Abstract
Ecologically sustainable buildings and their carbon emissions are two popular ideas for building life cycle systems. It is a challenge to comprehensively assess the sustainability of building cases using two different methods. Based on over a decade of research, this paper attempts to explore the possibility of quantitatively integrating both approaches. In this study, we adopted the emergy method and carbon emission approach to assess and analyze a building system. In particular, similarities and differences have been identified through emergy and carbon emissions at each stage of the building’s whole life cycle. The results demonstrate that the building operation phase is the critical contributor (Approximately 79.6% of the total emergy and 97.9% of the entire carbon emission), which occupies the most emergy and carbon emission amounts of the whole building system. In order to improve the ecological sustainability of the building system, renewable energy subsystems are considered and explored. While the overall sustainability of the building system is enhanced, the new systems will aggrandize the carbon emissions. Therefore, the ecological sustainability of building systems and carbon emissions should be considered comprehensively, and the relationship between the two views needs to be balanced.
1. Introduction
Increasingly affected by environmental degradation, the building system’s sustainability, as a gathering place for humans, is under scrutiny [,]. From the ecological field, ecological architecture is a professional term that defines that a building system is sustainable and can achieve long-term development, in a sustainable way [,]. However, in order to maintain the ecologically sustainable state of a building system, it needs the continuous support of continuous resources, energy and a service system, which objectively leads to the increase in carbon emissions. At the same time, global warming is caused by excess carbon emissions, and it is also a growing threat to the world’s living environment [,]. One obvious fact reveals the level of carbon emissions in the building system, which accounts for more than a third of total carbon emissions [,]. Therefore, an ecological sustainability study and the carbon emissions of building systems should be focused on simultaneously by scholars.
From the field of ecological economics, the emergy concept is a new viewpoint for the sustainability evaluation of several systems, including agriculture [,], urban systems [,,,], water treatment processes [,], industrial products [,,], material production systems [,], health systems [], plant ecology [], regional analysis [,], building systems analysis [,], economic subsystem [], etc.
Therein, the building system is an important focus based on emergy analysis. Simultaneously, a series of scholars conducted emergy calculations and assessments to explore the sustainability of building systems. For instance, Suman et al. (2021) integrated the emergy method and BIM to realize their union []. So as to confirm the environmental building design change, the emergy approach has been used to define a net zero energy building system []. By replacing disparate energy sources in green buildings, their sustainable evaluations have been revealed on the basis of an emergy view []. Taking the net-zero energy building system as an example, a sustainable assessment has been executed from the view of emergy considerations []. Because it involves a lot of data analysis, the sensitivity analysis of building systems has been investigated []. Through the integration of the emergy method and sensing system analysis, the effectiveness of smart building has been of concern []. Since a building system consists of multiple devices, to verify the utility, emergy analysis has been adopted to confirm the effect of the heating and cooling subsystem integrated with the air source heat pump subsystem []. At the same time, the evaluation and selection of construction equipment systems can also be confirmed using the emergy method []. Building material systems are also a key field of emergy analysis []. The emergy method can also be applied to the updating of the building system to guide the updating design [].
In addition to the above studies, it is a very popular idea to study the whole life cycle of a building system. Many scholars have studied the building system by leveraging the LCA method [,,,,,,]. However, there are few comprehensive studies integrating the LCA method and the emergy method. As an unusual combination, LCA–Emergy can conduct a sustainable exploration of building systems. After reviewing the literature in the last five years, several articles were discussed using the LCA–Emergy framework. For example, a residential building was selected for sustainability investigation in view of emergy analysis []. As a necessary part of the building system, the building cement material system was of concern and was analyzed using an emergy view []. As a special form of architecture, highway engineering has also been surveyed through emergy evaluation []. By relying on an LCA–Emergy approach, different renewal strategies for building systems are demonstrated, so as to select a better renewal strategy [].
From the perspective of the carbon emission of building systems, a lot of investigations have been explored by scholars for reducing the carbon emission of building systems, so as to mitigate the impact of climate change. Several different ideas have been tried to analyze, such as carbon emissions from the building sector [], a low-carbon cities view [,], public building type [], system dynamics carbon emission analysis [], building supply chain [], architectural renewal perspective [], green space [], passive architectural design [], building operations [], carbon emission quotas [], zero-carbon analysis [], etc. The details are as follows: Through the carbon emission model and data analysis, the challenges and opportunities of the building sector have been surveyed []. Models of carbon emissions up to 2060 are designed to predict the overall trajectory of carbon emissions []. From the perspective of a low-carbon city, the carbon emission of the building system was calculated and designed []. Taking public buildings as an example, the unbalanced state of carbon emissions is studied []. As an effective model, the carbon emission of urban buildings is analyzed and predicted using system dynamics []. On account of building supply chain consideration, the carbon emission reduction effect was focused on []. In order to improve living conditions, the renovation design of the building is combined with carbon emissions []. By integrating natural landscapes and building carbon emissions, green space and water bodies have been proposed due to their carbon reduction effects []. By focusing on passive house-certified measures, their carbon emissions and applications are taken into account []. The building operation stage has always been the most important aspect of the carbon emissions of a building system, which needs continuous attention []. Carbon emission quotas acting as a starting point, their fairness and balance are analyzed and explored []. Zero-carbon buildings, as the ultimate goal of building carbon emissions, are currently the research hotspot of building systems [].
Similarly, besides the above research on carbon emissions, the LCA–Carbon emission estimation of building systems is also a hot topic. Typical studies are as follows. Using BIM and LCA methodologies, the carbon emission intensity and cost have been studied recently []. Based on the carbon emission and driving factor perspective, a specific building case was selected and evaluated []. In terms of energy conservation, the LCA–Carbon emissions and economic effects of building systems have been investigated []. A large-scale national carbon emission study was carried out on the basis of the LCA approach []. Through ecological climate mitigation challenge analysis, the greenhouse gas of a building system was evaluated and displayed []. The life-cycle carbon emissions of zero-carbon building renewal design were followed with interest by several researchers []. In Sweden, a typical family house was selected for a life cycle cost study []. The carbon emissions of prefabricated building systems have been the focus recently, especially based on the integration of BIM and LCA []. Four types of rural houses were chosen for carbon reduction exploration by utilizing the LCA method [].
Up to now, the relationship between ecological sustainability and the carbon emissions of building systems has not been discussed in relation to each other under LCA assessments, which is limited by two completely different methodologies. In this study, it has been considered and preliminarily verified. The innovation of this article lies in the comprehensive evaluation of the sustainability of building systems using emergy methodology and carbon emissions calculation methods. The emergy methodology considers the relationship between building systems and the environment, while the carbon emissions methodology focuses on the carbon emissions of the entire building system, thereby assessing the impact of building systems on the environment. By focusing on the building systems, it compares the advantages and disadvantages of these two approaches, thereby providing valuable insights for sustainable architects and designers.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Research Framework
In order to achieve the research objective, two methods have been considered and utilized in this paper. The specific implementation path is displayed in Figure 1. For a building system, to explore the sustainability status, LCA–Emergy and LCA–Carbon emissions have been conducted and compared to evaluate and analyze the sustainable state. From the view of ecology, based on an emergy approach, their emergy quantity calculated to support sustainability indicators for the building system; meanwhile, carbon emission was another breakthrough from the point of view of sustainability. To ensure the integrity of the study, five stages of the whole life cycle of the building were divided and designed, including the building material production stage, building transportation stage, building operation stage, building construction and renewal phase and building demolition stage.
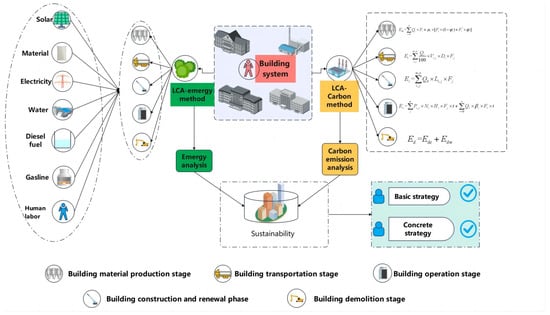
Figure 1.
Basic study framework and implementation path.
2.2. LCA–Emergy Introduction
2.2.1. Emergy Method
The core concept of Emergy (energy with an “m”) method, originated in the US by H.T. Odum [], is based on the notion that it represents the total sum of energy and resources involved in a specific process within an ecosystem. This includes both direct and indirect energy usage, as well as the energy gained through material and energy transformations. By aggregating all emergy values, the Emergy method allows for comprehensive evaluation and comparison of building systems, revealing their reliance on the environment and assessing their sustainability.
As a systems assessment approach, the Emergy method is used to measure and compare the value and contribution of different resources and energy sources within a building system. It is based on the concept of energy and converts all inputs and outputs of resources and energy into a unified unit of measure called emergy. By considering different resource types, qualities and energy efficiencies, the Emergy method quantitatively evaluates the performance of building systems regarding resource use and energy efficiency.
Compared with other sustainability methods, the Emergy method has several advantages. It comprehensively considers the quality and renewability of various resources and provides a unified metric to assess the contributions of diverse resources. Additionally, the Emergy method unveils external costs and environmental impacts that are often overlooked in traditional economic analyses, resulting in a more holistic evaluation of the true value and sustainability of building systems.
The Transformity/UEV refers to the amount of emergy required to produce a unit of specific output or service at a given scale. In this study, the benchmark for emergy calculations is 12 × 1024 sej/year [].
In Figure 2, the LCA–Emergy diagram has been designed and is displayed. There are four main subsections, including renewable energy input (right side), resource and service inputs (upper side), major building system (intermediate position) and external output (left side). Taking renewable energy inputs as an example, this section has five components, which are sunlight, rain-chemical, rain-geopotential, wind and geothermal heat. As the five stages of the building’s life cycle, they have been presented; simultaneously, three renewal strategies have been identified in Figure 2 [].
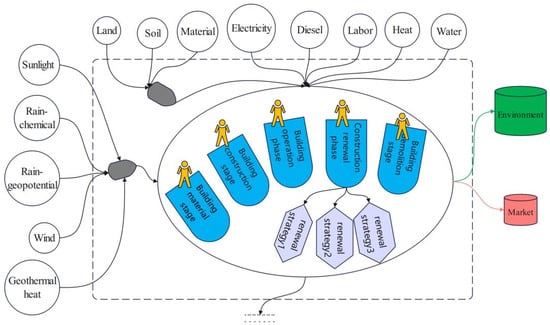
Figure 2.
LCA–Emergy diagram of the building system.
2.2.2. LCA–Emergy Model
- (1)
- Solar irradiation calculation model
The solar emergy can be obtained from Equation (1), as follows:
where represents the solar emergy in the construction process; A is the site surface; J is the solar radiation amount (3.5 × 109 J/m2) []; is the surface albedo (0.7); is the construction time; is the unit emergy values.
- (2)
- Mass calculation model
The mass represents the materials in the construction system and the emergy calculation model equation is calculated as follows [,]:
