SAFP-YOLO: Enhanced Object Detection Speed Using Spatial Attention-Based Filter Pruning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Attention mechanisms have been used to improve the accuracy of deep learning models, while pruning techniques have been used to improve the execution speed. A step is taken forward from previous research by combining attention and pruning to achieve real-time YOLO on a low-cost embedded board with acceptable accuracy. To the best of our knowledge, this represents the first instance of concurrently considering both the accuracy and speed of YOLO by comparing the foreground–background information derived from GT box locations and the feature map difference before and after spatial attention.
- To validate the feasibility of our proposed method, the experiments were conducted comparing the proposed method to baseline models in terms of accuracy and speed across various settings. The experiments with two datasets (pig and vehicle), two attention mechanisms (convolutional block attention network, CBAM and coordinate attention, CA), two detection models (YOLOv4 and YOLOv7), and two model sizes (medium and tiny) were conducted. Additionally, comparative experiments were carried out with conventional filter-pruning techniques based on magnitude and randomness.
2. Background
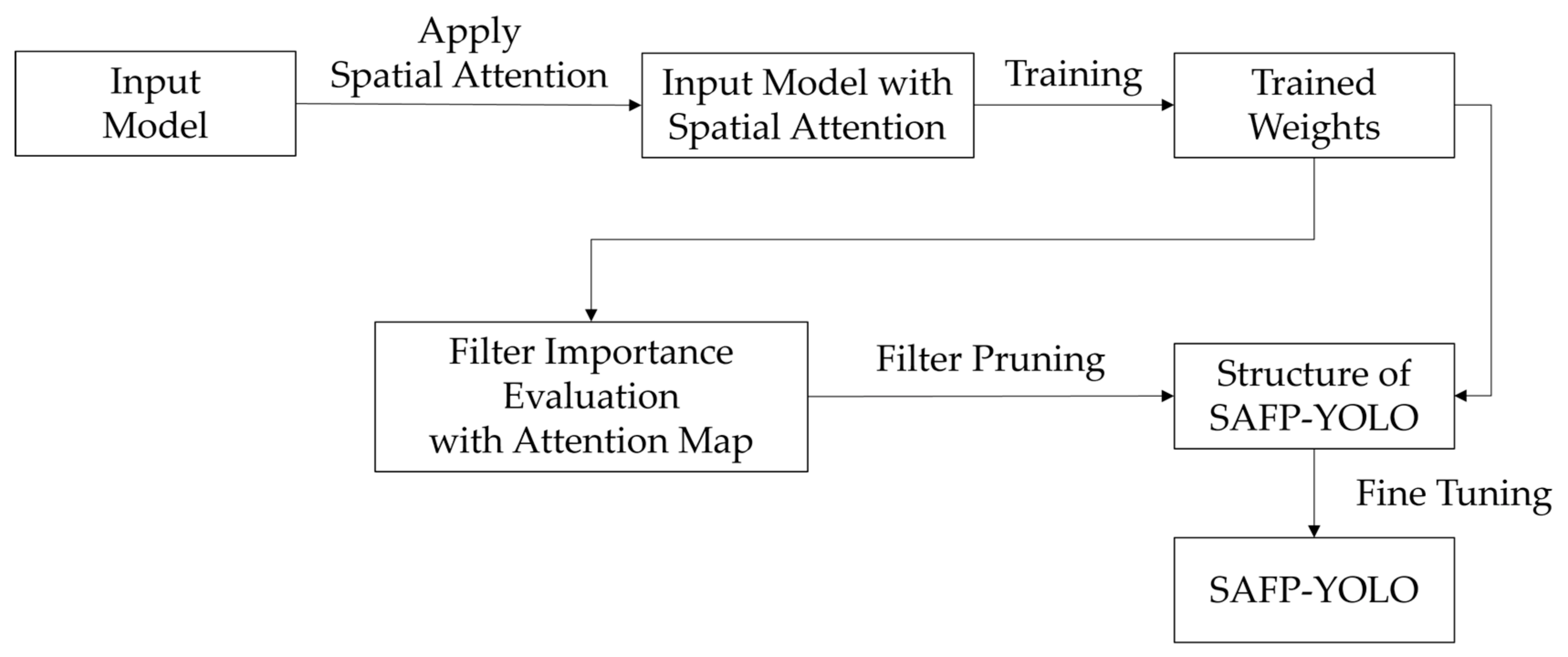
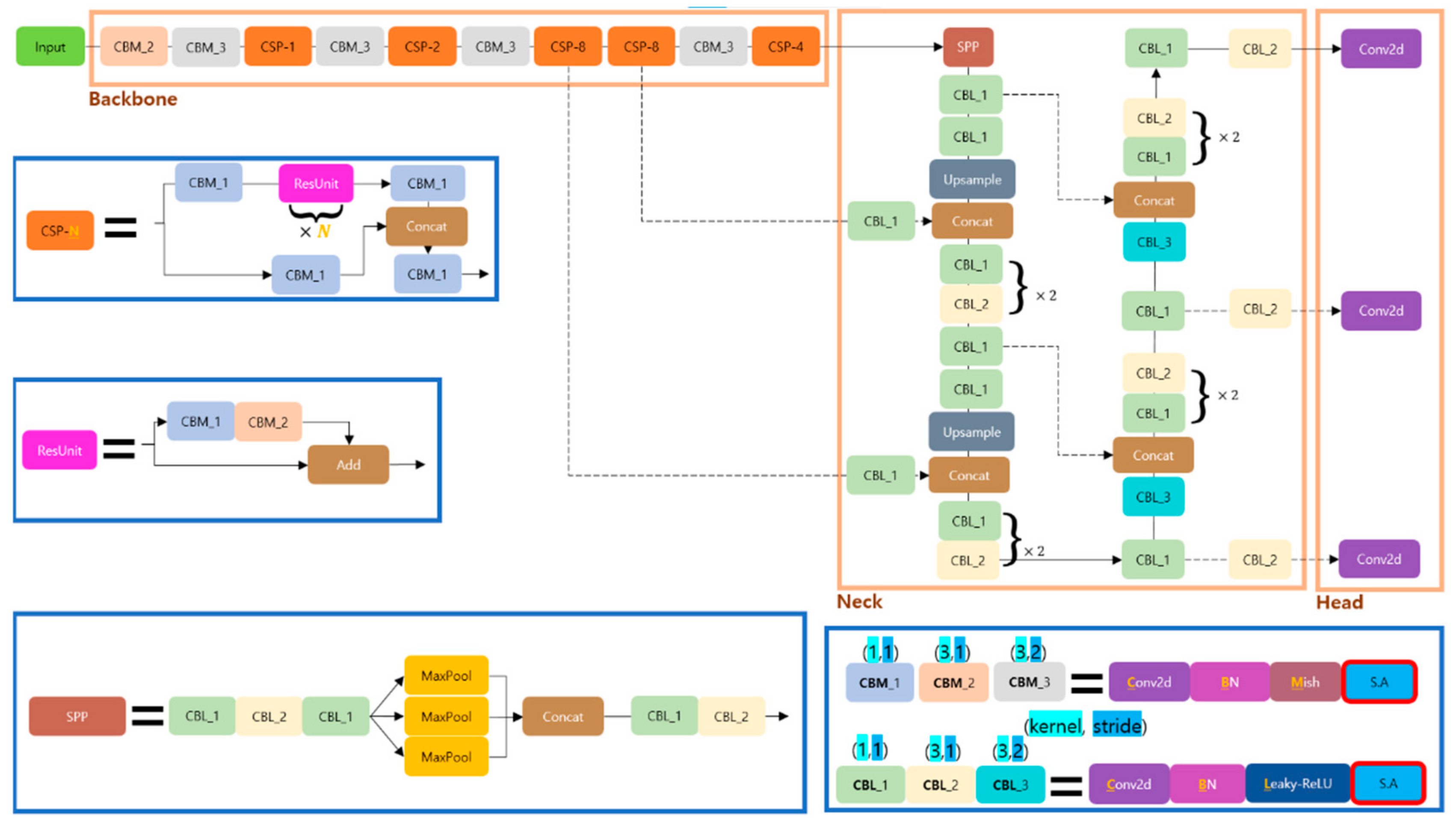
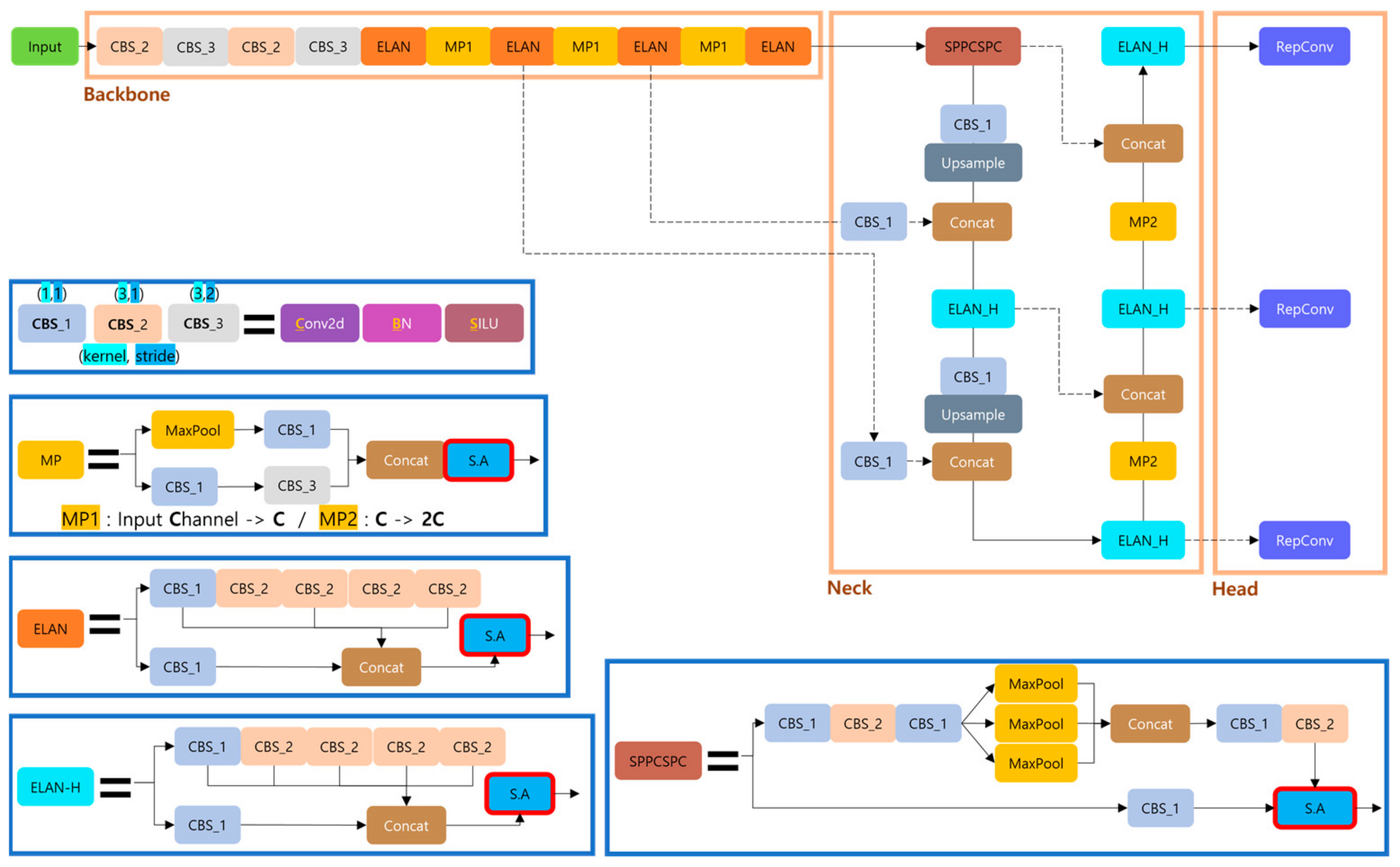
3. Proposed Method
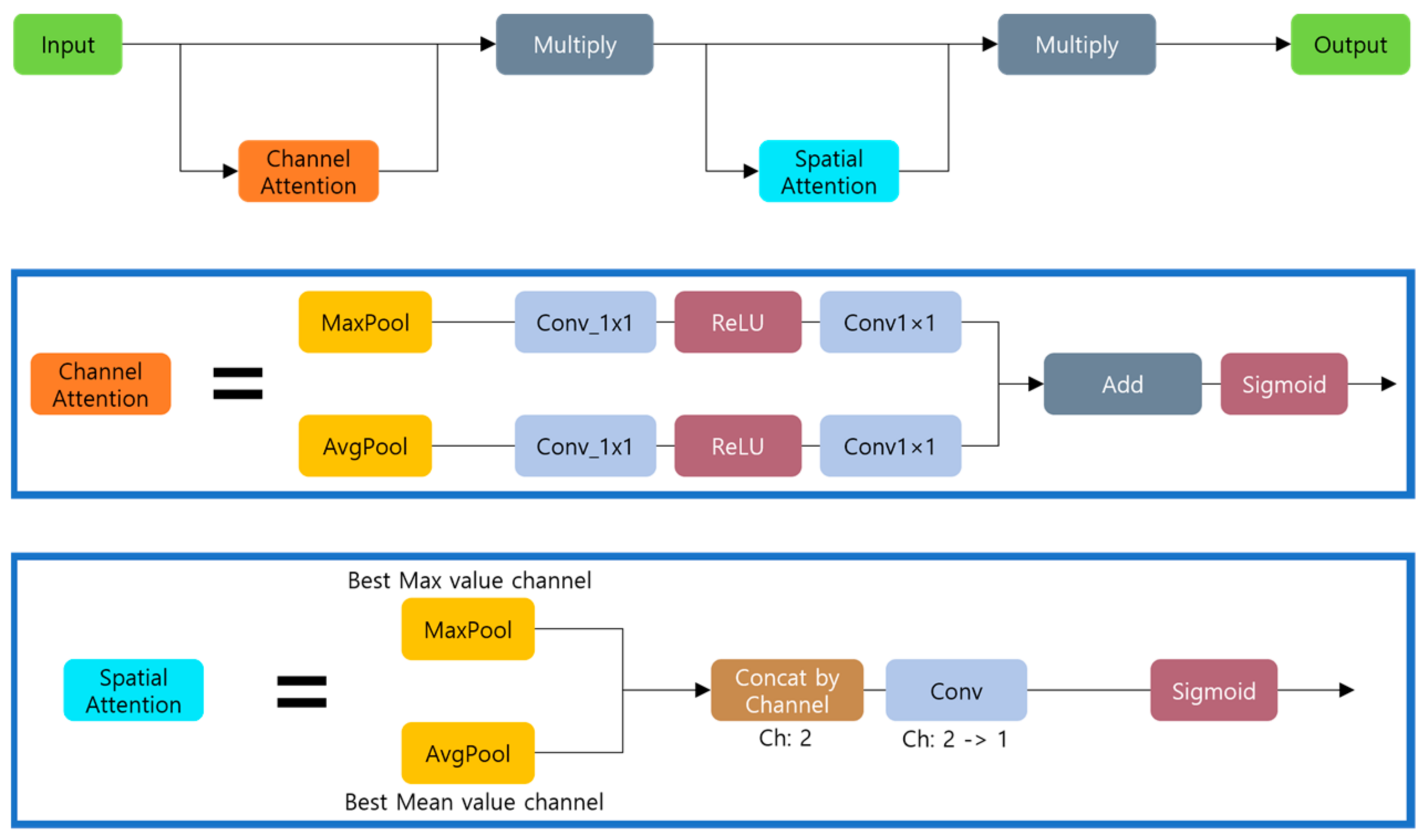
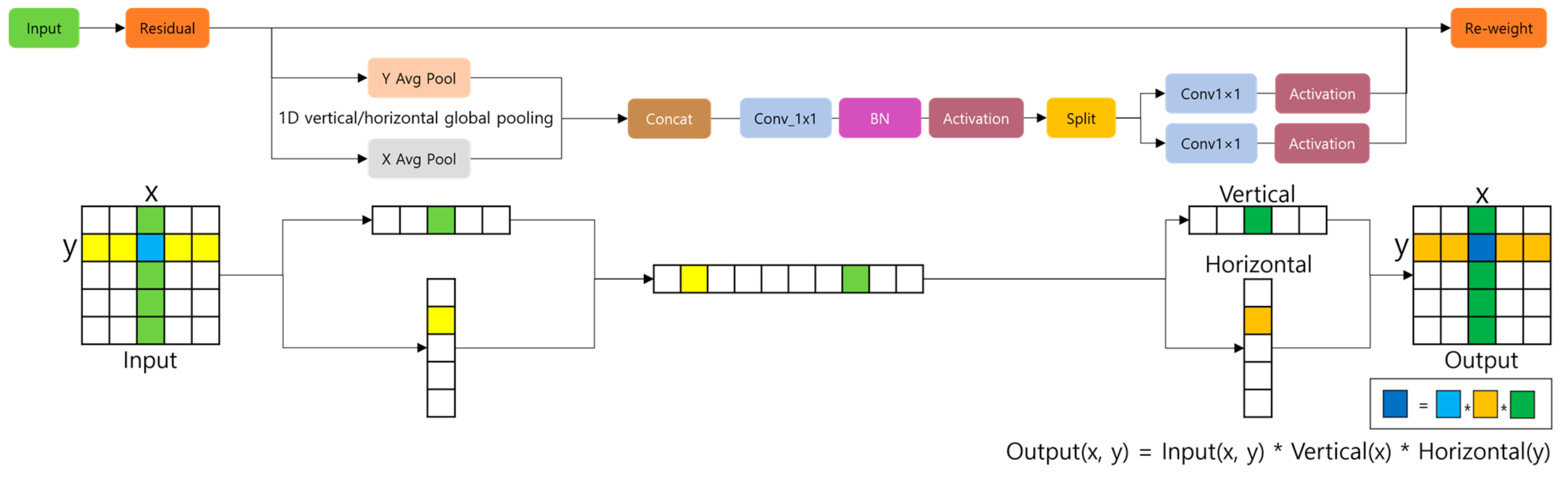
3.1. Spatial Attention
3.2. Filter Importance Evaluation
| Algorithm 1. Filter evaluation using attention map |
| Input: model, featureMaps, groundTruthBox, inputImage Output: optimizedModel |
| foreach (layer in convolutionLayers(model)) { featureMaps = extractFeatureMaps(layer, inputImage) foregroundRegion = getRegion(featureMaps, groundTruthBox) backgroundRegion = getRegion(featureMaps, complementOf(groundTruthBox)) L2NormForeground = calculateL2Norm(foregroundRegion) L2NormBackground = calculateL2Norm(backgroundRegion) difference = abs(L2NormForeground − L2NormBackground) if (difference is significantly large) { markFilterAsImportant(layer) } } rankedFilters = rankFiltersBasedOnImportance(convolutionLayers(model)) optimizedModel = applyOptimizations(model, rankedFilters) return optimizedModel |
3.3. Filter Pruning
| Algorithm 2. Filter pruning using attention map |
| Input: model Output: finalModel Initialize: reduction ratio r |
