Disturbance Observer-Based Anti-Shock Controller for Laser Beam Steering Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. FSM Control System
2.1. Dynamic Characteristics of PZT Actuator
2.2. Tip-Tilt Controller of FSM Control System
3. Anti-Shock Controller for FSM System
3.1. Shock Specifications
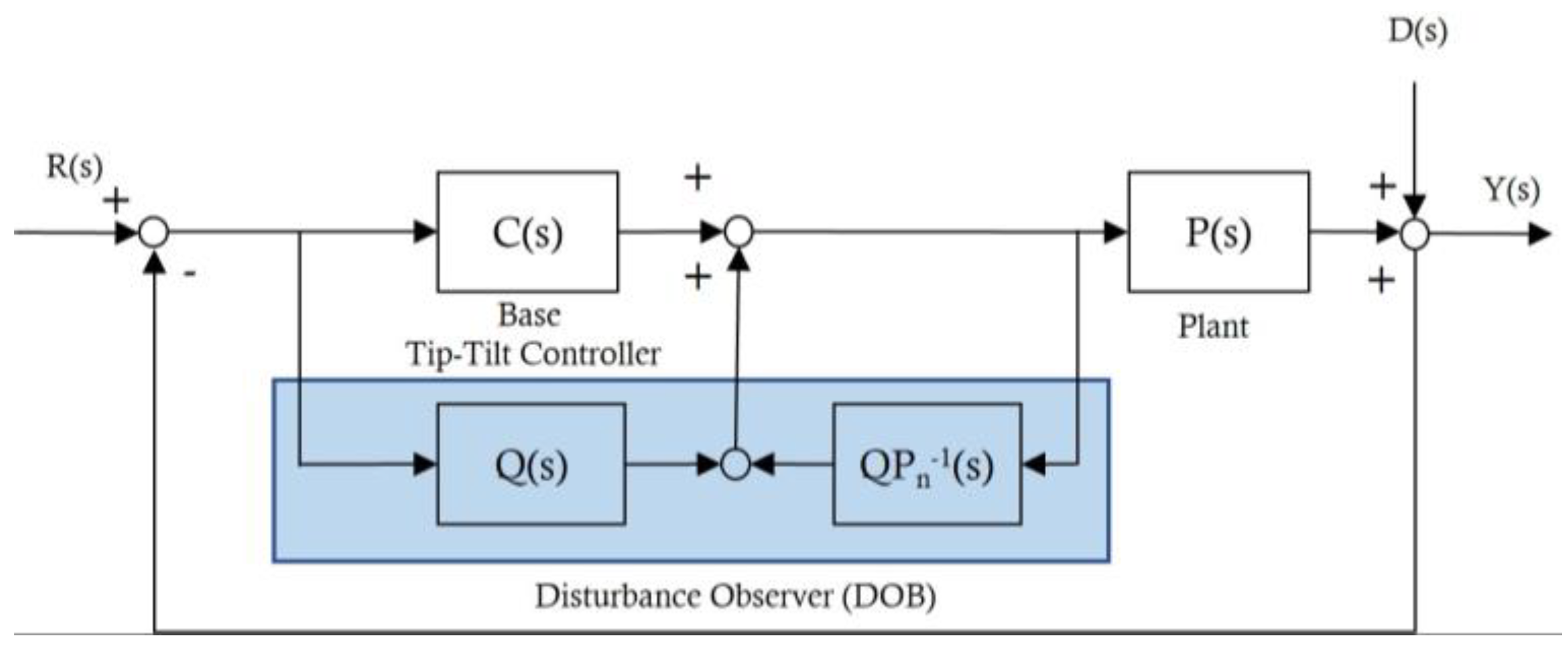
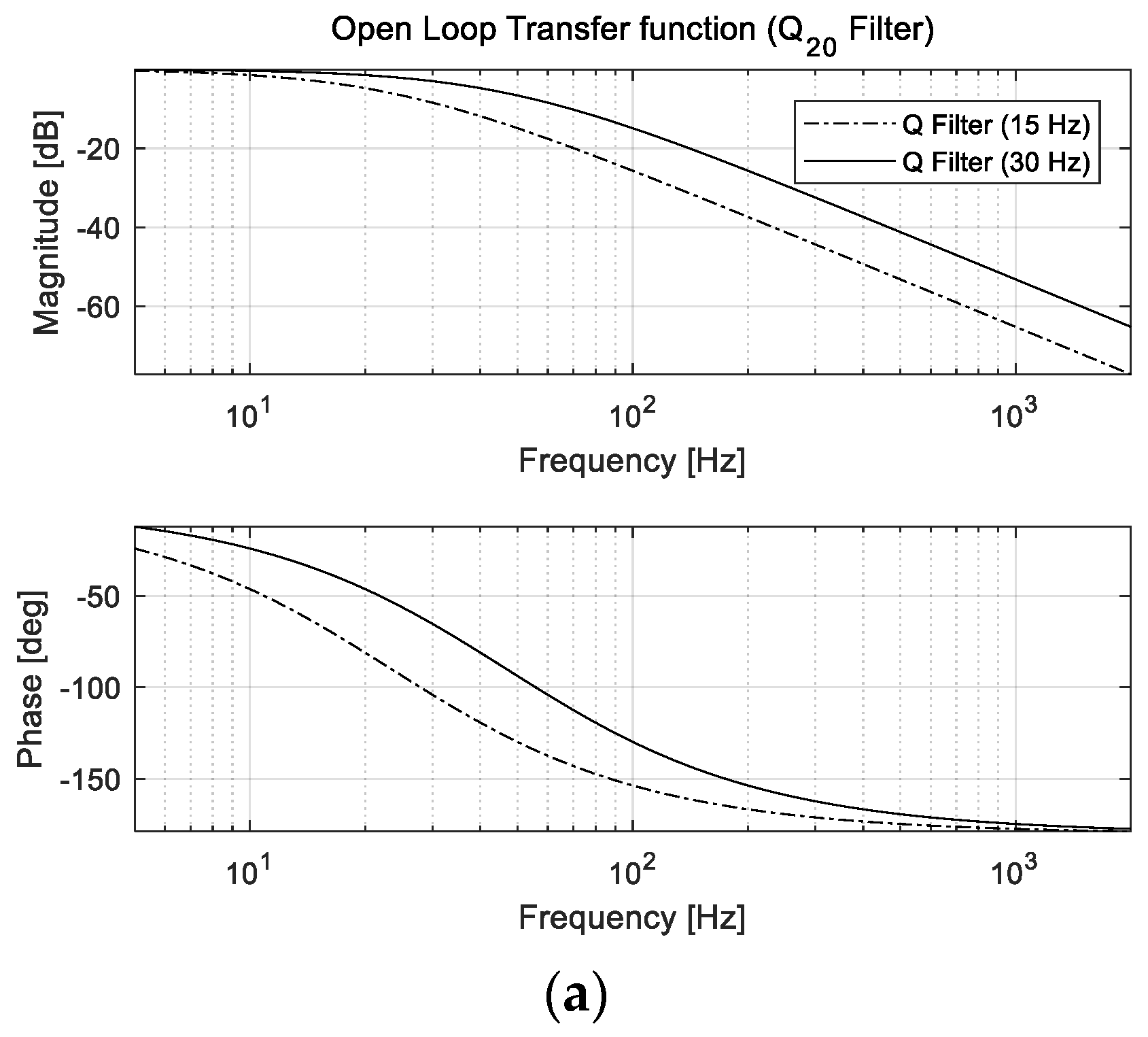
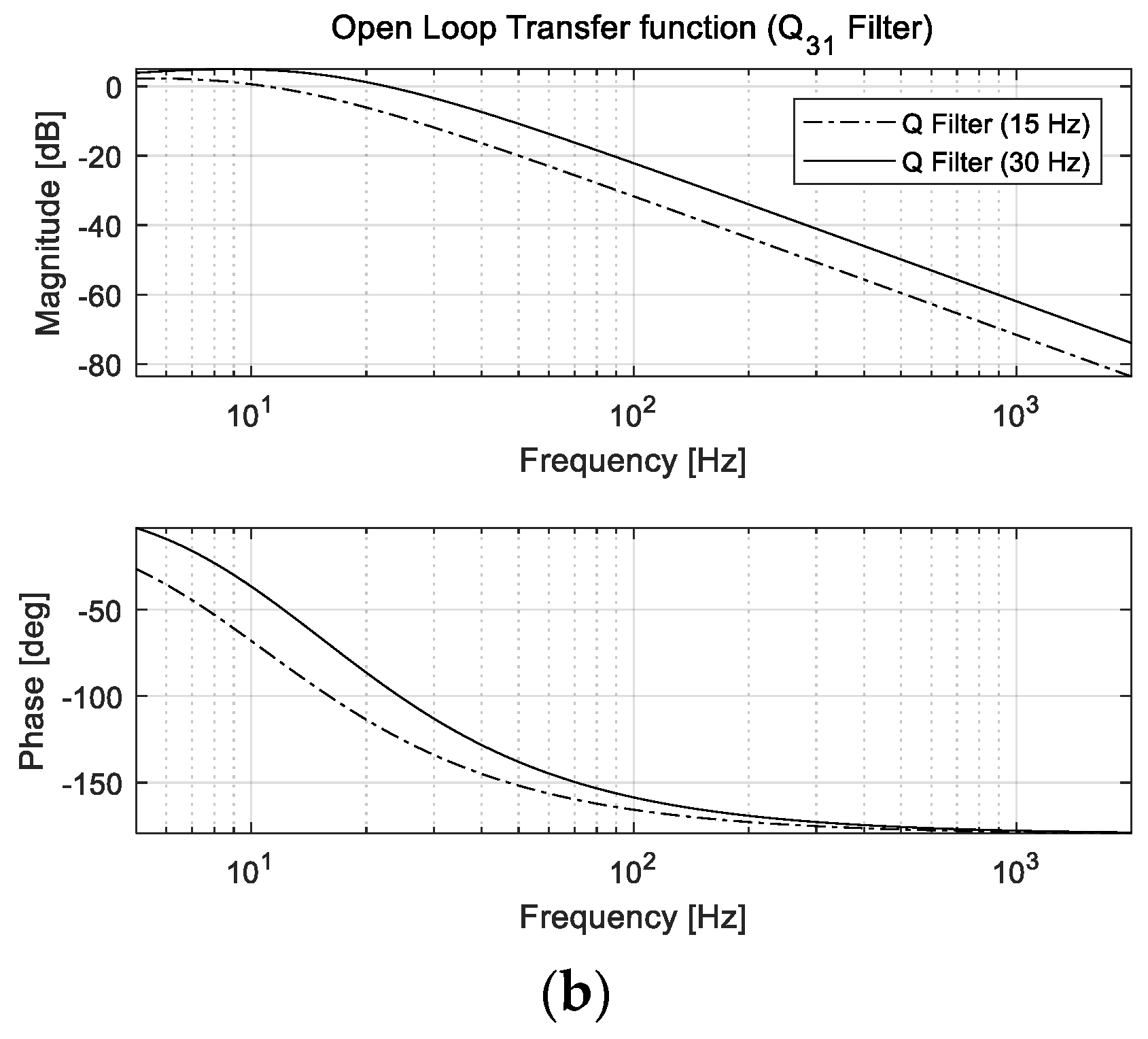
3.2. DOB-Based Anti-Shock Controller
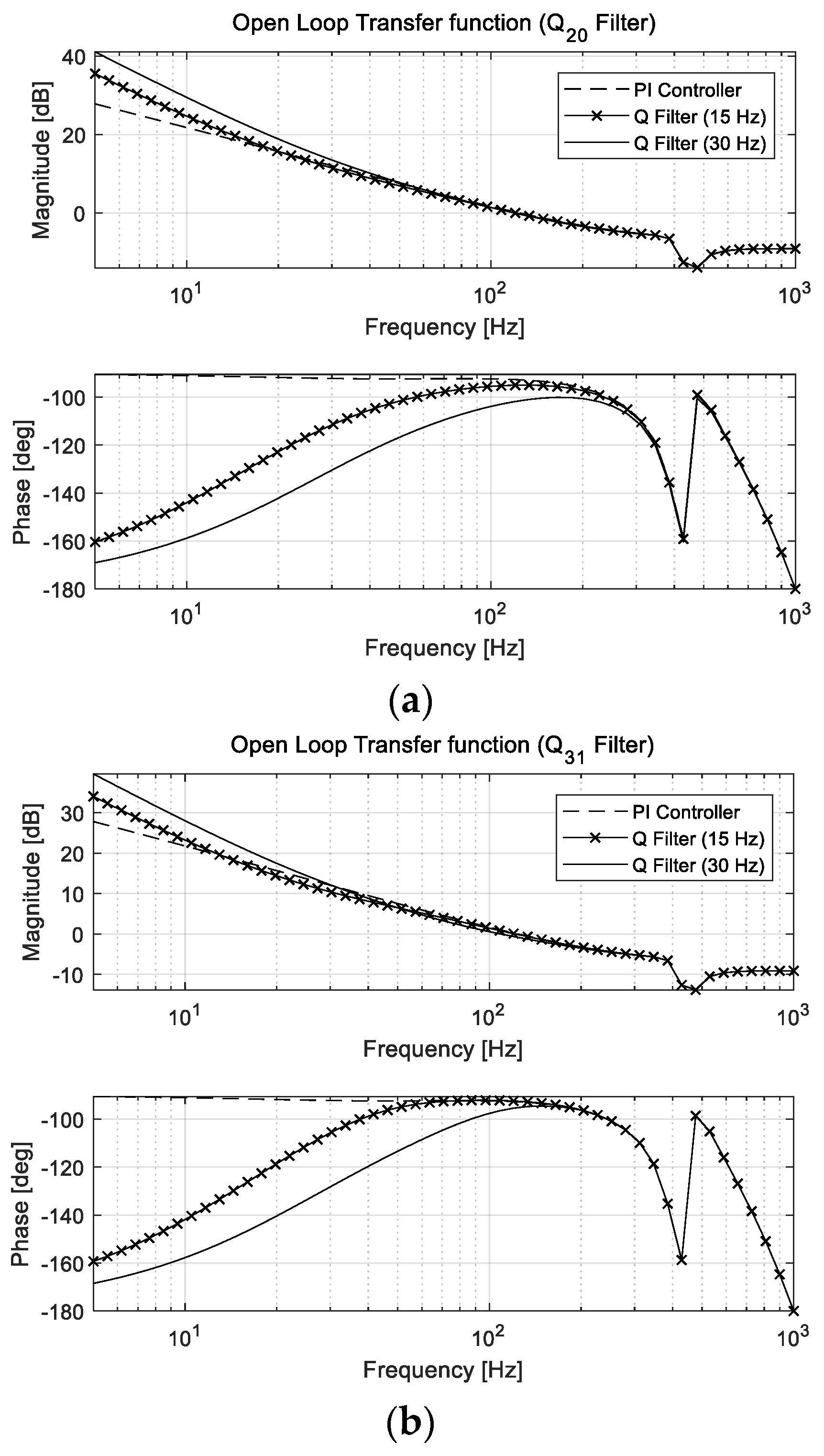
4. Performance of Anti-Shock Controller for FSM System
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, C.; Ding, Y.; Wang, D.; Tian, D. Backscanning step and stare imaging system with high frame rate and wide coverage. App. Opt. 2015, 54, 4960–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yao, K.; Huang, D.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Lv, Y. Performance evaluation of coherent free space optical communications with a double-stage fast-steering-mirror adaptive optics system depending on the Greenwood frequency. Opt. Exp. 2016, 24, 13288–13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokbel, H.F.; Yuan, W.; Ying, L.Q.; Hua, C.G.; Roshdy, A. Research on the mechanical design of two-axis fast steering mirror for optical beam guidance. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Material Science (MEMS 2012), Shanghai, China, 28–30 December 2012; pp. 