where is the emergy value of mass; is mass amount; represents the unit emergy value.
- (3)
- Electricity calculation model
The electricity calculation equation can be obtained, as follows:
where is the emergy of electricity in the building system; is the electricity quantity; is the unit emergy value of electricity.
- (4)
- Water
The water emergy has two aspects. On the one hand, the emergy should be calculated in the building demolition and construction stage. The specific Equation (4) can be used, as follows:
where is the water emergy; is the water volume; is the water density; G is the Gibbs energy of water (4.92 J/g); is the water transformity.
On the other hand, the water emergy should also be considered in the operation phase and the equation can be utilized as (5).
where is the water emergy in the building operation stage; is the water volume per day for one person (25 L/d/p); is the employee number (the number is 200); is the working time (280 days in this study).
- (5)
- Diesel fuel emergy calculation model
Because of the machinery used, diesel fuel is necessary for the building system. The equation can be obtained as follows:
where is the emergy of the diesel fuel; is the amount of diesel oil used in the buildings system; is the calorific value of diesel fuel; is the unit emergy value of diesel fuel.
- (6)
- Gasline emergy calculation model
The emergy value can be calculated as follows:
where is the gasoline emergy; is the gasoline quantity; is the calorific value of gasoline; is the unit emergy value of gasoline.
- (7)
- Human labor emergy calculation model
The emergy of human labor can be obtained, as follows:
where is the emergy of human labor; is the working time (8 h); is the number of employed workers; is the working day; is the unit emergy value of human labor.
- (8)
- Emergy indexes
Several indicators have been adopted to evaluate the ecological status in this paper. For example:
- (1)
- Renewable input (Ri) represents the emergy input of renewable resources, which has a positive effect on the sustainability in the building system. The calculation formula is as follows: Renewable input (Ri) = Renewable emergy/Total emergy.
- (2)
- Nonrenewable resource (Ns) is emergy input proportion of non-renewable resources. A higher proportion demonstrates a less sustainable role. The calculation formula is as follows: Nonrenewable resource (Ns) = Non-renewable emergy/Total emergy.
- (3)
- Emergy feedback input (Ef) is the emergy feedback based on the total emergy output. The calculation formula is as follows: Emergy feedback input (Ef) = Feedback emergy/Total emergy
- (4)
- Emergy yield ratio (EYR) can be obtained based on the total emergy and emergy feedback input, showing the ability to generate emergy. It uncovers the system structure and emergy distribution. The calculation formula is as follows: EYR = Comprehensive output emergy/Comprehensive input emergy.
- (5)
- The environmental loading ratio (ELR) reveals the ecological stress for the system. When the system has a higher number, it means that the system has a higher pressure. The calculation formula is as follows: ELR = Environmental resource consumption emergy/Comprehensive output emergy.
- (6)
- Emergy sustainability indicator (ESI) states the final ecological situation for a system from an emergy perspective. A value below 1 indicates that the entire system is unsustainable in the long run. The calculation formula is as follows: ESI = EYR/ELR.
2.3. LCA–Carbon Emission Calculation Model
The calculation formula of the carbon emission calculation model for the whole life cycle of buildings is as follows []:
where is the total carbon emission in the building system; is the carbon emission in the building material production stage; is the carbon emission in the construction material transport stage; is the carbon emission in the construction phase; is the carbon emission in the operational use and maintenance phase; is the carbon emission in the abandoned and dismantled stage.
- (1)
- Carbon emission calculation of building material production stage
The building materials production stage includes the carbon emissions generated by mining, production and processing. The calculation equation is as follows:
where is the carbon emission calculation of the building material production stage; n is the quantity of building materials; is the consumption of building material i; is the carbon emission factor in the initial state; is the carbon emission factor in the recycling state; is the rate of attrition; is the recovery utilization rate.
- (2)
- Carbon emission calculation of construction transport stage
The construction process needs a large number of vehicles, resulting in a mass of carbon emissions, which need to be counted and calculated. The transportation process includes two parts, one is the carbon emission calculation of building materials and mechanical equipment transported to the construction site; the other is the carbon emissions from construction waste and earthmoving. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
where is the carbon emission calculation of the construction transport stage; n is the quantity of building materials; is the consumption of building material i; is the amount of energy used to transport materials (t/100 t·km); is the transportation distance of materials or equipment (km); is the carbon emission factor.
- (3)
- Carbon emission calculation of building construction and renewal stage
The carbon emissions of the construction phase is mainly the use of machinery and the electricity in the factory, which can be calculated by gasoline, diesel and electricity usage. The specific calculation equation is as follows:
where is the carbon emission calculation of the building construction stage; n is the quantity of equipment; m is the number of energy types; is the total number of machines; is the energy consumed by machinery; is the carbon emission factor.
- (4)
- Carbon emission calculation of operational use stage
There are two aspects of carbon emissions in this stage. On the one hand, it is the carbon emissions generated by the lighting load, air conditioning system load, refrigeration equipment, water supply and drainage load in the operation stage. On the other hand, the carbon emissions are generated by the upgrading and maintenance of building materials and facilities.
The specific calculation equation is as follows:
where is the carbon emission calculation of operational use stage; m is the total types of energy; n is the material renewal quantity; t is the life of the building (year); is the energy expended per hour; is the total number of equipment; is the average operating hours of the device; is the carbon emission factor of equipment; is the maintenance update consumption; is the annual renewal rate; is the carbon emission factor of alternate material.
- (5)
- Carbon emission calculation of building demolition stage
The carbon emission at the stage of building demolition consists of two parts: the carbon emission of mechanical equipment and the carbon emission of waste transportation. The specific equation is shown in (14).
where is the carbon emission at the stage of building demolition; is the carbon emission of mechanical equipment; is the carbon emission of waste transportation.
- (6)
- Carbon dioxide emissions
In the whole life cycle of the building, the most carbon dioxide is emitted in the building material production stage, at approximately 85%. In this paper, the carbon dioxide can be computed by Equation (15).
where is the amount of carbon dioxide emissions; is the mass amount; is the emission factors of different building materials.
3. Case Study
3.1. Update Policy
Because the building needs to be updated, the basic renewal strategy should take functional and aesthetic aspects into consideration. There are two aspects of the renovation design. On the one hand, the interior decoration design of the building is carried out. On the other hand, the facade of the building also needs to be updated. The list of required architectural design details and materials can be obtained from the architect.
3.2. Case Introduction
A type of commercial complex was selected for the updated design, which is located in Nanjing, China. The buildings are more than 20 years old, and the poor indoor and outdoor conditions need to be improved, such as being renovated internally and updated externally.
A commercial complex is revealed in Figure 3. A five-story commercial center and a twelve-story hotel make up the commercial complex, covering an area of over 51,000 square meters. The whole building complex adopts the classical design strategy and the facade is decorated with a roof component form. In addition to the commonly used building materials, the whole building materials are made of white mortar walls, decorative wood and black metal.
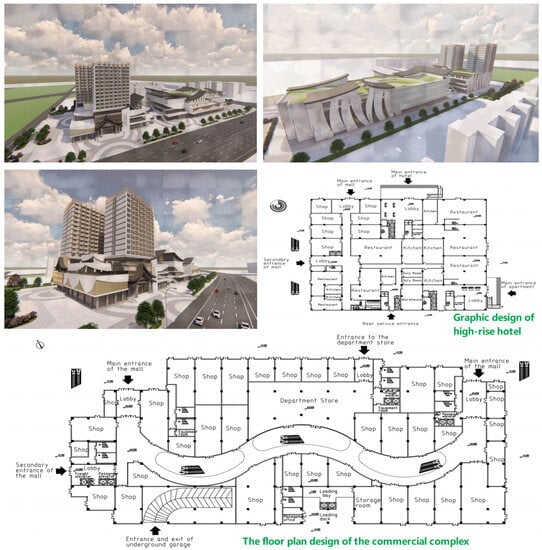
Figure 3.
A commercial complex building case.
The renovation design strategy for this building is based on low-energy building standards, with the following specific parameters:
- (1)
- The annual heating demand per unit area of the building, Qh, is ≤15 kWh/(m2·a).
- (2)
- The heating load per unit area of the building, qh, is ≤10 W/m2.
- (3)
- The annual cooling demand per unit area of the building, Qc, is ≤15 kWh/(m2·a).
- (4)
- The maximum cooling load per unit area of the building, qc, max, is ≤20 W/m2.
- (5)
- The total primary energy demand per unit area of the building, EPT, is ≤120 kWh/(m2·a).
3.3. Data Collection
The basic building data can be obtained from the design and construction documents. Updated design data can be obtained from design and construction units. The specific data include a building material data list, a building energy use data list and a labor data list. In addition, carbon emission factor data and emergy conversion rates need to be collected.
The carbon emission factor is derived from the emission coefficient method, which is one of the most widely used carbon emission accounting methods. The carbon emission factor is defined as the production of greenhouse gases associated with the consumption per unit of substance. For the construction field, the most commonly used carbon emission factors include three types: the fossil energy carbon emission factor, the electric power carbon emission factor and the building material carbon emission factor.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), as an authoritative international institution, has conducted sufficient research on the carbon emission factors of fossil energy. In this paper, energy carbon emission factors are selected based on the IPCC Guidelines for the Preparation of National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. There are various types of building materials in this study, and carbon emission measurement data from authoritative institutions are adopted. The details are shown in Appendix A.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. LCA–Emergy Analysis
4.1.1. Dominated Contributor
The five stages of the whole life cycle of the building are studied and discussed. Firstly, the largest emergy contribution is the building run phase because the running emergy of 20 years is calculated in this paper (6.09 × 1020 sej). The secondary contributor is the emergy in the stage of building materials (8.73 × 1019 sej), followed by the building construction stage (5.55 × 1019 sej), building demolition stage (1.12 × 1019 sej) and building renewal stage (1.42 × 1018 sej) in Figure 4.
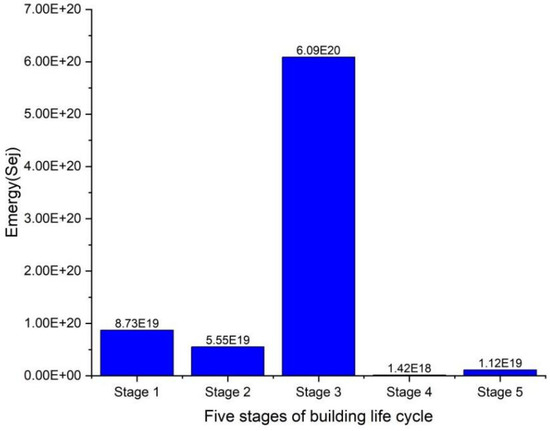
Figure 4.
Comparative analysis of each stage. (stage 1—building material production stage; stage 2—building construction stage; stage 3—building operation stage; stage 4—building renewal stage; stage 5—building demolition stage).
As the primary impact element, the building operation stage contains four types of inputs, which are Solar, Electricity, Heat and Water. Therein, electricity plays a major role from an emergy point of view to analyze (98.3% of the entire operation’s emergy in the building).
There are 19 categories of materials for the building materials stage (in Figure 3). Among them, steel, cement and brick are the key inputs, which account for 60.14%, 15.83% and 12.14% of the total building material emergy.
During the building construction phase, there are six subsystems that need to be designed and analyzed, involving environmental inputs, water supply and sewage system treatment facilities, heating and cooling systems, electricity installations, telecommunications systems, the elevator system, etc. Their emergy ratio is shown in Figure 5.
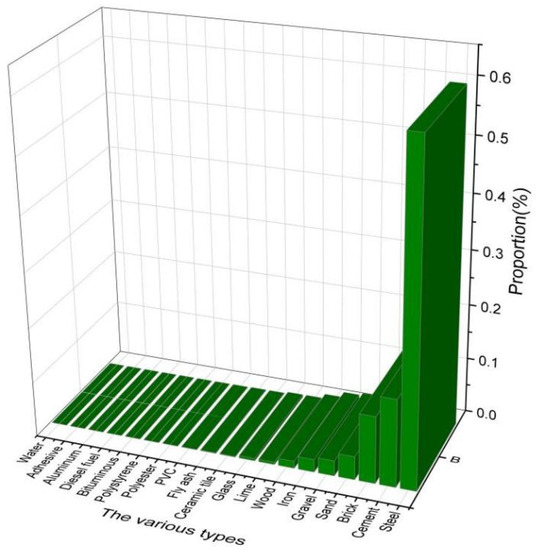
Figure 5.
The order of all kinds of materials.
Figure 6 demonstrates that water supply and sewage system treatment facilities are critical subsystems, accounting for roughly 73% of the total emergy in the building construction stage, followed by environmental inputs (14%), electricity installations (7%), the telecommunications system (3%), heating and cooling systems (2%) and the elevator system (1%).
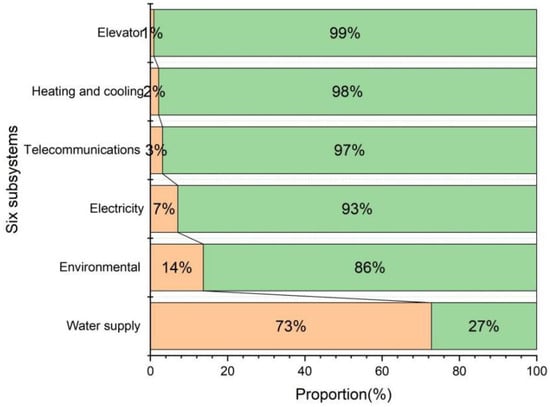
Figure 6.
Six subsystems on the stage of building construction.
In order to better update building types, there are three renewal strategies, respectively, and the specific details can be obtained in Table 1. The unit emergy value reference can be found in the literature [].

