Abstract
Emotion recognition, a rapidly evolving domain in digital health, has witnessed significant transformations with the advent of personalized approaches and advanced machine learning (ML) techniques. These advancements have shifted the focus from traditional, generalized models to more individual-centric methodologies, underscoring the importance of understanding and catering to the unique emotional expressions of individuals. Our study delves into the concept of model personalization in emotion recognition, moving away from the one-size-fits-all approach. We conducted a series of experiments using the Emognition dataset, comprising physiological and video data of human subjects expressing various emotions, to investigate this personalized approach to affective computing. For the 10 individuals in the dataset with a sufficient representation of at least two ground truth emotion labels, we trained a personalized version of three classical ML models (k-nearest neighbors, random forests, and a dense neural network) on a set of 51 features extracted from each video frame. We ensured that all the frames used to train the models occurred earlier in the video than the frames used to test the model. We measured the importance of each facial feature for all the personalized models and observed differing ranked lists of the top features across the subjects, highlighting the need for model personalization. We then compared the personalized models against a generalized model trained using data from all 10 subjects. The mean F1 scores for the personalized models, specifically for the k-nearest neighbors, random forest, and dense neural network, were 90.48%, 92.66%, and 86.40%, respectively. In contrast, the mean F1 scores for the generic models, using the same ML techniques, were 88.55%, 91.78% and 80.42%, respectively, when trained on data from various human subjects and evaluated using the same test set. The personalized models outperformed the generalized models for 7 out of the 10 subjects. The PCA analyses on the remaining three subjects revealed relatively little facial configuration differences across the emotion labels within each subject, suggesting that personalized ML will fail when the variation among data points within a subject’s data is too low. This preliminary feasibility study demonstrates the potential as well as the ongoing challenges with implementing personalized models which predict highly subjective outcomes like emotion.
1. Introduction
Emotion, a dynamic state influenced by cognitive and physiological factors, arises from stimuli such as experiences, thoughts, or social interactions. It encompasses personal experience, thought processes, behavioral impacts, physical reactions, and communication. Emotion recognition is vital in fields like marketing, human–robot interaction, healthcare, mental health monitoring, and security [1]. In healthcare, affective computing is crucial for understanding various neurological disorders, including sleep disorders [2], schizophrenia [3], sleep quality assessment [4], autism spectrum disorder [5,6], and Parkinson’s disease [7,8,9]. Emotions are also significant in identifying physiological states like fatigue, drowsiness, depression, and pain [10,11,12]. Emotions may be conveyed through a combination of facial expressions, vocalizations, gestures, and body movements [13,14,15]. This multifaceted nature of emotional expression underlines the complexity in accurately capturing and interpreting emotions through technology. Many existing works in this area rely on a one-size-fits-all emotion recognition computer vision model. However, this approach may overlook individual variations in emotional expressions and could result in less accurate assessments for certain individuals. Additionally, factors such as cultural disparities, age, and personal characteristics can influence emotional expression, posing further challenges to the effectiveness of the generic model.
Personalized models, or the creation of a separate AI model per person, offer the advantage of tailoring the emotional assessment and therapy process to each individual’s unique facial dynamics. By primarily considering the specific emotional nuances of the individual, these personalized models enhance the accuracy of emotion recognition, resulting in more effective outcomes for digital therapeutics and digital phenotyping. Prior work has demonstrated that personalization can enhance the performance of emotion recognition systems [16,17,18]. Personalized ML techniques have the potential to unlock more precise and context-aware emotion recognition capabilities compared to the traditional paradigm of using generic models.
Here, we study the personalization of emotion recognition models using a video dataset called Emognition. As a stride towards making our models explainable, we focus in this paper on the feature extraction of interpretable facial features fed into classical ML models rather than using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to automatically learn complex features. We train separate models per human subject and evaluate on that individual’s data, ensuring that all data in the training set occur earlier temporally than the evaluation set. Our findings demonstrate that the personalized models consistently outperform their baseline counterparts, which rely on data from other subjects within the dataset. This suggests the potential advantages of model personalization in optimizing the performance of applications requiring intricate and potentially subjective automated assessments for end-users. The implications of our study extend to domains where nuanced and individualized predictions play a crucial role in enhancing user experience and outcomes.
The code we used to train and evaluate our personalized and generalized models is available at Supplementary Materials part: https://github.com/aliknd/Personalized_Affective_Models_AMP_Paper (accessed on 2 December 2023).
2. Prior Work and Background
In the expansive realm of digital health, facial emotion recognition has emerged as a focal point of research, presenting an array of applications across various health domains. This dynamic field faces significant challenges rooted in the inherent subjectivity of observer perception, influenced by factors such as gender, age, and ethnicity. The intricate task of accurately interpreting the diverse spectrum of human facial expressions adds complexity to this endeavor [19,20,21].
Within this multifaceted landscape, the application of facial emotion recognition holds particular relevance in understanding and addressing health challenges faced by diverse populations. One noteworthy area is autism spectrum disorder (ASD), where individuals often encounter difficulties in recognizing and interpreting facial expressions. This unique challenge intersects with the broader complexities in facial emotion recognition, underscoring the need for nuanced approaches to cater to the diverse needs of individuals on the autism spectrum.
One family of approaches to building affective computing models involves the extraction of domain-specific features which are fed as input into classical ML models. For example, the local binary pattern (LBP) method transforms an image into a configuration of micro-patterns [22,23]. In 2009, Shan et al. [24] evaluated the effectiveness of LBP features in recognizing expressions. The results of the experiment confirmed that LBP features possess a certain level of efficiency. However, despite their usefulness, facial expression recognition methods based on LBP also suffer from challenges including low accuracy in recognition and vulnerability to interference [25]. Another feature extraction approach involves the use of Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HoG) features to recognize facial expressions. In Dahmane et al.’s study, a combination of feature extractors, such as LBP, PCA, and HoG, was used together with a SVM classifier to categorize static face images into six distinct emotions [26]. In a study conducted in 2012, Satiyan et al. [27] used Haar wavelet features along with multiscale analysis and statistical analysis to recognize facial expressions. However, the use of Haar-based facial expression recognition presents challenges, including a high rate of false recognition and the incomplete extraction of facial expression information. Another method called scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) was used by Soyel et al. [28] in 2011 to describe face pose and achieve expression recognition through the extraction of principal component information using singular value decomposition (SVD). Nevertheless, using the SIFT-based method for expression recognition faces obstacles such as limited computational efficiency and vulnerability to dimensionality problems.
An alternative strategy for recognizing facial expressions involves deep learning. In 2006, Hinton introduced the layer-by-layer training approach to tackle the complex task of training neural networks with multiple layers [29]. As a result, robust open-source learning frameworks such as Torch, Caffe, Deep Learn Toolbox, and Cxxnet were created, supported by substantial contributions from researchers and institutions. Deep learning has the capability to approximate high-dimensional data spaces, making it well suited for learning intricate functions and extracting high-dimensional feature representations from images. While initially used for object image classification, deep learning has gradually found applications in face recognition as well [15,30,31].
In 2016, Zhang and colleagues presented a new method for recognizing facial expressions that are invariant to attitude. Their approach involved combining deep learning techniques, a principal component analysis network, and CNN. Through extensive experiments on two publicly available databases, they demonstrated substantial enhancements in their method compared to traditional techniques used for expression recognition [32]. In 2017, Zhang [33] introduced in their study an algorithm for extracting facial expressions using deep learning. They conducted an analysis of the existing approaches in this field and compared different methods. The findings revealed that deep learning techniques excel at extracting hierarchical features and leveraging them for image classification based on expressions. Consequently, these methods significantly improve the recognition accuracy when compared to conventional approaches [34,35,36].
Several research studies rely on facial images as a primary focus. For instance, Wells et al. [37] used transfer learning for emotion recognition with a MobileNet model. The experimental outcomes demonstrated an accuracy of 89% and an F1 score of 87%. Similarly in 2022, Ahmed et al. [38] used three pre-trained models, including MobileNet, Xception, and Inception V3, to detect ASD based on facial features. The accuracies were 95%, 94%, and 89% for MobileNet, Xception, and Inception, respectively. Another study by Akter et al. in 2021 [39] enhanced MobileNet V1 by adding layers to improve performance, achieving a classification accuracy of 90.67%.
Various studies have also analyzed the facial images of autistic children for diverse purposes. For example, in 2021, Banire et al. [40] developed a deep learning (DL) model to recognize attention from facial analysis, achieving an 88.89% accuracy and 53.1% in terms of the ACC and AUC, respectively. Washington et al. [41] conducted a study on automated emotion classification for children using a gamified approach with the GuessWhat smartphone game. The resulting extensive pediatric emotion-centric database facilitated the training of a CNN classifier, achieving a balanced accuracy of 66.9% and an F1 score of 67.4% on the entire dataset (CAFE). Notably, in a subset with at least 60% human agreement, the classifier achieved a 79.1% balanced accuracy and a 78.0% F1 score, showcasing significant improvements over previous classifiers. Kalantarian et al. [42] conducted a study evaluating the suitability of off-the-shelf emotion classifiers from Microsoft, Amazon, Google, and Sighthound for pediatric populations, specifically children with parent-reported ASD. Using the Guess What? mobile game, 21 children with ASD engaged in social interactions, producing 2602 emotive frames for evaluation. The study revealed that while these classifiers performed well for happy emotions, their accuracy was notably poor for other emotions, indicating a need for improved training data before integrating them into AI-enabled social therapy for ASD treatment. In the context of children with ASD, several other studies use DL and CNN for diagnosis based on facial analysis. In 2020, Beary et al. [43] introduced a DL model to classify children as normal or potentially autistic, achieving an accuracy of 94.6% using the pre-trained MobileNet model. In 2021, Nagy et al. [44] compared the accuracy of responses to six emotions (neutral, sad, disgust, anger, fear, and surprise) in normal and autistic children under non-timed and timed conditions. The results indicated that children with autism are less accurate in identifying surprise and anger compared to their normal counterparts. For more comprehensive insights into emotion recognition among individuals with ASD, more expansive review papers, such as that by Rashidan et al. [45], provide detailed information.
