Study on Vibration Damping Characteristics of Mounting Structure Based on the High Damping Alloy Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Measurement of Damping Parameters
2.1. Parameters Describing the Damping
2.2. Half-Power Bandwidth Method
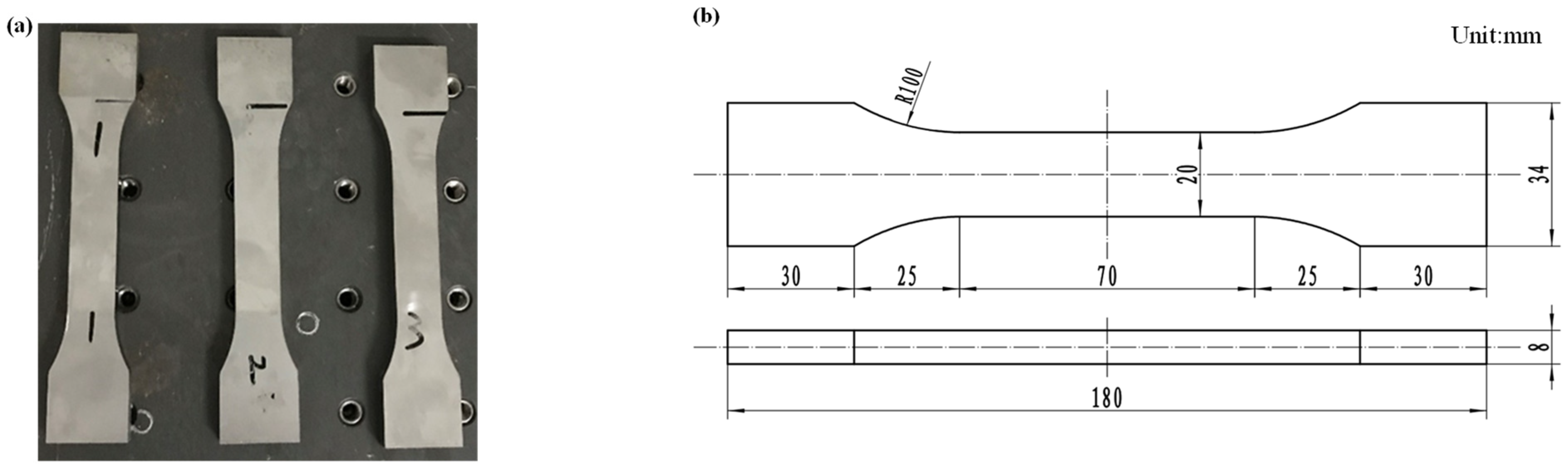
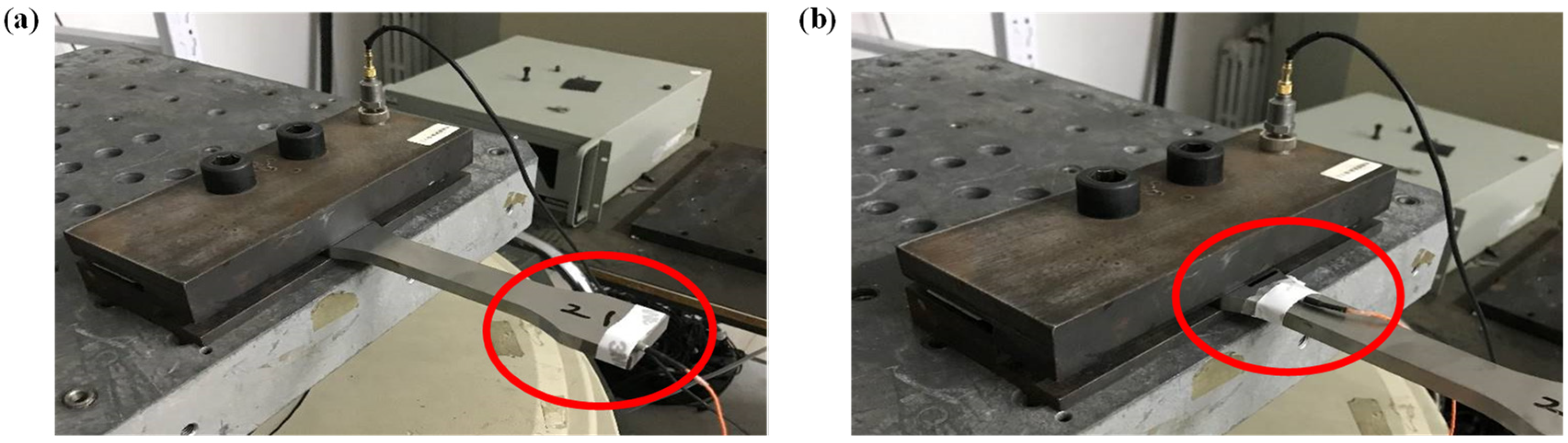
2.3. Damping Parameter Identification Test
3. Dynamic Characterization of High Damping Alloy Mounted Structures Calculations
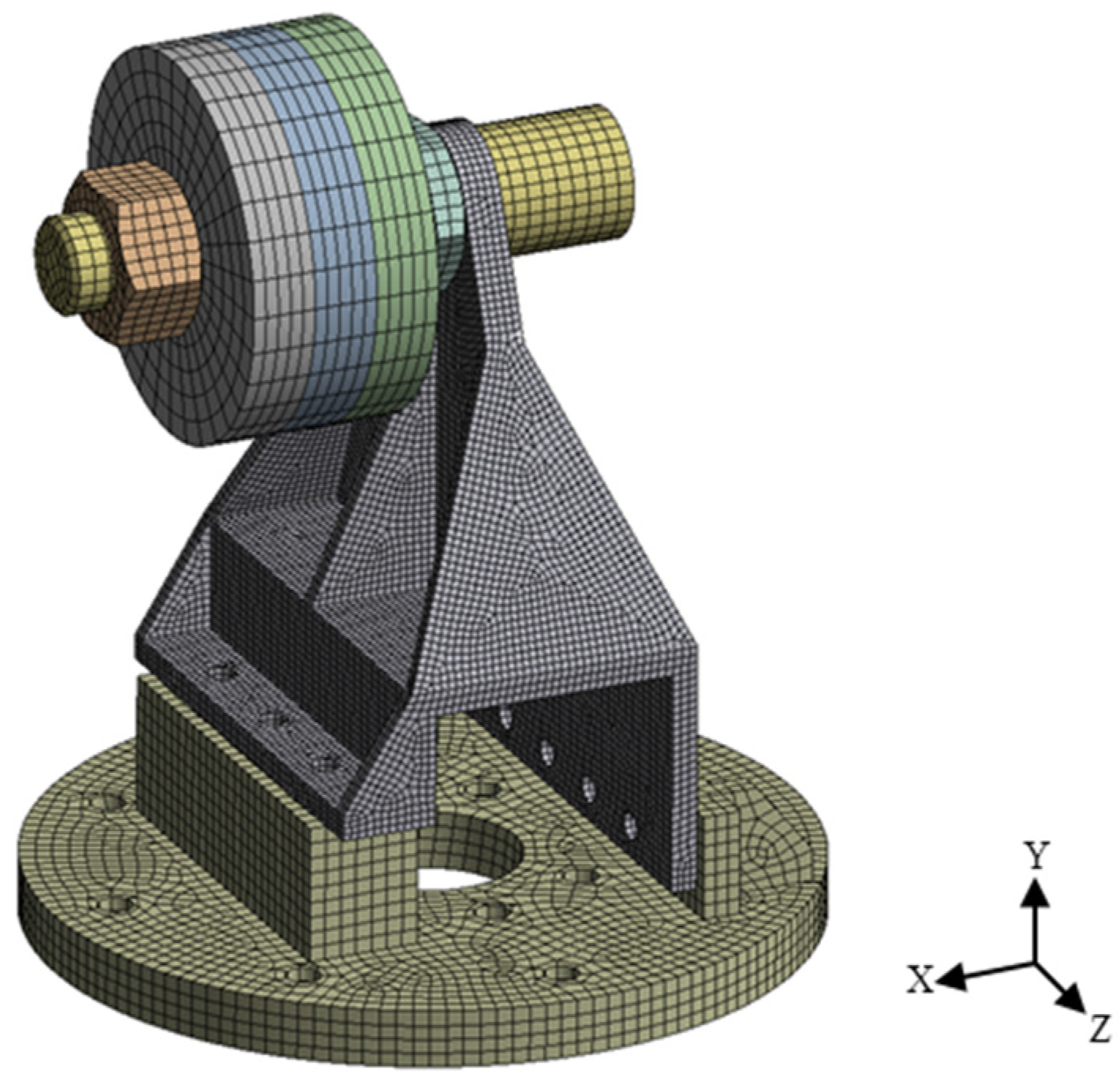
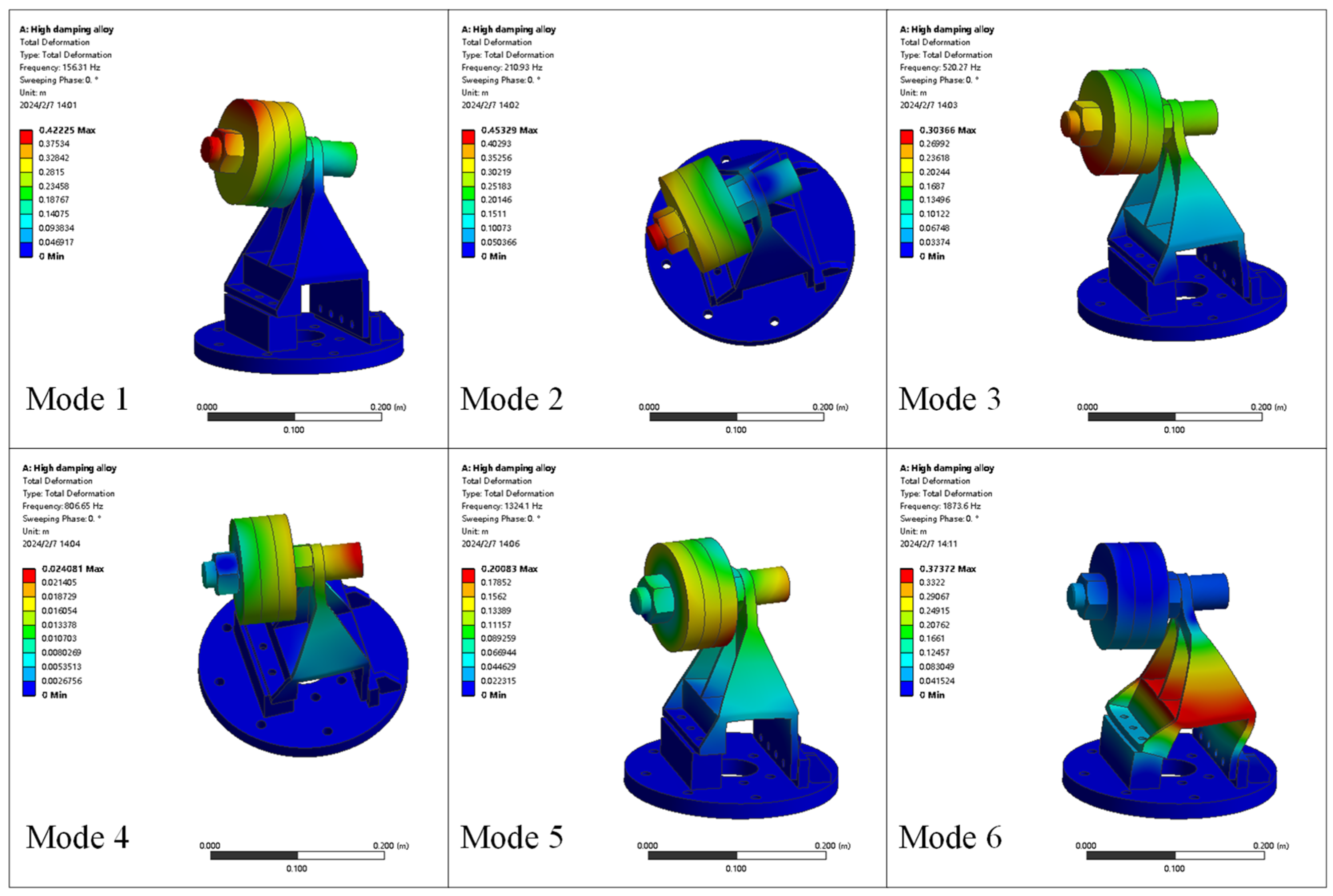
3.1. Modal Analysis
3.2. Harmonic Response Analysis
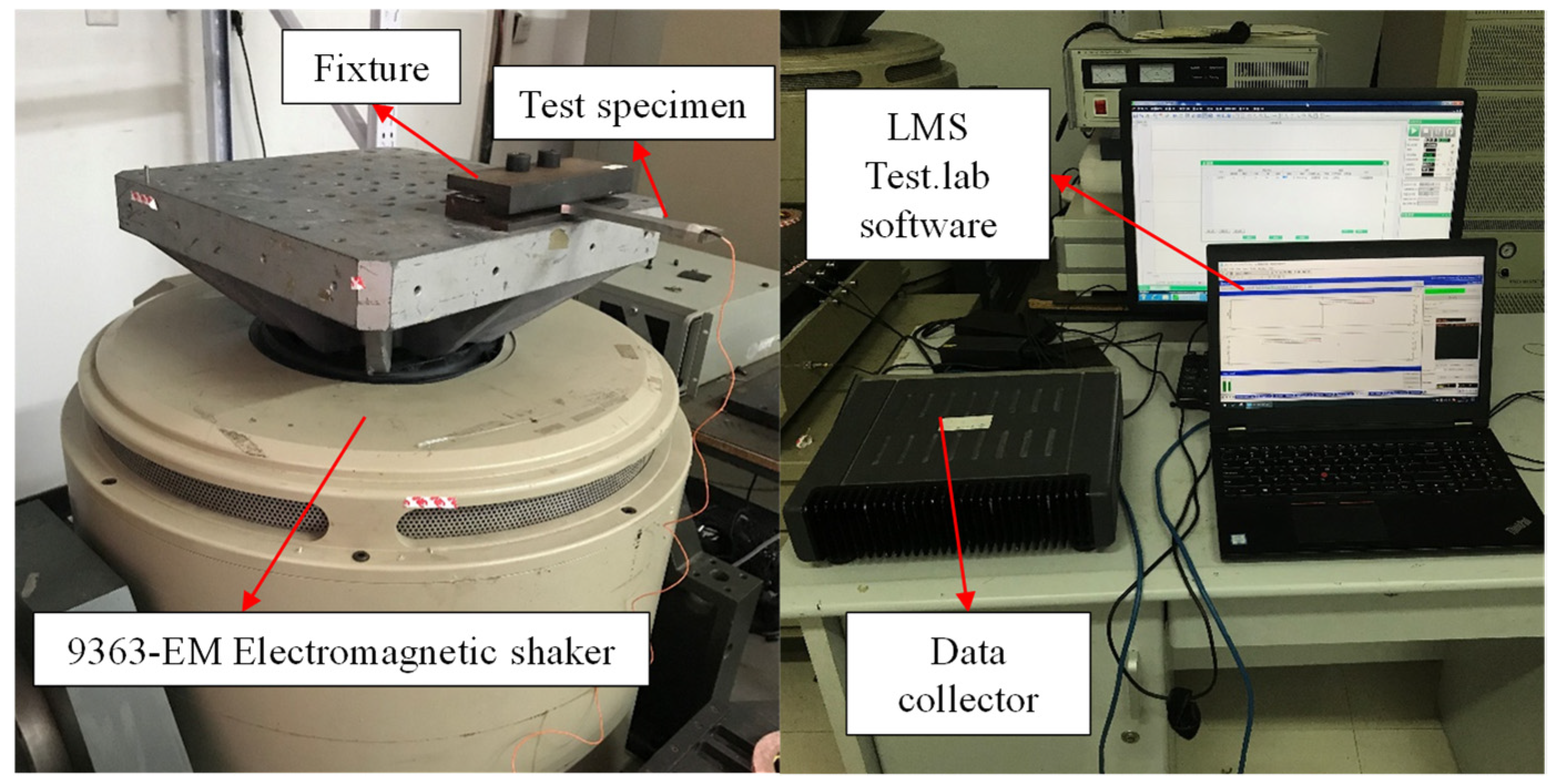
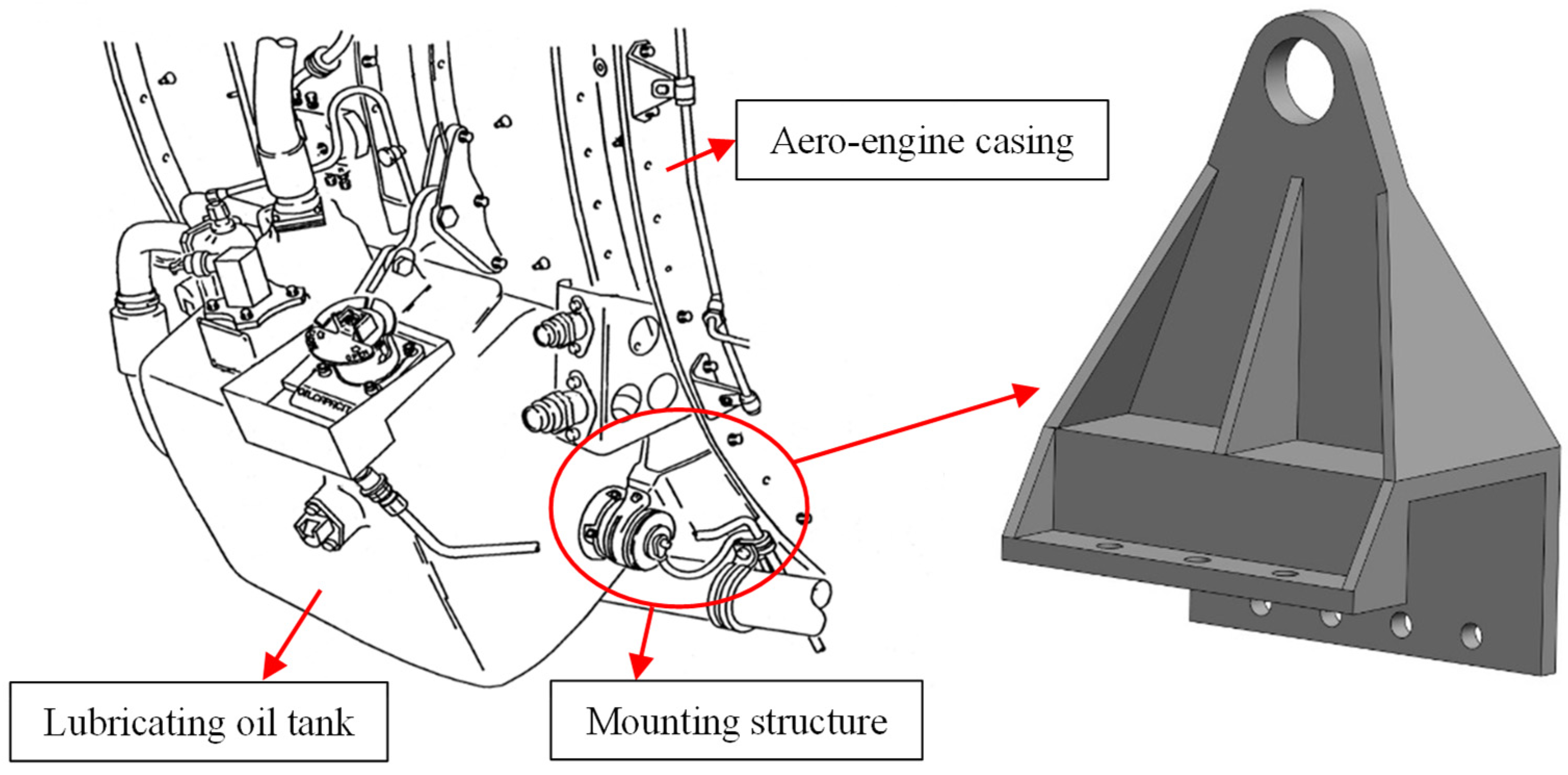
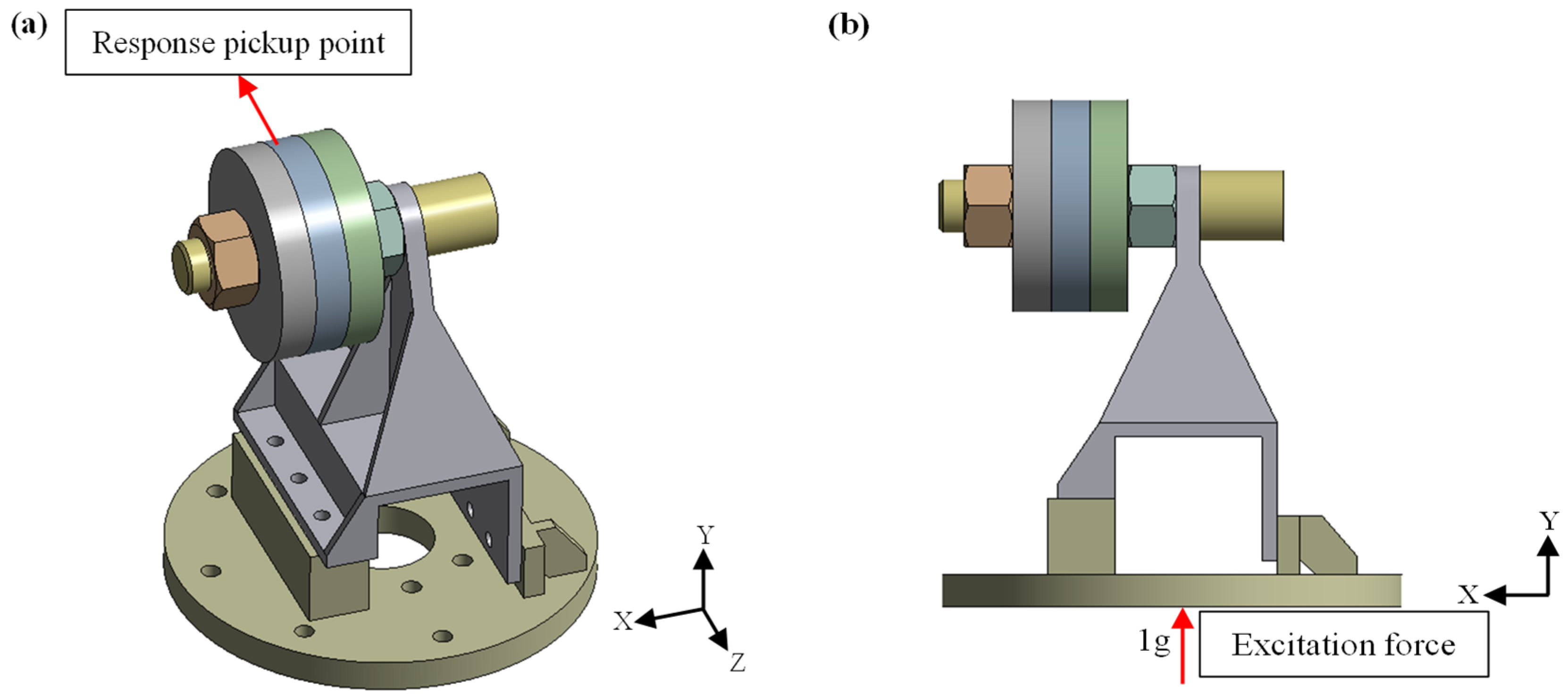
4. High Damping Alloy Mounting Structure Test
4.1. Sweep Test
4.2. Fixed Frequency Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussain, T.; Sarangi, N.; Sivaramakrishna, M.; Kumar, M.U. A Simulation Study of Lubricating Oil Pump for an Aero Engine. J. Mech. Eng. (JMechE) 2021, 18, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, R. Metal matrix composites, a smart choice for high damping materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 355, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H.; Wen, Y. Effect of up-quenching time on damping capacity in a ductile Cu-16.59 Al-10.55 Mn shape memory alloy. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 095703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, N.; Xu, Y. Microstructure regulation and internal friction behavior of Fe45Mn20Cr15Co20 duplex high-entropy damping alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, I.G.; Pan, Z.L.; Sprungmann, K.W.; Schmidt, H.K.; Dutton, R. High damping alloys—The Metallurgist’s cure for unwanted vibrations. Can. Metall. Q. 1987, 26, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igata, N. Applications of high damping stainless alloy (HIDAS). Key Eng. Mater. 2006, 319, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Peng, H.; Wen, Y. A novel sandwich Fe-Mn damping alloy with ferrite shell prepared by vacuum annealing. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdadi, A.; Nartey, M.A.; Xu, Y.G.; Golovin, I.S. Study of damping capacity of Fe–5.4 Al–0.05 Ti alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 653, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; Liu, W.; Hao, T.; Gao, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. High-temperature order-disorder phase transition in Fe-18Ga alloy evaluated by internal friction method. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 750, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantozzi, G.; Esnouf, C.; Reihani, S.S.; Revel, G. Anelastic behaviour of plastically deformed high purity magnesium between 10 and 500 K. Acta Metall. 1984, 32, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; Liu, W.; Hao, T.; Gao, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Influence of alloy elements (Mo, Nb, Ti) on the strength and damping capacity of Fe-Cr based alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 667, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- O’Toole, J.F., Jr. An Investigation of the Damping Properties of Vacrosil-010. Ph.D. Thesis, Institutional Archive of the Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Azcoïtia, C.; Karimi, A. Magnetomechanical damping in Fe–Cr alloys and effect of Al and Mo addition. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 310, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.K.; Zadorozhnyy, M.Y.; Saveliev, D.V.; Chudakov, I.B.; Golovin, I.S. Damping capacity, magnetic and mechanical properties of Fe-18Cr alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 494, 