Table 1.
Emergy of building renewal stage.
According to Table 1, in the three kinds of updating strategies, emergy accounted for 71.86%, 22.99% and 5.3%, respectively. However, for the building as a whole, they did not display the major roles.
The stage of building demolition is distinguished in two ways. On the one hand, some materials will be recycled, such as glass, PVC, iron, diesel fuel, concrete, bricks and aluminum, which account for about 84% of the total demolition emergy. On the other hand, approximately 16% of the entire emergy will be lost because of the landfill style.
4.1.2. Emergy Indexes Analysis
In Table 2, six primary indexes have been shown for the sustainable state. Compared with renewable input and emergy feedback input, the nonrenewable resource input occupies a dominant position. Based on the Ri, Ns and Ef, EYR and ELR have been calculated as 69.1 and 81.4. Then, the Emergy sustainability indicator (ESI) is computed and the value is 0.849. According to the sustainable standard (the eligibility standard is 1), the ESI is close to 1, which illustrates that the whole building system needs continuous improvement in order to improve its sustainability.

Table 2.
Emergy indexes list.
4.1.3. The Sustainability Impact of Different Update Strategies
In Table 3 and Figure 7, the sustainability of the three renewal strategies has been shown. Compared with the original version, the total emergy of the three renewal versions has been supplemented. Due to the use of renewable materials in the renewal phase, the environmental load decreased in the three stages, and the overall sustainability index improved significantly. In Figure 8, to compare and analyze three kinds of indicators, it is obvious that ESI has made significant changes (Red cloud map).

Table 3.
Sustainability effects of three renewal strategies.
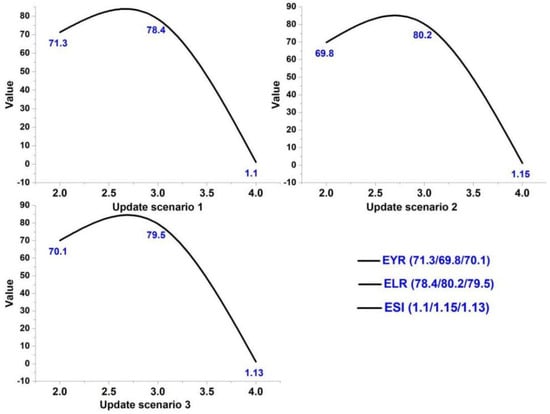
Figure 7.
Sustainability comparison trend of three renewal strategies.
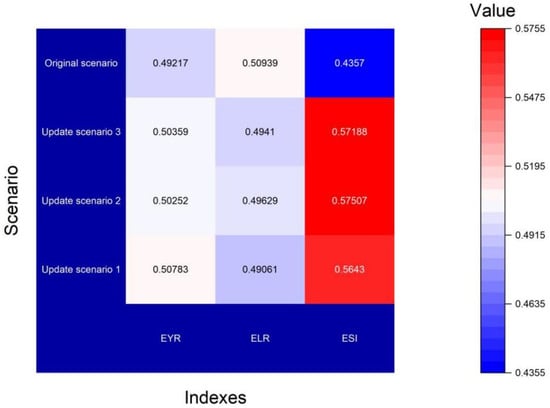
Figure 8.
Sustainability changes of three renewal strategies.
In Figure 9, the change ranges of sustainability indicators have been visualized. Therein, the ESI indexes proportion of the renewal stage displays evident improvements from the original scenario (from 0.56/0.58/0.57 to 0.44).
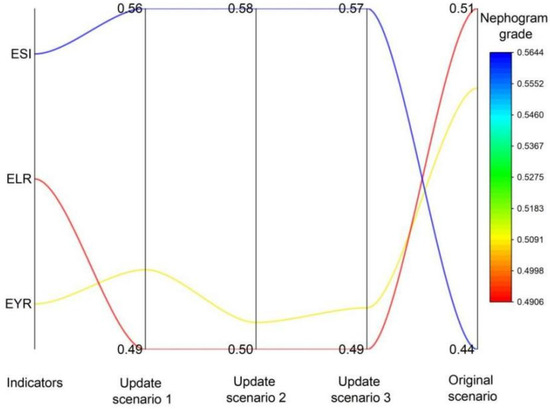
Figure 9.
Sustainability index variation.
4.1.4. Sensitivity Analysis of LCA–Emergy View
According to the main contributors, the building operation stage and building material stage have the primary impact on the total emergy amount for the entire building. Therefore, their sensitivity analysis needs to be considered for accuracy.
The specific assumptions are as follows:
Hypothesis 1 (H1)

(Table 4). At the stage of building operation, six subsystems should be investigated, including environmental inputs, water supply and sewage system treatment facilities, heating and cooling systems, electricity installations, telecommunications system, elevator system, etc. The emergy of each subsystem varies by 5% and 10%, and then the amplitude of the final sustainability indicator change will be verified.

Table 4.
Sensitivity analysis of sustainable indicators under Hypothesis 1.
Hypothesis 2 (H2)

(Table 5). At the stage of building material, seven main types of building materials are selected, involving steel, cement, brick, sand, gravel, iron, and wood, etc. (accounting for about 98.7% of the total emergy on the stage of building material). Similarly, under the changes of 5% and 10% for each material value, the magnitude of changes in sustainability indicators needs to be displayed.

Table 5.
Sensitivity analysis of sustainable indicators under Hypothesis 2.
Figure 10A shows the sensitivity analysis under hypothesis 1. Based on a 10% change, three sustainable indexes have a consistent float and it is close to a linear trend, which demonstrates the validity of the calculation results. Under the 10% change, EYR (10.32%) has a more distinct difference than ELR (7.8%) and ESI (2.24%). Similar results at a 5% alteration can be obtained from Figure 10B. The difference is that a 5% linearity is worse than a 10% linearity, which illustrates that a 5% variation is more sensitive to the impact of sustainability indicators under Hypothesis 1. For Hypothesis 2, the data validity is also verified at 10% and 5% changes. However, a clear distinction is that a 10% change in the data has a large impact on sustainable indexes, which can be found in Figure 10C,D. It can be concluded that the building operation phase is more sensitive to small changes in data (5% variation), whereas the building materials phase is more sensitive to large changes in data (10% variation). The reason for this result is that the subsystems of the building operation stage are multiple mechanical systems, whose sensitivity to data is significantly higher than that of the building material stage.
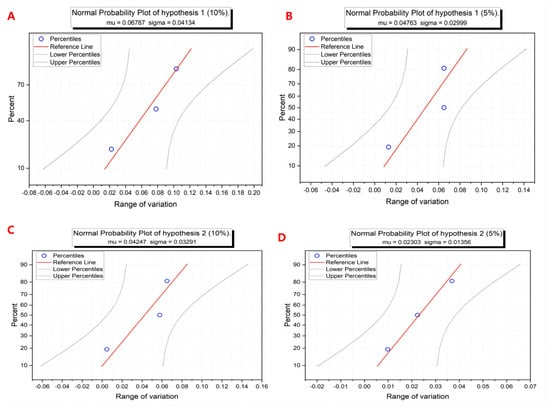
Figure 10.
Sensitivity analysis under Hypothesis 1 and 2.
4.1.5. Unit Emergy Values (UEVs)
Generally speaking, unit emergy value is the core concept of LCA–Emergy analysis. However, in the field of architectural research, not many people calculate and evaluate it, resulting in a lack of sustainability assessment based on the emergy method. In this paper, the UEV has been computed (1.49 × 1016 sej/m2), which has a relatively high value.
To compare and analyze the latest article [], the UEV is 2.14 × 1018 sej/m2, which is higher than that studied in this article (1.49 × 1016 sej/m2). It indicates that the whole building system needs more emergy input, which will consume a lot of resources and energy. The UEV of the entire building system studied in this paper is smaller, elucidating that the design of building renewal in this paper is feasible.
4.2. LCA–Carbon Emission Analysis
In this section, the life-cycle carbon emissions of the building system are calculated and demonstrated. Among them, the carbon emission factor can be obtained from reference [,].
4.2.1. The Carbon Emission of the Building Material Stage
In the building materials stage, there are 19 types of material inputs, of which the largest carbon emission output is steel, followed by gravel and iron, which are 66,750 tCO2, 30,400 tCO2 and 1312 tCO2 (as shown in Table 6 and Figure 11). Depending on the carbon emissions of individual materials, carbon reduction measures need to target the major materials (steel, gravel and iron).

