Calculation Method of Earth Pressure Considering Wall Displacement and Axial Stress Variations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis
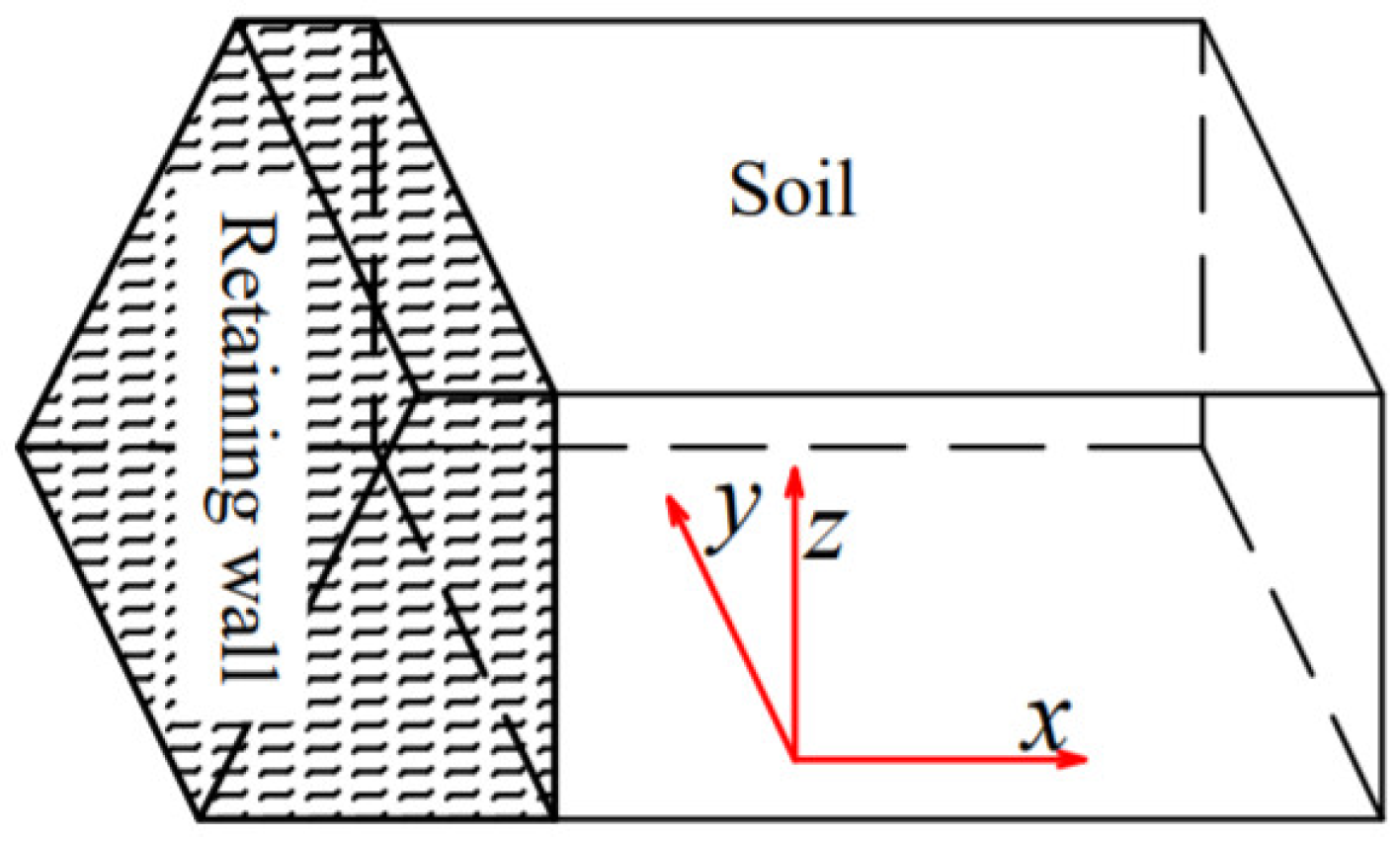
2.1. Calculation Method for Earth Pressure Considering Axial Stress
2.2. Calculation Method for Earth Pressure Considering Material Non-Linear
2.3. Special Earth Pressure Points
2.4. Earth Pressure Zoning
- (1)
- Active failure zone: < . The stresses in the x, y, and z directions in the soil are the minor, intermediate and major principal stresses, respectively. A failure plane has developed in the soil behind the wall and active failure has occurred.
- (2)
- Active earth pressure zone: ∈, . The stresses in the x, y, and z directions in the soil are the minor, intermediate and major principal stresses, respectively. The major principal stress is the self-weight stress , while the earth pressure on the retaining wall in the x direction represents the minor principal stress.
- (3)
- Passive earth pressure zone before the major principal stress reversal: ∈. The stresses in the x, y, and z directions in the soil are the intermediate, minor and major principal stresses, respectively. Compared to the active earth pressure zone, the direction of the minor principal stress has changed.