165777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Pan, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Investigation of the effect of alloying elements on damping capacity and magnetic domain structure of Fe-Cr-Al based vibration damping alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Yan, W.; Jiang, X. Effect of Gd on microstructure, mechanical properties and damping properties of Fe-Cr-Al alloys. Mater. Charact. 2022, 187, 111841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Woodhouse, J. Identification of damping: Part 1, viscous damping. J. Sound Vib. 2001, 243, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancic, F.; Palazotto, A. Experimental considerations for determining the damping coefficients of hard coatings. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2005, 18, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewins, D.J. Modal Testing: Theory, Practice and Application; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E756-05(2017); Standard Test Method for Measuring Vibration-Damping Properties of Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Xu, W.; Cheng, Q.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Dynamic analysis and looseness evaluation of bolted connection under vibration of machine tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 124, 3761–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Fu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Lu, K.; Francis, E.M. Dimensional decomposition-aided metamodels for uncertainty quantification and optimization in engineering: A review. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 428, 117098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zou, B.; Yang, J.; Fu, R.; Ding, X.; Zhang, D.; Bin, G. Simulated vibration characterization of the aero-turbine engine vibration isolation system under broadband random excitation. Mech. Sci. 2024, 15, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



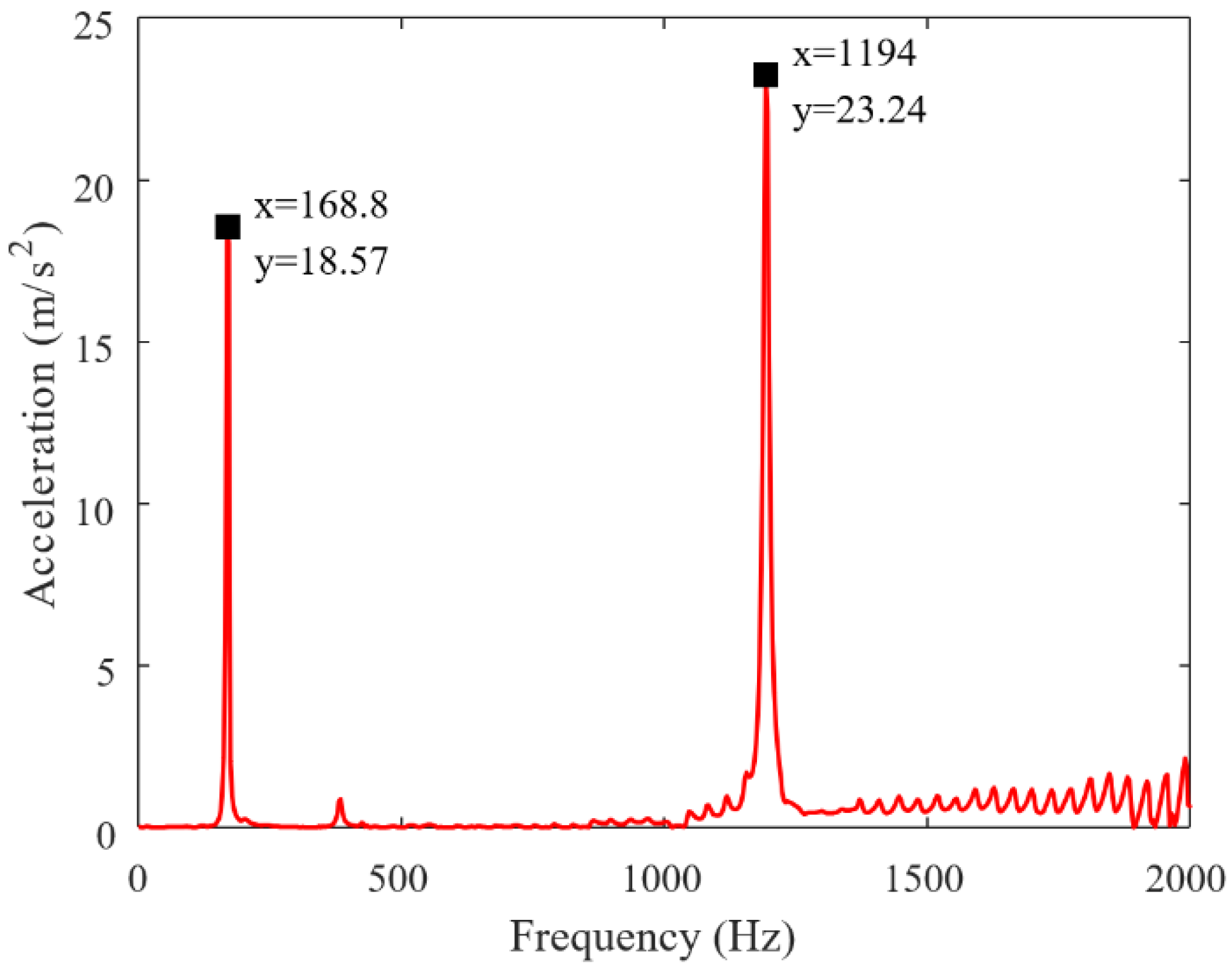
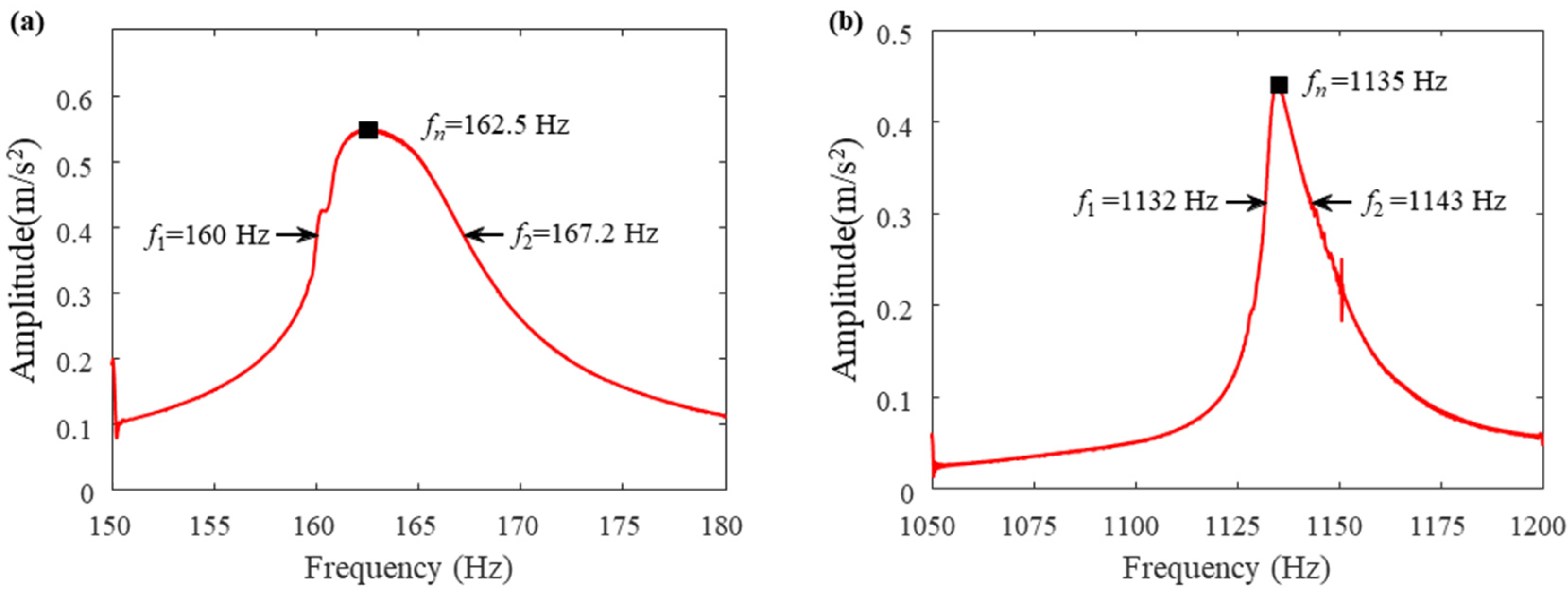





| Modal Order | Measurement Points | Modal Test | Sweep Test | Relative Error | Damping Ratio | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First order | Point 1 | 168.8 Hz | 162.5 Hz | 3.73% | 0.02215 | 0.02234 |
| Point 2 | 168.8 Hz | 162.0 Hz | 4.03% | 0.02253 | ||
| Second order | Point 1 | 1194.0 Hz | 1135 Hz | 4.94% | 0.00484 | 0.00484 |
| Point 2 | 1194.0 Hz | 1134 Hz | 5.02% | 0.00485 |
| Modal Order | Material | Damping Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen 1 | Specimen 2 | Specimen 3 | Average | ||
