Abstract
This study examines the residual stress characteristics of spot welding in newly developed high-strength steel for automotive body construction through experimental and numerical methods. The effects of sheet thickness, nugget size, and the presence or absence of spacers on residual stress distribution and fracture stability were evaluated. Measurements using XRD and HDR revealed tensile residual stress below the yield strength at the nugget center. A numerical analysis system corroborated experimental findings, demonstrating that larger nugget sizes reduce tensile residual stress at the nugget center, enhancing fracture stability. However, for nugget sizes of 3 (t: thickness), high tensile stress at the nugget edge compromised stability, while sizes of 3.5 or larger improved fracture resistance. The study also found that thicker sheets increased fracture safety with larger nugget sizes, and the presence of spacers induced tensile stress through spring-back effects, which shifted to compressive stress as the nugget size increased. These results provide critical insights into optimizing welding parameters to improve the structural integrity of automotive components.
1. Introduction
Spot welding is a widely used method for assembling automobile structures, offering the advantages of high productivity and low cost. It is extensively applied in the automotive industry, particularly for assembling components such as auto-body panels and chassis. Its utility in mass production lines stems from its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, enabling rapid and streamlined vehicle assembly. Recent advancements in spot welding technology and quality assurance methods have enhanced the consistency of welding quality, even under varying material properties and assembly conditions. With the growing emphasis on lightweight automotive designs, spot welding has been increasingly employed for joining high-strength and lightweight materials. While high-strength materials are advantageous for weight reduction, they pose challenges in weldability. Numerous studies have investigated the applicability of spot welding under different welding conditions, such as current and electrode force [1,2,3,4,5]. The influence of welding current on nugget size was evaluated by observing the nugget growth rate under varying welding times and currents. It was found that the nugget growth rate decreased as both welding time and current increased, with the most rapid growth occurring during the initial welding cycle. This behavior suggests that the majority of nugget formation transpires early in the welding process, after which the growth rate diminishes. This observation aligns with the existing literature, which indicates that the nugget growth rate is most pronounced at the onset of welding and tapers off with prolonged welding time and increased current. For instance, a study on the effect of welding current on nugget geometry reported that at higher welding currents, the nugget size remains almost constant, indicating a reduced growth rate [6]. Understanding this relationship is crucial for optimizing welding parameters to achieve desired nugget sizes and ensuring the structural integrity of welded joints.
Furthermore, research has demonstrated that the magnitude and distribution of welding residual stress within specimens expand with increasing welding time and current, with the welding current exerting a more significant influence on residual stress compared to welding time [7]. Investigations into the effect of electrode force on nugget diameter and residual stress in the spot welding of high-strength steel have shown that varying electrode force conditions significantly influence the residual stress distribution in weld joints [8,9]. The nugget diameter was found to increase with higher electrode force, which also impacted the residual stress distribution.
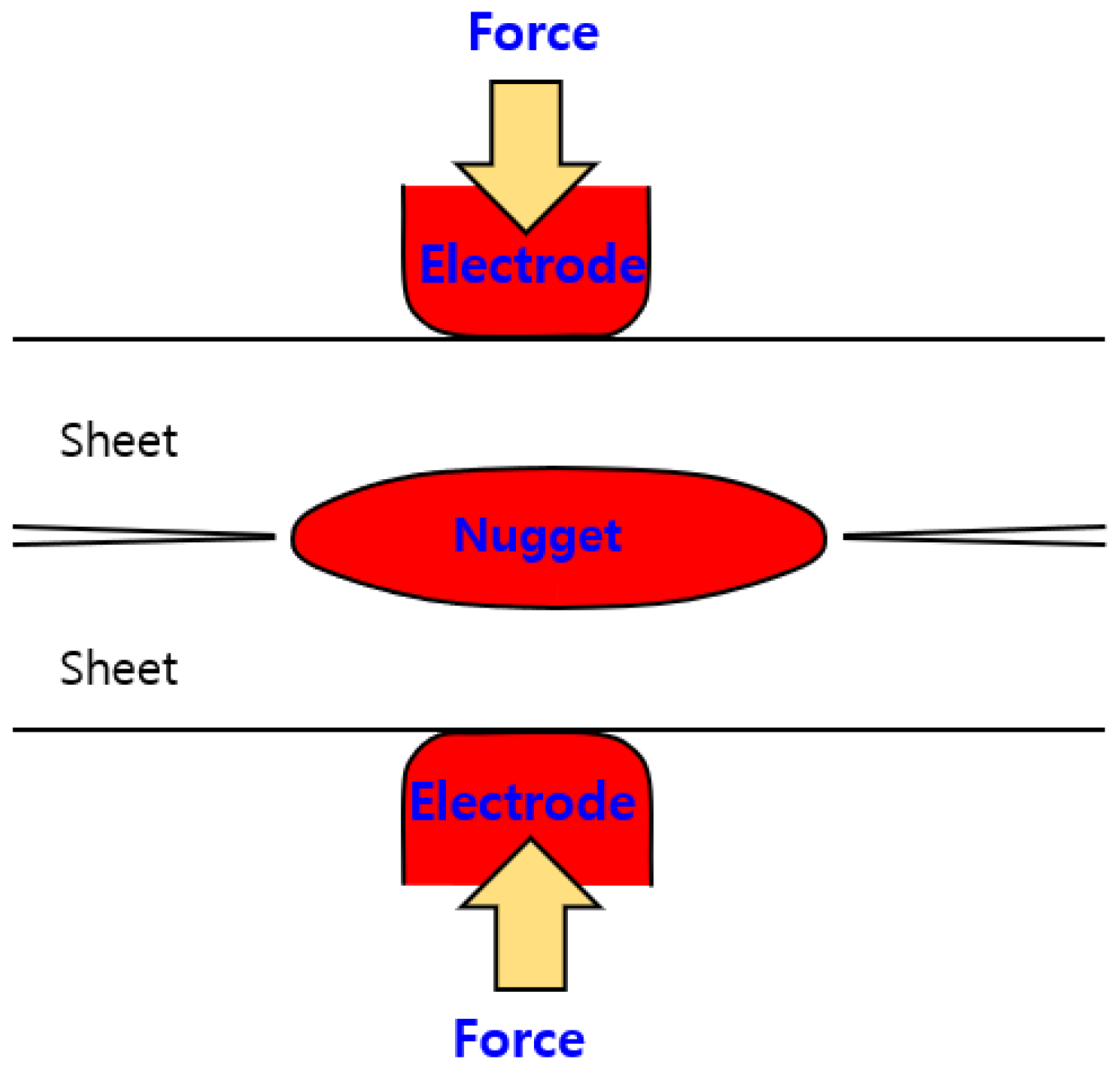
In addition, the potential for delayed fracture in spot weld joints has been explored by analyzing residual stress and hydrogen diffusion, focusing on the increased hydrogen concentration and its spread within the metal under high-temperature and high-residual-stress conditions [10]. Welding residual stress is a critical factor affecting the quality and strength of spot weld joints, motivating extensive research in this area [11,12]. For spot welding in car body manufacturing, however, gaps between sheets often arise due to spring-back effects after applying electrode pressure, as illustrated in Figure 1 [13]. These gaps can lead to deformation and misalignment during welding, thereby reducing weld integrity and productivity [14].
Figure 1.
Balance in a welded sheet under idealized conditions.
Spot welding in such high-strength steels results in the rapid formation of a martensitic structure due to the fast cooling rate, which increases the brittleness of the weld joint and makes it more prone to cracking [15]. It is well known from research findings that there is a close correlation between hardness and residual stress, as high hardness and residual stress are observed at the nugget center, while both hardness and residual stress decrease significantly in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) [16]. This martensitic transformation significantly affects residual stress, and the spring-back process is also found to have a considerable impact on residual stress [17]. Many studies analyze the residual stress in spot welding through numerical simulation, and to achieve more accurate predictions, it is essential to consider the phase transformation occurring during the spot welding process [18,19]. Based on these results, this study was conducted to predict residual stress more accurately by considering the phase transformation.
To address these issues, this study introduced a spacer between sheets to prepare spot welding specimens with simulated gaps in spot weld joints. The investigation involved the following:
- 1.
- Identifying the quantitative characteristics of residual stress on the spot weld surface through experimental examinations using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and hole-drilling (HDR) methods.
- 2.
- Constructing a finite element method (FEM) analysis system to examine the characteristics of residual stress distributed within the nugget of spot weld joints.
- 3.
- Analyzing the residual stress distribution characteristics based on nugget size, with sizes of 3, 3.5, 4, and 4.5 (t: thickness).
- 4.
- Investigating the residual stress distribution characteristics as a function of sheet thickness for each nugget size.
- 5.
- Examining the characteristics of residual stress distribution at spot weld joints with and without the spacer.
This study aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of residual stress characteristics in spot weld joints, with a focus on the effects of gaps and other critical parameters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Applied Steel and Specimen Preparation
Recent research has focused on examining the residual stress distribution characteristics of the weld nugget in spot welding, a process widely used in automotive structural welding. This study used high-strength steel with a yield stress of 1300 MPa, developed specifically to reduce the weight of car bodies. The mechanical properties of the automotive high-strength steel employed are presented in Table 1. The steel exhibits a high yield strength (approximately 1300 MPa) and a tensile strength of approximately 1500 MPa, making it one of the strongest steels recently applied to automotive structures.

Table 1.
Mechanical properties of martensitic steel.
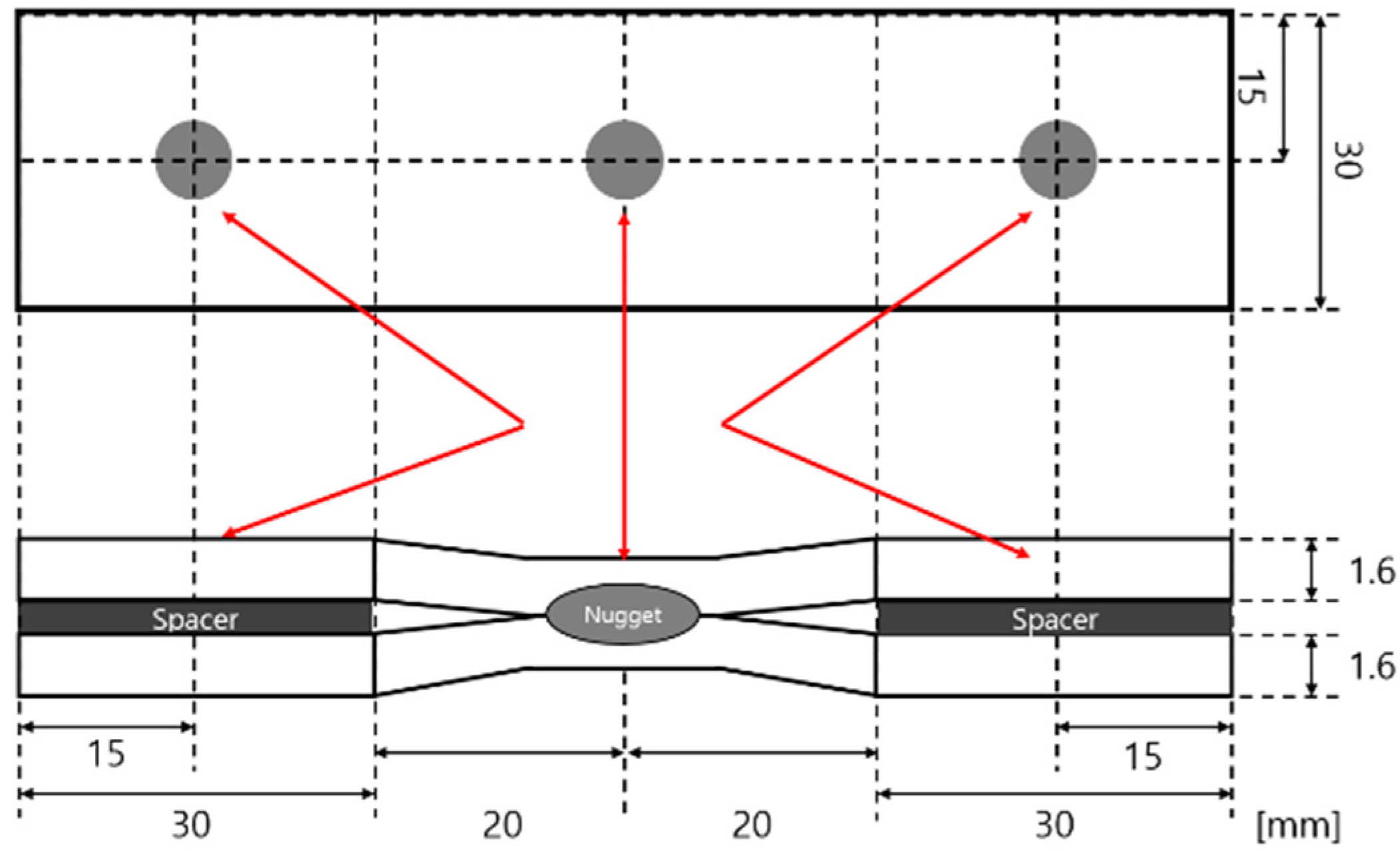
The welding conditions used for specimen preparation are detailed in Table 2. A DR-type Cu-Cr electrode with a 6 mm tip was utilized, alongside an electrode force of 3730 N, a current of 3400 A, a squeeze time of 5 cycles/50 Hz (0.10 s), a holding time of 10 cycles/50 Hz (0.20 s), and a welding time of 14 cycles/50 Hz (0.28 s). These conditions were selected to achieve a nugget size of 3. Figure 2 illustrates the specimen geometry, which had a total length of 100 mm and comprised sheets with a thickness of 1.6 mm. To simulate gaps that may occur during actual car body welding, a spacer of the same thickness (1.6 mm) was inserted between the sheets. The spacer was secured using tack welding at both ends via spot welding.