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, D.; Li, S.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. A new method for incoherent combining of far-field laser beams based on multiple faculae recognition. In Young Scientists Forum; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10710, p. 1071034. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, P.H.; Albertine, J.R. Beam control for high-energy laser devices. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perram, G.P.; Marciniak, M.A.; Goda, M. High-energy laser weapons: Technology overview. Laser Technol. Def. Secur. 2004, 5414, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Meline, M.E.; Harrell, J.P.; Lohnes, K.A. Universal beam steering mirror design using the cross blade flexure. In Acquisition, Tracking, and Pointing VI; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1992; Volume 1697, pp. 424–443. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Tang, J.; ElDeeb, Y. Design of dual-stage actuation system for high precision optical manufacturing. In Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2008; Volume 6928, p. 692828. [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens, P.; Rosielle, N.; Vermeulen, H.; Vermeulen, M.M.P.A.; Wetzels, S.F.C.L.; Pril, W. Design for precision: Current status and trends. CIRP Ann. 1998, 47, 557–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluk, D.J.; Boulet, M.T.; Trumper, D.L. A high-bandwidth, High-precision, two-axis steering mirror with moving iron actuator. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, T.; Ji, Y.; Li, X. Model analysis and resonance suppression of wide-bandwidth inertial reference system. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2019, 2, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.Y.; Zhu, L.M.; Su, C.Y.; Ding, H.; Fatikow, S. Modeling and control of piezo-actuated nanopositioning stages: A survey. IEEE Trans. Auto. Sci. Eng. 2016, 13, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Feng, Z.; Ming, M.; Xiao, X. Damping controller design for nanopositioners: A hybrid reference model matching and virtual reference feedback tuning approach. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 19, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.Y.; Zhu, L.M.; Su, C.Y. Integral resonant damping for high-bandwidth control of piezoceramic stack actuators with asymmetric hysteresis nonlinearity. Mechatronics 2014, 24, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEver, M.A.; Cole, D.G.; Clark, R.L. Adaptive feedback control of optical jitter using Q-parameterization. Opt. Eng. 2004, 43, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancibia, N.O.P.; Chen, N.; Gibson, S.; Tsao, T.C. Adaptive control of a MEMS steering mirror for free-space laser communications. In Free—Space Laser Communications V; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5892, p. 589210. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Chen, G.; Bai, F. High-speed and precision control of a piezoelectric positioner with hysteresis, resonance and disturbance compensation. Microsyst. Technol. 2016, 22, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schitter, G.; Thurner, P.J.; Hansma, P.K. Design and input-shaping control of a novel scanner for high-speed atomic force microscopy. Mechatronics 2008, 18, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odgaard, P.F.; Stoustrup, J.; Andersen, P.; Wickerhauser, M.V.; Mikkelsen, H.F. A simulation model of focus and radial servos in compact disc players with disc surface defects. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Taipei, Taiwan, 2–4 September 2004; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Hilkert, J.M. A comparison of inertial line-of-sight stabilization techniques using mirrors. In Acquisition, Tracking, and Pointing XVIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5430, p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Steinbuch, M. Estimator-based sliding mode control of an optical disc drive under shock and vibration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control Applications, Glasgow, UK, 18–20 September 2002; pp. 631–636. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, G.Y.; Zhu, L.M. Motion control of piezoceramic actuators with creep, hysteresis and vibration compensation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 197, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M.; Pott, J.U.; Kürster, M.; Sawodny, O.; Defrere, D.; Hinz, P. Delay compensation for real time disturbance estimation at extremely large telescopes. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2016, 25, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glück, M.; Pott, J.U.; Sawodny, O. Piezo-actuated vibration disturbance mirror for investigating accelerometer-based tip-tilt reconstruction in large telescopes. IFAC Papersonline 2016, 49, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Ohnishi, K.; Miyachi, K.A. Robust decentralized joint control based on interference estimation. In Proceedings of the 1987 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Raleigh, NC, USA, 31 March–3 April 1987; pp. 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi, K.; Ohde, H. Collision and force control for robot manipulator without force sensor. In Proceedings of the IECON’94—20th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics, Bologna, Italy, 5–9 September 1994; Volume 2, pp. 766–771. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.K.; Chung, W.K.; Youm, Y. Robust learning control for robot manipulators based on disturbance observer. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE IECON. 22nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Control, and Instrumentation, Taipei, Taiwan, 9 August 1996; pp. 1276–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Su, J.; Xiang, G. Robust motion control system design with scheduled disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6519–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Li, S. Disturbance-observer-based control and related methods—An overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Ma, J.; Ge, R. PID-I controller of charge coupled device-based tracking loop for Fast-steering mirror. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Tomizuka, M. Robust motion controller design for high-accuracy positioning systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2000, 2, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- White, M.; Tomizuka, M.; Smith, C. Improved track following in magnetic disk drives using a disturbance observer. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2000, 5, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, S.N. Control System Engineering, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.L.; Teo, C.S.; Tan, K.K. An iterative data-based approach to disturbance observer sensitivity shaping. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016—42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 24–27 October 2016; pp. 6067–6072. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Liu, P.; Ding, H. Structural parameter design method for a Fast-steering mirror based on a closed-loop bandwidth. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 15, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ren, W.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Mao, Y. A modified observer structure based on acceleration measurement for disturbance suppression in tracking control system. App. Sci. 2018, 8, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, B.U.; Gimm, H.; Kang, D.; Gweon, D. Design and analysis of a tip-tilt guide mechanism for the fast steering of a large-scale mirror. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, B.U.; Gimm, H.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, G.T.; Kim, B.U. Development of a fast steering mirror of large diameter. In Integrated Photonics: Materials, Devices, and Applications IV; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10249, p. 102490R. [Google Scholar]
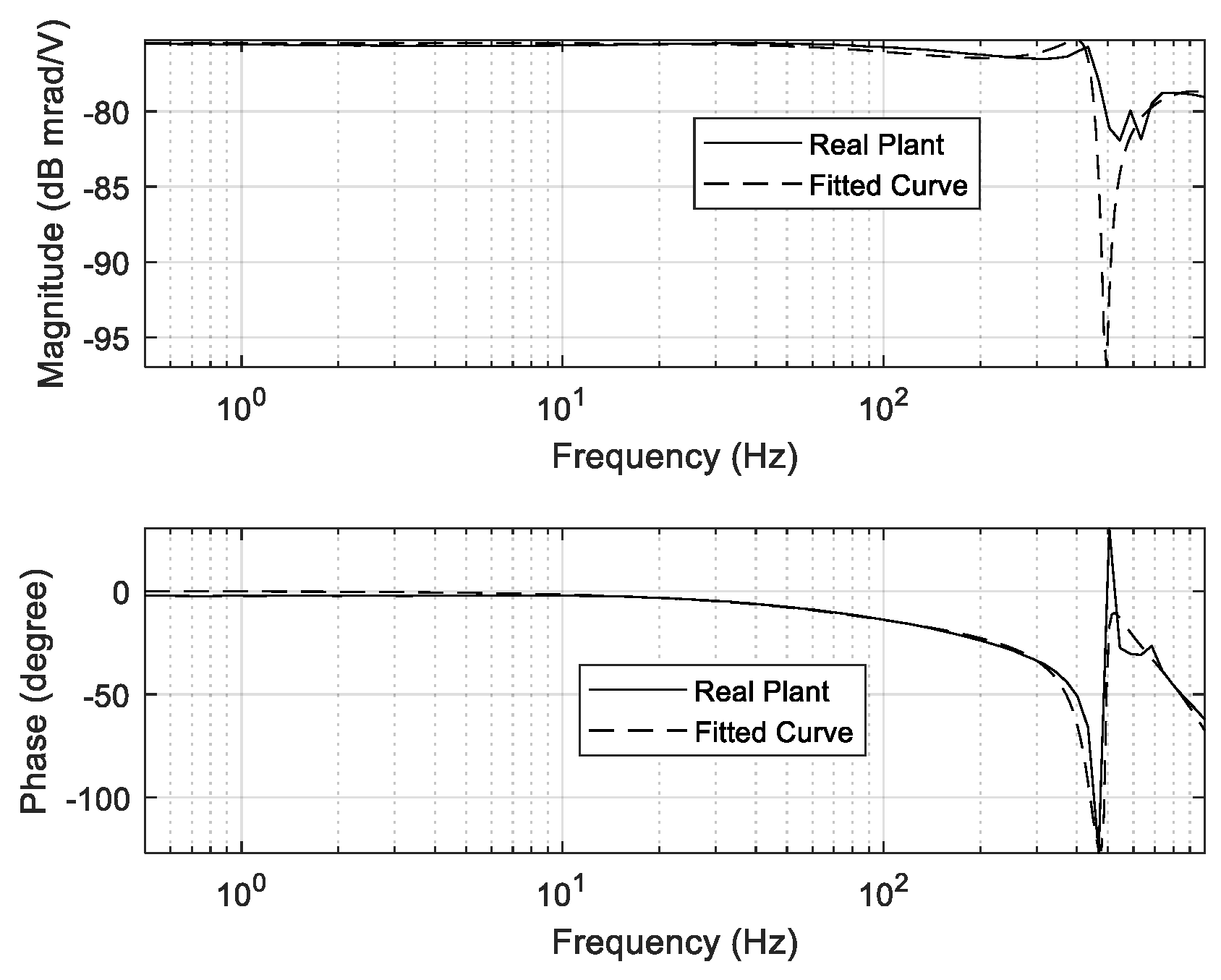
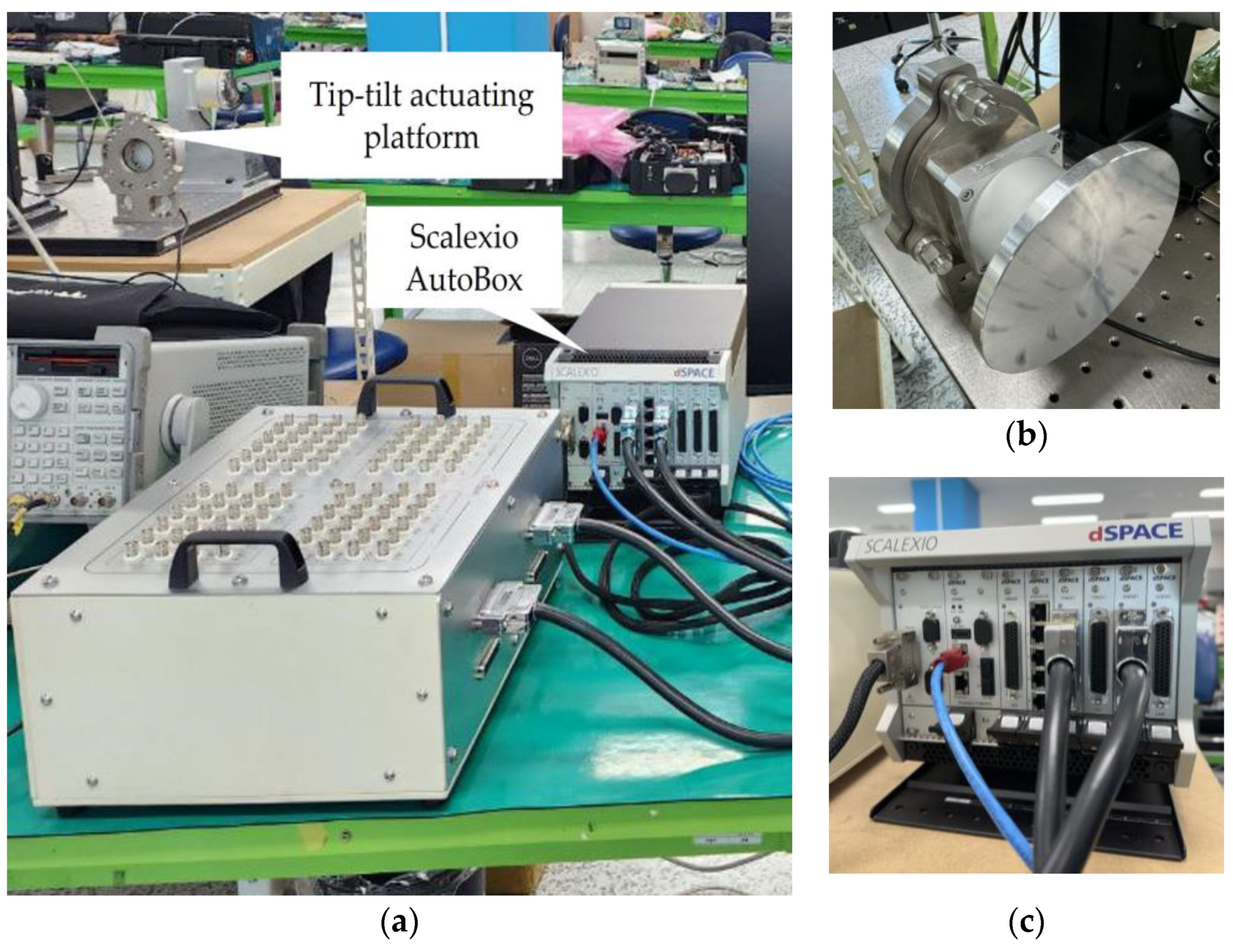
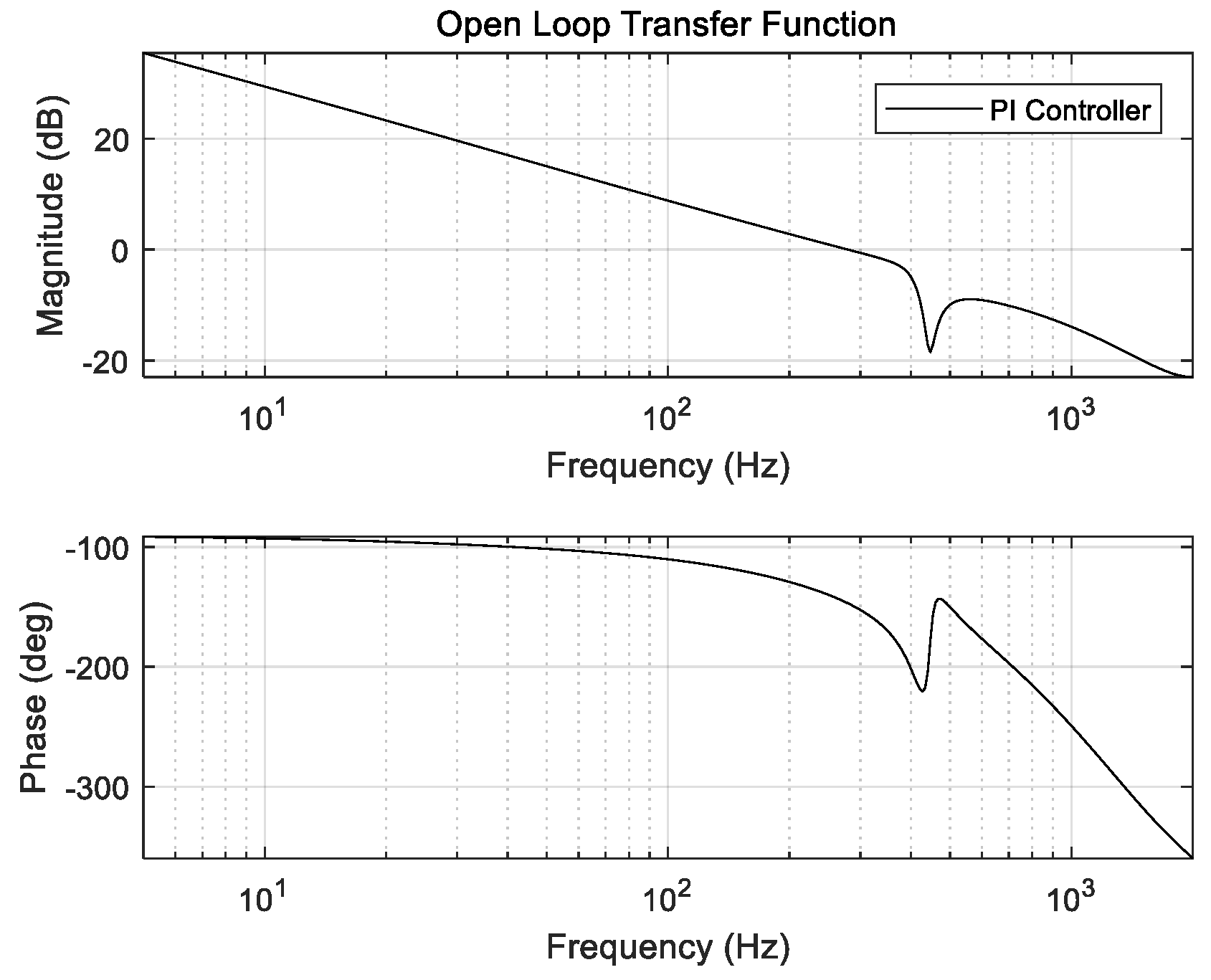
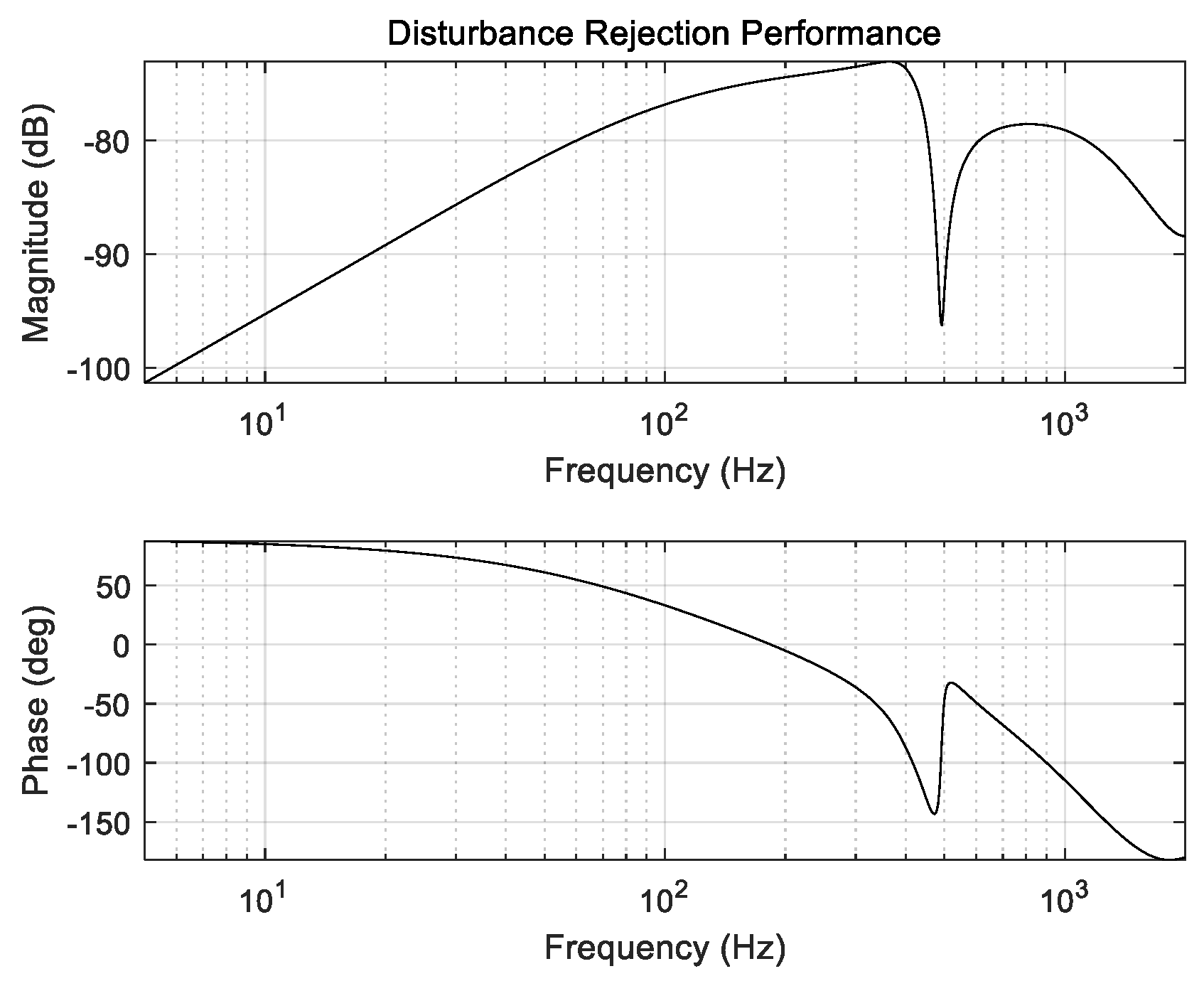

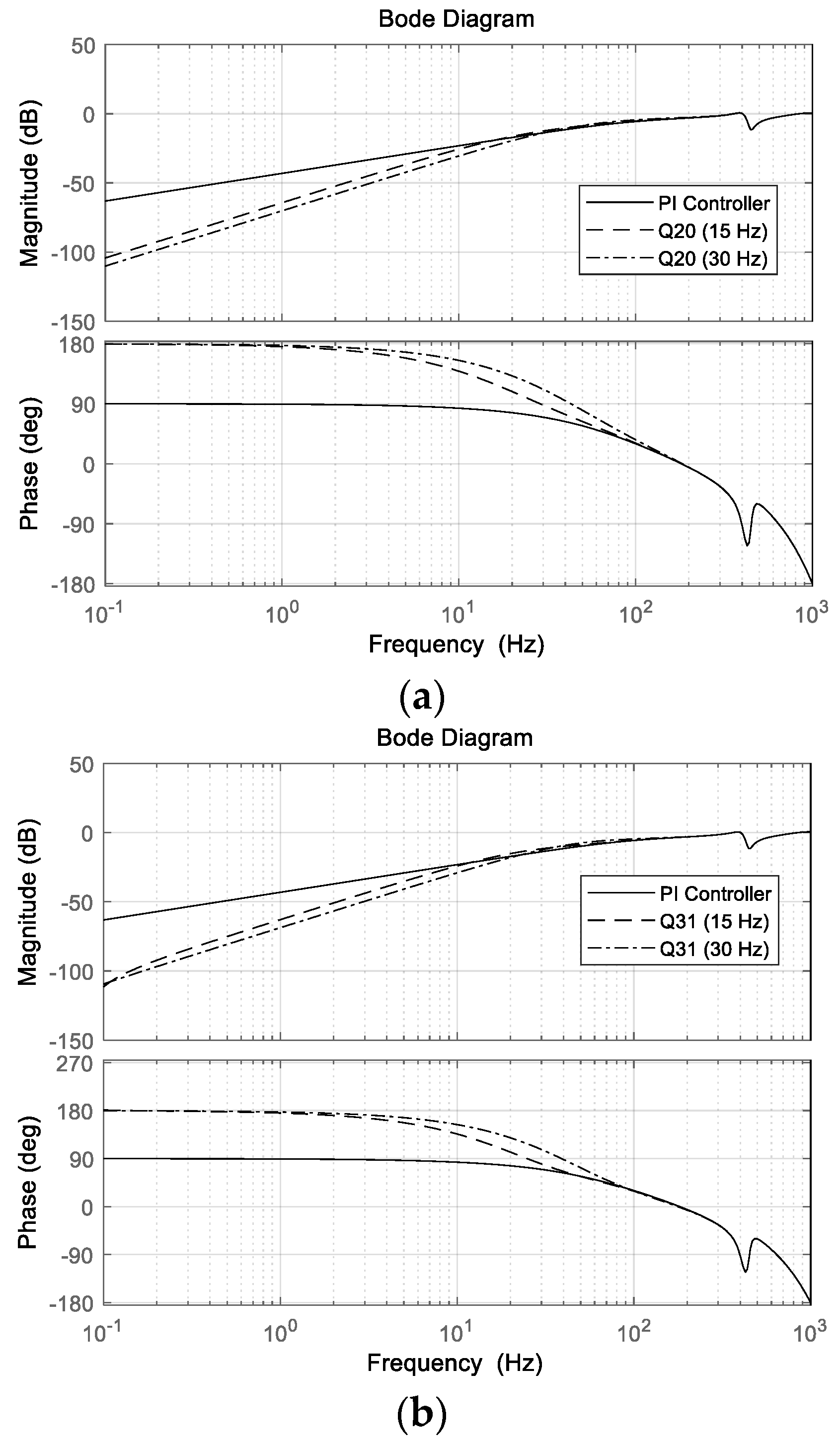
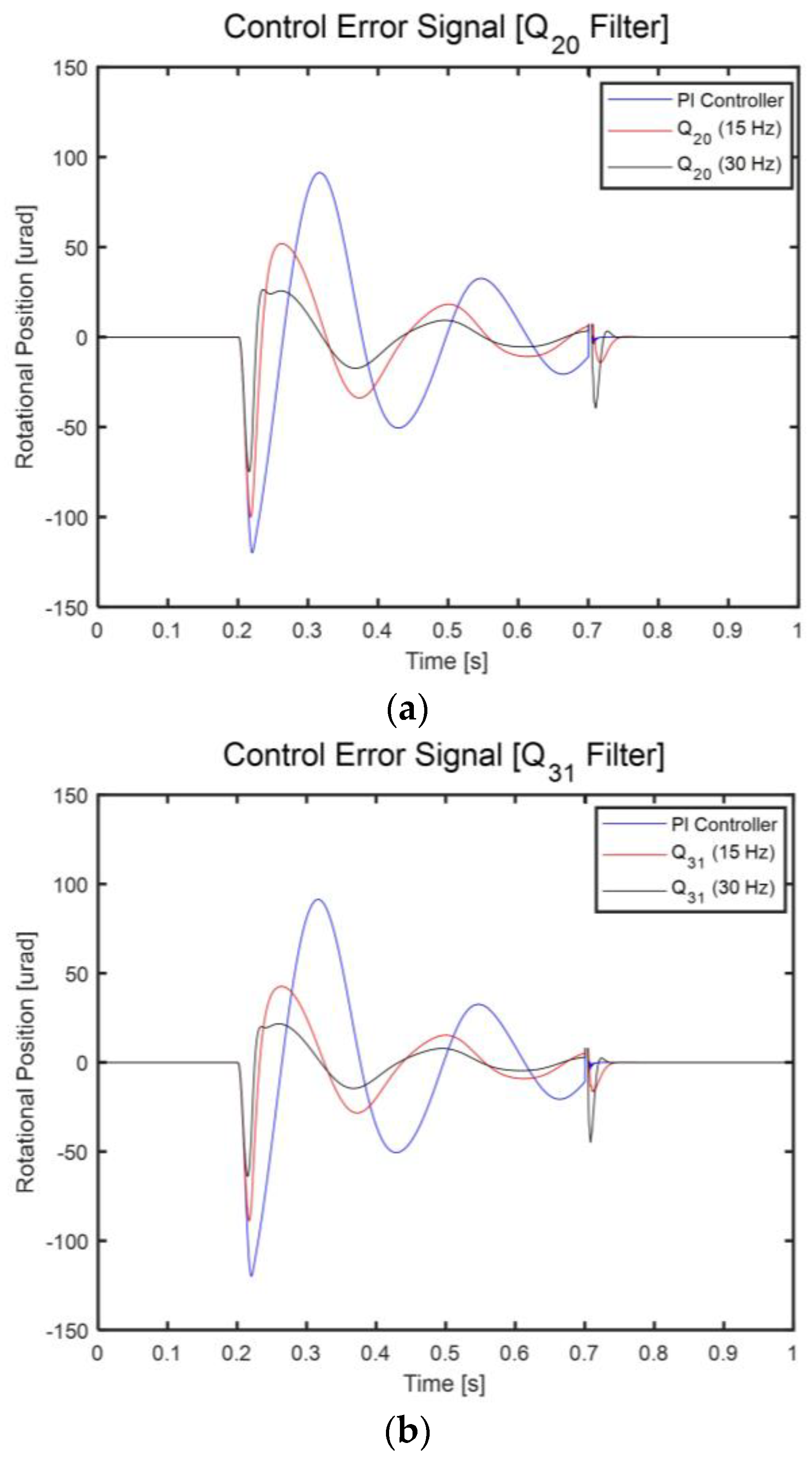
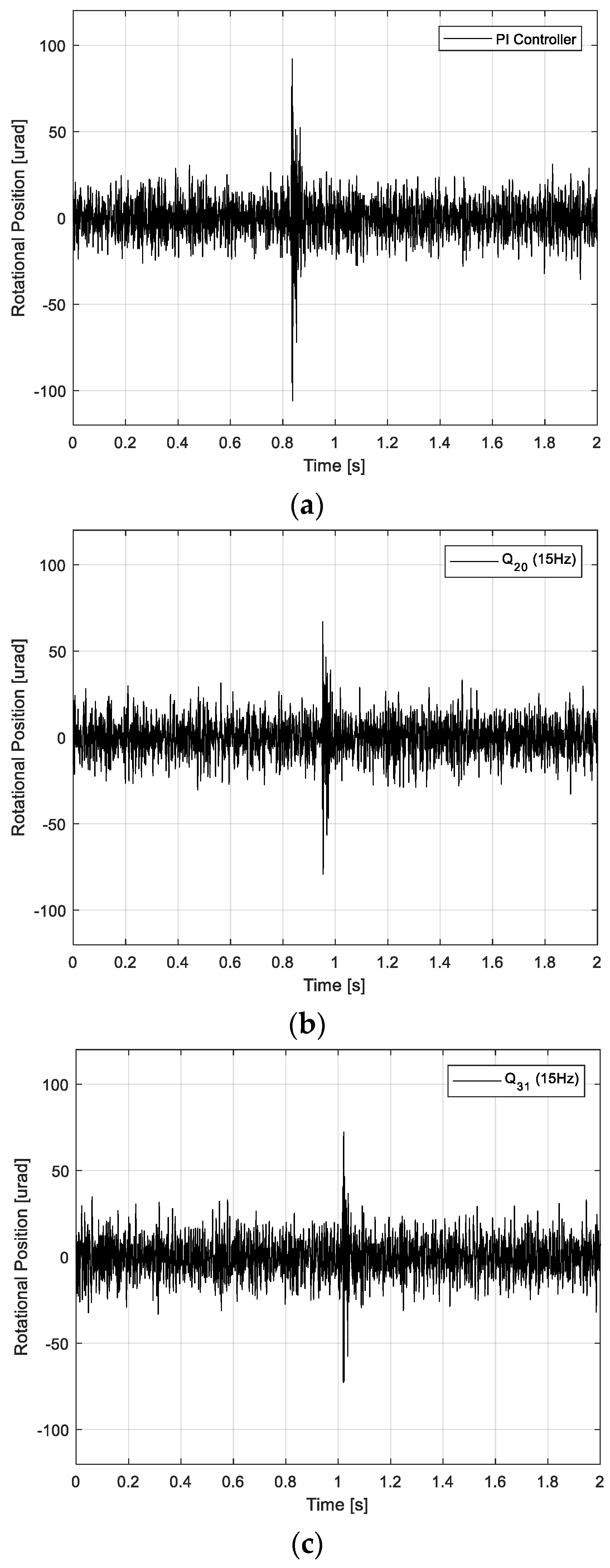
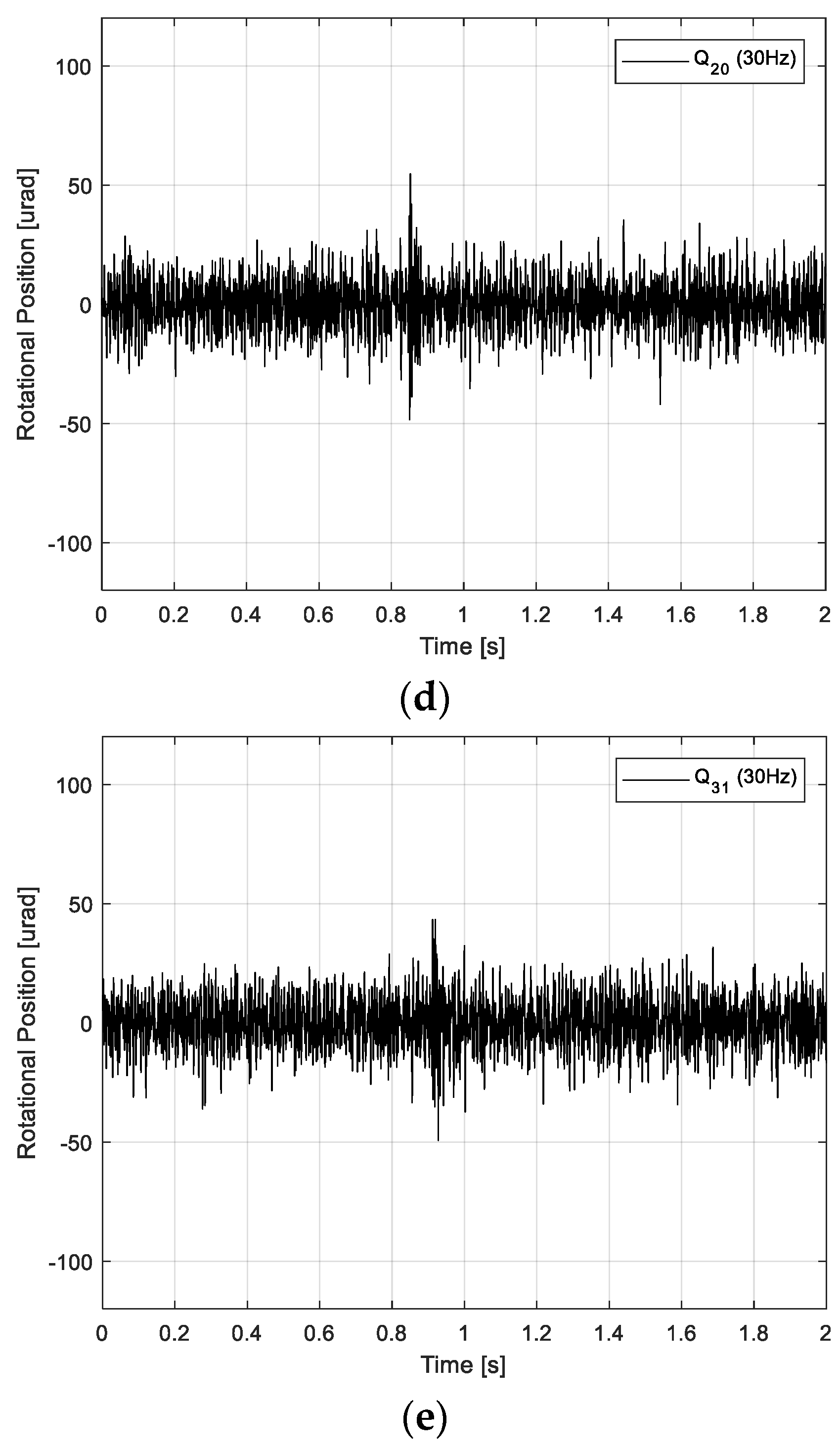
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Resonance frequency | 450.2 Hz |
| 5 Hz sensitivity | 168.3 µrad/V |
| Gain of voltage amplifier | 10 V/V |
| Gain of sensor amplifier | 0.0059 V/µrad |
