A Long-Term Split-Mouth Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess Implant Treatment Outcome Using Implants with a Different Surface Roughness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
- Totally edentulous for at least four months [18];
- Presence of sufficient residual bone volume to place two implants of 4 mm in diameter and 9–11 mm in length.
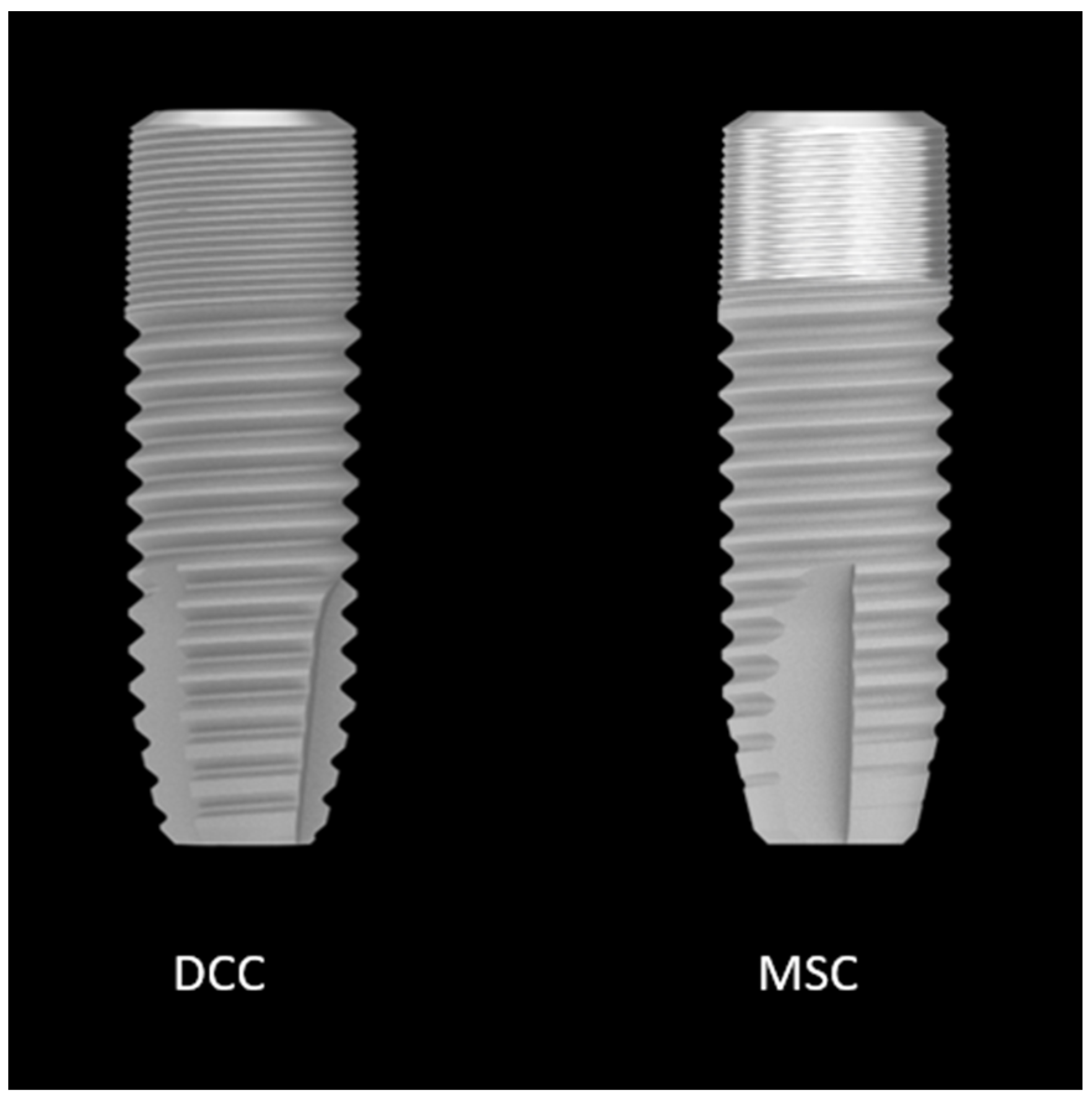
2.2. Surgical Procedure
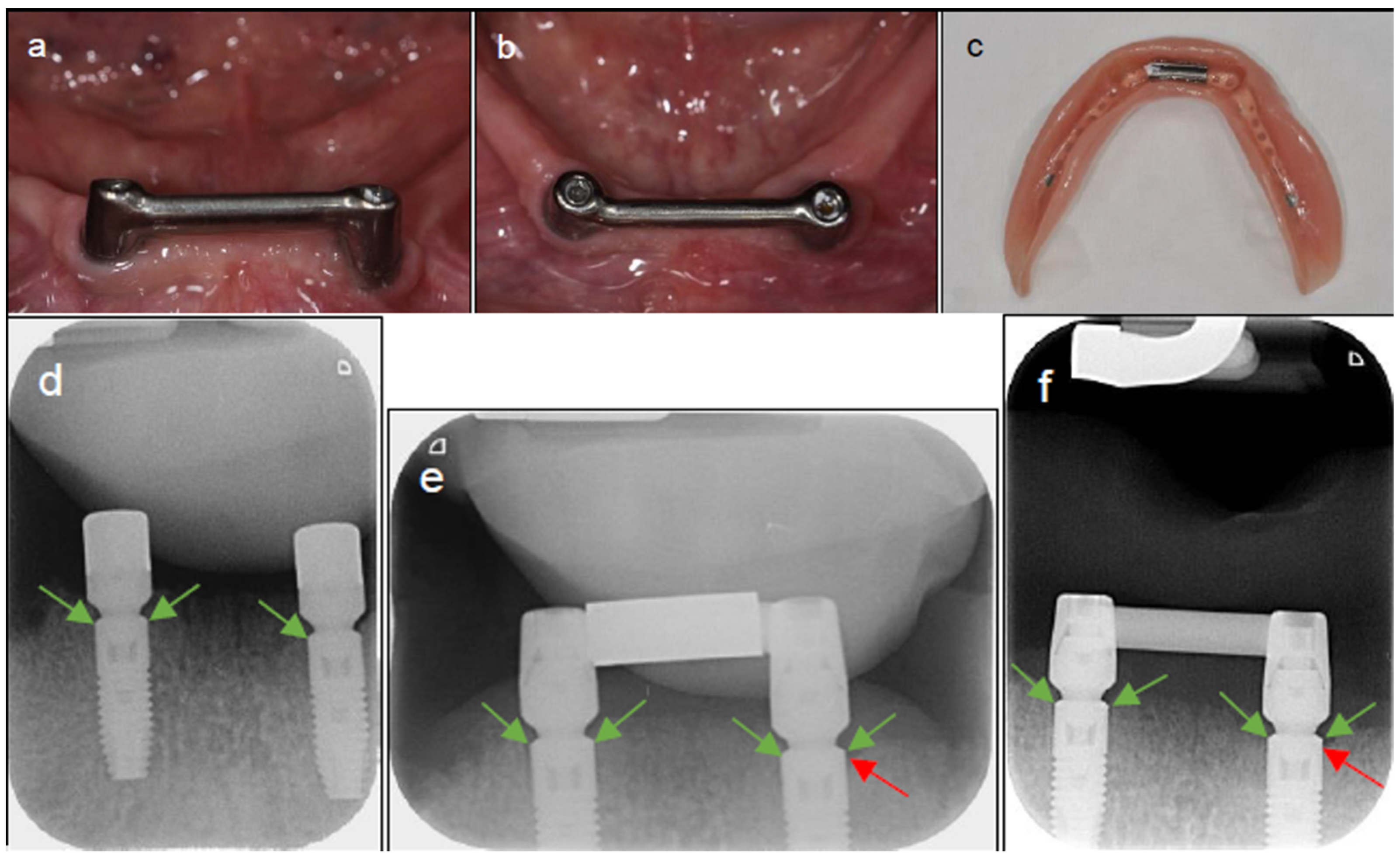
2.3. Prosthetic Procedure
2.4. Crestal Bone Loss
2.5. Peri-Implant Health
2.6. Prosthetic Functioning and Oral Health Quality of Life
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
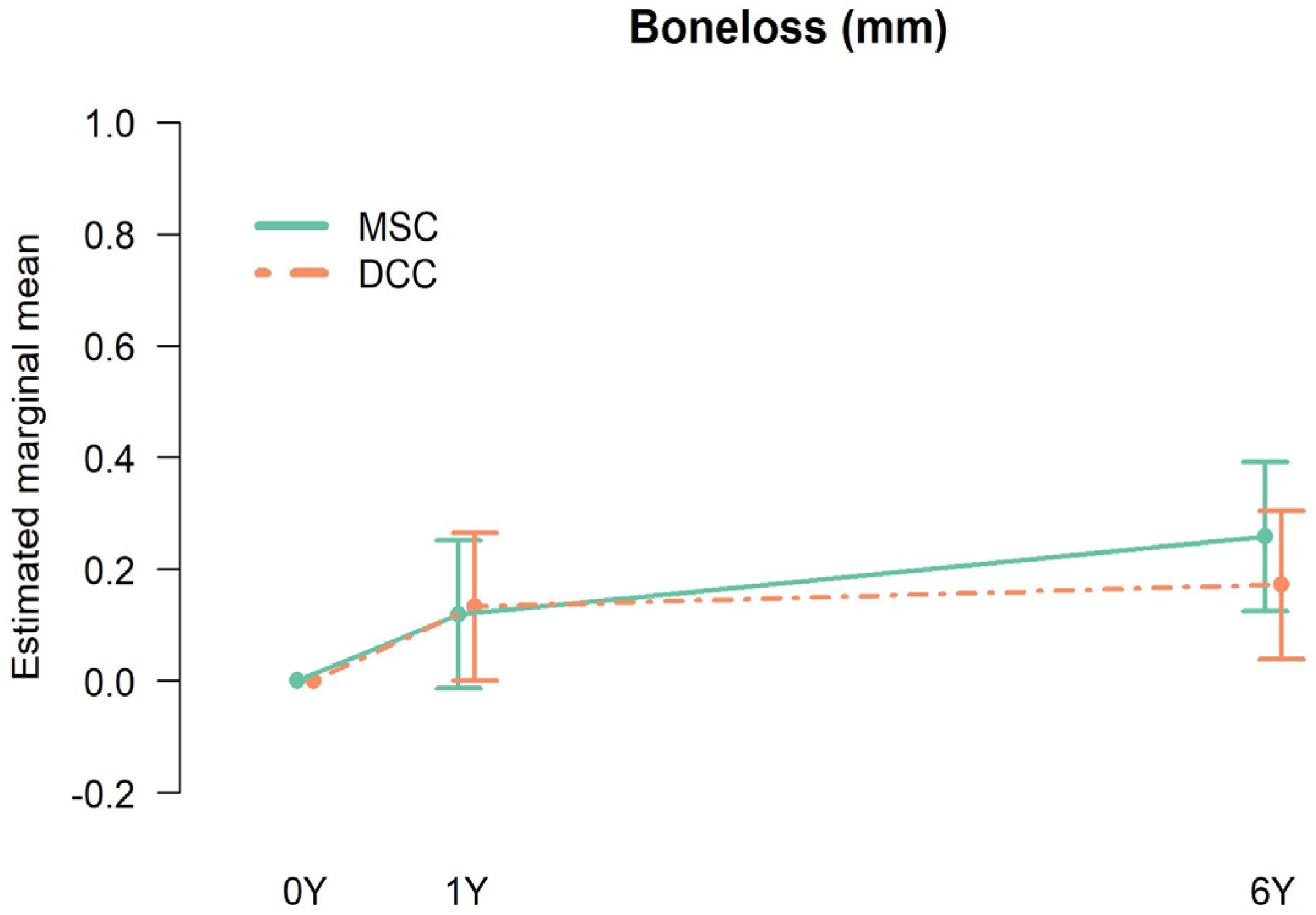
3.1. Crestal Bone Loss
3.2. Peri-Implant Health
3.3. Quality of Life
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burns, D.R. The mandibular complete overdenture. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 48, 603–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Society for the Study of Prosthetic Dentistry. The York consensus statement on implant-supported overdentures. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2009, 17, 164–165. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.J.; Saponaro, P.C. Management of Edentulous Patients. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 63, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Nagrath, R.; Lahori, M. A comparative evaluation of chewing efficiency, masticatory bite force, and patient satisfaction between conventional denture and implant-supported mandibular overdenture: An in vivo study. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2017, 17, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogle, O.E. Implant Surface Material, Design, and Osseointegration. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 59, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. On implant surfaces: A review of current knowledge and opinions. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2010, 25, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Raes, M.; D’hondt, R.; Teughels, W.; Coucke, W.; Quirynen, M. A 5-year randomized clinical trial comparing minimally with moderately rough implants in patients with severe periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnhart, C.; Dvorak, G.; Trefil, C.; Huber, C.; Watzek, G.; Zechner, W. Impact of implant surface topography: A clinical study with a mean functional loading time of 85 months. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeweghe, S.; Ferreira, D.; Vermeersch, L.; Mariën, M.; De Bruyn, H. Long-term retrospective follow-up of turned and moderately rough implants in the edentulous jaw. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetterqvist, L.; Feldman, S.; Rotter, B.; Vincenzi, G.; Wennström, J.L.; Chierico, A.; Stach, R.M.; Kenealy, J.N. A Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized-Controlled 5-Year Study of Hybrid and Fully Etched Implants for the Incidence of Peri-Implantitis. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teughels, W.; Van Assche, N.; Sliepen, I.; Quirynen, M. Effect of material characteristics and/or surface topography on biofilm development. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2006, 17, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervaeke, S.; Dierens, M.; Besseler, J.; De Bruyn, H. The influence of initial soft tissue thickness on peri-implant bone remodeling. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doornewaard, R.; Christiaens, V.; De Bruyn, H.; Jacobsson, M.; Cosyn, J.; Vervaeke, S.; Jacquet, W. Long-Term Effect of Surface Roughness and Patients’ Factors on Crestal Bone Loss at Dental Implants. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 372–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Chrcanovic, B.; Östman, P.; Sennerby, L. Initial and long-term crestal bone responses to modern dental implants. Periodontology 2000 2017, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, R.; Stadlinger, B.; Schwarz, F.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.; Jung, O.; Precht, C.; Kloss, F.; Gröbe, A.; Heiland, M.; Ebker, T. Impact of Dental Implant Surface Modifications on Osseointegration. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6285620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windael, S.; Collaert, B.; De Buyser, S.; De Bruyn, H.; Vervaeke, S. Early peri-implant bone loss as a predictor for peri-implantitis: A 10-year prospective cohort study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, M.; Matthys, C.; Maat, R.; De Bruyn, H.; Vervaeke, S. A randomized controlled clinical trial assessing initial crestal bone remodeling of implants with a different surface roughness. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donos, N.; Van Asche, N.; Akbar, A.N.; Francisco, H.; Gonzales, O.; Gotfredsen, K.; Haas, R.; Happe, A.; Leow, N.; Navarro, J.M.; et al. Impact of timing of dental implant placement and loading: Summary and consensus statements of group 1—The 6th EAO Consensus Conference 2021. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32 (Suppl. 21), 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, J.P.; Schatz, J.P.; Christou, P.; Belser, U.; Kiliaridis, S. Long-term vertical changes of the anterior maxillary teeth adjacent to single implants in young and mature adults. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2004, 31, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, I.N.R.; Amaral, G.C.L.S.D.; Hassan, M.A.; Villar, C.C.; Romito, G.A.; Spin-Neto, R.; Pannuti, C.M. The influence of smoking on the incidence of peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2023, 34, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanborg, L.M.; Andersson, M.; Wennerberg, A. Surface characterization of commercial oral implants on the nanometer level. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 92, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, H.; Vandeweghe, S.; Ruyffelaert, C.; Cosyn, J.; Sennerby, L. Radiographic evaluation of modern oral implants with emphasis on crestal bone level and relevance to peri-implant health. Periodontology 2000 2013, 62, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, G.E.; Lang, N.P. Diagnostic parameters for monitoring peri-implant conditions. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2004, 19, 116–127. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, L.A.; Peltomäki, T.; Marôco, J.; Campos, J.A.D.B. Use of Oral Health Impact Profile-14 (OHIP-14) in Different Contexts. What Is Being Measured? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, G.D. Derivation and validation of a short-form oral health impact profile. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1997, 25, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebić, A.; Knezović-Zlatarić, D. A comparison of patient’s satisfaction between complete and partial removable denture wearers. J. Dent. 2003, 31, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikicier, S.; Atay, A.; Korkmaz, C. Health-related quality of life in edentulous patients. J. Med. Life 2021, 14, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Tran, D.; Jeng, M.; Shen, Y. Survival rates of hybrid rough surface implants and their alveolar bone level alterations. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarda, A.J.; Durand, R.; Benkarim, M.; Rompré, P.H.; Guertin, G.; Ciaburro, H. Prospective randomized clinical trial evaluating the effects of two different implant collar designs on peri-implant healing and functional osseointegration after 25 years. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinato, S.; Bernardello, F.; Sassatelli, P.; Zaffe, D. Hybrid and fully-etched surface implants in periodontally healthy patients: A comparative retrospective study on marginal bone loss. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothamel, D.; Heinz, M.; Ferrari, D.; Eissing, A.; Holtmann, H.; Schorn, L.; Fienitz, T. Impact of machined versus structured implant shoulder designs on crestal bone level changes: A randomized, controlled, multicenter study. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2022, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Buser, D.; Sennerby, L. Crestal Bone Loss and Oral Implants. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; León-Cano, A.; Ortega-Oller, I.; Monje, A.; O’Valle, F.; Catena, A. Marginal bone loss as success criterion in implant dentistry: Beyond 2 mm. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, e28–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaramakrishnan, G.; Sridharan, K. Comparison of implant supported mandibular overdentures and conventional dentures on quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Aust. Dent. J. 2016, 61, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-Y.; Lee, H.-E.; Wu, Y.-M.; Lan, S.-J.; Wang, W.-C.; Du, J.-K.; Huang, S.-T.; Hsu, K.-J. Impact of removable dentures on oral health-related quality of life among elderly adults in Taiwan. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Time | Type | Mean (mm) | Lower Bound 95% CI | Upper Bound 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | DCC | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.27 |
| 1 Year | MSC | 0.12 | −0.01 | 0.25 |
| 6 Year | DCC | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.31 |
| 6 Year | MSC | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.40 |
| Test | Reference | At/With | Estimated Mean Difference | Lower Limit 95% CI | Upper Limit 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSC | DCC | 1 Year | −0.014 | −0.157 | 0.128 | 0.844 |
| MSC | DCC | 6 Year | 0.086 | −0.056 | 0.229 | 0.231 |
| 6 Year | 1 Year | DCC | 0.039 | −0.103 | 0.182 | 0.586 |