| newModel = createModelWithoutSpatialAttention() foreach (layer in convolutionLayers(model)) { sortedFilters = sortFiltersByImportance(layer) int numFiltersToPrune = numberOfFilters(layer) * r for int i = 0 to numFiltersToPrune do removeFilter(sortedFilters, sortedFilters[numberOfFilters(sortedFilters) – i − 1]) applyPrunedFiltersToNewModel(sortedFilters, newModel) } finalModel = fineTuning(newModel) return finalModel |
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Setup and Resources for the Experiment
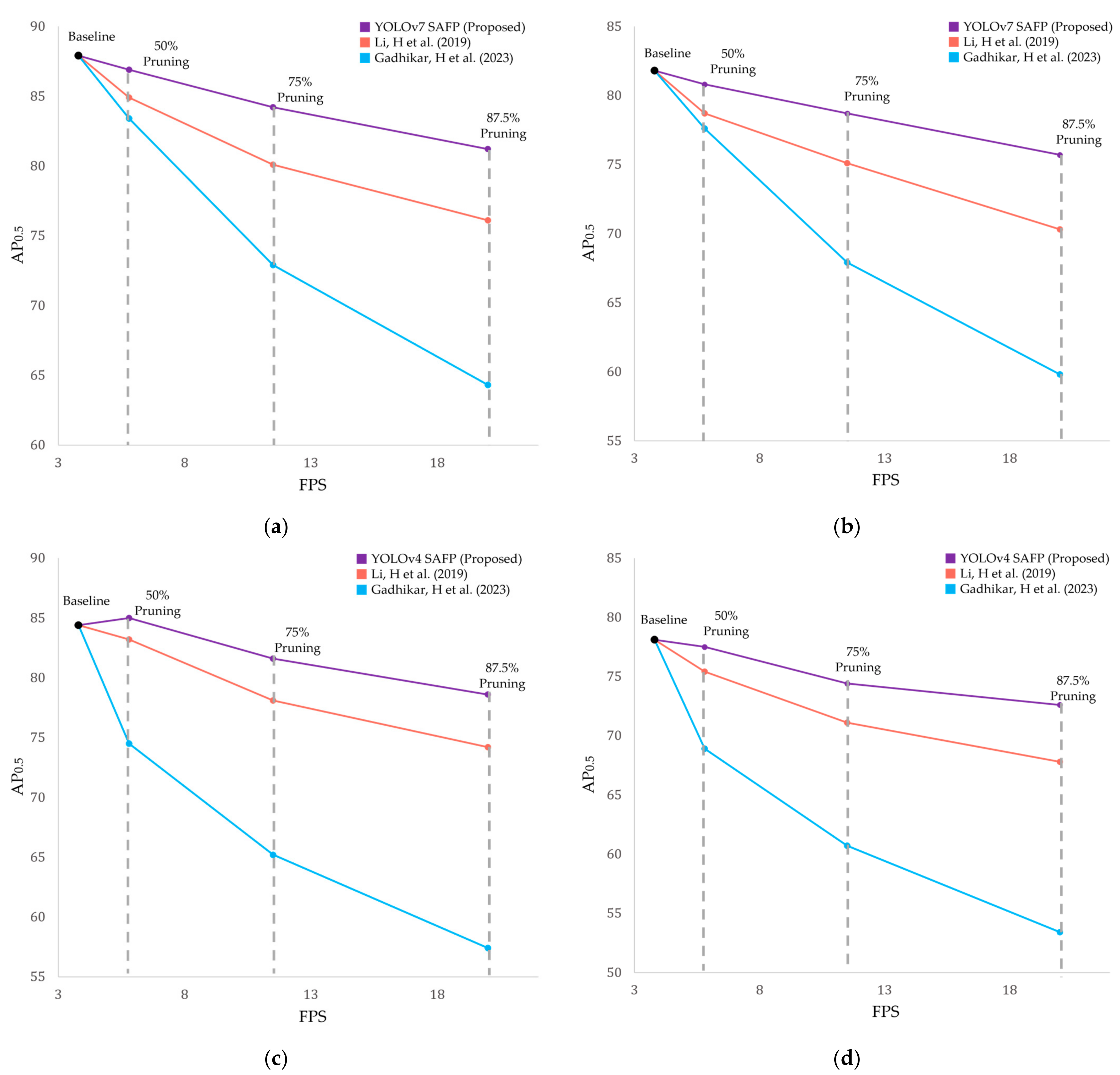
4.2. Evaluation of Detection Performance
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Z.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.; Wu, X. Object Detection with Deep Learning: A Review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 11, 3212–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.; Liao, H. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Ultralytics/yolov5. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. YOLOx: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02696. [Google Scholar]
- Shirke, A.; Saifuddin, A.; Luthra, A.; Li, J.; Williams, T.; Hu, X.; Kotnana, A.; Kocabalkanli, O.; Ahuja, N.; Green-Miller, A.; et al. Tracking Grow-Finish Pigs across Large Pens using Multiple Cameras. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.10971. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, H.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Chung, Y.; Park, D. EnsemblePigDet: Ensemble Deep Learning for Accurate Pig Detection. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Pu, J.; Mu, J. Pig-Posture Recognition based on Computer Vision: Dataset and Exploration. Animals 2021, 11, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujel, A.; Arulmozhi, E.; Moon, B.; Kim, H. Deep-Learning-based Automatix Monitoring of Pigs’ Physico-Temporal Activities at Different Greenhouse Gas Concentrations. Animals 2021, 11, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Lu, H.; Lv, E. Posture Detection of Individual Pigs based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks and Efficient Channel-Wise Attention. Sensors 2021, 21, 8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, G. Detection Method for Individual Pig based on Improved YOLOv4 Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Data Science and Information Technology, Shanghai, China, 23–25 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Witte, J.; Gomez, J. Introducing a New Workflow for Pig Posture Classification based on a Combination of YOLO and EfficientNet. In Proceedings of the 55th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ocepek, M.; Žnidar, A.; Lavrič, M.; Škorjanc, D.; Andersen, I. DigiPig: First Developments of an Automated Monitoring System for Body, Head, and Tail Detection in Intensive Pig Farming. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Yu, J.; Lao, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Teng, G. Automatic Position Detection and Posture Recognition of Grouped Pigs based on Deep Learning. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Suh, Y.; Lee, J.; Chae, H.; Ahn, H.; Chung, Y.; Park, D. EmbeddedPigCount: Pig Counting with Video Object Detection and Tracking on an Embedded Board. Sensors 2022, 22, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, Z.; Atif, O.; Lee, J.; Park, D.; Chung, Y. GAN-based Video Denoising with Attention Mechanism for Field-Applicable Pig Detection System. Sensors 2022, 22, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.; Ahn, H.; Baek, H.; Yu, S.; Suh, Y.; Lee, S.; Chung, Y.; Park, D. StaticPigDet: Accuracy Improvement of Static Camera-based Pig Monitoring using Background and Facility Information. Sensors 2022, 22, 8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Chen, J.; Shen, M.; Liu, L. Activity Detection of Suckling Piglets based on Motion Area Analysis using Frame Differences in Combination with Convolution Neural Network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 194, 106741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Liu, L.; Lu, M.; Liu, K.; Chen, J.; Shen, M. Social Density Detection for Sucking Piglets based on Convolutional Neural Network Combined with Local Outlier Factor Algorithm. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Ko, J. Estimation of Number of Pigs Taking in Feed using Posture Filtration. Sensors 2023, 23, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L.; Shu, C.; Shen, M.; Yao, W. Sow Farrowing Early Warning and Supervision for Embedded Board Implementations. Sensors 2023, 23, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shi, G.; Jiao, J. YOLOv5-KCB: A New Method for Individual Pig Detection using Optimized K-Means, CA Attention Mechanism, and a Bi-Directional Feature Pyramid Network. Sensors 2023, 23, 5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Liang, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Xie, Z.; He, H.; Zhuo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Huang, Z. IO-YOLOv5: Improved Pig Detection under Various Illuminations and Heavy Occlusion. