Experimental Study on the Seismic Performance of Shear Walls with Different Coal Gangue Replacement Rates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Design
2.2. Material Properties Test
2.2.1. Test Materials
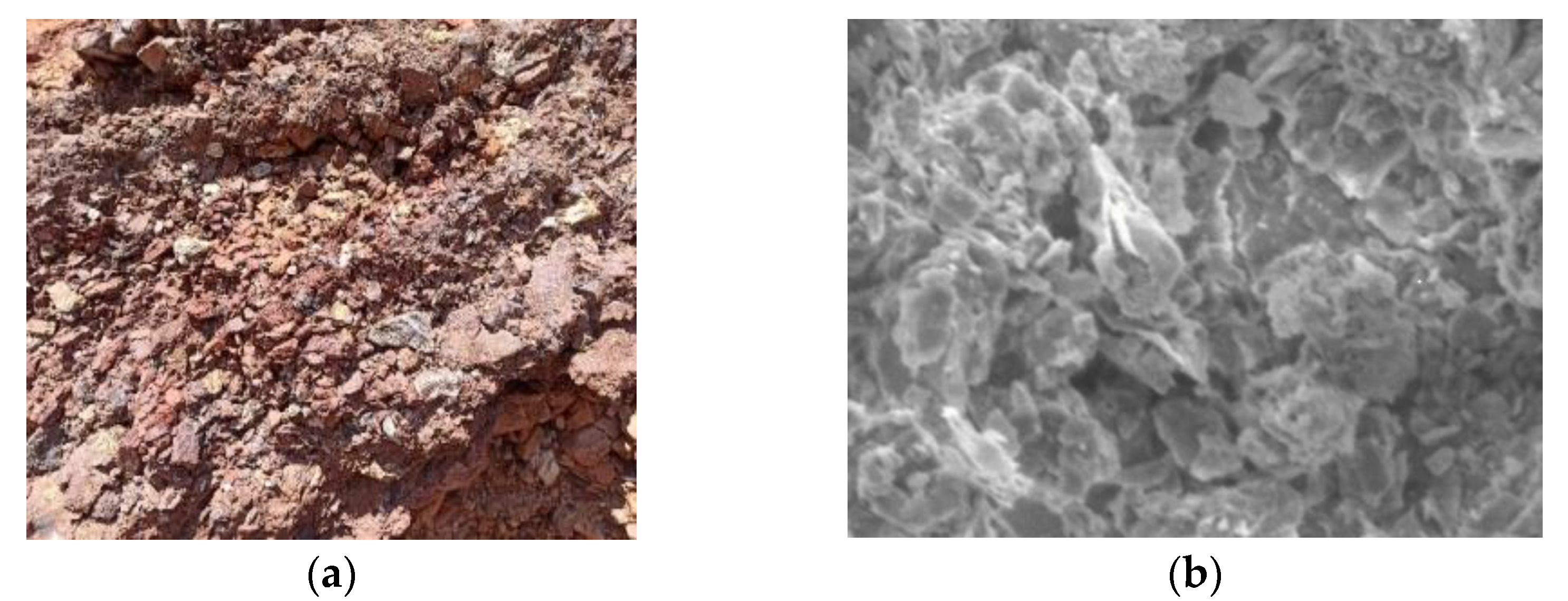
2.2.2. Basic Properties of Coal Gangue
- 1.
- Strength
- 2.