Researchers have advocated diverse architectural modifications to CNNs, such as by incorporating the integration of attention mechanisms [46]. The visual attention mechanism enables models to concentrate on specific image regions, enhancing the overall performance. Taking inspiration from the triumph of transformer networks in natural language processing (NLP), vision transformers have been introduced. Prominent among these large transformer-based models are ViT [47], Swin [48], MobileViT [49], BiT [50], and ConvNeXt [51]. Vision transformers use attention mechanisms to encompass global context and extract intricate features from image patches. Consequently, they emerge as a promising alternative to CNNs, surmounting their challenges in feature position encoding.
Some research endeavors have harnessed transfer learning with contemporary pre-trained vision and brain transformers for ASD diagnosis. Pioneering developments in this realm involve the utilization of VGG [52,53,54] and ResNet [55,56] for ASD diagnosis.
The DEAP database [57], compiled by researchers including Koelstra from various universities, serves as a valuable resource for studying human emotional states through multi-channel data. This publicly available database contains recordings of EEG signals and physiological signals (PPS) from 32 subjects. Researchers frequently use DEAP to explore and analyze the intricate aspects of human emotions. Tang et al. [58] and Yin et al. [59] are two additional studies that used a multimodal approach to emotion recognition. Both studies used deep neural networks in conjunction with the DEAP dataset, which encompasses various modalities of data such as EEG signals and physiological signals. By leveraging these multimodal data sources, Tang et al. and Yin et al. aimed to enhance the accuracy and robustness of their emotion recognition systems. The eNTERFACE’05 dataset [60] is a widely used benchmark dataset in the field of facial expression analysis and emotion recognition. The dataset consists of synchronized video recordings of facial expressions along with corresponding emotion labels. It includes expressions of basic emotions such as happiness, sadness, anger, surprise, fear, and disgust. The dataset is valuable for developing and evaluating algorithms and models for facial expression analysis, as it provides a diverse range of facial expressions and emotions in different individuals and scenarios. Zhang et al. [61] and Nguyen et al. [62] are two notable studies that focused on the task of using the eNTERFACE’05 dataset for their respective investigations. In their work, Zhang et al. and Nguyen et al. recognized the potential of the eNTERFACE’05 dataset as a valuable resource for their study on a specific topic. By leveraging the diverse and comprehensive nature of the eNTERFACE’05 dataset, they were able to conduct in-depth analyses and draw meaningful conclusions. These studies contribute to the growing body of knowledge surrounding the eNTERFACE’05 dataset and its applicability in various domains.
Building on the foundations laid by previous research in emotion recognition, our study introduces a novel approach by focusing on the personalization of video analysis using classical ML models based on PCA features. This strategy diverges from conventional deep learning methods, presenting a distinct advantage by requiring less training data. This creates a more feasible option in scenarios with limited data availability. Moreover, PCA-based models, characterized by their reduced parameter count, are ideally suited for integration into compact health monitoring devices such as those used for digital interventions for ASD. Such an approach not only ensures computational efficiency but also enhances the interpretability of models, a key aspect of human-centered AI for healthcare.
3. Methods
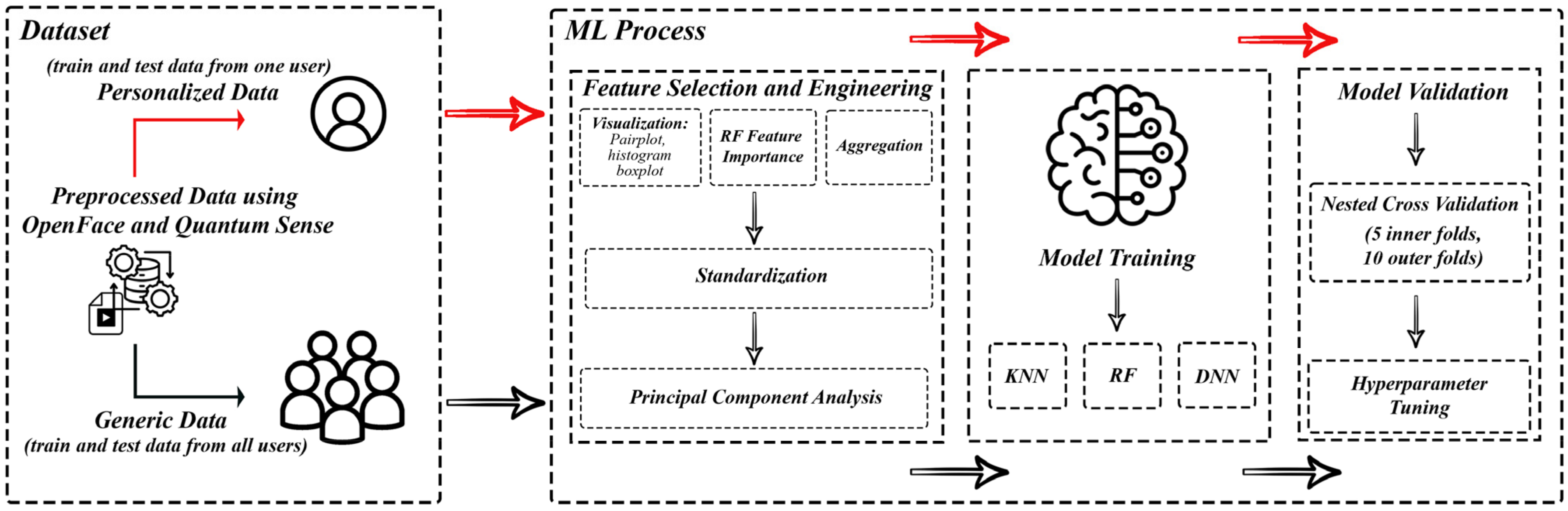
In our study, we developed personalized emotion recognition models, as depicted in Figure 1, targeting a specific subset of subjects from the Emognition dataset.
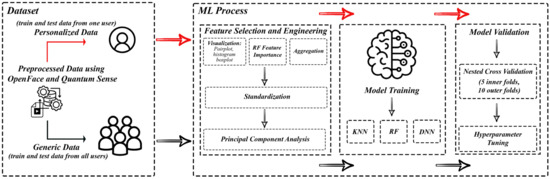
Figure 1.
Personalized vs. generic model workflow. In addition to training a traditional one-size-fits-all model, we propose the development of a single model per individual. While we evaluate this procedure for affective computing, this paradigm can be applied to precision health more broadly.
We trained three distinct ML models: k-nearest neighbors (KNN), random forest (RF), and a dense neural network (DNN). Each of these models was applied to analyze 51 extracted facial features from each video frame, ensuring a comprehensive approach to interpreting facial expressions. The facial features were carefully chosen for their interpretability and relevance in conveying emotional states. These features include key facial landmarks, expressions, and orientations, which are pivotal in differentiating between various emotions.
3.1. Emognition Dataset
The Emognition dataset [63] encompasses data from 43 subjects aged between 19 and 29, including 21 females, who were exposed to emotionally stimulating film clips specifically designed to evoke nine distinct emotions (Table 1). The short film clips were chosen from databases with established reliability and validity for eliciting targeted emotions. The duration of each clip is typically short, often ranging from a few seconds to a few minutes, to maintain participant engagement and ensure a focused emotional response. These selections were made based on prior research indicating their effectiveness in evoking specific emotional responses. Facial features were automatically extracted using the OpenFace toolkit [64] (version 2.2.0, default parameters) and Quantum Sense software (Research Edition 2017, Quantum CX, Poland). The OpenFace library provides essential facial landmark points and Action Units’ values while the Quantum Sense software identifies fundamental emotions including neutral, anger, disgust, happiness, sadness, surprise (Table 1), and head pose. The ground truth for emotions was determined through participant self-selection from a pool of nine emotions: amusement, anger, awe, disgust, enthusiasm, fear, liking, sadness, and surprise, alongside assessments of valence, arousal, and motivation.

Table 1.
The discrepancy between the emotions evoked (actual) for one demonstrative subject vs. the emotional stimulus provided (prompt). We use the emotions evoked for our ground truth labels.
We initially considered all 43 subjects from the Emognition dataset. However, a critical challenge we faced was the uneven distribution and scarcity of emotion labels across different subjects. A significant number of subjects predominantly displayed neutral expressions, leading to an inadequate representation of diverse emotions necessary even for binary classification. To address this, we established specific selection criteria, prioritizing subjects with a balanced and sufficient number of emotion labels. This process led us to focus on 10 subjects whose data not only met our criteria for label balance but also offered a fair representation of at least two distinct emotions. This decision was pivotal in ensuring the effectiveness and accuracy of our emotion recognition analysis, albeit at the cost of reducing our sample size. The selection of these 10 subjects was imperative for maintaining the integrity of our classification task, as it provided a more reliable and representative dataset for recognizing and differentiating emotional states. Because the ≥2 emotions available in the dataset varied across these 10 subjects, we performed different classification tasks based on the label population for each emotion, ranging from binary classification to the classification of all six emotion labels.