Table 6.
The carbon emission in the building material production stage.
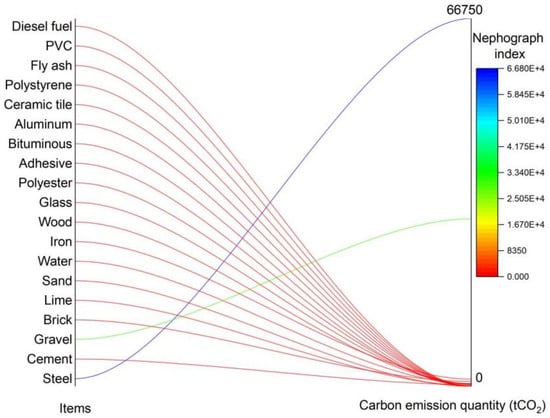
Figure 11.
Dominated carbon emission differentiation.
4.2.2. The Carbon Emission of Building Construction Stage
During the construction phase, the specific carbon emissions of six subsystems are shown in Table 7. Therein, water supply and sewage system treatment facilities emit the most carbon dioxide, at approximately 22,640 tCO2, accounting for 38.55% of the total construction carbon emission, followed by the telecommunications system (18,370.3 tCO2, roughly 31.28%); labor and service (6341 tCO2, roughly 10.79%); heating and cooling systems (5125.2 tCO2, roughly 8.73%); the elevator system (4102.8 tCO2, roughly 6.98%) and electricity installations (2151.1 tCO2, roughly 3.66%), etc. In Figure 12A, the trend of fluctuation can be clearly identified.

Table 7.
The carbon emission in the building construction stage.
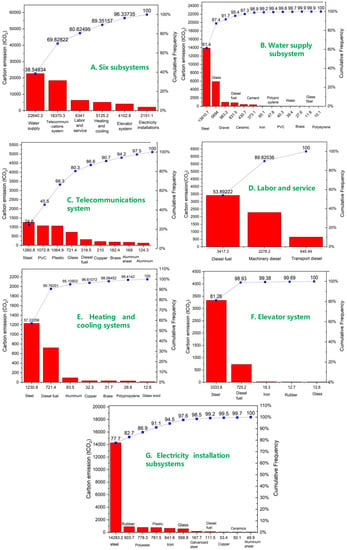
Figure 12.
The carbon emission trend of six subsystems.
Taking the water supply subsystem as an example, it has thirteen components (shown in Figure 10B), including steel, glass, gravel, diesel fuel, ceramic, cement, iron, polypropylene, PVC, water, brass, glass fiber and polystyrene, accounting for about 61.4% of entire water supply subsystem, at 26%, 4.3%, 3.7%, 1.9%, 1.6%, 0.3%, 0.2%, 0.2%, 0.1%, 0.1%, 0.1%, 0.1% and 0.1%, respectively.
For the same reason, telecommunications systems, labor and service, heating and cooling systems and electricity installations have been analyzed according to carbon emission trends. Specific changes are referred to in Figure 12C–G. For the telecommunications system, the top six inputs account for 90.7% of total carbon emissions (which are steel, PVC, plastic, glass, diesel fuel and copper). For labor and service, diesel fuel incurs a main effect for the subsystem. For heating and cooling systems, steel and diesel fuel are the primary contributors, which account for 57.2% and 23.5% of the total carbon emission amounts, respectively. For the elevator system, similar results can be obtained. Steel and diesel fuel are the dominant inputs, accounting for about 81.26% and 17.67%. For electricity installations, steel, rubber, polyester, plastic, iron, and glass, are leading elements (97.6% of carbon emission).
4.2.3. The Carbon Emission in the Building Operation Stage
Because the operational phase takes into account a 20-year period, the amount of carbon emissions is huge, amounting to 1.14 × 107 tons. In total, heat carbon emission has 9.62 × 106 tCO2, electricity (1.78 × 106 tCO2) and water (2.71 × 102 tCO2), as seen in Table 8 and Figure 13. Through the overall study of this paper, the building operation stage has the most carbon emissions in the whole building system, which needs to be paid more attention.

Table 8.
The carbon emission of the building operation stage (tCO2).
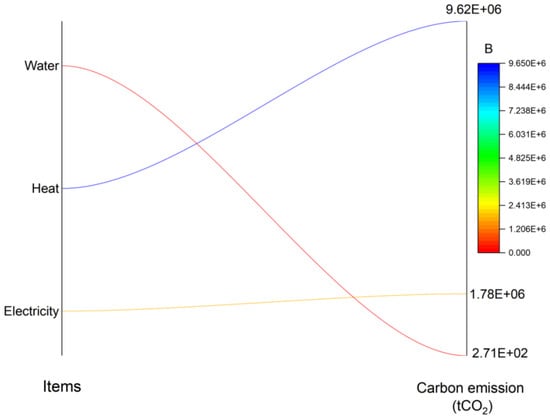
Figure 13.
The carbon emission in the building operation stage.
4.2.4. The Carbon Emission in the Building Renewal Stage
There are three categories of upgrading strategies that focus on sustainable goals. Design strategy 1 revolves around green vegetation, including measures such as vertical landscape walls, rooftop gardens and sunken plaza gardens. Design strategy 2 emphasizes equipment upgrades, such as adding solar photovoltaic power generation devices, rainwater collection systems, heat pump technology utilization and updating the fresh air system. Design strategy 3 aims to improve the spatial performance of the building complex, involving the replacement of energy-saving walls and the use of phase change storage walls, etc.
From the view of a renewal operation, three scenarios have been executed. The specific data and calculation processes are displayed in Table 9. In Figure 14, the change trend is clear. Updated scenario 3 discharged 2584 tCO2, more than updated scenario 1 (1650.3 tCO2) and updated scenario 2 (1092.2 tCO2). This update process is designed for a usage of 20 years.

Table 9.
The carbon emission of the building renewal stage.
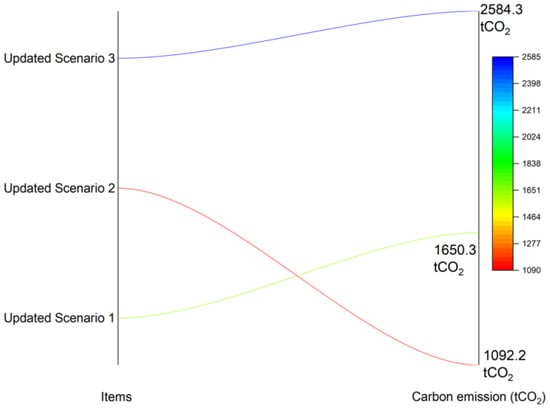
Figure 14.
The carbon emission in the building renewal stage.
4.2.5. The Carbon Emission in the Building Demolition Stage
For the building demolition stage, there are seven major categories, as seen in Table 10. Figure 15 reveals the changes in each input. Depending on 59,860 tCO2, iron played a pivotal role, producing far more carbon than any other term. Then, glass was the second most important factor on the basis of 7630 tCO2. The carbon emissions of the other inputs performed a subordinate function, such as Aluminum (538.78 tCO2), Concrete (153.4 tCO2), PVC (106.82 tCO2), Bricks (13.75 tCO2) and Diesel fuel (0.85 tCO2).

Table 10.
The carbon emission of the building demolition stage.
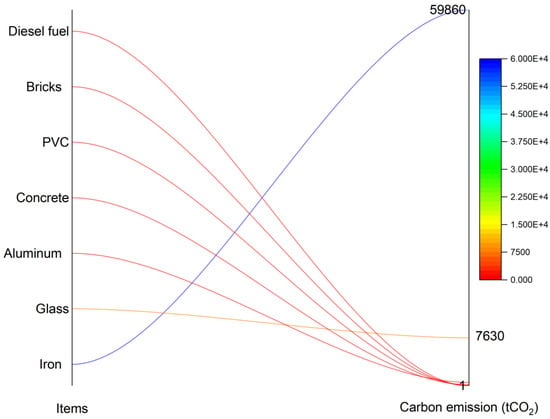
Figure 15.
The carbon emission in the building demolition stage.
4.2.6. LCA–Carbon Emissions Analysis
Table 11 presents the carbon emission situations of the five stages. In accordance with the 20-year service life, the operating phase has the largest carbon footprint (1.14 × 107 tCO2), followed by the building material production stage (1.02 × 105 tCO2), the building demolition stage (6.83 × 104 tCO2), the building construction stage (5.87 × 104 tCO2) and the building renewal stage (5.33 × 103 tCO2). Figure 16 explains the changing trend by comparing it with five stages. The carbon emissions of the operational phase are much higher than those of the other four phases (accounting for 97.9%, roughly; shown in Figure 17).

