Effects of Hiking-Dependent Walking Speeds and Slopes on Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters and Ground Reaction Forces: A Treadmill-Based Analysis in Healthy Young Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
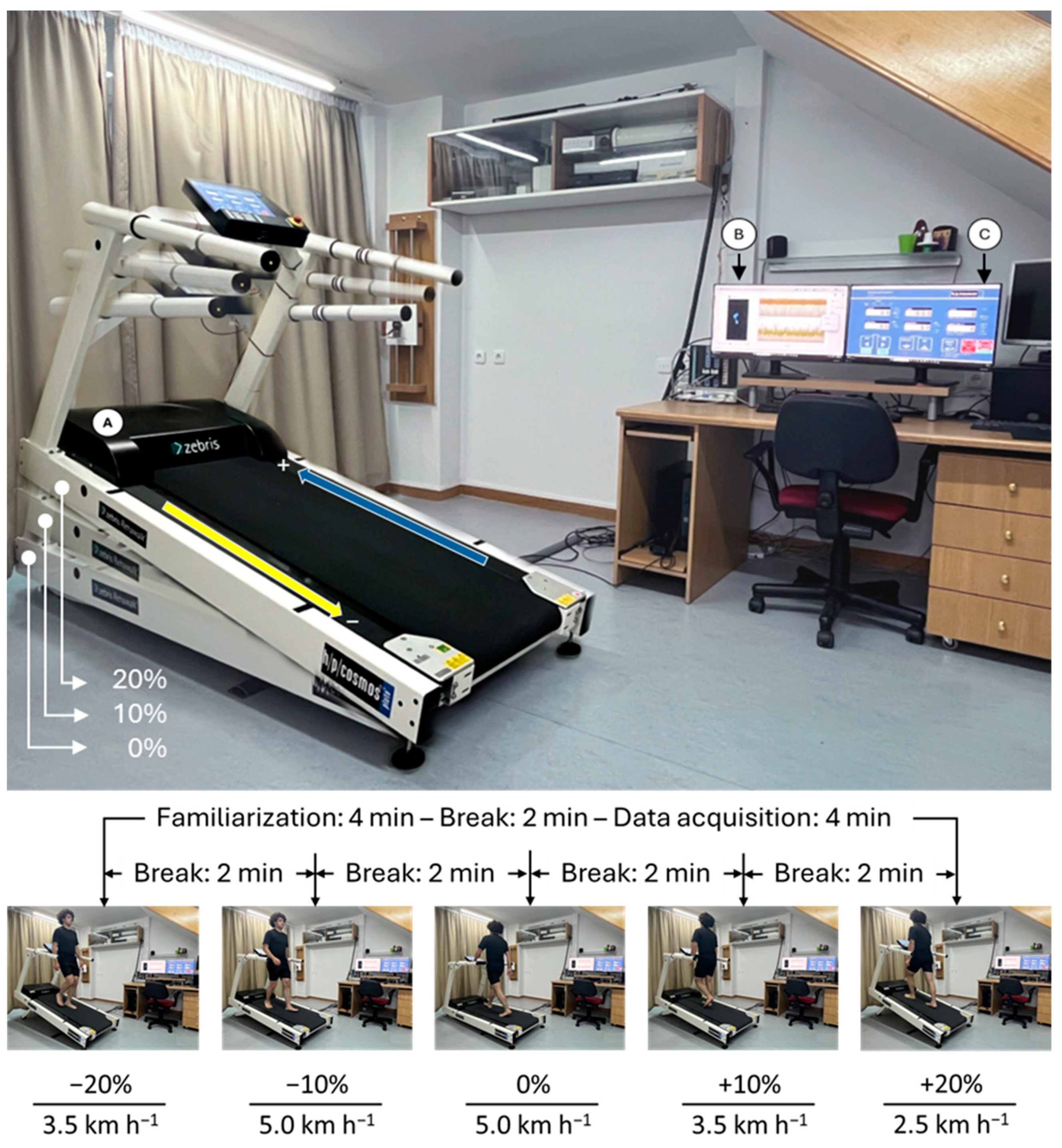
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Testing Protocol
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
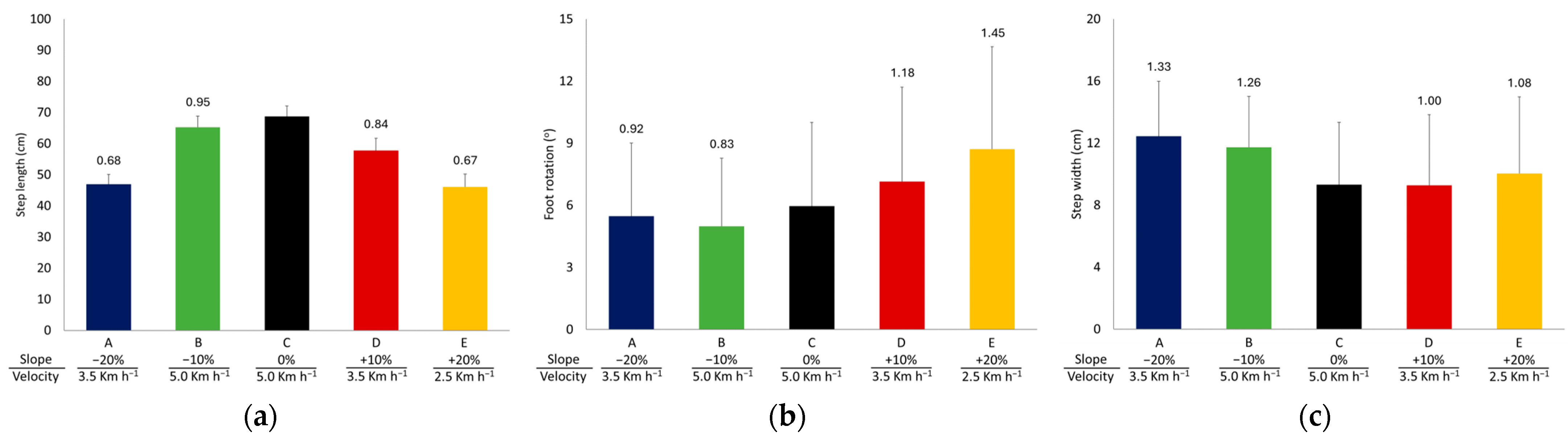
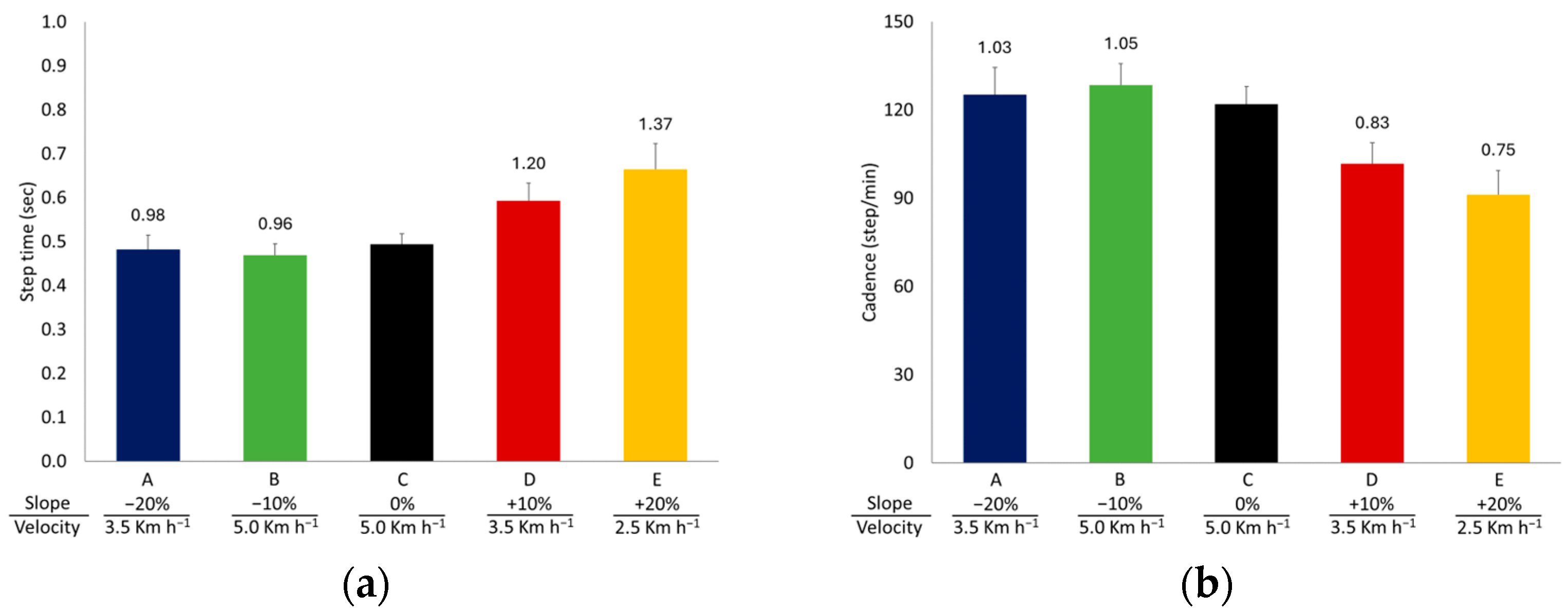
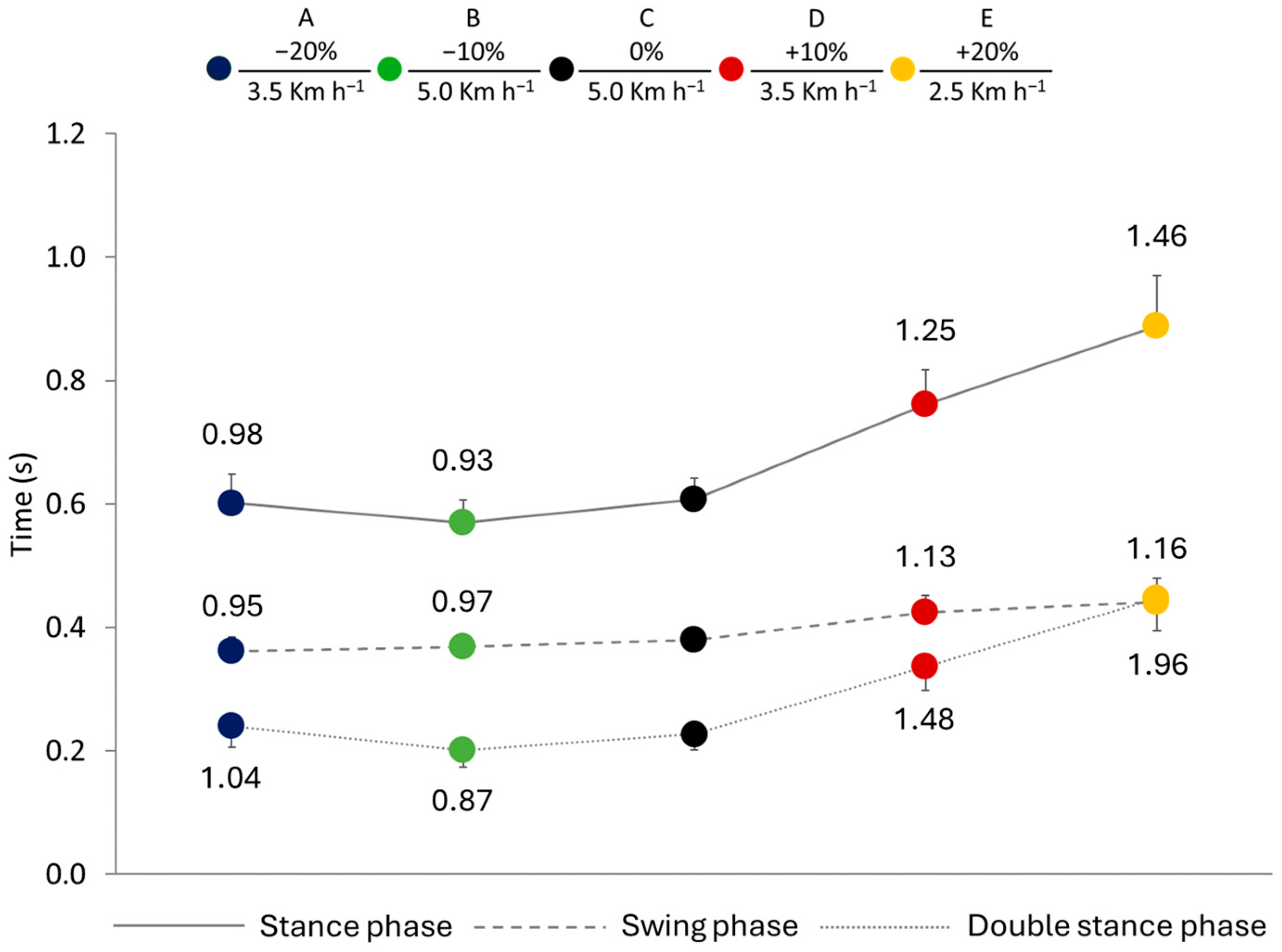
3.1. Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters
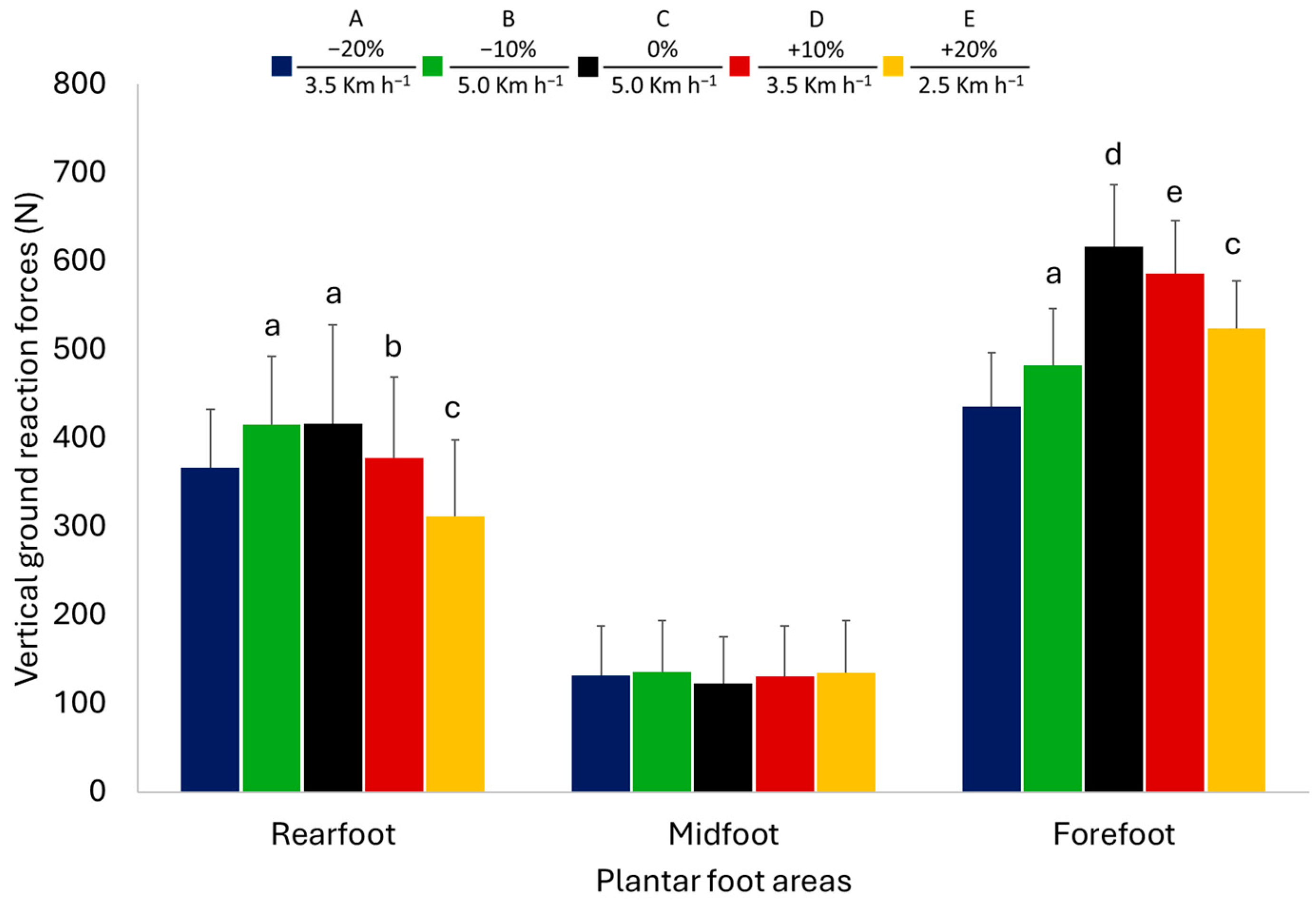
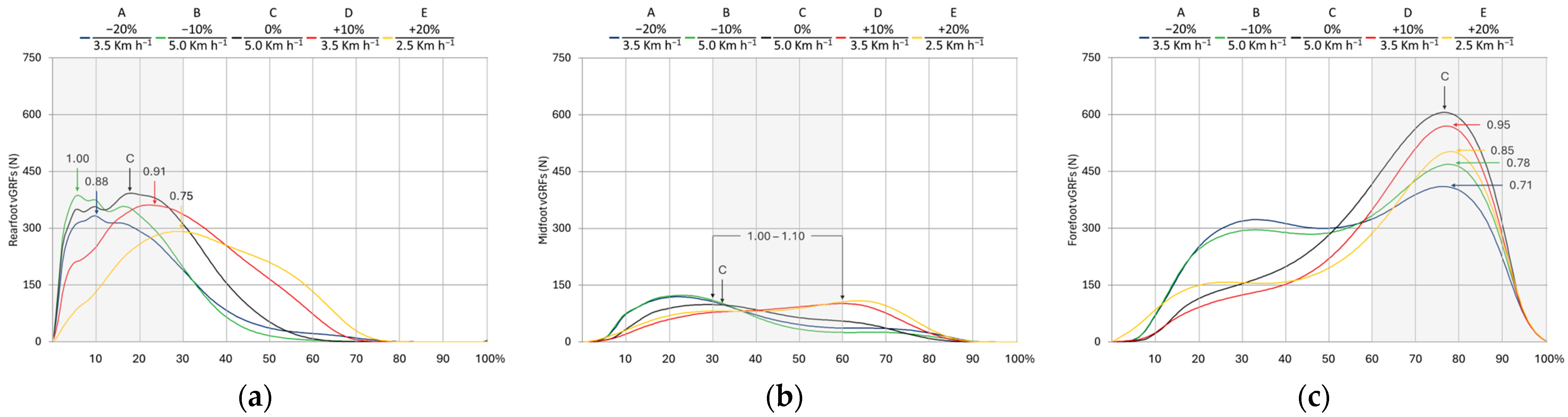
3.2. Vertical Ground Reaction Forces
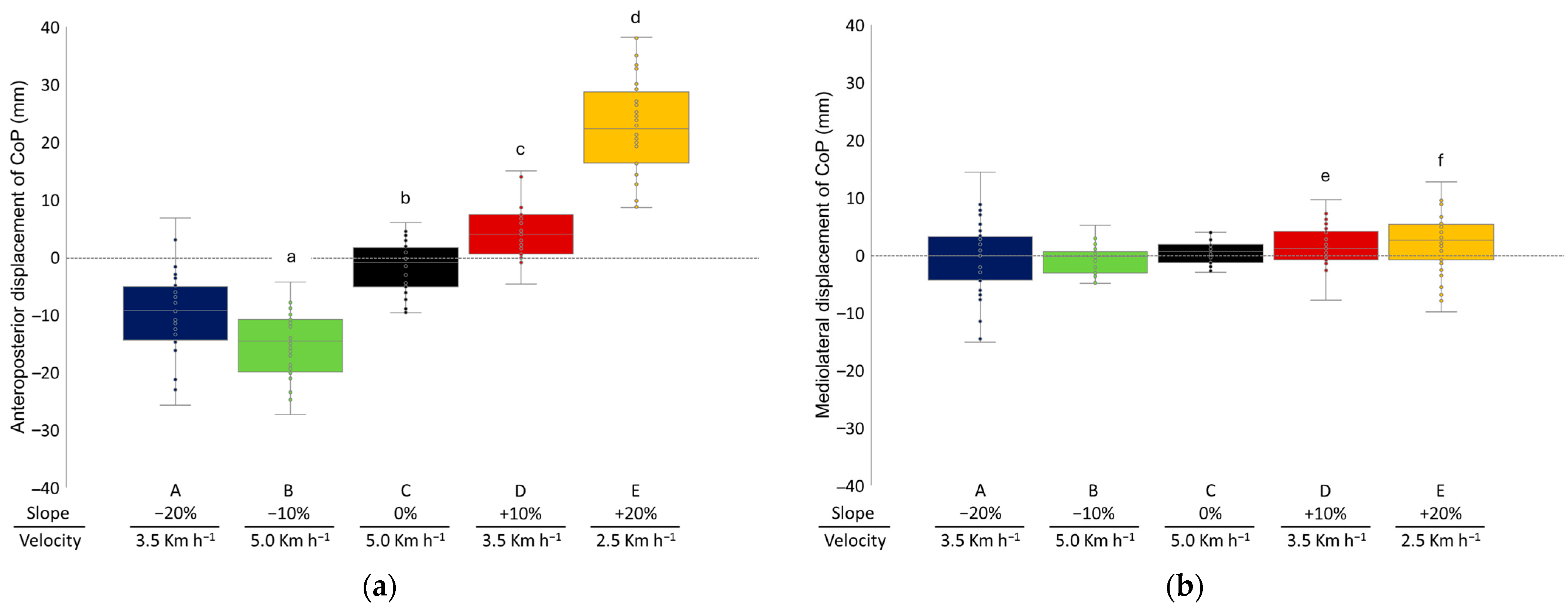
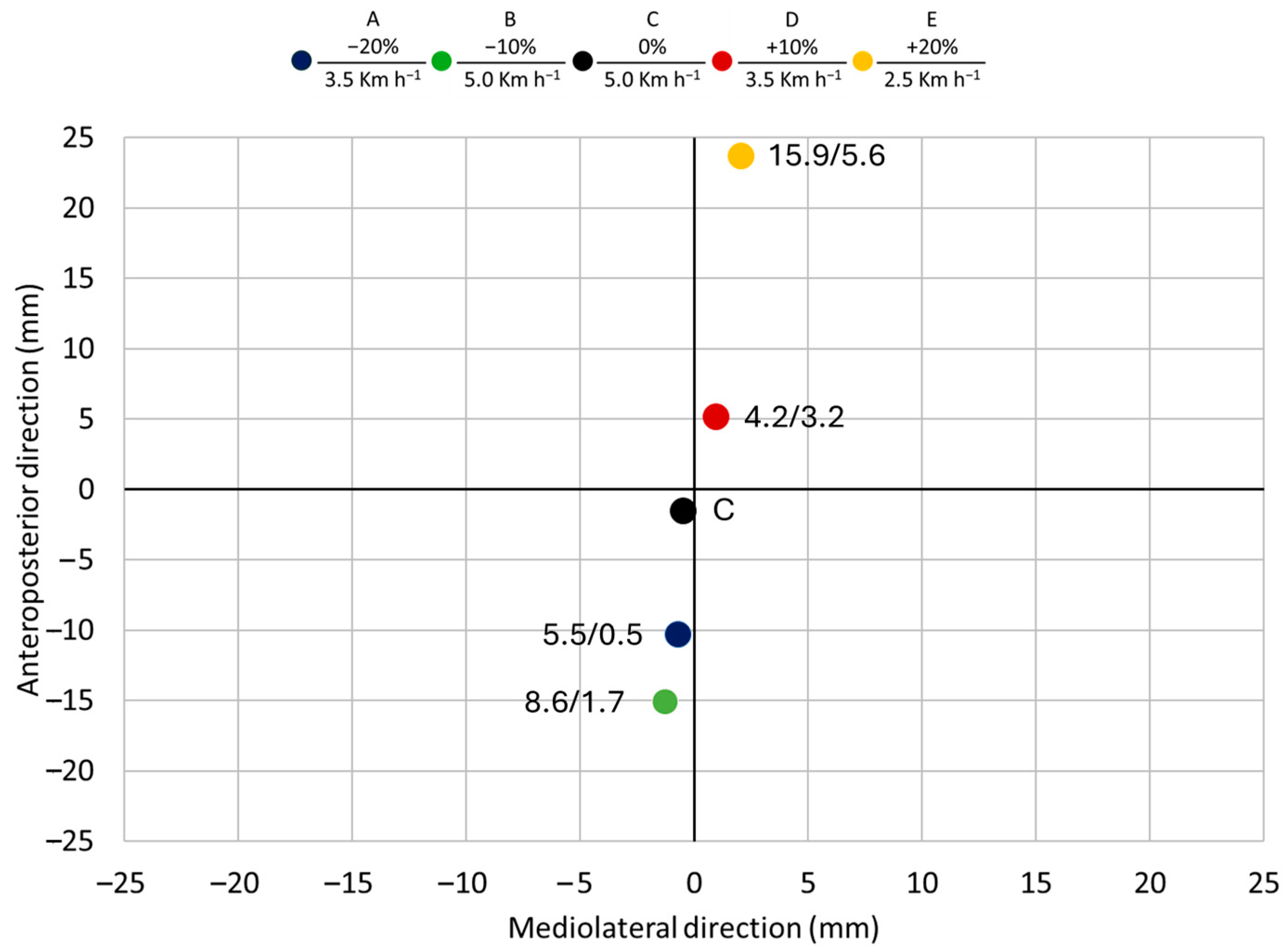
3.3. COP Position in the Anteroposterior and Mediolateral Direction
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Parameters
4.2. Vertical Ground Reaction Forces
4.3. COP Position in Anteroposterior and Mediolateral Direction
4.4. Clinical Implications
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molokáč, M.; Hlaváčová, J.; Tometzová, D.; Liptáková, E. The Preference Analysis for Hikers’ Choice of Hiking Trail. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, M.; Lonsdorfer-Wolf, E.; Isner-Horobeti, M.E.; Kouassi, B.Y.L.; Geny, B.; Favret, F.; Dufour, S.P. Cardiorespiratory Responses to Downhill Versus Uphill Running in Endurance Athletes. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2018, 89, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, S.; Patil, P.P. Effect of Uphill, Level, and Downhill Walking on Cardiovascular Parameters among Young Adults. Indian J. Health Sci. Biomed. Res. (KLEU) 2018, 11, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Narayan, J.; Sharma, P.; Singh, S.; Tiwari, S. Acute Effect of Uphill and Downhill Treadmill Walk on Cardiovascular Response and Perceived Exertion in Young Sedentary Individual. Int. J. Med. Sci. Public Health 2017, 6, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinbockel, T.C.; Craighead, D.H. Case Studies in Physiology: Impact of a Long-Distance Hike on the Pacific Crest Trail on Arterial Function and Body Composition in a Highly Fit Young Male. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, K.; Knuiman, M.; Koohsari, M.; Hickey, S.; Foster, S.; Badland, H.; Nathan, A.; Bull, F.; Giles-Corti, B. People Living in Hilly Residential Areas in Metropolitan Perth Have Less Diabetes: Spurious Association or Important Environmental Determinant? Int. J. Health Geogr. 