, E.V.; Michailenko, A.G. Mus spicilegus. Mamm. Spec. 1998, 592, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bihari, Z. A güzüegér (Mus spicilegus) életmódjának sajátságai és mezőgazdasági jelentősége. Növényvédelem 2004, 40, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Szenczi, P.; Bánszegi, O.; Dúcs, A.; Gedeon, C.I.; Markó, G.; Németh, I.; Altbäcker, V. Morphology and function of communal mounds of overwintering mound-building mice (Mus spicilegus). J. Mamm. 2011, 92, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carenzi, C.; Verga, M. Animal welfare: Review of the scientific concept and definition. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, C.L.; Pedemonte, K.A.; Boggs, K.N.; Flinn, J.M. Nest building behavior as an early indicator of behavioral deficits in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 152, 60139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Weerd, H.A.; Baumans, V.; Koolhaas, J.M.; van Zutphen, L.F.M. Nesting material as enrichment in two mouse strains. Scand. J. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1996, 23, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Weerd, H.A.; van Loo, P.L.P.; van Zutphen, L.F.M.; Koolhaas, J.M.; Baumans, V. Preferences for nesting material as environmental enrichment for laboratory mice. Lab. Anim. 1997, 31, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedeon, C.; Markó, G.; Németh, I.; Nyitrai, V.; Altbäcker, V. Nest material selection affects nest insulation quality for the European ground squirrel (Spermophilus citellus). J. Mammal. 2010, 91, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.A. Endothermy and ectothermy in mice at −3 °C. J. Exp. Biol. 1956, 33, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfie, J.L.; Barnett, S.A. Effects of cold on nest-building by wild and domestic mice, Mus musculus L. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1977, 9, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.A.; Manly, B.M. Breeding of mice at 3 °C. Nature 1954, 173, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinder, E.F. A study of the nest-building activity of the albino rat. J. Exp. Zool. 1927, 47, 117–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, G. Hormonale und psychische Steuerung beim Nestbau weisser Mause. Zool. Anz. Suppl. 1956, 19, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bailoo, J.D.; Murphy, E.; Boada-Saña, M.; Varholick, J.A.; Hintze, S.; Baussière, C.; Hahn, K.C.; Göpfert, C.; Palme, R.; Voelkl, B.; et al. Effects of Cage Enrichment on Behavior, Welfare and Outcome Variability in Female Mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latham, N.; Mason, G. Frustration and perseveration in stereotypic captive animals: Is a taste of enrichment worse than none at all? Behav. Brain. Res. 2010, 211, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).