Induction Motor Dynamics Regimes: A Comprehensive Study of Mathematical Models and Validation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Transient Process Modeling in Induction Motor
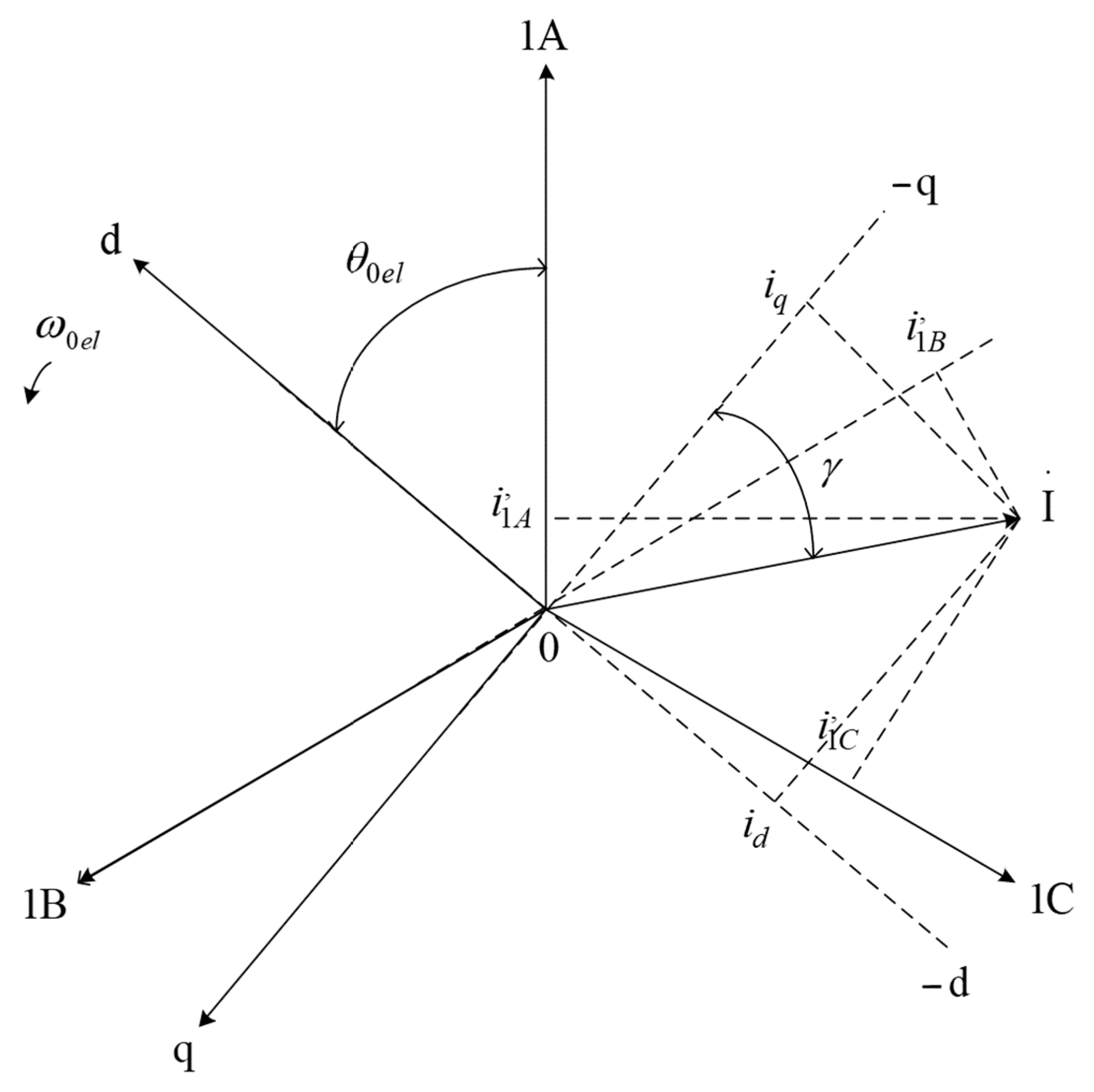
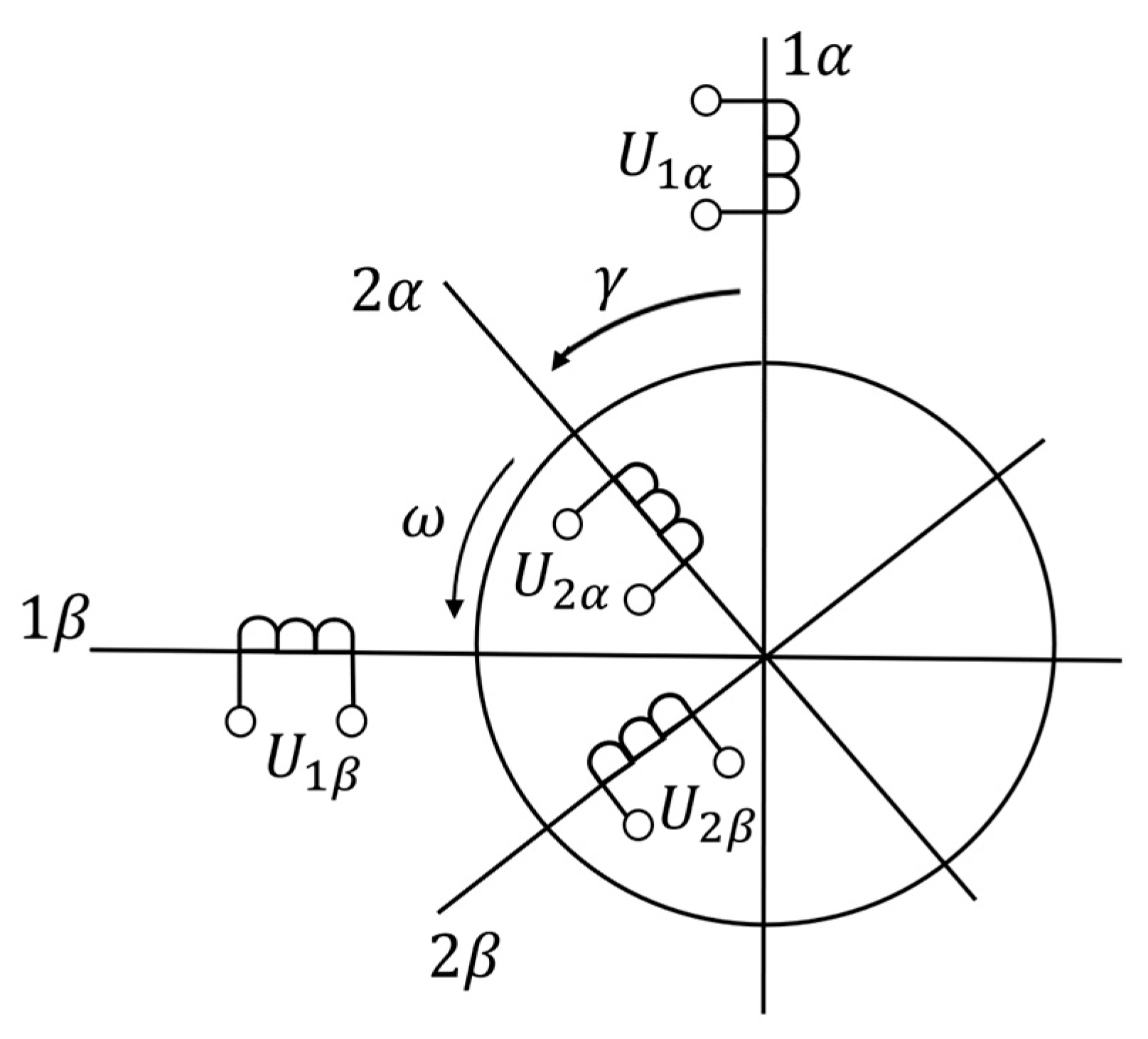
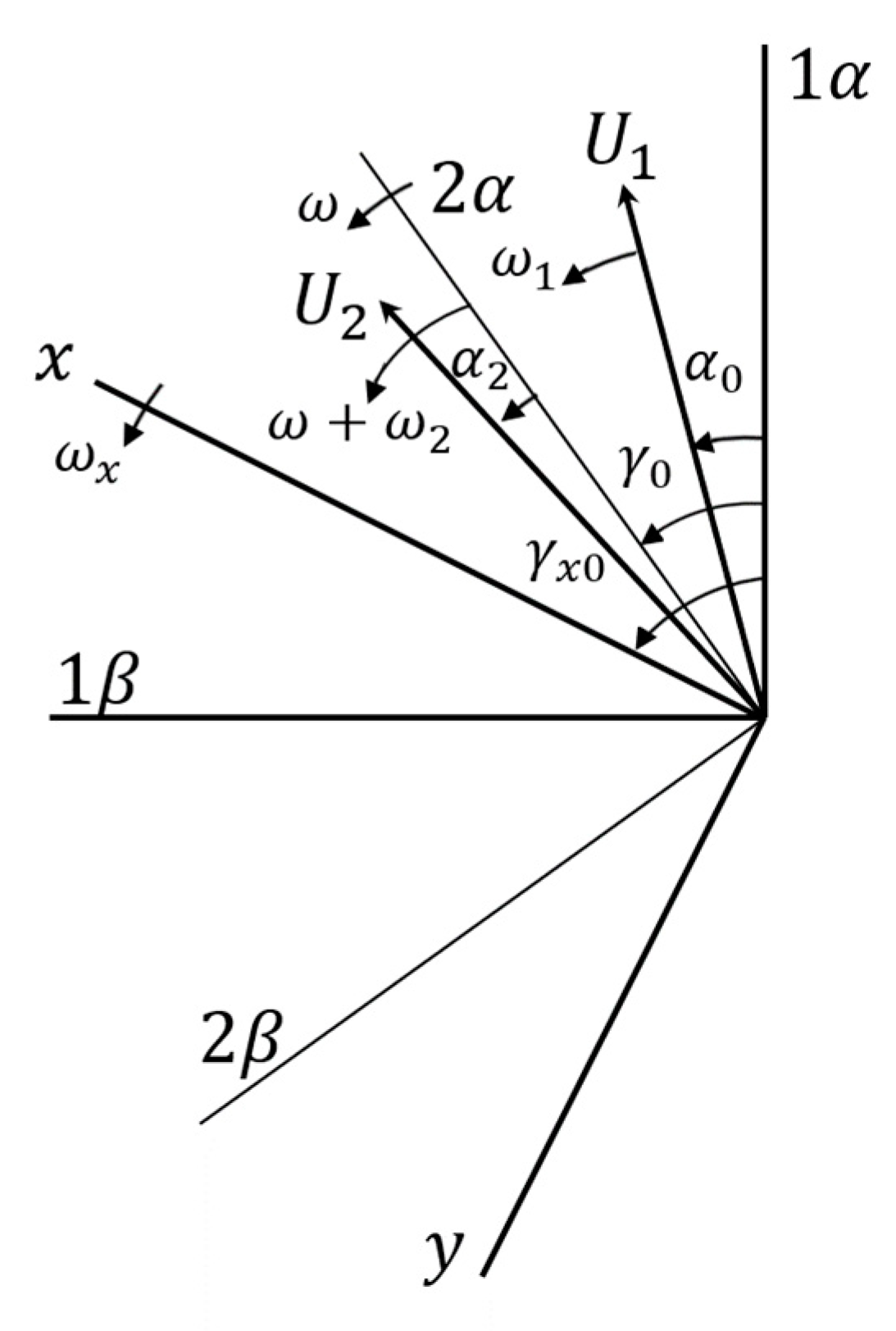
2.1. Coordinate Conversion
2.2. Generalized Electric Machine
2.3. Generalized Machine in a Common Coordinate System Rotating at Arbitrary Speed
- The rotor’s rotating windings are conceptually treated as stationary (braked); or
- The stator’s stationary windings are assumed to rotate at the same speed as the rotor.
3. Models of Induction Motors
3.1. Induction Motor Model in the αβ Coordinate System
3.2. The Model of the Induction Motor in the d,q Coordinate System
3.3. The Model of the Induction Motor in the d,q Coordinate System in Flux Linkages
3.4. Induction Motor Model in Flux Linkages with Rotor Windings Electromagnetic Time Constant in d,q Coordinate System
4. Induction Motor Starting Mode Modeling
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| t (s) | Model I | Model II | Model III | Model IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.07 | 0.067 |
| 0.05 | 0.643 | 0.643 | 0.65 | 0.625 |
| 0.1 | 1.005 | 1.005 | 1.003 | 1.011 |
| 0.15 | 1.001 | 1.001 | 1.00 | 1.004 |
| 0.2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1.00 |
| 0.25 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 0.3 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 0.35 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 0.4 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 0.45 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 0.5 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 0.55 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 0.6 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| t (s) | Model I | Model II | Model III | Model IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 5.585 | 5.585 | 5.557 | 5.647 |
| 0.05 | 4.977 | 4.977 | 4.925 | 5.087 |
| 0.1 | 0.788 | 0.789 | 0.739 | 0.707 |
| 0.15 | 0.401 | 0.402 | 0.385 | 0.405 |
| 0.2 | 0.32 | 0321 | 0315 | 0341 |
| 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.301 | 0.299 | 0.312 |
| 0.3 | 0.295 | 0.296 | 0.296 | 0.303 |
| 0.35 | 0.293 | 0.294 | 0.294 | 0.3 |
| 0.4 | 0.293 | 0.293 | 0.293 | 0.303 |
| 0.45 | 0.292 | 0.293 | 0.293 | 0.298 |
| 0.5 | 0.292 | 0.293 | 0.293 | 0.298 |
| 0.55 | 0.292 | 0.293 | 0.293 | 0.298 |
| 0.6 | 0.292 | 0.293 | 0.293 | 0.298 |
| t (s) | Model I | Model II | Model III | Model IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 2.461 | 2.460 | 2.491 | 2.392 |
| 0.05 | 1.424 | 1.424 | 1.459 | 1.34 |
| 0.1 | −0.421 | −0.421 | −0.391 | −0.481 |
| 0.15 | −0.127 | −0.127 | −0.111 | −0.161 |
| 0.2 | −0.14 | −0.14 | −0.006 | −0.031 |
| 0.25 | 0.027 | 0.027 | 0.03 | 0.019 |
| 0.3 | 0.041 | 0.042 | 0.043 | 0.038 |
| 0.35 | 0.047 | 0.047 | 0.048 | 0.045 |
| 0.4 | 0.049 | 0.049 | 0.049 | 0.048 |
| 0.45 | 0.049 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.049 |
| 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 0.55 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 0.6 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
References