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, W.; Park, J. A Study on Tracking Moving Objects: Pig Counting with YOLOv5 and StrongSORT. In Proceedings of the 29th International Workshop on Frontiers of Computer Vision (IW-FCV 2023), Yeosu, Republic of Korea, 20–22 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, E.; He, Z.; Mao, A.; Ceballos, M.; Parsons, T.; Liu, K. A Semi-Supervised Generative Adversarial Network for Amodal Instance Segmentation of Piglets in Farrowing Pens. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 209, 107839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odo, A.; Muns, R.; Boyle, L.; Kyriazakis, I. Video Analysis using Deep Learning for Automated Quantification of Ear Biting in Pigs. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 59744–59757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Bai, B.; Xing, T.; Liu, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Liao, H.; Zhang, G.; et al. 2nd Place Solution for Waymo Open Dataset Challenge—Real-Time 2D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the CVPRW, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolay, S. 3rd Place Waymo Real-Time 2D Object Detection: YOLOv5 Self-Ensemble. In Proceedings of the CVPRW, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.; Tran, D.; Pham, L.; Nguyen, H.; Tran, T.; Jeon, J. Object Detection with Camera-Wise Training. In Proceedings of the CVPRW, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Song, L.; Liu, S.; Ge, Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Workshop on Autonomous Driving at CVPR 2021: Technical Report for Streaming Perception Challenge. In Proceedings of the CVPRW, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, D.; Xu, G.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, F. Solution to Streaming Perception Challenge for Detection-Only and Full-Stack Tracks. In Proceedings of the CVPRW, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Q. Team CASIT_CV: Solution to Streaming Perception Challenge for Detection-Only Track. In Proceedings of the CVPRW, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, J. Real-Time Object Detection for Streaming Perception. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, A.; Hussain, F.; Khan, K.; Shahzad, M.; Khan, U.; Mahmood, Z. A Fast and Accurate Real-Time Vehicle Detection Method using Deep Learning for Unconstrained Environments. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Son, S.; Ahn, H.; Baek, H.; Nam, K.; Chung, Y.; Park, D. EnsembleVehicleDet: Detection of Faraway Vehicles with Real-Time Consideration. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, W.; Zheng, C.; Li, L. Exploration of Vehicle Target Detection Method based on Lightweight YOLOv5 Fusion Background Modeling. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y. YOLOv7-RAR for Urban Vehicle Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, A.; Koubaa, A.; Boulila, W.; Benjdira, B.; Alhabashi, Y. A Multi-Stage Deep-Learning-based Vehicle and License Plate Recognition System with Real-Time Edge Inference. Sensors 2023, 23, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Guo, J.; Shivanna, V.; Chang, S. Deep Learning Derived Object Detection and Tracking Technology based on Sensor Fusion of Millimeter-Wave Radar/Video and Its Application on Embedded Systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Y. An Introductory Survey on Attention Mechanisms in Computer Vision Problems. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Big Data and Information Analytics (BigDIA), Shenzhen, China, 4–6 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Xu, T.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, P.; Mu, T.; Zhang, S.; Martin, R.; Cheng, M.; Hu, S. Attention Mechanisms in Computer Vision: A Survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.07624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Kweon, I. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedev, V.; Lempitsky, V. Speeding-up Convolutional Neural Networks: A Survey. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2018, 66, 799–810. [Google Scholar]
- Blalock, D.; Ortiz, J.; Frankle, J.; Guttag, J. What is the State of Neural Network Pruning? arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.03033. [Google Scholar]
- Vadera, S.; Ameen, S. Methods for Pruning Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 63280–63300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xiao, L. Structured Pruning for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks: A Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.00566. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Kadav, A.; Durdanovic, I.; Samet, H.; Graf, P. Pruning Filters for Efficient Convnets. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.08710. [Google Scholar]