Table 2.
Welding conditions used in the study.
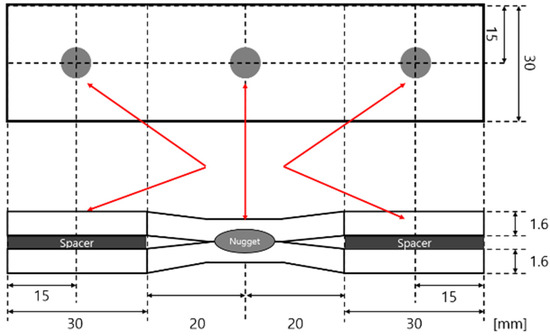
Figure 2.
Schematic of specimen dimensions.
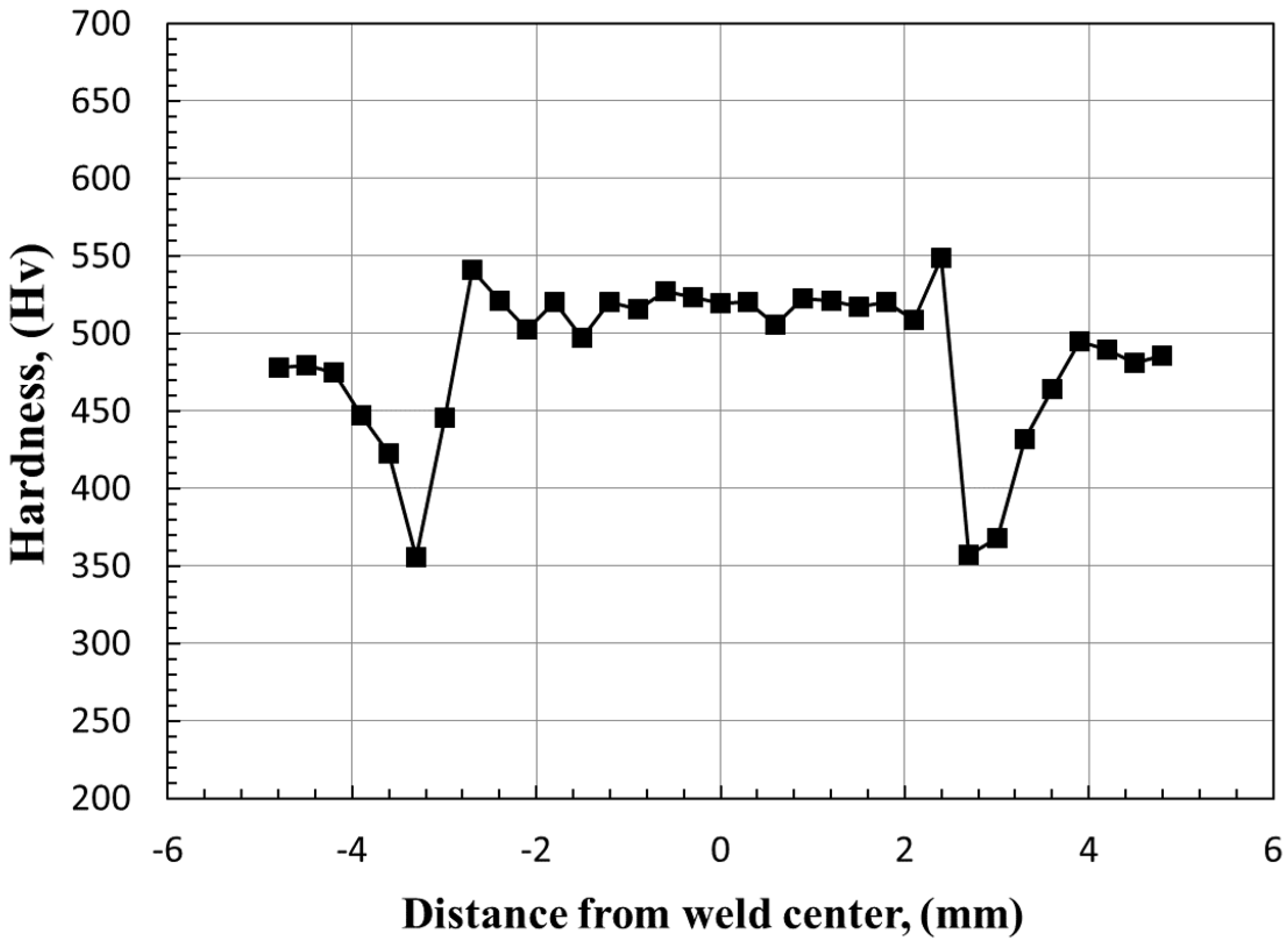
Figure 3 shows the Vickers hardness distribution of 3 (t: thickness) nugget size in SPOT welding. In this study, the hardness of the weld nugget was found to be higher than that of the parent metal, indicating superior strength in the nugget region. Conversely, the heat-affected zone (HAZ) exhibited a slight reduction in strength compared to the parent metal. Specifically, the nugget’s strength was approximately 117% of the parent metal’s strength, the HAZ adjacent to the parent metal was about 80%, and the HAZ near the nugget was around 122%. These findings suggest that the HAZ, particularly the region closer to the parent metal, may be more susceptible to failure due to its comparatively lower strength. This variation in hardness and strength across different weld regions is consistent with observations in similar studies. For instance, research on resistance spot welding of Zn–Al–Mg galvanized steel reported that the fusion zone (nugget) exhibited higher hardness due to the formation of lath martensite, while the HAZ showed varying hardness levels depending on its proximity to the nugget and base metal [20].
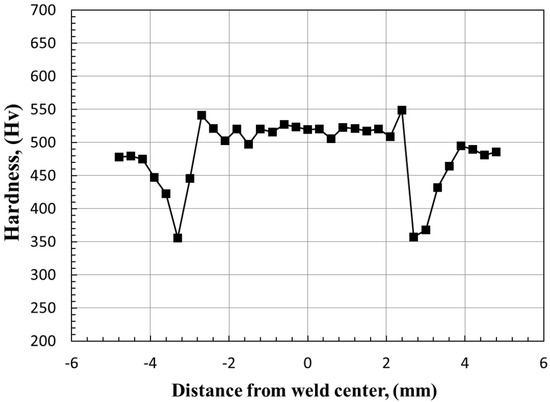
Figure 3.
Vickers hardness distribution in SPOT welding area.
2.2. Method for Examining Residual Stress Distribution Characteristics of Spot Weld Joints
2.2.1. Residual Stress Measurement by Experimental Method
This study analyzed the residual stress distribution on the surface of spot weld joints to identify the residual stress characteristics in the nugget. Residual stress was measured using the XRD and hole-drilling HDR methods, both commonly employed for evaluating welding residual stress on specimen surfaces [21,22]. For XRD measurements, residual stress was recorded at 2 mm intervals along the length (y-direction) and width (x-direction) up to 10 mm from the center of the nugget, as shown in Figure 4a. The XRD measurements were conducted in accordance with ASTM E915-16 and ISO EN 15305 (2008) standards [23,24]. Residual stress refers to internal stresses that remain within a material in the absence of external forces. Accurate measurement of these stresses is crucial for assessing material performance and preventing potential failures. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a widely used non-destructive technique for evaluating residual stresses, particularly in crystalline materials. This method leverages the interaction between X-rays and the crystal lattice to determine stress-induced changes in lattice spacing. When X-rays are directed at a crystalline material, they are diffracted by the crystal planes according to Bragg’s Law using Equation (1).
n: order of diffraction;
λ: wavelength of the X-rays;
d: interplanar spacing;
θ: Bragg angle (the angle of diffraction).
Residual stresses cause distortions in the crystal lattice, leading to changes in the interplanar spacing d. These changes result in shifts in the diffraction angle θ. By precisely measuring these shifts, the strain within the material can be determined, which is then used to calculate the residual stress. Surface preparation is crucial in X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements to ensure accurate residual stress analysis. In this study, scratches on the sample surface were addressed using an electrolyte solution, as such imperfections can introduce residual stresses that may skew results. The sample, a spot weld, exhibited a concave central region, resulting in a non-flat surface. To accommodate this geometry, the reflection angle was adjusted by repositioning the XRD contactor during measurement. Residual stress measurements were conducted using the Xstress 3000+G2R system from stress tech Oy (Helsinki, Finland). After removing the superficial stress at the measurement location using electropolishing equipment, the metal components were analyzed with XRF equipment (X-MET8000, HITACHI, Hitachi, Japan), and the data were correctly aligned. To ensure data reliability, the collimator size was increased to 2 mm, and sufficient exposure time was applied. Given the larger measurement size and extended exposure time, the results are considered reliable. Additionally, for the measurement of the nugget area in SPOT welding, a tilting detector was utilized to determine the interplanar spacing for crystals with varying orientations. This was achieved by segmenting the measurements into specific angles and repeatedly measuring the same point, allowing for precise analysis. An X-ray diffractometer equipped with appropriate optics and detectors is used to direct X-rays onto the sample and measure the resulting diffraction patterns. The diffraction angle θ is measured at various tilt angles to capture the strain in different orientations. The strain ϵ is calculated using the change in interplanar spacing, , where is the stress-free interplanar spacing. Using the material’s elastic constants (Young’s modulus, E, and Poisson’s ratio, ν) the residual stress σ is determined using Equation (2) and measurement parameter show Table 3.

Table 3.
Welding residual stress measurement parameters.
