Evolution of Solid Waste Management System in Lahore: A Step towards Sustainability of the Sector in Pakistan
Abstract
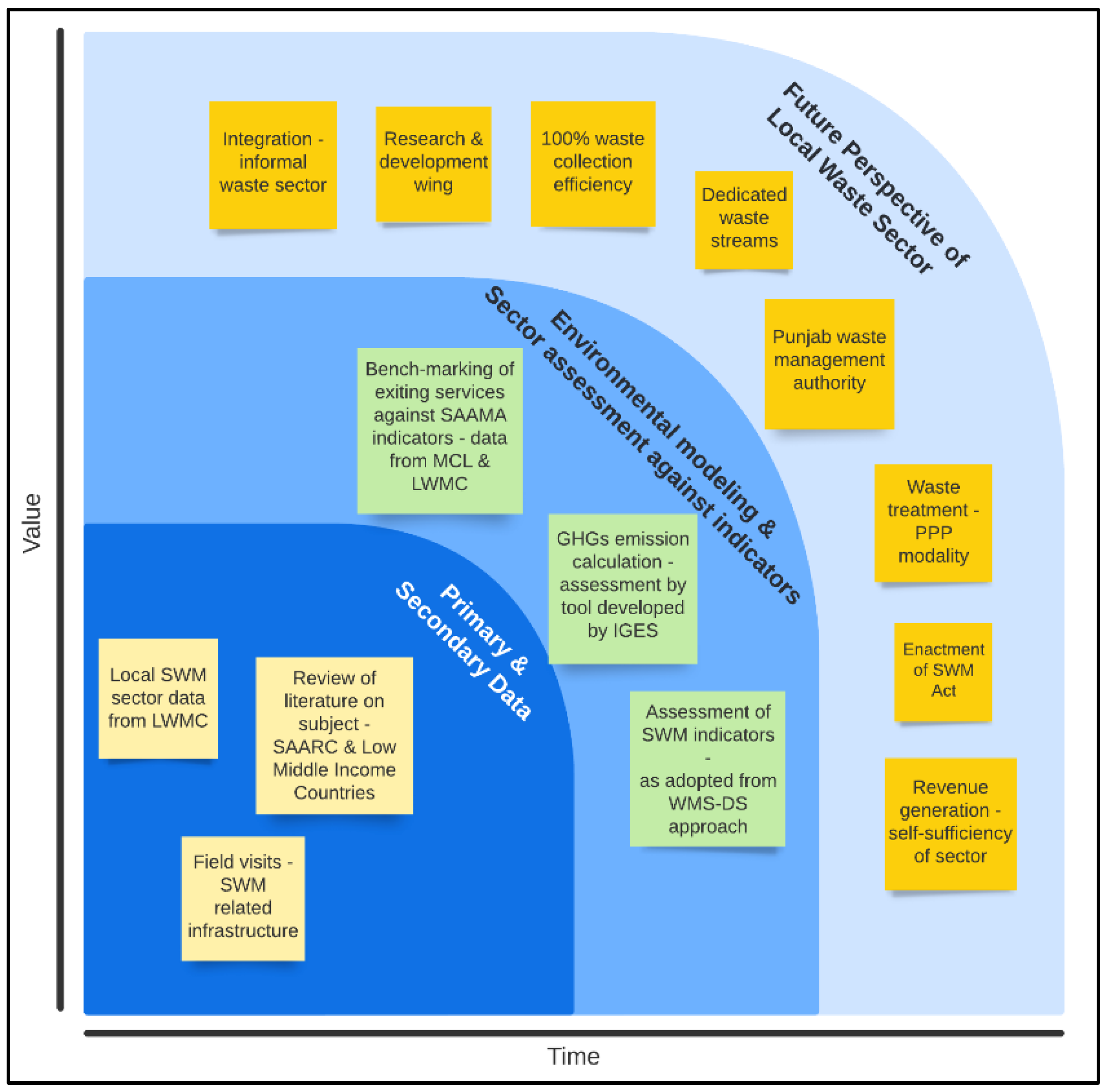
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data on City Waste Management
2.2. Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emission for Waste Treatments for Business as Usual (BAU)
2.3. Indicators for Sectoral Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Efforts and Strategies for Improvement of SWM in Lahore
3.1.1. Formation of Solid Waste Management Department
3.1.2. Bylaws for Municipal Solid Waste
3.1.3. Lahore High Court Report on Waste Management
3.1.4. Establishment of Compost Plant
3.1.5. Performance-Based System (PBS)
3.1.6. Formation of Project Management Unit
3.1.7. Formation of Lahore Waste Management Company (LWMC)
3.1.8. Establishment of Six Model Areas/UCs
3.1.9. Consultancy Agreement with Istanbul Municipality
3.1.10. Services and Assets Management Agreement (SAAMA)
3.1.11. Establishment of Material Recovery Facility (MRF) for Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF)
3.1.12. Outsourcing of SWM Services to Turkish Companies
3.1.13. Lesson Learned from SWM Outsourcing
3.1.14. Establishment of Hospital Waste Management System
3.2. Present Status of Waste Management Services
3.3. Municipal Solid Waste Characteristics
3.4. Procurement of New Fleet by LWMC
3.5. Outsourcing of Secondary Collection by LWMC
3.6. Waste Collection Efficiency of Current Model
3.7. Municipal Waste Treatment
3.8. Waste Disposal
3.9. Detail of Existing HR Deployed
3.10. Expenditures on SWM
4. Discussions
5. Future Perspective for Lahore Waste Sector
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, D.C. Development drivers for waste management. Waste Manag. Res. 2007, 25, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, I.M.; Dias, M.F. Evolution on the solid urban waste management in Brazil: A portrait of the Northeast Region. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Bridging the Gap in Solid Waste Management: Governance Requirements for Results; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, T. Synergy degree evaluation of stakeholder engagement in integrated municipal solid waste management: A case study in Harbin, China. Energies 2022, 15, 5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, S.A.; Christensen, T.H.; Damgaard, A. Environmental performance of household waste management in Europe-An example of 7 countries. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abis, M.; Bruno, M.; Kuchta, K.; Simon, F.G.; Grönholm, R.; Hoppe, M.; Fiore, S. Assessment of the synergy between recycling and thermal treatments in municipal solid waste management in Europe. Energies 2020, 13, 6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimov, U.; Okoro, V.; Hernandez, H.H. Recent progress and trends in the development of microbial biofuels from solid waste—A review. Energies 2021, 14, 6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laso, J.; García-Herrero, I.; Margallo, M.; Bala, A.; Fullana-i-Palmer, P.; Irabien, A.; Aldaco, R. LCA-based comparison of two organic fraction municipal solid waste collection systems in historical centres in Spain. Energies 2019, 12, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minelgaitė, A.; Liobikienė, G. Waste problem in European Union and its influence on waste management behaviours. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.; Martinho, G. Waste hierarchy index for circular economy in waste management. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollikkathara, N.; Feng, H.; Stern, E. A purview of waste management evolution: Special emphasis on USA. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, A.K. An Economic Analysis of Solid Waste Management Outsourcing in Myanmar; The Asia Foundation: Yangon, Myanmar, 2020; pp. 3–45. [Google Scholar]