Table 11.
The carbon emission calculation of the LCA–Carbon method.
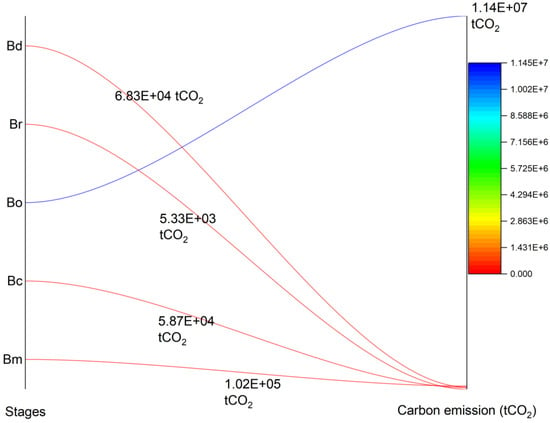
Figure 16.
The carbon emission of LCA–Carbon emission stage.
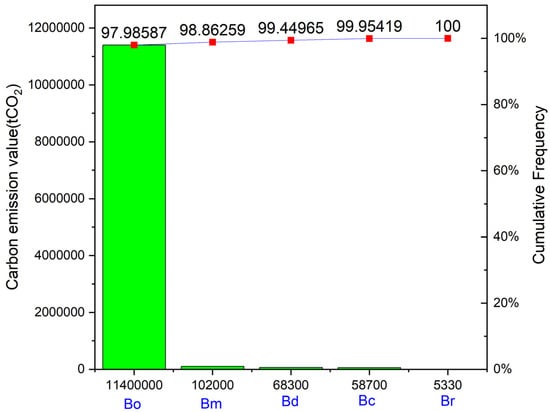
Figure 17.
The carbon emission comparison of the five stages.
4.2.7. Sensitivity Analysis of LCA–Carbon Emissions View
On account of carbon emission amount, the building operation stage plays a critical role. Because it has a decisive effect on the overall carbon output, its sensitivity should be selected and analyzed to ensure the accuracy of this study.
From Section 4.2.3, a fact can be found that electricity and heating consumption are the primary influence factors. To confirm the accuracy of this, four hypotheses were set out and tested.
Hypothesis 1—A 5% change in electricity will be carried out to verify the impact on total carbon emission amount.
Hypothesis 2—A 10% change in electricity will be considered to explore the impact on total carbon emission amount.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
A 5% change in heat will be conducted to test the impact on total carbon emission amount.
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
A 10% change in heat will be performed to confirm the impact on the total carbon emission amount.
According to the calculation results, Figure 18 has been manufactured. In Figure 18, two distinct features can be obtained. On the one hand, Hypothesis 3 and Hypothesis 4 have a larger float than Hypothesis 1 and Hypothesis 2 (to distinguish size based on the cloud color), which illustrates that the sensitivity of heat input is higher than that of electricity. On the other hand, the larger the data of the operation stage, the greater the change in the carbon emissions of the whole building. Hence, to ensure the study accuracy, heat input sensitivity is the first consideration, followed by electrical input sensitivity.
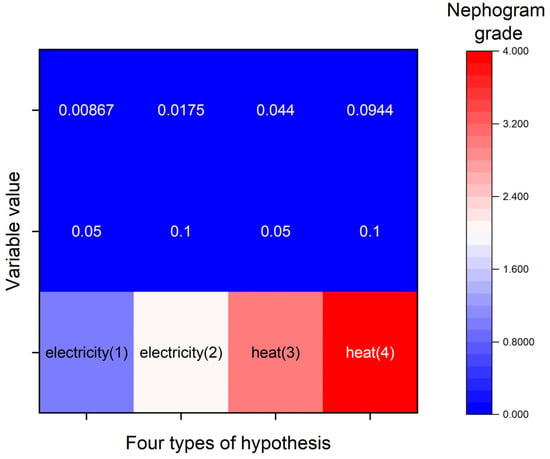
Figure 18.
The sensitivity analysis based on the variation of the operation stage.
5. A New Type of Energy System Reuse Analysis
According to the research in this paper, the building operation stage is the main influencing factor, no matter whether this is from the emergy perspective or the carbon emission perspective. Among them, the building operation stage is mainly composed of the thermal subsystem and the electrical subsystem. Therefore, the strategy improvement in this paper will focus on the thermal subsystem and the electrical subsystem.
To verify the influence of heat and electric energy on the whole building system, a new power and heat supply subsystem has been designed and is displayed in Figure 19. The most obvious highlight of the system is that the energy comes from the waste heat recycling of the glass manufacturing system, which belongs to the reuse of surplus energy. It provides new energy supplies while reducing waste.
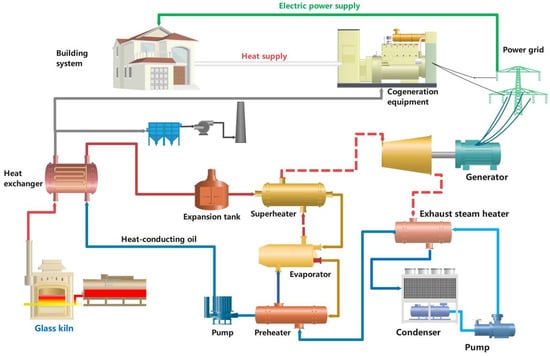
Figure 19.
A new power and heat supply subsystem.
In Figure 19, a glass kiln is the energy source used to provide heat energy through a range of mechanical devices to convert it into electricity, including a heat exchanger, heat-conducting oil, pump, preheater, evaporator, super-heater, expansion tank, exhaust stream heater, condenser, pump, generator, etc. Finally, electricity is produced by the new power generation subsystem, some of which goes to the grid, and some of which goes to the cogeneration machine, where it is used to generate heat for the building system.
- (1)
- From the emergy point of view
Through the data collection, the total emergy of the new power and heat supply subsystem has been calculated. Thus, it provides support for the completion of the calculation of sustainability indicators in Table 12.

Table 12.
Sustainable emergy index progress.
Table 12 and Figure 20 clearly show the change differences between the previous index and the improved indicator. As a whole, with the new system connected, four indexes are increased, including Renewable input (Ri), Nonrenewable resource (Ns), Emergy feedback input (Ef) and the Emergy sustainability indicator (ESI). The remaining two indicators are decreased (Emergy yield ratio (EYR) and Environmental loading ratio (ELR)). Although the emergy of the whole system is increased, the addition of a renewable energy system leads to an environmental pressure reduction, which enhances the sustainability effect of the whole building system. Taking the ESI as an example, the sustainability effect was significantly boosted (from 0.849 to 2.197), with an increment of 1.58 times.
- (2)
- From the carbon emission point of view consider
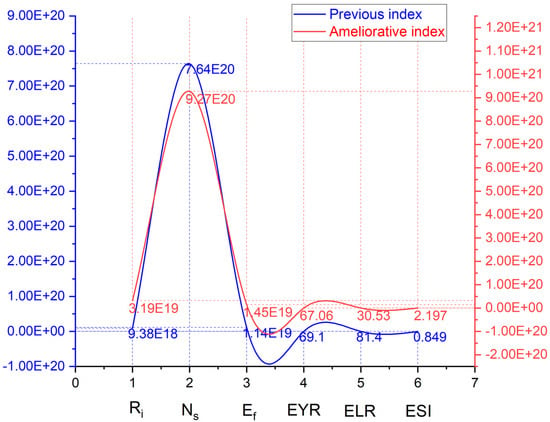
Figure 20.
Index improvement range based on the new power and heat supply subsystem.
As this subsystem is embedded in the daily operation of the building system, the carbon emission of the whole building system in the operation stage is greatly incremental, increasing carbon emissions by about 13.45%. This phenomenon explains that no matter what kind of system is embedded, carbon emissions are raised. However, from the ecosystem perspective, sustainability is improved, which is an evident distinction between the two views.
6. Improvement Strategies
In addition to embedding new systems, two other categories of improvement are also being explored, in terms of renewable energy reuse and alternative resource utilization.
6.1. Clean Energy Reuse
At present, the Chinese government is vigorously developing clean energy utilization. If a building system can adopt clean energy, it will greatly promote the sustainable level of the building system. In China, there are three main types of clean energy, which are solar energy [,], wind energy [,] and hydroelectric power energy [,], respectively. Among them, the use of solar energy is the most popular method.
Taking solar energy as an example to assess, if the entire building system increases emergy by 10%, the related indexes will change significantly. Table 13 exhibits the changing situation. Figure 21 explains the comparison between the previous indicator and the improved index. The most meaningful change is the increase in the sustainability parameter (0.849 to 0.98 of ESI), which was enhanced by 15.43% than before. It is a clear and positive trend to illustrate that solar energy replacement is positive for the building system.

Table 13.
Sustainable emergy index progress.
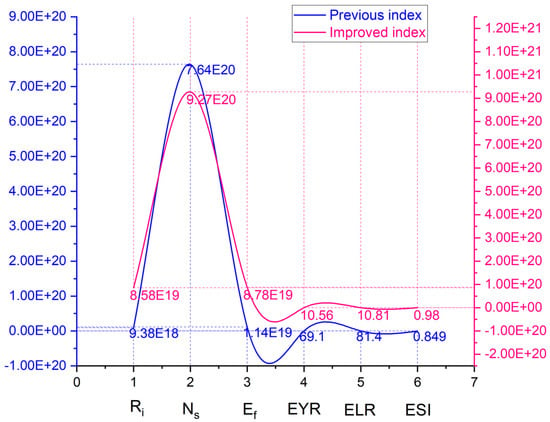
Figure 21.
Index improvement range based on solar energy replacement.
In terms of a carbon emissions viewpoint, assuming that solar power emits one-tenth as much carbon as fossil fuels, it could save 1.6 × 106 tCO2 in building systems, roughly. It accounts for about 14.05% of the total carbon emissions in the building system, with a good performance.
6.2. Alternative Resource Utilization
As the second factor for emergy analysis and carbon emission evaluation in this paper, the influence of the building material phase cannot be ignored. According to the data in Appendix A, steel, cement and brick lead the role in the building material phase. Hence, the hypothesis was carried out according to their substitution. In this paper, we designed and implemented a hypothesis, as follows: how do the sustainability and carbon emissions of the entire building system change if the steel and cement materials are replaced with new renewable materials?
Table 14 lists the calculation results and Figure 22 reveals the change after the assumption. From the point of view of renewable parameters (ESI), it has a noticeable improvement, from 0.849 to 1.487, with a 42.9% advancement.

