Roughness Evolution of Granite Flat Fracture Surfaces during Sliding Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Roughness Measurement Indicators
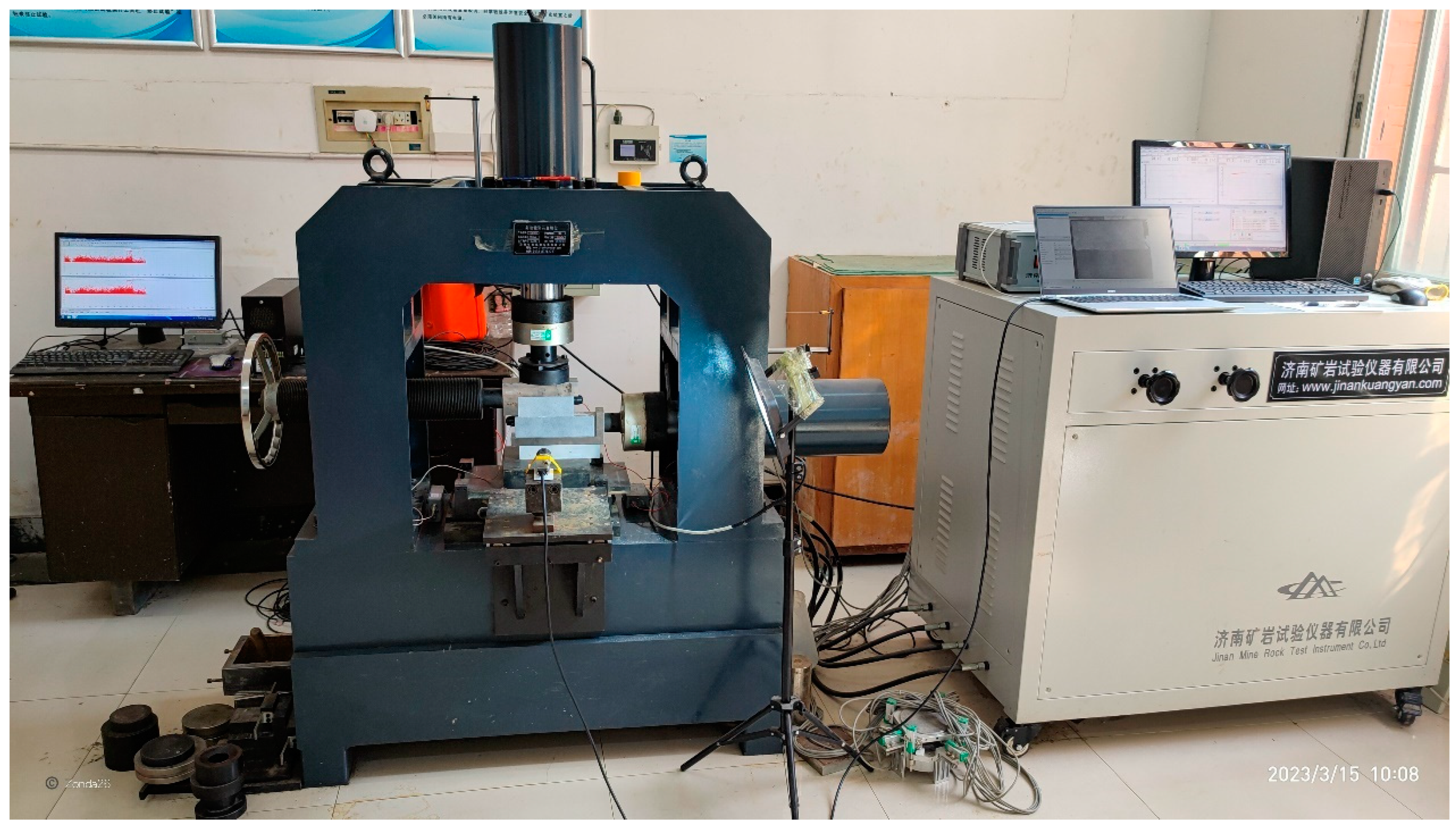
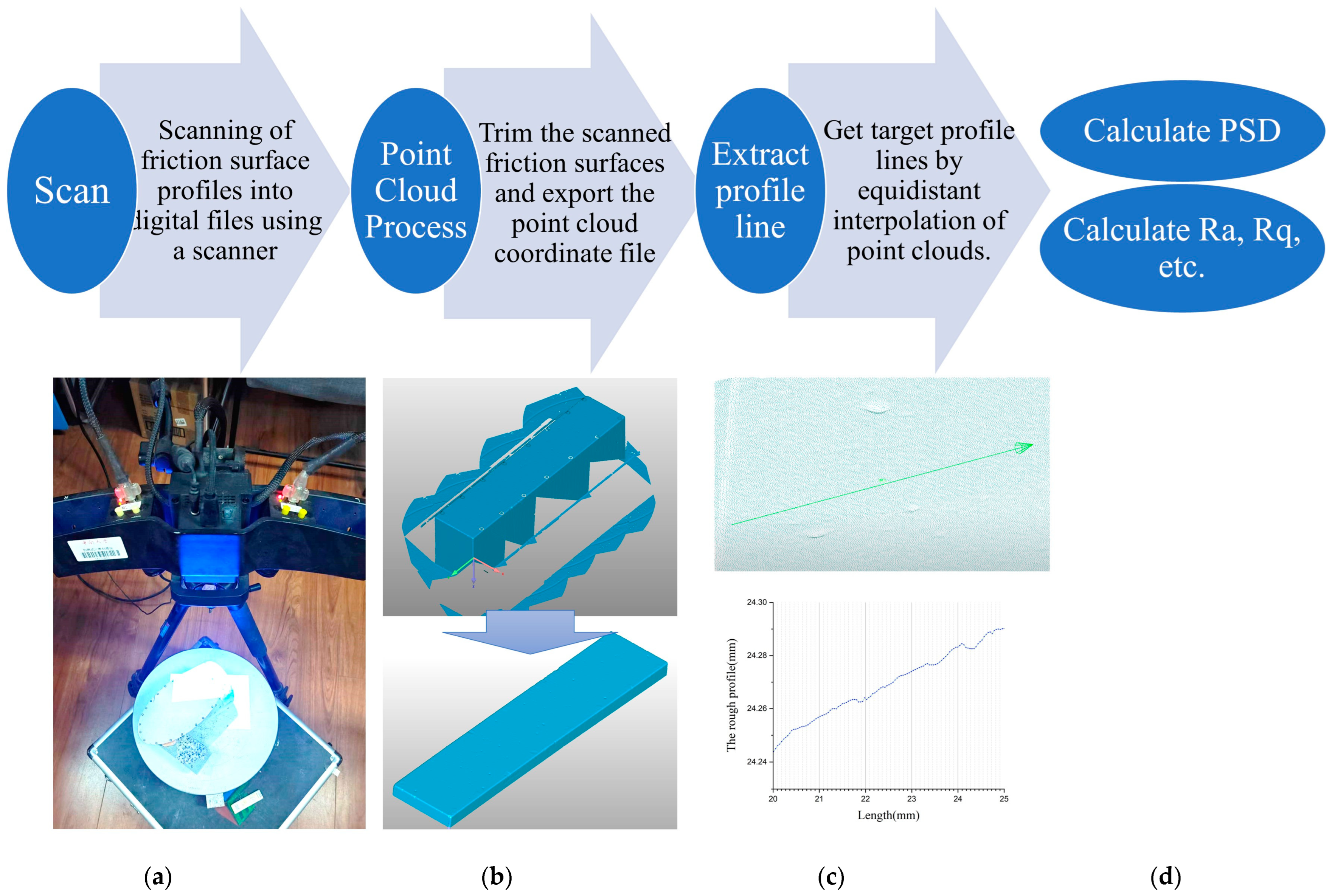
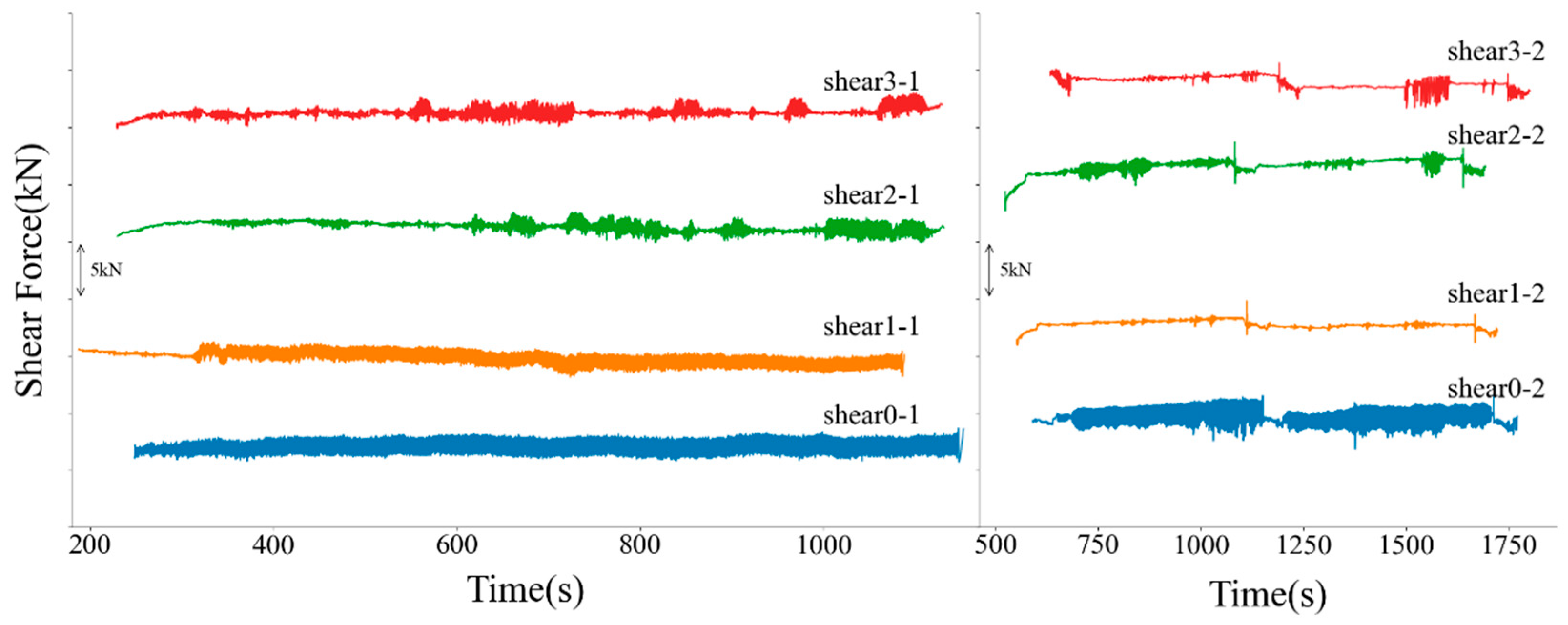
3. Experimental Preparation
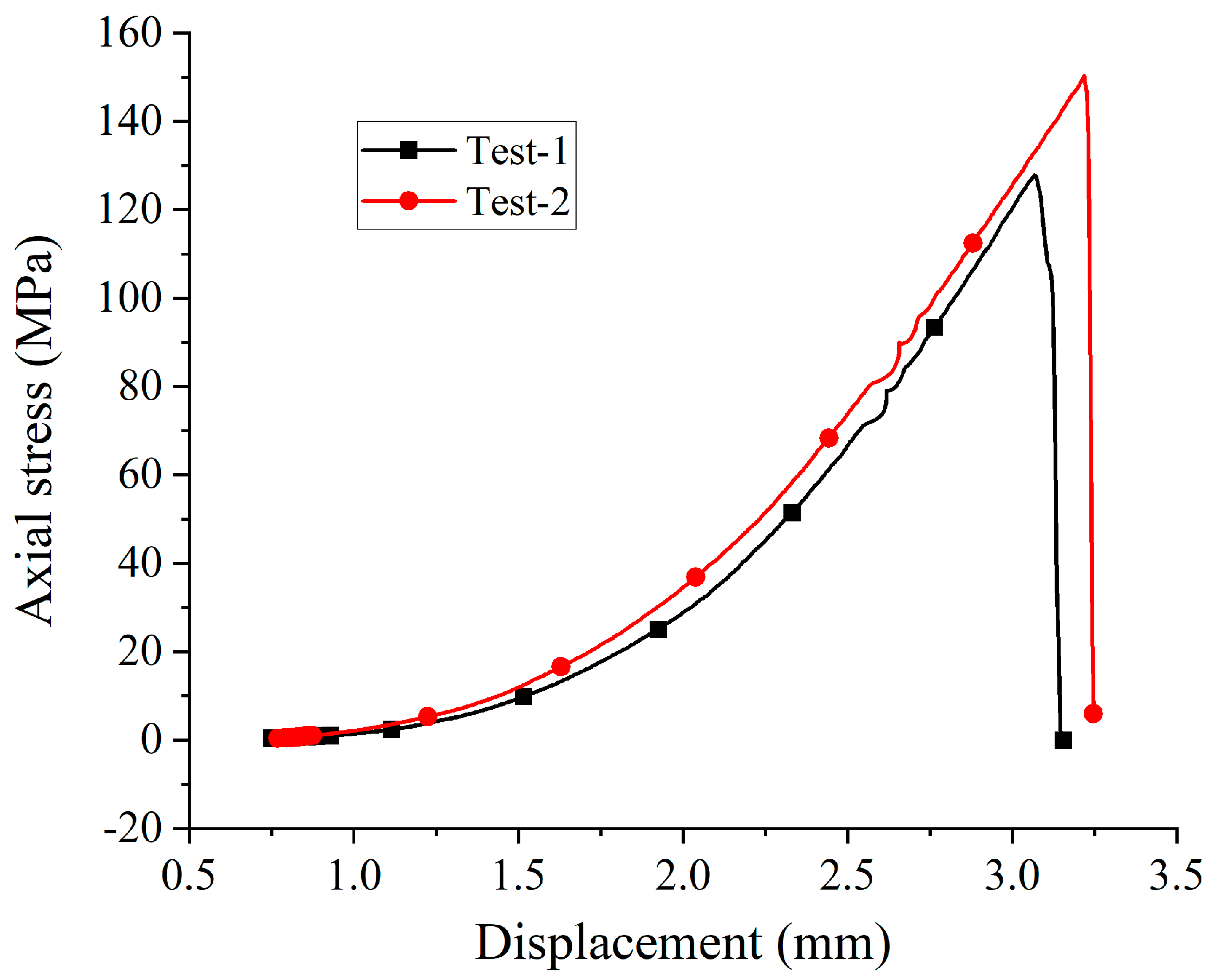
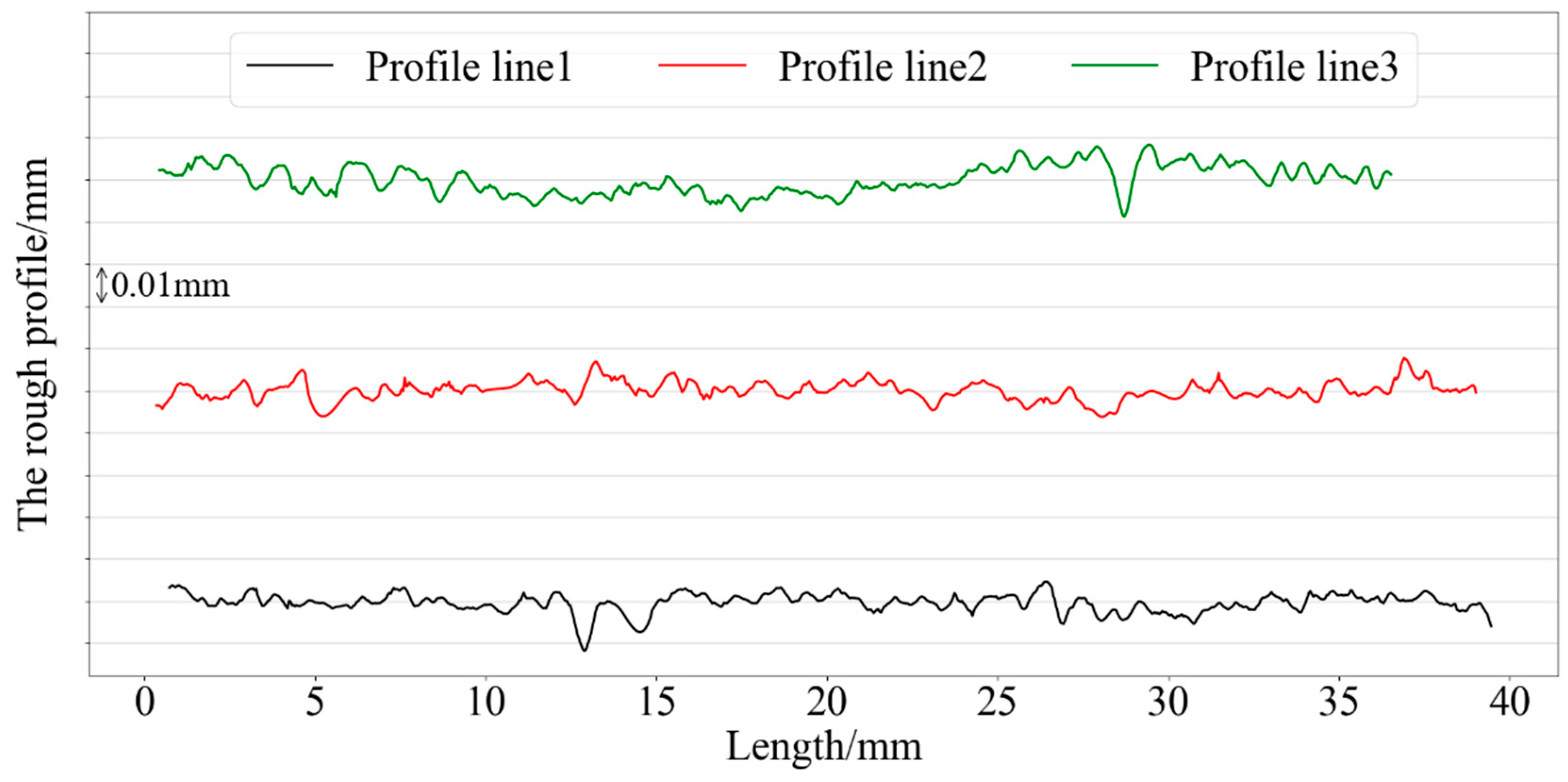
4. Results
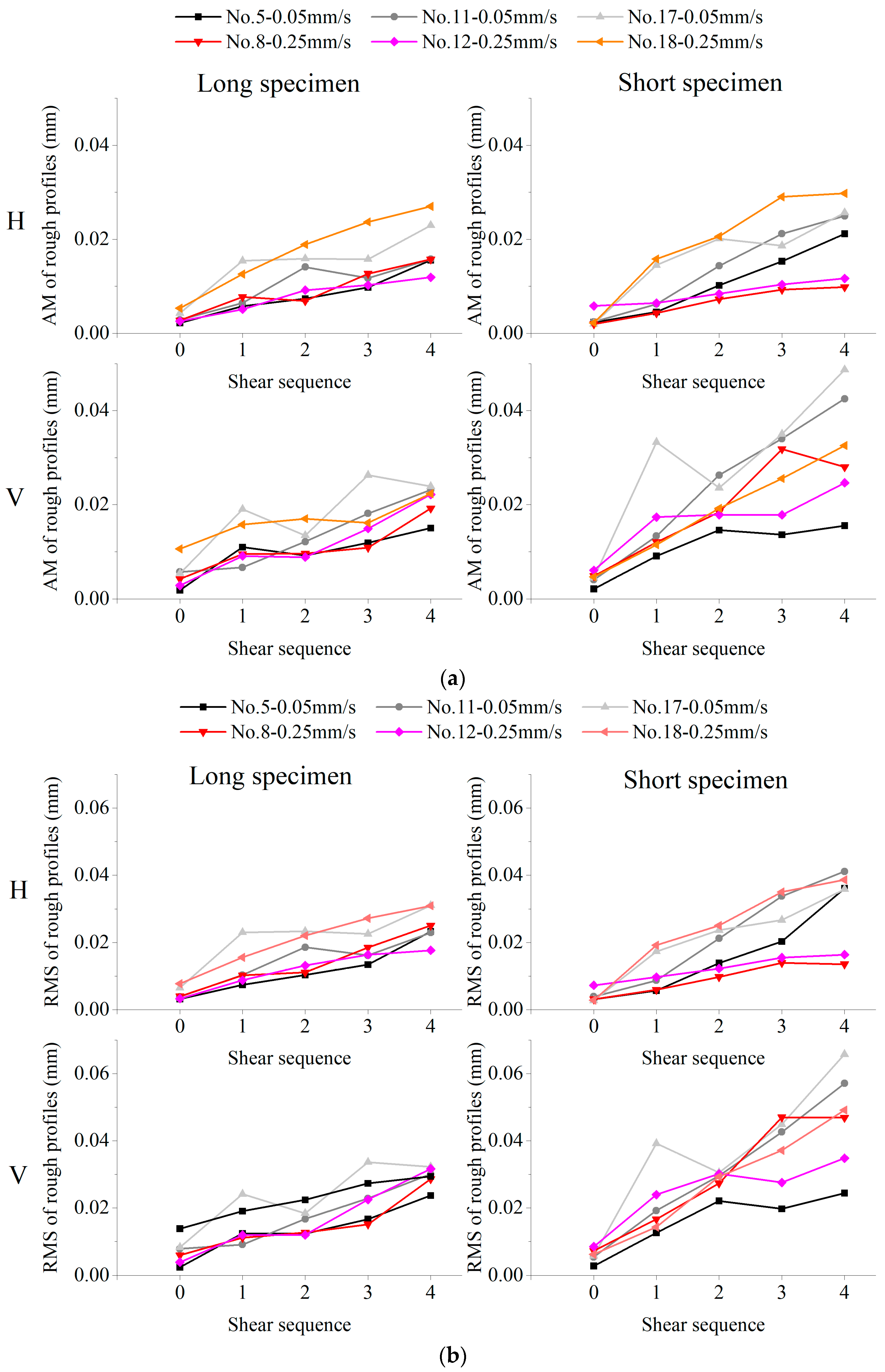
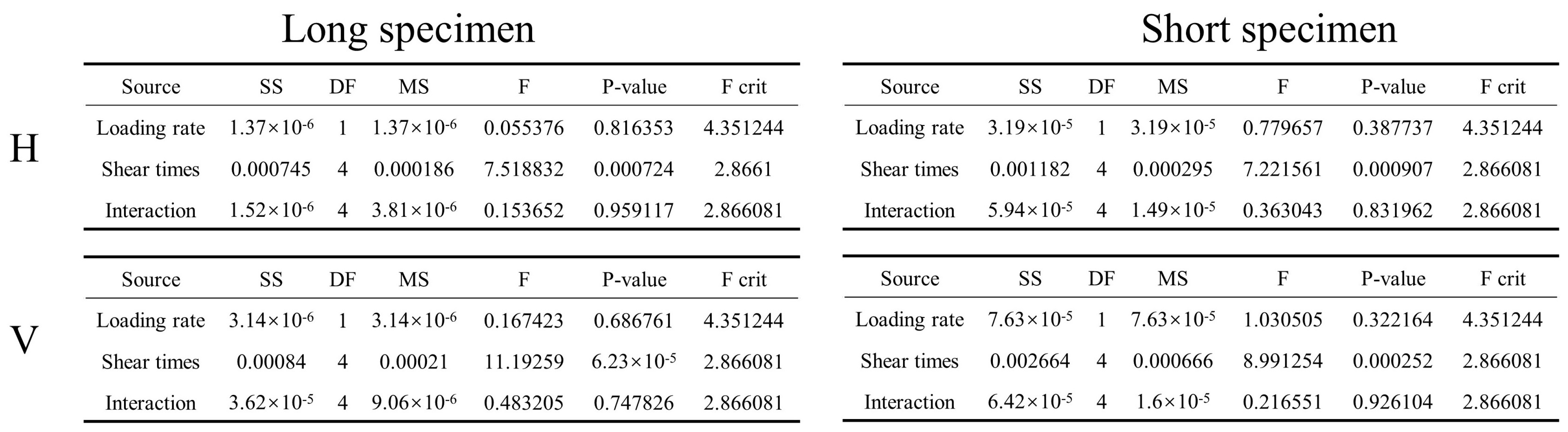
4.1. Summary of Amplitude Parameters
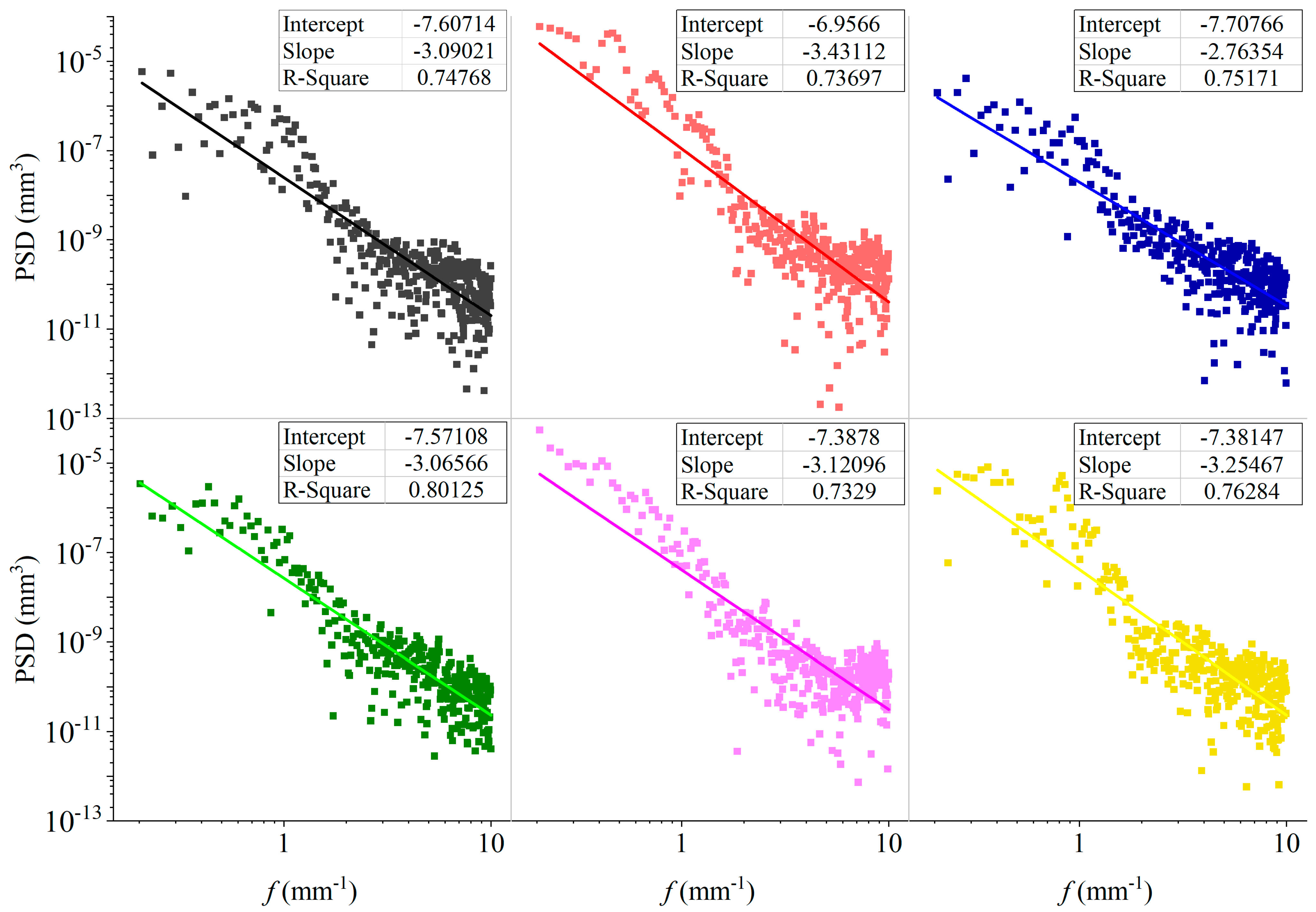
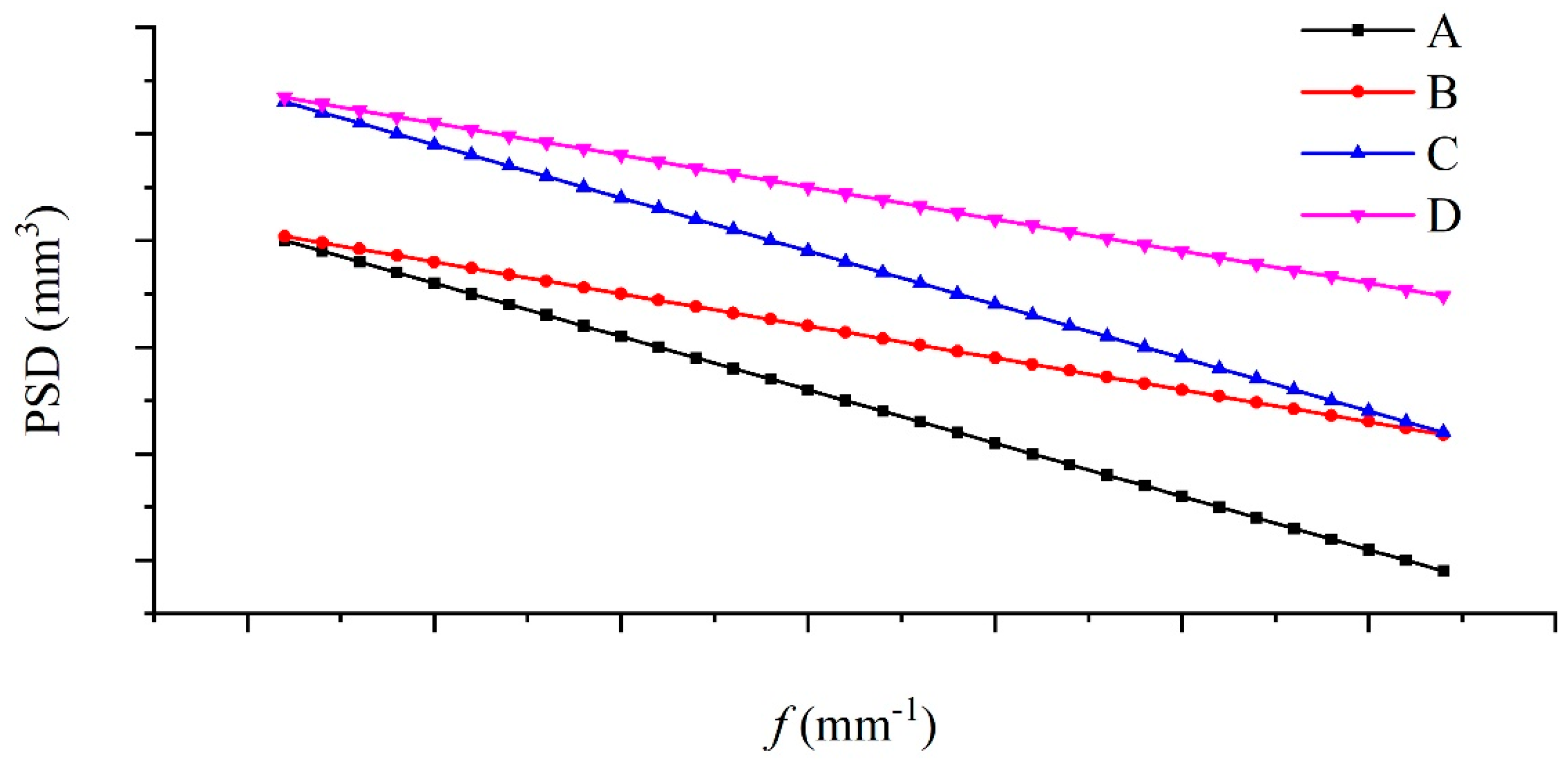
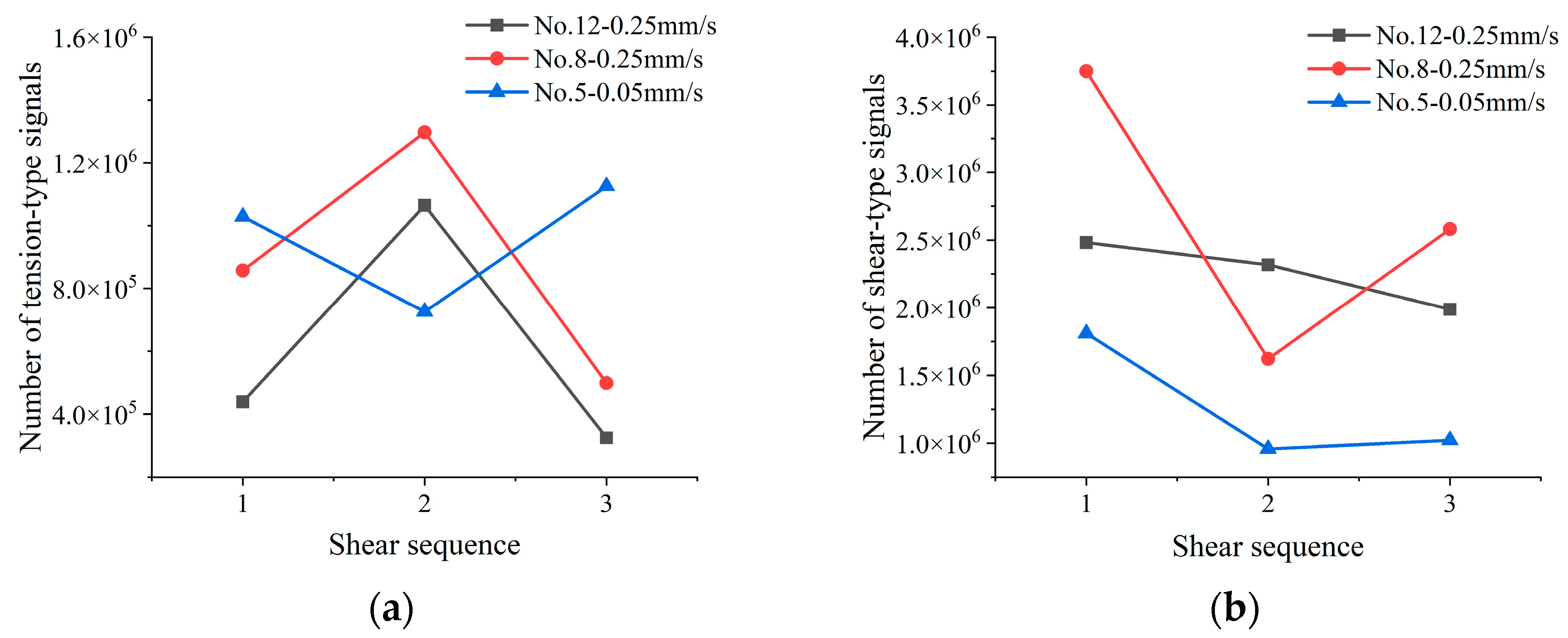
4.2. Summary of Power Spectral Density with Shear Slip
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.; Bai, B.; Lin, H. Seismic magnitude calculation based on rate- and state-dependent friction law. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 30, 2671–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, Y.; Sun, S.; Zha, W.; Lin, H. Automatic recognition of slide mass and inversion analysis of landslide based on discrete element method. Comput. Geosci. 2023, 176, 105338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, M.; Collettini, C.; Marone, C. Frictional stability and earthquake triggering during fluid pressure stimulation of an experimental fault. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 477, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kwiatek, G.; Rybacki, E.; Bonnelye, A.; Bohnhoff, M.; Dresen, G. Laboratory Study on Fluid-Induced Fault Slip Behavior: The Role of Fluid Pressurization Rate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Laboratory Simulation of Injection-Induced Shear Slip on Saw-Cut Sandstone Fractures under Different Boundary Conditions. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wu, W. Injection-driven fracture instability in granite: Mechanism and implications. Tectonophysics 2020, 791, 228572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, D.; Sagy, A.; Hatzor, Y. The significance of displacement control mode in direct shear tests of rock joints. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 134, 104444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, C.; Renard, F.; Grasso, J.-R. Long Term Friction: From Stick-Slip to Stable Sliding. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Rosakis, A.; Lapusta, N. Rupture modes in laboratory earthquakes: Effect of fault prestress and nucleation conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, B12302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidesko, G.; Sagy, A.; Hatzor, Y. Evolution of slip surface roughness through shear. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badt, N.; Hatzor, Y.; Toussaint, R.; Sagy, A. Geometrical evolution of interlocked rough slip surfaces: The role of normal stress. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 443, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Elsworth, D.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, F. Influence of fracture roughness on shear strength, slip stability and permeability: A mechanistic analysis by three-dimensional digital rock modeling. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 12, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Elsworth, D.; Wang, C.; Ishibashi, T.; Fitts, J. Frictional Stability-Permeability Relationships for Fractures in Shales: Friction-Permeability Relationships. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 1760–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Lin, H. Influence of Morphology Characteristics on Shear Mechanical Properties of Sawtooth Joints. Buildings 2022, 12, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lin, H.; Feng, J.; Cao, R.-H.; Hu, H. Mechanical Properties and Acoustic Emission Characteristics of Anchored Structure Plane with Different JRC under Direct Shear Test. Materials 2022, 15, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, H.; Qin, J.; Cao, R.