- Gadhikar, H.; Mukherjee, S.; Burkholz, R. Why Random Pruning Is All We Need to Start Sparse. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yao, W.; Fu, H. A Convolutional Neural Network Pruning Method based on Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Software Engineering and Knowledge Engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, 10–12 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K.; Maeno, K. PCAS: Pruning Channels with Attention Statistics for Deep Network Compression. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1806.05382. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, G.; Gu, J.; Han, J. Pruning Convolutional Neural Networks with an Attention Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Classification. Electronics 2020, 9, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Qi, H.; Liang, Y.; Yang, M. Identification of Plant Leaf Diseases by Deep Learning based on Channel Attention and Channel Pruning. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1023515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shuai, M.; Lou, S.; An, Z.; Zhang, Y. FPAR: Filter Pruning via Attention and Rank Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Riekert, M.; Klein, A.; Adrion, F.; Hoffmann, C.; Gallmann, E. Automatically Detecting Pig Position and Posture by 2D Camera Imaging and Deep Learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argoverse-HD. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/mtlics/argoversehd (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- NVIDIA. NVIDIA Jetson TX2. Available online: http://www.nvidia.com/object/embedded-systems-dev-kitsmodules.html (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Selvaraju, R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-Cam: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
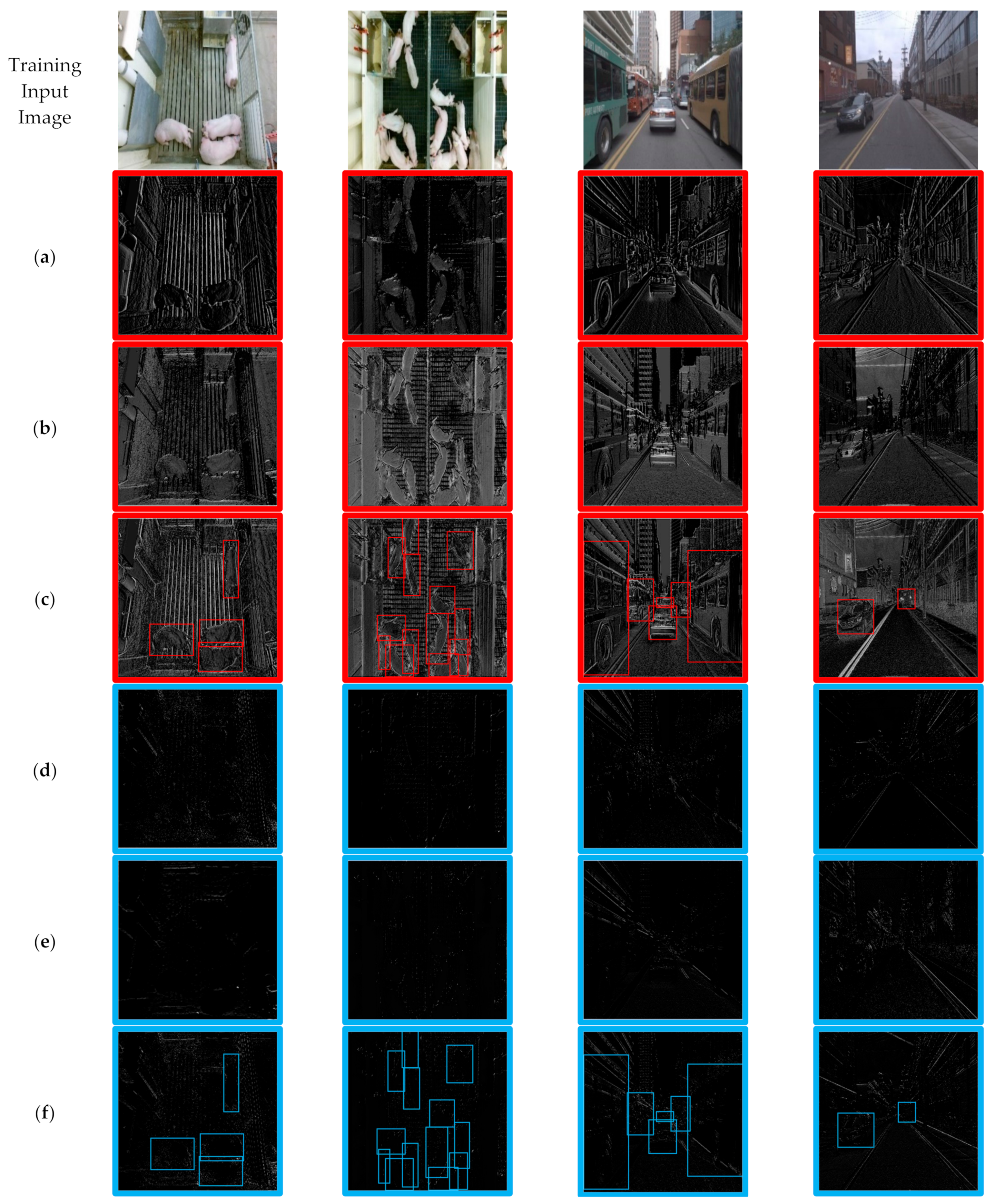





| Computer Vision Task | Attention or Pruning | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Image Classification | Channel Attention for Speed | [53] |
| Channel Attention for Speed | [54] | |
| Channel Attention for Speed | [55] | |
| Channel Attention for Speed | [56] | |
| Channel Attention for Speed | [57] | |
| Object Detection | Attention for Accuracy (Not Report Speed/Model Size) | [13] |
| Attention for Accuracy (Not Report Speed/Model Size) | [25] | |
| Attention for Accuracy (Speed Degradation) | [26] | |
| Attention for Accuracy (Model Size Increase) | [39] | |
| Pruning for Speed (Not Report Accuracy) | [18] | |
| Spatial Attention-based Pruning for Accuracy and Speed | Proposed Method |