The HDM (hole-drilling method) operates on the principle that introducing a hole into a stressed material causes localized deformation as the material seeks a new equilibrium.
The equipment used for HDR measurements was the RS-2000 (Micro-Measurements, Wendell, NC, USA), and the software utilized for residual stress analysis was H-Drill (Micro-Measurements, Wendell, NC, USA). A biaxial strain gauge, FRS-2-11 (TML, Tokyo, Japan), was employed, and the analysis was conducted using the uniform stress method. Residual stress measurements were performed in accordance with ASTM E837 standards. By measuring these deformations, the original residual stresses can be inferred. This method involves drilling a small hole into the material’s surface, which leads to the redistribution of stresses and subsequent strain relief around the hole. These relieved strains are measured using strain gauges or optical methods, and the data obtained is used to calculate the residual stress present before drilling. Proper attachment of strain gauges is crucial in the HDM for accurate residual stress measurements. In this study, the subject was a spot weld characterized by a concave geometry, presenting challenges for strain gauge application. To ensure optimal adhesion and measurement accuracy, the weld area was meticulously ground to achieve a smooth and even surface, facilitating effective strain gauge bonding. Epoxy-based adhesives were employed to securely attach the strain gauge to the SPOT welding area. For the HDR method, residual stress was measured at the center (0 mm) of the spot weld joint and at a position 6 mm away from the center, as depicted in Figure 4b. Measurements were taken along both the length and width of the specimen using a biaxial strain gauge. The deformation data obtained through experimentation were converted into residual stress using Equation (2).
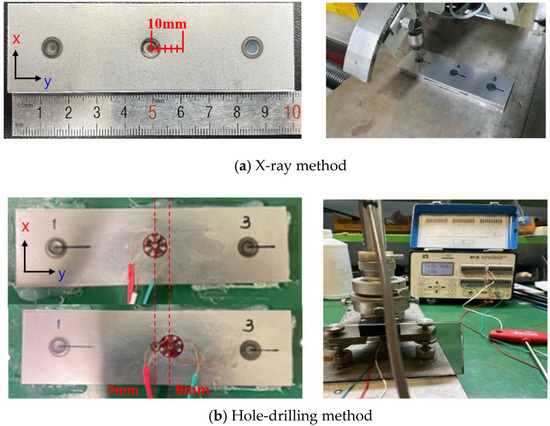
Figure 4.
Measurement positions for surface residual stress using each method: (a) X-ray method; (b) hole-drilling method.
Figure 4.
Measurement positions for surface residual stress using each method: (a) X-ray method; (b) hole-drilling method.
2.2.2. Construction of FEM Analysis System for Examining Residual Stress
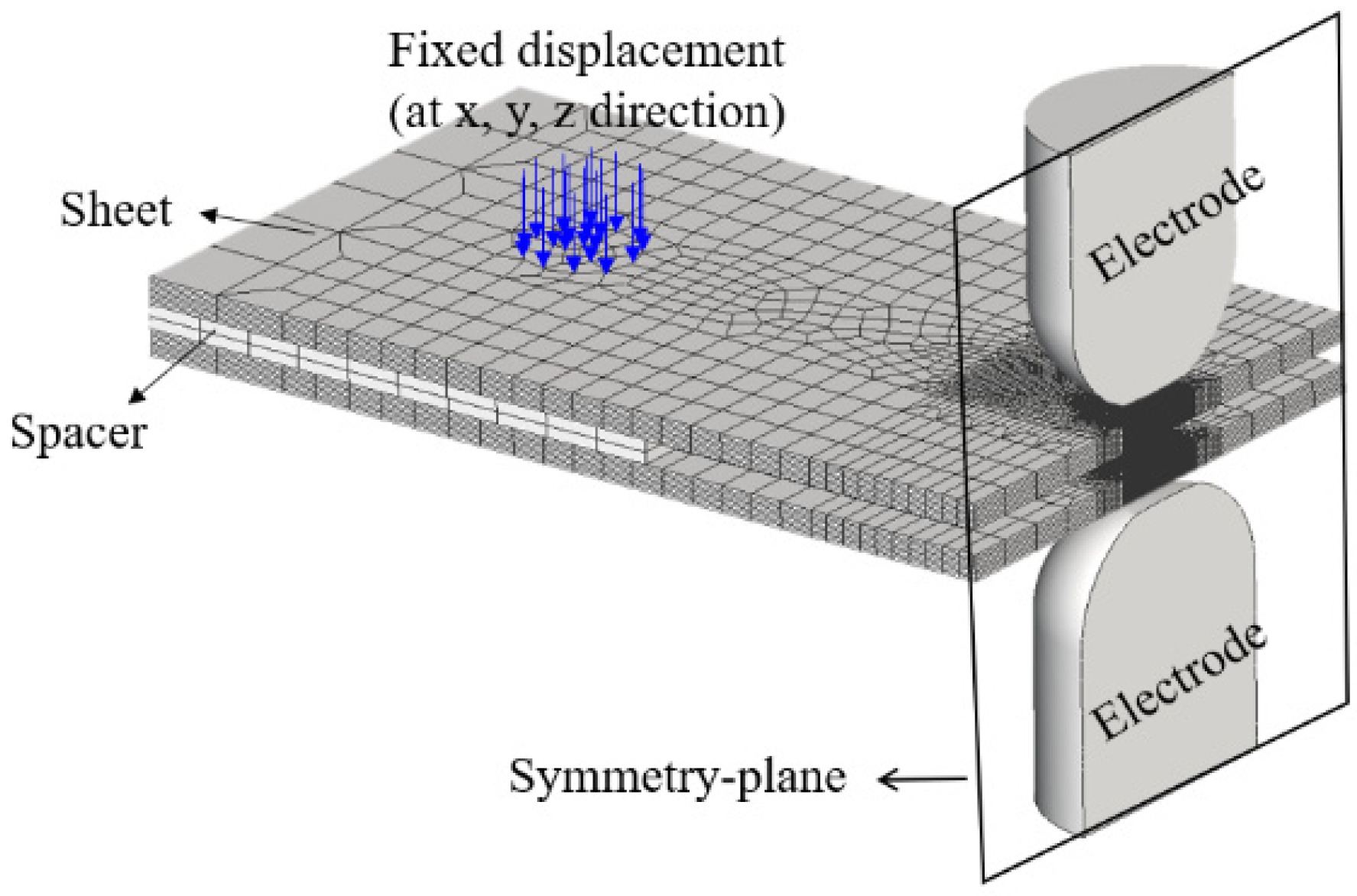
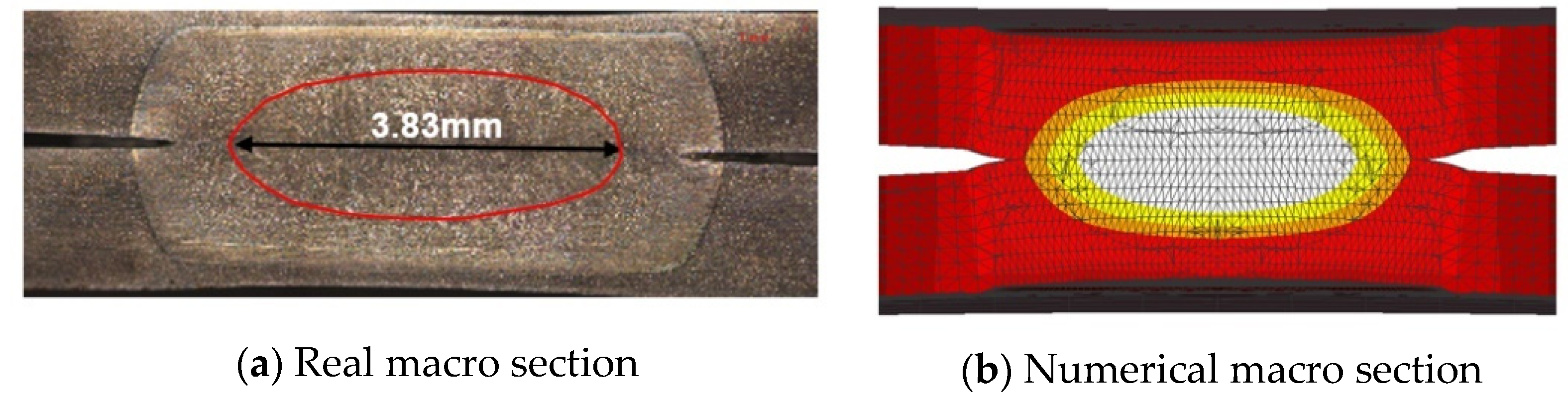
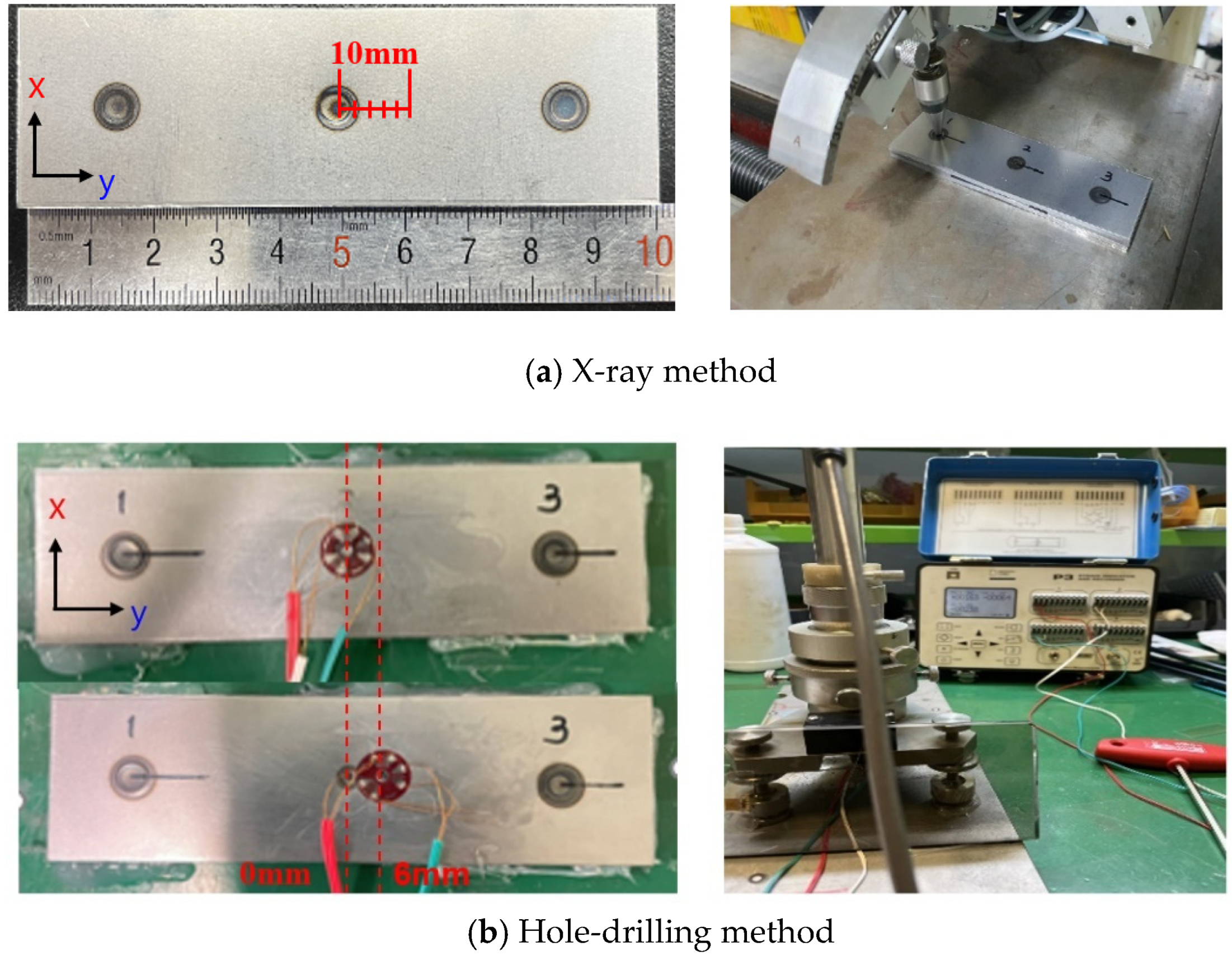
The experimental method has limitations in assessing residual stress within the nugget due to its small size. To overcome these challenges, a FEM analysis system was constructed to examine the residual stress characteristics inside the nugget numerically. To ensure the validity of the FEM analysis model, the residual stress characteristics obtained numerically were compared with those measured on the specimen surface. Simufact Welding ver. 2022.0.1, a commercial software program [25], was employed for the analysis. The finite element model was numerically analyzed using the axisymmetric model as shown in Figure 5. Figure 5 illustrates the boundary conditions for the FE analysis. The displacements in the x-, y-, and z-directions were fully constrained at the connection point between the sheet and spacer, while the remaining parts were analyzed in a free state to minimize the influence of residual stress caused by constraints. In the analysis of the temperature field and stress field, the commercial software of Simufact Welding was used to perform the electrical-thermal stress coupling analysis. The electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties used the material property data of the high-strength steel plate. In addition, the material properties of the weld were divided into two types, martensite (base material) and austenite, and the effects of the phase transformation of austenite and martensite during cooling were considered. The sheet thickness was 1.6 mm, and the total specimen length was 100 mm. The nugget shape used in the FEM analysis was modeled to match the nugget size of the macro section of the actual spot weld joint, as shown in Figure 6a. Figure 6b illustrates the temperature distribution cross-section for the 3 nugget shape, enabling a comparison between the modeled nugget shape and the actual weld during the spot weld FE analysis. The minimum element size in the nugget was set to 0.1 mm × 0.1 mm to accurately capture the residual stress distribution characteristics.