| First order | Fe-12Cr-3Al | 0.02234 | 0.01278 | 0.01848 | 0.01787 |
| Q235 | 0.00643 | 0.00655 | 0.00653 | 0.00650 | |
| Second order | Fe-12Cr-3Al | 0.00484 | 0.00517 | 0.00420 | 0.00474 |
| Q235 | 0.00353 | 0.00334 | 0.00314 | 0.00334 | |
| Materials | Modulus of Elasticity (MPa) | Densities (kg/m3) | Poisson’s Ratio | Yield Strength (MPa) | Modal Damping Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-12Cr-3Al | 1.62 × 105 | 7460 | 0.28 | 450 | 0.01787 |
| Q235 | 2.10 × 105 | 7750 | 0.3 | 235 | 0.0065 |
| Modal Order | High Damping Alloy | Carbon Steel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modal Frequency/Hz | Modal Damping Ratio | Modal Frequency/Hz | Modal Damping Ratio | |
| First order | 156.31 | 0.01726 | 176.84 | 0.006491 |
| Second order | 210.93 | 0.01681 | 236.46 | 0.006489 |
| Third order | 520.27 | 0.01623 | 580.43 | 0.006486 |
| Fourth order | 806.65 | 0.01556 | 890.32 | 0.006489 |
| Fifth order | 1324.1 | 0.01311 | 1417.6 | 0.006484 |
| Sixth order | 1873.6 | 0.01445 | 2012.7 | 0.006488 |
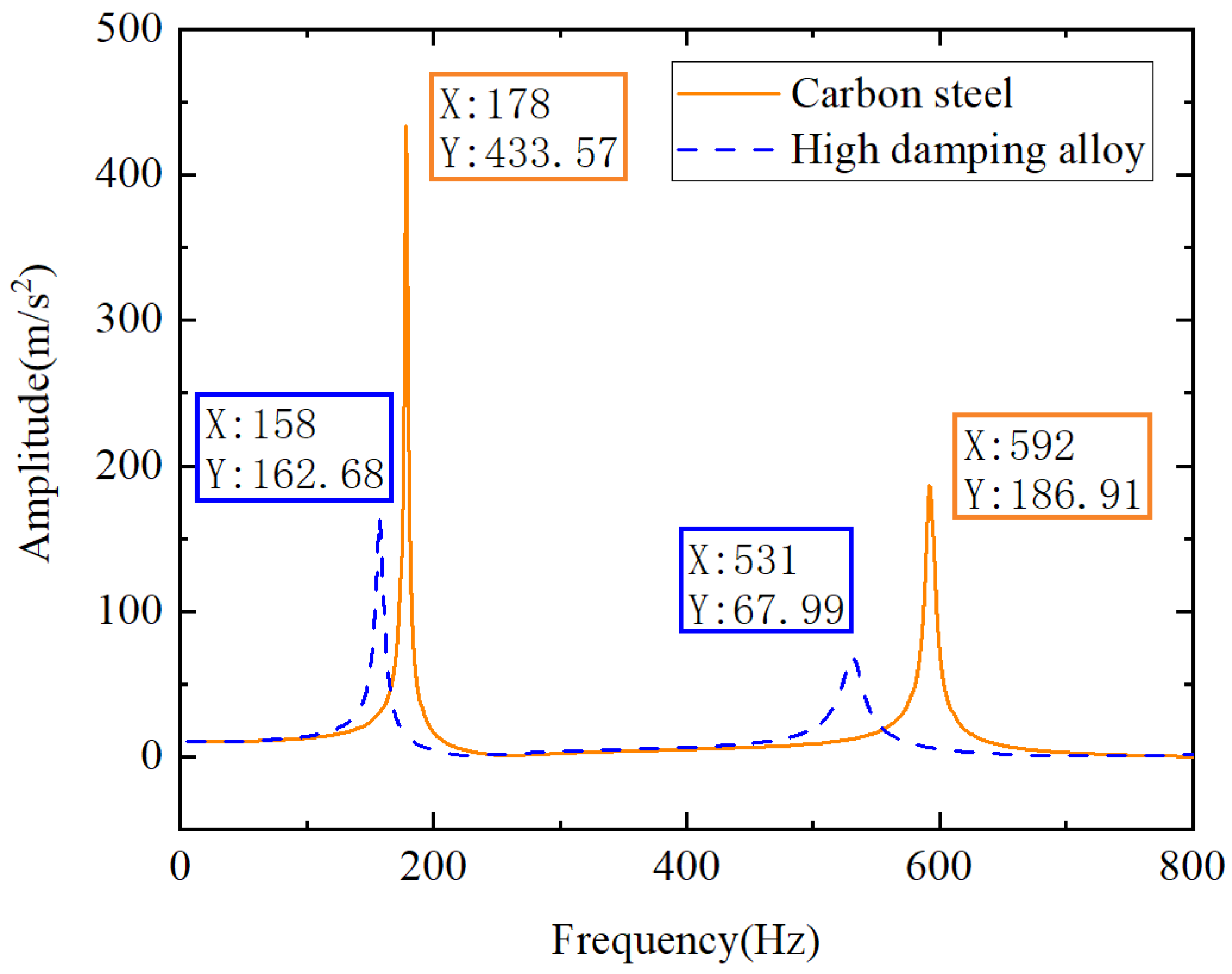
| Modal Order | High Damping Alloy | Carbon Steel | Amplitude Reduction Rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modal Frequency/Hz | Response Amplitude/m/s2 | Modal Frequency/Hz | Response Amplitude/m/s2 | ||