| Method | Accuracy ↑ (AP0.5, %) | Speed ↑ (FPS) | No. of Model Parameters ↓ (M) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv4 [5] | Baseline YOLOv4 | 84.4 | 3.9 | 52.5 | |
| Proposed SAFP with CBAM [45] | 50% Pruning | 84.7 | 6.0 | 36.7 | |
| 75% Pruning | 80.5 | 12.0 | 25.7 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 78.1 | 20.9 | 15.7 | ||
| Proposed SAFP with CA [46] | 50% Pruning | 85.0 | 6.0 | 36.7 | |
| 75% Pruning | 81.6 | 12.0 | 25.7 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 78.6 | 20.9 | 15.7 | ||
| YOLOv7 [8] | Baseline YOLOv7 | 87.9 | 3.8 | 36.7 | |
| Proposed SAFP with CBAM [45] | 50% Pruning | 86.7 | 5.8 | 25.8 | |
| 75% Pruning | 83.7 | 11.5 | 16.3 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 80.5 | 20.0 | 10.2 | ||
| Proposed SAFP with CA [46] | 50% Pruning | 86.9 | 5.8 | 25.8 | |
| 75% Pruning | 84.2 | 11.5 | 16.3 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 81.2 | 20.0 | 10.2 | ||
| Method | Accuracy ↑ (AP0.5, %) | Speed ↑ (FPS) | No. of Model Parameters ↓ (M) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv4 [5] | Baseline YOLOv4 | 78.1 | 3.9 | 52.5 | |
| Proposed SAFP with CBAM [45] | 50% Pruning | 77.4 | 6.0 | 36.7 | |
| 75% Pruning | 74.3 | 12.0 | 25.7 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 72.1 | 20.9 | 15.7 | ||
| Proposed SAFP with CA [46] | 50% Pruning | 77.5 | 6.0 | 36.7 | |
| 75% Pruning | 74.4 | 12.0 | 25.7 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 72.6 | 20.9 | 15.7 | ||
| YOLOv7 [8] | Baseline YOLOv7 | 81.8 | 3.8 | 36.7 | |
| Proposed SAFP with CBAM [45] | 50% Pruning | 80.7 | 5.8 | 25.8 | |
| 75% Pruning | 78.2 | 11.5 | 16.3 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 75.4 | 20.0 | 10.2 | ||
| Proposed SAFP with CA [46] | 50% Pruning | 80.8 | 5.8 | 25.8 | |
| 75% Pruning | 78.7 | 11.5 | 16.3 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 75.7 | 20.0 | 10.2 | ||
| Method | Accuracy ↑ (AP0.5, %) | Speed ↑ (FPS) | No. of Model Parameters ↓ (M) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiny YOLOv4 [5] | Baseline TinyYOLOv4 | 78.2 | 19.2 | 6.1 | |
| Proposed SAFP with CBAM [45] | 50% Pruning | 76.8 | 28.4 | 2.4 | |
| 75% Pruning | 74.1 | 40.2 | 1.0 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 71.4 | 52.9 | 0.4 | ||
| Proposed SAFP with CA [46] | 50% Pruning | 77.4 | 28.4 | 2.4 | |
| 75% Pruning | 74.9 | 40.2 | 1.0 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 72.3 | 52.9 | 0.4 | ||
| Tiny YOLOv7 [8] | Baseline TinyYOLOv7 | 81.9 | 18.3 | 6.0 | |