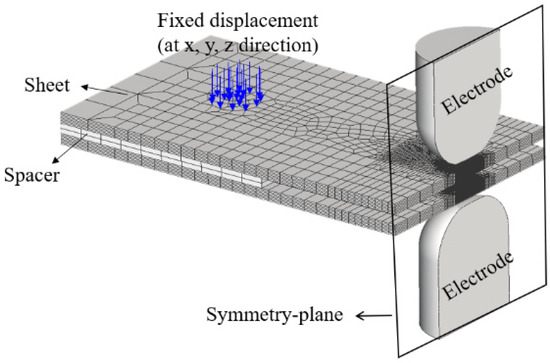
Figure 5.
Numerical analysis model for calculating welding residual stress in SPOT weld joint.
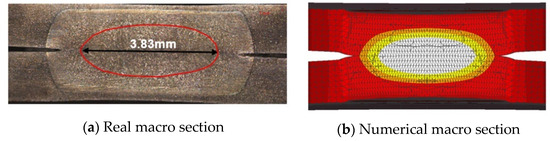
Figure 6.
Real macro section of SPOT weld and finite element model of the residual stress test specimen: (a) real macro section; (b) numerical macro section.
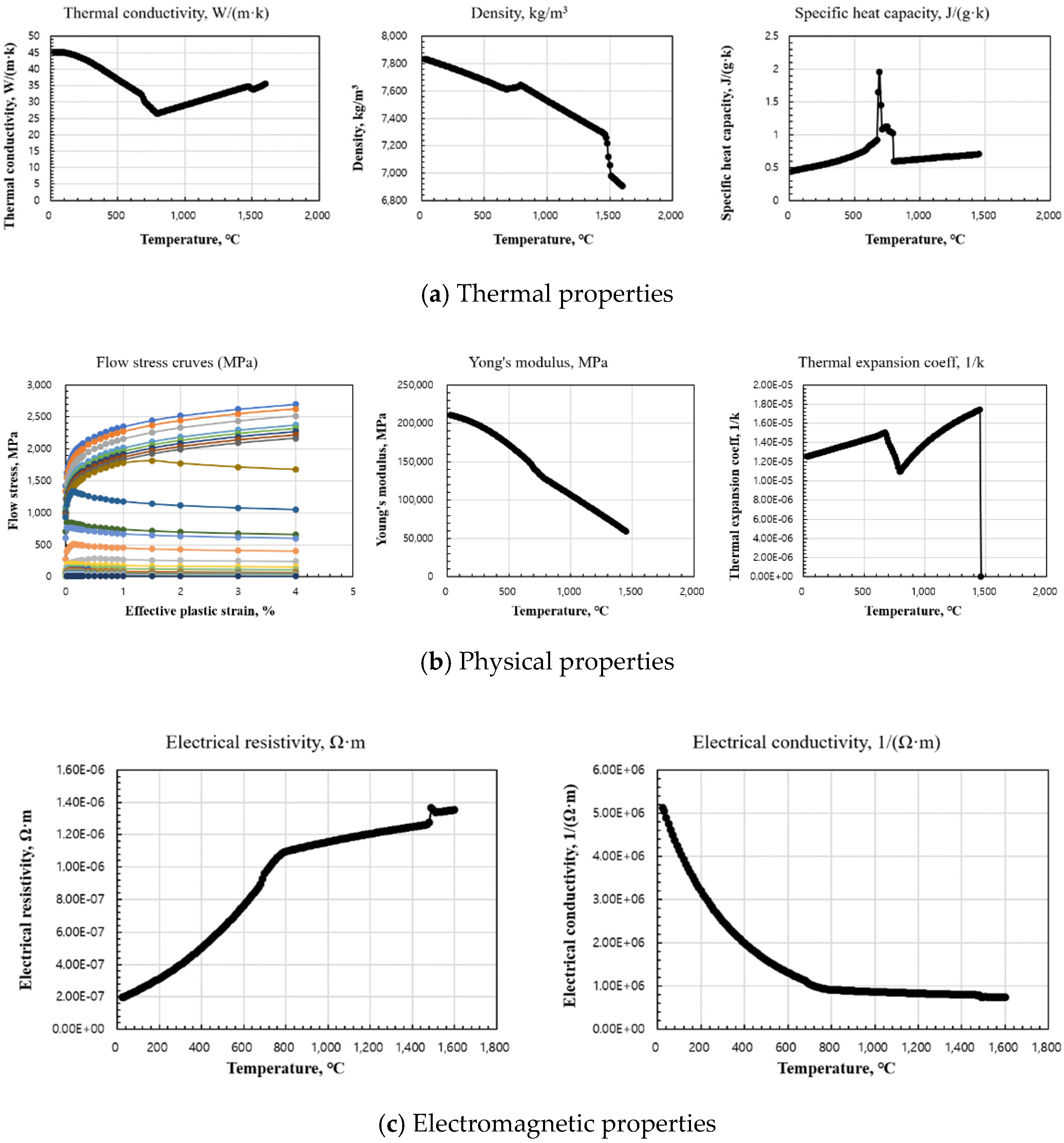
The mechanical properties required for welding analysis, including temperature-dependent physical properties, were derived using JMatPro ver. 8.0 [26], a commercial software program that predicts high-temperature material properties based on chemical composition. Figure 7 presents the input parameter values used in the analysis. Figure 7a illustrates thermal properties, including thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity, and density as functions of temperature. Figure 7b depicts mechanical properties, such as the flow stress curve, Young’s modulus, and thermal expansion coefficient relative to temperature. Figure 7c shows electromagnetic properties, including electrical resistivity and conductivity as functions of temperature. The validity of the residual stress analysis system developed in this study was confirmed through comparisons between the FEM analysis results and the experimentally measured residual stress values at corresponding positions on the specimen surface.
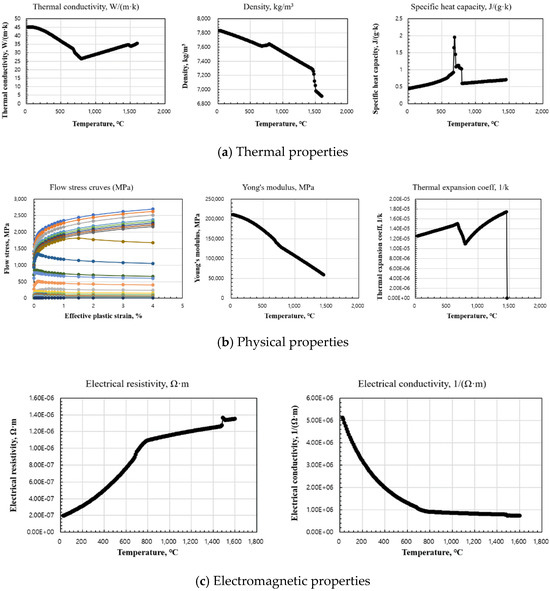
Figure 7.
Temperature dependence of various physical properties: (a) thermal properties; (b) physical properties; (c) electromagnetic properties.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Residual Stress Distribution Characteristics on the Nugget Surface of the Spot Weld Joint
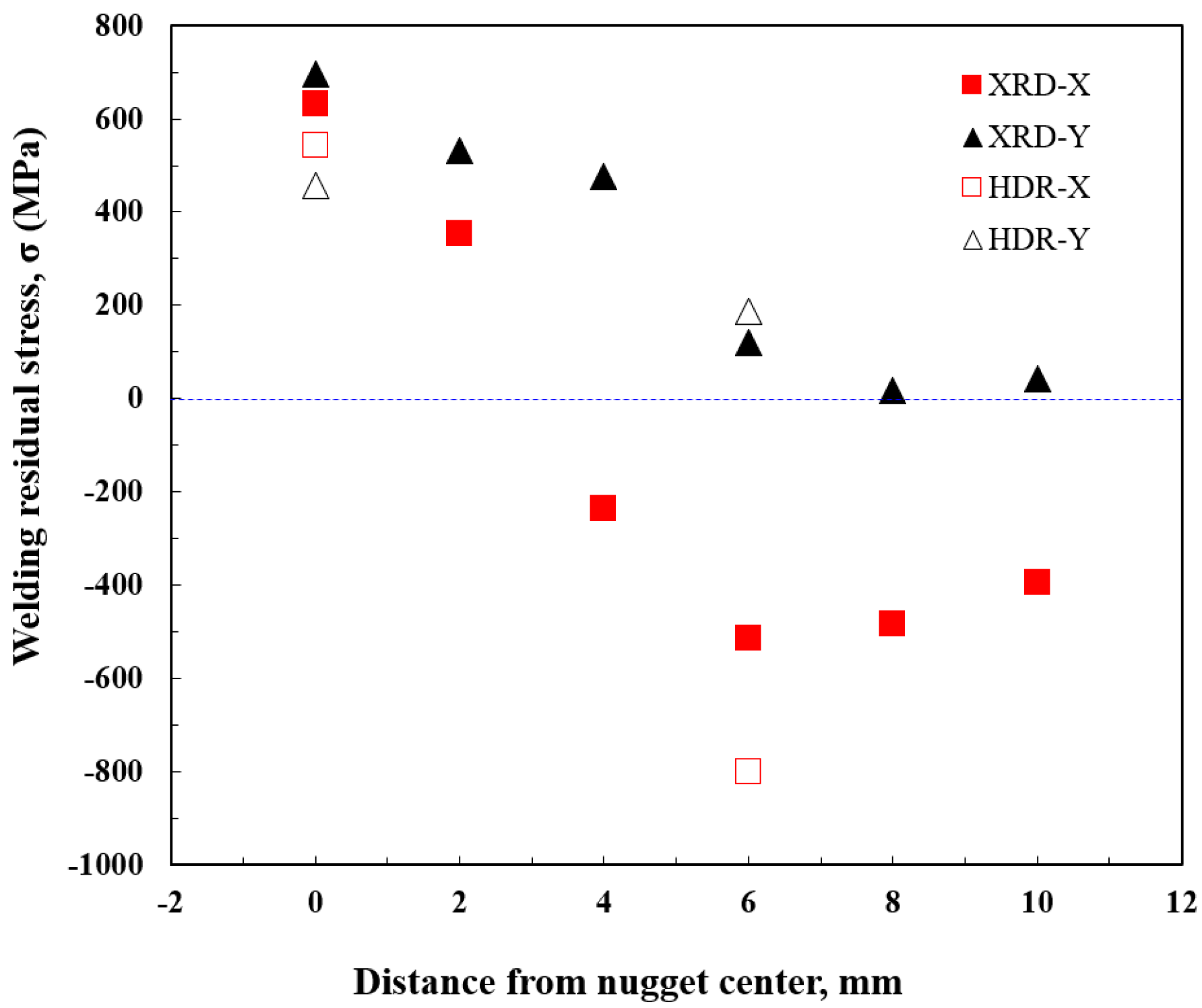
Figure 8 presents the experimentally measured residual stress distribution characteristics of the spot weld joint. The results obtained from the XRD and HDR methods indicate the distribution of residual stress with respect to the distance from the nugget center. The largest tensile residual stress was observed at the nugget center, while the tensile residual stress decreased progressively with increasing distance from the nugget center. The maximum compressive residual stress occurred at a distance of 6 mm from the nugget center. In the specimen length direction (y-direction), substantial tensile residual stress was observed up to a distance of 3 mm in the region in contact with the electrode, beyond which the stress level diminished. Similarly, in the specimen width direction (x-direction), tensile residual stress extended up to a distance of 3 mm in the region in contact with the electrode, after which significant compressive residual stress was detected. The residual stress values obtained using the XRD and HDR methods were found to be in good agreement for both directions. Due to the small nugget size (approximately 4 mm), HDR measurements were conducted only at two positions: the nugget center and a point 6 mm from the center. Although this limited the resolution of HDR measurements, the results were consistent with those obtained at 2 mm intervals using XRD. This consistency suggests that the residual stress of the spot weld joint was accurately measured by both methods.