- Boldea, I. Induction Machines Handbook: Transients, Control Principles, Design and Testing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, R. (Ed.) Induction Motors: Applications, Control and Fault Diagnostics; BoD–Books on Demand, InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Madhavan, S.; P B, R.D.; Gundabattini, E.; Mystkowski, A. Thermal Analysis and Heat Management Strategies for an Induction Motor, a Review. Energies 2022, 15, 8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumalo, N.S.; Memane, N.P.; Akuru, U.B. Performance and Safety Improvement of Induction Motors Based on Testing and Evaluation Standards. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2024, 8, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goman, V.; Prakht, V.; Kazakbaev, V.; Dmitrievskii, V. Comparative Study of Induction Motors of IE2, IE3 and IE4 Efficiency Classes in Pump Applications Taking into Account CO2 Emission Intensity. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, S.; Konuhova, M.; Kamolins, E.; Otankis, R. Design of magnetic couplings for bioreactors: Analytical treatment and optimization. In Proceedings of the 2018 20th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’18 ECCE Europe), Riga, Latvia, 17–21 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Suleiko, A.; Vanags, J.; Konuhova, M.; Dubencovs, K.; Grigs, O. The application of novel magnetically coupled mixer drives in bioreactors of up to 15 m3. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 154, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezrukovs, V.; Bezrukovs, V.; Konuhova, M.; Bezrukovs, D.; Kaldre, I.; Popov, A.I. Numerical Simulations of Thermodynamic Processes in the Chamber of a Liquid Piston Compressor for Hydrogen Applications. Technologies 2024, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlip, D. Hydrogen Compressor Reliability Investigation and Improvement; Cooperative Research and Development Final Report; CRADA Number CRD-13-514 (No. NREL/TP-5400-66027); National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bezrukovs, V.; Bezrukovs, V.; Konuhova, M.; Bezrukovs, D.; Berzins, A. Hydrogen hydraulic compression system for refuelling stations. Latv. J. Phys. Tech. Sci. 2022, 59, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J Chapman, S. Electric Machinery Fundamentals; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Agamloh, E.B.; Cavagnino, A. High efficiency design of induction machines for industrial applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Electrical Machines Design, Control and Diagnosis (WEMDCD), Paris, France, 11–12 March 2013; pp. 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA Energy Efficient End-Use Equipment (4E). Available online: https://www.iea-4e.org/emsa/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Okoro, O.I.; Ogbuka, C.U.; Agu, M.U. Simulation of dc machines transient behaviors: Teaching and research. Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2008, 9, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Beňová, M.; Dobrucký, B.; Šedo, J.; Praženica, M.; Koňarik, R.; Šimko, J.; Kuchař, M. A Novel Approach to Transient Fourier Analysis for Electrical Engineering Applications. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Navarro, A.; Ruiz-Sarrio, J.E.; Biot-Monterde, V.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Becker, V.; Urschel, S. Application of Transient Analysis Techniques to Fault Diagnosis in Low- and Medium-Power Synchronous Machines. Machines 2023, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostajeran, E.; Amiri, N.; Ebrahimi, S.; Jatskevich, J. Electrical Machines in Electromagnetic Transient Simulations: Focusing on efficient and accurate models. IEEE Electrif. Mag. 2023, 11, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkebeek, J.A. Transient Phenomena in Electrical Machines. In Electrical Machines and Drives. Power Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Zhang, P.; Tan, L.; Gu, J.; Li, H. Improved MSTOGI-PLL with enhanced control under non-ideal grid voltage conditions. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 238, 111060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnaciński, P.; Pepliński, M.; Muc, A.; Hallmann, D. Induction Motors Under Voltage Unbalance Combined with Voltage Subharmonics. Energies 2024, 17, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachini, F.; de Castro, M.; Bogodorova, T.; Vanfretti, L. Modeling of Induction Motors and Variable Speed Drives for Multi-Domain System Simulations Using Modelica and the OpenIPSL Library. Electronics 2024, 13, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuhova, M. Modeling of Induction Motor Direct Starting with and without Considering Current Displacement in Slot. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cureño-Osornio, J.; Alvarez-Ugalde, C.A.; Zamudio-Ramirez, I.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Dunai, L.; Tsurcanu, D.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Start-Up and Steady-State Regimes Automatic Separation in Induction Motors by Means of Short-Time Statistics. Electronics 2024, 13, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G. Soft Start Analysis of Induction Motor Using Current Phase Angle. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 17, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Ali, J.A.; Ker, P.J.; Mohamed, A.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Hussain, A. Switching Techniques and Intelligent Controllers for Induction Motor Drive: Issues and Recommendations. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 47489–47510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jidin, A.; Karim, K.A.; Rahim, K.; Raj, L.; Victor, L.; Ramahlingam, S.; Sutikno, T. A Review on Constant Switching Frequency Techniques for Direct Torque Control of Induction Motor. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2017, 7, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, M.; Fard, M.T.; Abapour, M.; Hagh, M.T. DC–AC Converter-Fed Induction Motor Drive With Fault-Tolerant Capability Under Open- and Short-Circuit Switch Failures. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aree, P. Effects of unbalanced voltage on induction motor operating points under different load torque profiles. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 28 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laadjal, K.; Sahraoui, M.; Alloui, A.; Cardoso, A.J.M. Three-Phase Induction Motors Online Protection against Unbalanced Supply Voltages. Machines 2021, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S. Three-Phase Unbalance Analysis Method Based on Three-Phase Motor Current Instantaneous Information. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.; Siam, J.; Abdou, A.; Shehadeh, H.; Mustafa, R. Practical Test on the Operation of the Three-Phase Induction Motor under Single-Phasing Fault. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almounajjed, A.; Sahoo, A.K.; Kumar, M.K.; Bakro, M.W. Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor—An Experimental Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Electrical Energy Systems (ICEES), Chennai, India, 11–13 February 2021; pp. 