3.2. Data Preprocessing and Arrangement
We observed varying elicited emotional expressions across subjects. For example, some individuals had no labels for certain emotion stimulus videos (e.g., no anger labels for anger video, no surprise label for surprise video, etc.), indicating insufficient facial expression stimulation. This disparity in label counts suggests that the threshold and manner of eliciting each emotion differ between individuals. The distribution of labels for each emotion across 9 stimulus videos and a neutral video for one demonstrative subject (no. 22) is shown in Table 1.
Notably, there were no labels for anger, surprise, and disgust emotions in subject 22′s respective video stimulus experiments. Additionally, the dataset contained only a few labels for anger and no labels for disgust at all, presenting challenges in achieving a balanced dataset for training and classification. To address this challenge, we created separate models for specific recognition tasks. To overcome the label imbalance, we collected all emotion labels specific to each discrete emotion from several video stimulus experiments into a single dataset for training each subject’s model. To mitigate the impact of imbalanced label distribution, we carefully curated emotions with a substantial number of labels for accurate and unbiased classification results. For example, for subject no. 22, we trained a model to only recognize sadness, neutral, and happiness, which were the only well-represented labels for this subject. To ensure a robust analysis, we sampled a reduced balanced subset of 1600 instances for each of the emotions for ML model training.
In contrast, for generic models, we consolidated data across all subjects, creating a “one-size-fits-all” dataset. This dataset was used to train generalized models that served as a baseline for comparison against the personalized models. The models were trained on combinations of emotions that were adequately represented across the dataset, providing a holistic view of emotion recognition across a varied population. We trained a separate model for each combination of emotions sufficiently represented by a subject (e.g., a one-size-fits-all model for happy vs. sad vs. neutral, a one-size-fits-all model for happy vs. neutral, etc.).
We refer to these approaches as the “personalized dataset” method, where datasets are tailored to individual emotional profiles, and the “generic dataset” method, where data from multiple subjects are aggregated. This distinction is crucial for our study, as it highlights the differences in model training and effectiveness between personalized and generalized emotion recognition approaches.
3.3. Feature Extraction and Selection
As a stride towards the development of interpretable models, we identified eye gaze, eye landmarks, pose landmarks, and Action Unit (AU) features which displayed the most predictive saliency. Eye gaze and landmarks consist of x, y, and z components. We aggregated features by calculating the mean values of each feature within each positional direction, resulting in a single combined feature value. To normalize the data, we implemented z-score standardization.
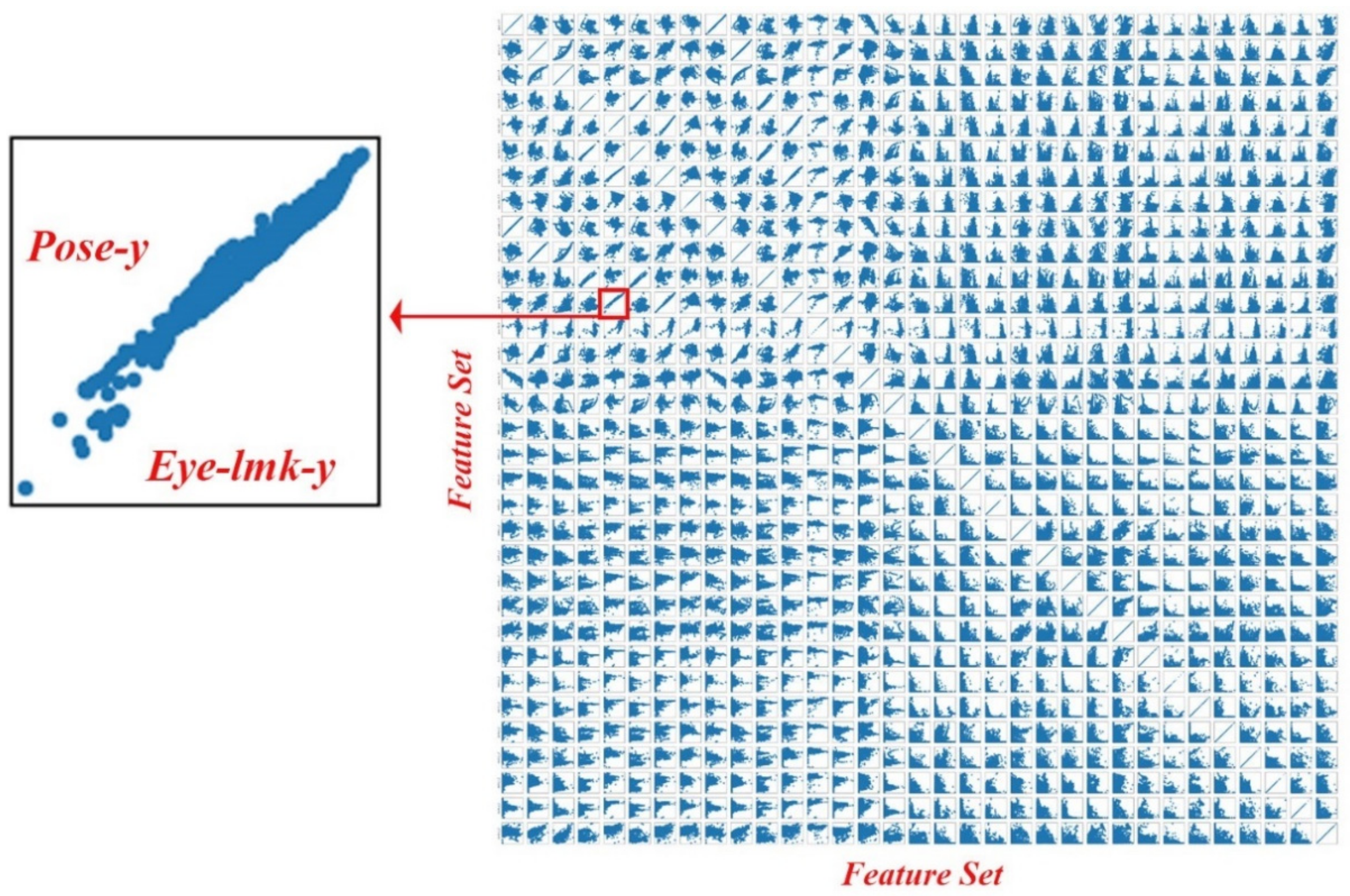
We explored the relationships between each feature and the target variable. The scatterplots for all feature combinations revealed intricate patterns, correlations, and trends, providing valuable insights for feature selection and modeling. A pairwise feature correlation matrix for a demonstrative user (Figure 2) uncovered complex data relationships, including noticeable linear and nonlinear associations between various pairs of variables, such as the average y-axis coordination values of pose and eye landmarks.
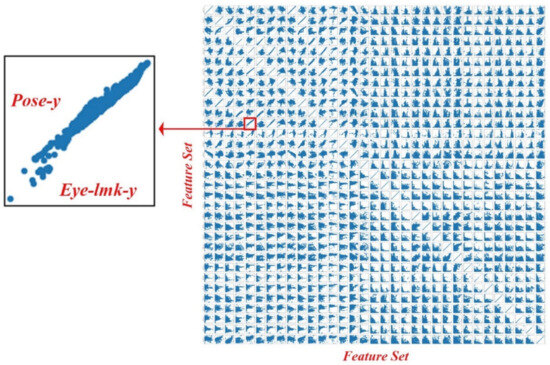
Figure 2.
Pairwise feature correlation matrix for a demonstrative subject. We plot each feature against value against every other feature to observe correlations between features.