- Water absorption rate
- 3.
- Bulk density and apparent density
- 4.
- Crushing value
2.2.3. Material Properties Test
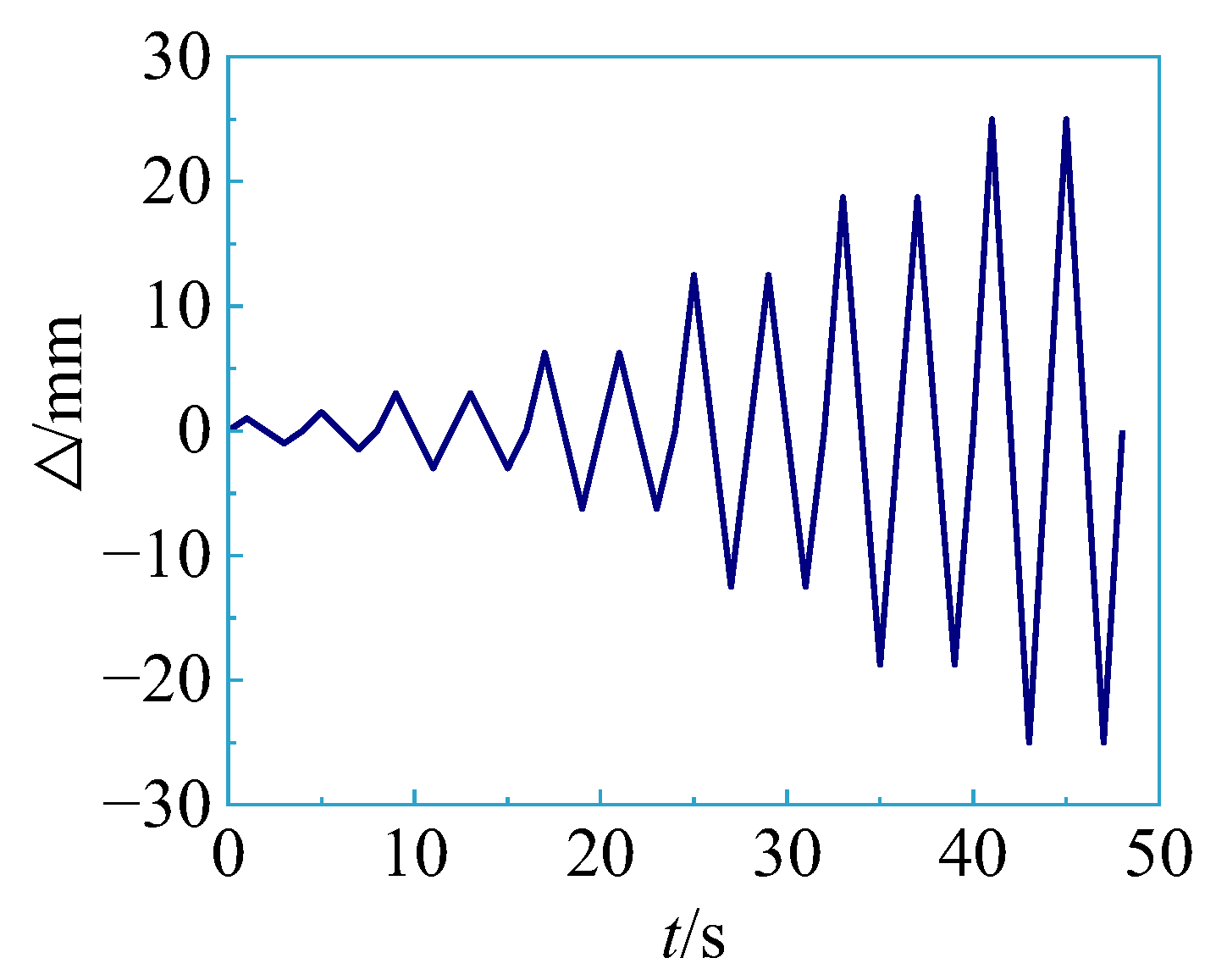
2.3. Loading Protocol
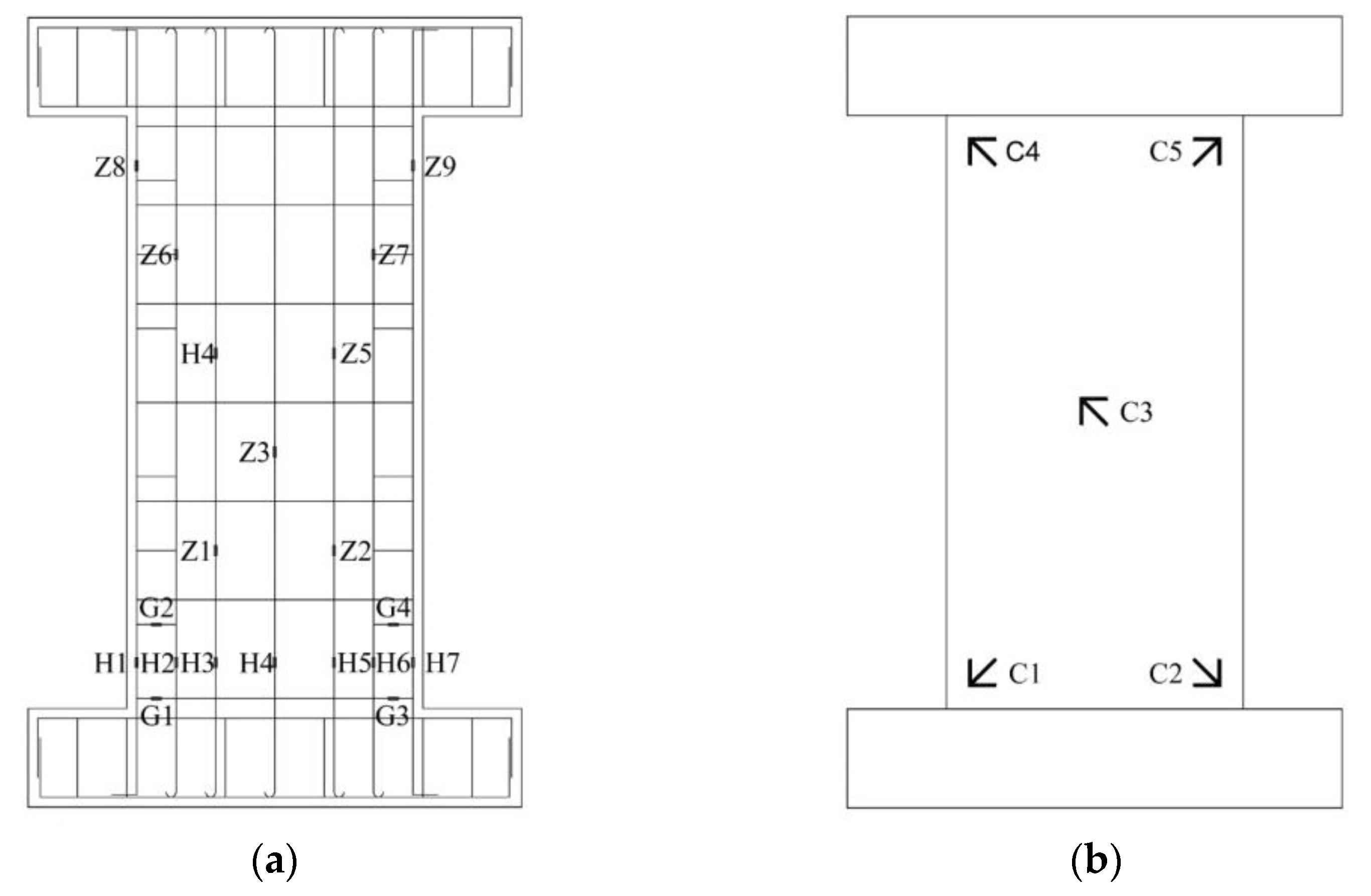
2.4. Test Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
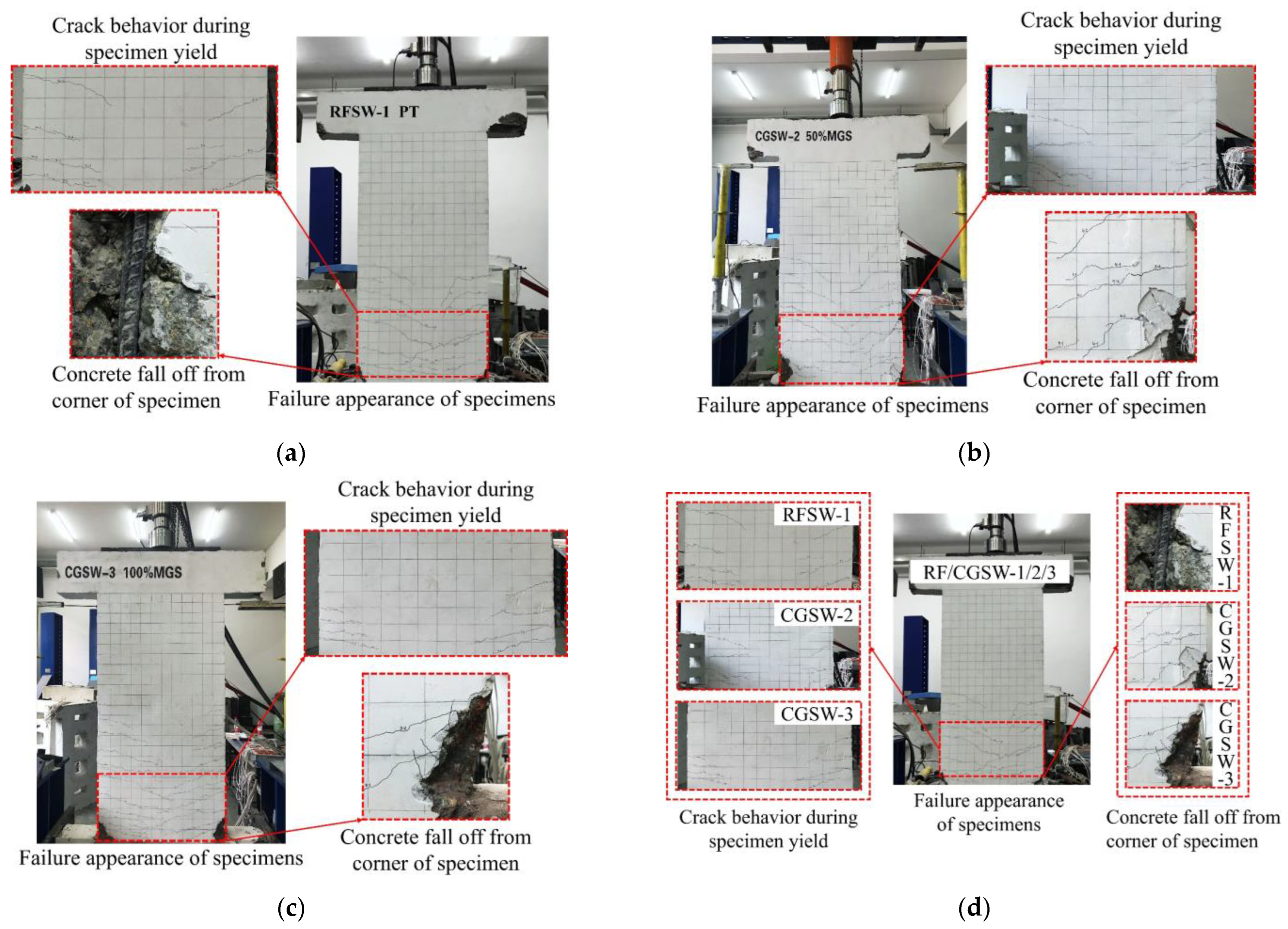