| 1st order | 158 | 162.68 | 178 | 433.57 | 62.48% |
| 3rd order | 531 | 67.99 | 592 | 186.91 | 63.62% |
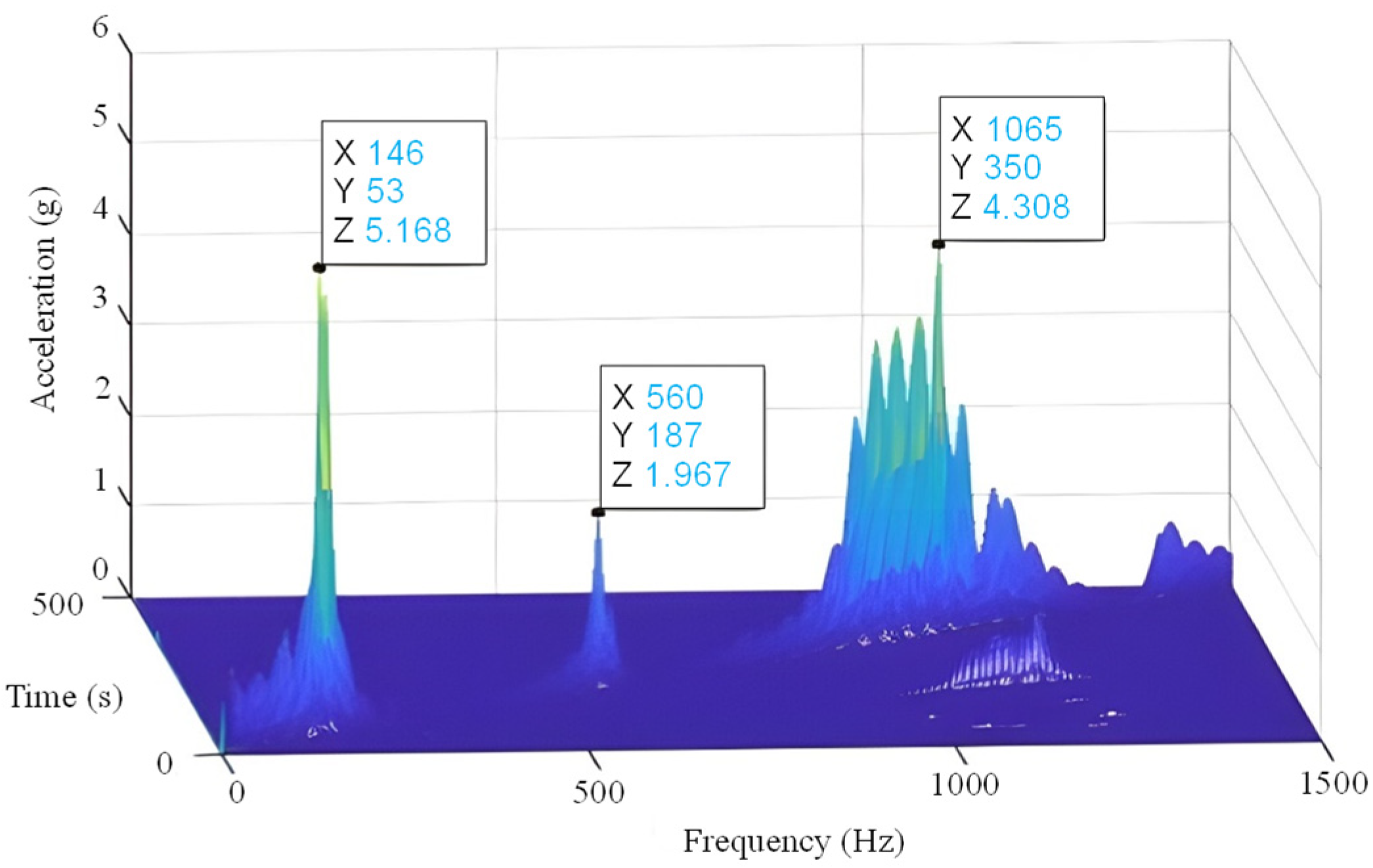
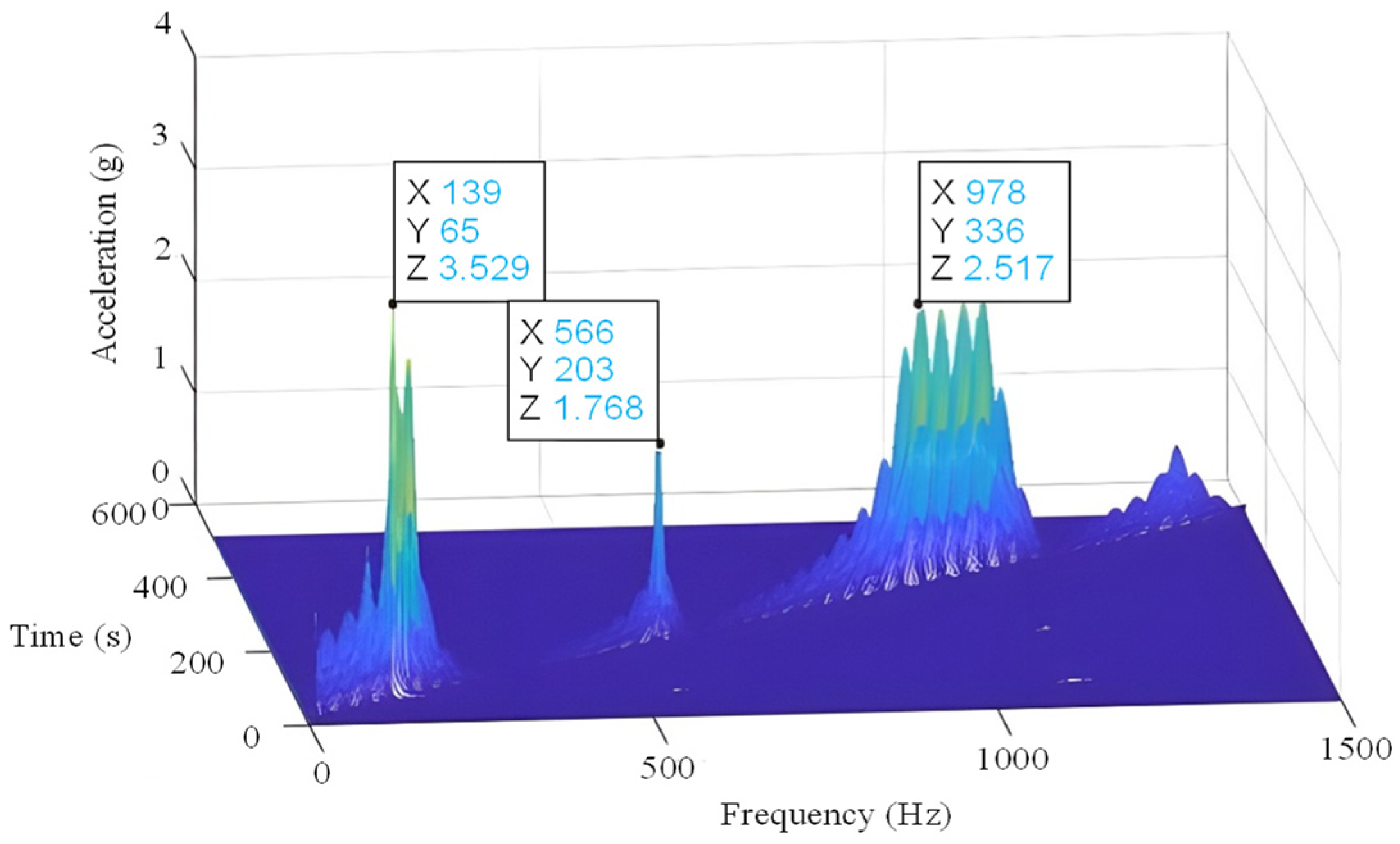
| Parameters | Materials | First Order | Second Order | Third Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Frequency | Carbon Steel | 146 Hz | 560 Hz | 1065 Hz |
| High Damping Alloy | 139 Hz | 566 Hz | 978 Hz | |
| Response Amplitude | Carbon Steel | 5.168 g | 1.967 g | 4.308 g |
| High Damping Alloy | 3.529 g | 1.768 g | 2.517 g | |
| Reduction Rate | --- | 31.7% | 10.1% | 41.5% |
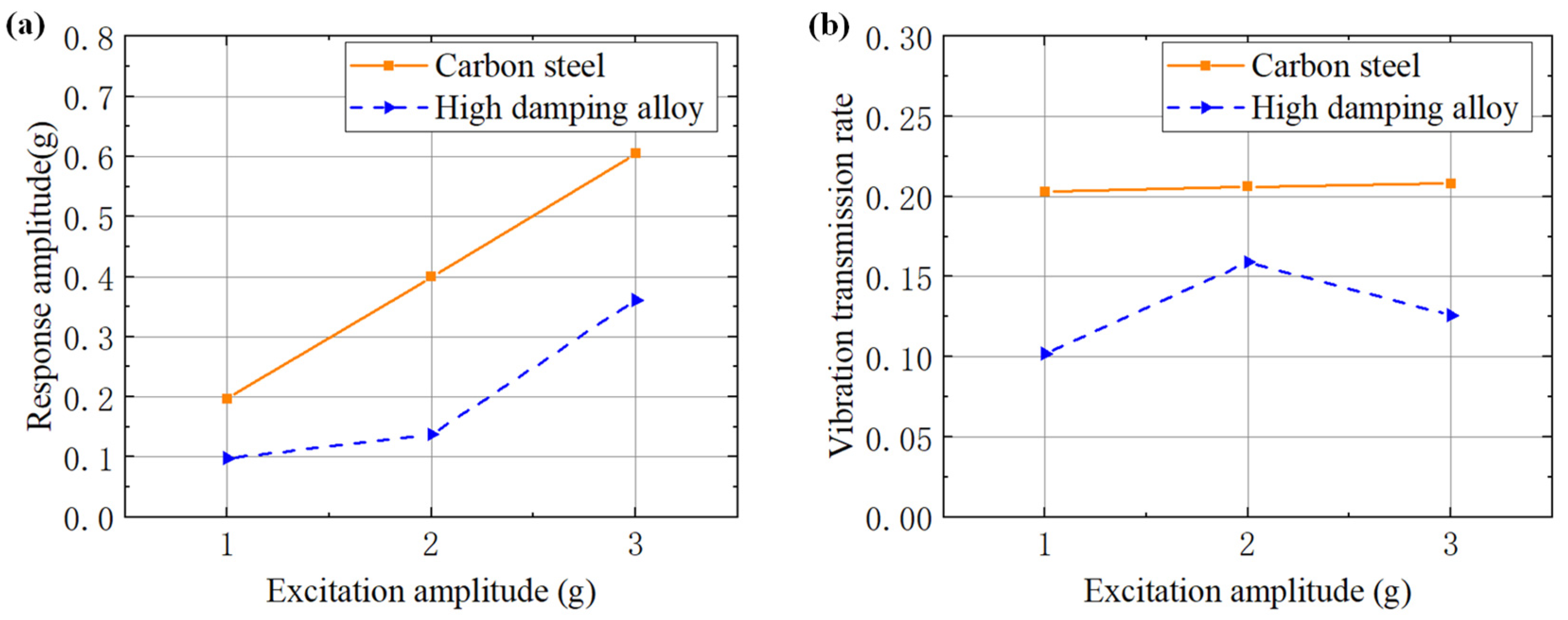
| Parts | Materials | Excitation Amplitude | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | 2 g | 3 g | ||
| Base | Carbon steel | 0.9704 | 1.94 | 2.91 |
| High damping alloy | 0.954 | 1.293 | 2.864 | |
| Mounting Structure | Carbon steel | 0.9264 | 1.849 | 2.772 |
| High damping alloy | 0.9238 | 1.252 | 2.772 | |
| Mass Block | Carbon steel | 0.1972 | 0.3994 | 0.6047 |
| High damping alloy | 0.09775 | 0.1376 | 0.3611 | |
| Transmission Rate | Carbon steel | 0.203 | 0.206 | 0.208 |
| High damping alloy | 0.102 | 0.159 | 0.126 | |
| Reduction Rate | 49.8% | 22.8% | 39.4% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, H.; Han, Q. Study on Vibration Damping Characteristics of Mounting Structure Based on the High Damping Alloy Material. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11056. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311056
Lin J, Li W, Chen H, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Ma H, Han Q. Study on Vibration Damping Characteristics of Mounting Structure Based on the High Damping Alloy Material. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(23):11056. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311056
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Junzhe, Wenbiao Li, Haiyang Chen, Hongxu Zhang, Yulai Zhao, Hui Ma, and Qingkai Han. 2024. "Study on Vibration Damping Characteristics of Mounting Structure Based on the High Damping Alloy Material" Applied Sciences 14, no. 23: 11056. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311056
APA StyleLin, J., Li, W., Chen, H., Zhang, H., Zhao, Y., Ma, H., & Han, Q. (2024). Study on Vibration Damping Characteristics of Mounting Structure Based on the High Damping Alloy Material. Applied Sciences, 14(23), 11056. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311056