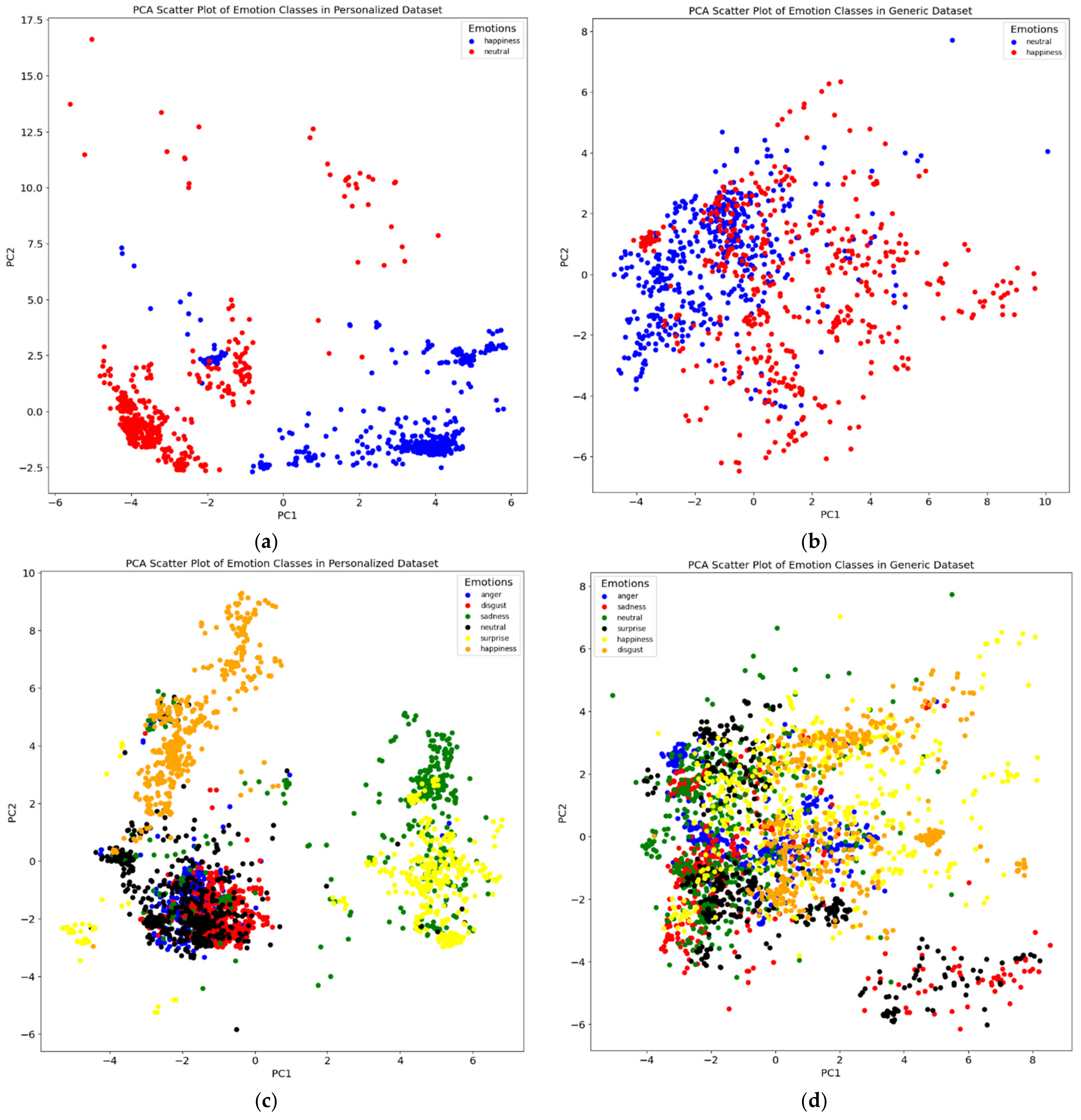
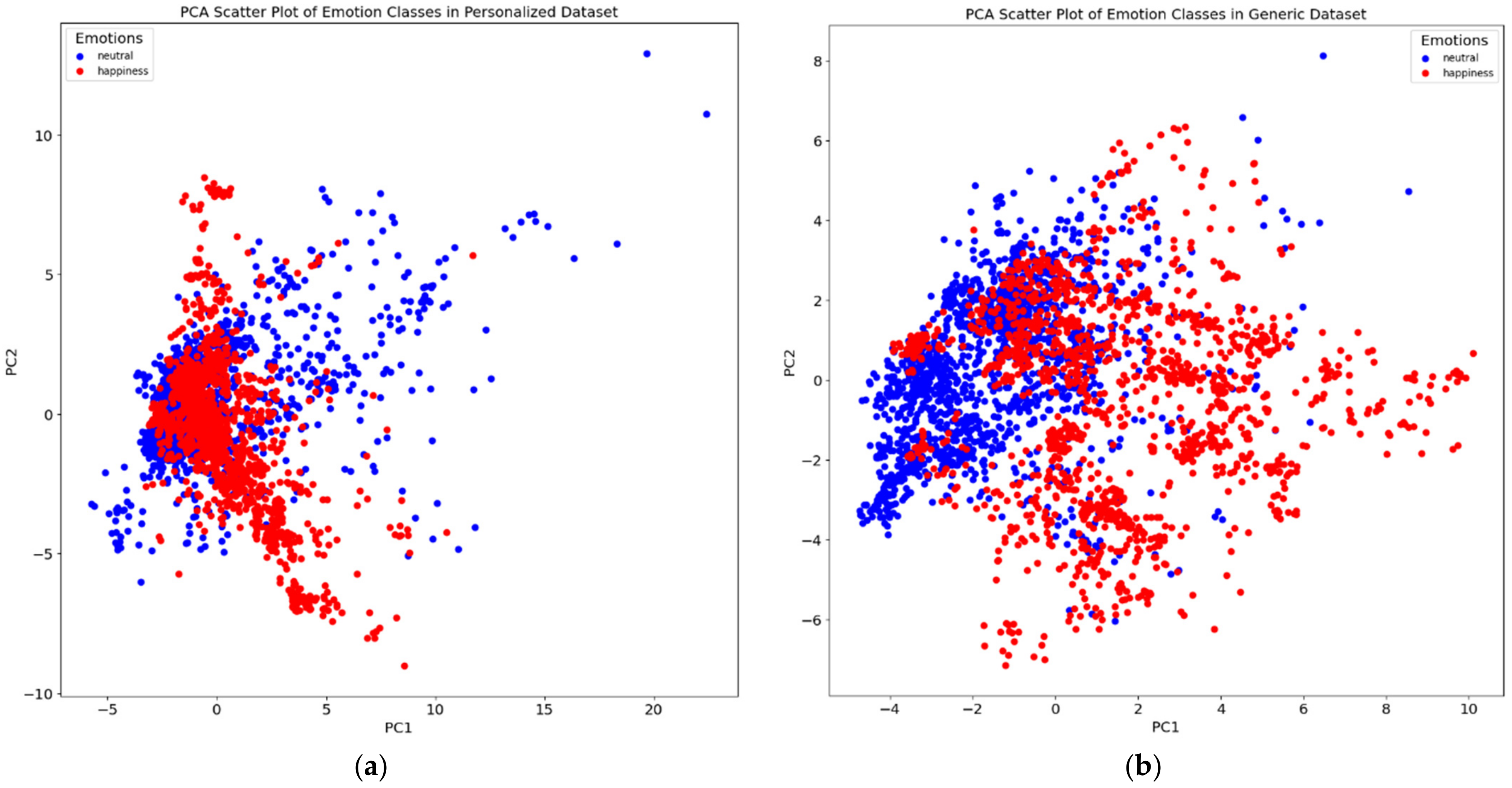
We applied principal component analysis (PCA) to the features and color-coded each data point (i.e., video frame) based on the corresponding emotion (Figure 3 displays a demonstrative example for 2 subjects. When comparing the plots for both the personalized dataset (one individual) and the generic dataset (all ten individuals), we observed a clear difference in the separation of data points relevant to each emotion class. We observe that the personalized dataset consistently yielded a better cluster visualization compared to the generic model, suggesting the potential of the downstream ML models to result in superior performance.
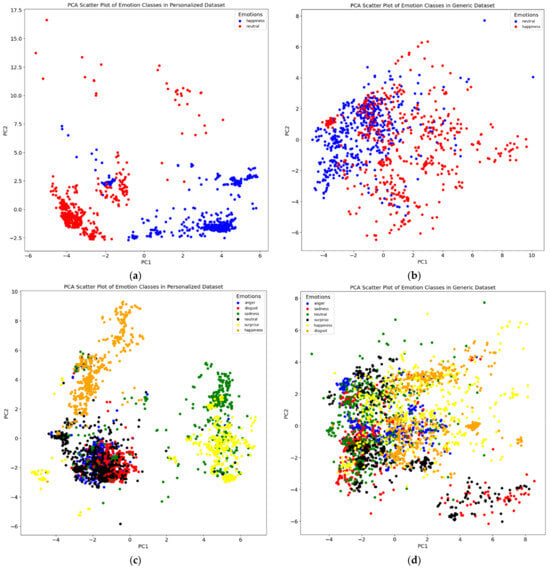
Figure 3.
PCA visualizations of the personalized dataset for two subjects (a,c) as well as the corresponding generalized dataset (b,d).
3.4. Model Selection and Evaluation
We performed a nested cross-validation procedure to simultaneously optimize hyperparameters and assess each classifier’s performance. We performed hyperparameter tuning using grid search with an inner cross-validation of 5 folds. The best model for each classifier was selected based on evaluating different sets of hyperparameters, and its performance was evaluated on the test data using 10-fold outer cross-validation. This process ensured rigorous optimization of the classifier and complete assessment of its classification performance. We used both AUC—ROC and F1 score as our primary evaluation metrics in a one-vs-rest multiclass approach.
4. Results
We conducted a comprehensive evaluation of the models, including the KNN classifier, RF, and DNN, using a rigorous procedure involving component setup, cross-validation, and performance assessment. In the personalized experiment, the KNN model achieved an average F1 score of 0.904, while in the generic experiment, it attained an average F1 score of 0.885. Similarly, the RF yielded average F1 scores of 0.926 and 0.917 in the personalized and generic experiments, respectively, while the MLP classifier obtained average F1 scores of 0.864 and 0.804 for the personalized and generic experiments, respectively.
We directly compare the F1 score of the personalized vs. generic models for all 10 subjects (Table 2). The personalized ML approach outperformed the general-purpose models for emotion recognition in 7 out of the 10 individuals.

Table 2.
Overall performance (F1 score) of the models in both personalized and generic approaches on the same evaluation task. Subjects whose performance in the personalized model was lower than for the generic model are highlighted in red.
