Oxygenated Diesel Fuels and Their Effect on PM Emissions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
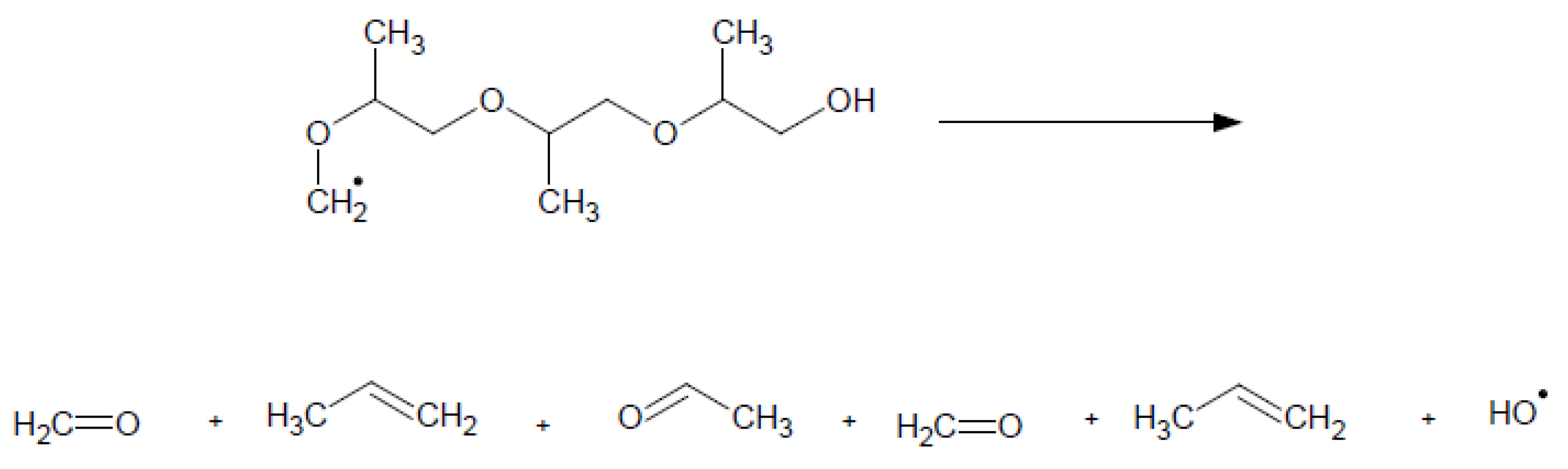
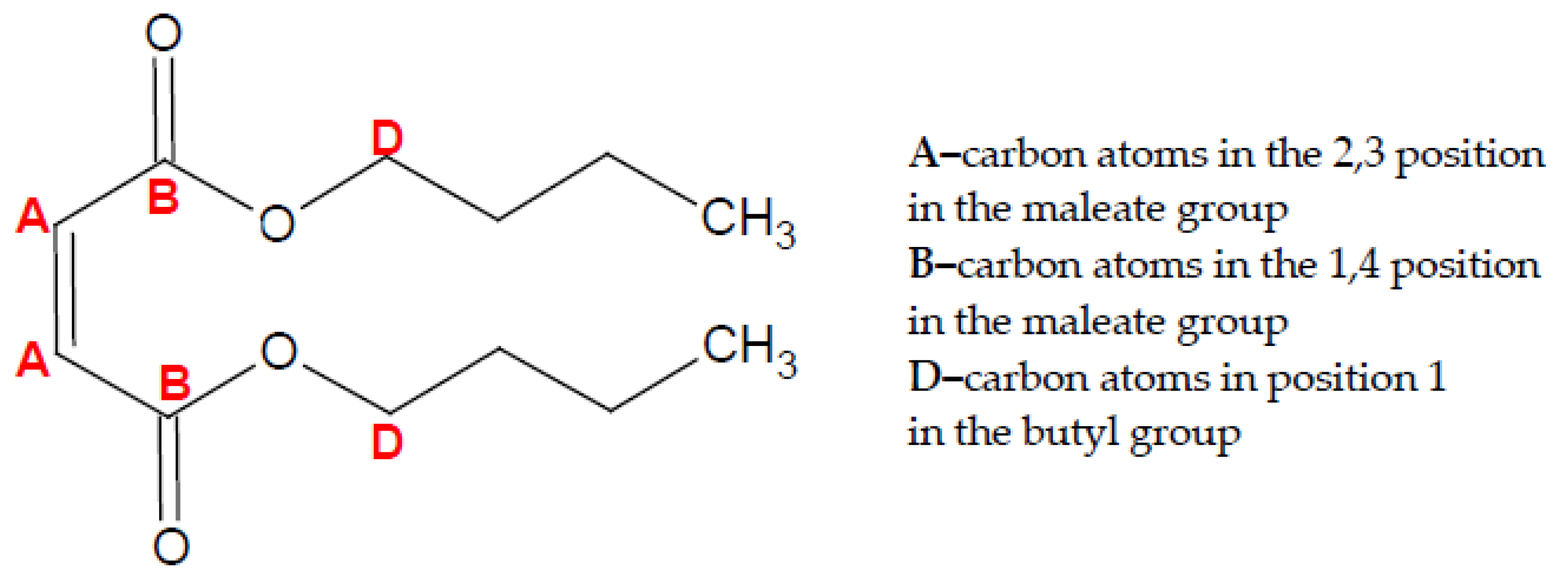
2. The Mechanism of the Influence of Fuel Oxygenates on the Process of Soot Formation in Diesel Engines
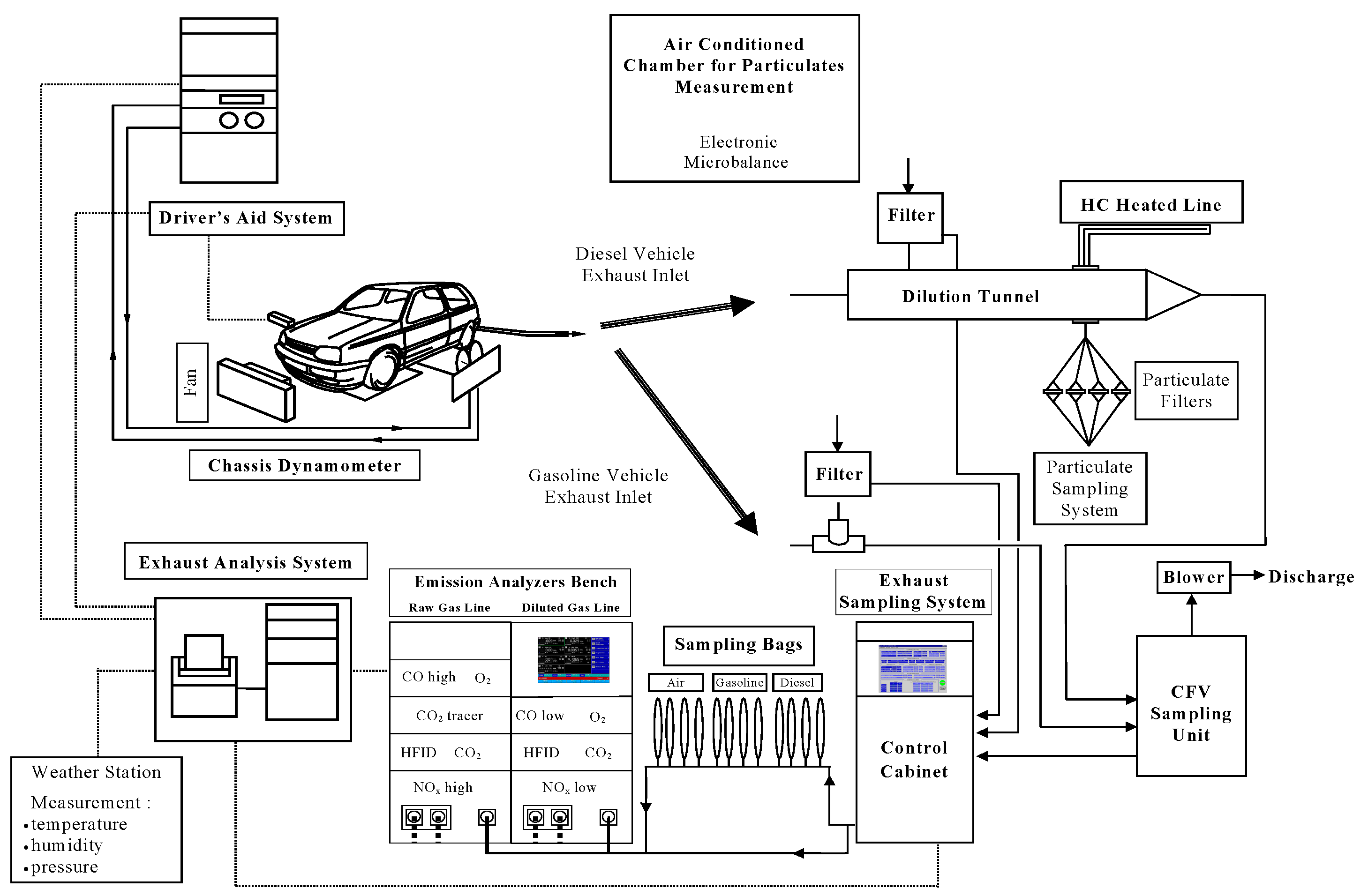
3. Materials and Methods
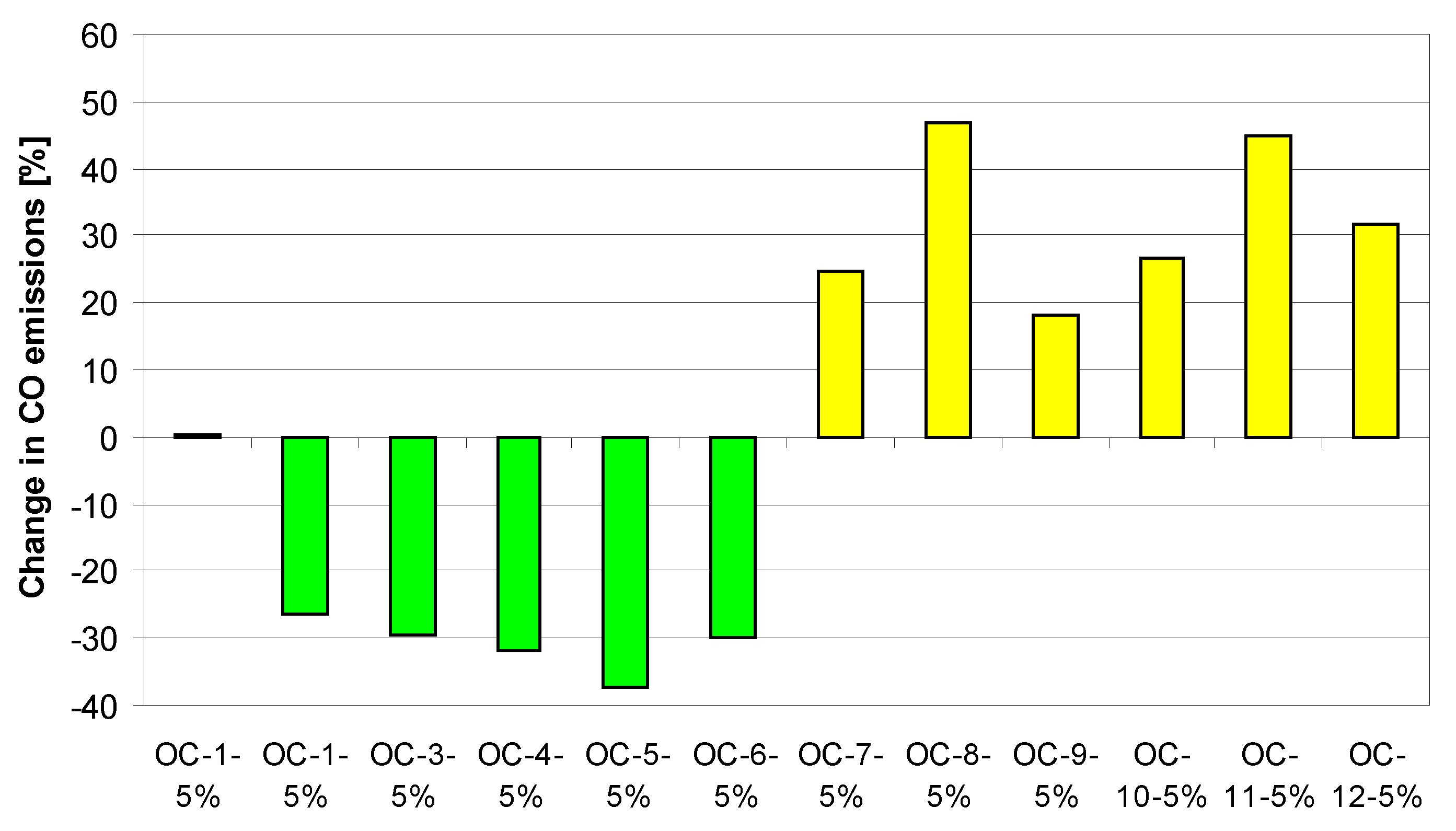
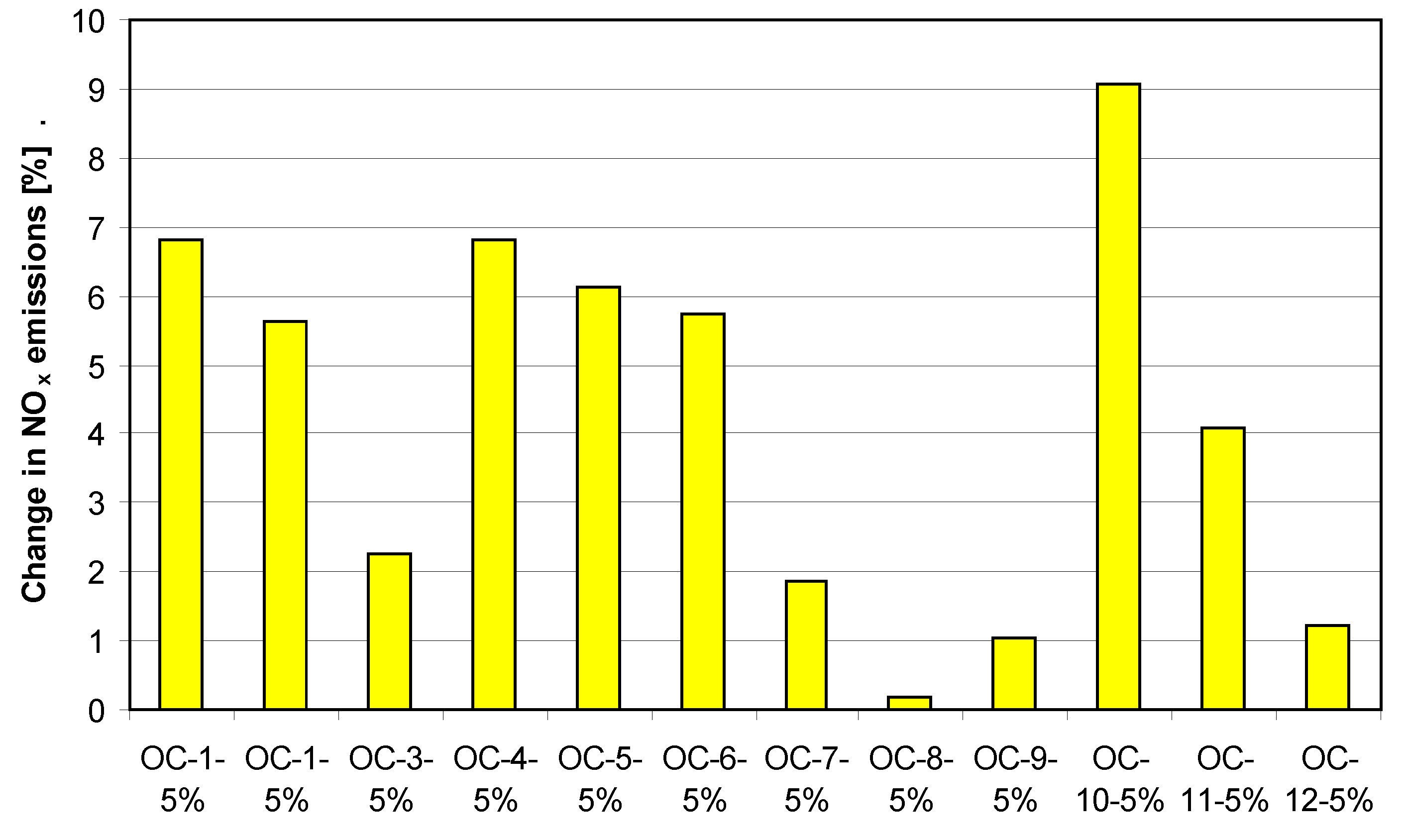
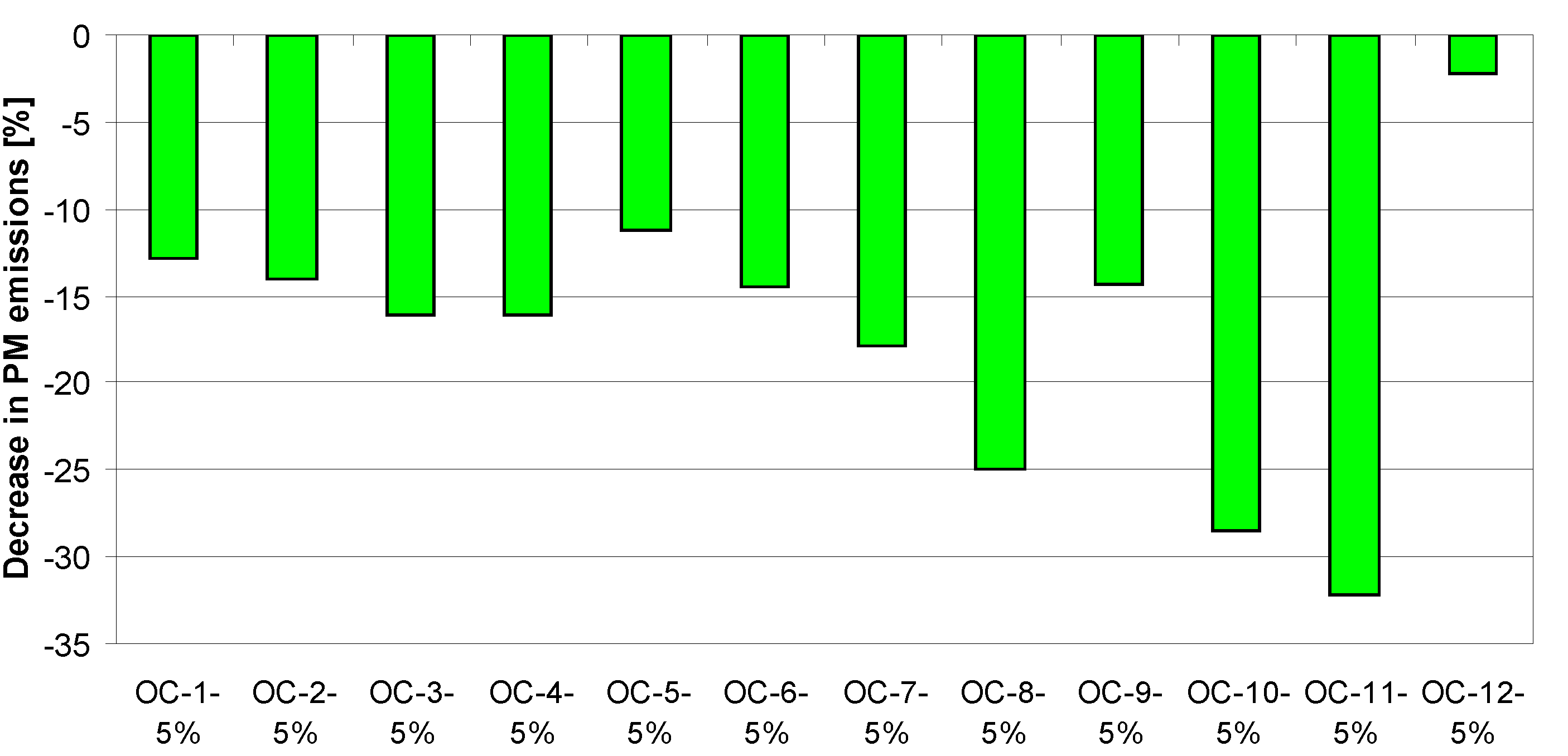
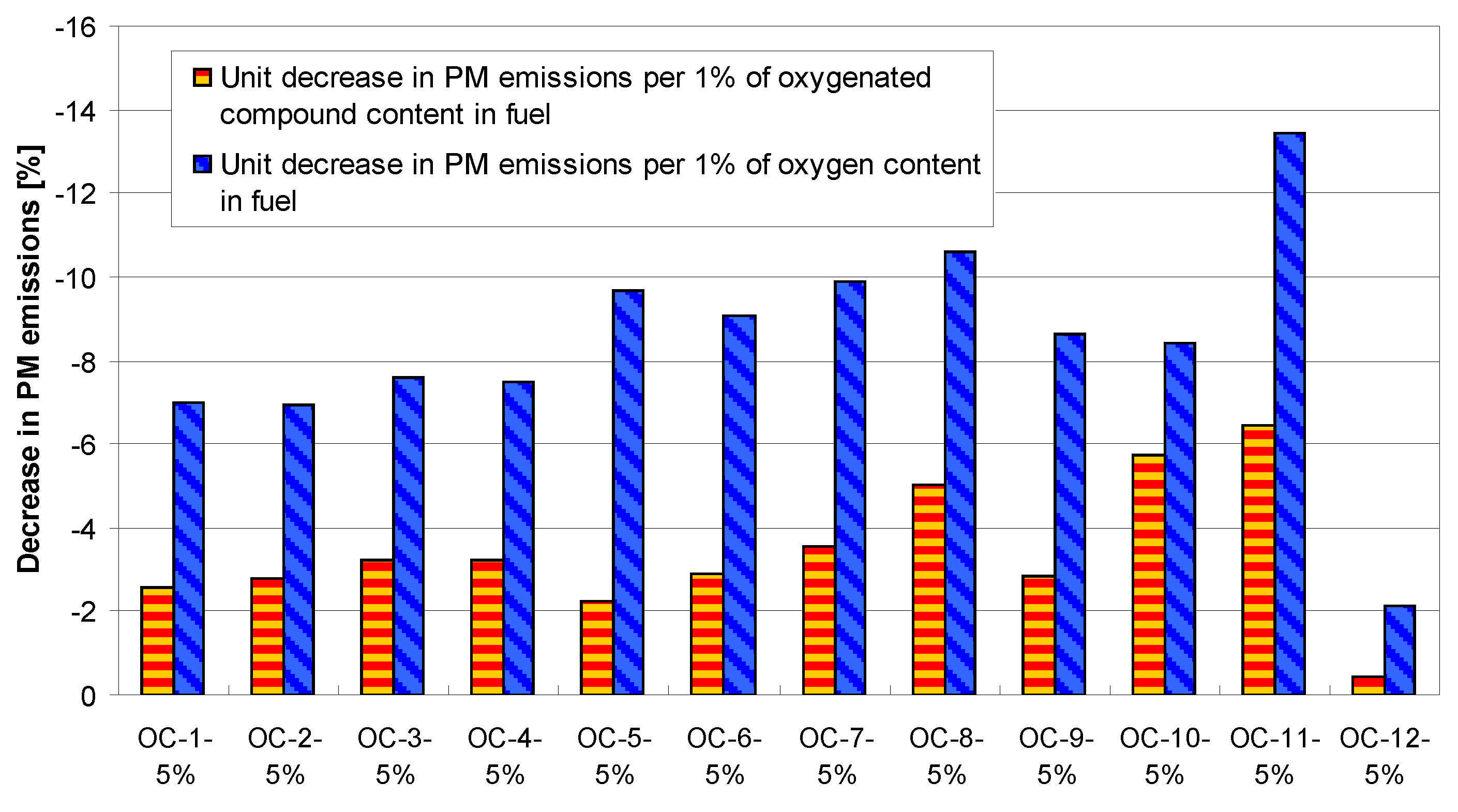
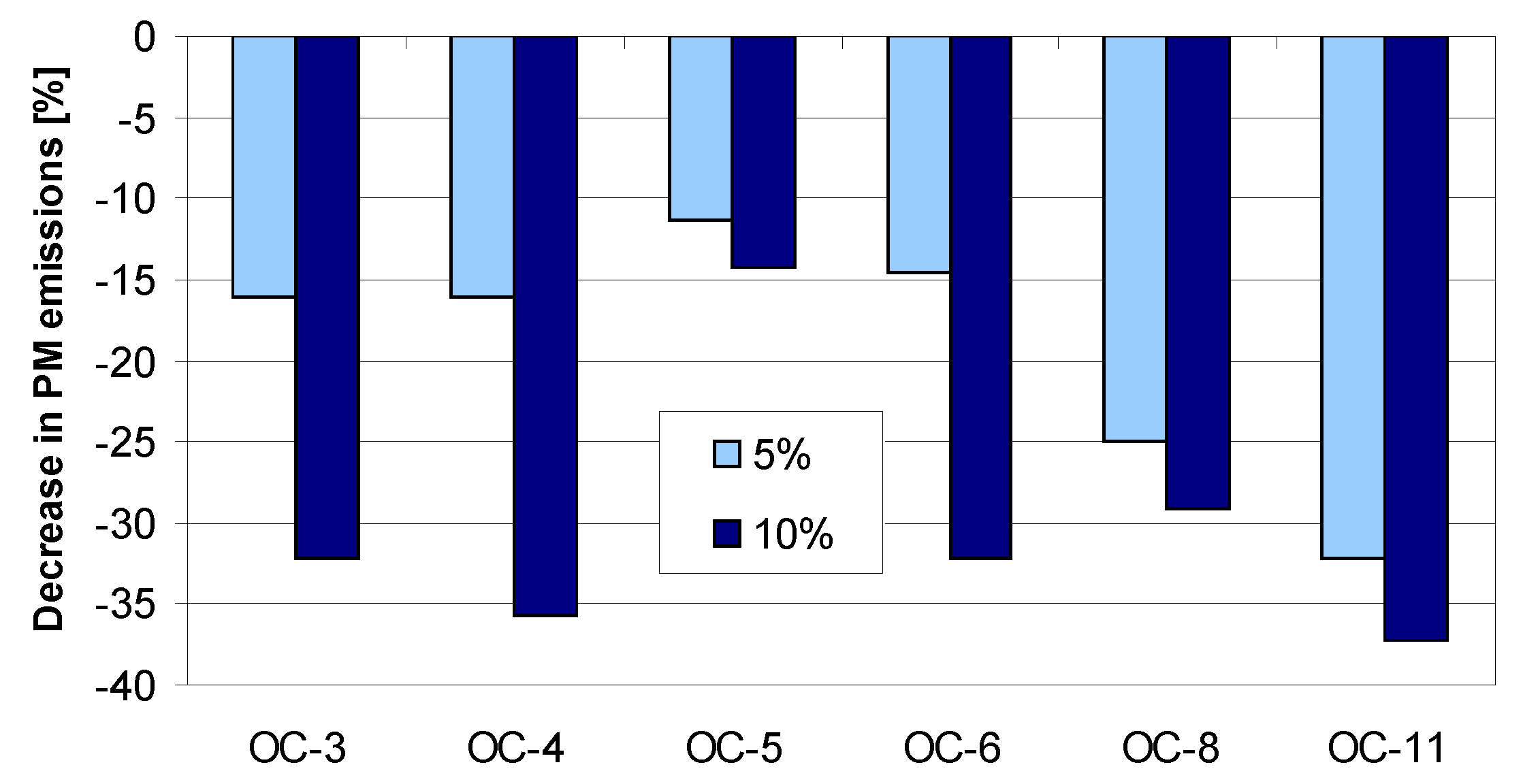
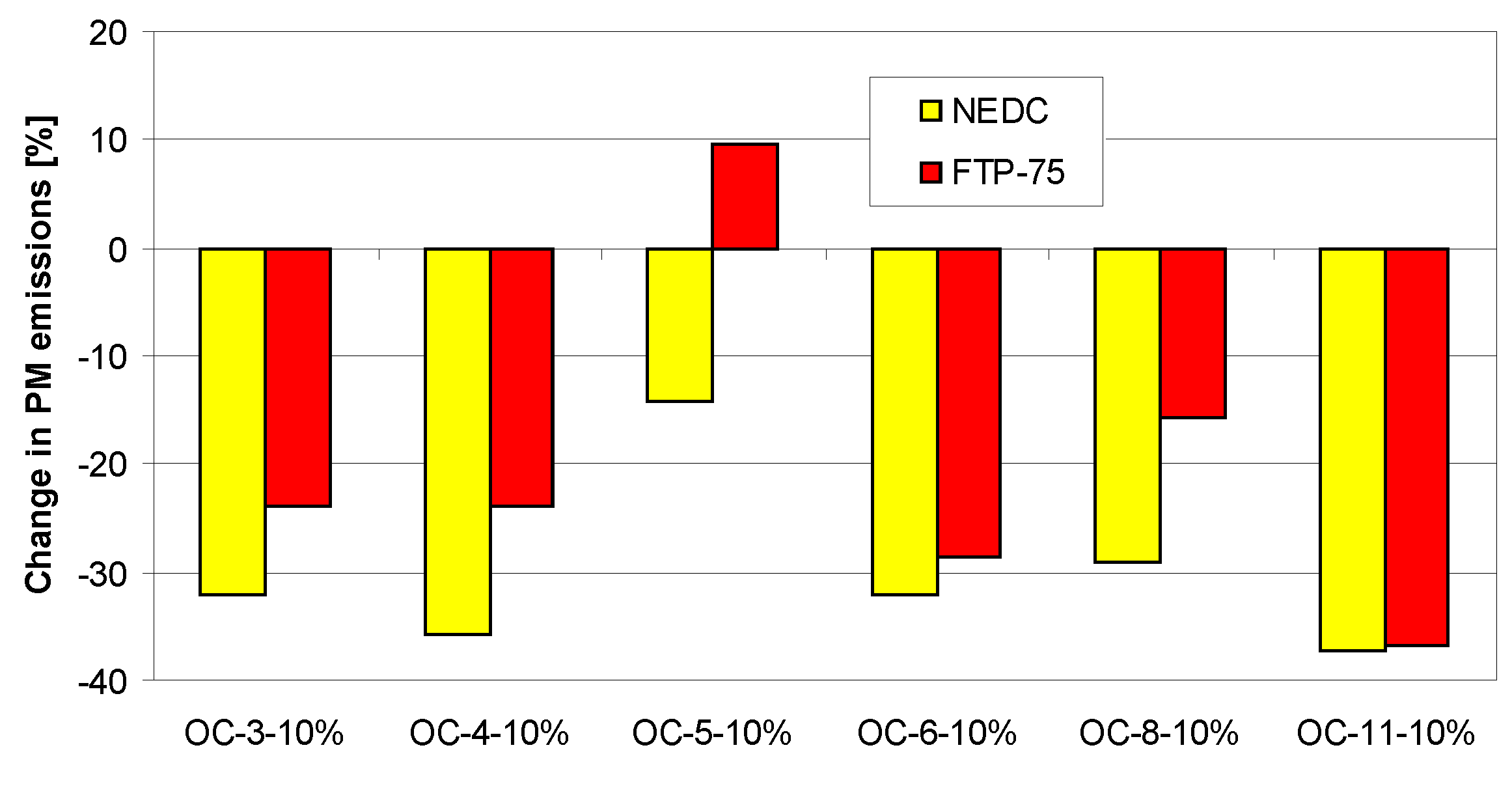
4. Tests Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- AVL Instrumentation & Test Systems AVL Tech Days 2012: Physical Background—Particle Structure, Particle Distribution, Particle Formation, Loss Mechanisms. Available online: https://www.avl.com/documents/10138/0/01-MA-Caroca.pdf/399f5ce2-4404-4de3-b906-1cf967c1437e (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Viskup, R.; Wolf, C.; Baumgartner, W. Major Chemical Elements in Soot and Particulate Matter Exhaust Emissions Generated from In-Use Diesel Engine Passenger Vehicles. In Introduction to Diesel Emissions; Viskup, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozak, M. Study on the Influence of Diesel Fuel’s Oxygenated Compounds on Exhaust Emissions from Diesel Engines; Publishing House of Poznań University of Technology: Poznań, Poland, 2013. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood, P. Particulate Emissions from Vehicles; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, S.; Bisig, C.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Diesel exhaust: Current knowledge of adverse effects and underlying cellular mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wichmann, H.-E. Diesel Exhaust Particles. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Deddens, J.; Stayner, L. Diesel exhaust and lung cancer in the trucking industry: Exposure-response analyses and risk assessment. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1998, 34, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laden, F.; Hart, J.E.; Eschenroeder, A.; Smith, T.J.; Garshick, E. Historical estimation of diesel exhaust exposure in a cohort study of U.S. railroad workers and lung cancer. Cancer Causes Control 2006, 17, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, R.; Silverman, D.T.; Garshick, E.; Vlaanderen, J.; Portengen, L.; Steenland, K. Exposure-response estimates for diesel engine exhaust and lung cancer mortality based on data from three occupational cohorts. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer—Diesel Engine Exhaust Carcinogenic. Press Release No. 213 of 12 June 2012. Available online: https://www.iarc.who.int/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/pr213_E.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Lu, J.; Tang, M. Toxicity of diesel exhaust particles on central nervous system. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 1751–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Ashok, B.; Vignesh, R.; Balusamy, S.; Alagumalai, A. NOx and PM trade-off in IC engines. In NOx Emission Control Technologies in Stationary and Automotive Internal Combustion Engines; Ashok, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Chapter 3; pp. 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DELPHI Technologies. 