2013, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, J.R.; Kram, R. The Effects of Grade and Speed on Leg Muscle Activations during Walking. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickle, N.T.; Grabowski, A.M.; Auyang, A.G.; Silverman, A.K. The Functional Roles of Muscles during Sloped Walking. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 3244–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, I.D.; Wohlfart, T. Walking, Hiking and Running in Parks: A Multidisciplinary Assessment of Health and Well-Being Benefits. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 130, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, M.; Aaby, A.; Klausen, S.H.; Roessler, K.K. Are Long-Distance Walks Therapeutic? A Systematic Scoping Review of the Conceptualization of Long-Distance Walking and Its Relation to Mental Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottoni, G.; Heinrich, D.; Kofler, P.; Hasler, M.; Nachbauer, W. The Effect of Uphill and Downhill Walking on Joint-Position Sense: A Study on Healthy Knees. J. Sport Rehabil. 2015, 24, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camillo, C.A.; Burtin, C.; Hornikx, M.; Demeyer, H.; De Bent, K.; Van Remoortel, H.; Osadnik, C.R.; Janssens, W.; Troosters, T. Physiological Responses during Downhill Walking: A New Exercise Modality for Subjects with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Chronic Respir. Dis. 2015, 12, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camillo, C.A.; Osadnik, C.R.; Burtin, C.; Everaerts, S.; Hornikx, M.; Demeyer, H.; Loeckx, M.; Rodrigues, F.M.; Maes, K.; Gayan-Ramirez, G.; et al. Effects of Downhill Walking in Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Patients with COPD: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, A.N.; Hass, C.J.; Gregor, R.J. The Effects of Sloped Surfaces on Locomotion: A Kinematic and Kinetic Analysis. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, A.; Fung, J.; Barbeau, H. Postural Adaptation to Walking on Inclined Surfaces: I. Normal Strategies. Gait Posture 2002, 15, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimel-Naor, S.; Gottlieb, A.; Plotnik, M. The Effect of Uphill and Downhill Walking on Gait Parameters: A Self-Paced Treadmill Study. J. Biomech. 2017, 60, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Al-Juaid, R.; Al-Amri, M. Gait Stability Characteristics in Able-Bodied Individuals During Self-Paced Inclined Treadmill Walking: Within-Subject Repeated-Measures Study. JMIR Form. Res. 2023, 7, e42769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lay, A.N.; Hass, C.J.; Richard Nichols, T.; Gregor, R.J. The Effects of Sloped Surfaces on Locomotion: An Electromyographic Analysis. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Yamin, N.A.A.; Basaruddin, K.S.; Abu Bakar, S.; Salleh, A.F.; Mat Som, M.H.; Yazid, H.; Hoang, T.D. Quantification of Gait Stability during Incline and Decline Walking: The Responses of Required Coefficient of Friction and Dynamic Postural Index. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7716821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, A.S.; Beatty, K.T.; Dwan, L.N.; Vickers, D.R. Gait Dynamics on an Inclined Walkway. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grampp, J.; Willson, J.; Kernozek, T. The Plantar Loading Variations to Uphill and Downhill Gradients During Treadmill Walking. Foot Ankle Int. 2000, 21, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, S.; Park, M.S.; Chung, C.Y.; Yoon, J.S.; Park, C.; Lee, K.M. Effects of Walking Speed and Slope on Pedobarographic Findings in Young Healthy Adults. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobler, W. Three Presentations on Geographical Analysis and Modeling: Non-Isotropic Geographic Modeling; Speculations on the Geometry of Geography and Global Spatial Analysis; Technical report; National Center for Geographic Information and Analysis: Santa Barbara, CA, USA; Buffalo, NY, USA; Orono, ME, USA, 1993; Volume 93, 22p. [Google Scholar]
- Faulhaber, M.; Ruedl, G.; Schneider, F.; Walter, D.; Sterr, R.; Schobersberger, W.; Schwendinger, F.; Pocecco, E. Characteristics of Victims of Fall-related Accidents during Mountain Hiking. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulware, D.R.; Forgey, W.W.; Martin, W.J. Medical Risks of Wilderness Hiking. Am. J. Med. 2003, 114, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Mao, L. Construction of a National Trail Research Framework under a Natural Protected Area System. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, R.; Maupin, D.; Palmer, R.; Canetti, E.F.D.; Simas, V.; Schram, B. The Impact of Footwear on Occupational Task Performance and Musculoskeletal Injury Risk: A Scoping Review to Inform Tactical Footwear. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busk, H.; Ahler, J.; Bricca, A.; Mikal Holm, P.; Varning Poulsen, D.; Skou, S.T.; Tang, L.H. Exercise-Based Rehabilitation in and with Nature: A Scoping Review Mapping Available Interventions. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2267083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitten, D.; Overholt, J.R.; Haynes, F.I.; D’Amore, C.C.; Ady, J.C. Hiking: A Low-Cost, Accessible Intervention to Promote Health Benefits. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2018, 12, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Li, C.W.; Wang, W.C. Low-Impact Hiking in Natural Areas: A Study of Nature Park Hikers’ Negative Impacts and on-Site Leave-No-Trace Educational Program in Taiwan. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 87, 106544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, M.B.; Wallard, L.; Ruiz, V.; Gillet, C.; Leteneur, S.; Simoneau-Buessinger, E. Is Treadmill Walking Biomechanically Comparable to Overground Walking? A Systematic Review. Gait Posture 2022, 92, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colino, E.; Felipe, J.L.; Van Hooren, B.; Gallardo, L.; Meijer, K.; Lucia, A.; Lopez-Fernandez, J.; Garcia-Unanue, J. Mechanical Properties of Treadmill Surfaces Compared to Other Overground Sport Surfaces. Sensors 2020, 20, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedermeier, M.; Einwanger, J.; Hartl, A.; Kopp, M. Affective Responses in Mountain Hiking—A Randomized Crossover Trial Focusing on Differences between Indoor and Outdoor Activity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutson, G.A. Anatomic and Functional Leg-Length Inequality: A Review and Recommendation for Clinical Decision-Making. Part I, Anatomic Leg-Length Inequality: Prevalence, Magnitude, Effects and Clinical Significance. Chiropr. Osteopat. 2005, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnell, W.P. An Objective Criterion for Scoliosis Screening. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1984, 66, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, A.C.; Crosbie, J.; Ouvrier, R.A. Development and Validation of a Novel Rating System for Scoring Standing Foot Posture: The Foot Posture Index. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G.A.V. Psychophysical Bases of Perceived Exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillard, T. Effects of General and Local Fatigue on Postural Control: A Review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eston, R. Use of Ratings of Perceived Exertion in Sports. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2012, 7, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.; Killeen, T.; Easthope, C.S.; Curt, A.; Bolliger, M.; Linnebank, M.; Zörner, B.; Filli, L. Familiarization with Treadmill Walking: How Much Is Enough? Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Mu, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, S. Cities Are Going Uphill: Slope Gradient Analysis of Urban Expansion and Its Driving Factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, N. Terrain Analysis of the 50 Largest Cities in the USA. Available online: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/93b6c503d423499d93731cd5966e620e/print (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Zeller, J.; Doyle, R.; Snodgrass, K. Accessibility Guidebook for Outdoor Recreation and Trails. Available online: https://www.fs.usda.gov/t-d/pubs/htmlpubs/htm06232801/toc.htm (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Pingel, T.J. Modeling Slope as a Contributor to Route Selection in Mountainous Areas. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 37, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Williams Andrews, A. Normal Walking Speed: A Descriptive Meta-Analysis. Physiotherapy 2011, 97, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebris Medical GmbH. Software Manual Zebris FDM 2.0.x; Zebris Medical GmbH: Isny im Allgäu, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Strutzenberger, G.; Leutgeb, L.; Claußen, L.; Schwameder, H. Gait on Slopes: Differences in Temporo-Spatial, Kinematic and Kinetic Gait Parameters between Walking on a Ramp and on a Treadmill. Gait Posture 2022, 91, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Walters, M.; Svensson, N.; Lloyd, D. The Influence of Surface Slope on Human Gait Characteristics: A Study of Urban Pedestrians Walking on an Inclined Surface. Ergonomics 1996, 39, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Pérez, V.; Soler, A.; Ansa, A.; López-Samanes, Á.; Madruga-Parera, M.; Beato, M.; Romero-Rodríguez, D. Acute and Chronic Effects of Competition on Ankle Dorsiflexion ROM in Professional Football Players. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2020, 20, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Shin, G. Foot Kinematics and Leg Muscle Activation Patterns Are Altered in Those with Limited Ankle Dorsiflexion Range of Motion during Incline Walking. Gait Posture 2022, 92, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Phadke, C.P. Effects of Treadmill Incline and Speed on Peroneus Longus Muscle Activity in Persons with Chronic Stroke and Healthy Subjects. Gait Posture 2017, 54, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina McKeon, J.M.; Hoch, M.C. The Ankle-Joint Complex: A Kinesiologic Approach to Lateral Ankle Sprains. J. Athl. Train. 2019, 54, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaStayo, P.C.; Woolf, J.M.; Lewek, M.D.; Snyder-Mackler, L.; Reich, T.; Lindstedt, S.L. Eccentric Muscle Contractions: Their Contribution to Injury, Prevention, Rehabilitation, and Sport. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2003, 33, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchateau, J.; Enoka, R.M. Neural Control of Lengthening Contractions. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaleddini, K.; Nagamori, A.; Laine, C.M.; Golkar, M.A.; Kearney, R.E.; Valero-Cuevas, F.J. Physiological Tremor Increases When Skeletal Muscle Is Shortened: Implications for Fusimotor Control. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 7331–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, L.A.; Lo, I.K.Y.; Fowler, P. Effect of Fatigue on Knee Proprioception: Implications for Dynamic Stabilization. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2001, 31, 59–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, R. Effect of Exercise-Induced Fatigue on Position Sense of the Knee. Aust. J. Physiother. 1994, 40, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, B. Half of Emergency Calls in Hikers Are Injuries from Falls in 50–70 Year-Olds. Dtsch. Z. Sportmed. 2019, 70, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, D.W.; Thorsen, T.A.; Weinhandl, J.T.; Strohacker, K.A.; Zhang, S. Effects of Increased Step-Width on Knee Biomechanics During Inclined and Declined Walking. J. Appl. Biomech. 2020, 36, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuchi, C.A.; Fukuchi, R.K.; Duarte, M. Effects of Walking Speed on Gait Biomechanics in Healthy Participants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wai Ming Lee, E.; Li, T.; Jiang, N.; Ma, Y. Pedestrian Dynamics on Slopes: Empirical Analysis of Level, Uphill, and Downhill Walking. Saf. Sci. 2024, 172, 106429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.; Weisberger, A.; Ray, J.; Hasan, S.; Shiavi, R.; Spengler, D. Relationship between Vertical Ground Reaction Force and Speed during Walking, Slow Jogging, and Running. Clin. Biomech. 1996, 11, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, J.; Thorstensson, A. Ground Reaction Forces at Different Speeds of Human Walking and Running. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1989, 136, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.R.; Standifird, T.W.; Creer, A.; Fong, H.B.; Powell, D.W. Ground Reaction Force Profiles during Inclined Running at Iso-Efficiency Speeds. J. Biomech. 2020, 113, 110107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hong, Y.N.G.; Shin, C.S. The Alteration in the Center of Pressure and Duration Ratio of Stance Sub-Phases during Upslope Walking. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 19, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinier, D.; White, D.K. Walking, Running, and Recreational Sports for Knee Osteoarthritis: An Overview of the Evidence. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 11 (Suppl. 1), S21–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicharro-Luna, E.; Martínez-Nova, A.; Ortega-Ávila, A.B.; Requena-Martínez, A.; Gijón-Noguerón, G. Prevalence and Risk Factors Associated with the Formation of Dermal Lesions on the Foot during Hiking. J. Tissue Viability 2020, 29, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braybrook, P.J.; Tohira, H.; Birnie, T.; Brink, D.; Finn, J.; Buzzacott, P. Types and Anatomical Locations of Injuries among Mountain Bikers and Hikers: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, J.L.; Wimpey, J. Assessing the Influence of Sustainable Trail Design and Maintenance on Soil Loss. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 189, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.; Grey, M.J.; Heneghan, N.; Bowen, L.; Li, F.X. Barefoot vs Common Footwear: A Systematic Review of the Kinematic, Kinetic and Muscle Activity Differences during Walking. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rössler, R.; Wagner, J.; Knaier, R.; Rommers, N.; Kressig, R.W.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A.; Hinrichs, T. Spatiotemporal Gait Characteristics across the Adult Lifespan: Reference Values from a Healthy Population—Analysis of the COmPLETE Cohort Study. Gait Posture 2024, 109, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Kwon, S.Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Hong, J.; Yu, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, D. Influence of the Hawthorne Effect on Spatiotemporal Parameters, Kinematics, Ground Reaction Force, and the Symmetry of the Dominant and Nondominant Lower Limbs during Gait. J. Biomech. 2023, 152, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| Step length (cm) | Distance between the heel strike of one side of the body and the heel strike of the contralateral side |
| Step width (cm) | Distance between the right and left foot |
| Foot rotation (°) | Angle between the longitudinal axis of the foot and the direction of walking |
| Step time (s) | Time within a gait cycle between the heel strike of one side of the body and the heel strike of the contralateral side |
| Cadence (step/min) | Frequency of steps per unit time |
| Stance phase (s) | Time within a gait cycle when the foot is in contact with the ground |
| Swing phase (s) | Time within a gait cycle during which the foot is not in contact with the ground |
| Double-stance phase (s) | Time of the load response and the pre-swing phase collectively |
| Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters | Walking Conditions (Slope/Speed) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| −20% 3.5 km h−1 | −10% 5.0 km h−1 | 0% 5.0 km h−1 | +10% 3.5 km h−1 | +20% 2.5 km h−1 | |
| Step length (cm) | 46.9 ± 3.2 | 65.3 ± 3.6 a | 68.7 ± 3.4 b | 57.8 ± 3.9 c | 46.0 ± 4.1 d |
| Step width (cm) | 12.4 ± 2.3 | 11.7 ± 2.0 e | 9.3 ± 1.8 b | 9.3 ± 2.4 b | 10.0 ± 2.4 f |
| Foot rotation (°) | 5.5 ± 3.5 | 5.0 ± 3.3 | 6.0 ± 4.0 g | 7.1 ± 4.6 c | 8.7 ± 5.0 h |
| Step time (s) | 0.48 ± 0.03 | 0.47 ± 0.03 i | 0.49 ± 0.02 j | 0.59 ± 0.04 c | 0.67 ± 0.06 h |
| Cadence (step/min) | 125.2 ± 9.2 | 128.4 ± 7.3 k | 121.9 ± 6.0 j | 101.7 ± 7.1 c | 91.1 ± 8.3 d |
| Gait Phases | Walking Conditions (Slope/Speed) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| −20% 3.5 km h−1 | −10% 5.0 km h−1 | 0% 5.0 km h−1 | +10% 3.5 km h−1 | +20% 2.5 km h−1 | |
| Stance phase (s) | 0.60 ± 0.05 | 0.57 ± 0.04 a | 0.61 ± 0.04 b | 0.76 ± 0.06 c | 0.89 ± 0.08 d |
| Swing phase (s) | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.02 e | 0.43 ± 0.03 c | 0.44 ± 0.04 f |
| Double-stance phase (s) | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.03 a | 0.23 ± 0.03 g | 0.34 ± 0.04 c | 0.45 ± 0.05 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kafetzakis, I.; Konstantinou, I.; Mandalidis, D. Effects of Hiking-Dependent Walking Speeds and Slopes on Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters and Ground Reaction Forces: A Treadmill-Based Analysis in Healthy Young Adults. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114383
Kafetzakis I, Konstantinou I, Mandalidis D. Effects of Hiking-Dependent Walking Speeds and Slopes on Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters and Ground Reaction Forces: A Treadmill-Based Analysis in Healthy Young Adults. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(11):4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114383
Chicago/Turabian StyleKafetzakis, Ioannis, Ilias Konstantinou, and Dimitris Mandalidis. 2024. "Effects of Hiking-Dependent Walking Speeds and Slopes on Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters and Ground Reaction Forces: A Treadmill-Based Analysis in Healthy Young Adults" Applied Sciences 14, no. 11: 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114383
APA StyleKafetzakis, I., Konstantinou, I., & Mandalidis, D. (2024). Effects of Hiking-Dependent Walking Speeds and Slopes on Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters and Ground Reaction Forces: A Treadmill-Based Analysis in Healthy Young Adults. Applied Sciences, 14(11), 4383. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114383