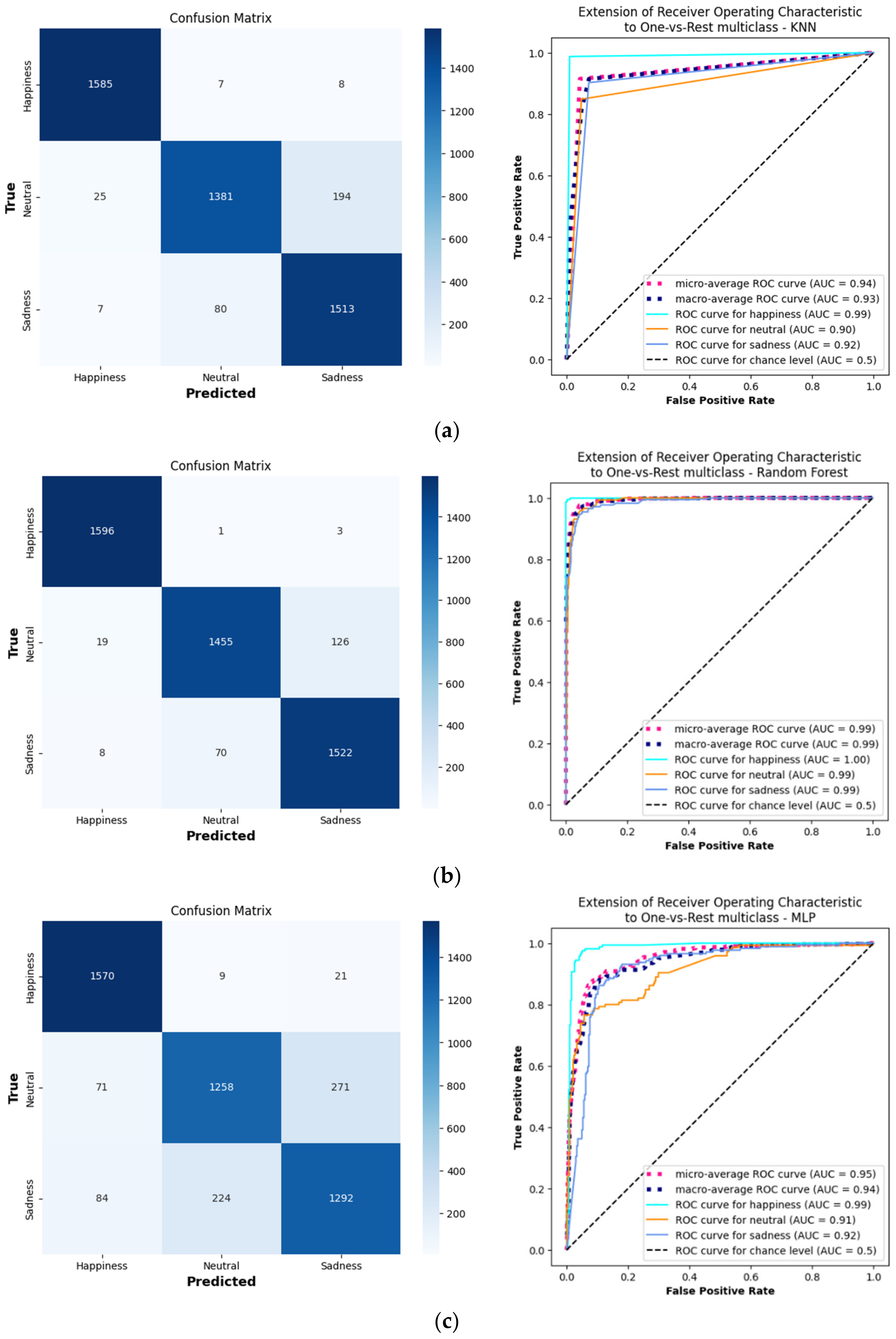
Analyzing the ROC curves and confusion matrices for a demonstrative subject (no. 22) provides insights into the personalized models’ classification capabilities (Figure 4). Retaining the best hyperparameter combinations aided in identifying the optimal settings and understanding the model’s behavior.
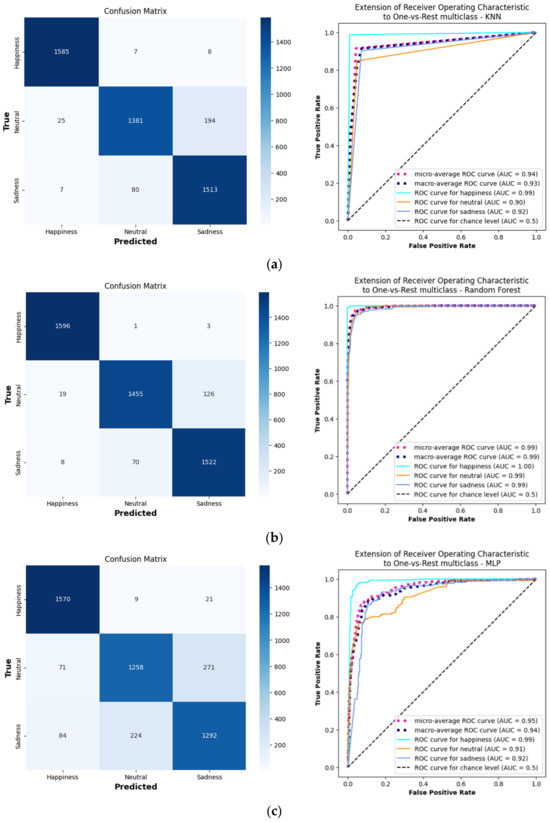
Figure 4.
Confusion matrices and ROC curves for 3 separate models, (a) KNN, (b) RF, and (c) DNN, each trained and evaluated on a demonstrative subject, no. 22.
In certain instances, the performance of the personalized models did not surpass that of the generic models (Table 2). To investigate this discrepancy, we analyzed the PCA plots for these individuals. The PCA plots revealed that the data points representing the emotional states did not form distinct clusters for these subjects, especially with respect to the separation of the generalized dataset containing data from all 10 subjects (e.g., Figure 5). Consequently, it is foreseeable that personalized models might encounter difficulty in accurately discerning individual emotional states compared to generic models in cases where the individual makes relatively little variation in their facial movement across emotions. The enhanced performance of generalized models in cases where subjects show little variation in emotional expressions can be attributed to their training on a more diverse range of data, which helps in better recognizing subtle emotional differences. Personalized models may struggle with these subtleties due to overfitting to specific, non-distinct features. Additionally, generalized models, being less sensitive to individual variability and noise in the data, can more effectively handle such minimal expression differences.
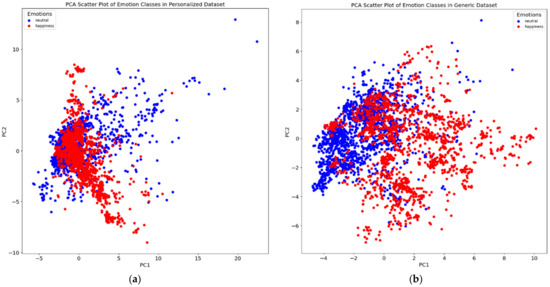
Figure 5.
PCA plot for subject no. 39, contrasting the results in a personalized dataset (a) with those in a generalized dataset (b). In (a), the PCA scatter plot shows a blend of data points for “happy” and “neutral” emotional states, indicating a significant overlap and lack of clear separability in the personalized dataset. Conversely, (b) demonstrates a clearer distinction between the two emotional states in the generalized dataset. This comparison underlines the reason for the observed lack of performance improvement in emotion classification for this subject when using a personalized approach as opposed to a generalized one.
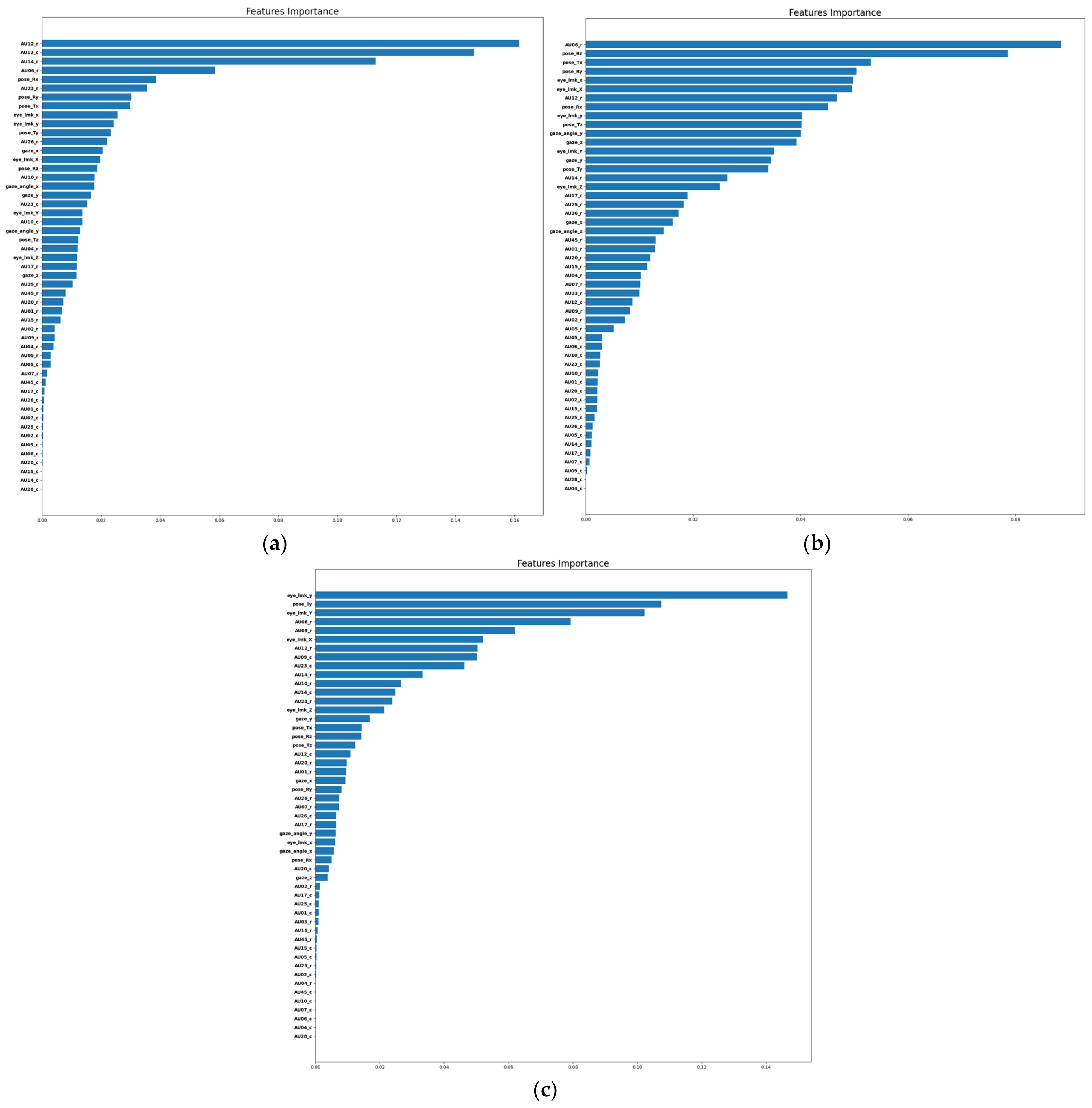
To explore the most salient features contributing to precise emotion classification, we computed the impurity-based importance of each feature of the RF model. This feature ranking approach inherently accounts for the correlations and complex nonlinear relationships between features. We plot the impurity-based importance of each feature in Figure 6 for a demonstrative set of three users whose ML models were all trained to predict happy vs. neutral. We observe that the top-ranked features across subjects vastly differ, further supporting the need for model personalization in affective computing.