2018–2019 Worldwide Emissions Standards—On and Off-Highway Commercial Vehicles. Available online: https://www.delphi.com/sites/default/files/2020-03/2018-2019%20Heavy-Duty%20&%20Off-Highway%20Vehicles.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- DELPHI Technologies. 2020–2021 Worldwide Emissions Standards—Passenger Cars and Light Duty Vehicles. Available online: https://www.delphi.com/sites/default/files/2020-04/DELPHI%20booklet%20emission%20passenger%20cars%202020%20online%20complet.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- BorgWarner. Worldwide Emission Standards 2022/2023 Passenger Cars and Light Duty Vehicles. Available online: https://cdn.borgwarner.com/docs/default-source/default-document-library/passenger-cars-and-light-duty-vehicles-emissions-standards-booklet.pdf?sfvrsn=437a0b3d_6 (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Zerboni, A.; Rossi, T.; Bengalli, R.; Catelani, T.; Rizzi, C.; Priola, M.; Casadei, S.; Mantecca, P. Diesel exhaust particulate emissions and in vitro toxicity from Euro 3 and Euro 6 vehicles. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 297, 118767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Kozak, M.; Merkisz, J. Effects of Fuel Properties on Exhaust Emissions from the Latest Light-Duty DI Diesel Engine. In Proceedings of the 2003 JSAE/SAE International Spring Fuels and Lubricants Meeting, Yokohama, Japan, 19–22 May 2003. SAE Technical Paper 2003-01-1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Hamje, H.; Rickeard, D.J.; Bartsch, T.; Fittavolini, C.; Van De Heijning, P.; Lehto, K.; Gunter, G.; Cortijo, J.A.; Zemroch, P.J.; et al. Effect of Diesel Properties on Emissions and Fuel Consumption from Euro 4, 5 and 6 European Passenger Cars. In Proceedings of the SAE 2016 International Powertrains, Fuels & Lubricants Meeting, Baltimore, MD, USA, 24–26 October 2016. SAE Technical Paper 2016-01-2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Pettinen, R.; Ziman, P.; Kar, K.; Dauphin, R. Fuel Effects on Regulated and Unregulated Emissions from Two Commercial Euro V and Euro VI Road Transport Vehicles. Sustainability 2021, 13, 47985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Dauphin, R.; Andersson, J.; Ziman, P.; Rogerson, J.; Hamje, H. Fuel Effects on Regulated and Unregulated Emissions from Three Light-Duty Euro 5 and Euro 6 Diesel Passenger Cars. SAE Int. J. Adv. Curr. Pract. Mobil. 2020, 3, 428–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontses, A.; Dimaratos, A.; Keramidas, C.; Williams, R.; Hamje, H.; Ntziachristos, L.; Samaras, Z. Effects of fuel properties on particulate emissions of diesel cars equipped with diesel particulate filters. Fuel 2019, 255, 115879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.K.; Ghadikolaei, M.A.; Chen, S.H.; Fadairo, A.A.; Ng, K.W.; Lee, S.M.Y.; Xu, J.C.; Lian, Z.D.; Li, S.; Wong, H.C.; et al. Physicochemical and cell toxicity properties of particulate matter (PM) from a diesel vehicle fueled with diesel, spent coffee ground biodiesel, and ethanol. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielaczyc, P.; Merkisz, J.; Kozak, M. Analysis of the Influence of Fuel Sulphur Content on Diesel Engine Particulate Emissions. In Proceedings of the International Body Engineering Conference & Exhibition and Automotive & Transportation Technology Congress, Paris, France, 9–11 July 2002. SAE Technical Paper 2002-01-2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasaka, Y.; Sakurai, Y. Effects of Oxygenated Fuel and Cetane Improver on Exhaust Emission from Heavy-Duty DI Diesel Engines. In Proceedings of the SAE International Fuels & Lubricants Meeting & Exposition, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–20 October 1994. SAE Technical Paper 942023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Reitz, R. An experimental study on the effects of oxygenated fuel blends and multiple injection strategies on DI diesel engine emissions. Fuel 1999, 78, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, N.; Ogawa, H.; Nurun, N.M.; Obata, K.; Arima, T. Smokeless, Low NOx, High Thermal Efficiency, and Low Noise Diesel Combustion with Oxygenated Agents as Main Fuel. In Proceedings of the SAE International Congress & Exposition, Detroit, MI, USA, 23–26 February 1998. SAE Technical Paper 980506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, T.; Zheng, M.; Chikahisa, T.; Oh, Y.-T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tosaka, S.; Yamashita, M.; Yoshitake, H. Simultaneous Reductions of Smoke and NOx from a DI Diesel Engine with EGR and Dimethyl Carbonate. J. Fuels Lubr. 1995, 104, 1887–1896, SAE Technical Paper 952518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, M.; Litzinger, T. Effects of Structure and Boiling Point of Oxygenated Blending Compounds in Reducing Diesel Emissions. In Proceedings of the SAE International Fuels & Lubricants Meeting & Exposition, Dearborn, MI, USA, 3–6 May 1999. SAE Technical Paper 1999-01-1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, K.; Takei, Y.; Fujimoto, Y.; Matsudaira, J.; Kumamoto, M. The Effects of Fuel Properties and Oxygenates on Diesel Exhaust Emissions. In Proceedings of the 1995 SAE International Fall Fuels and Lubricants Meeting and Exhibition, Toronto, Canada, 16–19 October 1995. SAE Technical Paper 952349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakopoulos, C.D.; Hountalas, D.T.; Zannis, T.C.; Levendis, Y.A. Operational and Environmental Evaluation of Diesel Engines Burning Oxygen-Enriched Intake Air or Oxygen-Enriched Fuels: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2004 Powertrain & Fluid Systems Conference & Exhibition, Tampa, FL, USA, 25–28 October 2004. SAE Technical Paper 2004-01-2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, K.S.; Kokturk, U.; Bartels, C.R. Effects of Oxygen-Enriched Air on Diesel Engine Exhaust Emissions and Engine Performance. In Proceedings of the SAE International Congress & Exposition, Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 March 1993. SAE Technical Paper 931004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, H.C.; Milkins, E.E.; Rigby, G.R. A New Look at Oxygen Enrichment 1) The Diesel Engine. J. Engines Part 1 1990, 99, 775–792, SAE Technical Paper 900344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Ma, Z.; Meng, H. Potential improvement in combustion behavior of a downsized rotary engine by intake oxygen enrichment. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 205, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, L.; Thomson, M.J. The Effect of Oxygenated Additives on Soot Precursor Formation in a Counterflow Diffusion Flame. In Proceedings of the SAE International Fuels & Lubricants Meeting & Exposition, Dearborn, MI, USA, 3–6 May 1999. SAE Technical Paper 1999-01-3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, C.; Van Tiggelen, P.; Vandooren, J. Effect of Dimethoxymethane Addition on the Experimental Structure of a Rich Ethylene/Oxygen/Argon Flame. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2022, 29, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Ito, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Ueda, M.; Senda, J.; Fujimoto, H. Soot Kinetic Modeling and Empirical Validation on Smokeless Diesel Combustion with Oxygenated Fuels. J. Fuels Lubr. 2003, 112, 945–963, SAE Paper 2003-01-1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Ito, T.; Senda, J.; Fujimoto, H. Detailed Chemical Kinetic Modeling of Diesel Spray Combustion with Oxygenated Fuels. J. Engines 2001, 110, 1560–1578, SAE Paper 2001-01-1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, C.K.; Pitz, W.J.; Curran, H.J. Chemical Kinetic Modeling Study of the Effects of Oxygenated Hydrocarbons on Soot Emissions from Diesel Engines. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 6912–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dec, J.E. A Conceptual Model of DI Diesel Combustion Based on Laser-Sheet Imaging. J. Engines 1997, 106, 1319–1348, SAE Technical Paper 970873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frenklach, M.; Wang, H. Detailed modeling of soot particle nucleation and growth. Symp. (Int.) Combust. 1991, 23, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenklach, M. Reaction Mechanism of Soot Formation in Flames. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, H.J.; Fisher, E.M.; Glaude, P.-A.; Marinov, N.M.; Pitz, W.J.; Westbrook, C.K.; Layton, D.W.; Flynn, P.F.; Durrett, R.P.; Loye, A.O.Z.; et al. Detailed Chemical Kinetic Modeling of Diesel Combustion with Oxygenated Fuels. In Proceedings of the SAE 2001 World Congress, Detroit, MI, USA, 5–8 March 2001. SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-0653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flynn, P.F.; Durrett, R.P.; Hunter, G.L.; Loye, A.O.Z.; Akinyemi, O.C.; Dec, J.E.; Westbrook, C.K. Diesel Combustion: An Integrated View Combining Laser Diagnostics, Chemical Kinetics, And Empirical Validation. In Proceedings of the Future Transportation Technology Conference & Exposition International Congress & Exposition, Costa Mesa, CA, USA, 17–19 August 1999. SAE Technical Paper 1999-01-0509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appel, J.; Bockhorn, H.; Frenklach, M. Kinetic modeling of soot formation with detailed chemistry and physics: Laminar premixed flames of C2 hydrocarbons. Combust. Flame 2000, 121, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebers, D.L.; Higgins, B. Flame Lift-Off on Direct-Injection Diesel Sprays Under Quiescent Conditions. In Proceedings of the SAE 2001 World Congress, Detroit, MI, USA, 5–8 March 2001. SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-0530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, C.K.; Dryer, F.L. Comprehensive Mechanism for Methanol Oxidation. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1979, 20, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.J.; Martin, G.C. Effects of Oxygenated Compounds on Combustion and Soot Evolution in a DI Diesel Engine: Broadband Natural Luminosity Imaging. In Proceedings of the Spring Fuels & Lubricants Meeting & Exhibition, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 May 2002. SAE Technical Paper 2002-01-1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.J.; Pitz, W.J.; Pickett, L.M.; Martin, G.C.; Siebers, D.L.; Westbrook, C.K. Effects of Oxygenates on Soot Processes in DI Diesel Engines: Experiments and Numerical Simulations. In Proceedings of the 2003 JSAE/SAE International Spring Fuels and Lubricants Meeting, Yokohama, Japan, 19–22 May 2003. SAE Technical Paper 2003-01-1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.; Pitz, W.; Curran, H.; Westbrook, C. Detailed chemical kinetic mechanisms for combustion of oxygenated fuels. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2000, 28, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchholz, B.A.; Mueller, C.J.; Upatnieks, A.; Martin, G.C.; Pitz, W.J.; Westbrook, C.K. Using Carbon-14 Isotope Tracing to Investigate Molecular Structure Effects of the Oxygenate Dibutyl Maleate on Soot Emissions from a DI Diesel Engine. J. Fuels Lubr. 2004, 113, 846–857, SAE Technical Paper 2004-01-1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchholz, B.A.; Cheng, A.S.; Dibble, R.W. Isotopic Tracing of Bio-Derived Carbon from Ethanol-in-Diesel Blends in the Emissions of a Diesel Engine. In Proceedings of the Spring Fuels & Lubricants Meeting & Exhibition, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 May 2002. SAE Technical Paper 2002-01-1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.S.; Dibble, R.W.; Buchholz, B.A. The Effect of Oxygenates on Diesel Engine Particulate Matter. In Proceedings of the Spring Fuels & Lubricants Meeting & Exhibition, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 May 2002. SAE Technical Paper 2002-01-1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.; Muether, M.; Pischinger, S.; Kolbeck, A.; Lamping, M. Tailor-Made Fuels: The Potential of Oxygen Content in Fuels for Advanced Diesel Combustion Systems. In Proceedings of the SAE 2009 Powertrains Fuels and Lubricants Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 2–4 November 2009. SAE Technical Paper 2009-01-2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, N.M. A Detailed Chemical Kinetic Model for High Temperature Ethanol Oxidation. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1999, 31, 183–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Park, S.; Reitz, R.D.; Kurtz, E. The effect of oxygenated fuel properties on diesel spray combustion and soot formation. Combust. Flame 2017, 180, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozak, M.; Merkisz, J.; Bielaczyc, P.; Szczotka, A. The Influence of Oxygenated Diesel Fuels on a Diesel Vehicle PM/NOx Emission Trade-Off. In Proceedings of the SAE 2009 Powertrains Fuels and Lubricants Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 2–4 November 2009. SAE Technical Paper 2009-01-2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, N.; Minami, M.; Ogawa, H.; Miyamoto, N. Ultra Low Emission and High Performance Diesel Combustion with Highly Oxygenated Fuel. In Proceedings of the SAE 2000 World Congress, Detroit, MI, USA, 6–9 March 2000. SAE Technical Paper 2000-01-0231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tree, D.R.; Svensson, K.I. Soot Processes in Compression Ignition Engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 272–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, M.D.; Frijters, P.J.; Klein-Douwel, R.J.; Baert, R.S. Oxygenated Fuel Composition Impact on Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine Emissions. In Proceedings of the JSAE/SAE International Fuels & Lubricants Meeting, Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 July 2007. SAE Technical Paper 2007-01-2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallgren, B.E.; Heywood, J.B. Effects of Oxygenated Fuels on DI Diesel Combustion