3.1. Test Phenomenon
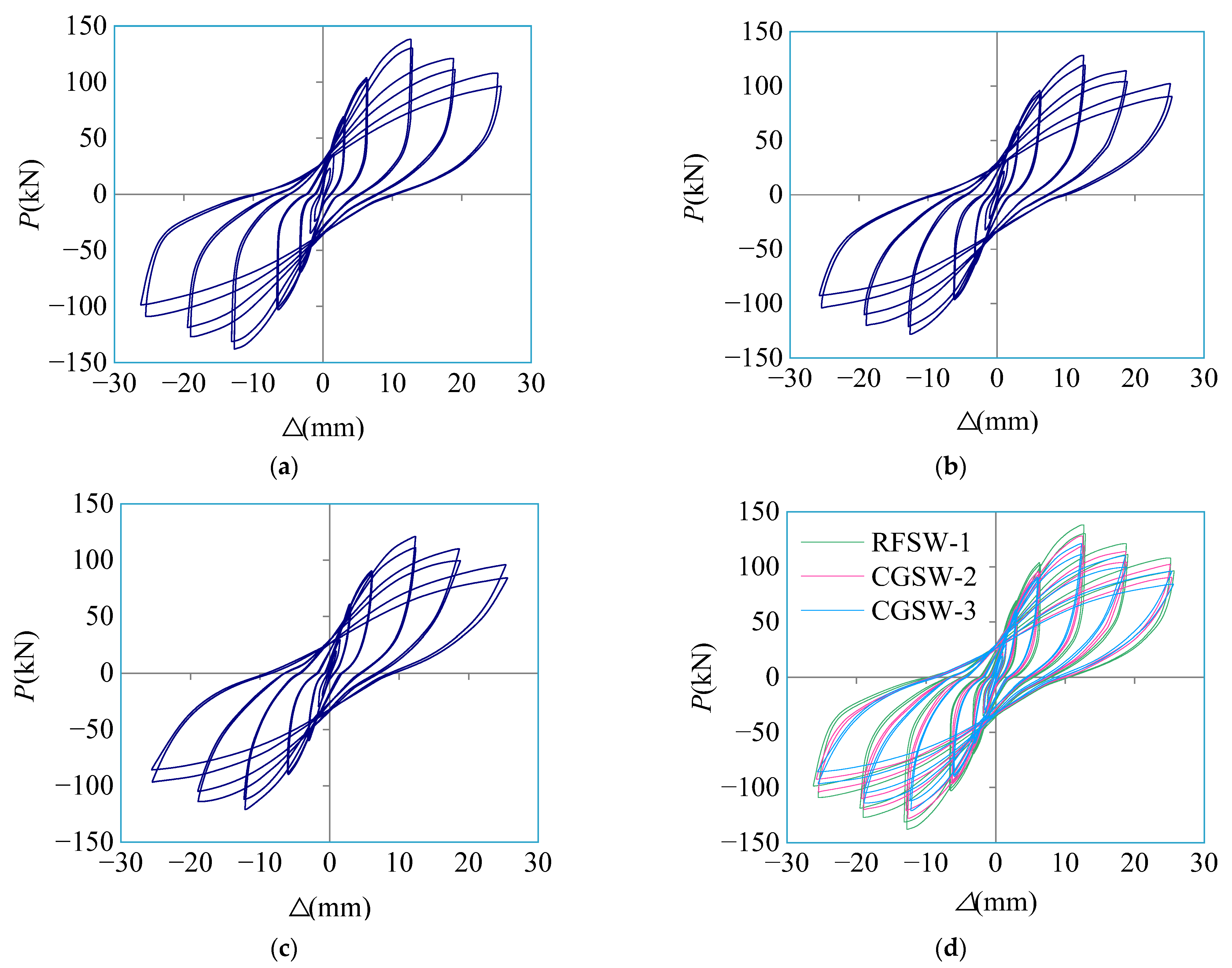
3.2. Hysteretic Curve
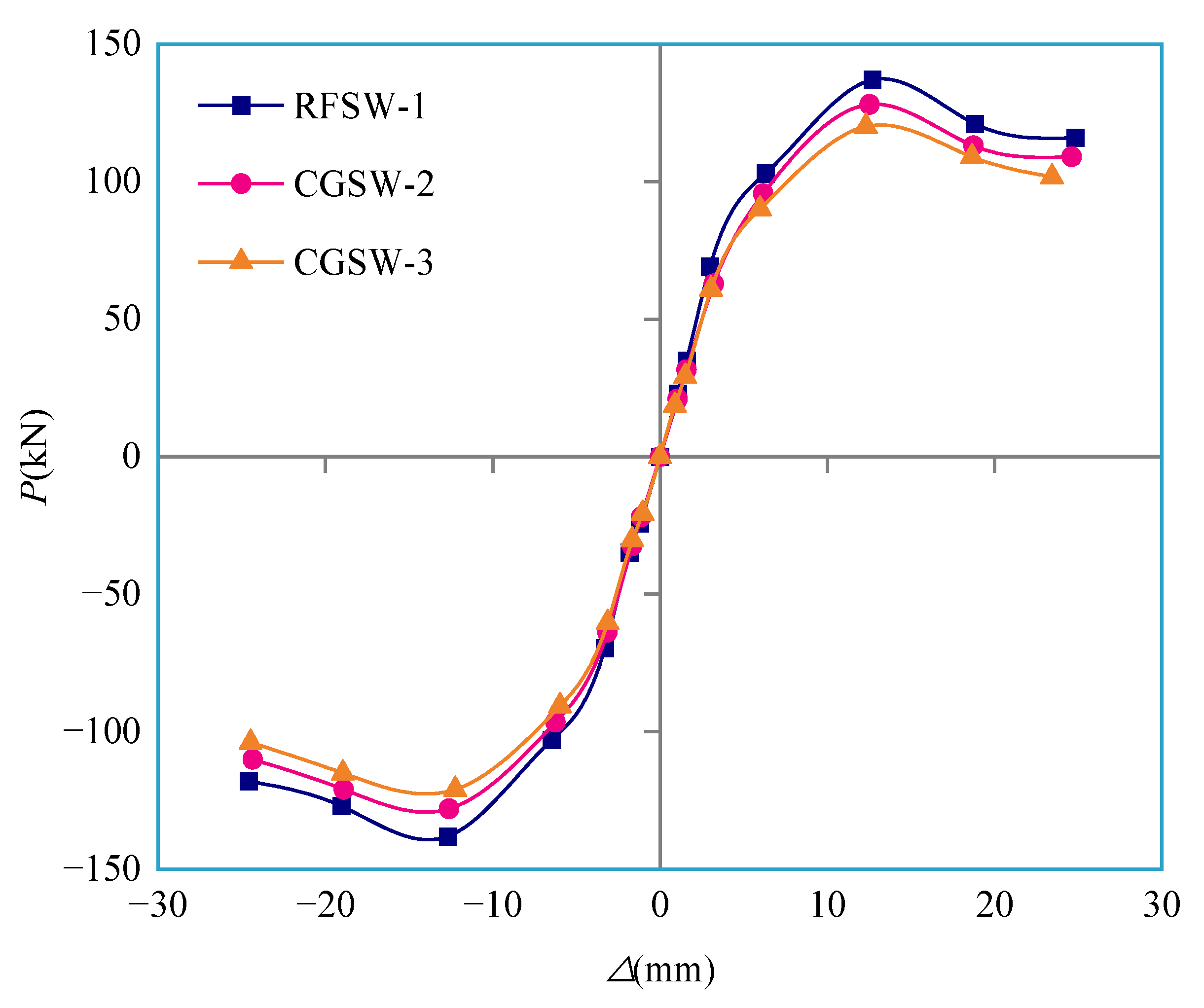
3.3. Backbone Curve
3.4. Load Carrying Capacity
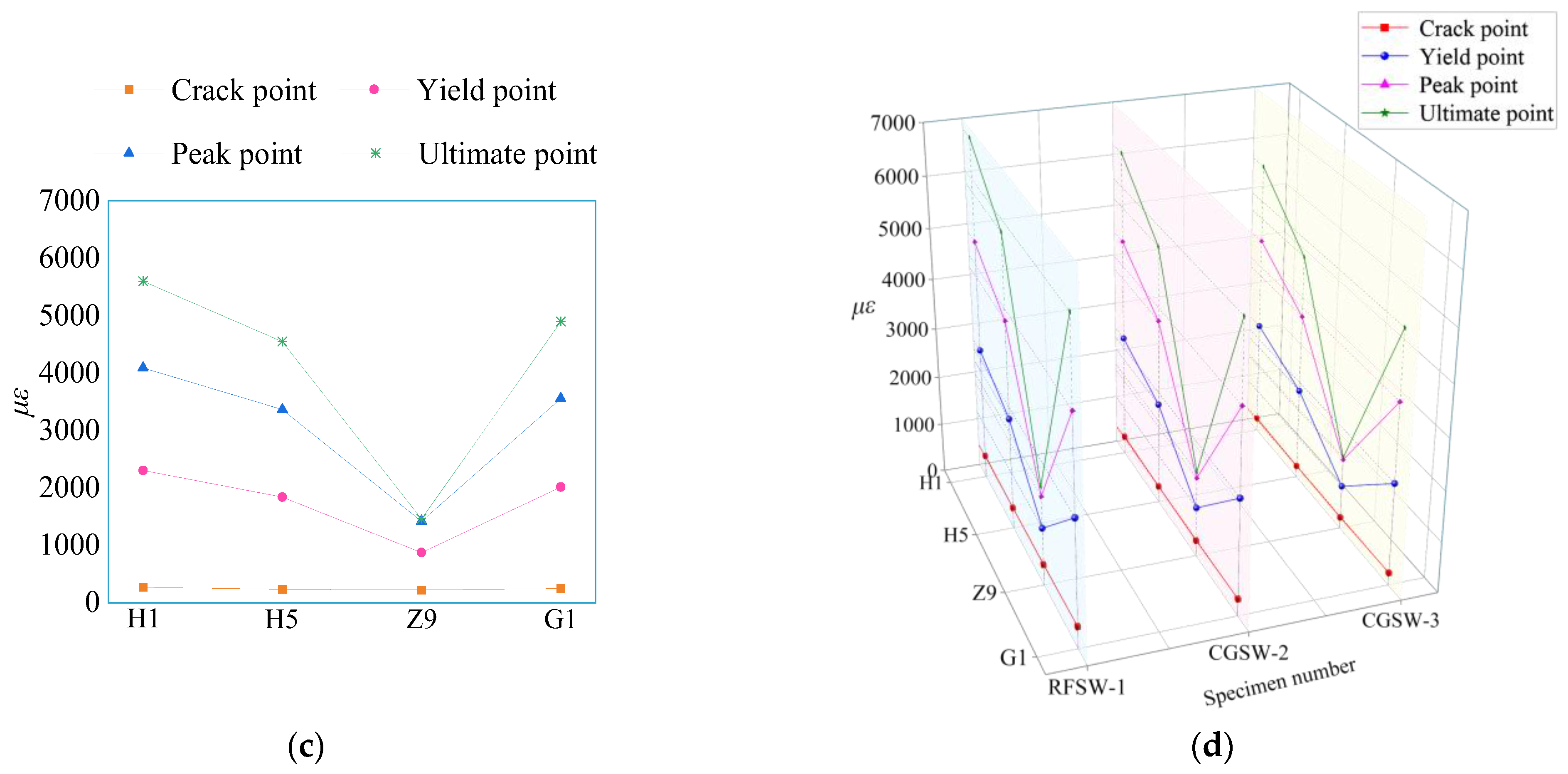
3.5. Steel Strain
3.6. Deformation Capacity
3.7. Stiffness Degradation
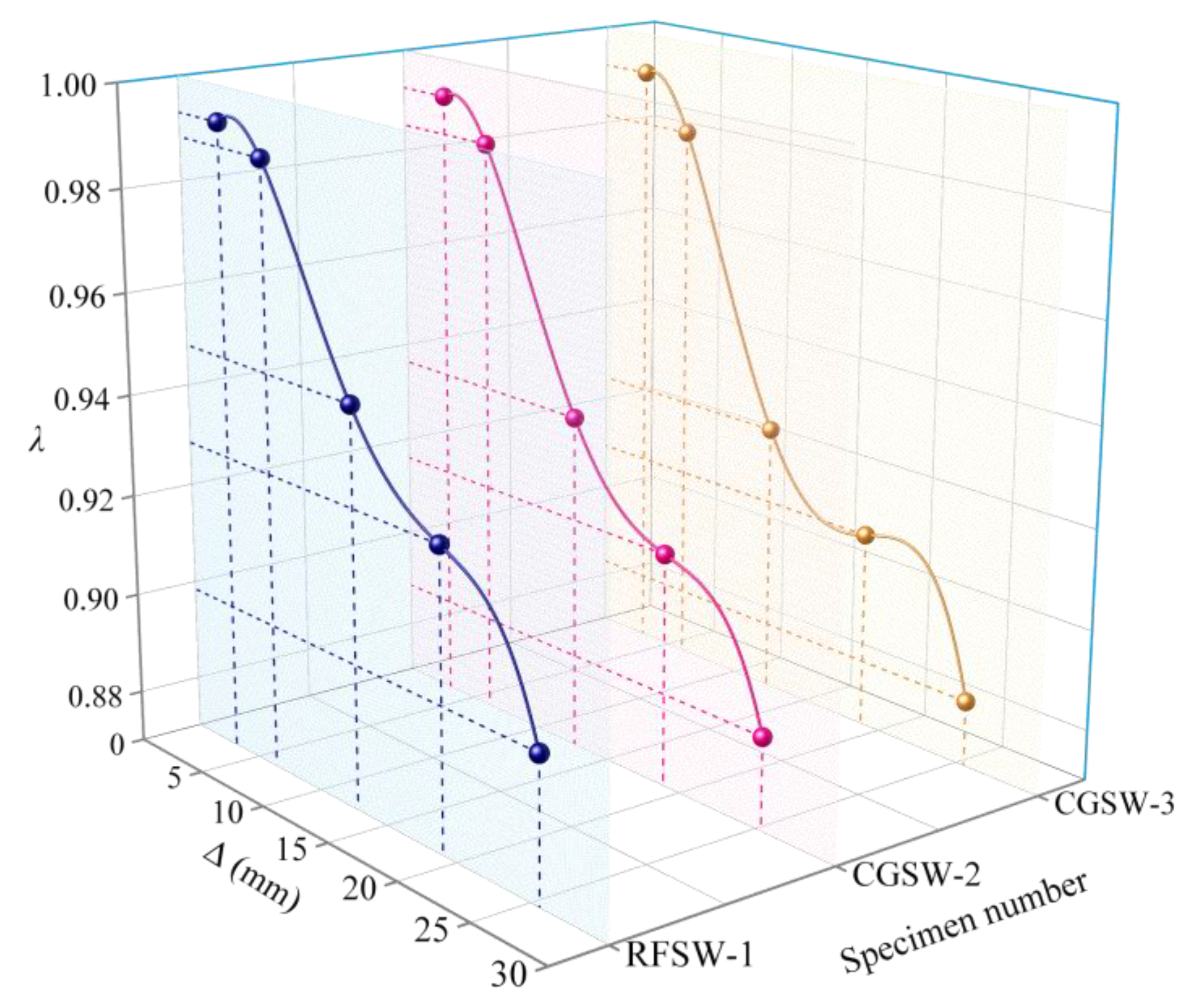
