Analysis of the Influence and Propagation Law of Urban Rail Transit Disruptions: A Case Study of Beijing Rail Transit
Abstract
1. Introduction
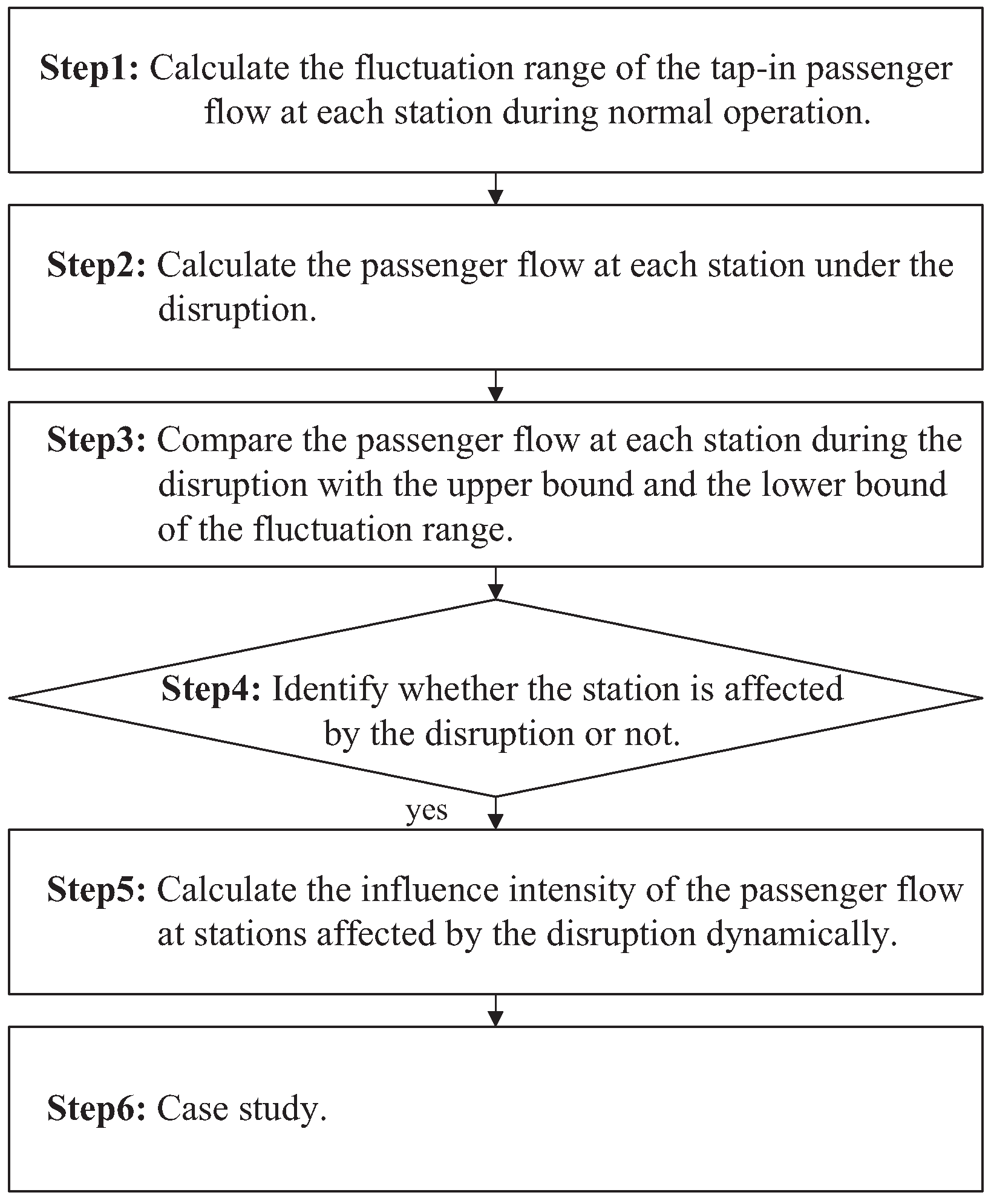
2. Identification of Abnormal Stations and Estimation of Influence Intensity
2.1. Identification of Stations Affected by Disruptions
2.2. Influence Intensity of Passenger Flow at Stations
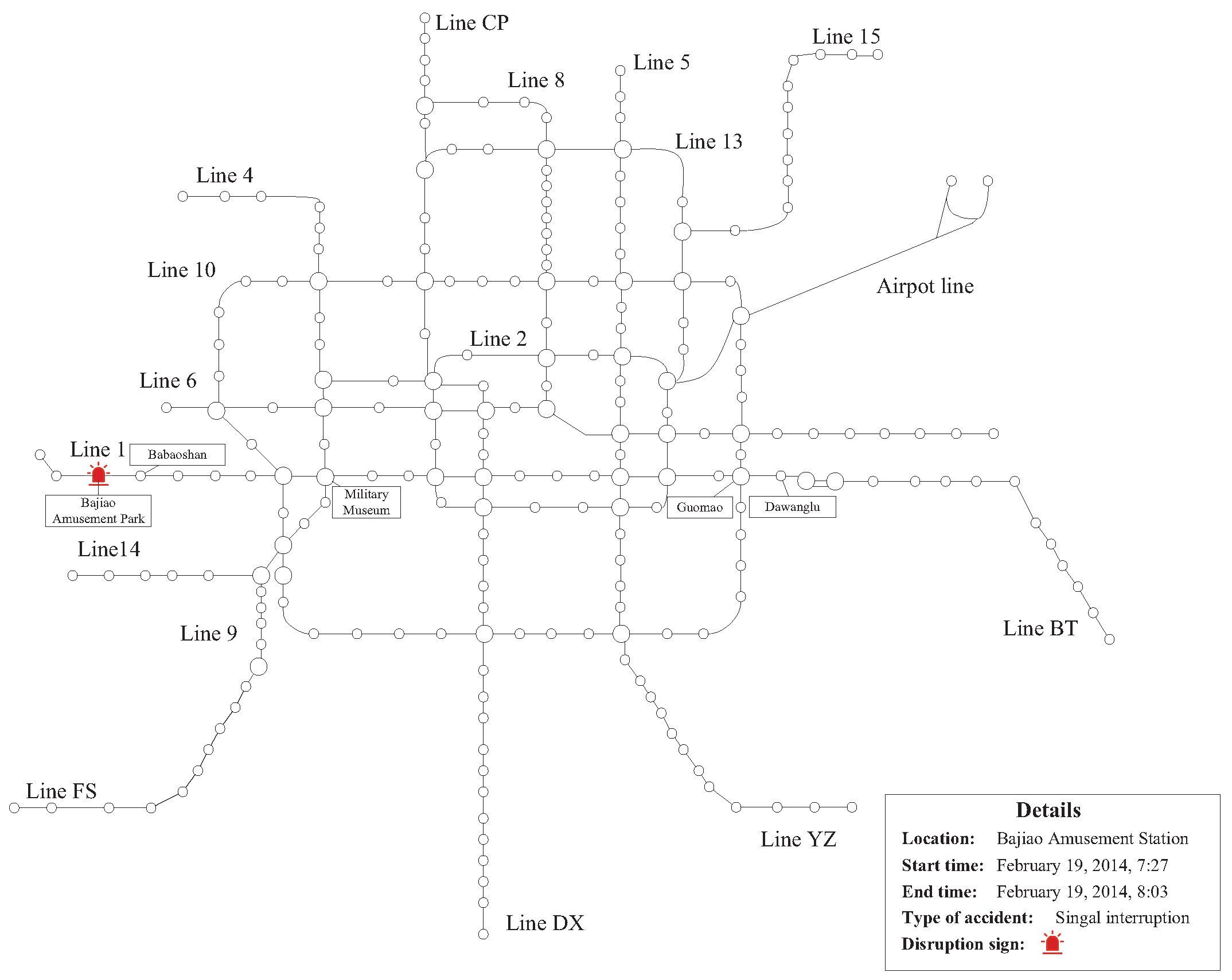
3. Case Study
3.1. Data Description
3.2. Results and Analysis of Abnormal Stations
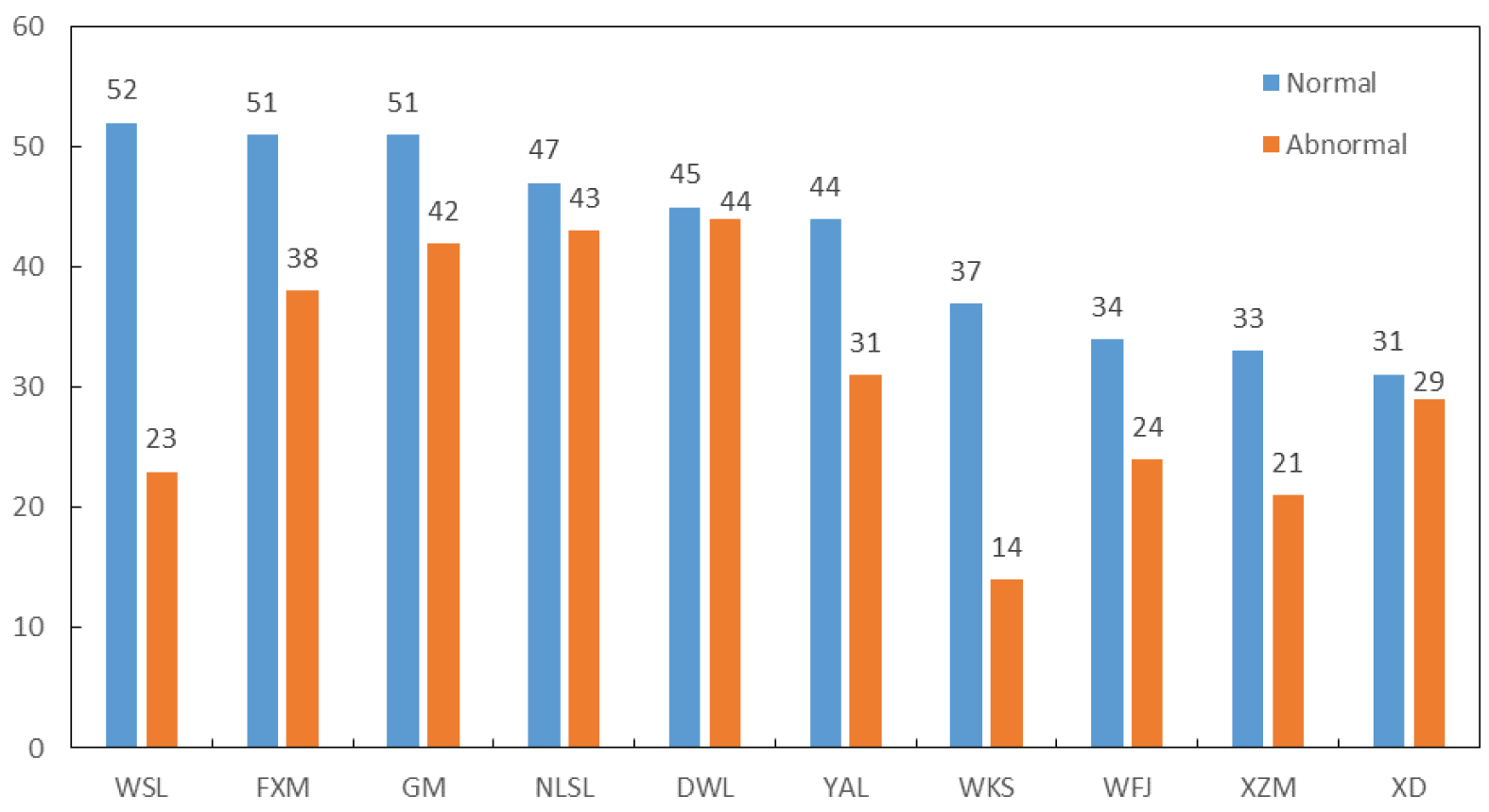
3.2.1. Analysis of Abnormal Stations in the Whole Network
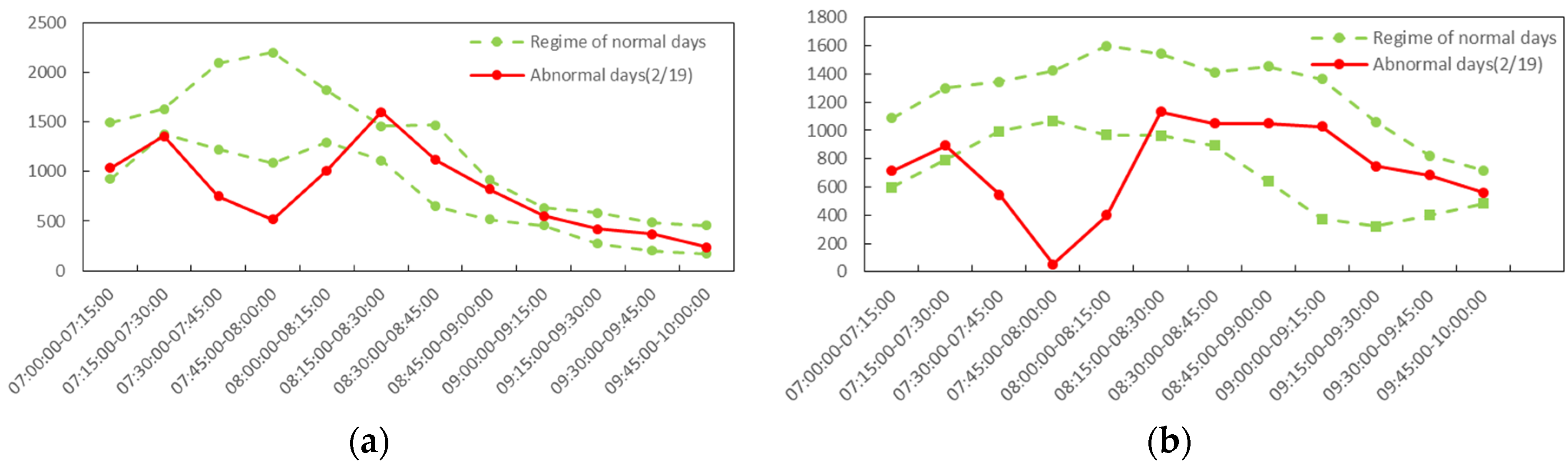
3.2.2. Analysis of Representative Ordinary Stations
3.2.3. Analysis of Representative Transfer Stations
3.3. Analysis of Influence Intensity
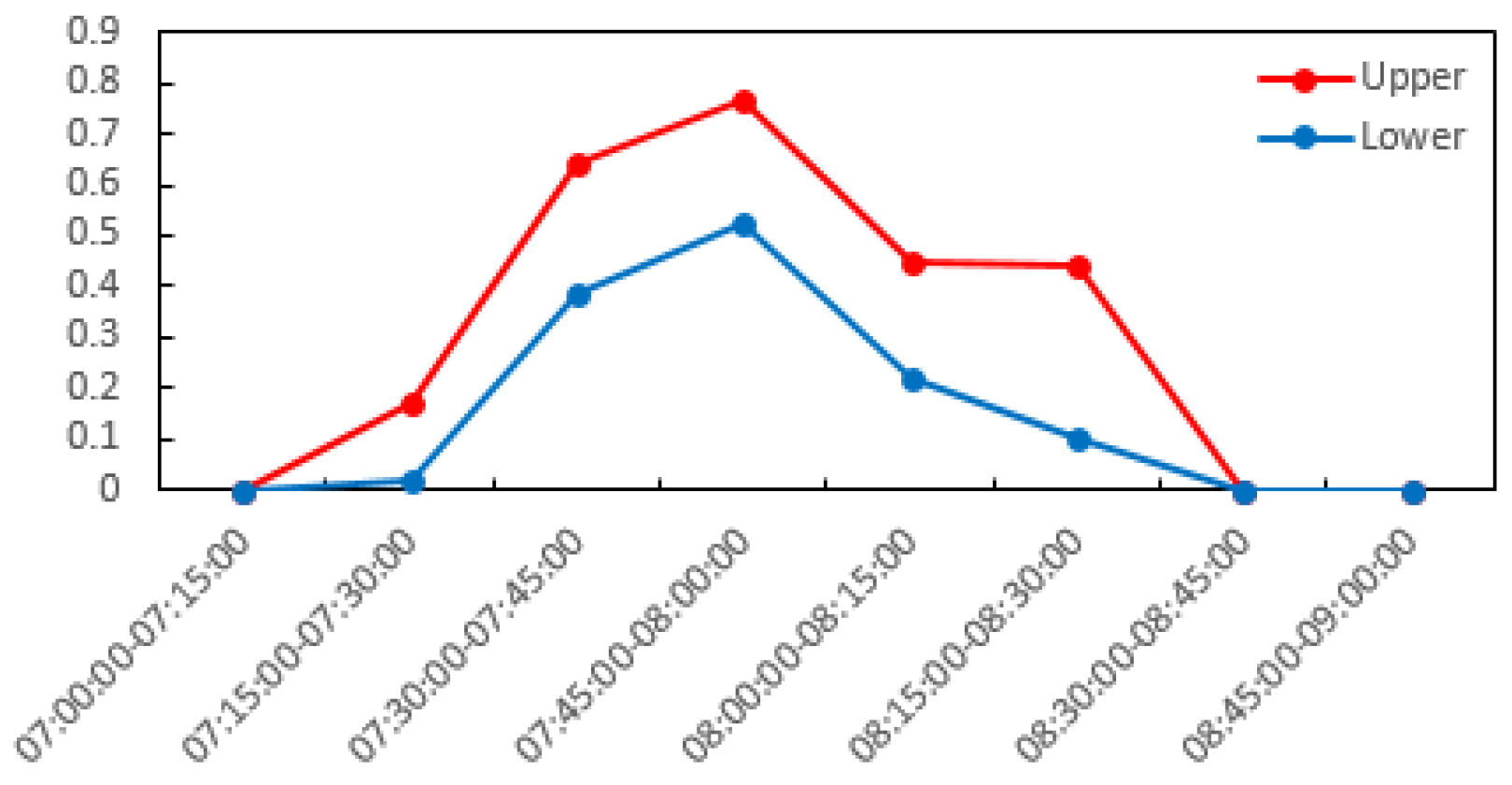
3.3.1. Influence Intensity Analysis from the Perspective of the Whole Network
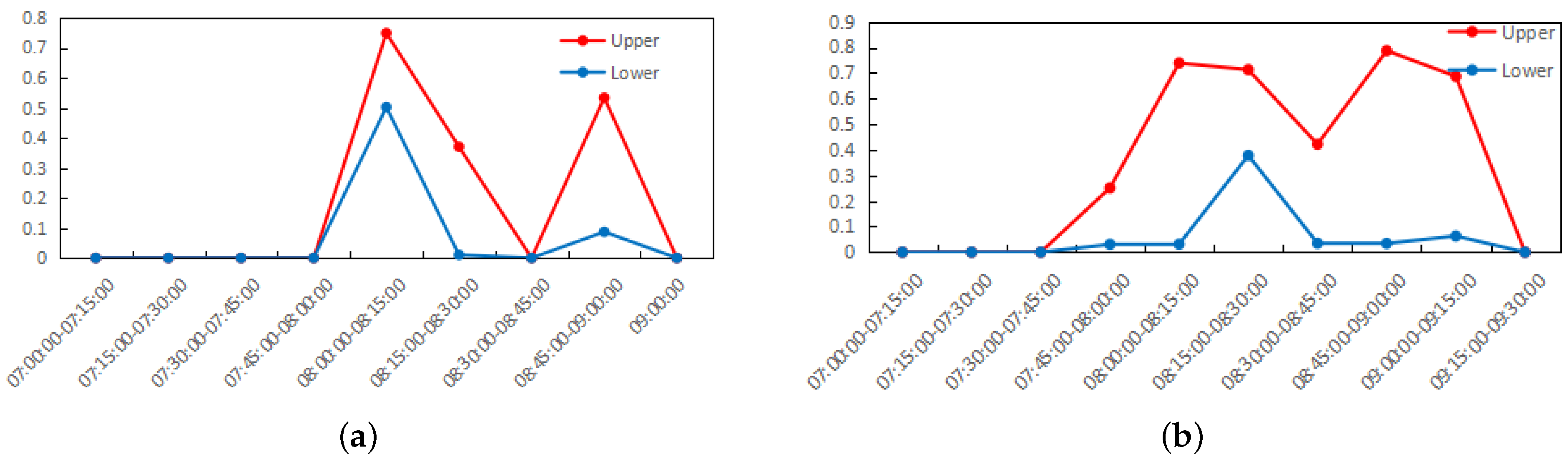
3.3.2. Influence Intensity Analysis from the Perspective of Representative Stations
3.4. Analysis of Influenced OD Passenger Flow
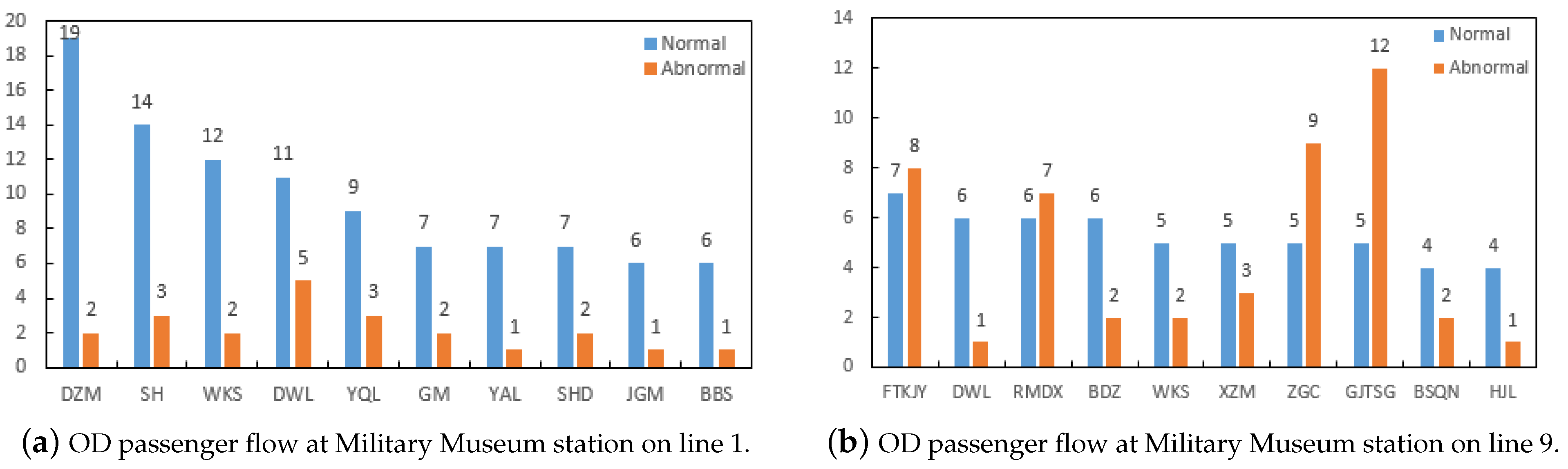
3.4.1. OD Passenger Flow at the Station with the Disruption
3.4.2. OD Passenger Flow at an Ordinary Station
3.4.3. OD Passenger Flow at the Transfer Station
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, R.; Yin, J.; Dai, P.; Jiao, L.; Li, R.; Li, T.; Wu, J. Optimal topology of multilayer urban traffic networks. Complexity 2019, 2019, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, J. Topologic characteristics and sustainable growth of worldwide urban rail networks. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2021, 35, 2150151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Li, T. Multi-Objective Bus Timetable Coordination Considering Travel Time Uncertainty. Processes 2023, 11, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ding, R.; Xue, S. Analysis of jobs-housing relationship and commuting characteristics around urban rail transit stations. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 175083–175092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, D. Dynamic data-driven computation method for the number of waiting passengers and waiting time in the urban rail transit network. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 17, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Qu, Y.; Sun, H. Optimizing the release of passenger flow guidance information in urban rail transit network via agent-based simulation. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 72, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ren, X.; Liu, R.; Tang, T.; Su, S. Quantitative analysis for resilience-based urban rail systems: A hybrid knowledge-based and data-driven approach. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 219, 108183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocera, S. An operational approach for quality evaluation in public transport services. Ing. Ferrov. 2010, 65, 363–383. [Google Scholar]
- Nocera, S. The key role of quality assessment in public transport policy. Traffic Eng. Control 2011, 52, 394–398. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Huang, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, T.; Peng, F. Optimal network design of battery-powered electric feeder bus with determination of fleet size and number of chargers. J. Transp. Eng. Part A Syst. 2022, 148, 04021097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, M.; Sun, H.; Xiong, J.; Dou, X. Stochastic ridesharing equilibrium problem with compensation optimization. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2023, 170, 102999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Gao, Z. Integrated co-evolution model of land use and traffic network design. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2016, 16, 579–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sun, H.; Wu, J.; Ge, Y.E. Optimal toll of new highway in the equilibrium framework of heterogeneous households’ residential location choice. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2017, 105, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sun, H.; Wu, J.; Gao, Z.; Ge, Y.E.; Ding, R. Optimal urban expressway system in a transportation and land use interaction equilibrium framework. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2019, 15, 1247–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cao, Y.; Xu, M.; Sun, H. Optimal intersection design and signal setting in a transportation network with mixed HVs and CAVs. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2023, 175, 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, M.; Dong, H. Cpt model-based prediction of the temporal and spatial distributions of passenger flow for urban rail transit under emergency conditions. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 2020, 8850541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Olio, L.; Ibeas, A.; Barreda, R.; Sañudo, R. Passenger behavior in trains during emergency situations. J. Saf. Res. 2013, 46, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Kang, S.M.; Airoldi, E.M. Predicting traffic volumes and estimating the effects of shocks in massive transportation systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5643–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, R.; Sugiyama, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Fujinami, K.; Arisawa, R.; Nakagawa, T. Route-choice support system for passengers in the face of unexpected disturbance of train operations. WIT Trans. Built Environ. 2006, 88, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan Asim, M.; Weiss, A.; Kattan, L.; Wirasinghe, S. Transit Users’ Mode Choice Behavior During Light Rail Transit Short-Term Planned Service Disruption. Transp. Res. Rec. 2021, 2675, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, J.; Wu, L.; Yan, X.; Gao, Z. Estimating the influence of common disruptions on urban rail transit networks. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2016, 94, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Han, B.; Li, D.; Wu, J.; Sun, H. Modeling and simulating passenger behavior for a station closure in a rail transit network. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.; Si, B.; Zhi, K.; Zhao, B.; Zheng, X. Simulation-Based Method for the Calculation of Passenger Flow Distribution in an Urban Rail Transit Network Under Interruption. Urban Rail Transit 2023, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almodóvar, M.; García-Ródenas, R. On-line reschedule optimization for passenger railways in case of emergencies. Comput. Oper. Res. 2013, 40, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Ma, J. Using agent-based simulation model for studying fire escape process in metro stations. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 32, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, J.; Marinov, M. Analysis of delays and delay mitigation on a metropolitan rail network using event based simulation. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2015, 52, 52–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xu, J.; Li, S.; Xu, L. Forecast of passenger flow under the interruption of urban rail transit operation. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies for Rail Transportation (EITRT) 2019: Rail Transportation System Safety and Maintenance Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zarboutis, N.; Marmaras, N. Searching efficient plans for emergency rescue through simulation: The case of a metro fire. Cogn. Technol. Work 2004, 6, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ling, Y.; Hu, C.; Yang, Z.; Ding, H.; Chow, W.K. Numerical simulation of emergency evacuation of a subway station: A case study in Beijing. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2009, 52, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadarso, L.; Marín, Á.; Maróti, G. Recovery of disruptions in rapid transit networks. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2013, 53, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadarso, L.; Marín, Á. Recovery of disruptions in rapid transit networks with origin-destination demand. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 111, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wu, J.; Qu, Y.; Yin, H.; Qu, X.; Gao, Z. Robust bus bridging service design under rail transit system disruptions. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2019, 132, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Xu, M.; Meng, Q.; Li, Z.C. Evacuating metro passengers via the urban bus system under uncertain disruption recovery time and heterogeneous risk-taking behaviour. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 119, 102761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Fan, W.; Liu, W.; Zhu, B.; Gu, J. Reinforcement learning approach for coordinated passenger inflow control of urban rail transit in peak hours. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 88, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Shen, Q. Cluster-based LSTM network for short-term passenger flow forecasting in urban rail transit. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147653–147671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xue, Q.; Yang, X.; Yin, H.; Qu, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, J. A novel prediction model for the inbound passenger flow of urban rail transit. Inf. Sci. 2021, 566, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
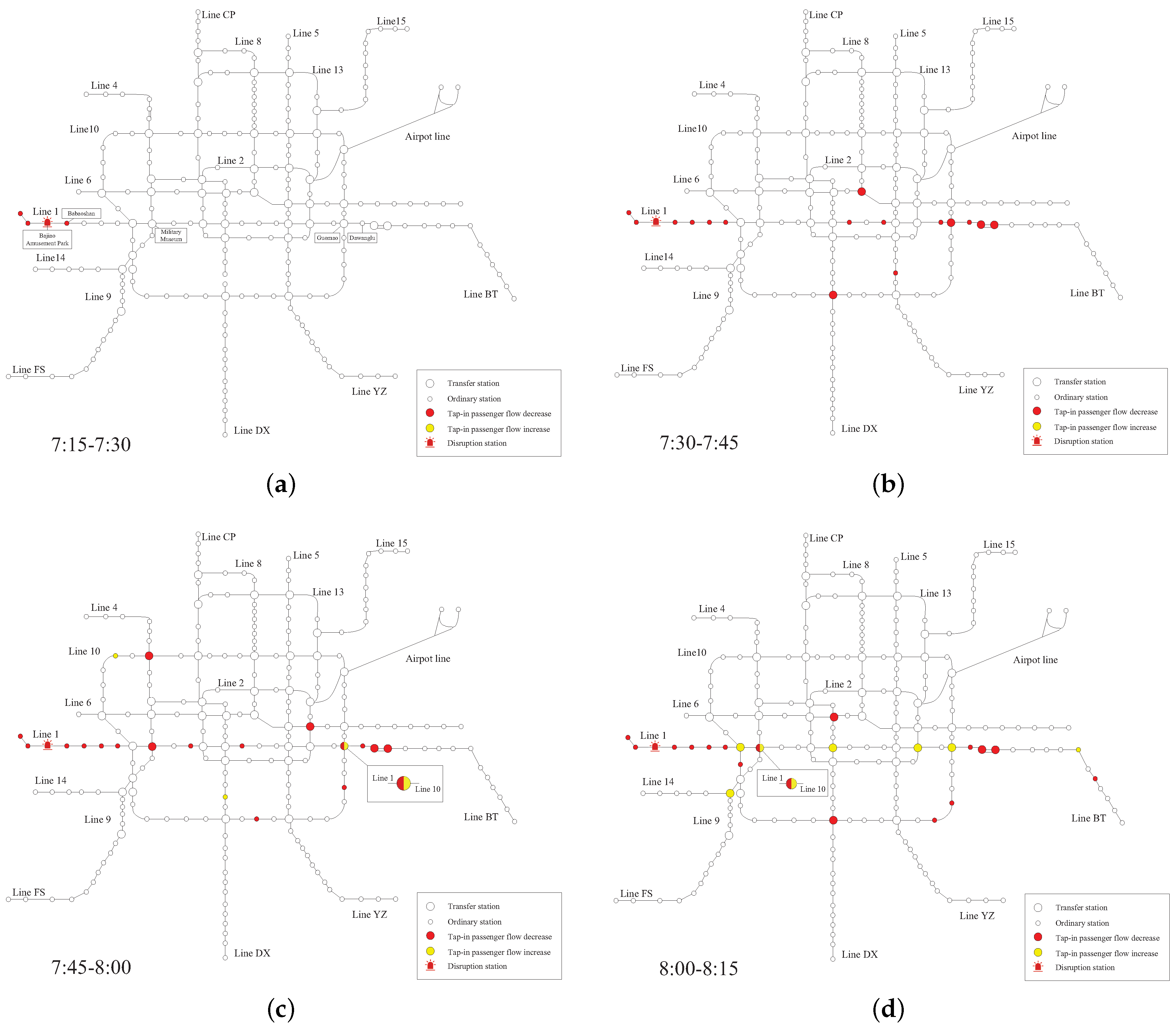
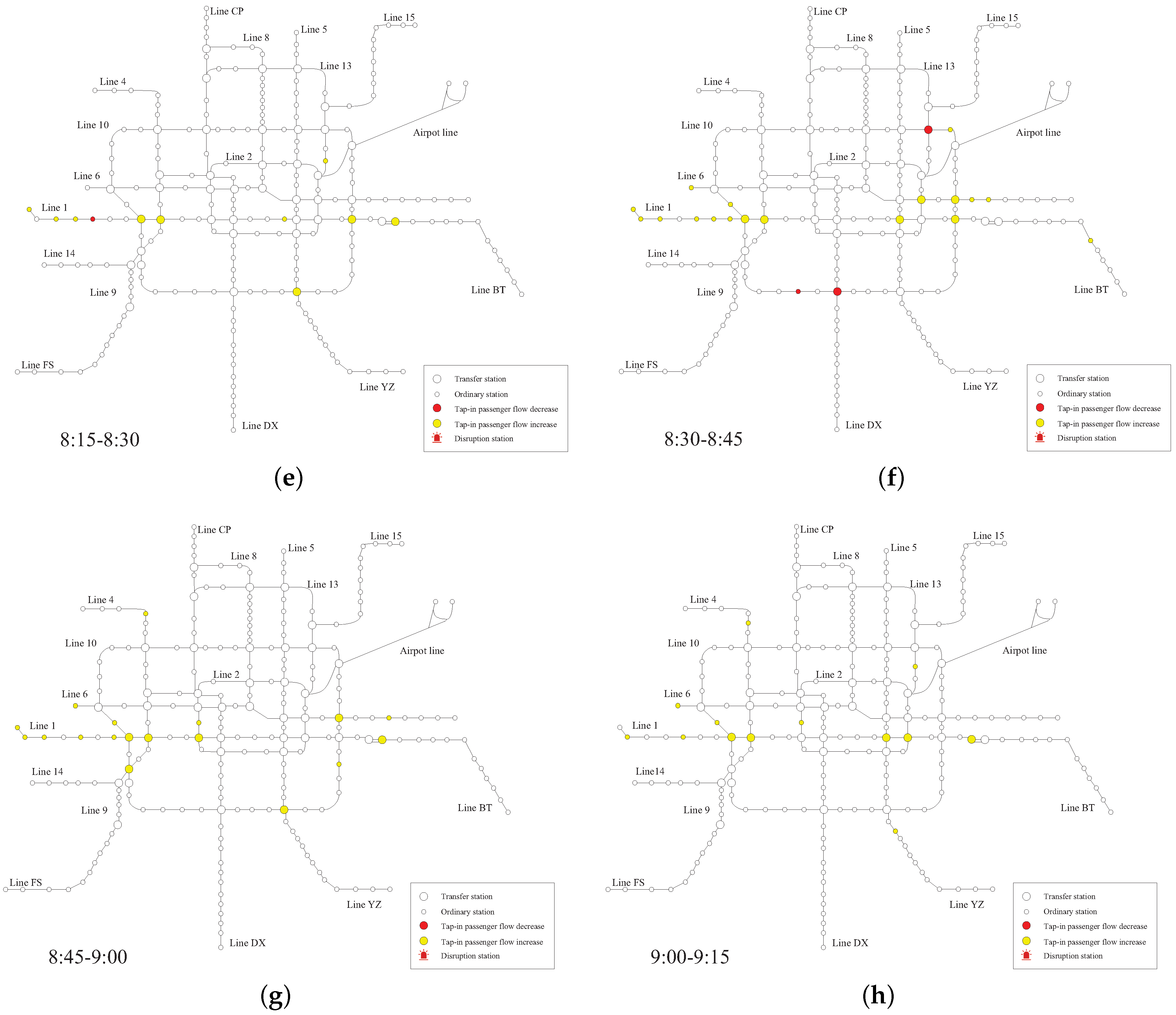


| Time Period | Number of Abnormal Stations | Number of Stations with Decreased Tap-In Passenger Flow | Number of Stations with Increased Tap-In Passenger Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7:00–7:15 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 7:15–7:30 | 19 | 18 | 1 |
| 7:30–7:45 | 25 | 24 | 1 |
| 7:45–8:00 | 23 | 20 | 3 |
| 8:00–8:15 | 29 | 20 | 9 |
| 8:15–8:30 | 15 | 3 | 12 |
| 8:30–8:45 | 24 | 6 | 18 |
| 8:45–9:00 | 22 | 3 | 19 |
| 9:00–9:15 | 13 | 0 | 13 |