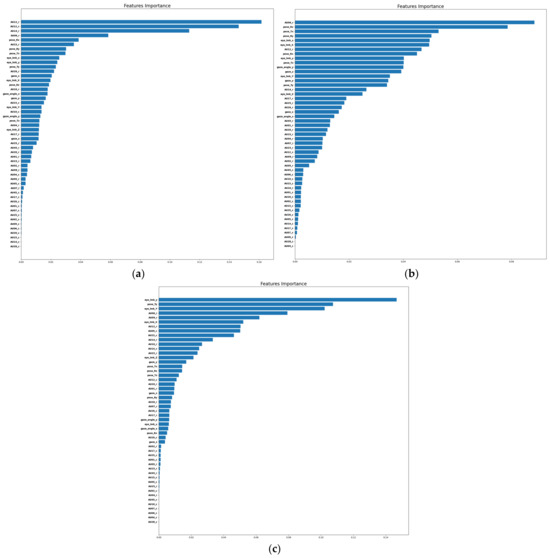
Figure 6.
Impurity-based importance of each facial feature according to the RF model for 3 subjects’ personalized models. The model for all 3 subjects is predicting happy vs. neutral. (a) The signifi-cance of features for participant 32 demonstrates that specific facial action units (AU12, AU14, AU06 etc.), specific pose parameters, eye landmarks, and gaze angles are of utmost importance for distin-guishing between the two emotional states (happy vs. neutral). (b) Participant number 39 demon-strates that AU06, certain pose and eye landmarks, among other factors, hold significant importance. (c) Similarly, participant number 40 highlights the significance of specific eye and pose landmarks, along with particular action units such as AU06 and AU09, in distinguishing between the target emotions.
In a further analysis, our personalized and generic ML models, using three distinct approaches, surpassed previous general-purpose models in emotion recognition. Table 3 offers a detailed comparison, showcasing the superior performance of our methods over past approaches.

Table 3.
Overall performance of the generic/personalized models using in this paper and previous general model on the same task (emotion recognition).
In our comparative analysis of emotion recognition approaches, we examined a range of studies across different datasets to contextualize our findings. Koelstra’s study achieved a 61.5% accuracy on the DEAP dataset using EEG and physiological signals (PPS), employing traditional signal processing techniques. Tang and Yin’s work, also on the DEAP dataset, attained an 83.5% accuracy using deep learning models that integrated EEG and PPS data, highlighting the efficacy of multimodal deep learning approaches. Nguyen’s study achieved a notable 90.85% accuracy on the eNTER-FACE’05 dataset, utilizing a combination of speech data and facial images, thereby demonstrating the potential of integrating auditory and visual cues. Zhang, using a similar dataset, achieved an accuracy of 85.97% with a focus on advanced facial expression analysis techniques. In contrast, our work with the Emognition dataset, primarily using Pose/Facial Landmarks data, yielded accuracies of 88.50% (KNN), 91.78% (RF), and 80.42% (DNN) for the generic models. Our personalized models further improved these figures to 90.48%, 92.66%, and 86.40%, respectively. These results not only underscore the effectiveness of personalized ML models in emotion recognition but also demonstrate their competitive edge in achieving high accuracy compared to generalized approaches. Our study’s reliance on Pose/Facial Landmarks data, distinct from the multimodal data used in the aforementioned studies, suggests a unique pathway in emotion recognition, relying less on physiological signals and more on visual cues.
5. Discussion
In most cases, the personalized ML approach demonstrated a slightly stronger ability to distinguish the nuances of each subject’s emotion expressions compared to the general-purpose models. In cases where an improved performance was not observed for a subject, the PCA revealed a lack of sufficient data separation for the subject’s expressions with respect to the general-purpose models. These results support the effectiveness of the personalized ML approach in classifying emotions and highlight its potential for further advancements in the field of emotion recognition. While our examination focused on model personalization within the field of affective computing, this approach can be extended to various precision health tasks where a specific characteristic (e.g., predicting stress levels [9,15,65,66]) needs to be recurrently predicted for an individual user.
In addressing the concerns of overfitting in our emotion recognition models, we used rigorous methodologies, including cross-validation, regularization, and advanced feature engineering and selection. These steps were crucial to mitigate the traditional risks of overfitting. However, it is pertinent to note that any residual model specificity, which might be perceived as overfitting in a generic context, is actually advantageous in our personalized framework. This specificity enhances the model’s ability to accurately capture and interpret the unique emotional patterns of an individual, a critical factor in the success of personalized applications. The superior performance of our personalized models, as demonstrated by higher F1 scores compared to the generalized models, underscores the effectiveness of this approach in individual-focused emotion recognition.
Although convolutional neural networks and vision transformers offer the possibility of better performance gains, we deliberately opted to use classical ML methods to prioritize the interpretability of our ML models. While these state-of-the-art models have demonstrated remarkable success in image recognition, their complex architecture often renders them as “black-box” models, making it challenging to interpret and understand the learned features influencing their predictions. By contrast, the automatic feature extraction we performed enabled us to inspect and comprehend the specific facial features that contribute to emotion recognition between subjects. Notably, we learned that the top facial features in the personalized models differed across subjects, highlighting the need for personalized ML.
Our study, while demonstrating promise for the personalized learning of relatively subjective tasks like affective computing, contains several limitations and can therefore only be considered as a feasibility study. We evaluated our method on only 10 subjects. While this experimental paradigm can be viewed as 10 independent N = 1 studies, we hope to expand this set of experiments in future work to more and larger datasets.
Both the evocation and understanding of emotional expressions play a crucial role in detecting certain types of developmental disorders. For instance, ASD affects almost 1 in 44 people in America [67], and it is the fastest-growing developmental disorder in the United States [68,69]. ASD is a multifaceted neuropsychiatric disorder that appears in diverse phenotypic forms. Children with autism tend to evoke emotions differently to their neurotypical peers, and they find it challenging to identify facial expressions conveyed by other individuals [70,71,72]. To improve the social communication of children with ASD, a variety of AI-powered mobile digital therapeutics have been developed which target emotion expression in particular [73,74,75]. These digital health innovations consist of smartphone apps and wearable devices that enable families to provide therapy in the comfort of their home setting with the ability to customize the intervention structure to suit their child’s needs [76,77,78,79]. For example, Superpower Glass [76,77] is an artificial-intelligence (AI)-powered digital therapeutic designed to aid children in understanding emotion evocations by conversation partners by providing real-time feedback from a facial expression recognition model. The therapeutic operates on a Google Glass connected to a smartphone and provides real-time social cues to children with ASD. “Guess What” [75] is another digital therapy encouraging, among other therapeutic behaviors, increased emotion expression using a Charades-style mobile game. Although considerable progress has been made in providing sensitive and specific emotion expression feedback to children using such digital health therapeutics, there remain several technical challenges that must be addressed to facilitate near-perfect performance.
Importantly, this study serves as a preliminary feasibility study, laying the groundwork for future work where we aim to apply these methodologies to a dataset collected from individuals with ASD. The success of our approach with the current non-ASD dataset bolsters our plan to replicate this experiment with a similar quality dataset from ASD individuals, thereby extending our study into more specialized and clinically relevant domains. An especially promising avenue of future work is the exploration of self-supervised pre-training to enhance the personalization capabilities of deep learning models. By pre-training deep learning models on large and diverse datasets using self-supervised learning, each personalized model can learn the baseline dynamics of each individual’s face without any training labels. These pre-trained models can then be fine-tuned with relatively few labeled examples. We note that this self-supervised learning paradigm would only be possible with a deep learning model rather than the classical ML approaches we present. There is a clear tradeoff between interpretability and performance.
The scalability and generalizability of personalized emotion recognition models to larger datasets and diverse populations is a crucial aspect in assessing their robustness and practical applicability. Personalized models, while highly effective in tailored scenarios, face challenges in scalability due to their inherent design for specific individuals’ emotional patterns. Generalizing these models to broader populations involves addressing variations in emotional expression across different demographics and cultures. Studies have shown that factors like cultural background and individual differences significantly impact emotional expressions and recognition [80,81]. This variability poses a challenge for personalized models when applied to a more heterogeneous group. Furthermore, scalability in terms of the dataset size can affect the model’s performance, as training on larger datasets might introduce a higher degree of variability and potential noise [82]. It is essential to consider these factors when expanding the scope of personalized models to ensure their effectiveness and reliability in diverse real-world applications.