and Emissions. In Proceedings of the SAE 2001 World Congress, Detroit, MI, USA, 5–8 March 2001. SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-0648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zannis, T.C.; Papagiannakis, R.G.; Pariotis, E.G.; Kourampas, M.I. Experimental Study of DI Diesel Engine Operational and Environmental Behavior Using Blends of City Diesel with Glycol Ethers and RME. Energies 2019, 12, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delfort, B.; Durand, I.; Jaecker-Voirol, A.; Lacome, T.; Paille, F.; Montagne, X. Oxygenated Compounds and Diesel Engine Pollutant Emissions Performances of New Generation of Products. J. Fuels Lubr. 2002, 111, 1871–1880, SAE Technical Paper 2002-01-2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.I.; Rickeard, D.J.; Duff, J.L.C.; Bateman, J.R.; Schlosberg, R.H.; Caers, R.F. Oxygenates: An Evaluation of their Effects on Diesel Emissions. J. Fuels Lubr. 2001, 110, 1482–1498, SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porai, P.T.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Subramaniyam, S.; Jancirani, J.; Sahoo, B.B. Combustion and Performance of a Diesel Engine with Oxygenated Diesel Blend. In Proceedings of the SAE 2004 World Congress & Exhibition, 8–11 March 2004. SAE Technical Paper 2004-01-0082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yage, D.; Junjie, Z.; Shun, C.C.; Xuelong, M.; Jinbao, Z.; Haiyong, P.; Tao, W. Comparative study on combustion and particulate emissions for diesel-biodiesel and diesel-diglyme blends. Fuel 2022, 313, 122710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, N.; Rasul, M.G.; Brown, R.J. Notable reductions in blow-by and particle emissions during cold and hot start operations from a turbocharged diesel engine using oxygenated fuels. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 203, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, N.; Tsolakis, A.; Martos, F.J. Effect of propylene glycol ether fuelling on the different physico-chemical properties of the emitted particulate matters: Implications of the soot reactivity. Fuel 2018, 219, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natarajan, M.; Frame, E.A.; Naegeli, D.W.; Asmus, T.; Clark, W.; Garbak, J.; Manuel, A.; González, D.; Liney, E.; Piel, W.; et al. Oxygenates for Advanced Petroleum-Based Diesel Fuels: Part 1. Screening and Selection Methodology for the Oxygenates. J. Fuels Lubr. 2001, 110, 2221–2245, SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, D.M.A.; Piel, W.; Asmus, T.; Clark, W.; Garbak, J.; Liney, E.; Natarajan, M.; Naegeli, D.W.; Yost, D.; Frame, E.A.; et al. Oxygenates screening for Advanced Petroleum-Based Diesel Fuels: Part 2. The Effect of Oxygenate Blending Compounds on Exhaust Emissions. In Proceedings of the SAE 2001 International Fall Fuels & Lubricants Meeting & Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 5–7 September 2001. SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.M.A.; Clark, W.; Wolf, L.R.; Garbak, J.A.; Wright, K.J.; Natarajan, M.; Yost, D.M.; Frame, E.A.; Kenney, T.E.; Ball, J.C.; et al. Impact of Engine Operating Conditions on Low-NOx Emissions in a Light-Duty CIDI Engine Using Advanced Fuels. In Proceedings of the SAE 2002 Powertrain & Fluid Systems Conference & Exhibition, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–24 October 2002. SAE Technical Paper 2002-01-2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocis, D.; Song, K.; Lee, H.; Litzinger, T. Effects