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y. Motor Fault Diagnostics Based on Current Signatures: A Review. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 3520919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeriwala, S. Induction Motor Diagnostics Using Vibration and Motor Current Signature Analysis. In Special Topics in Structural Dynamics & Experimental Techniques; Allen, M., Blough, J., Mains, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeva, G.; Saad, K.I.; Jahromi, M.G. Comprehensive Diagnostics of Induction Motor Faults Based on Measurement of Space and Time Dependencies of Air Gap Flux. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F.; Chen, J.; Diao, L.; Liu, Z. Parameter Identification of Inverter-Fed Induction Motors: A Review. Energies 2018, 11, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, S.L.; Donolo, P.D.; Pezzani, C.M.; Quispe, E.C.; De Angelo, C.H. Identification of induction motor parameters using genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Workshop on Power Electronics and Power Quality Applications (PEPQA), Cali, Colombia, 4–5 October 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S. Parameter Identification of Five-Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Based on Extended Kalman Filter. Processes 2022, 10, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véliz-Tejo, A.; Travieso-Torres, J.C.; Peters, A.A.; Mora, A.; Leiva-Silva, F. Normalized-Model Reference System for Parameter Estimation of Induction Motors. Energies 2022, 15, 4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsuk, S.; Areerak, K.; Areerak, T.; Areerak, K. Online Estimation of Three-Phase Induction Motor Parameters Using an Extended Kalman Filter for Energy Saving. Energies 2024, 17, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, S.A.; Dybkowski, M. Estimation of the Induction Motor Stator and Rotor Resistance Using Active and Reactive Power Based Model Reference Adaptive System Estimator. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.K.; Ayyagari, K.S.; Kumar, Y.P.; Giri, N.C.; Rajgopal, P.V.; Fotis, G.; Mladenov, V. Experimental Benchmarking of Existing Offline Parameter Estimation Methods for Induction Motor Vector Control. Technologies 2024, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosowski, Z.; Fajfer, M.; Ludwikowski, Z. Reduction of the Electromagnetic Torque Oscillation during the Direct on Line (DOL) Starting of a 6 kV Motor by Means of a Controlled Vacuum Circuit-Breaker. Energies 2022, 15, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 3002.7-2018; IEEE Recommended Practice for Conducting Motor-Starting Studies and Analysis of Industrial and Commercial Power Systems. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–107. [CrossRef]
- Meshcheryakov, V.; Belousov, A. Development of a method for reducing starting currents and electromagnetic torque of a two-phase induction motor by delaying voltage supply. In Proceedings of the 2021 XVIII International Scientific Technical Conference Alternating Current Electric Drives (ACED), Ekaterinburg, Russia, 24–27 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnett, A.H. The impact that voltage and frequency variations have on AC induction motor performance and life in accordance with NEMA MG-1 standards. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of 1999 Annual Pulp and Paper Industry Technical Conference (Cat. No. 99CH36338), Seattle, WA, USA, 21–25 June 1999; pp. 