| Specification | PI Controller | Q20 Filter | Q31 Filter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 Hz | 30 Hz | 15 Hz | 30 Hz | ||
| Minimum rotational position error (rms) | 119.9 μrad | 100.1 μrad | 74.9 μrad | 88.8 μrad | 63.9 μrad |
| Reduced rate | - | 16.5% | 37.6% | 25.9% | 46.7% |
| Specification | PI Controller | Q20 Filter | Q31 Filter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 Hz | 30 Hz | 15 Hz | 30 Hz | ||
| Minimum rotational position error (rms) | 106.0 μrad | 79.1 μrad | 54.7 μrad | 72.2 μrad | 43.4 μrad |
| Reduced rate | - | 25.3% | 48.4% | 31.9% | 59.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-G. Disturbance Observer-Based Anti-Shock Controller for Laser Beam Steering Systems. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114774
Kim J-G. Disturbance Observer-Based Anti-Shock Controller for Laser Beam Steering Systems. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(11):4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114774
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jung-Gon. 2024. "Disturbance Observer-Based Anti-Shock Controller for Laser Beam Steering Systems" Applied Sciences 14, no. 11: 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114774
APA StyleKim, J.-G. (2024). Disturbance Observer-Based Anti-Shock Controller for Laser Beam Steering Systems. Applied Sciences, 14(11), 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114774