of Dimethoxymethane and Dimethylcarbonate on Soot Production in an Optically-accessible DI Diesel Engine. In Proceedings of the CEC/SAE International Fuels & Lubricants Meeting & Exposition, Paris, France, 19–22 June 2000. SAE Paper 2000-01-2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Huang, Z.; Miao, H.; Di, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zeng, K.; Liu, B.; Wang, C.X. Combustion and emissions of a DI diesel engine fuelled with diesel-oxygenate blends. Fuel 2008, 87, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürre, P. Biobutanol: An attractive biofuel. Biotechnol. J. 2007, 2, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürre, P. Fermentative Butanol Production. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1125, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.; Saha, B.; Hector, R.; Hughes, S.; Cotta, M. Butanol production from wheat straw by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation using Clostridium beijerinckii: Part I—Batch fermentation. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.; Saha, B.; Hector, R.; Hughes, S.; Cotta, M. Butanol production from wheat straw by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation using Clostridium beijerinckii: Part II—Fed-batch fermentation. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Lapuerta, M.; German, L. Progress in the Use of Biobutanol Blends in Diesel Engines. Energies 2021, 14, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Tong, C.; Qian, W.; Lu, F.; Yin, J.; Huang, H. The effect of butanol isomers on diesel engine performance, emission and combustion characteristics under different load conditions. Fuel 2020, 277, 118188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Yao, M. Experimental study on diesel conventional and low temperature combustion by fueling four isomers of butanol. Fuel 2015, 141, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Sun, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Y.; Zeng, W.; Lin, S. Comparative assessment of n-butanol addition in CTL on performance and exhaust emissions of a CI engine. Fuel 2021, 303, 121223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, O. The influence of n-butanol/diesel fuel blends utilization on a small diesel engine performance and emissions. Fuel 2011, 90, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Ramos, A.; Barba, J.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D. Cold- and warm-temperature emissions assessment of n-butanol blends in a Euro 6 vehicle. Appl. Energy 2018, 218, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Hernández, J.J.; Rodríguez-Fernández, J.; Barba, J.; Ramos, A.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D. Emission benefits from the use of n-butanol blends in a Euro 6 diesel engine. Int. J. Engine Res. 2017, 19, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Lee, C. Combustion and emissions characteristics of high n-butanol/diesel ratio blend in a heavy-duty diesel engine and EGR impact. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 78, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipanluisa, L.; Fonseca, N.; Casanova, J.; López, J.