- Muttamara, S.; Leong, S.T.; Somboonjaroensri, C.; Wongpradit, W. The evolution of solid waste management in Bangkok: Implications for the future. Sci. Technol. Asia. 2004, 9, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mmereki, D.; Baldwin, A.; Li, B. A comparative analysis of solid waste management in developed, developing and lesser developed countries. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2016, 5, 120–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periathamby, A.; Hamid, F.S.; Khidzir, K. Evolution of solid waste management in Malaysia: Impacts and implications of the solid waste bill, 2007. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2009, 11, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J. Evolving partnerships in the collection of urban solid waste in the developing world. In Solid Waste Management and Recycling; Baud, I., Post, J., Furedy, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, F.A.S. Solid waste management system in Dhaka city of Bangladesh. J. Mod. Sci. Technol. 2016, 4, 192–209. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, M.A.; Ahmed, M.M.; Aziz, M.; Beg, M.R.; Hoque, M.E. Municipal solid waste management and waste-to-energy potential from rajshahi city corporation in Bangladesh. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Ismail, S.A.; Singh, P.; Singh, R.P. Urban solid waste management in the developing world with emphasis on India: Challenges and opportunities. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoann, V.; Fujiwara, T.; Seng, B.; Lay, C.; Yim, M. Assessment of public–private partnership in municipal solid waste management in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imam, T.; McInnes, A.; Colombage, S.; Grose, R. Opportunities and Barriers for FinTech in SAARC and ASEAN Countries. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2022, 15, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cherian, J.; Shabbir, M.S.; Sial, M.S.; Li, J.; Mester, I.; Badulescu, A. Exploring the relationship between renewable energy sources and economic growth. The case of SAARC countries. Energies 2021, 14, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Abdullah, Y.; Nizami, A.-S.; Sultan, I.A.; Sharif, F. Assessment of solid waste management system in Pakistan and sustainable model from environmental and economic perspective. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.; Sharholy, M.; Alam, P.; Al-Mansour, A.I.; Ahmad, K.; Kamal, M.A.; Alam, S.; Pervez, M.N.; Naddeo, V. Evaluation of cost benefit analysis of municipal solid waste management systems. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajul, I. Urban Waste Management in Bangladesh: An Overview with a Focus on Dhaka. In Proceedings of the 23rd ASEF Summer University—Education Department, Singapore, 11–29 October 2021; Available online: https://asef.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/ASEFSU23-Background-Paper_Waste-Management-in-Bangladesh.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Jerin, D.T.; Sara, H.H.; Radia, M.A.; Hema, P.S.; Hasan, S.; Urme, S.A.; Audia, C.; Hasan, M.T.; Quayyum, Z. An overview of progress towards implementation of solid waste management policies in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostakim, K.; Arefin, M.A.; Islam, M.T.; Shifullah, K.M.; Islam, M.A. Harnessing energy from the waste produced in Bangladesh: Evaluating potential technologies. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvin, F.; Tareq, S.M. Impact of landfill leachate contamination on surface and groundwater of Bangladesh: A systematic review and possible public health risks assessment. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adib, A.; Mahapatro, M. Private sector involvement in waste management of metropolises: Insights from Dhaka city. Waste Manag. 2022, 142, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilake, N.; Kumara, I.U.; Fernando, S. Solid and Liquid Waste Management and Resource Recovery in Sri Lanka: A 20 City Analysis; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2020; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bikash, B.; Ichihashi, M. Household preferences for improved solid waste management (SWM) services: A randomized conjoint analysis in Kathmandu metropolitan ward no. 10. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, A. Livelihood status of itinerant waste buyers in Kathmandu. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flacke, J.; Maharjan, B.; Shrestha, R.; Martinez, J. Environmental inequalities in Kathmandu, Nepal: Household perceptions of changes between 2013 and 2021. Front. Sustain. Cities 2022, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Kathmandu Post. Available online: https://kathmandupost.com/valley/2021/04/16/how-kathmandu-s-waste-management-emerged-as-a-perennial-problem (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Deuja, A.; Christensen, D.A.; Mungkalasiri, J.; Prapaspongsa, T. Assessment of integrated solid waste management systems in Kathmandu Metropolitan City. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Green and Sustainable Innovation (ICGSI 2021), Nakhon Pathom, Thailand, 10–12 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pucino, N. Wastes in Paradise: Volumes, Composition and Management of Municipal Solid Wastes in Maldives. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303939961_Wastes_in_Paradise_Volumes_composition_and_management_of_municipal_solid_wastes_in_Maldives (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Royle, J.; Jack, B.; Parris, H.; Elliott, T.; Castillo, A.C.; Kalawana, S.; Nashfa, H.; Woodall, L.C. Plastic Drawdown: A rapid assessment tool for developing national responses to plastic pollution when data availability is limited, as demonstrated in the Maldives. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2022, 72, 102442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatesta, S. Energy Production and Waste Management: The Human Ecology of Maldivian Islands. In Atolls of the Maldives Nissology and Geography; Rowman & Littlefield: Lanham, MD, USA, 2021; Volume 16, p. 64. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/349408383_Atolls_of_the_Maldives_Nissology_and_Geography (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Choden, Y.; Tenzin, T.; Karchung, K.; Norbu, K.; Wangmo, S.; Zangmo, P. Estimation of energy content in municipal solid waste of Bhutan and its potential as alternate powers source. Environ. Conserv. J. 2021, 22, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshering, D.; Dorji, S.; Norbu, D.; Jamtsho, L. Assessment of Municipal Solid Waste Generation and its Management in Trashigang Municipality, Bhutan. Sherub Doenme 2021, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaforzai, A.; Ullah, S.; Asir, M. Household waste management in formal housing developments in Afghanistan: A case study of Kabul city. Aust. J. Eng. Innov. Technol. 2021, 3, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Bibi, S.; Ali, S.; Noman, M.; Rukh, G.; Nafees, M.; Bibi, H.; Qiao, X.; Khan, S.; Hamidova, E. Analysis of municipal solid waste management in Afghanistan, current and future prospects: A case study of Kabul city. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 2485–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/country/XN (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Rahimi, F.; Atabi, F.; Nouri, J.; Omrani, G.A. Using life cycle assessment method for selecting optimal waste management system in Tehran city. J. Environ. Health Sustain. Dev. 2019, 4, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamialahmadi, N.; Hashemi, M.; Jalili-Ghazizade, M. Assessment of the current municipal solid waste management system in Tehran, Iran: Challenges and opportunities for sustainable development. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 2054–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radkevich, M.; Mukhammadaliyeva, F.; Shipilova, K.; Umarova, N.; Gapirov, A. Land pollution by illegal dumps in the Tashkent region. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1068, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, R.; Kourani, H.; Halwani, J.; Nehme, N. Landfills in greater Beirut area: A protracted part of municipal solid waste management. J. Genet. Environ. Resour. Conserv. 2022, 10, 184–185. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznietsova, A.; Gorkovchuk, J. GIS modeling of waste containers’ placement in urban areas. Geod. Cartogr. 2021, 47, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano Lazo, D.P.; Gasparatos, A. Sustainability transitions in the municipal solid waste management systems of Bolivian cities: Evidence from La paz and Santa Cruz de la Sierra. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferronato, N.; Gorritty Portillo, M.A.; Guisbert Lizarazu, E.G.; Torretta, V.; Bezzi, M.; Ragazzi, M. The municipal solid waste management of La Paz (Bolivia): Challenges and opportunities for a sustainable development. Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 36, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.T.; Yabar, H.; Mizunoya, T. Characterization and analysis of household solid waste composition to identify the optimal waste management method: A case study in Hanoi city, Vietnam. Earth 2021, 2, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byamba, B.; Ishikawa, M. Municipal solid waste management in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia: Systems analysis. Sustainability 2017, 9, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naimi, Y.; Saghir, M.; Cherqaoui, A.; Chatre, B. Energetic recovery of biomass in the region of Rabat, Morocco. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, N.M.; Wilson, D.C.; Velis, C.A.; Smith, S.R. Waste management and recycling in the former Soviet Union: The City of Bishkek, Kyrgyz Republic (Kyrgyzstan). Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.O.; Tun, Y.; Lwin, N.H.; Moe, T.; Eaindray, J. Estimation of the Recyclable Waste amount Collected by Informal Recycling Shops: Case Study in Nay Pyi Taw, Myanmar. Environ. Nat. Resour. J. 2021, 19, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbengue, R.; Thiam, M.D.; Traore, V.B. Impacts of household solid urban waste on the coast of Ngor (Dakar/Senegal). Eur. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wafi, T.; Ben Othman, A.; Besbes, M. Qualitative and quantitative characterization of municipal solid waste and the unexploited potential of green energy in Tunisia. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2019, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ailton, J.G.; Juliano, C.G.; Joana, D.B.; Armando, B.D. Application of a decision support tool for municipal solid waste open dumps remediation in Cape Verde. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 14, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopera, D.C.; Lopera, G.I.; Lopera, H.C. Logistics as an essential area for the development of the solid waste management in Colombia. Inf. Técnico 2019, 83, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brotosusilo, A.; Nabila, S.H.; Negoro, H.A.; Utari, D. The level of individual participation of community in implementing effective solid waste management policies. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2020, 6, 341–354. [Google Scholar]
- Shimura, S.; Yokota, I.; Nitta, Y. Research for MSW flow analysis in developing nations. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2001, 3, 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sapuay, G.P. Resource recovery through RDF: Current trends in solid waste management in the Philippines. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhubu, T.; Mbohwa, T.C.; Muzenda, E.; Patel, B. A review of municipal solid waste data for Harare, Zimbabwe. In Wastes: Solutions, Treatments and Opportunities III; CRC Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 367–374. [Google Scholar]
- Oteng-Ababio, M. Private sector involvement in solid waste management in the Greater Accra Metropolitan Area in Ghana. Waste Manag. Res. 2010, 28, 322–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, C. Waste picker livelihoods and inclusive neoliberal municipal solid waste management policies: The case of the La Chureca garbage dump site in Managua, Nicaragua. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otumawu-Apreku, K. Solid Waste Management: A Socio-Economic Perspective of Urban and Peri-Urban Communities in Honiara. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2020, 25, 180–192. [Google Scholar]
- Dongo, K.; Kouamé, P.K.; Nguyen-Viet, H.; Do-Thu, N.; Biémi, J.; Zurbrügg, C. In-depth analysis of nitrogen flow in urban system in Low Income Countries: The case of Yamoussoukro in Côte d’Ivoire. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2017, 11, 3034–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogutu, F.A.; Kimata, D.; Kweyu, R. The role of institutions in SWM in Nairobi County using environmental SWM policy frameworks for sustainable waste management. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Educ. 2018, 2, 158–167. [Google Scholar]
- Scarlat, N.; Motola, V.; Dallemand, J.F.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Mofor, L. Evaluation of energy potential of municipal solid waste from African urban areas. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1269–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrour, S.; Moore, J.; Grimes, S. Assessment of the ecological footprint associated with consumer goods and waste management activities of south Mediterranean cities: Case of Algiers and Tipaza. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2021, 12, 100154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSaid, S.; Aghezzaf, E.H. A progress indicator-based assessment guide for integrated municipal solid-waste management systems. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, A. Solid Waste Management in the Pacific: Vanuatu Country Snapshot, Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong City 1550, Metro Manila, Philippines, 2014. Available online: https://www.adb.org/countries/vanuatu/main (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Ximenes, M.B.; Maryono, M. Study of Waste Generation and Composition in the Capital of Dili, Dili Municipality, Timor-Leste. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 317, 01099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhindu, E.; Gumbo, T.; Gondo, T. Waste management threats to human health and urban aquatic habitats—A case study of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. In Waste Management—An Integrated Vision; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 21–54. [Google Scholar]
- Noel, C. Solid waste workers and livelihood strategies in Greater Port-au-Prince, Haiti. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babel, S.; Vilaysouk, X. Greenhouse gas emissions from municipal solid waste management in Vientiane, Lao PDR. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, J.D. Sustainability of wastewater treatment and excess sludge handling practices in the federated states of Micronesia. Sustainability 2013, 5, 4183–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anyaegbunam, F.N. Environmentally Friendly and Sustainable Municipal Solid Waste Management in Abuja. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. (IJESI) 2013, 2, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, L.P.; Prasad, R. Assessing the sustainable municipal solid waste (MSW) to electricity generation potentials in selected Pacific Small Island Developing States (PSIDS). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tleuken, A.; Tokazhanov, G.; Jemal, K.M.; Shaimakhanov, R.; Sovetbek, M.; Karaca, F. Legislative, Institutional, Industrial and Governmental Involvement in Circular Economy in Central Asia: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Muferreh, S.A. Development of Solid Waste Management and its National Strategy in Palestine. In Proceedings of the 29th World Waste Congress, International Solid Waste Association (ISWA), Bilbao, Spain, 7–9 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sotamenou, J.; De Jaeger, S.; Rousseau, S. Drivers of legal and illegal solid waste disposal in the Global South-The case of households in Yaoundé (Cameroon). J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, A. Solid Waste Management in the Pacific: Samoa Country Snapshot, Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong City 1550, Metro Manila, Philippines, 2014. Available online: https://www.adb.org/countries/samoa/main (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Nyampundu, K.; Mwegoha, W.J.; Millanzi, W.C. Sustainable solid waste management Measures in Tanzania: An exploratory descriptive case study among vendors at Majengo market in Dodoma City. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senekane, M.F.; Makhene, A.; Oelofse, S. A critical analysis of indigenous systems and practices of solid waste management in rural communities: The case of Maseru in Lesotho. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2022, 19, 11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvat, V. Coastal protection structures in Tarawa atoll, Republic of Kiribati. Sustain. Sci. 2013, 8, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.I.; Karouach, F.; Lahboubi, N.; Bakraoui, M.; El Bari, H. Perception and Behavior Analysis of Comorians Citizens on the Solid Household Waste Problems. Eur. Sci. J. 2018, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Doumenq, P.; Awaleh, M.O.; Syakti, A.D.; Asia, L.; Chiron, S. Levels and sources of heavy metals and PAHs in sediment of Djibouti-city (Republic of Djibouti). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R. Solid Waste Management in Eswatini: Challenges and Opportunities; Centre for Science and Environment: New Delhi, India, 2021; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Karak, T.; Bhagat, R.M.; Bhattacharyya, P. Municipal solid waste generation, composition, and management: The world scenario. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1509–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, M.B.; Dick, B.A.; Sidi, Y.M.; Dieh, H.; Mohamed, L.S.; Lemine, Y.M.; Sadegh, V.; Fekhaoui, M. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Medical Solid Waste Leachate–Case of the Hospital de l’Amitié of Nouakchott-Mauritania. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, G.; Zsigraiova, Z.; Semiao, V.; da Graça Carvalho, M. A case study of fuel savings through optimisation of MSW transportation routes. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2008, 19, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H.; Cui, L.; Liu, J. Mathematical modeling for identifying cost-effective policy of municipal solid waste management under uncertainty. J. Environ. Inform. 2019, 34, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menikpura, N.; Sang-Arun, J. User Manual: Estimation Tool for Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions from Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Management in a Life Cycle Perspective; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Hayama, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Campitelli, A.; Schebek, L. How is the performance of waste management systems assessed globally? A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campitelli, A.; Kannengießer, J.; Schebek, L. Approach to assess the performance of waste management systems towards a circular economy: Waste management system development stage concept (WMS-DSC). MethodsX 2022, 9, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cointreau-Levine, S. Private Sector Participation in Municipal Solid Waste Services in Developing Countries; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Lahore Waste Management Company (LWMC). Available online: https://www.lwmc.com.pk/istacrole.php (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Lahore Waste Management Company (LWMC). Available online: https://lwmc.com.pk/uploads/istac%20reports/Legal_Framework_Report_Draft.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Iqbal, A.; Jatoi, M.R. Lahore Solid Waste Management Master Plan-2007–2021. Lahore, Pakistan, 2006. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365561034_Lahore_Solid_Waste_Management_Master_Plan_-_2007_-_2021 (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Azeem, M. Law, State and Inequality in Pakistan: Explaining the Rise of the Judiciary; Springer: Singapore, 2017; p. 259. [Google Scholar]
- The World Bank. Available online: https://documents.worldbank.org/pt/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/254301468283489886/pakistan-lahore-composting-project (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Hameed, R.; Nazir, S. Improving secondary collection of solid waste: The experience of performance based system in Lahore. J. Am. Sci. 2011, 7, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Joeng, H.; Kim, K. KOICA-World Bank Joint Study on Solid Waste Management in Punjab, Pakistan. Available online: https://www.urbanunit.gov.pk/publications (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- The Nation. Available online: https://www.nation.com.pk/22-Jun-2010/project-management-unit-gets-control-of-swm (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Local Government and Community Development Department (LG&CD). Available online: https://lgcd.punjab.gov.pk/solid_waste_management_companies (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Climate and Clean Air Coalition. Available online: https://www.waste.ccacoalition.org/sites/default/files/files/lahore_city_profile.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- The News. Available online: https://www.thenews.com.pk/tns/detail/568462-solid-system-lahore (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Dawn. Available online: https://www.dawn.com/news/1525334 (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Auditor General of Pakistan. Available online: https://agp.gov.pk/SiteImage/Policy/LWMC%20report%202016-17%20(3-2-2017)-approved.