3.8. Strength Degradation
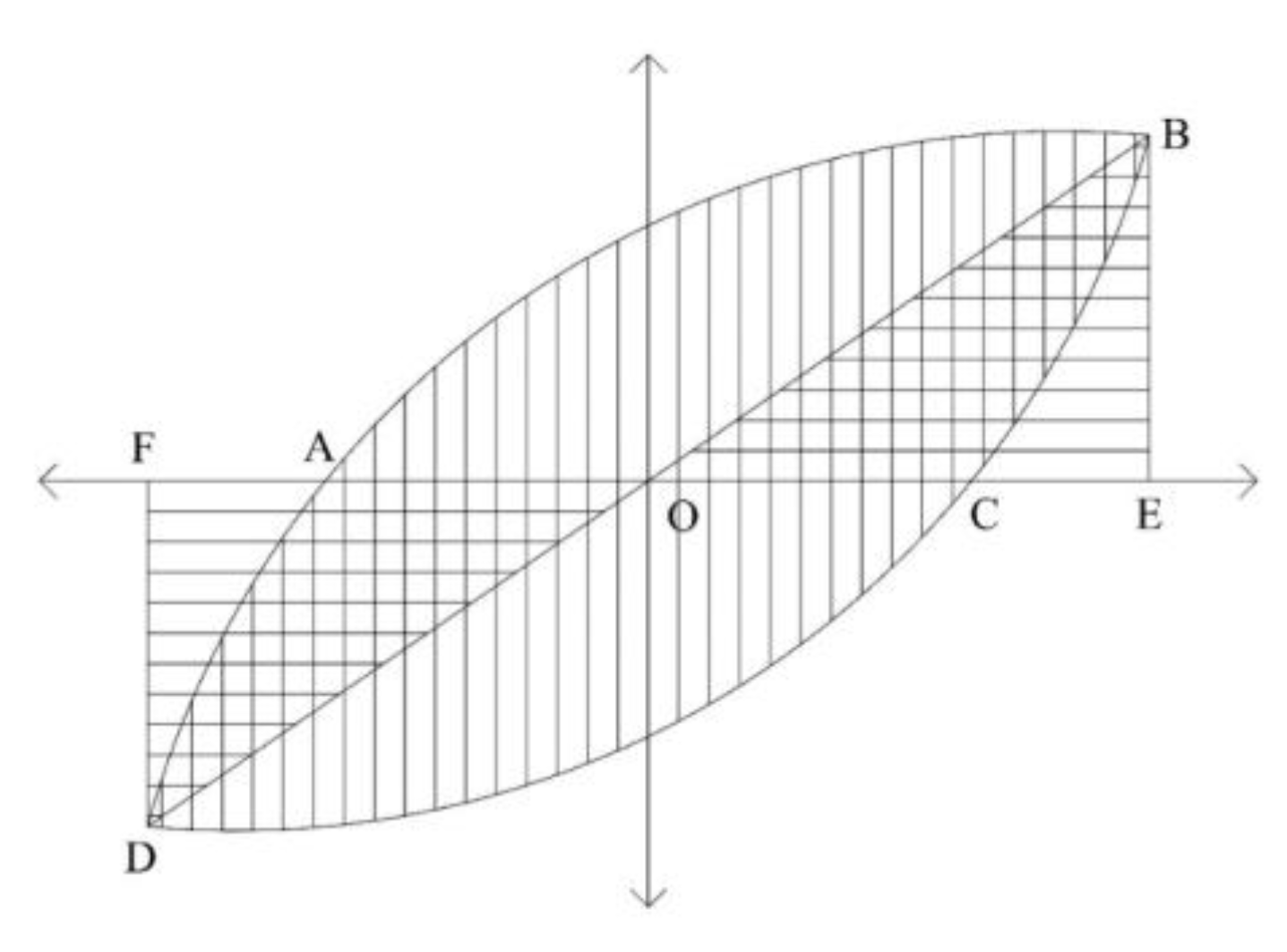
3.9. Energy Dissipation Capacity
4. Finite Element Analysis
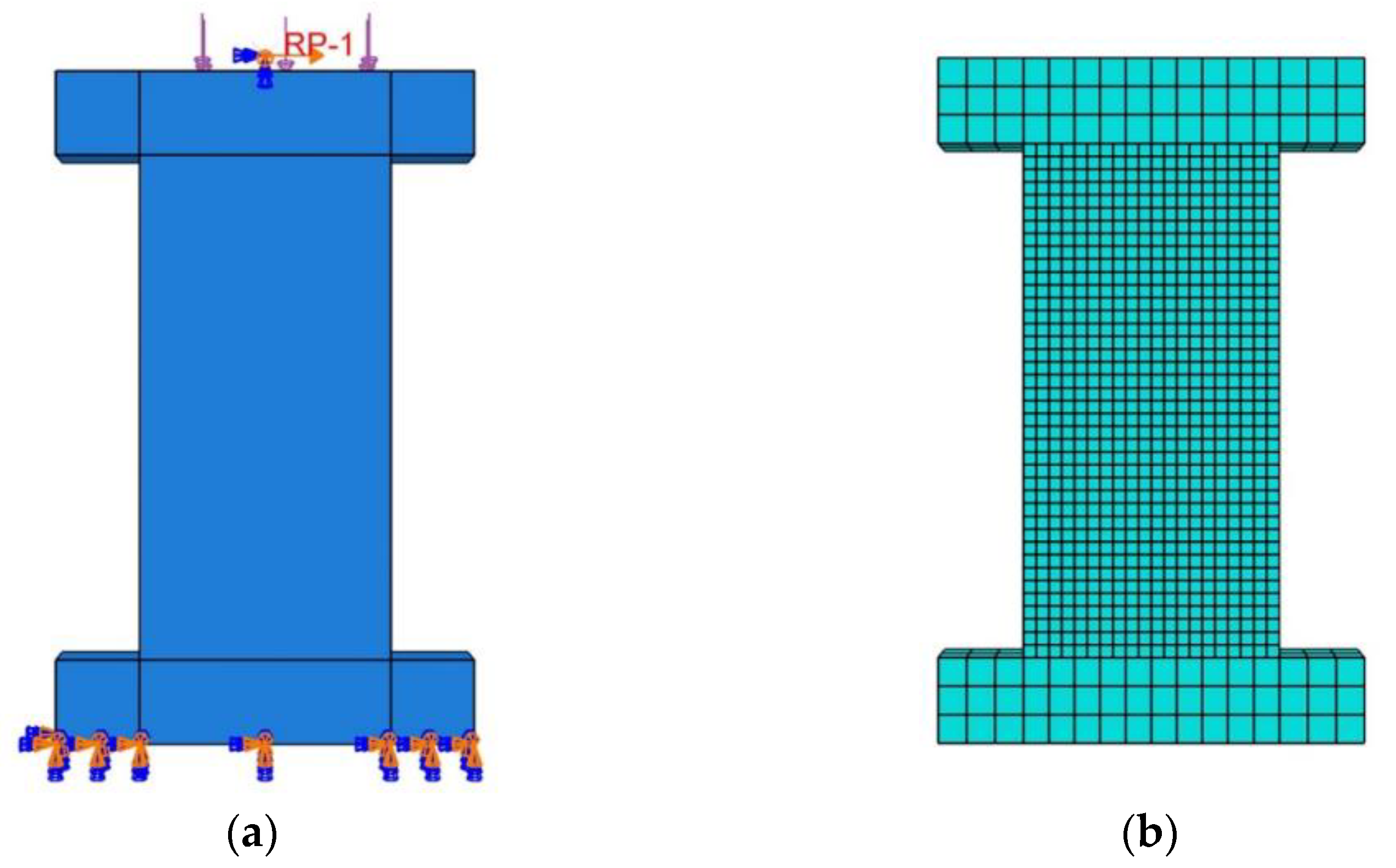
4.1. Finite Element Model Establishment
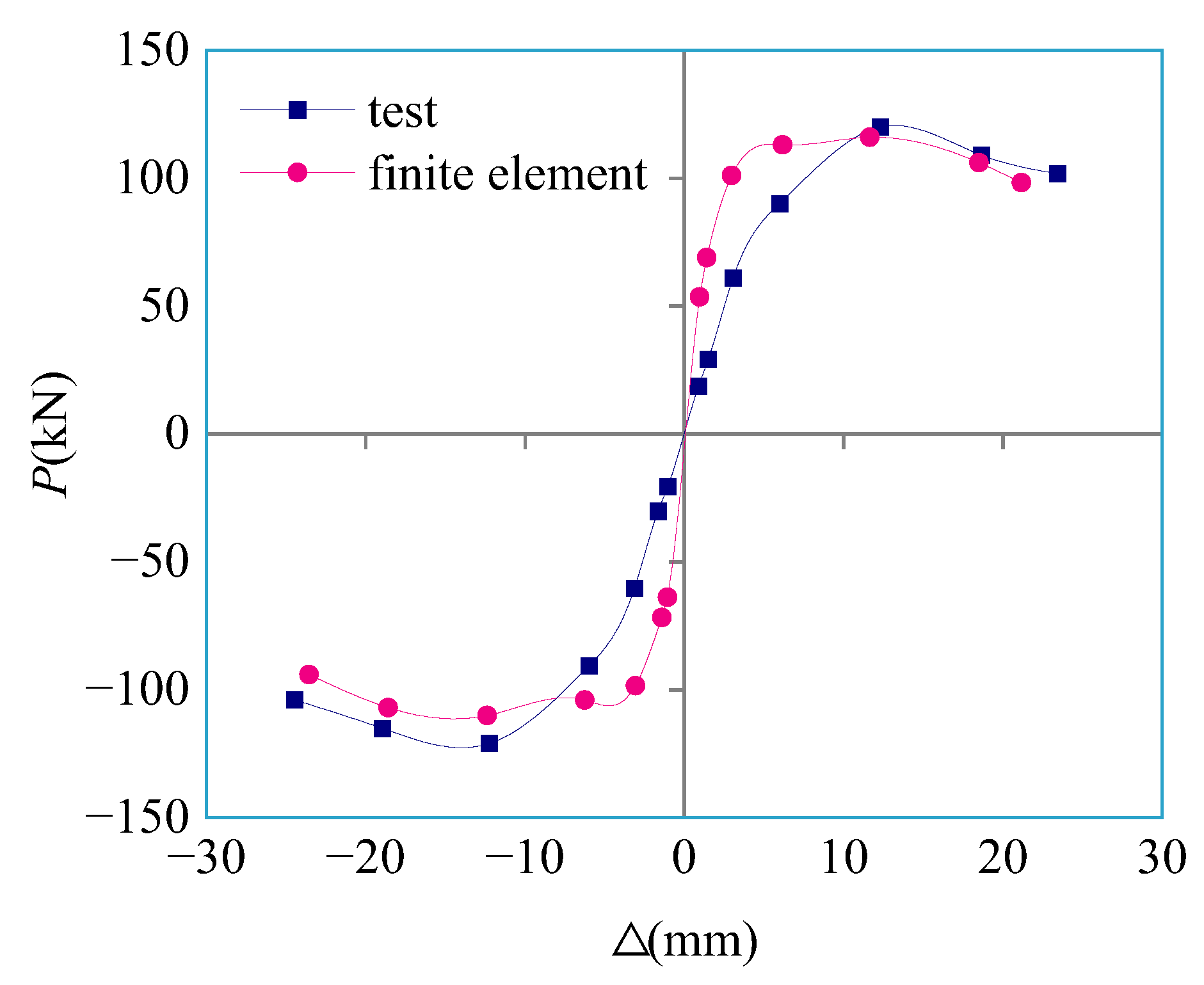
4.2. Finite Element Model Validation
4.3. Finite Element Model Parameter Analysis
5. Conclusions
- The crack development of shear wall specimen RFSW-1 with a coal gangue replacement rate of 0% was dispersed and uniform, and the crack width was small. The shear wall specimens CGSW-2 and CGSW-3 with coal gangue replacement rates of 50% and 100%, respectively, had denser crack development and larger crack widths.
