Location and Capacity Optimization of Waste Recycling Centers: Mathematical Models and Numerical Experiments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
| Studies | Facility Planning Methods | Objective (s) | Uncertain Factors Considered | Deciding the Optimal Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [29] | AHP | NA | No | No |
| [30] | AHP | NA | No | No |
| [31] | Stakeholder network | Provide high-value recycled material | No | No |
| [33] | MILP | Minimize the total costs | No | No |
| [21] | MILP | Maximize the recycling rate; Maximize the profits of recycling firms; Minimize the costs of contractors for disposing of CDW | No | Yes |
| [40] | Swarm algorithm | Minimize environmental impact; Minimize total costs | No | Yes |
| [39] | Swarm algorithm | Minimize total costs | Demand for goods | No |
| [41] | GA-PSO algorithm | Minimize total costs | No | No |
| [42] | LCA | Minimize environmental impact | All input data | No |
| Yang and Chen (2020) [26] | RO | Minimize total costs | Construction waste generation | No |
| [43] | RO | Minimize total costs | Construction waste generation; Transportation cost | No |
| [25] | RO | Minimize total costs | Construction waste generation; Demand for recycled construction material | No |
| [44] | RO | Minimize total costs | Construction waste generation | No |
| [45] | RO | Minimize total costs | Construction waste generation | No |
| [46] | SO | Maximize the expected profit | Construction waste generation; Recycling rate in recycling facility | No |
3. Problem Description and Model Formulation
3.1. Problem Statement
3.2. Model Formulation
- Indices:
- : index for the location of the recycling center
- : index for the construction site
- : index for the scenario
- Parameters:
- : the number of candidate locations for establishing recycling centers
- : the number of construction sites that generate construction waste ()
- : the number of construction sites that require recycled building materials ()
- : the number of scenarios
- : the maximum area of the recycling center at location
- : the waste handling capacity per unit area of recycling centers
- : the weight of building materials recycled per ton of construction waste
- : the unit cost of establishing a recycling center at a location
- : the unit cost of delivering one ton of construction waste from the construction site to the recycling center or the unit cost of delivering one ton of recycled materials from the recycling center to the construction site (CNY/ton)
- : the unit cost of delivering one ton of construction waste from the construction site to the landfill site (CNY/ton)
- : the maximum total costs
- : the possibility of scenario
- : the weight of construction waste generated by the construction site or the weight of recycled building materials required by the construction site in scenario
- Variables:
- : continuous, the constructed area of the recycling center at location
- : continuous, the weight of construction waste delivered from construction site to recycling center or the weight of recycled building materials from recycling center to construction site in scenario
- : continuous, the weight of construction waste delivered from the construction site to the landfill site in the scenario
- Mathematical model:
4. Computational Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setting
4.2. Experimental Results
4.2.1. Mean Value Problem
- Newly defined parameters:
- : the average weight of construction waste generated by the construction site or the average weight of recycled building materials required by the construction site of all scenarios
- Newly defined variables:
- : continuous, the weight of construction waste delivered from the construction site to recycling center or the weight of recycled building materials from recycling center to construction site
- : continuous, the weight of construction waste delivered from the construction site to the landfill site
- Mathematical model:
4.2.2. Comparative Results
- (1)
- [M1] is solved to obtain the optimal solution, , alongside the corresponding optimal objective value, .
- (2)
- Subsequently, [M2] is resolved to determine the solution, . For each scenario , the comparison model [M3] is then solved to obtain the objective value specific to each scenario. Following the acquisition of objective values across all scenarios, we compute the mean objective value, , serving as a critical measure for assessing model performance under varied conditions.
- (3)
- The final stage of our analysis involves a comprehensive comparison between the objective values and .