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, A.; Łukasik, Z.; Popenda, A.; Szafraniec, A. Mathematical Modelling of Transient Processes in an Asynchronous Drive with a Long Shaft Including Cardan Joints. Energies 2021, 14, 5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gong, P. Transient and Steady-State Performance Improvement of IM Drives Based on Dual-Torque Model. Machines 2023, 11, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B. Transient behaviour of three phase induction motor under supply interruption of one phase during starting. In Proceedings of the National Power Systems Conference-IIT, Kharagpur, India, 27–29 December 2002; pp. 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Ali, A.; Karrar, A.; Bowman, M.; Cooper, P. Estimating the Effects of Small Voltage and Frequency Changes on Industrial Induction Motor Loading. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Atlanta, GA, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo-Dorantes, J.J.; Jaen-Cuellar, A.Y.; Perez-Cruz, A.; Elvira-Ortiz, D.A. Detection of Inter-Turn Short Circuits in Induction Motors under the Start-Up Transient by Means of an Empirical Wavelet Transform and Self-Organizing Map. Machines 2023, 11, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srndovic, M.; Fišer, R.; Grandi, G. Analysis of Equivalent Inductance of Three-Phase Induction Motors in the Switching Frequency Range. Electronics 2019, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabaci, S.B.; Atalay, A.K.; AhmetKocabaş, D. Design of an innovative mathematical model for transient response of three phase induction machine. In Proceedings of the 2016 National Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Biomedical Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 1–3 December 2016; pp. 344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Goolak, S.; Gubarevych, O.; Yermolenko, E.; Slobodyanyuk, M.; Gorobchenko, O. Mathematical modeling of an induction motor for vehicles. East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2020, 2, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamola, O.Y.; Maday, V.S.; Vasylchyshyn, I.I. Mathematical Modelling of Starting Modes of Induction Motors with Squirrel-Cage Rotor. Electr. Eng. Electromech. 2021, 2, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengamalai, U.; Anbazhagan, G.; Thamizh Thentral, T.M.; Vishnuram, P.; Khurshaid, T.; Kamel, S. Three Phase Induction Motor Drive: A Systematic Review on Dynamic Modeling, Parameter Estimation, and Control Schemes. Energies 2022, 15, 8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, P.F.; Ngwenyama, M.K. Static and Dynamic Simulation of an Induction Motor Using Matlab/Simulink. Energies 2022, 15, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alitasb, G.K. Assessment of Fractional and Integer Order Models of Induction Motor Using MATLAB/Simulink. Model. Simul. Eng. 2024, 2739649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Chaturvedi, D.K. Simulink Model of Induction Motor Under Faulty Conditions. 12 May 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, A.; Ismeil, M.A.; Hussein, H.S.; Hasaneen, B.M.; Abdel-Aziz, A.M. An Efficient Protection Scheme Against Single-Phasing Fault for Three-Phase Induction Motor. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 6298–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, B.H.; Elhay, E.A.; Elkholy, M.M. Advanced fault detection technique of three phase induction motor: Comprehensive review. Discov. Electron. 