Table 14.
Sustainable emergy index change based on reuse material replacement.
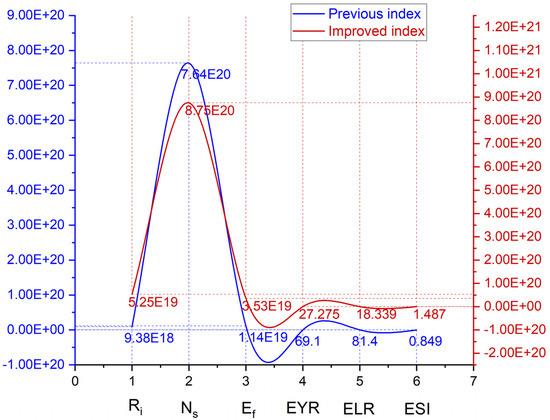
Figure 22.
Index improvement range based on alternative material replacement.
In addition, many researchers have investigated alternative materials for building sustainability enhancement and carbon reduction effects. For instance, for enhancing the performance of fibers reinforced cementitious composites, a steel–basalt hybrid substitution has been considered []. Cement substitution has also been widely investigated and explored for cement production and cementitious composites [,].
7. The Final Discussion
From an LCA–Emergy point of view, the dominant impact element is the building operation stage, followed by the building material production stage, which is similar to study result based on the LCA–Carbon emission perspective. This clarifies that, in the long run, both the building operation stage and the building material stage are factors that cannot be ignored from the perspective of ecology or carbon emission. Meanwhile, the building renewal stage plays a subordinate effect on the basis of the LCA–Emergy and LCA–Carbon emission methods. This stage verifies the consistency of emergy and carbon emission results based on the whole life cycle consideration in the building system.
The difference is that there are a series of sustainable indicators that can display the sustainability status based on LCA–Emergy. However, in accordance with the LCA–Carbon emission view, carbon emissions at each stage can be calculated and analyzed, which cannot be used to assess a sustainable situation in view of the indicators.
At present, there is a lack of scholarly research that combines energy valuation studies with carbon emission calculations. For instance, a study conducted in Spain focused on carbon reduction in building systems from an energy renovation perspective. The analysis highlighted economic factors, inadequate owner awareness and construction sound insulation as barriers to implementing energy renovation []. In Romania, researchers extensively discussed the transformation of inefficient buildings into smart buildings to achieve low-carbon and high-efficiency structures []. A comparative analysis of energy consumption before and after the use of novel insulation materials has been conducted, contributing to the exploration of innovative energy-saving systems for buildings []. Utilizing the Web of Science core collection database, research related to energy and buildings has been analyzed, indicating significant interest and recognition among scholars [].
To summarize the above study, through the LCA–Emergy–Carbon emission methodology, an integrated analysis can be realized. Ecological sustainability is considered, while carbon emissions are analyzed simultaneously. In this way, the study of the building system can be more accurate and comprehensive, so as to provide corresponding improvement strategies.
In the context of this study, the research focuses on the analysis from two perspectives: emergy valuation and carbon emissions. This provides a comprehensive assessment of sustainability for building systems, which is more advantageous compared with single-method analyses of building system sustainability. Additionally, the framework of LCA–Emergy–Carbon emission can serve as a reference for the design of building renovations. However, there are limitations to this study as well. Further research is needed to investigate the cross-research mechanisms and models of these two approaches in order to obtain more accurate sustainability results for building systems.
8. Conclusions
This study is aimed at the whole life cycle of building systems, using calculation and evaluation based on the emergy method and the carbon emission method, which has been shown and analyzed from the sustainability point of view.
LCA–Emergy analysis reveals the sustainable state of the building system. The building operation stage is the main emergy input item; as the primary contributor, it should be much accounted for. Meanwhile, its emergy sustainability index needs to be perfected, which can be verified using unit emergy values.
An LCA–Carbon emission exploration yields a number of similar results; for instance, the operating phase of the building system emits the most carbon, which displays an analogous outcome, and is consistent with the LCA–Emergy analysis results. However, there are also differences: although the coupling of the new energy subsystem can reduce the level of sustainability in the building system, its carbon emissions are increasing, which is contradictory from an environmental sustainability perspective.
To sum up, the LCA–Emergy-Carbon emission methodology is available, and it provides a positive reference for architects and designers. In addition to focusing on emergy input and carbon emissions during the building operation phase, a higher level of sustainable systems does not mean a reduction in carbon emissions and requires comprehensive and adequate consideration. This provides new insights for future researchers, indicating that the assessment of sustainable building systems can go beyond the use of a single energy-based method or carbon emission approach. The integration of both approaches proves to be a viable alternative. Further research can focus on exploring the long-term sustainability indicators of building systems and utilizing machine learning techniques to predict their changing trends. This will realize the comprehensive monitoring and validation of buildings throughout their life cycle.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z.; investigation, A.T.A.; formal analysis, J.Z.; methodology, J.Z.; resources, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.T.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work described in this paper was supported by the State Key Laboratory of Silicate Materials for Architectures (Wuhan University of Technology) (SYSJJ2022-16); the XJTLU Urban and Environmental Studies University Research Centre (UES) (UES-RSF-23030601).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
This study did not report any data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| BIM | Building Information Modeling |
| UEV | Unit Emergy Value |
| Ri | Renewable Input |
| Ns | Nonrenewable Resource |
| Ef | Emergy Feedback Input |
| EYR | Emergy Yield Ratio |
| ELR | Environmental Loading Ratio |
| ESI | Emergy Sustainability Indicator |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
Appendix A

Table A1.
The emergy in the building material production stage.
Table A1.
The emergy in the building material production stage.
| Item | Data | Unit | UEVs | Emergy (sej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | 2.5 × 107 | Kg | 2.1 × 1012 | 5.25 × 1018 |
| Cement | 4.7 × 106 | Kg | 2.94 × 1012 | 1.38 × 1019 |
| Gravel | 1.9 × 106 | Kg | 1.27 × 1012 | 2.41 × 1018 |
| Brick | 3.8 × 106 | Kg | 2.79 × 1012 | 1.06 × 1019 |
| Lime | 3.1 × 105 | Kg | 1.28 × 1012 | 3.97 × 1017 |
| Sand | 2.9 × 106 | Kg | 1.27 × 1012 | 3.68 × 1018 |
| Water | 5.9 × 105 | Kg | 2.67 × 109 | 1.58 × 1015 |
| Iron | 6.4 × 105 | Kg | 3.15 × 1012 | 2.02 × 1018 |
| Wood | 1.7 × 106 | Kg | 6.68 × 1011 | 1.14 × 1018 |
| Glass | 3.5 × 105 | Kg | 1.07 × 1012 | 3.75 × 1017 |
| Polyester | 4.6 × 103 | Kg | 7.34 × 1012 | 3.38 × 1016 |
| Adhesive | 7.8 × 103 | Kg | 7.25 × 1011 | 5.66 × 1015 |
| Bituminous | 9.1 × 103 | Kg | 2.4 × 1012 | 2.18 × 1016 |
| Aluminum | 6.3 × 103 | Kg | 9.65 × 1011 | 6.08 × 1015 |
| Ceramic tile | 4.7 × 104 | Kg | 2.43 × 1012 | 1.14 × 1017 |
| Polystyrene | 5.1 × 103 | Kg | 5.23 × 1012 | 2.67 × 1016 |
| Fly ash | 5.9 × 103 | Kg | 1.78 × 1013 | 1.05 × 1017 |
| PVC | 7.4 × 103 | Kg | 7.49 × 1012 | 5.54 × 1016 |
| Diesel fuel | 5.1 × 1010 | J | 1.36 × 105 | 6.94 × 1015 |

Table A2.
The emergy in the building construction stage.
Table A2.
The emergy in the building construction stage.
| Item | Data | Unit | UEVs | Emergy (sej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental inputs | ||||
| Land use | 5.73 × 1010 | J | 9.42 × 104 | 5.40 × 1015 |
| Solar | 4.31 × 109 | J | 1.00 × 100 | 4.31 × 109 |
| Labor and service | ||||
| Diesel fuel | 2.35 × 106 | J | 1.28 × 1012 | 3.01 × 1018 |
| Machinery diesel | 3.61 × 106 | J | 1.27 × 1012 | 4.58 × 1018 |
| Transport diesel | 6.99 × 106 | J | 2.67 × 109 | 1.87 × 1016 |
| Water supply and sewage system treatment facilities | ||||
| Steel | 5.21 × 106 | Kg | 3.53 × 1012 | 1.84 × 1019 |
| PVC | 8.41 × 103 | Kg | 7.49 × 1012 | 6.30 × 1016 |
| Polystyrene | 2.67 × 103 | Kg | 6.7 × 1012 | 1.79 × 1016 |
| Brass | 7.40 × 103 | Kg | 1.33 × 1012 | 9.84 × 1015 |
| Polypropylene | 7.99 × 103 | Kg | 7.49 × 1012 | 5.98 × 1016 |
| Glass fiber | 8.41 × 103 | Kg | 2.28 × 1012 | 1.92 × 1016 |
| Iron | 2.93 × 104 | Kg | 3.15 × 1012 | 9.23 × 1016 |
| Ceramic | 5.82 × 105 | Kg | 2.43 × 1012 | 1.41 × 1018 |
| Glass | 4.21 × 106 | Kg | 1.07 × 1012 | 4.50 × 1018 |
| Cement | 5.33 × 106 | Kg | 2.94 × 1012 | 1.57 × 1019 |
| Water | 4.81 × 104 | Kg | 2.67 × 1012 | 1.28 × 1017 |
| Gravel | 6.02 × 104 | Kg | 1.27 × 1012 | 7.65 × 1016 |
| Diesel fuel | 8.98 × 107 | J | 1.36 × 105 | 1.22 × 1013 |
| Heating and cooling systems | ||||
| Steel | 4.61 × 105 | Kg | 2.1 × 1012 | 9.68 × 1017 |
| Polypropylene | 4.78 × 103 | Kg | 6.7 × 1012 | 3.20 × 1016 |
| Aluminum | 5.92 × 103 | Kg | 9.65 × 1011 | 5.71 × 1015 |
| Glass wool | 9.03 × 103 | Kg | 7.28 × 1012 | 6.57 × 1016 |
| Brass | 8.51 × 103 | Kg | 1.33 × 1013 | 1.13 × 1017 |
| Copper | 8.66 × 103 | Kg | 1.52 × 1012 | 1.32 × 1016 |
| Diesel fuel | 7.72 × 106 | J | 1.36 × 105 | 1.05 × 1012 |
| Electricity installations | ||||
| Copper | 1.34 × 104 | Kg | 1.52 × 1012 | 2.04 × 1016 |
| Aluminum sheet | 4.82 × 104 | Kg | 1.25 × 1012 | 6.03 × 1016 |
| Galvanized steel | 5.72 × 104 | Kg | 3.53 × 1012 | 2.02 × 1017 |
| Steel | 9.04 × 105 | Kg | 2.1 × 1012 | 1.90 × 1018 |
| Rubber | 6.99 × 104 | Kg | 5.48 × 1012 | 3.83 × 1017 |
| Polyester | 7.83 × 104 | Kg | 7.34 × 1012 | 5.75 × 1017 |
| Iron | 5.44 × 104 | Kg | 3.15 × 1012 | 1.71 × 1017 |
| Ceramics | 6.78 × 104 | Kg | 2.43 × 1012 | 1.65 × 1017 |
| Plastic | 9.94 × 104 | Kg | 4.37 × 1012 | 4.34 × 1017 |
| Glass | 3.82 × 104 | Kg | 1.07 × 1012 | 4.09 × 1016 |
| Diesel fuel | 6.91 × 107 | J | 1.36 × 105 | 9.40 × 1012 |
| Telecommunications system | ||||
| Copper | 5.63 × 104 | Kg | 1.52 × 1012 | 8.56 × 1016 |
| PVC | 6.67 × 104 | Kg | 7.49 × 1012 | 5.00 × 1017 |
| Aluminum sheet | 7.98 × 104 | Kg | 1.25 × 1012 | 9.98 × 1016 |
| Plastic | 2.33 × 104 | Kg | 4.37 × 1012 | 1.02 × 1017 |
| Brass | 4.53 × 104 | Kg | 1.33 × 1012 | 6.02 × 1016 |
| Aluminum | 6.74 × 104 | Kg | 9.65 × 1012 | 6.50 × 1017 |
| Glass | 8.88 × 104 | Kg | 1.07 × 1012 | 9.50 × 1016 |
| Steel | 6.79 × 104 | Kg | 2.1 × 1012 | 1.43 × 1017 |
| Diesel fuel | 7.78 × 107 | J | 1.36 × 105 | 1.06 × 1013 |
| Elevator system | ||||
| Steel | 2.11 × 105 | Kg | 2.1 × 1012 | 4.43 × 1017 |
| Rubber | 5.32 × 103 | Kg | 5.48 × 1012 | 2.92 × 1016 |
| Iron | 8.93 × 103 | Kg | 3.15 × 1012 | 2.81 × 1016 |
| Glass | 9.06 × 103 | Kg | 1.07 × 1012 | 9.69 × 1015 |
| Diesel fuel | 7.82 × 108 | J | 1.36 × 105 | 1.06 × 1014 |