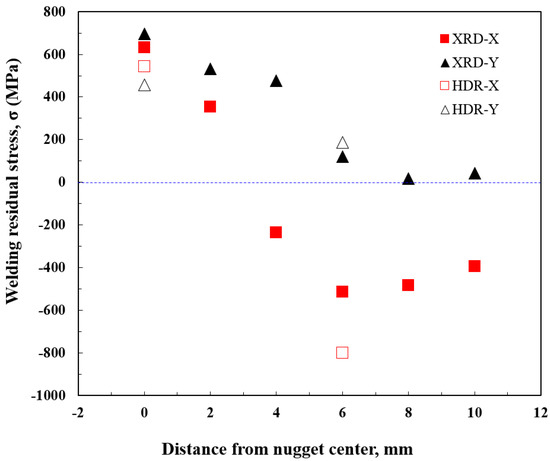
Figure 8.
Welding residual stress distribution in nugget obtained using X-ray diffraction analysis and the hole-drilling method.
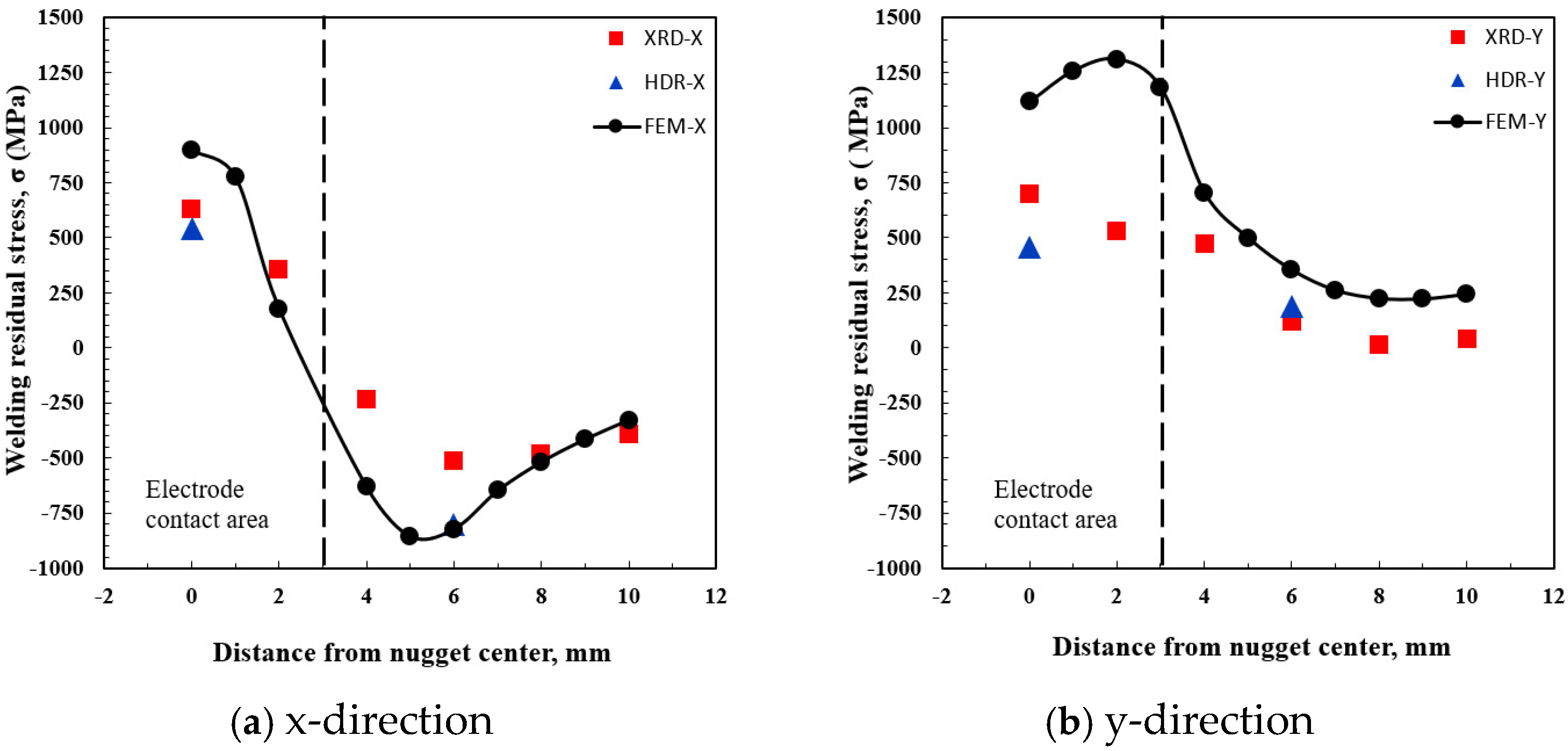
Figure 9 compares the residual stress distribution obtained through FEM analysis with the experimental results. The agreement between the experimental and numerical results was strong for the residual stress in the x-direction. However, in the y-direction, the numerical values were slightly higher than the experimental results. Despite this discrepancy, the residual stress distribution patterns were comparable. Within the nugget, the y-direction residual stress values derived from FEM analysis were higher than those obtained experimentally. Outside the nugget, the experimental and numerical values aligned closely. The observed differences in the nugget region, where the temperature was relatively high, are likely attributable to variations in material properties at elevated temperatures. In the FEM analysis, the same spot-welding conditions as in the experiment were used, and the temperature-dependent mechanical properties were predicted based on the material’s chemical composition. Overall, the FEM analysis model demonstrated strong validity and was applied in this study to conduct various examinations of the spot weld joint.
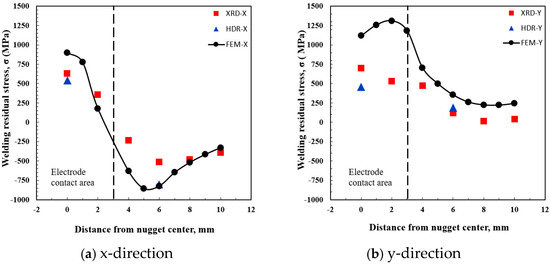
Figure 9.
Comparison of welding residual stress distribution in spot welds based on experimental and numerical results: (a) x-direction; (b) y-direction.