- Newly defined parameters:
- : the optimal value of by solving the model [M2] (i.e., )
- : the weight of construction waste generated by the construction site or the weight of recycled building materials required by the construction site
- Newly defined variables:
- : continuous, the weight of construction waste delivered from the construction site to the recycling center or the weight of recycled building materials from the recycling center to the construction site
- : continuous, the weight of construction waste delivered from the construction site to the landfill site
- Mathematical model:
| Algorithm 1: Calculating the optimality gap of the solutions derived by deterministic and stochastic programming | |
| 1: | Input: and all other deterministic parameters |
| 2: | Output: |
| 3: | |
| 4: | For |
| 5: | |
| 6: | End for |
| 7: | For |
| 8: | For |
| 9: | |
| 10: | End for |
| 11: | Solve model [M3] and define as the optimal objective value of [M3] |
| 12: | |
| 13: | End for |
| 14: | |
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4.4. Summary of Results and Managerial Insights
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Yi, W.; Zhen, L.; Chan, A.P. Cost–Optimized Transport Planning for Prefabricated Modules with the Implementation of the Just–in–Time Strategy. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2024, 150, 04024093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liao, L.; Yi, W.; Zhen, L. Transportation scheduling for modules used in modular integrated construction. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 3918–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Shen, L. Trend of the research on construction and demolition waste management. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, M.S.; Huang, B.; Cui, L. Review of construction and demolition waste management in China and USA. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, A.; Sarmah, A.K. Construction and demolition waste generation and properties of recycled aggregate concrete: A global perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 262–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Li, B.; Zhou, T.; Wanatowski, D.; Piroozfar, P. An empirical study of perceptions towards construction and demolition waste recycling and reuse in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Chini, A.R.; Lu, Y.; Shen, L. A dynamic model for assessing the effects of management strategies on the reduction of construction and demolition waste. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzouk, M.; Azab, S. Environmental and economic impact assessment of construction and demolition waste disposal using system dynamics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 82, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafesse, S.; Girma, Y.E.; Dessalegn, E. Analysis of the socio–economic and environmental impacts of construction waste and management practices. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.X.; Jiang, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wu, H. Discussion on management mode of construction waste in China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 374, 1920–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; He, Q.; Wang, X. Estimating the environmental costs and benefits of demolition waste using life cycle assessment and willingness-to-pay: A case study in Shenzhen. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Magalhães, R.F.; Danilevicz, Â.d.M.F.; Saurin, T.A. Reducing construction waste: A study of urban infrastructure projects. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Yuan, H. A framework for understanding waste management studies in construction. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Li, J. Construction and demolition waste management: China’s lessons. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, F.d.A.; Silva, F.d.A. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste towards an application on structural concrete: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.H.; Ishigaki, T.; Kubota, R.; Tong, T.K.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, H.G.; Yamada, M.; Kawamoto, K. Financial and economic evaluation of construction and demolition waste recycling in Hanoi, Vietnam. Waste Manag. 2021, 131, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisku, N.; Joshi, H.; Ansari, M.; Panda, S.K.; Nayak, S.; Dutta, S.C. A critical review and assessment for usage of recycled aggregate as sustainable construction material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.U.; Poon, C.S.; Lo, I.M.; Cheng, J.C. Comparative environmental evaluation of aggregate production from recycled waste materials and virgin sources by LCA. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 109, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Le, K.N.; Li, W. Challenges in current construction and demolition waste recycling: A China study. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 610–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yi, W.; Tian, X.; Zhen, L. Prescriptive analytics for intelligent transportation systems with uncertain demand. J. Transp. Eng. Part A Syst. 2023, 149, 04023118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Xie, Q.; Feng, Y. Designing recycling networks for construction and demolition waste based on reserve logistics research field. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 120841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Ghezavati, V. Sustainable multi–period reverse logistics network design and planning under uncertainty utilizing conditional value at risk (CVaR) for recycling construction and demolition waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1567–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulubeyli, S.; Kazaz, A.; Arslan, V. Construction and demolition waste recycling plants revisited: Management issues. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Modern Building Materials, Structures and Techniques (MBMST), Vilnius, Lithuania, 26–27 May 2016; pp. 1190–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzouridis, C.; Komilis, D. A methodology to optimally site and design municipal solid waste transfer stations using binary programming. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 60, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Feng, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P. Optimizing site selection for construction demolition waste treatment plants considering demand and supply uncertainty: A case study in Chongqing, China. Eng. Optim. 2022, 56, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, J. Robust design for a multi–echelon regional construction and demolition waste reverse logistics network based on decision Maker’s conservative attitude. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, M.; Di Maio, F.; Sprecher, B.; Yang, X.; Tukker, A. An overview of the waste hierarchy framework for analyzing the circularity in construction and demolition waste management in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.F.S.; Nunes, K.R.; Xavier, L.H.; Cardoso, R.; Valle, R. Multicriteria decision making applied to waste recycling in Brazil. Omega 2008, 36, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhu, M.; Wu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X. Combining AHP–Entropy Approach with GIS for Construction Waste Landfill Selection—A Case Study of Shenzhen. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto–Paz, J.; Hernandez, A.; Mejia–Parada, C.A.; Mora–Ruiz, V.; Hernandez, W.; Luna–Guevara, F.; Casallas–Ojeda, M.; Parra–Orobio, B.A. A Hybrid Decision Tool for Site Selection of Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW) Facilities in Developing Countries. Environ. Process. 2023, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabek, M.; Jegen, P.; Kreiss, L. Introducing a Novel Concept for an Integrated Demolition Waste Recycling Center and the Establishment of a Stakeholder Network: A Case Study from Germany. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, I.M.; Alreshaid, K. Decision support system for selecting the proper project delivery method using analytical hierarchy process (AHP). Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2005, 23, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, B.; Viguri, J.R.; Cifrian, E.; Dosal, E.; Andres, A. Influence of input streams on the construction and demolition waste (CDW) recycling performance of basic and advanced treatment plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yi, W.; Zhen, L. Optimal policy for scheduling automated guided vehicles in large–scale intelligent transportation systems. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2024, 179, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Wang, H.; Zhen, L.; Chan, A.P. Optimal Tri–Level Government–Manufacturers–Contractors Subsidy Plan: Maximizing Local Prefabricated Product Usage and Minimizing Transport Emissions. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 71, 3530–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Tan, Z. A decision model on human–robot collaborative routing for automatic logistics. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 53, 101681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Wang, H.; Zhen, L.; Liu, Y. Automated generation of horizontal precast slab stacking plans. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 04023121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yi, W.; Zhen, L.; Wang, H.; Chan, A.P. Automated generation of stacking plans for prefabricated panels transported by A–frame trailers. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 57, 102077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Guo, M.; Jiao, Y.; Cao, J.D.; Qiu, J.L. A distribution center location optimization model based on minimizing operating costs under uncertain demand with logistics node capacity scalability. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 610, 128392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Gong, Z.; Wu, J. Dynamic Optimization of Layout of Construction Waste Recycling Facilities: A Case Study of Xining, China. Environ. Eng. 2023, 41. 194–201, 258. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Y. Innovative Design of Urban Domestic Waste Reverse Logistics Network from the Perspective of Ecological Civilization a Case Study of Hefei, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024, 33, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, I.; Bakhoum, E.S. Environmental feasibility of recycling construction and demolition waste. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 2675–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, J.; Giordano, A. Robust optimization of construction waste disposal facility location considering uncertain factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 353, 131455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, A.; Asadi-Gangraj, E.; Nemati, A. Designing a reverse logistics network to manage construction and demolition wastes: A robust bi-level approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Mei, S.; Xu, H.; Hsu, W. –L. Urban Construction Waste Recycling Path: Robust Optimization. Buildings 2023, 13, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, Y.; Rizwan, M.; Almansoori, A.; Elkamel, A. Municipality solid waste supply chain optimization to power production under uncertainty. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 121, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrel, V.; Murat, C.; Thiele, A. Recent advances in robust optimization: An overview. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 235, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadeh, K.S.; Tucker, E.L. Stochastic optimization models for location and inventory prepositioning of disaster relief supplies. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2022, 144, 103871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listeş, O. A generic stochastic model for supply–and–return network design. Comput. Oper. Res. 2007, 34, 417–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Cheng, R.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Larsen, A.; Nielsen, O.A. Risk–averse optimization of disaster relief facility location and vehicle routing under stochastic demand. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 141, 102015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layout Planning of Construction waste Disposal Facilities in Guangzhou (from 2021 to 2035). Available online: https://www.gz.gov.cn/zwgk/ghjh/zxgh/content/post_8892743.html (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Technical Standard for Construction and Demolition Waste Treatment. Available online: https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/zhengce/zhengcefilelib/201910/20191012_242186.html (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- 2023 Guangzhou State–owned Construction Land Benchmark Land Value Land Level Scope and Price. Available online: https://ghzyj.gz.gov.cn/xwzx/tzgg/content/post_9406828.html (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Conversion Factors for Calculation of Weight to Volume for Use When Completing Template 3. Available online: https://www.sustainabilityexchange.ac.uk/conversion_factors_for_calculation_of_weight_to_vo (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Ding, Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zuo, J.; Zillante, G. Cost–benefit analysis of demolition waste management via agent–based modelling: A case study in Shenzhen. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Leeftink, R.; Rotter, V. Evaluation of the economic feasibility for the recycling of construction and demolition waste in China—The case of Chongqing. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RMB Exchange Rate Midpoint (Historical Data). Available online: https://www.safe.gov.cn/safe/2020/1218/17833.html (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Ma, C.F.; Liang, W.; Zheng, M.; Xia, X.F.; Chen, L. A Voronoi Diagram and Q–Learning based Relay Node Placement Method Subject to Radio Irregularity. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2024, 20, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.W.; Acquah, M.A.; Seo, M.Y.; Han, S. Optimal Siting and Sizing of EV Charging Station Using Stochastic Power Flow Analysis for Voltage Stability. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begic, H.; Galic, M.; Klansek, U. Active BIM system for optimized multi–project ready-mix-concrete delivery. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasovic, B.; Galic, M.; Klansek, U. Active BIM Approach to Optimize Work Facilities and Tower Crane Locations on Construction Sites with Repetitive Operations. Buildings 2019, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
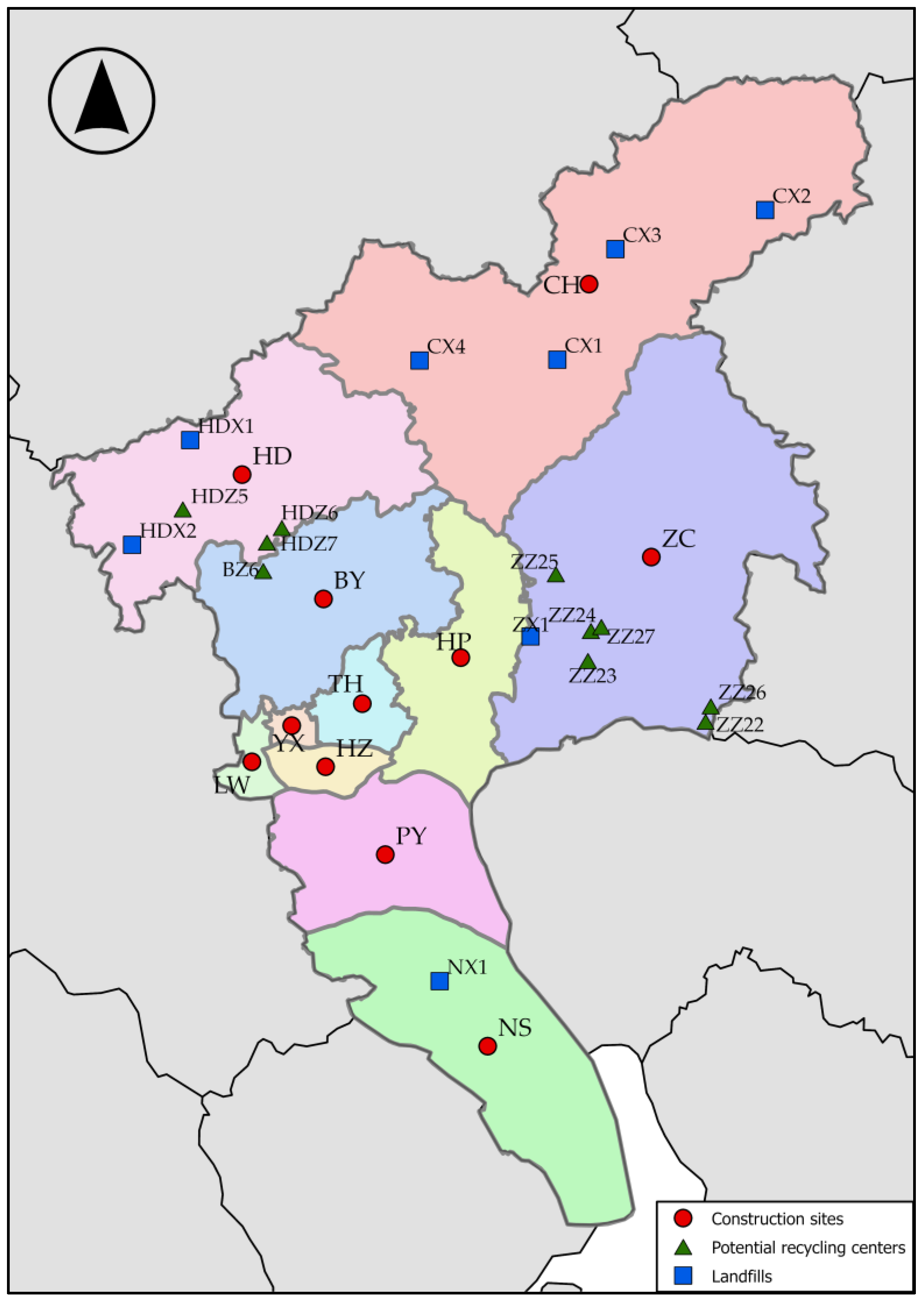

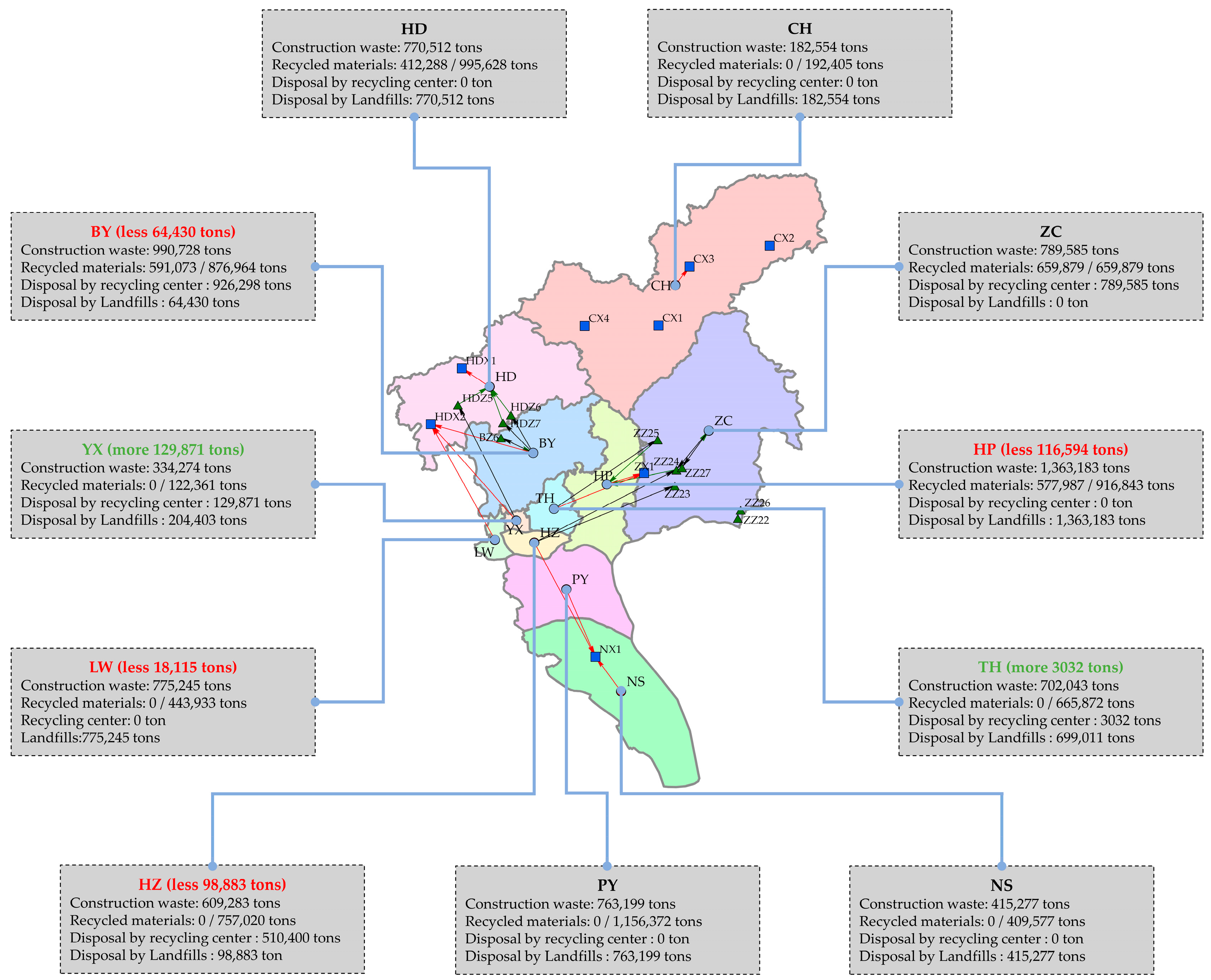


| No. | Name of the Official Documents or Literature | Related Inputs |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Layout Planning of Construction Waste Disposal Facilities in Guangzhou (from 2021 to 2035) [51] | , , , , , , , and |
| 2 | Technical Standard for Construction and Demolition Waste Treatment (CJJ/T134-2019) [52] | |
| 3 | 2023 Guangzhou State-owned Construction Land Benchmark Land Value Land Level Scope and Price [53] | |
| 4 | UK Waste Classification Scheme [54] | |
| 5 | Cost-benefit analysis of demolition waste management via agent-based modeling: A case study in Shenzhen [55] | and |
| 6 | Evaluation of the economic feasibility for the recycling of construction and demolition waste in China—The case of Chongqing [56] |
| Recycling Center ID | The Optimal Area (m2) | The Maximum Area (m2) |
|---|---|---|
| HDZ5 | 4392.0 | 4392.0 |
| HDZ6 | 6665.5 | 6665.0 |
| HDZ7 | 3619.6 | 3619.6 |
| BZ6 | 21,041.0 | 21,041.0 |
| ZZ22 | 0.0 | 27,573.6 |
| ZZ23 | 10,242.0 | 10,242.0 |
| ZZ24 | 29,255.7 | 30,221.6 |
| ZZ25 | 2228.7 | 12,096.9 |
| ZZ26 | 0.0 | 132,471.5 |
| ZZ27 | 7923.0 | 7923.0 |
| Recycling Center ID | The Optimal Area (m2) | The Maximum Area (m2) |
|---|---|---|
| HDZ5 | 4392.0 | 4392.0 |
| HDZ6 | 6665.5 | 6665.0 |
| HDZ7 | 3619.6 | 3619.6 |
| BZ6 | 21,041.0 | 21,041.0 |
| ZZ22 | 0 | 27,573.6 |
| ZZ23 | 10,242.0 | 10,242.0 |
| ZZ24 | 25,798.0 | 30,221.6 |
| ZZ25 | 102.5 | 12,096.9 |
| ZZ26 | 0 | 132,471.5 |
| ZZ27 | 7923.0 | 7923.0 |
| Recycling Center ID | The Maximum Area of the Recycling Center (m2) | Land Price Class | Land Cost (CNY/m2) | Total Cost (CNY/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDZ5 | 4392.00 | 6 | 655 | 1415.58 |
| HDZ6 | 6665.00 | 5 | 975 | 1735.58 |
| HDZ7 | 3619.60 | 4 | 1317 | 2077.58 |
| BZ6 | 21,041.00 | 5 | 975 | 1735.58 |
| ZZ22 | 27,573.60 | 6 | 655 | 1415.58 |
| ZZ23 | 10,242.00 | 6 | 655 | 1415.58 |
| ZZ24 | 30,221.60 | 7 | 470 | 1230.58 |
| ZZ25 | 12,096.90 | 6 | 655 | 1415.58 |
| ZZ26 | 132,471.50 | 6 | 655 | 1415.58 |
| ZZ27 | 7925.50 | 7 | 470 | 1230.58 |
| Construction Site ID | The Weight of Construction Waste Generated (ton) | The Weight of Recycled Building Materials Required (ton) |
|---|---|---|
| YX | 288,200 | 510,171 |
| LW | 675,960 | 2,276,147 |
| TH | 796,480 | 3,374,977 |
| HZ | 708,710 | 3,296,489 |
| BY | 1033,590 | 3,688,928 |
| PY | 898,660 | 4,630,783 |
| HP | 1,147,560 | 4,513,051 |
| HD | 848,880 | 4,042,124 |
| NS | 463,740 | 1,844,464 |