- The stress performance and failure morphology of the three specimens were very similar, and the characteristics of the hysteretic and backbone curves were roughly the same. The failure modes of the three specimens were all typical bending-shear failure.
- By comparing the bearing capacity, deformation capacity, strength degradation, stiffness degradation, and energy dissipation capacity of the specimens, the bearing capacity, deformation capacity, strength degradation, and energy dissipation capacity of the specimens were negatively correlated with the replacement rate of coal gangue, but the difference was small. However, the stiffness degradation of the specimen is positively correlated with the replacement rate of coal gangue.
- Although the shear wall specimens CGSW-2 and CGSW-3 with coal gangue replacement rates of 50% and 100%, respectively, were worse than the shear wall specimen RFSW-1 with a coal gangue replacement rate of 0% in bearing capacity and deformation capacity, the difference is not obvious, and the requirements of seismic performance can be met. Through finite element simulation, it can also be seen that coal gangue concrete shear walls have the best seismic performance at the axial pressure ratio between 0.2 and 0.3. In addition, shear walls made using coal gangue can reduce the weight of the wall, save cost and reduce waste. Therefore, it is feasible to make shear walls using coal gangue concrete instead of conventional concrete.
6. Prospect
- The number of specimens can be increased, and the appropriate range of replacement can be determined by changing the coal gangue replacement rate.
- The different design parameters can be tested and studied, such as shear span-to-depth ratio, concrete strength grade, etc. Through the comparison of different design parameters, the seismic performance of the gangue concrete shear wall is further understood.
- The seismic performance of more structures, such as gangue concrete beams, plates, columns, nodes and frames can be studied. The research results can be applied to different building structures by comprehensively evaluating different gangue concrete structures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| The list contains the nomenclature employed in the current study. | |
| Latin Letters | |
| K | Secant stiffness |
| E | Energy dissipation coefficient |
| Greek Letters | |
| θ | Drift ratio |
| μ | Displacement ductility coefficient |
| Δ | Displacement |
| β | Stiffness attenuation coefficients |
| λ | Strength degradation coefficient |
| ξ | Equivalent viscous damping coefficient |
References
- Yao, Z.T.; Ji, X.S.; Sarker, P.K.; Tang, J.H.; Ge, L.Q.; Xia, M.S.; Xi, Y.Q. A comprehensive review on the applications of coal fly ash. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 141, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, G.; Ji, Y.; Li, J.; Hou, Z.; Dong, Z. Improving strength of calcinated coal gangue geopolymer mortars via increasing calcium content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, B.; Kityk, A.V.; Busch, M.; Huber, P. The structural and surface properties of natural and modified coal gangue. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Qu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Wu, L.L.; Luo, H.J.; Tong, G.P. Experimental study on ball milling and briquetting of coal gangue and lignite. J. Mater. Metall. 2021, 20, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.M.; Yang, Z.T.; Xue, X.Y.; Huang, L.P.; Wang, N.; Chen, Z.S. Bond properties of bimetallic steel bar in seawater sea-sand concrete at different ages. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.P. Feasibility of applying coal gangue to the aggregate. J. Huaqiao Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 1994, 15, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Chen, W.L.; Yang, R.J. Experimental study on basic properties of coal gangue aggregate. J. Build. Mater. 2010, 13, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Ni, W.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wang, S.; Gai, G.S.; Wang, W.K. Preparation and properties of autoclaved aerated concrete using coal gangue and iron ore tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 104, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, G.N.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, H.B. Study on application of spontaneous combustion coal gangue aggregate in ready-mixed concrete. J. Build. Mater. 2015, 5, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, G.W.; Dou, Y.W.; Li, S.W. Failure characteristics and strength analysis of spontaneous combustion gangue aggregate concrete under uniaxial compression. Silic. Bull. 2018, 37, 3528–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Dou, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, B.Q. Effects of the variety and content of coal gangue coarse aggregate on the mechanical properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 220, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Mix design for thermal insulation concrete using waste coal gangue as aggregate. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, S5-878–S5-884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Zhao, N. Influence of coal gangue aggregate grading on strength properties of concrete. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2015, 20, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Zhao, N. Properties of steel fiber reinforced coal gangue coarse aggregate concrete. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2014, 19, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.B.; Lü, M.X.; Luo, Y.B. Effects of surface-activated coal gangue aggregates on properties of cement-based materials. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Mater. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 28, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.L.; Li, J. Effect of coarse aggregate with different water absorption on strength and drying shrinkage of concrete. Silic. Bull. 2016, 35, 2396–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.L.; Hao, J.L.; Chen, L.; Lan, Y. Experimental study on strength and drying shrinkage crack of spontaneous combustion gangue concrete. Non-Met. Mines 2015, 38, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.Q.; Xing, S. Prediction of water transport and distribution of the gangue concrete. Silic. Bull. 2018, 37, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.Q. Experimental study on durability of the coal gauge concrete under acidic environment. Non-Met. Mines 2018, 41, 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.K.; Chen, Z.S.; Li, C.Y. A framework of structural damage detection for civil structures using a combined multi-scale convolutional neural network and echo state network. Eng. Comput 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.M.; Guo, M.H.; Wang, F.M. Seismic performance of reinforced coal gangue concrete low shear wall. J. South. China Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 1999, 27, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, Q.F.; Li, S.J. Nonlinear FEM analysis on seismic performance of beam to gangue concrete filled steel tubular column joints under reversed low cyclic loads. J. Shenyang Jianzhu Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2011, 27, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.F. Experimental study of reinforced coal gangue concrete beams under static loading. J. Anhui Inst. Archit. Ind. (Nat. Sci.) 2012, 20, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Xing, Y.; Han, J.J. Experimental research on mechanical behavior of coal gangue aggregate concrete pillar in different axial compression ratio. Ind. Constr. 2016, 46, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, B.Q.; Zhang, K. Flexural behavior of unidirectional laminated plate of spontaneous combustion gangue sand light concrete. J. Build. Mater. 2021, 24, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.Q.; Zhang, K. Study on flexural behavior of spontaneous combustion gangue sand light concrete composite slab. J. Build. Mater. 2021, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.Z. Effects of spontaneous-combustion coal gangue aggregate (SCGA) replacement ratio on flexural behavior of SCGA concrete beams. J. Build. Struct. 2020, 41, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.L.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.W.; Li, X.X.; Liu, H.; Lu, G.K. Experimental study on shear behavior of coal gangue concrete beams. J. Build. Struct. 2020, 41, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zheng, C.Y.; Zhao, Z.W.; Yang, B. Axial compression of glass fiber tube-gangue concrete-steel tubular hollow columns. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9930337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.L.; Yan, F.; Liu, H.Q. Experimental study on the seismic performance of coal gangue concrete frame columns. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 768, 012076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Gu, Y.; Liu, H. Experimental study on seismic behavior of gangue concrete frame middle joints with different gangue aggregate replacement rates. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1904, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ/T 101-2015; Specification for Seismic Test of Buildings. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- JGJ 3-2010; Technical Specification for Concrete Structures of Tall Building. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Zhou, M.; Pu, B.C.; Xu, M.; Tian, B.Y.; Zhong, Q. Effect of additional water and prewet time on the performance of spontaneous combustion gangue sand lightweight concrete. Silic. Bull. 2013, 32, 2421–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, L.M. Properties of Spontaneous Combustion Coal Gangue Coarse Aggregate and Its Influence on Concrete. J. Build. Mater. 2020, 23, 334–340+380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50081-2002; Standard for Test Method of Mechanical Properties on Ordinary Concrete. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- GB/T 228.1-2010; Metallic Materials-Tensile Testing-Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB 50011-2010; Code for Seismic Design of Buildings. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
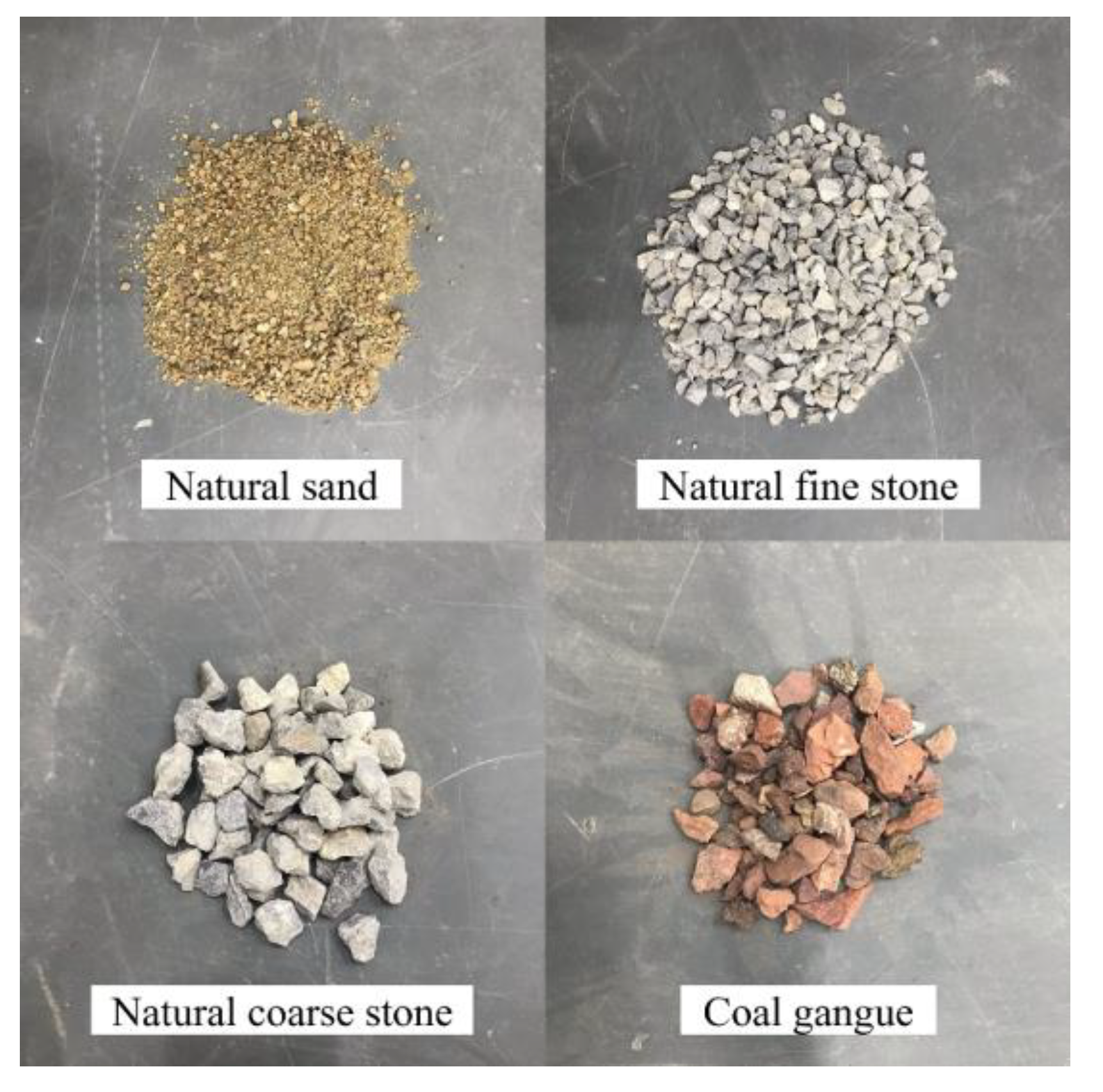





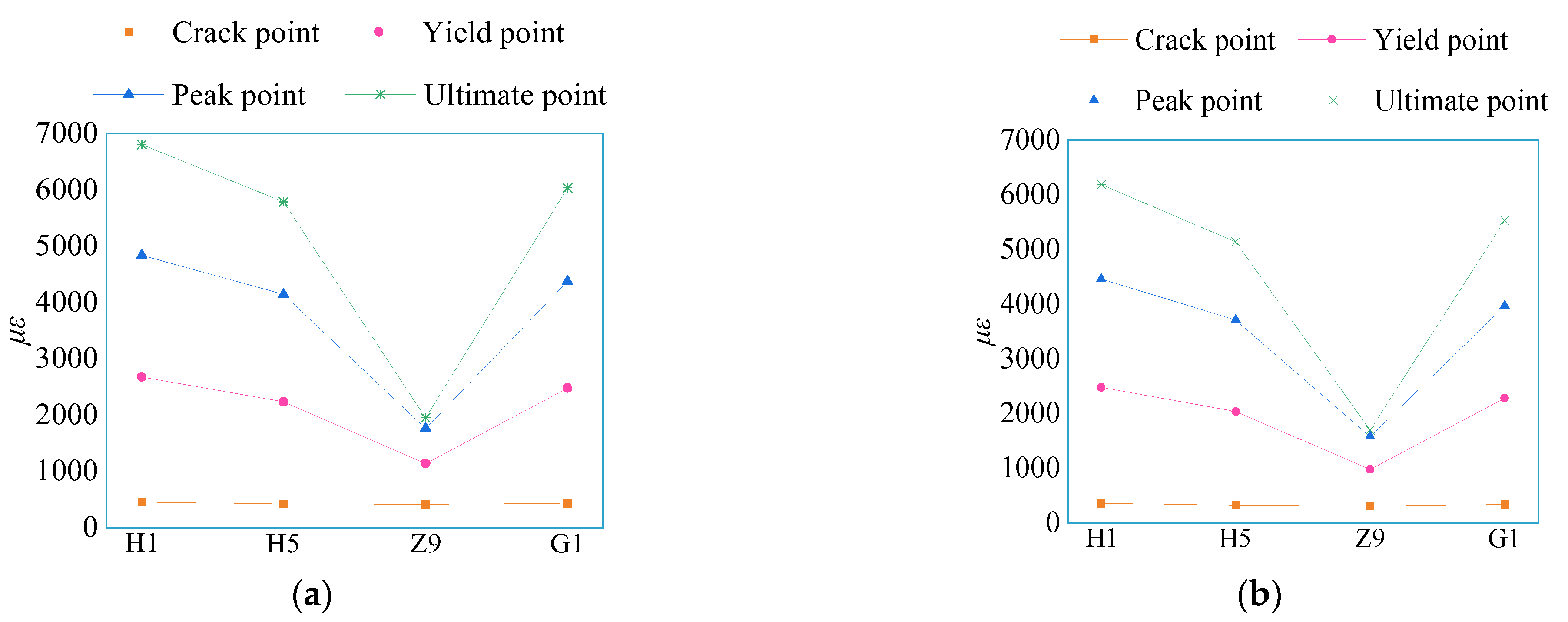



| Specimen Number | Specimen Size (mm) | Coal Gangue Replacement Rate | Coal Gangue Concrete Strength Grade | Axial Compression Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFSW-1 | 1200 × 600 × 120 | 0% | C30 | 0.1 |
| CGSW-2 | 1200 × 600 × 120 | 50% | C30 | 0.1 |