- (4)
- Passive earth pressure zone between the major and minor principal stress inflection points: ∈, . The stresses in the x, y, and z directions in the soil are the major, minor and intermediate principal stresses, respectively. In this zone, the self-weight stress is the intermediate principal stress, and the earth pressure on the retaining wall is the major principal stress.
- (5)
- Passive earth pressure zone after the second reversal of the minor principal stress: ∈, . The stresses in the x, y, and z directions in the soil are the major, intermediate and minor principal stresses, respectively. The major principal stress is the earth pressure on the retaining wall, while the self-weight stress in the soil is the minor principal stress.
- (6)
- Passive failure zone: . The direction of the principal stresses in this zone is consistent with the previous zone. The soil behind the wall undergoes passive failure along the failure plane.
2.5. Discussion on the Existence of Inflection Point
2.6. Earth Pressure under Different Displacement Modes
3. Example Verification
3.1. Discrete Element Experiment
3.2. Model Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rankine, W.J.M., II. On the stability of loose earth. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1857, 147, 9–27. [Google Scholar]
- Coulomb, C.A. Essai sur une Application des Règles de Maximis et Minimis Aquelques Problèmes de Statique, Relatifs a l’Architecture; Imprimerie Royale: Paris, France, 1776. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi, K. A fundamental fallacy in earth pressure computations. J. Boston Soc. Civ. Eng. 1936, 23, 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.S.; Chen, T.J.; Wu, B.F. Passive earth pressures with various wall movements. J. Geotech. Eng. 1994, 120, 1307–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, M.H.; Pipatpongsa, T.; Takemura, J. Experimental analysis of earth pressure against rigid retaining walls under translation mode. Géotechnique 2013, 63, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, R.; Ye, Y.Q.; Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, Y.X. Experimental and theoretical investigations on active earth pressure distributions behind rigid retaining walls with narrow backfill under a translational mode. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 04020178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.W.; Dou, G.T.; Su, Q.; Bai, W.G.; Yuan, F. Experiment study on non-limit passive earth pressure of clay under different displacement modes. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2019, 54, 769–777. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Zhu, X.; Hu, T.; Wang, W.; Lin, G. Non-limit passive earth pressure against cantilever flexible retaining wall in foundation pit considering the displacement. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, G.; Xia, J.; Yu, W.; Yuan, F.; Bai, W. Non-limit passive soil pressure on rigid retaining walls. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, D.M.; Fourie, A.B. The behaviour of a propped retaining wall: Results of a numerical experiment. Geotechnique 1984, 34, 383–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashita, K.; Oda, M. Rolling resistance at contacts in simulation of shear band development by DEM. ASCE J. Eng. Mech. 1998, 124, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, T. Finite element computations for active and passive earth pressure problems of retaining wall. Soils Found. 1985, 25, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.F. Lateral earth pressures behind rotating walls. Can. Geotech. J. 1997, 34, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejchman, J.; Bauer, E.; Tantono, S.F. Influence of initial density of cohesionless soil on evolution of passive earth pressure. Acta Geotech. 2007, 2, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lin, Y.; Li, D. Solution to active earth pressure of narrow cohesionless backfill against rigid retaining walls under translation mode. Soils Found. 2019, 59, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, H.F.; Tschuchnigg, F. A numerical study on undrained passive earth pressure. Comput. Geotech. 2021, 140, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, J.; Ahmad, S.M. A finite element performance-based approach to correlate movement of a rigid retaining wall with seismic earth pressure. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 114, 460–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.I.; Liu, H. Deformation analysis of reinforced soil retaining walls—Simplistic versus sophisticated finite element analyses. Acta Geotech. 2009, 4, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, M.A.; Yap, T.Y.; Abu Bakar, A. Adaptive and fixed mesh study of localization in a strain-softening soil. In Bifurcation and Localisation Theory in Geomechanics; Balkema: London, UK, 2001; pp. 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Gilabert, F.A.; Roux, J.N.; Castellanos, A. Computer simulation of model cohesive powders: Plastic consolidation, structural changes, and elasticity under isotropic loads. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 031305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Huang, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. DEM investigation of particle anti-rotation effects on the micromechanical response of granular materials. Granul. Matter 2013, 15, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, C.; Scheffler, O.C. Comparing particle shape representations and contact models for DEM simulation of bulk cohesive behaviour. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 159, 105449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Yin, Z.Y. Analysis of stress redistribution in soil and earth pressure on tunnel lining using the discrete element method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2012, 32, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejchman, J.; Kozicki, J.; Leśniewska, D. Discrete simulations of shear zone patterning in sand in earth pressure problems of a retaining wall. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2011, 48, 1191–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; He, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, W. Distinct simulation of earth pressure against a rigid retaining wall considering inter-particle rolling resistance in sandy backfill. Granul. Matter 2014, 16, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.H.; Zou, J.F.; Tian, J.; Pan, Q.J. Estimations of active and passive earth thrusts of non-homogeneous frictional soils using a discretization technique. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 119, 103366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xu, C.; Fan, X.; Chen, Q. Hyperbolic stress-strain behavior of sandy soil under plane strain unloading condition and its application on predicting displacement-dependent active earth pressure. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 155, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Mangalathu, S.; Song, L.; Mei, G.; Zhao, Y. Displacement-dependent lateral earth pressure models. J. Eng. Mech. 2018, 144, 04018032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Li, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, S. Calculation of Displacement-Dependent Active Earth Pressure for Deep Excavations in Soft Soil. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, M.; Matsuzawa, H. Earth pressure during earthquake. Soils Found. 1973, 13, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S. Active earth pressure behind retaining walls. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 1985, 111, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.S.; Ishibashi, I. Static earth pressure with various wall movements. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 1986, 112, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; Nayak, S.; Choudhury, D. Determination of displacement-related passive earth pressure. Geotech. Eng. 2004, 35, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.Q.; Gong, C.; Wei, G.; Wang, J.C. Theory of earth pressure against rigid retaining walls considering translational movement effect. J. Zhejiang. Univ. Eng. Sci. 2005, 39, 119–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, Z.X.; Wilkinson, S.P. Active earth pressure acting on retaining wall considering anisotropic seepage effect. J. Mt. Sci.-Engl. 2017, 14, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubra, A.H.; Macuh, B. Active and passive earth pressure coefficients by a kinematical approach. Geotech. Eng. 2002, 155, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, B.X.; Jia, J.Q. Research on active earth pressure behind rigid retaining wall from clayey backfill considering soil arching effects. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2012, 31, 1064–1070. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.P.; Wang, M. Simplified method for calculating active earth pressure on rigid retaining walls considering the arching effect under translational mode. Int. J. Geomech. 2014, 14, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patki, M.A.; Mandal, J.N.; Dewaikar, D.M. Determination of passive earth pressure coefficients using limit equilibrium approach coupled with the Kötter’s equation. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 52, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Active earth pressure of retaining wall considering wall movement. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2014, 18, 910–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, S. Calculation method for displacement-dependent earth pressure on a rigid wall rotating around its base. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04021132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, W. Calculation of nonlimit active earth pressure against rigid retaining wall rotating about base. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, G.; Chen, Q.; Song, L. Model for predicting displacement-dependent lateral earth pressure. Can. Geotech. J. 2009, 46, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, G.X.; Chen, R.; Liu, J. New insight into developing mathematical models for predicting deformation-dependent lateral earth pressure. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 06017003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Pei Li, J.; Ma, Y. Lateral earth pressure considering the displacement of a rigid retaining wall. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 06018031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.Q.; Li, X.B.; Ling, F.A.N.; Liu, A.H. A general method to calculate passive earth pressure on rigid retaining wall for all displacement modes. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.Z.; Xu, C.J.; Liang, L.J.; Chen, Q.Z.; Deng, J.L. Analytical solution for displacement-dependent passive earth pressure on rigid walls with various wall movements in cohesionless soil. Comput. Geotech. 2021, 140, 104470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Luo, Q. Macroscopic embodiment of stress–strain behavior of backfill soil on the displacement-dependent earth pressure curve. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 04018178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dang, F.N.; Wang, X.; Ding, J.L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y. Estimation of earth pressure against retaining walls with different limited displacement modes based on elastic theory. J. Mt. Sci.-Engl. 2021, 19, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, K.H.; Salgado, R. Estimation of active earth pressure against rigid retaining walls considering arching effects. Geotechnique 2003, 53, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadukuru, S.S.; Michalowski, R.L. Arching in distribution of active load on retaining walls. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2012, 138, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Specific Gravity of Soil Particle/Gs | Density/g·cm−3 | Void Ratio/e | c/kPa | φ/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.7 | 1.78 | 0.808 | 14 | 24.6 |
| Particle Density kg/m3 | Particle Radius Rmax/mm | Particle Radius Rmin/mm | Effective Modulus E*/MPa | Stiffness Ratio k* | Friction Coefficient μ | Rotational Friction Coefficient | Maximum Attraction N | Domain of Attraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2650 | 0.714 | 0.1785 | 33 | 3.6 | 0.21 | 0.8 | 10 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dang, F.; Wang, X.; Cao, X.; Gao, J.; Ding, J.; Zhang, L. Calculation Method of Earth Pressure Considering Wall Displacement and Axial Stress Variations. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9352. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169352
Dang F, Wang X, Cao X, Gao J, Ding J, Zhang L. Calculation Method of Earth Pressure Considering Wall Displacement and Axial Stress Variations. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(16):9352. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169352
Chicago/Turabian StyleDang, Faning, Xu Wang, Xiaoshan Cao, Jun Gao, Jiulong Ding, and Le Zhang. 2023. "Calculation Method of Earth Pressure Considering Wall Displacement and Axial Stress Variations" Applied Sciences 13, no. 16: 9352. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169352
APA StyleDang, F., Wang, X., Cao, X., Gao, J., Ding, J., & Zhang, L. (2023). Calculation Method of Earth Pressure Considering Wall Displacement and Axial Stress Variations. Applied Sciences, 13(16), 9352. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169352