3.2. Residual Stress Distribution Characteristics of the Spot Weld Joint According to the Nugget Size
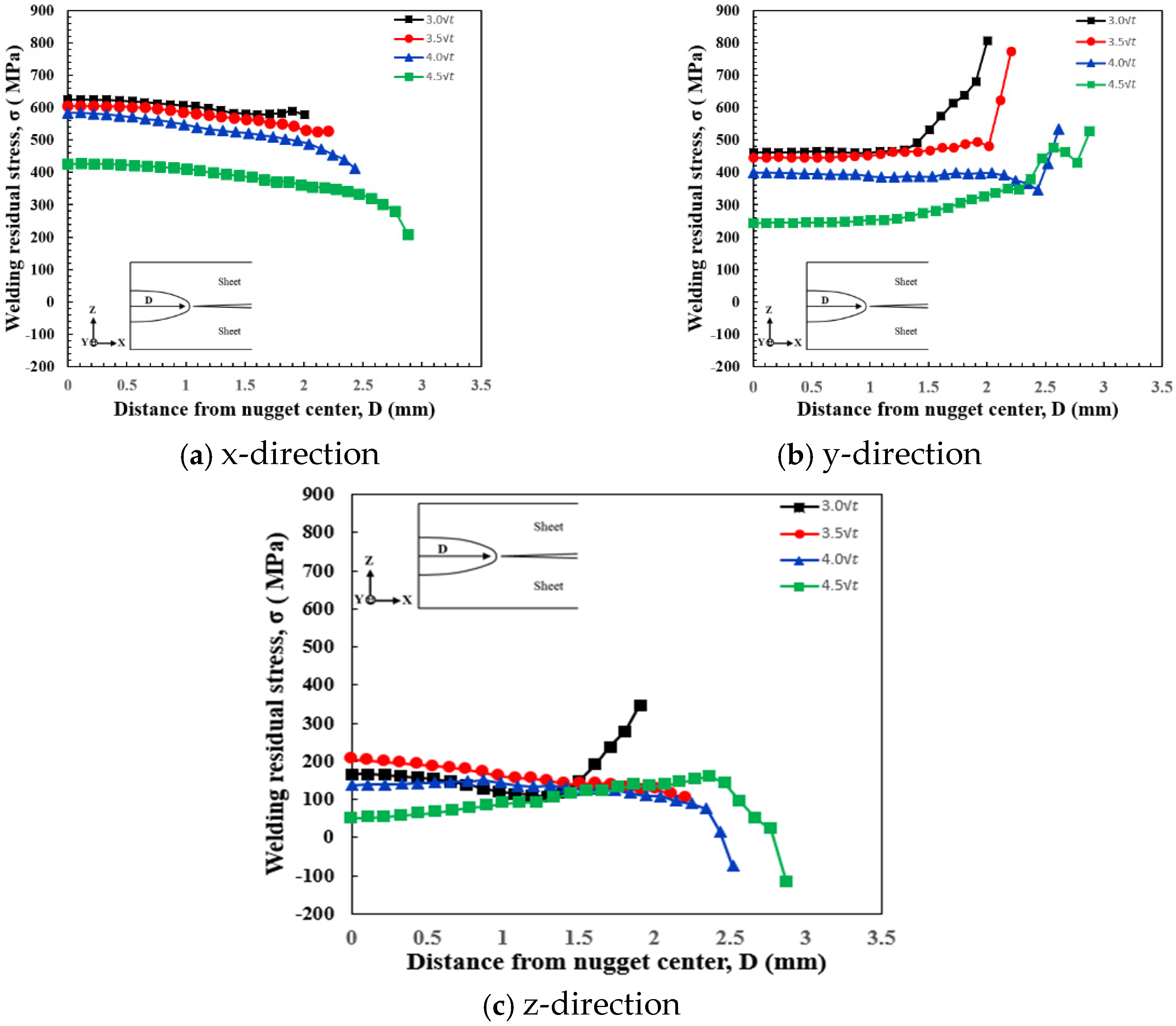
An analysis system was developed to examine the residual stress distribution characteristics of the spot welding nugget. Using this system, the residual stress distribution characteristics were analyzed in relation to variations in nugget size. The geometry of the nugget in the FEM analysis was compared to the macro section obtained through experimental procedures, and good agreement was confirmed. Four nugget sizes—, , , and —were selected for the analysis, which was conducted using identical material properties across all sizes. As increasing the nugget size requires a corresponding increase in heat input, the nugget size was varied by adjusting current conditions, consistent with the approach used in actual experiments. Residual stress was examined in the x-, y-, and z-directions, extending from the nugget center to the nugget edge. The numerical simulation results are illustrated in Figure 10, which displays the residual stress distribution along the nugget. For nugget sizes up to 4, the residual stress in all directions exhibited similar maximum values and followed the same trends. However, for the largest nugget size (4.5), the residual stress at the nugget center was slightly reduced. The analysis model included spacers on both sides, which introduced tensile forces (spring-back effects) due to the spacer. It is inferred that the tensile forces overlapped with the residual stresses induced by welding at the spot weld joint. As the nugget size decreased, the tensile stress increased, whereas the influence of pure residual stress became more dominant with larger nugget sizes. This trend was attributed to the increased stiffness of the nugget, which reduced the impact of tensile forces caused by the spacer. This phenomenon was particularly evident in the z-direction residual stress, where the tensile force was relatively pronounced. Regarding the influence of the spacer on spring-back effects, it is concluded that the level of residual stress decreases as the nugget size increases, as greater stiffness enhances resistance to spring back. An increase in nugget size correlates with a reduction in z-direction residual stress, which influences spring-back behavior. In , where spring-back effects are most pronounced, significant tensile forces are observed at the nugget periphery. As the nugget size enlarges, these tensile forces diminish, and compressive stresses become more prevalent. This trend suggests that larger nugget sizes mitigate the risk of failure by alleviating stress concentrations at the nugget boundary. This observation aligns with existing research indicating that larger weld nuggets enhance joint strength and alter stress distributions favorably [6]. For instance, studies have shown that increasing nugget diameter reduces the likelihood of interfacial failure. Additionally, larger nuggets distribute stresses more evenly, reducing peak stresses that can lead to crack initiation and propagation. Therefore, optimizing nugget size is crucial in resistance spot welding to improve joint performance and durability.
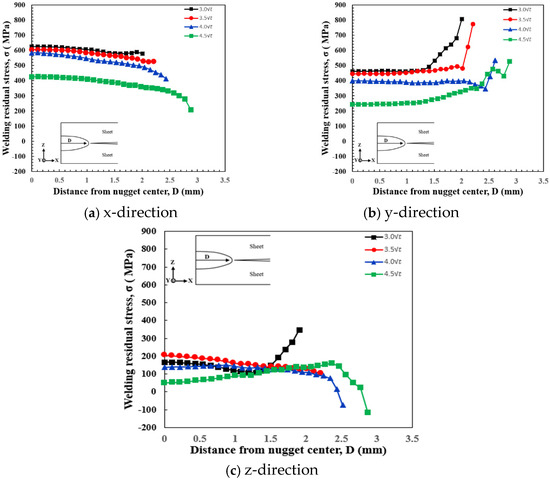
Figure 10.
Welding residual stress distribution obtained using different nugget sizes in the (a) x-, (b) y-, and (c) z-directions using FE-analysis.
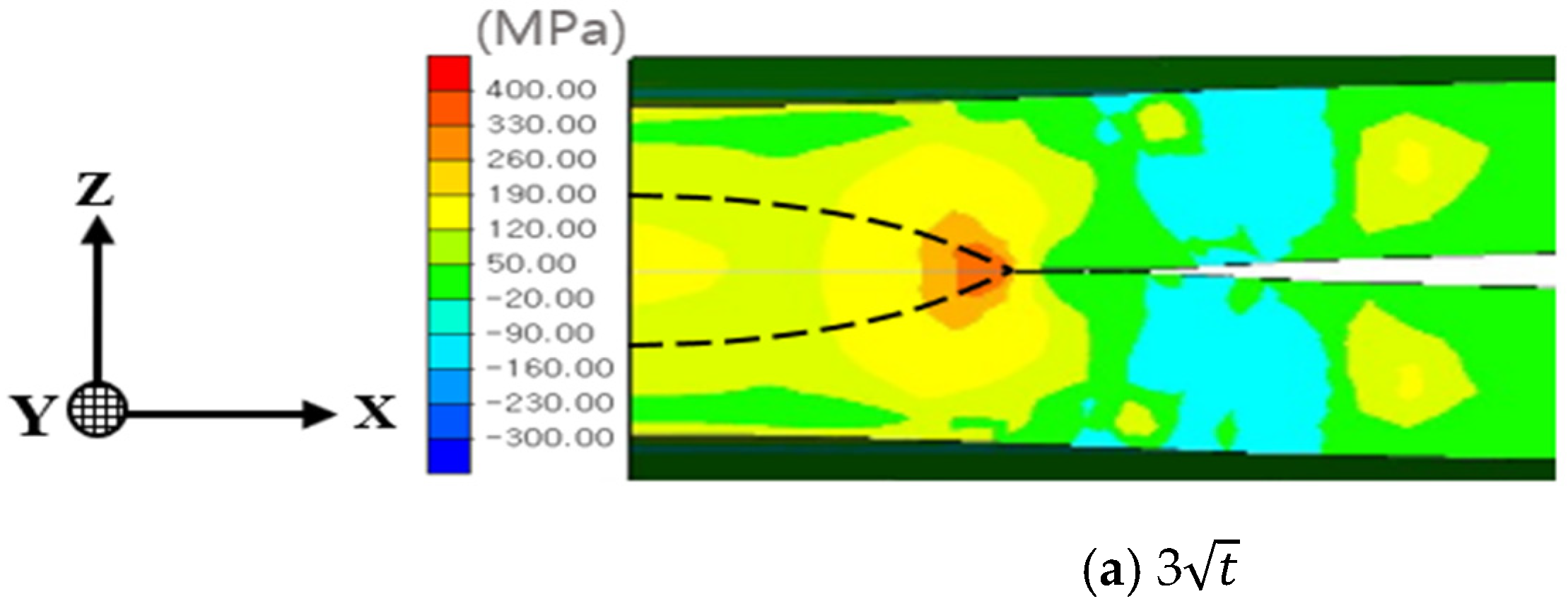
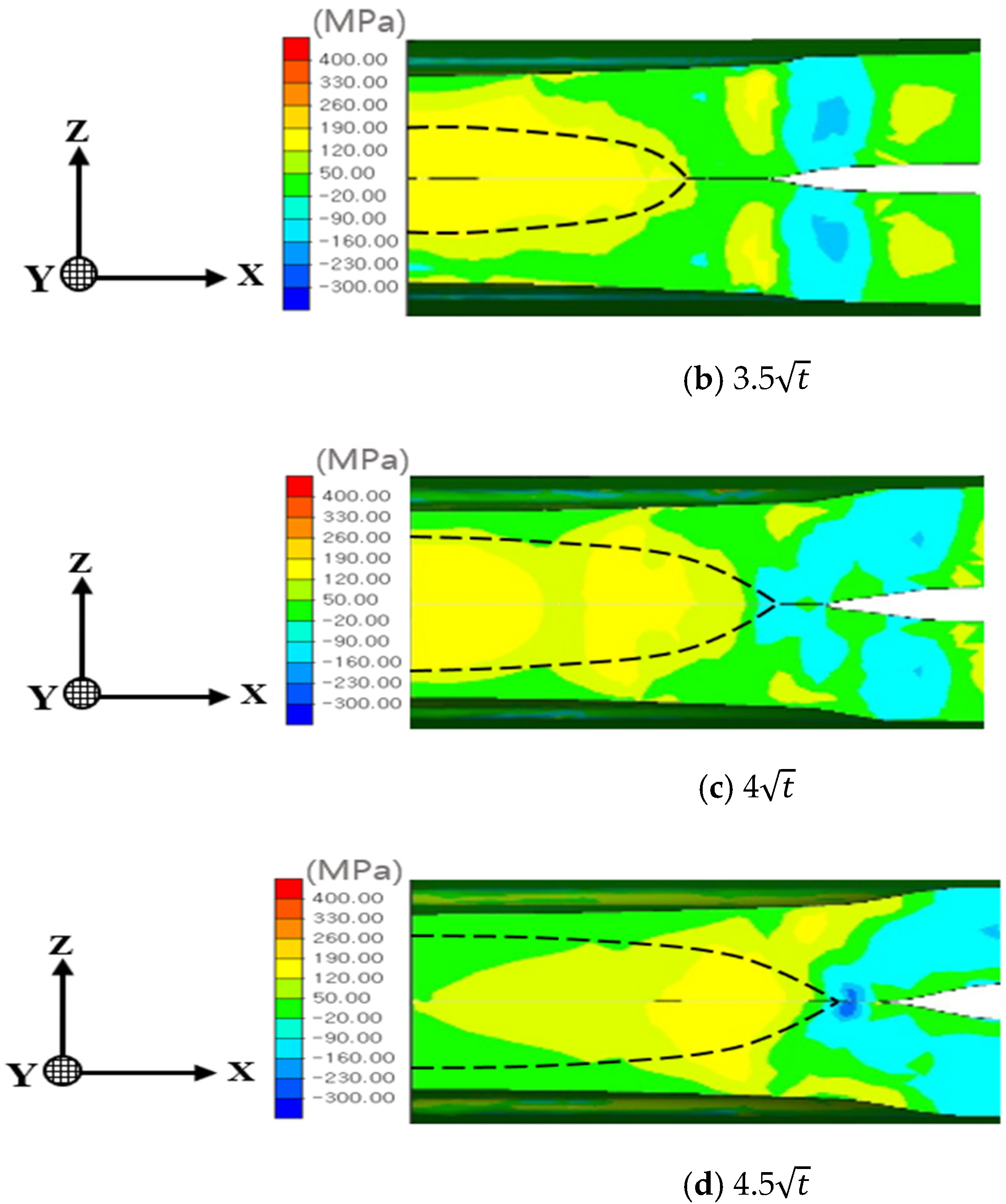
Figure 11 illustrates the z-direction stress distribution, highlighting the notch effect introduced by the spacer on nugget stress. For the 3 nugget, the stress at the nugget edge exceeded that at the nugget center. However, as the nugget size increased, the stress at the nugget edge diminished, eventually becoming lower than the stress at the center due to increased central stiffness. For nugget sizes of 4 and 4.5, the influence of welding residual stress at the nugget edge, combined with stress induced by indenter pressure, became more significant. The increased stiffness associated with larger nugget sizes mitigated the effects of spring back, thereby reducing edge stress and leading to the development of compressive stress at the nugget edge.