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Business Recorded. Available online: https://www.brecorder.com/news/512170/nab-takes-briefing-on-lwmc (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- LWMC. Available online: https://www.lwmc.com.pk/contract.php (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Dawn. Available online: https://www.dawn.com/news/1597079 (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Bureau of Statistics. Available online: https://www.bos.gop.pk/developmentstat (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- LWMC. Available online: https://www.lwmc.com.pk/it-monitoring.php (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Pakistan Observer. Available online: https://pakobserver.net/lwmc-set-to-revamp-its-compost-plant/ (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- World Bank. Available online: https://collaboration.worldbank.org/content/sites/collaboration-for-development/en/groups/results-based-financing/groups/results-based-financing-for-climate/documents.entry.html/2017/02/21/lahore_compost-carbo-ug6W.html (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- The Express Tribune. Available online: https://tribune.com.pk/story/1966466/lahore-stands-tall-generating-green-fuel-waste (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Dawn. Available online: https://www.dawn.com/news/1172589 (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- The Urban Unit. Available online: https://www.urbanunit.gov.pk/Download/publications/Files/11/2021/Lakhodair%20Landfill%20Site.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- LWMC. Available online: https://www.lwmc.com.pk/audited-accounts.php (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- LWMC. Available online: https://www.lwmc.com.pk/brochures.php (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Maasakkers, J.D.; Varon, D.J.; Elfarsdóttir, A.; McKeever, J.; Jervis, D.; Mahapatra, G.; Pandey, S.; Lorente, A.; Borsdorff, T.; Foorthuis, L.R.; et al. Using satellites to uncover large methane emissions from landfills. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn9683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, U.; Hameed, I.; Chaudhary, M.N. Solid waste management practices under public and private sector in Lahore, Pakistan. Bull. Environ. Stud. 2016, 1, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Falahi, M.; Avami, A. Optimization of the municipal solid waste management system using a hybrid life cycle assessment–emergy approach in Tehran. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Lipu, M.H.; Akhtar, M.; Begum, R.; Al Mamun, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Mia, M.S.; Basri, H. Solid waste collection optimization objectives, constraints, modeling approaches, and their challenges toward achieving sustainable development goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Yasar, A.; Nizami, A.-S.; Haider, R.; Sharif, F.; Sultan, I.A.; Tabinda, A.B.; Kedwaii, A.A.; Chaudhary, M.M. Municipal Solid Waste Collection and Haulage Modeling Design for Lahore, Pakistan: Transition toward Sustainability and Circular Economy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















| Groups | Waste Collection Efficiency (%) | Low–Middle-Income Counties/Cities |
|---|---|---|
| Group-A | 76–100% | Tehran, Beirut, Tashkent, Kyiv, La Paz, Hanoi, Ulaanbaatar, Lahore, Rabat, Phnom Penh, Delhi, Bishkek, Nay Pyi Taw, Dakar, Tunis, Praia, Dhaka |
| Group-B | 51–75% | Colombo, San Salvador, Jakarta, Tegucigalpa, Manila, Harare, Accra, Managua, Honiara, Yamoussoukro, Nairobi, Sao Tome, Kathmandu, Algiers, Cairo, Port Vila, Bhutan, Dili |
| Group-C | 26–50% | Lunda, Port-au-Prince, Vientiane, Palikir, Abuja, Port Moresby, Dushanbe, West Bank & Gaza, Yaoundé, Apia, Dodoma, Maseru, Tarawa, Moroni, Djibouti, Mbabane, Brazzaville |
| Group-D | 1–25% | Nouakchott and Porto-Novo |
| Limitations in Outsourcing Contracts | Positive Aspect of Outsourcing Contracts |
|---|---|
| Waste generation estimates were based on secondary data without an actual survey at the bid time. | A professionally staffed new organization was established in the form of LWMC, |
| DtD waste collection mechanism was mentioned in the contract, but specific fleet swaps with other fleets as it was permitted in agreements. Payment calculation method for DtD not defined in contracts. | LWMC has gained experience in contract design, implementation, and digital monitoring. |
| Contracts limited to domestic, municipal waste collection, i.e., container and DtD waste collection, without mentioning resources for bulk collection, i.e., green waste, debris, animal dung, and sludge; resultantly, sub-contractor’s focus was on bulk waste collection. | Technical capacity developed locally by gaining experience from Istanbul municipality and Turk contractors, this knowledge being shared with other municipalities and Waste Management Companies (WMCs). It helped to strengthen the waste sector in the country. |