| 6 Year | 1 Year | MSC | 0.139 | −0.003 | 0.282 | 0.055 |
| Estimated Mean | Estimated Mean Difference | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plaque | DCC | 0.52; 95% CI [0.43, 0.64] | 0.01; 95% CI [−0.10, 0.12] | 0.84 |
| MSC | 0.51; 95% CI [0.41, 0.63] | |||
| Bop | DCC | 0.44; 95% CI [0.30, 0.64] | 0.02; 95% CI [−0.13, 0.17] | 0.76 |
| MSC | 0.42; 95% CI [0.29, 0.60] | |||
| PPD | DCC | 2.28; 95% CI [1.93, 2.68] | 0.23; 95% CI [−0.13, 0.58] | 0.21 |
| MSC | 2.50; 95% CI [2.04, 3.05] |
| Median baseline | Median 1 year | Median 6 year | |
| OHIP-14 | 19.50 (IQR: 9.5–24.3) | 4.0 (IQR: 2.0–8.0) | 3.79 (IQR: 0.0–5.0) |
| Median baseline | Median 1 year | Median 6 year | |
| VAS | 32.90 (SD: 9.95; range: 6.7–48.5) | 17.21 (SD: 11.68; range: 1.7–43.7) | 16.29 (SD: 12.92; range: 0–38.8) |
| Ulcer L | Loose U | Calculus | Rebasing U | Repair U | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | 37 | 4 | 3 | - | - |
| CD-1Y | 3 | 4 | 8 | - | 3 |
| 1Y-6Y | 8 | 10 | 5 | 15 | 9 |
| Total | 48 | 18 | 16 | 15 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glibert, M.; Matthys, C.; Van Lancker, A.; Segers, A.; De Bruyn, H. A Long-Term Split-Mouth Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess Implant Treatment Outcome Using Implants with a Different Surface Roughness. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041658
Glibert M, Matthys C, Van Lancker A, Segers A, De Bruyn H. A Long-Term Split-Mouth Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess Implant Treatment Outcome Using Implants with a Different Surface Roughness. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(4):1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041658
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlibert, Maarten, Carine Matthys, Aurélie Van Lancker, Amber Segers, and Hugo De Bruyn. 2024. "A Long-Term Split-Mouth Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess Implant Treatment Outcome Using Implants with a Different Surface Roughness" Applied Sciences 14, no. 4: 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041658
APA StyleGlibert, M., Matthys, C., Van Lancker, A., Segers, A., & De Bruyn, H. (2024). A Long-Term Split-Mouth Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess Implant Treatment Outcome Using Implants with a Different Surface Roughness. Applied Sciences, 14(4), 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041658