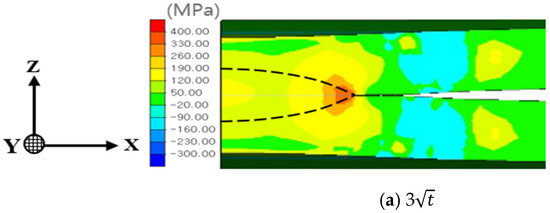
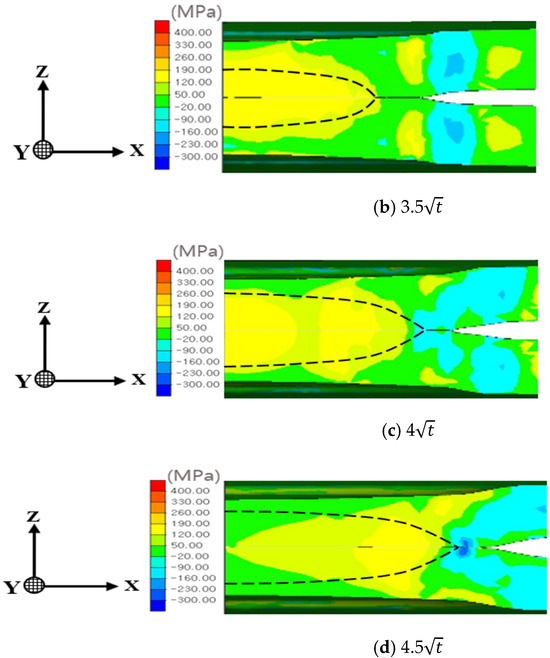
Figure 11.
Residual stress distribution in the z-direction (notch opening direction) for each nugget size: (a) 3, (b) 3.5, (c) 4, and (d) 4.5.
3.3. Residual Stress Distribution Characteristics According to Sheet Thickness
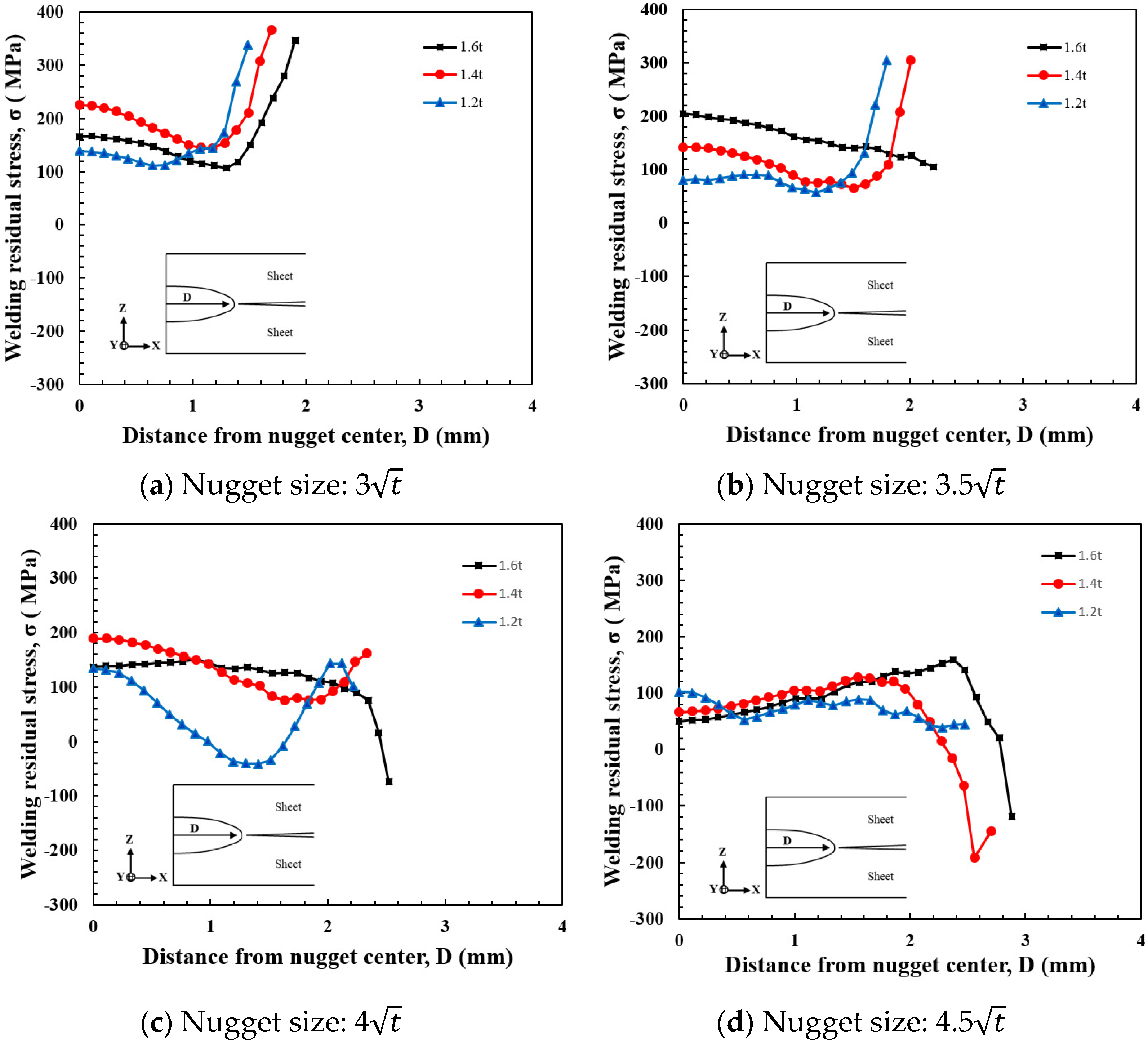
The magnitude of the residual stress distributed within the nugget varied depending on the nugget size. Additionally, the characteristics of the residual stress distribution within the nugget were examined in relation to the sheet thickness. It is believed that the stress distributed in the z-direction plays the most significant role in crack opening, and therefore, the stress distribution in this direction was specifically investigated. The sheet thicknesses selected for this study, which are commonly used in car bodies, were 1.6 mm, 1.4 mm, and 1.2 mm. Numerical analysis was performed using the same method for all three models. The results presented in Figure 12 illustrate the residual stress distribution in the z-direction (crack opening direction) from the nugget center to the nugget edge for nugget sizes of 3, 3.5, 4, and 4.5, according to the three sheet thicknesses. There was no significant difference in the maximum stress at the nugget center across the varying sheet thicknesses, but the residual stress distribution at the nugget edge exhibited some differences. Compressive residual stress was observed at the nugget edge starting from a nugget size of 4 for a sheet thickness of 1.6 mm and from a nugget size of 4.5 for 1.4 mm. For a sheet thickness of 1.2 mm, tensile stress was observed at the nugget edge for all nugget sizes. The tensile stress at the nugget edge decreased as the nugget diameter increased, with an almost uniform stress distribution throughout the nugget observed for the 4.5 nugget. As the sheet thickness decreased, the impact of spring back caused by the spacer became more pronounced compared to when the sheet thickness was higher. This is likely due to the reduction in compressive stress at the nugget edge, which is caused by the indentation of the electrode edge. When the nugget size is 3 with a sheet thickness of 1.6 mm, the joint strength is low due to the smaller nugget diameter. Consequently, despite the compressive stress at the nugget edge resulting from the electrode indentation, the tensile stress caused by the spring back effect becomes dominant, leading to a larger tensile stress distribution at the nugget edge compared to the nugget center. However, when the nugget size exceeds a certain diameter (e.g., 4 and 4.5), the increased stiffness of the nugget makes the impact of the compressive stress caused by the electrode indentation more significant than that of the spring back caused by the spacer. This results in the distribution of compressive stress at the nugget edge. The examination of the stress distribution at the nugget, considering both sheet thickness and nugget diameter, revealed that tensile stress is consistently distributed at the nugget edge for the 3 nugget size, regardless of sheet thickness. If the part is subjected to a tensile load, it will be more susceptible to fracture. On the other hand, when the nugget size increases, a higher sheet thickness proves to be beneficial in ensuring fracture resistance and safety.
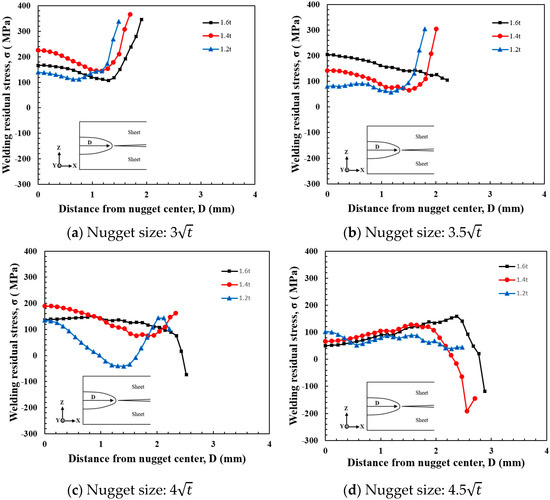
Figure 12.
Variation of opening stress(Z-direction) with sheet thickness.