| 9:15–9:30 | 8 | 4 | 4 |
| 9:30–9:45 | 10 | 6 | 4 |
| 9:45–10:00 | 9 | 4 | 5 |
| Ranking | Station | Influence Intensity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Guchenglu | 0.85 |
| 2 | Yuquanlu | 0.81 |
| 3 | Sihui | 0.77 |
| 4 | Dawanglu | 0.69 |
| 5 | Military Museum (line 1) | 0.67 |
| 6 | Guomao (line 1) | 0.55 |
| 7 | Pingguoyuan | 0.55 |
| 8 | Wukesong | 0.51 |
| 9 | Sihui East | 0.44 |
| 10 | Gongzhufen | 0.41 |
| 11 | Ti’anmen West | 0.40 |
| 12 | Tongzhoubeiyuan | 0.39 |
| 13 | Babaoshan | 0.35 |
| 14 | Military Museum (line 9) | 0.29 |
| 15 | Nanfaxin | 0.29 |
| Time Period | Upper Bound | Lower Bound | Tap-In Passenger Flow | Decreased Passenger Flow | Increased Passenger Flow |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7:00–7:15 | 1495 | 925 | 1034 | 0 | 0 |
| 7:15–7:30 | 1632 | 1379 | 1355 | 24 | 0 |
| 7:30–7:45 | 2097 | 1223 | 752 | 471 | 0 |
| 7:45–8:00 | 2202 | 1088 | 515 | 573 | 0 |
| 8:00–8:15 | 1821 | 1295 | 1009 | 286 | 0 |
| 8:15–8:30 | 1457 | 1112 | 1604 | 0 | 147 |
| 8:30–8:45 | 1468 | 647 | 1116 | 0 | 0 |
| 8:45–9:00 | 917 | 520 | 825 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 1354 | 147 | |||
| Time Period | Upper Bound | Lower Bound | Tap-In Passengers | Decrease in Passengers | Increase in Passengers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7:00–7:15 | 224 | 141 | 151 | 0 | 0 |
| 7:15–7:30 | 237 | 179 | 190 | 0 | 0 |
| 7:30–7:45 | 298 | 236 | 253 | 0 | 0 |
| 7:45–8:00 | 326 | 242 | 253 | 0 | 0 |
| 8:00–8:15 | 346 | 175 | 87 | 88 | 0 |
| 8:15–8:30 | 266 | 196 | 269 | 0 | 3 |
| 8:30–8:45 | 256 | 161 | 241 | 0 | 0 |
| 8:45–9:00 | 183 | 130 | 199 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 88 | 3 | |||