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, A.; Brokhausen, F.; Amorim, T.; Kehrer, T.; Vogelsang, A. Characteristics, potentials, and limitations of open-source Simulink projects for empirical research. Softw. Syst. Model 2021, 20, 2111–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blohm, P.; Herber, P.; Remke, A. Towards Quantitative Analysis of Simulink Models Using Stochastic Hybrid Automata. In Integrated Formal Methods. IFM 2024; Kosmatov, N., Kovács, L., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LinkedIn. What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Simulink? Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/what-advantages-disadvantages-using-simulink (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- ResearchGate. Are You Familiar with Strengths and Weaknesses of Simulink to Simulate Power Systems? Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/post/Are-you-familiar-with-strengths-and-weaknesses-of-Simulink-to-simulate-power-systems (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Metcalf, M.; Reid, J.; Cohen, M. Modern Fortran Explained: Incorporating Fortran 2018; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kopylov, I.P. Mathematical Models of Electric Machines; Mir Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 2001; p. 155. [Google Scholar]
- Dirba, J.; Ketners, K. Elektriskās mašīnas [Electrical Machines]; RTU Publishing House: Riga, Latvia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Muchande, S.; Kadam, A.; Unni, K.; Thale, S. Design and Implementation of a Direct Torque Control Space Vector Modulated Three Phase Induction Motor Drive. In Advances in Computing, Communication, and Control. ICAC3 2013; Unnikrishnan, S., Surve, S., Bhoir, D., Eds.; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Milestones, D.L. Hotspots and trends in the development of electric machines. iEnergy 2022, 1, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.N.; Liu, Y. A unified theory of flux-modulated electric machines. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Electrical Engineering (ISEE), Hong Kong, China, 14 December 2016; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramerdorfer, G.; Tapia, J.A.; Pyrhönen, J.J.; Cavagnino, A. Modern Electrical Machine Design Optimization: Techniques, Trends, and Best Practices. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7672–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljuchev, V.I. Theory of Electric Drives: Textbook for Universities; Energoizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Slemon, G.R. Modelling of induction machines for electric drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1989, 25, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.D.; Zhang, L.Z.; Wang, X.H. AC Machine Systems; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolevskaya, A.E.; Shlaf, M.M.; Afonin, V.I.; Sobolevskaya, E.A. Asynchronous Motors of the 4A Series: Handbook; Energoizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Qi, H.; Wang, S.; Hou, D.; Wang, C. Adaptive Stepsize Forward–Backward Pursuit and Acoustic Emission-Based Health State Assessment of High-Speed Train Bearings. Structural Health Monitoring. 2024. Available online: http://sage.cnpereading.com/paragraph/article/?doi=10.1177/14759217241271036 (accessed on 28 January 2025).