Table A3.
The emergy of building operation stage.
Table A3.
The emergy of building operation stage.
| Item | Data | Unit | UEVs | Emergy (sej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar | 6.52 × 1012 | J | 1.00 × 100 | 6.52 × 1012 |
| Electricity | 9.36 × 1015 | J | 6.39 × 104 | 5.98 × 1020 |
| Heat | 4.81 × 1012 | J | 2.01 × 106 | 9.67 × 1018 |
| Water | 3.31 × 108 | kg | 2.67 × 109 | 8.84 × 1017 |

Table A4.
The emergy of building renewal stage.
Table A4.
The emergy of building renewal stage.
| Item | Data | Unit | UEVs | Emergy (sej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Updated Scenario 1 | ||||
| PVC | 1.14 × 104 | Kg | 2.22 × 1011 | 2.53 × 1015 |
| Cement | 4.72 × 105 | Kg | 2.94 × 1012 | 1.39 × 1018 |
| Water | 9.52 × 106 | Kg | 2.67 × 109 | 2.54 × 1016 |
| Diesel fuel | 6.76 × 106 | Kg | 1.36 × 105 | 9.19 × 1011 |
| Updated Scenario 2 | ||||
| Bricks | 5.67 × 104 | Kg | 2.03 × 1011 | 1.15 × 1016 |
| Concrete | 3.71 × 105 | Kg | 1.19 × 1012 | 4.41 × 1017 |
| Diesel fuel | 4.48 × 106 | Kg | 1.36 × 105 | 6.09 × 1011 |
| Updated Scenario 3 | ||||
| Glass | 6.15 × 104 | Kg | 1.69 × 1012 | 1.04 × 1017 |
| Aluminum | 2.36 × 101 | Kg | 9.65 × 1011 | 2.28 × 1013 |
| Copper | 1.73 × 101 | Kg | 1.52 × 1012 | 2.63 × 1013 |
| Diesel fuel | 9.24 × 106 | J | 1.36 × 105 | 1.26 × 1012 |

Table A5.
The emergy of building demolition stage.
Table A5.
The emergy of building demolition stage.
| Item | Data | Unit | UEVs | Emergy (sej) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycling section | ||||
| Glass | 5.45 × 106 | Kg | 2.21 × 1011 | 1.20 × 1018 |
| Iron | 2.92 × 107 | Kg | 2.31 × 1011 | 6.75 × 1018 |
| PVC | 2.23 × 104 | Kg | 2.22 × 1011 | 4.95 × 1015 |
| Aluminum | 3.41 × 104 | Kg | 2.21 × 1011 | 7.54 × 1015 |
| Bricks | 5.73 × 104 | Kg | 2.03 × 1011 | 1.16 × 1016 |
| Concrete | 1.18 × 106 | Kg | 1.19 × 1012 | 1.40 × 1018 |
| Diesel fuel | 9.21 × 109 | J | 1.36 × 105 | 1.25 × 1015 |
| Landfill emergy | ||||
| Non-recycled materials | 8.53 × 106 | Kg | 2.1 × 1011 | 1.79 × 1018 |
| Diesel fuel | 6.75 × 109 | J | 1.36 × 105 | 9.18 × 1014 |