3.4. Welding Residual Stress Distribution Characteristics According to the Presence/Absence of the Spacer
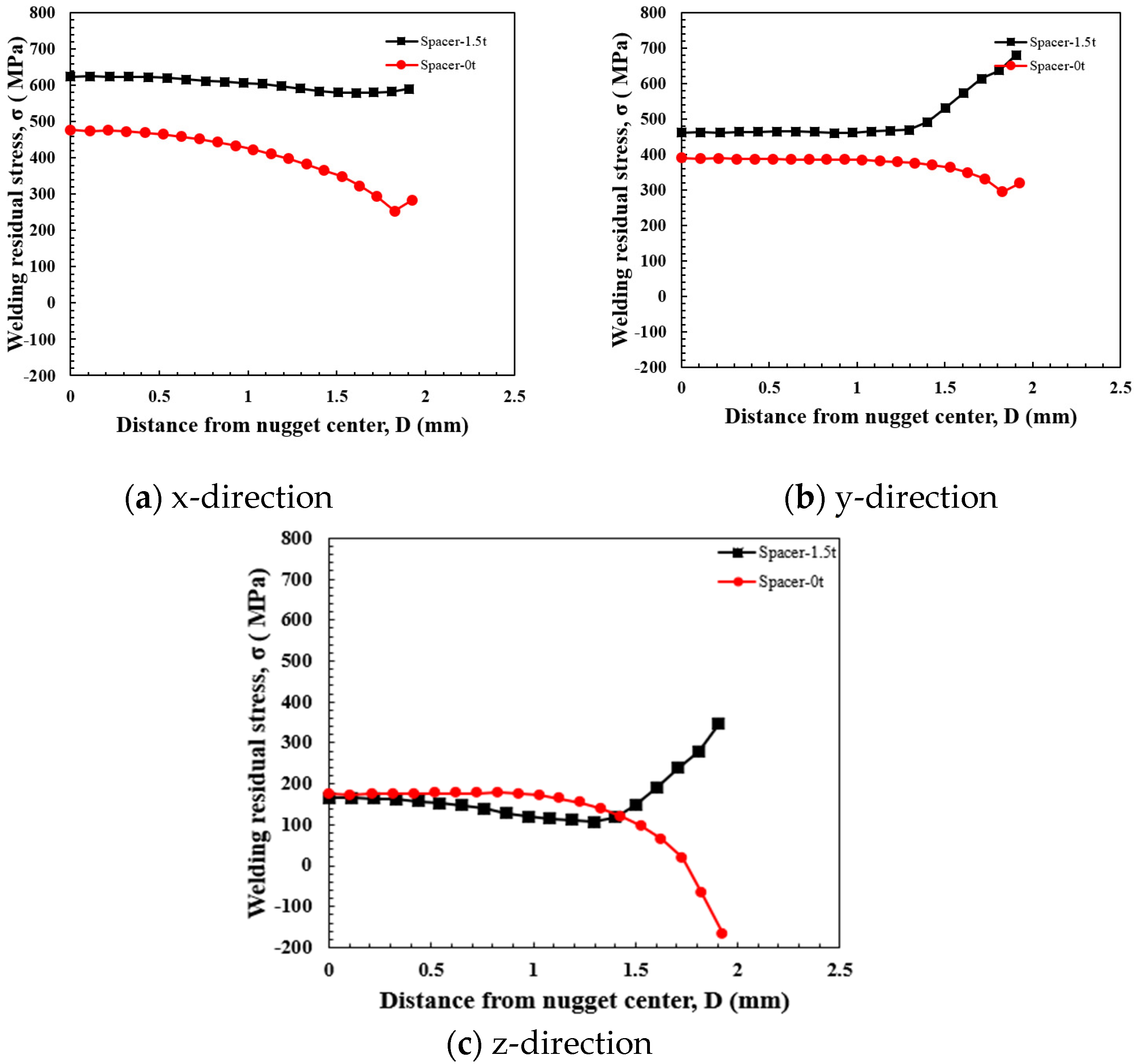
To investigate the impact of the tensile force induced by spring back on the nugget when spot welding is performed with a spacer inserted between the sheets, the residual stress distribution characteristics were examined based on the presence or absence of the spacer. The spacer used had a thickness of 1.5 mm, and a nugget size of 3 was selected for the analysis. Figure 13 presents the residual stress distribution from the nugget center to the edge in the x-, y-, and z-directions. In the presence of the spacer, the tensile residual stress at the nugget, resulting from spot welding, overlapped with the tensile stress caused by the spacer in all directions, leading to a larger distribution of tensile stress at the nugget center. In the z-direction, which plays a critical role in crack opening, compressive stress was observed at the nugget edge in the without of a spacer. Conversely, in the x- and y-directions, significant tensile residual stress was concentrated at the nugget center when a spacer was present. The stress distribution in the z-direction at the nugget center remained nearly unchanged regardless of the with or without of the spacer. However, tensile stress was observed near the electrode edge when a spacer was used, whereas compressive stress was induced at the nugget edge when no spacer was present [27,28,29]. These findings indicate that the spot weld joint with a spacer exhibits lower stability compared to the joint without a spacer [30]. This is likely due to the compressive stress induced by the electrode edge at the nugget edge. Therefore, it can be concluded that the joint with the spacer is less stable than the joint without it.
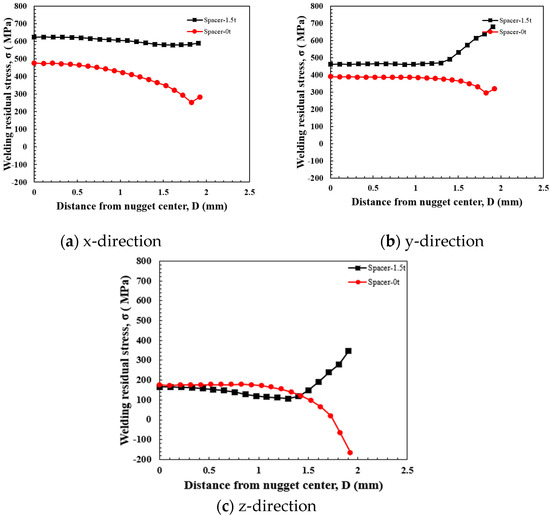
Figure 13.
Residual stress distribution in each direction with spacer (nugget size: 3).
4. Conclusions
In this study, quantitative examinations were conducted using both experimental and numerical methods to investigate the welding residual stress characteristics of recently developed high-strength steel for spot welding, which has been widely applied in automotive body construction. Additionally, the residual stress distribution characteristics of the nugget, as influenced by sheet thickness and nugget size, as well as the effects of the presence or absence of the spacer, were examined. The following conclusions were drawn.
When the residual stress of the spot weld joint was measured at both the nugget center and the affected area, based on nugget size, using the XRD and HDR methods, it was found that tensile residual stress, lower than the yield stress, was distributed at the nugget center. Furthermore, a numerical analysis system was developed to examine the residual stress distribution at the spot weld joint, yielding results in good agreement with the experimental findings.
When examining the effect of nugget size in the presence of the spacer, it was observed that the tensile residual stress at the nugget center decreased as the nugget size increased, indicating an improvement in the fracture stability of the weld joint. Regarding the distribution of residual stress in the z-direction, significant tensile residual stress was found at the nugget edge for a nugget size of 3, thereby reducing fracture stability and increasing the likelihood of fracture. However, for nugget sizes of 3.5 or larger, fracture resistance was judged to increase due to the reduction in tensile stress at the nugget edge.
Through the examination of stress changes in the nugget, based on sheet thickness and nugget diameter, it was found that tensile stress was consistently distributed at the nugget edge for a nugget size of 3, regardless of sheet thickness. Consequently, the part is expected to be vulnerable to fracture under tensile loading. However, as the nugget size increases, higher sheet thicknesses are more favorable for ensuring fracture safety.
Regarding the residual stress distribution in the nugget based on the presence or absence of the spacer, the spring back induced by the spacer generated tensile stress, leading to a larger distribution of tensile stress at the nugget edge. In the absence of the spacer, compressive stress was observed at the nugget edge. The stress level at the nugget was influenced by the spring back caused by the spacer, with its magnitude varying according to the nugget size. Specifically, the stress distribution at the nugget edge shifted from tensile residual stress to compressive residual stress as the nugget size increased.
Author Contributions
W.J. and G.A. jointly conceived and designed the experiment, performed the experiment, and conducted data analysis. G.A. and Y.M. analyzed the data, plotted the figures, and wrote this paper. I.W. provided scientific guidance. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the “Regional Innovation Strategy (RIS)” through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE) (2021RIS-002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
This is supported by POSCO project No. 20230094, Korea. Also, this work was partly performed under the Joint Usage/Research Center at the Joining and Welding Research Institute, the University of Osaka, Japan.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Insu Woo was employed by the company POSCO. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Zungia, S.; Sheppard, S. Determining the constitutive properties of the heat-affected zone in a resistance spot weld. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1995, 3, 391–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y. Ultimate strength and failure mechanism of resistance spot weld subjected to tensile, shear, or combined tensile/shear loads. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2003, 125, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslanlar, S. The effect of nucleus size on mechanical properties in electrical resistance spot welding of sheets used in automotive industry. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, B.; Rothwell, G.; English, R.; Ren, X.J. Numerical study of strengths of spot-welded joints of steel. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, M.; Kato, T.; Irie, T.; Takahashi, I. Improvement in fatigue strength of spot welded high strength sheet steel joints. Tetsu-Hagane 1982, 68, 1444–1451. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pouranvari, M.; Asgari, H.R.; Mosavizadch, S.M.; Marashi, P.H.; Goodarzi, M. Effect of weld nugget size on overload failure mode of resistance spot welds. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2007, 12, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshayedia, H.; Sattari-Fara, I. Resistance Spot Welding and the Effects of Welding Time and Current on Residual Stresses. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyota, M.; Mikami, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Ikeda, R.; Mochizuki, M. Effect of electrode force condition on nugget diameter and residual stress in resistance spot welded high-strength steel sheets. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 379, 012051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyota, M.; Mochizuki, M. Effects of welding condition on controlling the residual stress in resistance spot welds. Jpn. Weld. Soc. 2013, 31, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabe, N.; Matsuda, H.; Okita, Y.; Ikeda, R.; Mikami, Y.; Mochizuki, M. Hydrogen diffusion simulation model considering thermal and stress changes in sport welds. Weld. Int. 2019, 33, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnage, S.A.; Darling, K.A.; Rajagopalan, M.; Whittington, W.R.; Tschopp, M.A.; Peralta, P.; Solanki, K.N. Quantifying Structure-Property Relationships During Resistance Spot Welding of An Aluminum 6061-T6 Joint. Available online: https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1605/1605.04251.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2021).
- Florea, R.S.; Hubbardc, C.R.; Solanki, K.N.; Bammanna, D.J.; Whittington, W.R.; Marin, E.B. Quantifying residual stresses in resistance spot welding of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy sheets via neutron diffraction measurements. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 2358–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H.; Fukumoto, M.; Fujimoto, H.; Okamura, K.; Kikuchi, S.; Nakayama, E.; Okada, T.; Yasuyama, M. Finite element simulation of resistance spot welding process for automotive steel. Nippon. Steel Sumitomo Met. Tech. Rep. 2018, 119, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.S.; Lai, X.M. Influence of initial gap on weld expulsion in resistance spot welding of dual phase steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2010, 15, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabok, A.; Aa, E.; Basu, I.; Hosson, J.; Pei, Y. Effect of pulse scheme on the microstructural evolution, residual stress state and mechanical performance of resistance spot welded DP1000-GI steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2018, 23, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rrath, N.; Norman, D.; Mcgregor, I.; Dashwood, R.; Hughes, D. Effect of weld schedule on the residual stress distribution of boron steel spot welds. Metall. Mater. Trasactions A 2017, 48, 2900–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Huang, W.; Ma, N.; Watanabe, G.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, W. Numerical modeling from process to residual stress induced in resistance spot welding of DP980 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 3563–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkanen, J.; Vallant, R.; Kičin, M. Experimental investigation and numerical simulation of resistance spot welding for residual stress evaluation of DP1000 steel. Weld. World 2016, 60, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyota, M.; Mikami, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Ikeda, R.; Mochizuki, M. The effect of martensitic transformation on residual stress in resistance spot welded high-strength steel sheets. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577 (Suppl. S1), S684–S689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, L.; Qi, J.; Yuan, X.; Peng, J. Mechanical properties and nugget evolution in resistance spot welding of Zn–Al–Mg galvanized DC51D steel. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2023, 42, 20220243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkholz, M.; Genzel, C.; Jung, T. X-ray diffraction study on residual stress and prefred orientation in thin titanium films subjected to a high ion flux during deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 7202–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, M.; Bertini, L.; Mori, L.F. Evaluating Non-Uniform Residual Stress by the Hole-Drilling Method with Concentric and Eccentric Holes. Strain: Definition and Validation of the Influence Functions. Spec. Issue Dedic. Ital. Assoc. Stress Anal. (AIAS) 2010, 46 Pt 1, 305–405. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E915-16; Standard Test Method for Verifying the Alignment of X-Ray Diffraction Instrumentation for Residual Stress Measurement. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- ISO EN 15305; Non-Destructive Testing-Test Method for Residual Stress Analysis by X-Ray Diffraction. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- MSC. Simufact Welding Software, ver. 2022.0.1; HEXAGON: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022.
- JMatPro Sente Software, ver. 8.0; Sente Software Ltd.: Guildford, UK, 2023.
- Wang, C.; Chen, R.; Guo, S.; Zhu, M.; Xuan, F. Verification of stress transfer mechanism in fatigue crack growth under overload. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2023, 128, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Yan, B.; Wang, T.; Wu, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, M. Strain-based fracture analysis for internal surface cracks of X80 pipe girth welds. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2023, 203, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhu, M. Micromechanical Observation and Numerical imulation for Local Deformation Evolution of Duplex Stainless Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Z.; Zhen, X. Failure mechanisms and fatigue strength assessment of a low strength Cr−Ni−Mo−V steel welded joint: Coupled frequency and size effects. Mech. Mater. 2016, 100, 198–208. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).