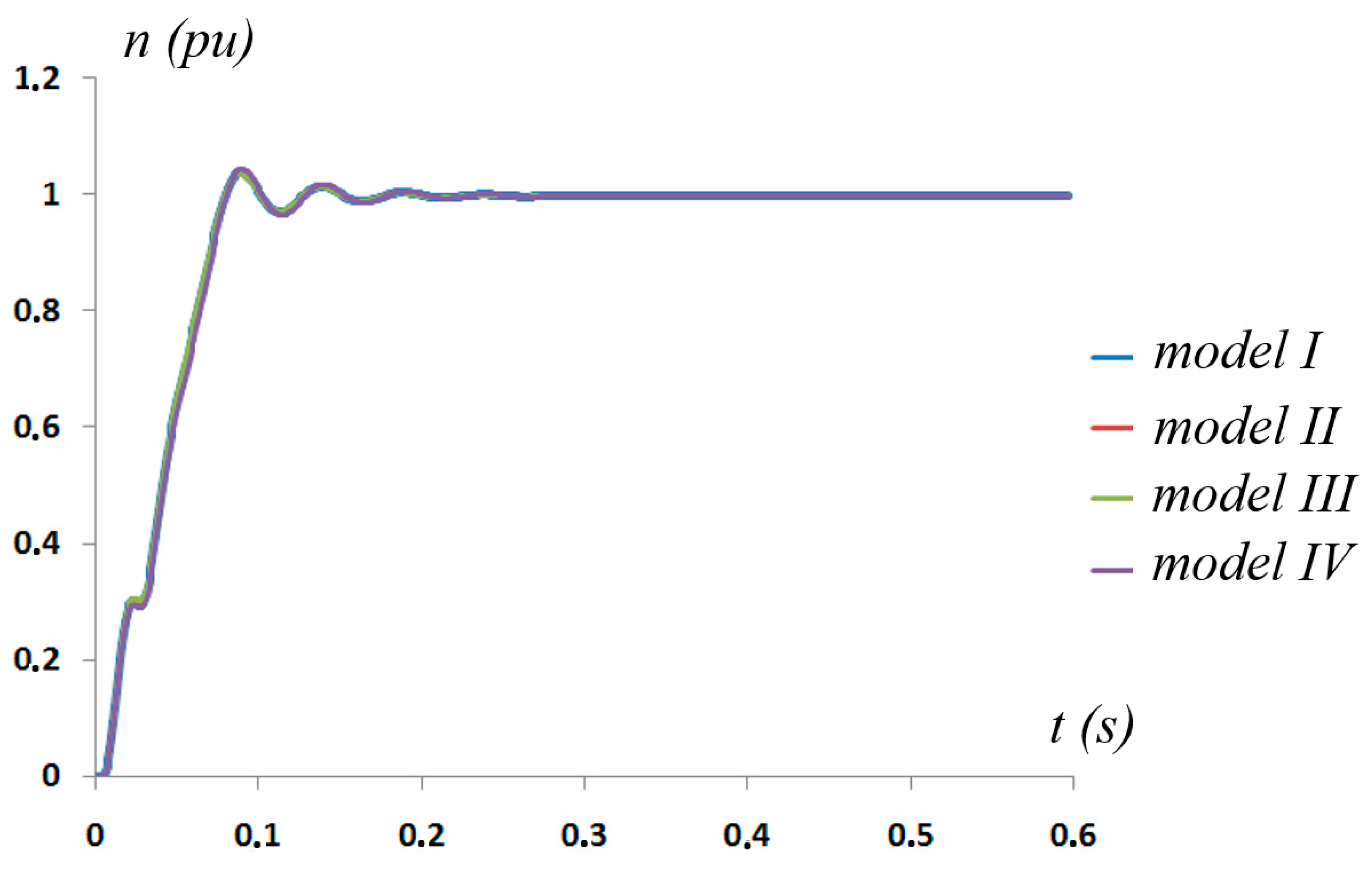
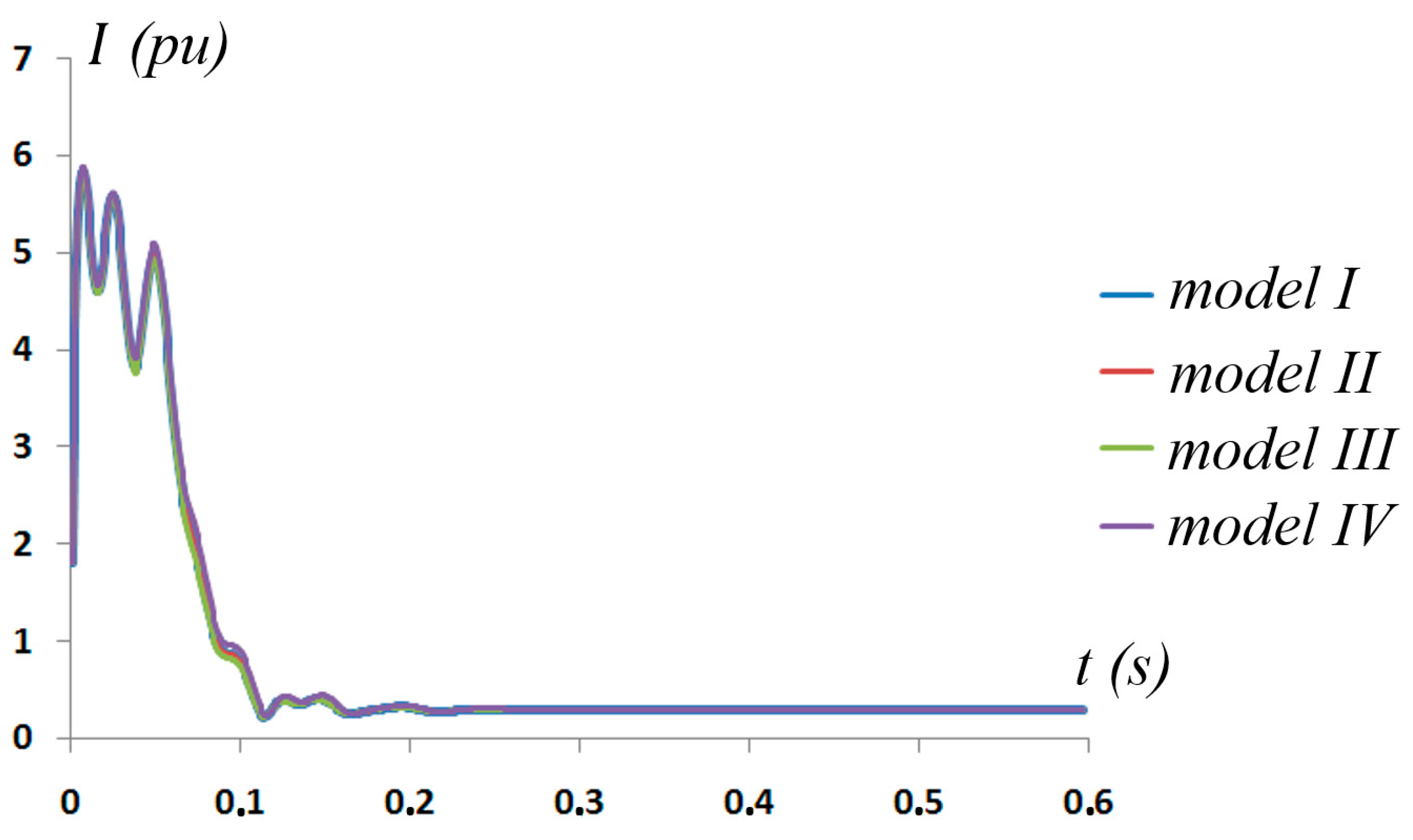

| Model | Coordinate System Type | Key Parameters Simulated | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Rotational frequency, current, torque | Simple implementation, direct experimental comparison | Suitable for basic dynamic studies and starting scenarios under no-load | |
| II | (Current) | Rotational frequency, current, torque | Enables integration of the motor’s mathematical model to evaluate its impact on the power supply system | Suitable for analyzing voltage unbalance, grid interaction, and power system effects during starting |
| III | (Flux linkage) | Rotational frequency, current, torque, flux linkages | Supports the analysis of autonomous operation regimes for motors fed by a power supply system with infinite capacity | Effective for stand-alone motor analysis and advanced control strategy development |
| IV | (Flux linkages with rotor constant) | Parameter variations during rundown | Analyzes motor parameter changes during rundown, emphasizing the rotor windings’ electromagnetic time constant. | Useful for studying transient torque oscillations and motor response during rundown scenarios |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konuhova, M. Induction Motor Dynamics Regimes: A Comprehensive Study of Mathematical Models and Validation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031527
Konuhova M. Induction Motor Dynamics Regimes: A Comprehensive Study of Mathematical Models and Validation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(3):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031527
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonuhova, Marina. 2025. "Induction Motor Dynamics Regimes: A Comprehensive Study of Mathematical Models and Validation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 3: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031527
APA StyleKonuhova, M. (2025). Induction Motor Dynamics Regimes: A Comprehensive Study of Mathematical Models and Validation. Applied Sciences, 15(3), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031527