Table A6.
Various input categories based on emergy analysis viewpoint.
Table A6.
Various input categories based on emergy analysis viewpoint.
| Renewable Part | Solar Irradiation |
|---|---|
| Non-renewable part | Materials |
| Purchased part | Electricity |
| Water | |
| Gasoline and Diesel fuel | |
| Labor services |
References
- Sherif, G.; Thomas, W.; Carmela, C.; Tyler, S. Green building standards and the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116552. [Google Scholar]
- Elena, G.; Maria, F. Embodied energy in existing buildings as a tool for sustainable intervention on urban heritage. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 88, 104284. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.W.; Ng, S.T.; Skitmore, M. Influence of procurement systems to the success of sustainable buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 1007–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Sudhakar, K.; Baredar, P.; Mamat, R. BIPV based sustainable building in South Asian countries. Sol. Energy 2018, 170, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyce, G.L.; Smith, A.J.; Kirwan, M.L.; Rich, R.L.; Megonigal, J.P. Oxygen priming induced by elevated CO2 reduces carbon accumulation and methane emissions in coastal wetlands. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Sonne, C.; You, S. Dynamic Carbon-Neutrality Assessment Needed to Tackle the Impacts of Global Crises. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9851–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Tsay, Y.-S.; Zhang, T. A multi-objective optimization strategy for building carbon emission from the whole life cycle perspective. Energy 2023, 262, 125373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Wang, Y.; Pang, Q.; Hao, T.; Zhou, Y. The dynamic analysis on low-carbon building adoption under emission trading scheme. Energy 2023, 263, 125946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufan, Z.; Yong, G.; Hengyu, P.; Fei, W.; Dong, W. Ecological and socioeconomic impacts of payments for ecosystem services e A Chinese garlic farm case. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharipour, M.R.; Amiri, Z.; Campbell, D.E. Evaluation of the sustainability of four greenhouse vegetable production ecosystems based on an analysis of emergy and social characteristics. Ecol. Model. 2020, 424, 109021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, D.; Garcia-Caro, D.; Joosse, S.; Granvik, M.; Peniche, F. The Sustainability of Living in a Green Urban District: An Emergy Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, L. Urban ecological security dynamic analysis based on an innovative emergy ecological footprint method. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 16163–16191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Multi-System Urban Waste-Energy Self-Circulation: Design of Urban Self-Circulation System Based on Emergy Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santagata, R.; Zucaro, A.; Viglia, S.; Ripa, M.; Tian, X.; Ulgiati, S. Assessing the sustainability of urban eco-systems through Emergy-based circular economy indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wu, Z.; Guo, X.; Yan, D. Emergy evaluation of positive and negative benefits of agricultural water use based on energy analysis of water cycle. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, L. Environmental Sustainability Assessment of a New Sewage Treatment Plant in China Based on Infrastructure Construction and Operation Phases Emergy Analysis. Water 2020, 12, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Cocozza, A.; Zucaro, A.; Santagata, R.; Ulgiati, S. Circular economy in the agro-industry: Integrated environmental assessment of dairy products. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 148, 111314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagata, R.; Zucaro, A.; Fiorentino, G.; Lucagnano, E.; Ulgiati, S. Developing a procedure for the integration of Life Cycle Assessment and Emergy Accounting approaches, The Amalfi paper case study. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Lyu, Y. Performance comparison of sewage treatment plants before and after their upgradation using emergy evaluation combined with economic analysis: A case from Southwest China. Ecol. Model. 2022, 472, 110077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Srinivasan, R.S.; Peng, C. A Systematic Approach to Calculate Unit Emergy Values of Cement Manufacturing in China Using Consumption Quota of Dry and Wet Raw Materials. Buildings 2020, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Asutosh, A.T.; Sun, N.; Fu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Ecological sustainability assessment of building glass industry in China based on the point of view of raw material emergy and chemical composition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 40670–40697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiano, S.; Ulgiati, S.; Gonella, F. Systemic sustainability and resilience assessment of health systems, addressing global societal priorities: Learnings from a top nonprofit hospital in a bioclimatic building in Africa. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibaba, M.; Pourdarbani, R.; Manesh, M.H.K.; Ochoa, G.V.; Forero, J.D. Thermodynamic, exergo-economic and exergo-environmental analysis of hybrid geothermal-solar power plant based on ORC cycle using emergy concept. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Tracing the spatial variation and value change of ecosystem services in Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, P.; Nie, L. Applying emergy and decoupling analysis to assess the sustainability of China’s coal mining area. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, S.; Gonella, F. To build or not to build? Megaprojects, resources, and environment: An emergy synthesis for a systemic evaluation of a major highway expansion. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 772–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadegaridehkordi, E.; Hourmand, M.; Nilashi, M.; Alsolami, E.; Samad, S.; Mahmoud, M.; Alarood, A.A.; Zainol, A.; Majeed, H.D.; Shuib, L. Assessment of sustainability indicators for green building manufacturing using fuzzy multi-criteria decision making approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 122905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, M.; Wang, S.; Chiu, A.S.; Wang, Y. Can an island economy be more sustainable? A comparative study of Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneru, S.; Jahromi, F.F.; Hatami, M.; Roudebush, W.; Jeelani, I. Integration of Emergy Analysis with Building Information Modeling. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.S.; Braham, W.W.; Campbell, D.E.; Curcija, C.D. Re (De) fining Net Zero Energy: Renewable Emergy Balance in environmental building design. Build. Environ. 2012, 47, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yao, R.; Shu, Z. Emergy-based sustainability assessment of different energy options for green buildings. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 100, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Srinivasan, R.S.; Braham, W.W.; Tilley, D.R. An ecological understanding of net-zero energy building: Evaluation of sustainability based on emergy theory. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Braham, W.W. Uncertainty characterization of building emergy analysis (BEmA). Build. Environ. 2015, 92, 538–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.; Srinivasan, R.; Mani, M. An Emergy-based Approach to Evaluate the Effectiveness of Integrating based Sensing Systems into Smart Buildings. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Ma, G.; Gou, Q.; Zhao, P.; Jia, X. Emergy analysis and optimization for a solar-driven heating and cooling system integrated with air source heat pump in the ultra-low energy building. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 63, 105467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Xie, K.; Wang, D. A novel emergy-based optimization model of a building cooling, heating and power system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 268, 115987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Praveen, A. Emergy parameters for ensuring sustainable use of building materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 122382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Du, B.; Zhu, J. Evaluating old community renewal based on emergy analysis: A case study of Nanjing. Ecol. Model. 2021, 449, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.; Zhou, Y.; Illankoon, C.; Le, K.N. A critical review on BIM and LCA integration using the ISO 14040 framework. Build. Environ. 2022, 213, 108865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Teng, Y.; Pan, W.; Zhang, Y. BIM-integrated LCA to automate embodied carbon assessment of prefabricated buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Xu, J.; Pan, W.; Zhang, Y. A systematic review of the integration of building information modeling into life cycle assessment. Build. Environ. 2022, 221, 109260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.R.; Megahed, N.A.; Eleinen, O.M.A.; Hassan, A.M. Toward a national life cycle assessment tool: Generative design for early decision support. Energy Build. 2022, 267, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fnais, A.; Rezgui, Y.; Petri, I.; Beach, T.; Yeung, J.; Ghoroghi, A.; Kubicki, S. The application of life cycle assessment in buildings: Challenges, and directions for future research. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2022, 27, 627–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, V.G.; Tollin, N.; Sattrup, P.A.; Birkved, M.; Holmboe, T. What are the challenges in assessing circular economy for the built environment? A literature review on integrating LCA, LCC and S-LCA in life cycle sustainability assessment, LCSA. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 50, 104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, F.; Guo, B.H. Stakeholders’ perspectives on BIM and LCA for green buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 48, 103931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Asutosh, A.T.; Wu, G.; Wei, G.; Shi, Y.; Yang, M. Sustainability Study of a Residential Building near Subway Based on LCA-Emergy Method. Buildings 2022, 12, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Xu, D.; Zhang, C. Sustainability Investigation in the Building Cement Production System Based on the LCA-Emergy Method. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, S. The “price” of saved time, the illusion of saved fuel: Life-Cycle Assessment of a major highway expansion. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 131087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Hong, J.; Liu, G.; Li, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L. Co-Benefifits Analysis of Buildings Based on Different Renewal Strategies: The Emergy-Lca Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yan, D.; Jiang, Y. Challenges and opportunities for carbon neutrality in China’s building sector—Modelling and data. Build. Simul. 2022, 15, 1899–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.; Xu, L.; Liu, B.; Cai, W.; Feng, W. China’s commercial building carbon emissions toward 2060: An integrated dynamic emission assessment model. Appl. Energy 2022, 325, 119828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Luo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Feng, W.; Zhou, N.; Yang, L. Towards low-carbon cities through building-stock-level carbon emission analysis: A calculating and mapping method. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 78, 103633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Q.; Cai, W.; Ren, H. Regional inequality in the carbon emission intensity of public buildings in China. Build. Environ. 2022, 225, 109657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.; Ma, Y.; Xu, L.; Feng, W.; Cai, W. Carbon emissions in China’s urban residential building sector through 2060: A dynamic scenario simulation. Energy 2022, 254, 124395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, Q.; Lu, C.; Li, J. Exploration in carbon emission reduction effect of low-carbon practices in prefabricated building supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ye, Y.; He, C.; Zuo, W. The economic impacts of carbon emission trading scheme on building retrofits: A case study with U.S. medium office buildings. Build. Environ. 2022, 221, 109311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zuo, B.; Qu, C.; Ge, L.; Shen, Q. A reasonable distribution of natural landscape: Utilizing green space and water bodies to reduce residential building carbon emissions. Energy Build. 2022, 267, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoruso, F.M.; Sonn, M.-H.; Schuetze, T. Carbon-neutral building renovation potential with passive house-certified components: Applications for an exemplary apartment building in the Republic of Korea. Build. Environ. 2022, 215, 108986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Bi, L. Study on spatio-temporal changes and driving factors of carbon emissions at the building operation stage- A case study of China. Build. Environ. 2022, 219, 109147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Ren, H.; Cai, W.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Allocation of carbon emission quotas for China’s provincial public buildings based on principles of equity and efficiency. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 108994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinham, J.; Fjeldheim, H.; Yan, B.; Helge, T.D.; Edwards, K.; Hegli, T.; Malkawi, A. Zero-carbon balance: The case of HouseZero. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Cui, C.; Skitmore, M. BIM-based approach for the integrated assessment of life cycle carbon emission intensity and life cycle costs. Build. Environ. 2022, 226, 109691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alcalá, J.; Yepes, V. Bridge Carbon Emissions and Driving Factors Based on a Life-Cycle Assessment Case Study: Cable-Stayed Bridge over Hun He River in Liaoning, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Lu, S.; Rong, X.; Xu, X.; Pang, F. Study on comprehensive whole life carbon emission reduction potential and economic feasibility impact based on progressive energy-saving targets: A typical renovated ultra-low energy office. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 58, 105029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhshik, M.; Panthapulakkal, S.; Tjong, J.; Bilton, A.; Singh, C.; Sain, M. Cross-country analysis of life cycle assessment–based greenhouse gas emissions for automotive parts: Evaluation of coefficient of country. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 138, 110546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, M.; Saade, M.R.M.; Balouktsi, M.; Rasmussen, F.N.; Birgisdottir, H.; Frischknecht, R.; Habert, G.; Lützkendorf, T.; Passer, A. Embodied GHG emissions of buildings—The hidden challenge for effffective climate change mitigation. Appl. Energy 2020, 258, 114107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Pan, Y.; Li, L.; Kong, M. Life Cycle Carbon Emission Assessment of Building Refurbishment: A Case Study of Zero-Carbon Pavilion in Shanghai Yangpu Riverside. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, B.; Zhang, X.; Eriksson, O.; Wallhagen, M. Life Cycle Cost Analysis of a Single-Family House in Sweden. Buildings 2021, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Xie, W.J.; Xu, L.; Li, L.L.; Jim, C.Y.; Wei, T.B. Holistic life-cycle accounting of carbon emissions of prefabricated buildings using LCA and BIM. Energy Build. 2022, 266, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Cang, Y.; Yang, L. Assessing the embodied carbon reduction potential of straw bale rural houses by hybrid life cycle assessment: A four-case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 303, 127002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Campbell, D.E.; Villbiss, C.; Ulgiati, S. The geobiosphere emergy baseline: A synthesis. Ecol. Model. 2016, 339, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrić, I.; Pina, A.; Ferrao, P.; Lacarriere, B.; Le Corre, O. The impact of renovation measures on building environmental performance: An emergy approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 51366-2019; Standard for Building Carbon Emission Calculation in China. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Lee, J.M.; Braham, W.W. Building emergy analysis of Manhattan: Density parameters for high-density and high-rise developments. Ecol. Model. 2017, 363, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPCD. China Products Carbon Footprint Factors Database. Available online: lca.cityghg.com (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Yu, W.; Su, H.; Chen, Y.; Lin, P. Solar-absorbing energy storage materials demonstrating superior solar-thermal conversion and solar-persistent luminescence conversion towards building thermal management and passive illumination. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 266, 115804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Kwan, T.H.; Dabwan, Y.N.; Hu, M.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Pei, G. Seasonal-regulatable energy systems design and optimization for solar energy year-round utilization. Appl. Energy 2022, 322, 119500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, S.; Chen, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xu, C. Assessment of combined wind and wave energy in the tropical cyclone affected region: An application in China seas. Energy 2022, 260, 125020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, T. Optimization strategy of wind energy harvesting via triboelectric-electromagnetic flexible cooperation. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, R.; Eskandarpanah, R.; Akbari, M.; Rezaei, N.; Mazloumin, P.; Farahani, O.N. Development of a New Simulation Model for the Reservoir Hydropower Generation. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 2241–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, P.T.; Tran, D.T.; Nguyen, T.T. Electricity generation cost reduction for hydrothermal systems with the presence of pumped storage hydroelectric plants. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 9931–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.; Ji, X. Effects of high temperature and substitution rates of fly ash on the mechanical properties and microstructures of steel-basalt hybrid fibers reinforced cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 352, 128895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordy, A.; Younsi, A.; Aggoun, S.; Fiorio, B. Cement substitution by a recycled cement paste fine: Role of the residual anhydrous clinker. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 132, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, Ş.; Ceylan, H. The effects on mechanical properties of sustainable use of waste andesite dust as a partial substitution of cement in cementitious composites. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 58, 104959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Navarro, J.; Bueso, M.C.; Vázquez, G. Drivers of and Barriers to Energy Renovation in Residential Buildings in Spain—The Challenge of Next Generation EU Funds for Existing Buildings. Buildings 2023, 13, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, M.; Prada, I.F.; Cristea, M.; Popescu, D.E.; Bungău, C.; Aleya, L. New solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through energy efficiency of buildings of special importance–Hospitals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoure, A.N.; Genovese, P.V. Comparative Study of the Impact of Bio-Sourced and Recycled Insulation Materials on Energy Effificiency in Offifice Buildings in Burkina Faso. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, C.C.; Prada, F.I.H.; Bungau, T.; Bungau, C.; Bendea, G.; Prada, M.F. Web of Science Scientometrics on the Energy Effificiency of Buildings to Support Sustainable Construction Policies. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).