| Quantity-based payments on tonnage collected by the contractors discouraged the segregation and recovery of recyclables from waste. | Promoted induced growth of local waste collection contractors. |
| No incentive for contractors to procure smaller vehicles for narrow streets and congested areas of the city. | Development of local vendors for supply of heterogeneous machinery and equipment for waste collection and haulage. |
| No separate mechanism for handling of green waste; debris and animal dung collection was defined in contracts despite the fact that such types of waste are included in waste generation estimates. | A gradual movement toward output-based KPIs. |
| Components | 2011 Winter | 2011 Summer | 2012 Summer | 2014 Summer | 2014 Autumn | 2019 Autumn | 2022 Winter | Avg. % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combustibles | 3.83 | 3.69 | 2.12 | 3.52 | 6.05 | 4.97 | 3.09 | 3.90 |
| Diaper | 5.35 | 6.76 | 3.11 | 2.88 | 5.06 | 5.42 | 15.78 | 6.34 |
| Elec.-electro. | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.08 |
| Glass | 0.43 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 1.13 | 0.82 | 0.78 |
| Hazardous | 0.18 | 0.91 | 1.52 | 2.14 | 1.33 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.89 |
| Biodegradable | 72.76 | 63.46 | 64.85 | 66.49 | 56.32 | 50.95 | 54.32 | 61.31 |
| Metals | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| Non-Combust. | 3.42 | 1.82 | 2.26 | 5.39 | 6.4 | 14.57 | 7.63 | 5.93 |
| Paper-card. | 2.34 | 3.84 | 2.43 | 1.67 | 2.18 | 3.87 | 1.38 | 2.53 |
| PET | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.88 | 0.04 | 0.23 |
| Nylon | 5.58 | 9.77 | 11.62 | 9.76 | 10.92 | 10.85 | 9.41 | 9.70 |
| Plastics | 0.45 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.59 | 0.63 | 1.44 | 0.68 | 0.74 |
| Tetrapak | 0.77 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 1.14 | 1.02 | 1.26 | 0.64 | 0.96 |
| Textile | 4.71 | 7.05 | 9.09 | 5.42 | 9.21 | 4.26 | 6.02 | 6.54 |
| TOTAL | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Waste Streams | Proposed Collection Mode | Target (Collection%) | Proposed Interim Haulage | Treatment on PPP Modality (Proposed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential Waste | Door-to-Door (DtD) | Initially for 25% areas | MRF/Recovery of recyclables | Recycling/RDF/compost |
| Container-Based Collection (CBC) | 75% residential area | Transfer Station | Compost/anaerobic digestion (AB)/LFG recovery/capturing | |
| Commercial Waste | DtD | 50% for planned markets | MRF/Recovery of recyclables | Recycling/RDF |
| CBC | 50% for congested markets | MRF/Recovery of recyclables | Recycling/RDF | |
| Housing Societies Waste | CBC | 100% | MRF/Recovery of recyclables | Recycling/Compost/AD |
| Institutions Waste | CBC | 100% | MRF/Recovery of recyclables | Recycling/RDF |
| Bulk Waste, i.e., C&D, animal dung & sludge | Direct Haulage | 100% | Transfer Station/Landfill site | C&D for landfill infrastructure/sludge as soil cover/dung for AD & compost |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, A.; Yasar, A.; Nizami, A.-S.; Sharif, F.; Tabinda, A.B.; Sultan, I.A.; Batool, S.A.; Haider, R.; Shahid, A.; Chaudhary, M.M.; et al. Evolution of Solid Waste Management System in Lahore: A Step towards Sustainability of the Sector in Pakistan. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020983
Iqbal A, Yasar A, Nizami A-S, Sharif F, Tabinda AB, Sultan IA, Batool SA, Haider R, Shahid A, Chaudhary MM, et al. Evolution of Solid Waste Management System in Lahore: A Step towards Sustainability of the Sector in Pakistan. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(2):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020983
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Asif, Abdullah Yasar, Abdul-Sattar Nizami, Faiza Sharif, Amtul Bari Tabinda, Imran Ali Sultan, Syeda Adila Batool, Rafia Haider, Anum Shahid, Muhammad Murtaza Chaudhary, and et al. 2023. "Evolution of Solid Waste Management System in Lahore: A Step towards Sustainability of the Sector in Pakistan" Applied Sciences 13, no. 2: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020983
APA StyleIqbal, A., Yasar, A., Nizami, A. -S., Sharif, F., Tabinda, A. B., Sultan, I. A., Batool, S. A., Haider, R., Shahid, A., Chaudhary, M. M., & Ahmad, M. (2023). Evolution of Solid Waste Management System in Lahore: A Step towards Sustainability of the Sector in Pakistan. Applied Sciences, 13(2), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020983







