Aerial Mapping of Coseismic Surface Rupture of 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo Earthquake, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Tectonic Setting
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. D-InSAR
3.2. Drone Mapping
4. Results
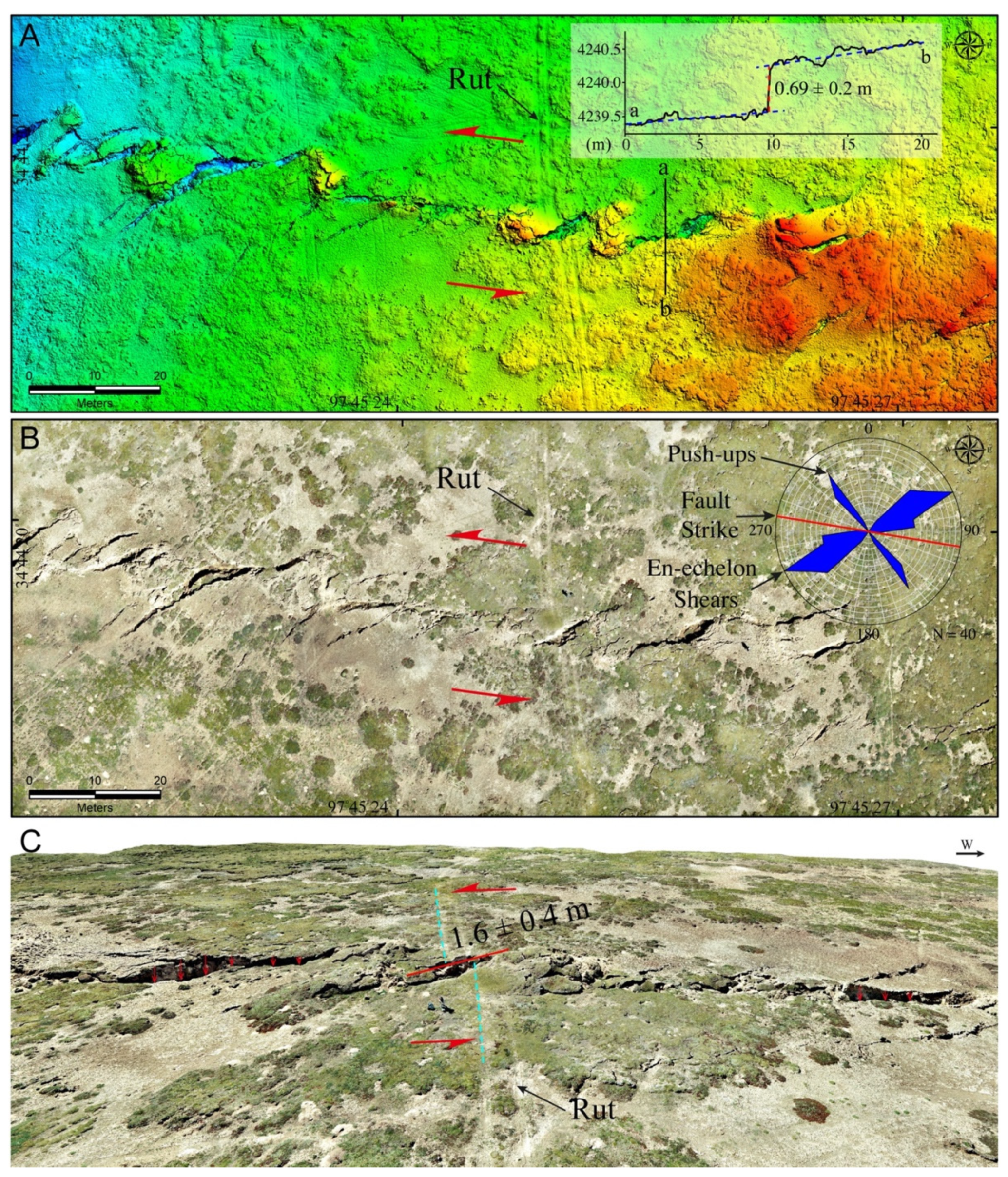
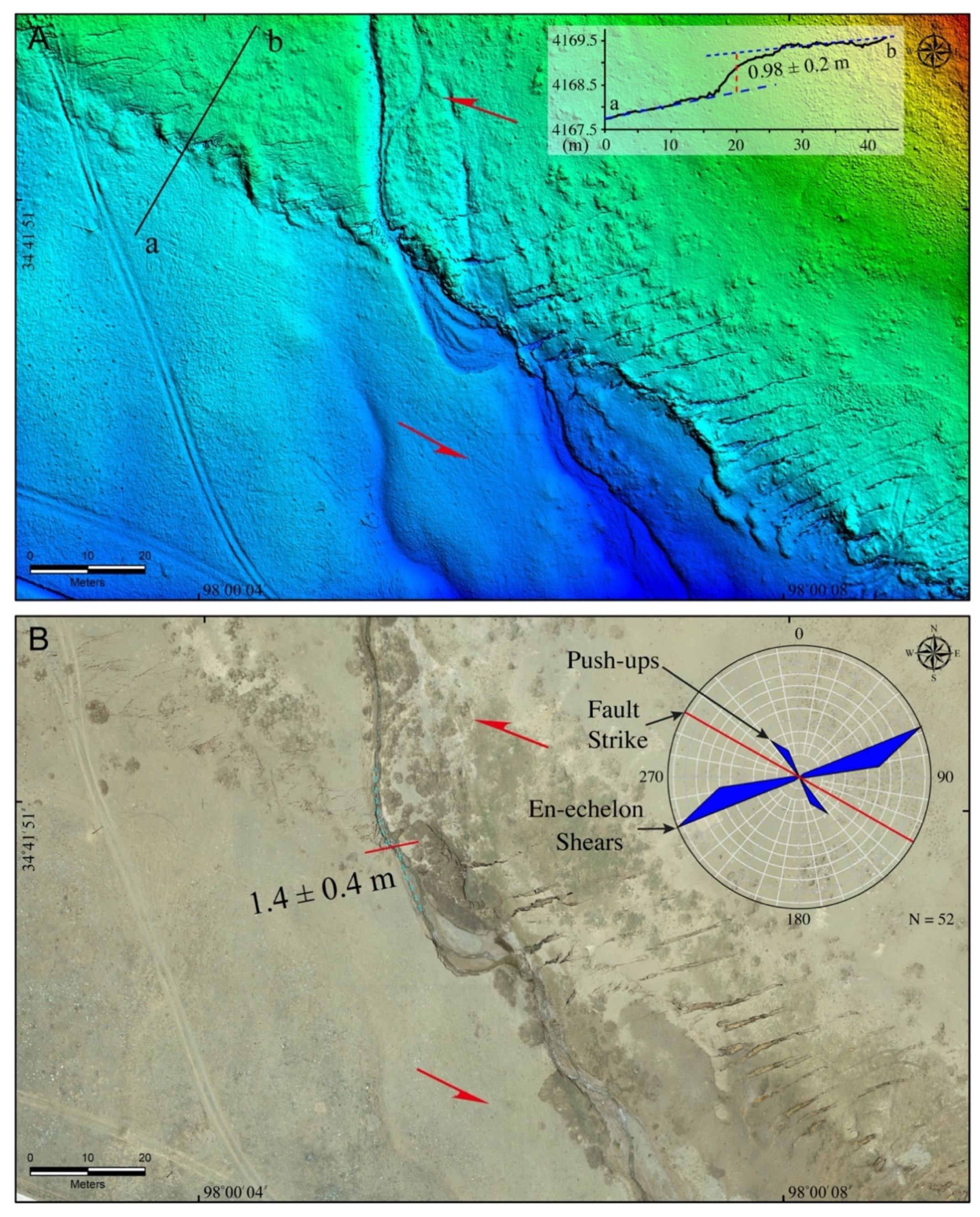
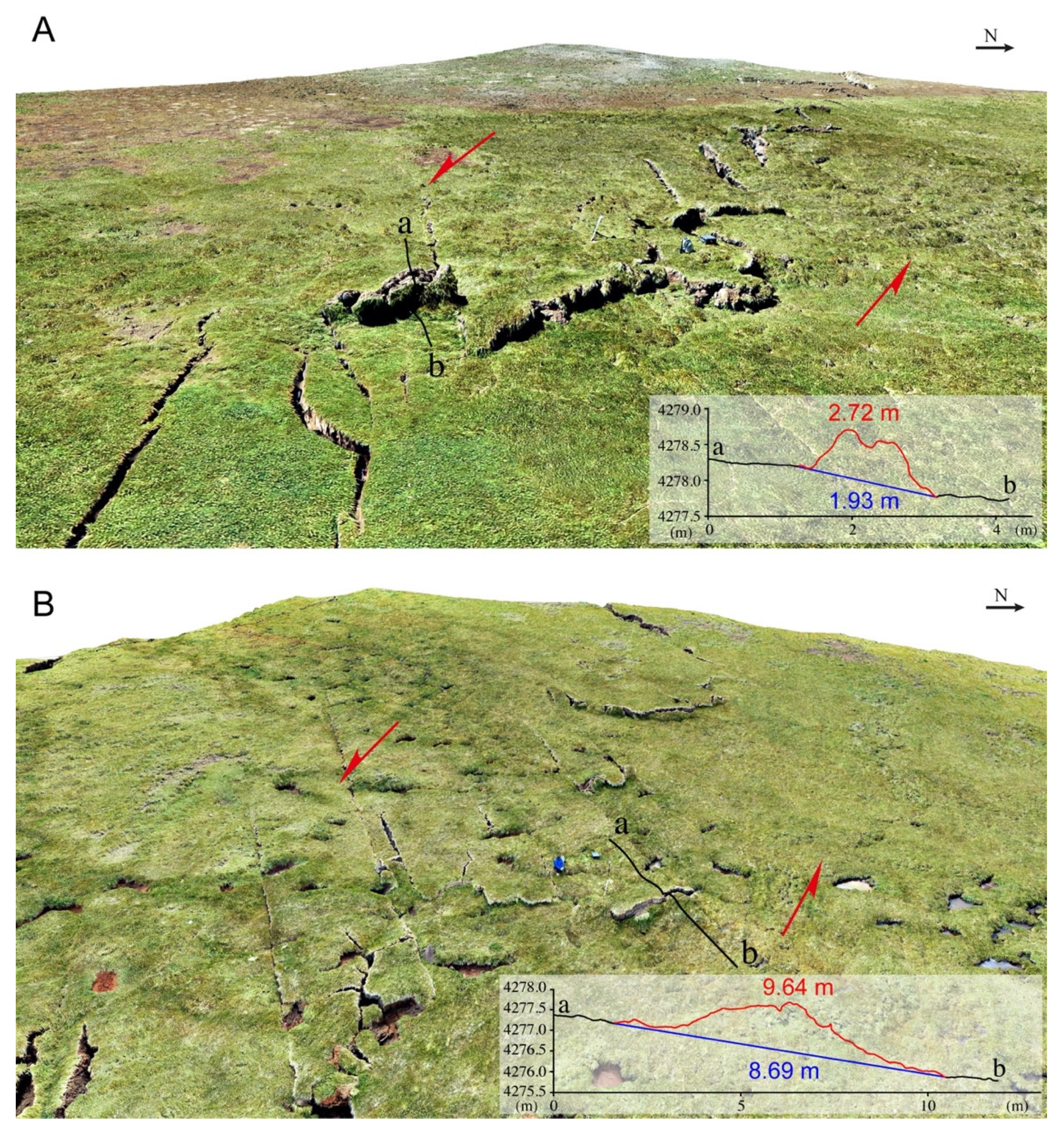
4.1. Coseismic Surface Rupture
4.2. Simple Shear Fractures
4.3. Fault Offset
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, R.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L. Complex Slip Distribution of the 2021 Mw 7.4 Maduo, China, Earthquake: An Event Occurring on the Slowly Slipping Fault. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2021, 93, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qu, C.; Zhao, D.; Ma, C.; Shan, X. Rupture Kinematics and Coseismic Slip Model of the 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo (China) Earthquake: Implications for the Seismic Hazard of the Kunlun Fault. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Fialko, Y. Coseismic and Early Postseismic Deformation Due to the 2021 M7.4 Maduo (China) Earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, G.; Crampé, F.; King, G. Evidence of Nonlinear Elasticity of the Crust from the Mw7.6 Manyi (Tibet) Earthquake. Science 1999, 286, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Yu, G.; Chen, G. Surface Rupture of the Kunlunshan Earthquake (Ms 8.1), Northern Tibetan Plateau, China. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2002, 73, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Zeng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, L.; Tapponnier, P.; Sun, J.; Xing, X.; Hu, G.; Xu, Q.; Zeng, L.; Ding, L.; et al. Co-seismic ruptures of the 12 May 2008, Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan: East–west crustal shortening on oblique, parallel thrusts along the eastern edge of Tibet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 286, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.M.; Zheng, J.J.; Guan, B.B.; Fu, B.H.; Shi, P.L.; Du, J.G.; Xie, C.; Liu, L. Coseismic Surface Rupture Structures Associated with 2010 Ms 7.1 Yushu Earthquake, China. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2012, 83, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Pan, J.; Lin, A.; Sun, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, K.; Chevalier, M.; Yun, K. Coseismic Surface Ruptures Associated with the 2014 Mw6.9 Yutian Earthquake on the Altyn Tagh Fault, Tibetan Plateau. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2016, 106, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Shi, P.; Guo, H.; Okuyama, S.; Ninomiya, Y.; Wright, S. Surface deformation related to the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, and mountain building of the Longmen Shan, eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 805–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, Z. Structural analysis of the 1997 Mw 7.5 Manyi earthquake and the kinematics of the Manyi fault, central Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 179, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Li, T.; Su, P.; Sun, H.; Ha, G.; Guo, P.; Chen, G.; Thompson Jobe, J. Large Surface-Rupture Gaps and Low Surface Fault Slip of the 2021 Mw 7.4 Maduo Earthquake Along a Low-Activity Strike-Slip Fault, Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096874. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Li, H.; Chevalier, M.-L.; Tapponnier, P.; Bai, M.; Li, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, D.; Wu, K.; Wang, P.; et al. Co-seismic rupture of the 2021, M 7.4 Maduo earthquake (northern Tibet): Short-cutting of the Kunlun fault big bend. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 594, 117703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Briole, P.; Arnaud, A. Deflation of Mount Etna monitored by spaceborne radar interferometry. Nature 1995, 375, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delouis, B.; Giardini, D.; Lundgren, P.; Salichon, J. Joint Inversion of InSAR, GPS, Teleseismic, and Strong-Motion Data for the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Earthquake Slip: Application to the 1999 Izmit Mainshock. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2002, 92, 278–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Shan, X.; Delouis, B.; Qu, C.; Balestra, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G. Rupture history of the 2010 Ms 7.1 Yushu earthquake by joint inversion of teleseismic data and InSAR measurements. Tectonophysics 2013, 584, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, E.J.; Sladen, A.; Li, Z.; Avouac, J.-P.; Bürgmann, R.; Ryder, I. Kinematic fault slip evolution source models of the 2008 M7.9 Wenchuan earthquake in China from SAR interferometry, GPS and teleseismic analysis and implications for Longmen Shan tectonics. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 194, 1138–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlgren, S.G. The nucleation and evolution of Riedel shear zones as deformation bands in porous sandstone. J. Struct. Geol. 2001, 23, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sylvester, A.G. Strike-slip faults. GSA Bull. 1988, 100, 1666–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gai, H.; Kang, W. Typical Riedel shear structures of the coseismic surface rupture zone produced by the 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo earthquake, Qinghai, China, and the implications for seismic hazards in the block interior. Nat. Hazard. Res. 2021, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergerat, F.; Angelier, J. Mechanical behaviour of the Árnes and Hestfjall Faults of the June 2000 earthquakes in Southern Iceland: Inferences from surface traces and tectonic model. J. Struct. Geol. 2003, 25, 1507–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelier, J.; Bergerat, F.; Bellou, M.; Homberg, C. Co-seismic strike–slip fault displacement determined from push-up structures: The Selsund Fault case, South Iceland. J. Struct. Geol. 2004, 26, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Fialko, Y. Shallow slip deficit due to large strike-slip earthquakes in dynamic rupture simulations with elasto-plastic off-fault response. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 186, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roten, D.; Olsen, K.B.; Day, S.M. Off-fault deformations and shallow slip deficit from dynamic rupture simulations with fault zone plasticity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 7733–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, P.; Tapponnier, P. Cenozoic Tectonics of Asia: Effects of a Continental Collision. Science 1975, 189, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, G.; Tapponnier, P. Formation and evolution of strike-slip faults, rifts, and basins during the India-Asia Collision: An experimental approach. J. Geophy. Res. Solid Earth 1988, 93, 15085–15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouac, J.-P.; Tapponnier, P. Kinematic model of active deformation in central Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapponnier, P.; Zhiqin, X.; Roger, F.; Meyer, B.; Arnaud, N.; Wittlinger, G.; Jingsui, Y. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet plateau. Science 2001, 294, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, P.; Molnar, P. Active Deformation of Asia: From Kinematicsto Dynamics. Science 1997, 278, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flesch, L.M.; Haines, A.J.; Holt, W.E. Dynamics of the India-Eurasia collision zone. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2001, 106, 16435–16460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.Z.; Freymueller, J.T.; Bilham, R.; Larson, K.M.; Lai, X.; You, X.; Niu, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Present-day crustal deformation in China constrained by global positioning system measurements. Science 2001, 294, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Shen, Z.; Min, W.; Gan, W.; Bürgmann, R.; Molnar, P.; Qi, W.; Niu, Z.; Sun, J.; Wu, J. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data. Geology 2004, 32, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilotte, J.P.; Daignières, M.; Madariaga, R. Numerical modeling of intraplate deformation: Simple mechanical models of continental collision. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1982, 87, 10709–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Shen, Z.-K. Block-like versus distributed crustal deformation around the northeastern Tibetan plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 140, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J. Aerial Mapping of Coseismic Surface Rupture of 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo Earthquake, China. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 13005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122413005
Guo J. Aerial Mapping of Coseismic Surface Rupture of 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo Earthquake, China. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):13005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122413005
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jianming. 2022. "Aerial Mapping of Coseismic Surface Rupture of 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo Earthquake, China" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 13005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122413005
APA StyleGuo, J. (2022). Aerial Mapping of Coseismic Surface Rupture of 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo Earthquake, China. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 13005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122413005