| ZC | 771,590 | 3,061,026 |
| CH | 226,630 | 745,634 |
| CNY/ton | YX | LW | TH | HZ | BY | PY | HP | HD | NS | ZC | CH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDZ5 | 116.37 | 125.77 | 127.19 | 141.43 | 80.30 | 192.21 | 151.51 | 32.78 | 296.47 | 226.37 | 222.36 |
| HDZ6 | 95.10 | 113.30 | 92.95 | 116.64 | 39.79 | 164.48 | 106.32 | 31.49 | 267.68 | 178.17 | 187.53 |
| HDZ7 | 88.81 | 105.65 | 90.08 | 111.38 | 38.60 | 160.25 | 108.47 | 34.19 | 264.02 | 184.91 | 197.47 |
| BZ6 | 75.70 | 92.00 | 79.76 | 98.84 | 32.11 | 148.35 | 103.84 | 46.72 | 252.43 | 186.67 | 207.55 |
| ZZ22 | 199.19 | 219.30 | 165.43 | 184.29 | 192.82 | 167.06 | 121.60 | 251.99 | 188.08 | 82.47 | 215.98 |
| ZZ23 | 145.92 | 168.93 | 110.57 | 136.25 | 130.47 | 134.92 | 61.17 | 188.35 | 191.28 | 57.87 | 179.51 |
| ZZ24 | 151.01 | 174.93 | 115.51 | 143.51 | 129.44 | 146.16 | 63.98 | 183.32 | 205.53 | 45.38 | 165.17 |
| ZZ25 | 146.47 | 171.87 | 112.11 | 144.44 | 112.39 | 157.73 | 61.02 | 157.94 | 228.93 | 46.54 | 138.95 |
| ZZ26 | 201.91 | 222.56 | 167.73 | 187.78 | 193.13 | 172.29 | 122.44 | 250.87 | 195.60 | 76.42 | 209.56 |
| ZZ27 | 156.38 | 180.31 | 120.88 | 148.86 | 134.21 | 151.00 | 69.29 | 187.15 | 208.67 | 40.76 | 163.34 |
| CNY/ton | YX | LW | TH | HZ | BY | PY | HP | HD | NS | ZC | CH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CX1 | 246.46 | 271.89 | 219.22 | 254.23 | 190.21 | 280.67 | 179.71 | 190.91 | 360.21 | 134.50 | 69.14 |
| CX2 | 365.07 | 390.88 | 334.92 | 369.54 | 311.71 | 387.97 | 288.85 | 310.76 | 451.51 | 204.34 | 121.50 |
| CX3 | 305.59 | 330.84 | 278.82 | 313.82 | 247.98 | 339.76 | 238.71 | 238.87 | 416.14 | 177.97 | 50.93 |
| CX4 | 214.94 | 238.09 | 196.28 | 229.38 | 152.84 | 266.80 | 173.31 | 131.05 | 359.74 | 175.59 | 119.02 |
| HDX1 | 174.93 | 186.69 | 180.71 | 199.21 | 129.26 | 249.32 | 196.46 | 59.85 | 353.53 | 258.45 | 235.26 |
| HDX2 | 145.62 | 148.76 | 164.25 | 171.19 | 125.54 | 221.87 | 196.96 | 92.63 | 324.92 | 279.61 | 282.12 |
| NX1 | 171.71 | 168.69 | 168.07 | 146.54 | 221.44 | 96.12 | 185.30 | 290.50 | 68.84 | 257.20 | 371.03 |
| ZX1 | 152.56 | 176.94 | 117.13 | 146.74 | 131.18 | 155.69 | 65.08 | 188.75 | 227.40 | 99.38 | 200.59 |
| Minimum price | 145.62 | 148.76 | 117.13 | 146.54 | 125.54 | 96.12 | 65.08 | 59.85 | 68.84 | 99.38 | 50.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, S.; Lim, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Yi, W.; Antwi-Afari, M.F. Location and Capacity Optimization of Waste Recycling Centers: Mathematical Models and Numerical Experiments. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167039
Xie S, Lim YT, Wang H, Yi W, Antwi-Afari MF. Location and Capacity Optimization of Waste Recycling Centers: Mathematical Models and Numerical Experiments. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(16):7039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167039
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Shenming, Ying Terk Lim, Huiwen Wang, Wen Yi, and Maxwell Fordjour Antwi-Afari. 2024. "Location and Capacity Optimization of Waste Recycling Centers: Mathematical Models and Numerical Experiments" Applied Sciences 14, no. 16: 7039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167039
APA StyleXie, S., Lim, Y. T., Wang, H., Yi, W., & Antwi-Afari, M. F. (2024). Location and Capacity Optimization of Waste Recycling Centers: Mathematical Models and Numerical Experiments. Applied Sciences, 14(16), 7039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167039