The integration of real-time emotion recognition models in mobile health (mHealth) applications poses significant challenges, necessitating advancements in processing speed, energy efficiency, and system compatibility. Baltrušaitis et al. [83] emphasize the importance of rapid processing for real-time interaction, a critical aspect for responsive healthcare applications. Concurrently, energy efficiency, as explored by Kumar et al. [84], is paramount in mobile contexts to mitigate power consumption constraints. Furthermore, seamless integration with existing mHealth platforms, as discussed by Luxton [85], raises considerations around compatibility, data privacy, and user experience. Addressing these challenges is essential for the effective deployment of emotion recognition technologies in real-world mHealth scenarios.
The ethical implications and potential biases inherent in personalized emotion recognition models are critical areas for consideration in our research. As outlined in Mohammad’s Ethics Sheet [86] for Automatic Emotion Recognition and Sentiment Analysis, a comprehensive understanding of the ethical landscape is essential for researchers and practitioners in this field. This includes acknowledging the complexity and sensitivity of emotion data, and the potential risks of bias and misuse in various applications. Moreover, Katirai’s review in AI and Ethics highlights the need for ethical scrutiny in the development and application of these technologies, underscoring the importance of maintaining privacy and addressing biases that may arise from the data or algorithms used. Additionally, the work of Boyd et al. [87] on Automated Emotion Recognition in the Workplace sheds light on the specific challenges and ethical considerations of deploying these technologies in high-stakes environments like the workplace, where issues of bias, validity, and privacy are especially pronounced. These references collectively underscore the necessity for a proactive and informed approach to ethical considerations in the development and application of emotion recognition technologies, ensuring they are used responsibly and equitably.
6. Conclusions
The reliability of personalized models stems from their ability to continuously learn and adapt to the evolving emotional expression patterns of the individual user. They are often dynamic, incorporating feedback and new data over time to refine their predictions. This ongoing adaptation makes them particularly effective in applications where long-term monitoring or interaction with a specific individual is involved. In contrast, general models, while robust in diverse scenarios, may not offer the same level of ongoing customization and therefore might not be as reliable in capturing the subtle changes in an individual’s emotional expressions over time. This study marks a stride in emotion recognition research, primarily through the development and validation of personalized models within the Emognition dataset framework. Our innovative dual-dataset approach, which adeptly navigates the intricacies of individual emotional patterns, sets a new benchmark in the accuracy and applicability of emotion recognition systems. As we extend our study to encompass ASD patient datasets, our focus will intensify on the unique emotional expression characteristics and the nuanced communication challenges commonly encountered in individuals with autism. ASD is often associated with atypical nonverbal communication, including divergences in facial expressions and emotional responses. Acknowledging these unique aspects, our future work will involve the careful integration of these specialized needs into the design and optimization of our emotion recognition models. This tailoring will not only enhance the applicability and effectiveness of our methods in clinical and professional settings but also promises to advance our understanding of emotional processing in ASD. By refining our models to be sensitive to the subtleties of emotional expressions in autistic individuals, we aim to contribute towards more empathetic and effective clinical tools. These tools will be instrumental in facilitating better communication and understanding between healthcare providers and individuals with ASD, ultimately leading to improved therapeutic outcomes and quality of life.
Supplementary Materials
The code and supplementary documents can be found at https://github.com/aliknd/Personalized_Affective_Models_AMP_Paper, accessed on 2 December 2023.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K. and P.W.; methodology, A.K. and P.W.; validation, A.K. and P.W.; formal analysis, A.K.; investigation, A.K. and P.W.; resources, A.K. and P.W.; data curation, A.K.; writing—original draft, A.K.; writing—review and editing, A.K. and M.K.; visualization, A.K.; supervision, M.K. and P.W.; project administration, P.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) grant number U54GM138062 and Medical Research Award fund of the Hawai‘i Community Foundation grant number MedRes_2023_00002689.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study as results are openly available in https://github.com/aliknd/Personalized_Affective_Models_AMP_Paper, accessed on 2 December 2023. The dataset used for this study can be accessed at: https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/R9WAF4. This dataset, known as Emognition, constitutes a valuable resource for the evaluation of methodologies in emo-tion recognition (ER) derived from physiological responses and facial expressions. It encompasses data obtained from a cohort of 43 participants who were exposed to brief film clips meticulously designed to elicit nine distinct emotions: amusement, awe, enthusiasm, liking, surprise, anger, dis-gust, fear, and sadness. Physiological recordings were conducted using three wearable devices, en-abling the capture of EEG, BVP (2x), HR, EDA, SKT, ACC (3x), and GYRO (2x) data, in conjunction with recordings of upper-body movements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kamble, K.; Sengupta, J. A comprehensive survey on emotion recognition based on electroencephalograph (EEG) signals. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 27269–27304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, C.; Wu, C. Facial Emotion Recognition in Sleep Deprivation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 2023, 36, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Garijo, J.; Lacruz, M.; Masanet, M.J.; Palop-Grau, A.; Plaza, R.; Hernandez-Merino, A.; Edo-Villamon, S.; Valllina, O. Specific facial emotion recognition deficits across the course of psychosis: A comparison of individuals with low-risk, high-risk, first-episode psychosis and multi-episode schizophrenia-spectrum disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 320, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Du, J.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, L. Insomnia and impacts on facial expression recognition accuracy, intensity and speed: A meta-analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 160, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavez, R.; Diaz, J.; Arango-Lopez, J.; Ahumada, D.; Mendez-Sandoval, C.; Moreira, F. Emo-mirror: A proposal to support emotion recognition in children with autism spectrum disorders. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 7913–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, P.; Wall, D.P. A Review of and Roadmap for Data Science and Machine Learning for the Neuropsychiatric Phenotype of Autism. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Data Sci. 2023, 6, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, M.; Murugappan, M.; Velichko, A.; Korzun, D. Entropy-Based Machine Learning Model for Fast Diagnosis and Monitoring of Parkinson’s Disease. Sensors 2023, 23, 8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelton, J.L.; Fittipaldi, S.; Fraile-Vazquez, M.; Sourty, M.; Legaz, A.; Hudson, A.L.; Cordero, I.G.; Salamone, P.C.; Yoris, A.; Ibañez, A. Thinking versus feeling: How interoception and cognition influence emotion recognition in behavioural-variant frontotemporal dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. Cortex 2023, 163, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargarandehkordi, A.; Washington, P. Personalized Prediction of Stress-Induced Blood Pressure Spikes in Real Time from FitBit Data using Artificial Intelligence: A Research Protocol. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmani, A.; Sabri, A.Q.M.; Aslan, S.; Chaieb, F.; Rameh, H.; Alfred, R.; Cohen, D. EEG-based neural networks approaches for fatigue and drowsiness detection: A survey. Neurocomputing 2023, 557, 126709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehlen, A.; Kellner, A.; Normann, C.; Heinrichs, M.; Domes, G. Reduced eye gaze during facial emotion recognition in chronic depression: Effects of intranasal oxytocin. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 159, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dildine, T.C.; Amir, C.M.; Parsons, J.; Atlas, L.Y. How Pain-Related Facial Expressions Are Evaluated in Relation to Gender, Race, and Emotion. Affect. Sci. 2023, 4, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clynes, M. Sentics: The Touch of Emotions; Anchor Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Heraz, A.; Clynes, M. Recognition of emotions conveyed by touch through force-sensitive screens: Observational study of humans and machine learning techniques. JMIR Ment. Health 2018, 5, e10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargarandehkordi, A.; Washington, P. Computer Vision Estimation of Stress and Anxiety Using a Gamified Mobile-based Ecological Momentary Assessment and Deep Learning: Research Protocol. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.V.; Grennan, G.; Zafar-Khan, M.; Alim, F.; Dey, S.; Ramanathan, D.; Mishra, J. Personalized machine learning of depressed mood using wearables. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoli, A.; Sozio, E.; Sbrana, F.; Bertolino, G.; Pallotto, C.; Cardinali, G.; Meini, S.; Pieralli, F.; Azzini, A.M.; Concia, E. Personalized machine learning approach to predict candidemia in medical wards. Infection 2020, 48, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leeuw, A.-W.; van der Zwaard, S.; van Baar, R.; Knobbe, A. Personalized machine learning approach to injury monitoring in elite volleyball players. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2022, 22, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalitharatne, T.D.; Tan, Y.; Leong, F.; He, L.; Van Zalk, N.; De Lusignan, S.; Iida, F.; Nanayakkara, T. Facial expression rendering in medical training simulators: Current status and future directions. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 215874–215891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, R.W. Affective Computing; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Picard, R.W. Affective computing: Challenges. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2003, 59, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahonen, T.; Hadid, A.; Pietikainen, M. Face description with local binary patterns: Application to face recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 2037–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, D.; Jeong, S.; Lee, J.; Park, S.H. Facial expression recognition based on local region specific features and support vector machines. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 7803–7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Gong, S.; McOwan, P.W. Facial expression recognition based on local binary patterns: A comprehensive study. Image Vis. Comput. 2009, 27, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Liu, Z. Facial expression recognition algorithm based on parameter adaptive initialization of CNN and LSTM. Vis. Comput. 2020, 36, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmane, M.; Meunier, J. Emotion recognition using dynamic grid-based HoG features. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; pp. 884–888. [Google Scholar]