| CGSW-3 | 1200 × 600 × 120 | 100% | C30 | 0.1 |
| Chemical Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal gangue (%) | 59.34 | 25.28 | 4.66 | 2.00 | 0.20 | 2.53 | 1.15 |
| Natural coarse stone (%) | 4.05 | 1.60 | 0.77 | 0.67 | 60.44 | 0.28 | 0.11 |
| Specimen Number | Mix Proportion (kg/m3) | Mechanical Properties | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | Water | Fly Ash | Water Reducing Agent | Natural Sand | Natural Stone | Coal Gangue | Compressive Strength (N/mm2) | Elastic Modulus (×104 N/mm2) | |
| RFSW-1 | 262.50 | 150.00 | 70.00 | 4.11 | 753.00 | 1040.00 | – | 38.42 | 3.18 |
| CGSW-2 | 348.00 | 178.00 | 87.00 | 7.91 | 860.00 | 395.00 | 395.00 | 35.54 | 3.11 |
| CGSW-3 | 376.00 | 171.25 | 94.00 | 7.05 | 769.00 | – | 710.00 | 33.86 | 3.05 |
| Rebar Specifications | Diameter (mm) | Elongation (%) | Yield Strength (N/mm2) | Ultimate Strength (N/mm2) | Elastic Modulus (×105 N/mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRB335 | 6 | 16 | 508 | 665 | 2.1 |
| HRB335 | 12 | 14 | 465 | 658 | 2.0 |
| Loading Step | Displacement Amplitude (mm) | Cycle Number | Drift Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ±1.00 | 1 | 1/1500 |
| 2 | ±1.50 | 1 | 1/1000 |
| 3 | ±3.00 | 2 | 1/500 |
| 4 | ±6.25 | 2 | 1/240 |
| 5 | ±12.50 | 2 | 1/120 |
| 6 | ±18.75 | 2 | 1/80 |
| 7 | ±25.00 | 2 | 1/60 |
| Specimen Number | Characteristic Point Bearing Capacity (kN) | Yield Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crack Load | Yield Load | Peak Load | Ultimate Load | ||
| RFSW-1 | 68.980 | 102.091 | 137.961 | 117.267 | 0.74 |
| CGSW-2 | 66.052 | 96.394 | 128.525 | 109.246 | 0.75 |
| CGSW-3 | 62.716 | 93.427 | 120.905 | 102.769 | 0.77 |
| Specimen Number | Characteristic Point Displacement (mm) | Ductility Coefficient | Drift Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crack Displacement | Yield Displacement | Peak Displacement | Ultimate Displacement | |||
| RFSW-1 | 2.67 | 6.24 | 12.78 | 24.71 | 3.96 | 1/52 |
| CGSW-2 | 2.82 | 6.48 | 12.67 | 24.48 | 3.78 | 1/53 |
| CGSW-3 | 2.98 | 6.68 | 12.47 | 23.95 | 3.59 | 1/54 |
| Specimen Number | Characteristic Point Secant Stiffness | βyc | βyc | βum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crack Stiffness | Yield Stiffness | Peak Stiffness | Ultimate Stiffness | ||||
| RFSW-1 | 22.84 | 15.76 | 10.78 | 5.40 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.53 |
| CGSW-2 | 20.42 | 14.57 | 10.14 | 4.86 | 0.71 | 0.7 | 0.48 |
| CGSW-3 | 18.05 | 13.99 | 9.70 | 4.29 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 0.44 |
| RFSW-1 | CGSW-2 | CGSW-3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loading Displacement | ξ | Loading Displacement | ξ | Loading Displacement | ξ |
| 1.00 | 0.159 | 1.00 | 0.116 | 1.00 | 0.079 |
| 1.50 | 0.176 | 1.50 | 0.141 | 1.50 | 0.111 |
| 3.00 | 0.182 | 3.00 | 0.147 | 3.00 | 0.114 |
| 0.189 | 0.155 | 0.120 | |||
| 6.25 | 0.190 | 6.25 | 0.173 | 6.25 | 0.161 |
| 0.194 | 0.177 | 0.167 | |||
| 12.50 | 0.195 | 12.50 | 0.184 | 12.50 | 0.173 |
| 0.193 | 0.187 | 0.177 | |||
| 18.75 | 0.200 | 18.75 | 0.188 | 18.75 | 0.178 |
| 0.196 | 0.189 | 0.181 | |||
| 25.00 | 0.207 | 25.00 | 0.192 | 25.00 | 0.187 |
| 0.203 | 0.195 | 0.190 | |||
| Data Type | Characteristic Point Bearing Capacity (kN) | Characteristic Point Displacement (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield Load | Peak Load | Peak Displacement | Ultimate Displacement | |
| test | 93.427 | 120.905 | 12.47 | 23.95 |
| finite element | 101.837 | 113.099 | 12.13 | 22.36 |
| Error (%) | 9.00 | 6.46 | 2.73 | 6.64 |
| Specimen Number | Axial Pressure Ratio | Characteristic Point Bearing Capacity (kN) | Characteristic Point Displacement (mm) | Ductility Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield Load | Peak Load | Yield Displacement | Ultimate Displacement | |||
| CGSWN-1 | 0.1 | 101.837 | 113.099 | 3.76 | 22.36 | 5.95 |
| CGSWN-2 | 0.2 | 123.724 | 137.054 | 3.72 | 21.80 | 5.86 |
| CGSWN-3 | 0.3 | 137.069 | 152.586 | 3.69 | 21.38 | 5.79 |
| CGSWN-4 | 0.4 | 152.381 | 163.810 | 3.63 | 19.54 | 5.38 |
| CGSWN-5 | 0.5 | 165.397 | 170.159 | 3.61 | 19.11 | 5.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, J.; Tse, T.K.T.; Li, C.Y.; Fu, Y. Experimental Study on the Seismic Performance of Shear Walls with Different Coal Gangue Replacement Rates. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10622. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010622
Wang S, Liu H, Wang Y, Qiao Y, Wang L, Bai J, Tse TKT, Li CY, Fu Y. Experimental Study on the Seismic Performance of Shear Walls with Different Coal Gangue Replacement Rates. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(20):10622. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010622
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shixin, Haiqing Liu, Yue Wang, Yizhi Qiao, Liang Wang, Jie Bai, Tim K. T. Tse, Cruz Y. Li, and Yunfei Fu. 2022. "Experimental Study on the Seismic Performance of Shear Walls with Different Coal Gangue Replacement Rates" Applied Sciences 12, no. 20: 10622. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010622
APA StyleWang, S., Liu, H., Wang, Y., Qiao, Y., Wang, L., Bai, J., Tse, T. K. T., Li, C. Y., & Fu, Y. (2022). Experimental Study on the Seismic Performance of Shear Walls with Different Coal Gangue Replacement Rates. Applied Sciences, 12(20), 10622. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010622