| Proposed SAFP with CBAM [45] | 50% Pruning | 79.3 | 27.2 | 2.3 | |
| 75% Pruning | 77.6 | 38.4 | 1.0 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 74.7 | 50.7 | 0.4 | ||
| Proposed SAFP with CA [46] | 50% Pruning | 81.0 | 27.2 | 2.3 | |
| 75% Pruning | 78.5 | 38.4 | 1.0 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 75.8 | 50.7 | 0.4 | ||
| Method | Accuracy ↑ (AP0.5, %) | Speed ↑ (FPS) | No. of Model Parameters ↓ (M) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tiny YOLOv4 [5] | Baseline TinyYOLOv4 | 68.5 | 19.2 | 6.1 | |
| Proposed SAFP with CBAM [45] | 50% Pruning | 68.1 | 28.5 | 2.4 | |
| 75% Pruning | 65.7 | 40.2 | 1.0 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 63.3 | 52.9 | 0.4 | ||
| Proposed SAFP with CA [46] | 50% Pruning | 67.7 | 28.5 | 2.4 | |
| 75% Pruning | 65.7 | 40.2 | 1.0 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 63.4 | 52.9 | 0.4 | ||
| Tiny YOLOv7 [8] | Baseline TinyYOLOv7 | 71.3 | 18.3 | 6.0 | |
| Proposed SAFP with CBAM [45] | 50% Pruning | 70.9 | 27.2 | 2.3 | |
| 75% Pruning | 68.4 | 38.4 | 1.0 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 65.9 | 50.7 | 0.4 | ||
| Proposed SAFP with CA [46] | 50% Pruning | 71.0 | 27.2 | 2.3 | |
| 75% Pruning | 68.4 | 38.4 | 1.0 | ||
| 87.5% Pruning | 66.0 | 50.7 | 0.4 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, H.; Son, S.; Roh, J.; Baek, H.; Lee, S.; Chung, Y.; Park, D. SAFP-YOLO: Enhanced Object Detection Speed Using Spatial Attention-Based Filter Pruning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11237. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011237
Ahn H, Son S, Roh J, Baek H, Lee S, Chung Y, Park D. SAFP-YOLO: Enhanced Object Detection Speed Using Spatial Attention-Based Filter Pruning. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(20):11237. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011237
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Hanse, Seungwook Son, Jaehyeon Roh, Hwapyeong Baek, Sungju Lee, Yongwha Chung, and Daihee Park. 2023. "SAFP-YOLO: Enhanced Object Detection Speed Using Spatial Attention-Based Filter Pruning" Applied Sciences 13, no. 20: 11237. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011237
APA StyleAhn, H., Son, S., Roh, J., Baek, H., Lee, S., Chung, Y., & Park, D. (2023). SAFP-YOLO: Enhanced Object Detection Speed Using Spatial Attention-Based Filter Pruning. Applied Sciences, 13(20), 11237. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011237