- Satiyan, M.; Hariharan, M.; Nagarajan, R. Recognition of facial expression using Haar wavelet transform. J. Electr. Electron. Syst. Res. JEESR 2010, 3, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Soyel, H.; Demirel, H. Improved SIFT matching for pose robust facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG), Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–25 March 2011; pp. 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Mutlu, O.C.; Kline, A.; Surabhi, S.; Washington, P.; Wall, D.P. Training and profiling a pediatric facial expression classifier for children on mobile devices: Machine learning study. JMIR Form. Res. 2023, 7, e39917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Kargarandehkordi, A.; Mutlu, O.C.; Surabhi, S.; Honarmand, M.; Wall, D.P.; Washington, P. Computer Vision Estimation of Emotion Reaction Intensity in the Wild. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.10741. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, Y.; Mao, Q.; Gou, J.; Zhan, Y. Pose-robust feature learning for facial expression recognition. Front. Comput. Sci. 2016, 10, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T. Facial expression recognition based on deep learning: A survey. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Interactive Applications, Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Intelligent and Interactive Systems and Applications (IISA2017), Beijing, China, 17–18 June 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Huang, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, L. Facial expression recognition based on deep evolutional spatial-temporal networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 4193–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liang, X.; Liu, L.; Li, T.; Han, Y.; Vasconcelos, N.; Yan, S. Peak-piloted deep network for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 425–442. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Weng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Tong, Y.; Zhou, K. Facewarehouse: A 3D facial expression database for visual computing. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2013, 20, 413–425. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, L.J.; Gillespie, S.M.; Rotshtein, P. Identification of emotional facial expressions: Effects of expression, intensity, and sex on eye gaze. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.A.; Aldhyani, T.H.; Jadhav, M.E.; Alzahrani, M.Y.; Alzahrani, M.E.; Althobaiti, M.M.; Alassery, F.; Alshaflut, A.; Alzahrani, N.M.; Al-Madani, A.M. Facial features detection system to identify children with autism spectrum disorder: Deep learning models. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 3941049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, T.; Ali, M.H.; Khan, M.I.; Satu, M.S.; Uddin, M.J.; Alyami, S.A.; Ali, S.; Azad, A.; Moni, M.A. Improved transfer-learning-based facial recognition framework to detect autistic children at an early stage. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banire, B.; Al Thani, D.; Qaraqe, M.; Mansoor, B. Face-based attention recognition model for children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2021, 5, 420–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washington, P.; Kalantarian, H.; Kent, J.; Husic, A.; Kline, A.; Leblanc, E.; Hou, C.; Mutlu, C.; Dunlap, K.; Penev, Y. Improved Digital Therapy for Developmental Pediatrics Using Domain-Specific Artificial Intelligence: Machine Learning Study. JMIR Pediatr Parent 2022, 5, e26760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantarian, H.; Jedoui, K.; Dunlap, K.; Schwartz, J.; Washington, P.; Husic, A.; Tariq, Q.; Ning, M.; Kline, A.; Wall, D.P. The performance of emotion classifiers for children with parent-reported autism: Quantitative feasibility study. JMIR Ment. Health 2020, 7, e13174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beary, M.; Hadsell, A.; Messersmith, R.; Hosseini, M.-P. Diagnosis of autism in children using facial analysis and deep learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.02890. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, E.; Prentice, L.; Wakeling, T. Atypical facial emotion recognition in children with autism spectrum disorders: Exploratory analysis on the role of task demands. Perception 2021, 50, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidan, M.A.; Na’im Sidek, S.; Yusof, H.M.; Khalid, M.; Dzulkarnain, A.A.A.; Ghazali, A.S.; Zabidi, S.A.M.; Sidique, F.A.A. Technology-assisted emotion recognition for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) children: A systematic literature review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 33638–33653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. Mobilevit: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnikov, A.; Beyer, L.; Zhai, X.; Puigcerver, J.; Yung, J.; Gelly, S.; Houlsby, N. Big transfer (bit): General visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 491–507. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, H.; Khan, R.A. A novel machine learning based framework for detection of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 2004655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liao, H. Single volume image generator and deep learning-based ASD classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 3044–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cao, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, G.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Large-scale brain functional network integration for discrimination of autism using a 3-D deep learning model. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 687288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Cai, S.; Wang, J. Multisite autism spectrum disorder classification using convolutional neural network classifier and individual morphological brain networks. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 629630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Kumar, P.; Chen, H.; Shrivastava, A. Deep multimodal learning for the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.-S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. Deap: A database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, W.; Zheng, W.-L.; Lu, B.-L. Multimodal emotion recognition using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing: 24th International Conference, ICONIP 2017, Guangzhou, China, 14–18 November 2017; pp. 811–819. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Recognition of emotions using multimodal physiological signals and an ensemble deep learning model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 140, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, O.; Kotsia, I.; Macq, B.; Pitas, I. The eNTERFACE’05 audio-visual emotion database. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW’06), Atlanta, GA, USA, 3–7 April 2006; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, T.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Learning affective features with a hybrid deep model for audio–visual emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2017, 28, 3030–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Nguyen, K.; Sridharan, S.; Dean, D.; Fookes, C. Deep spatio-temporal feature fusion with compact bilinear pooling for multimodal emotion recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2018, 174, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saganowski, S.; Komoszyńska, J.; Behnke, M.; Perz, B.; Kunc, D.; Klich, B.; Kaczmarek, Ł.D.; Kazienko, P. Emognition dataset: Emotion recognition with self-reports, facial expressions, and physiology using wearables. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrusaitis, T.; Zadeh, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Morency, L.-P. Openface 2.0: Facial behavior analysis toolkit. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE international conference on automatic face & gesture recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Parousidou, V.-C. Personalized Machine Learning Benchmarking for Stress Detection. Master’s Thesis, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tazarv, A.; Labbaf, S.; Reich, S.M.; Dutt, N.; Rahmani, A.M.; Levorato, M. Personalized stress monitoring using wearable sensors in everyday settings. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), virtually, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 7332–7335. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, D.L.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Baio, J.; Bilder, D.; Charles, J.; Constantino, J.N.; Daniels, J.; Durkin, M.S.; Fitzgerald, R.T.; Kurzius-Spencer, M. Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2012. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2018, 65, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardhanareeswaran, K.; Volkmar, F. Introduction. Focus: Autism spectrum disorders. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon-Lipkin, E.; Foster, J.; Peacock, G. Whittling down the wait time: Exploring models to minimize the delay from initial concern to diagnosis and treatment of autism spectrum disorder. Pediatr. Clin. 2016, 63, 851–859. [Google Scholar]
- Manfredonia, J.; Bangerter, A.; Manyakov, N.V.; Ness, S.; Lewin, D.; Skalkin, A.; Boice, M.; Goodwin, M.S.; Dawson, G.; Hendren, R. Automatic recognition of posed facial expression of emotion in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, A.; Haber, N.; Voss, C.; Tamura, S.; Daniels, J.; Ma, J.; Chiang, B.; Ramachandran, S.; Schwartz, J.; Winograd, T. Toward continuous social phenotyping: Analyzing gaze patterns in an emotion recognition task for children with autism through wearable smart glasses. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakkapragada, A.; Kline, A.; Mutlu, O.C.; Paskov, K.; Chrisman, B.; Stockham, N.; Washington, P.; Wall, D.P. The classification of abnormal hand movement to aid in autism detection: Machine learning study. JMIR Biomed. Eng. 2022, 7, e33771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, P.; Voss, C.; Haber, N.; Tanaka, S.; Daniels, J.; Feinstein, C.; Winograd, T.; Wall, D. A wearable social interaction aid for children with autism. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; pp. 2348–2354. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, C.; Haber, N.; Wall, D.P. The potential for machine learning–based wearables to improve socialization in teenagers and adults with autism spectrum disorder—Reply. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantarian, H.; Washington, P.; Schwartz, J.; Daniels, J.; Haber, N.; Wall, D.P. Guess What? Towards Understanding Autism from Structured Video Using Facial Affect. J. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2019, 3, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, A.; Voss, C.; Washington, P.; Haber, N.; Schwartz, H.; Tariq, Q.; Winograd, T.; Feinstein, C.; Wall, D.P. Superpower glass. GetMobile Mob. Comput. Commun. 2019, 23, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, N.; Voss, C.; Wall, D. Making emotions transparent: Google Glass helps autistic kids understand facial expressions through augmented-reaiity therapy. IEEE Spectr. 2020, 57, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, P.; Voss, C.; Kline, A.; Haber, N.; Daniels, J.; Fazel, A.; De, T.; Feinstein, C.; Winograd, T.; Wall, D. SuperpowerGlass: A wearable aid for the at-home therapy of children with autism. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2017, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, C.; Washington, P.; Haber, N.; Kline, A.; Daniels, J.; Fazel, A.; De, T.; McCarthy, B.; Feinstein, C.; Winograd, T. Superpower glass: Delivering unobtrusive real-time social cues in wearable systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing: Adjunct, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 1218–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Elfenbein, H.A.; Ambady, N. On the universality and cultural specificity of emotion recognition: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2002, 128, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, R.E.; Garrod, O.G.; Yu, H.; Caldara, R.; Schyns, P.G. Facial expressions of emotion are not culturally universal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7241–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Pantic, M.; Roisman, G.I.; Huang, T.S. A survey of affect recognition methods: Audio, visual and spontaneous expressions. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces, Nagoya, Japan, 12–15 November 2007; pp. 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Robinson, P.; Morency, L.-P. Openface: An open source facial behavior analysis toolkit. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W. Energy-efficient machine learning on the edges. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–22 May 2020; pp. 912–921. [Google Scholar]
- Luxton, D.D. Artificial Intelligence in Behavioral and Mental Health Care; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.M. Ethics sheet for automatic emotion recognition and sentiment analysis. Comput. Linguist. 2022, 48, 239–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, K.L.; Andalibi, N. Automated emotion recognition in the workplace: How proposed technologies reveal potential futures of work. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2023, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).