-M. Effect of n-butanol/diesel blends on performance and emissions of a heavy-duty diesel engine tested under the World Harmonised Steady-State cycle. Fuel 2021, 302, 121204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M.; Lijewski, P.; Waligórski, M. Exhaust Emissions from a Hybrid City Bus Fuelled by Conventional and Oxygenated Fuel. Energies 2022, 15, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, R.; Aguado-Deblas, L.; López-Tenllado, F.J.; Luna, C.; Calero, J.; Romero, A.A.; Bautista, F.M.; Luna, D. Biodiesel Is Dead: Long Life to Advanced Biofuels—A Comprehensive Critical Review. Energies 2022, 15, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, R.; Aguado-Deblas, L.; Bautista, F.M.; Luna, D.; Luna, C.; Calero, J.; Posadillo, A.; Romero, A.A. Biodiesel at the Crossroads: A Critical Review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Group | Glycol Ethers | Maleates | Carbonates | Alcohols | ||||||||
| Chemical Name | Ethylene Glycol Dimethyl Ether | Diethylene Glycol Dimethyl Ether | Triethylene Glycol Dimethyl Ether | Tetraethylene Glycol Dimethyl Ether | Diethylene Glycol Dibutyl Ether | Dipropylene Glycol Dimethyl Ether | Tripropylene Glycol Methyl Ether | Diethyl Maleate | Dibutyl Maleate | Dimethyl Carbonate | Diethyl Carbonate | N-Butanol |
| Molecular weight, amu | 90.12 | 134.17 | 178.23 | 222.28 | 218.33 | 162.23 | 206.28 | 172.18 | 228.28 | 90.08 | 118.13 | 74.12 |
| Oxygen content, % (m/m) | 35.6 | 35.8 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 22.0 | 29.6 | 31.1 | 37.3 | 28.1 | 53.3 | 40.7 | 21.6 |
| Boiling point, °C | 85 | 162 | 220 | 275 | 256 | 175 | 243 | 225 | 281 | 90 | 127 | 117 |
| Density @ 20 °C, kg/m3 | 867 | 944 | 987 | 1010 | 884 | 903 | 963 | 1064 | 988 | 1069 | 975 | 810 |
| Viscosity @ 20 °C, mm2/s | 0.5 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 4.1 | 2.3 | 1.12 | 5.5 | n.a. | n.a. | 0.56 | 0.78 | 3.64 |
| Flash point, °C | −6 | 51 | 113 | 141 | 120 | 65 | >110 | 93 | >110 | 18 | 25 | 34 |
| Cetane number (calculated) | 86 | 112 | 144 | 144 | 144 | 86 | 58 | 57 | 44 | 10 | 14 | 10 |
| Unit | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Cetane number | - | 52.0 |
| Cetane index | - | 53.1 |
| Density @ 20 °C | kg/m3 | 830.8 |
| Viscosity @ 40 °C | mm2/s | 4.188 |
| Evaporation @ 250 °C (E250) | % (v/v) | 36.9 |
| Evaporation @ 350 °C (E350) | % (v/v) | 97.8 |
| Temp. at which 90% of the fuel evaporates (T95) | °C | 340.0 |
| Final Boiling Point (FBP) | °C | 350.2 |
| Total aromatic hydrocarbons | % (m/m) | 23.9 |
| Polyaromatic hydrocarbons | % (m/m) | 2.5 |
| Sulfur content | ppm | 8.9 |
| Oxygen content | % (m/m) | 0.0 |
| Vehicle Type | Passenger Car |
|---|---|
| Weight | 950 kg |
| Engine type | Diesel, 4-cylinder in-line |
| Engine capacity | 1.3 dm3 |
| Maximum power | 51 kW @ 4000 rpm |
| Maximum torque | 145 Nm @ 1500 rpm |
| Combustion type | Direct injection Common Rail, turbocharged (intercooled) |
| Emission control | Oxidation catalyst, Exhaust gas recirculation |
| Emissions level | Euro 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozak, M.; Merkisz, J. Oxygenated Diesel Fuels and Their Effect on PM Emissions. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157709
Kozak M, Merkisz J. Oxygenated Diesel Fuels and Their Effect on PM Emissions. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157709
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozak, Miłosław, and Jerzy Merkisz. 2022. "Oxygenated Diesel Fuels and Their Effect on PM Emissions" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157709
APA StyleKozak, M., & Merkisz, J. (2022). Oxygenated Diesel Fuels and Their Effect on PM Emissions. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157709