-H.; Ma, S.; Hu, H. Numerical Analysis of Microcrack Propagation Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Serrated Structural Plane. Materials 2022, 15, 5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielke, O.; Galis, M.; Mai, P. Fault roughness and strength heterogeneity control earthquake size and stress drop: Fault roughness and EQ stress drop. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, Y.; Hager, B.; Ampuero, J.P. The Effects of Fault Roughness on the Earthquake Nucleation Process. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 123, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nielsen, S.; Carpenter, B. The onset of laboratory earthquakes explained by nucleating rupture on a rate-and-state fault. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 6071–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, H.; Nakatani, M.; Hori, T. Large nucleation before large earthquakes is sometimes skipped due to cascade-up-Implications from a rate and state simulation of faults with hierarchical asperities. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 2924–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, C.H. Earthquakes and friction laws. Nature 1998, 391, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadelmawla, E.S.; Koura, M.; Maksoud, T.; Elewa, I.; Soliman, H. Roughness parameters. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 123, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagy, A.; Brodsky, E.; Axen, G. Evolution of fault-surface roughness with slip. Geology 2007, 35, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, N.; Choubey, V. The shear strength of rock joints in theory and practice. Rock Mech. Felsmech. Mec. Des Roches 1977, 10, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, M.; Faramarzi, L.; Goli, S.; Fahimifar, A.; Rahmati, A.; Mehinrad, A. Development of a new equation for joint roughness coefficient (JRC) with fractal dimension: A case study of Bakhtiary Dam site in Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 8, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, R.; Cruden, D. Estimating joint roughness coefficients. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1979, 16, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, H. A new peak shear strength model of rock joints. Rock Soil Mech. 2018, 39, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Xia, C.; Song, Y. New peak shear strength criteria for roughness joints. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 35, 571–577. [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky, E.; Gilchrist, J.; Sagy, A.; Collettini, C. Faults smooth gradually as function of slip. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 302, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, T.; Renard, F.; Klinger, Y.; Mair, K.; Schmittbuhl, J.; Brodsky, E. Roughness of fault surfaces over nine decades of length scales. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, B08409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, D.; Hatzor, Y.; Sagy, A. Rate Effects on Shear Deformation of Rough Limestone Discontinuities. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C. A study on the surface morphological feathers of rock structural faces. J. Eng. Geol. 1996, 4, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Gołąbczak, M.; Golabczak, A.; Konstantynowicz, A. Estimating and Extracting of the Surface Profile Waviness by Use of the Spatial Notch Filters in the Roughness Profile Analysis. Defect Diffus. Forum 2017, 371, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadakci Koca, T. The investigation of the effect of waviness and roughness of weathered discontinuity surfaces in andesite rock mass on planar sliding. In Proceedings of the National Symposium on Engineering Geology and Geotechnics, İstanbul, Turkey, 2–5 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tomanik, E.; Souza, R.; Profito, F.; El Mansori, M. Effect of Waviness and Roughness on Cylinder Liner Friction(at Leeds-Lyon 2017). Tribol. Int. 2017, 120, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaskey, G. Earthquake Initiation from Laboratory Observations and Implications for Foreshocks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 12882–12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapusta, N.; Rice, J. Nucleation and early seismic propagation of small and large events in a crustal earthquake model. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaskey, G.; Yamashita, F. Slow and fast ruptures on a laboratory fault controlled by loading characteristics. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 3719–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin-Marthe, S.; Nielsen, S.; Bird, R.; Giani, S.; Di Toro, G. Earthquake Nucleation Size: Evidence of Loading Rate Dependence in Laboratory Faults. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

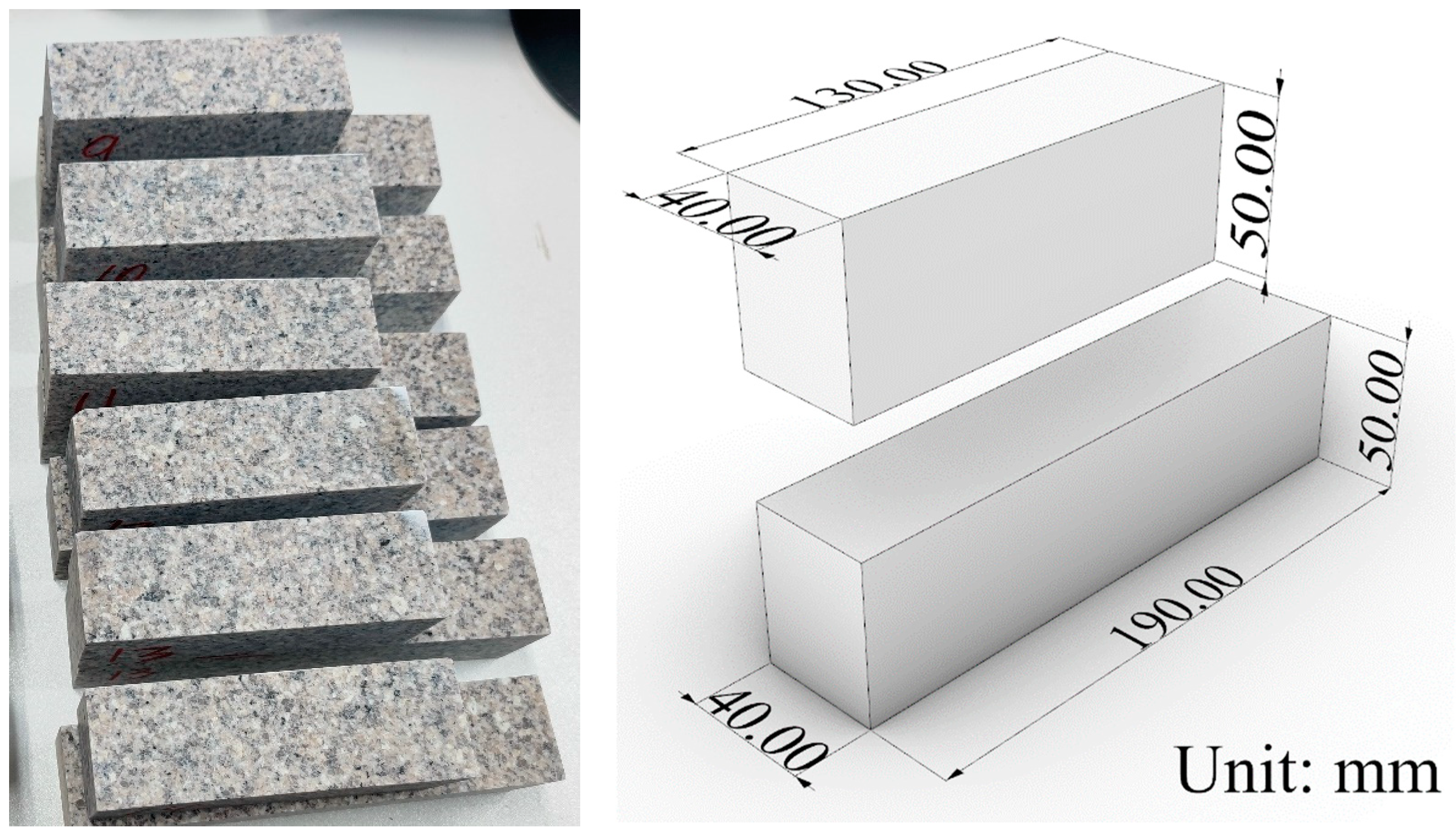

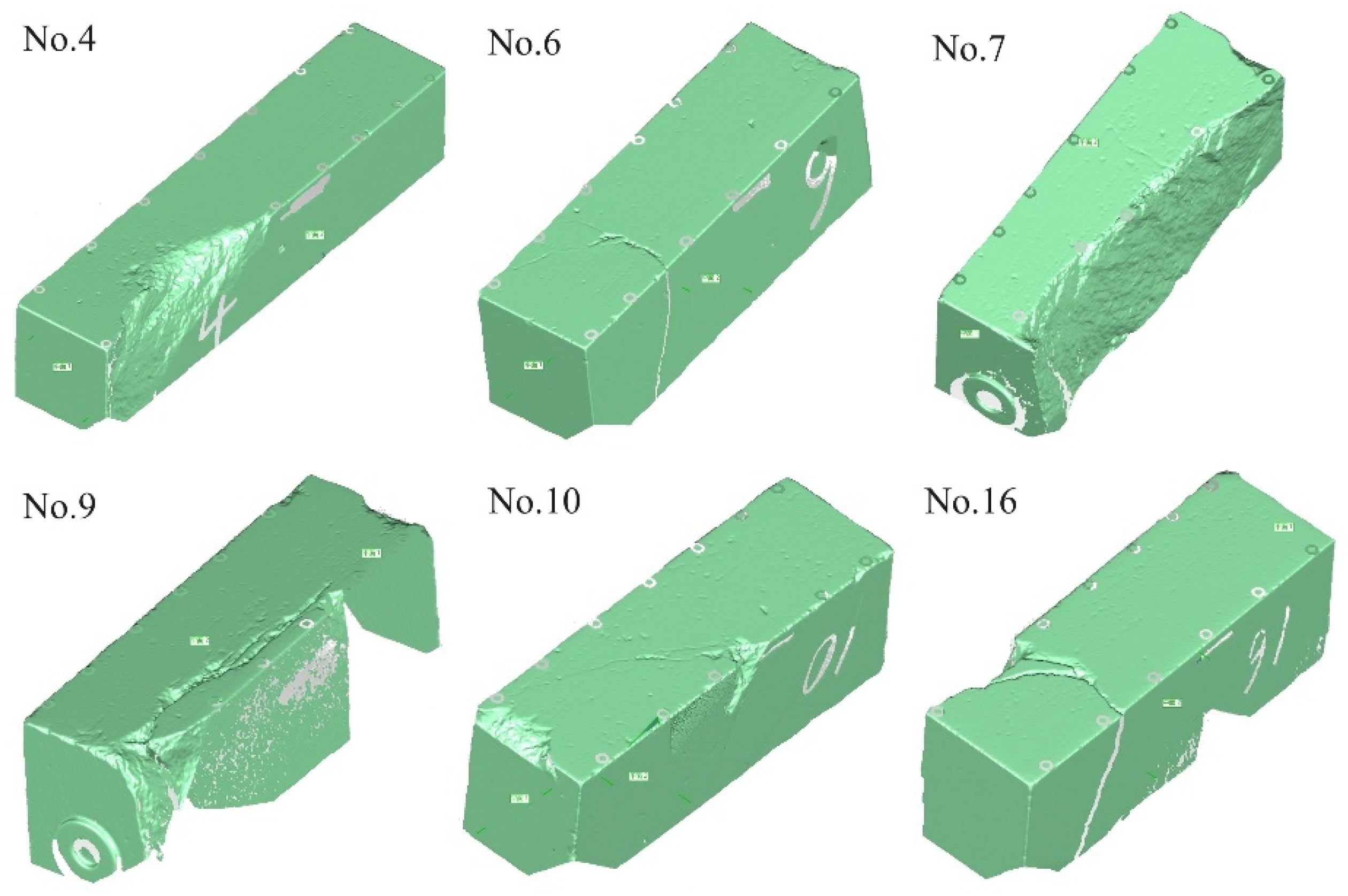
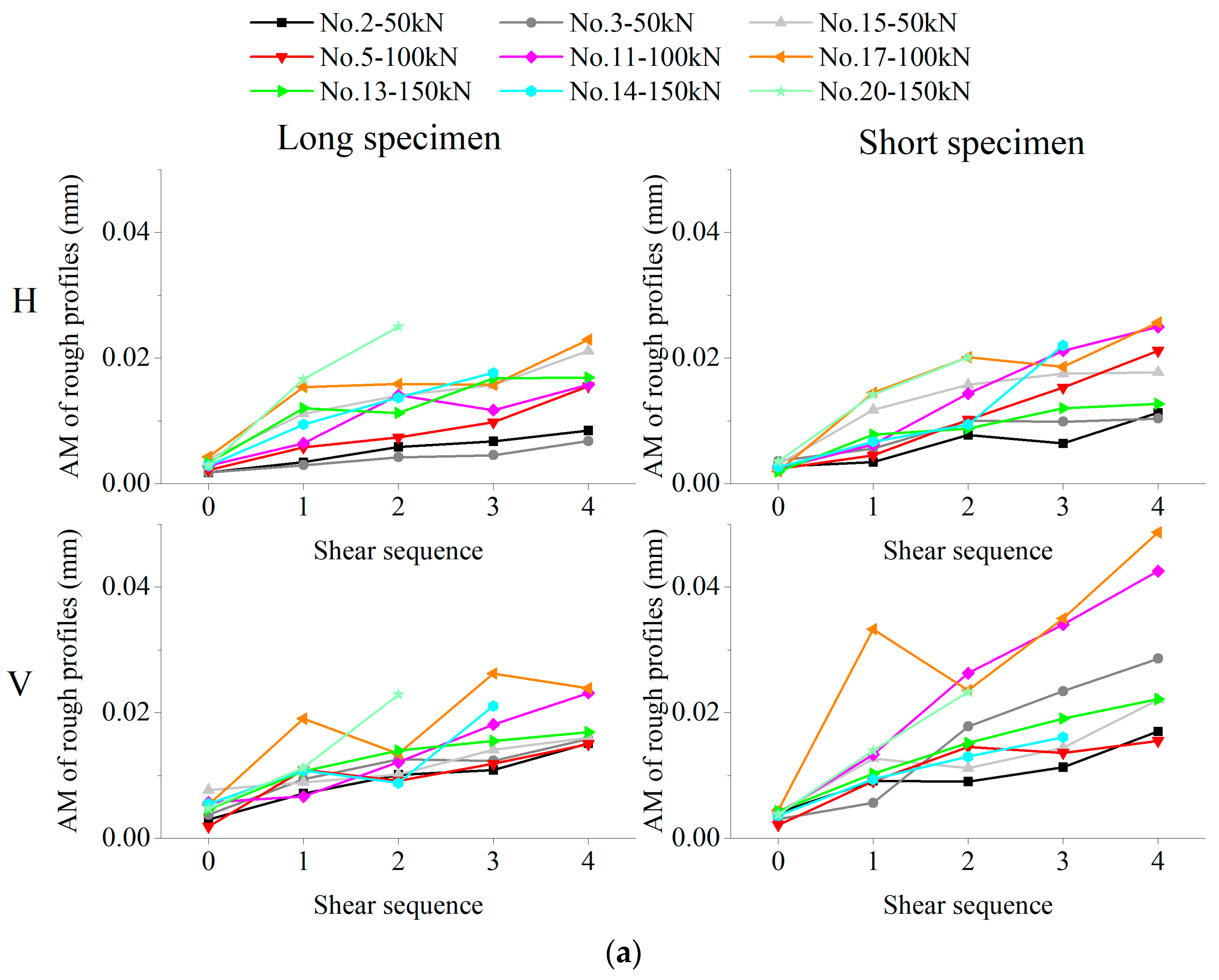
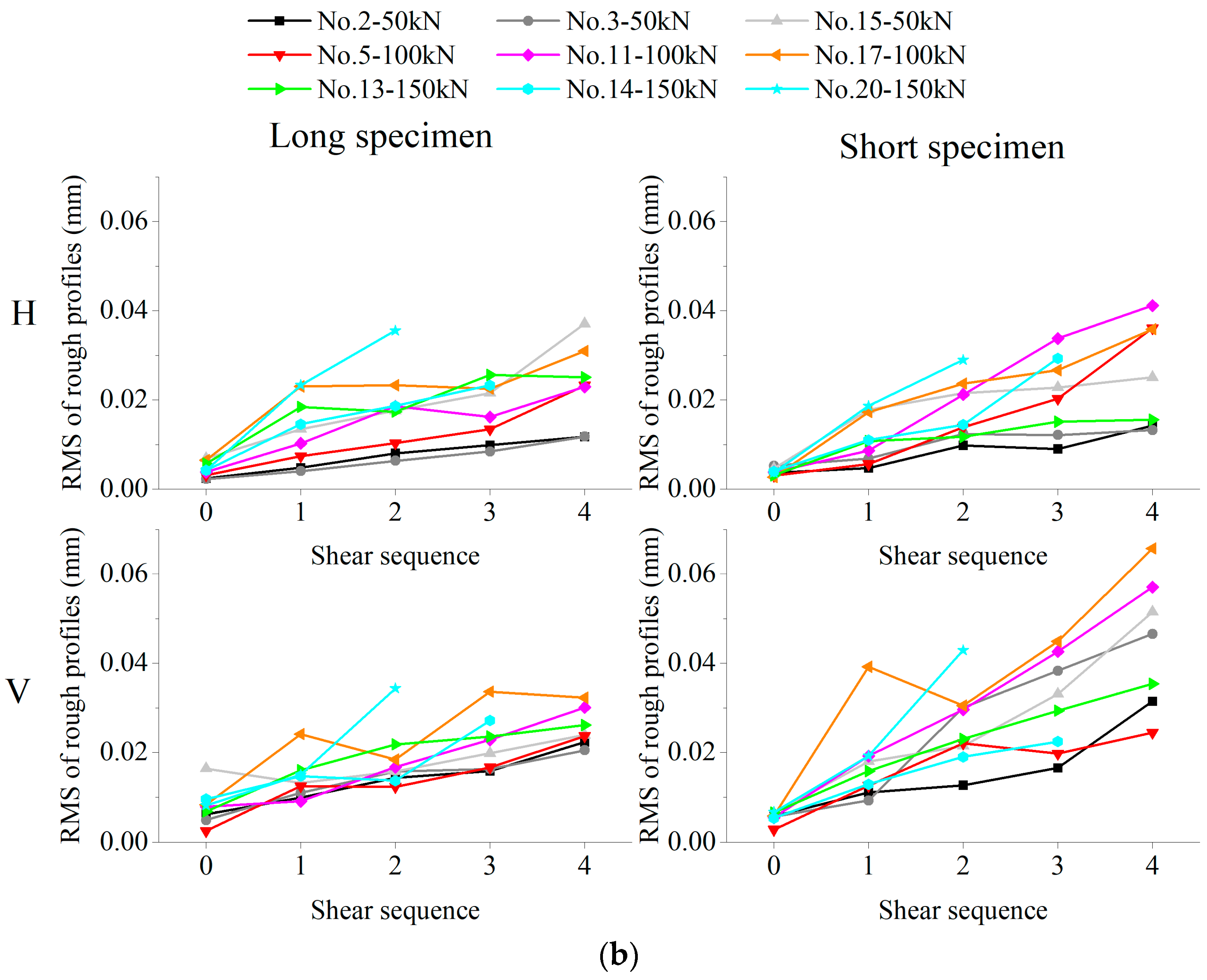
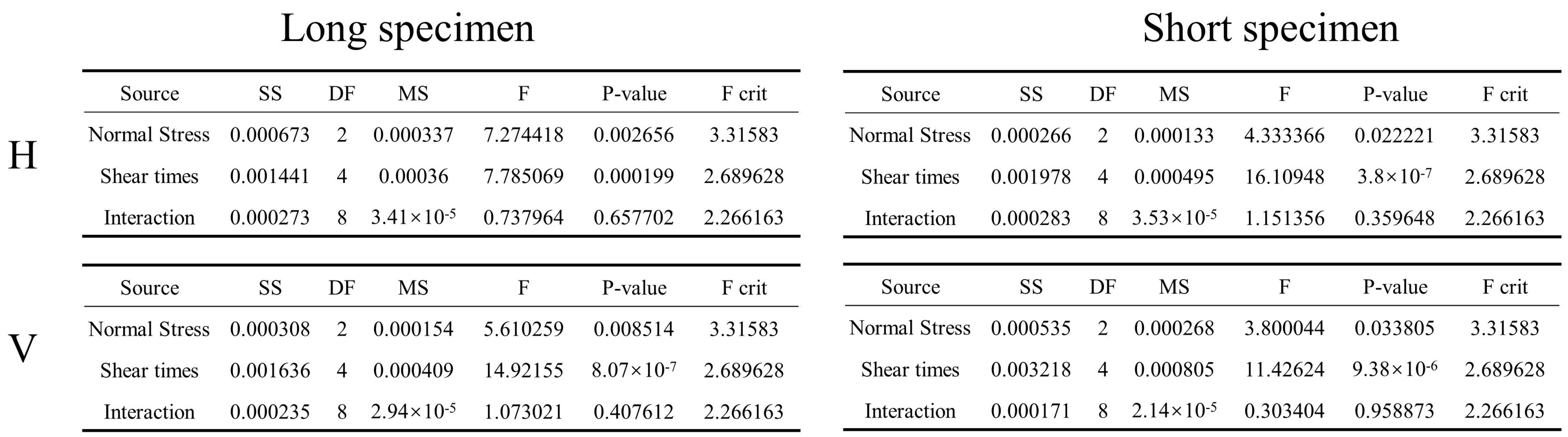




| Level | Normal Force /kN | Loading Rate ) |
|---|---|---|
| Level 0 | 50 | 0.01 |
| Level 1 | 100 | 0.05 |
| Level 2 | 150 | 0.25 |
| Specimen Number | 2, 3, 9, 15 | 5, 11, 17 | 4, 7, 13, 14, 19, 20 | 6, 10, 16 | 8, 12, 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal force level | −0 | −1 | −2 | −1 | −1 |
| Loading rate level | −1 | −1 | −1 | −0 | −2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Bai, B.; Lin, H. Roughness Evolution of Granite Flat Fracture Surfaces during Sliding Processes. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5935. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135935
Yang H, Bai B, Lin H. Roughness Evolution of Granite Flat Fracture Surfaces during Sliding Processes. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(13):5935. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135935
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hengtao, Bing Bai, and Hang Lin. 2024. "Roughness Evolution of Granite Flat Fracture Surfaces during Sliding Processes" Applied Sciences 14, no. 13: 5935. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135935
APA StyleYang, H., Bai, B., & Lin, H. (2024). Roughness Evolution of Granite Flat Fracture Surfaces during Sliding Processes. Applied Sciences, 14(13), 5935. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135935