| Time Period | Upper Bound | Lower Bound | Tap-In Passengers | Decrease in Passengers | Increase in Passengers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7:00–7:15 | 91 | 37 | 60 | 0 | 0 |
| 7:15–7:30 | 112 | 65 | 102 | 0 | 0 |
| 7:30–7:45 | 127 | 88 | 98 | 0 | 0 |
| 7:45–8:00 | 156 | 121 | 117 | 0 | 0 |
| 8:00–8:15 | 195 | 116 | 201 | 0 | 6 |
| 8:15–8:30 | 145 | 117 | 200 | 0 | 55 |
| 8:30–8:45 | 125 | 91 | 129 | 0 | 4 |
| 8:45–9:00 | 121 | 70 | 125 | 0 | 4 |
| Total | 0 | 69 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Li, T.; Ding, R.; Xiong, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F. Analysis of the Influence and Propagation Law of Urban Rail Transit Disruptions: A Case Study of Beijing Rail Transit. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148040
Zhou W, Li T, Ding R, Xiong J, Xu Y, Wang F. Analysis of the Influence and Propagation Law of Urban Rail Transit Disruptions: A Case Study of Beijing Rail Transit. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148040
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Wenhan, Tongfei Li, Rui Ding, Jie Xiong, Yan Xu, and Feiyang Wang. 2023. "Analysis of the Influence and Propagation Law of Urban Rail Transit Disruptions: A Case Study of Beijing Rail Transit" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148040
APA StyleZhou, W., Li, T., Ding, R., Xiong, J., Xu, Y., & Wang, F. (2023). Analysis of the Influence and Propagation Law of Urban Rail Transit Disruptions: A Case Study of Beijing Rail Transit. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8040. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148040







