A Comparative Study of Arc Welding and Laser Welding for the Fabrication and Repair of Multi-Layer Hydro Plant Bellows
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
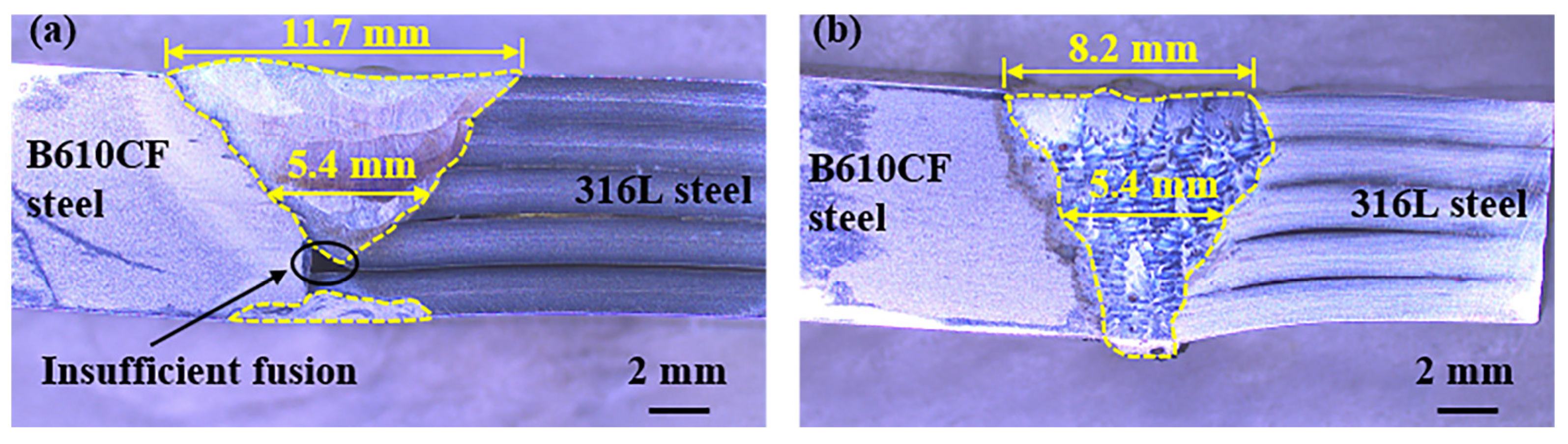
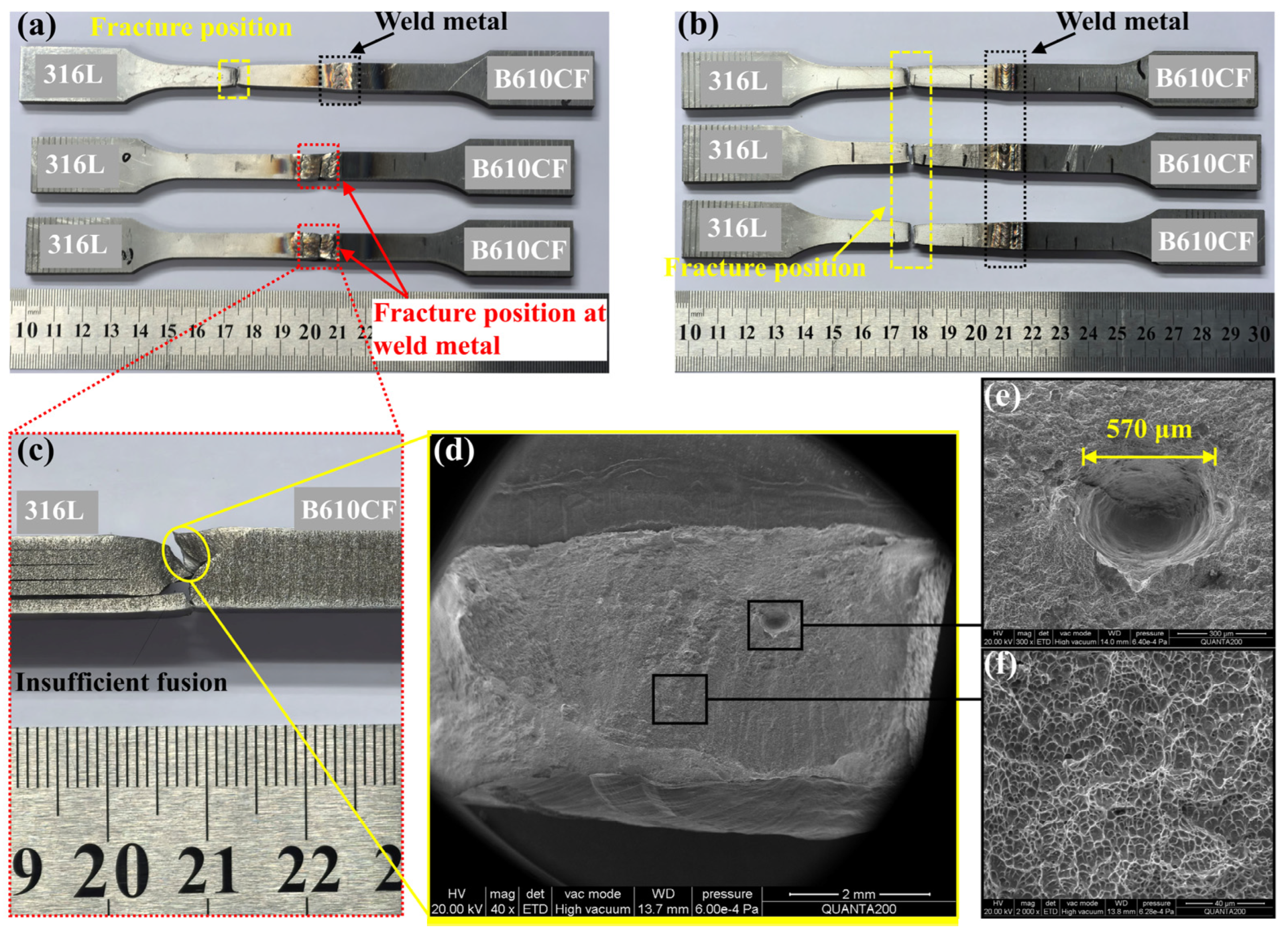
3.1. Forming Quality
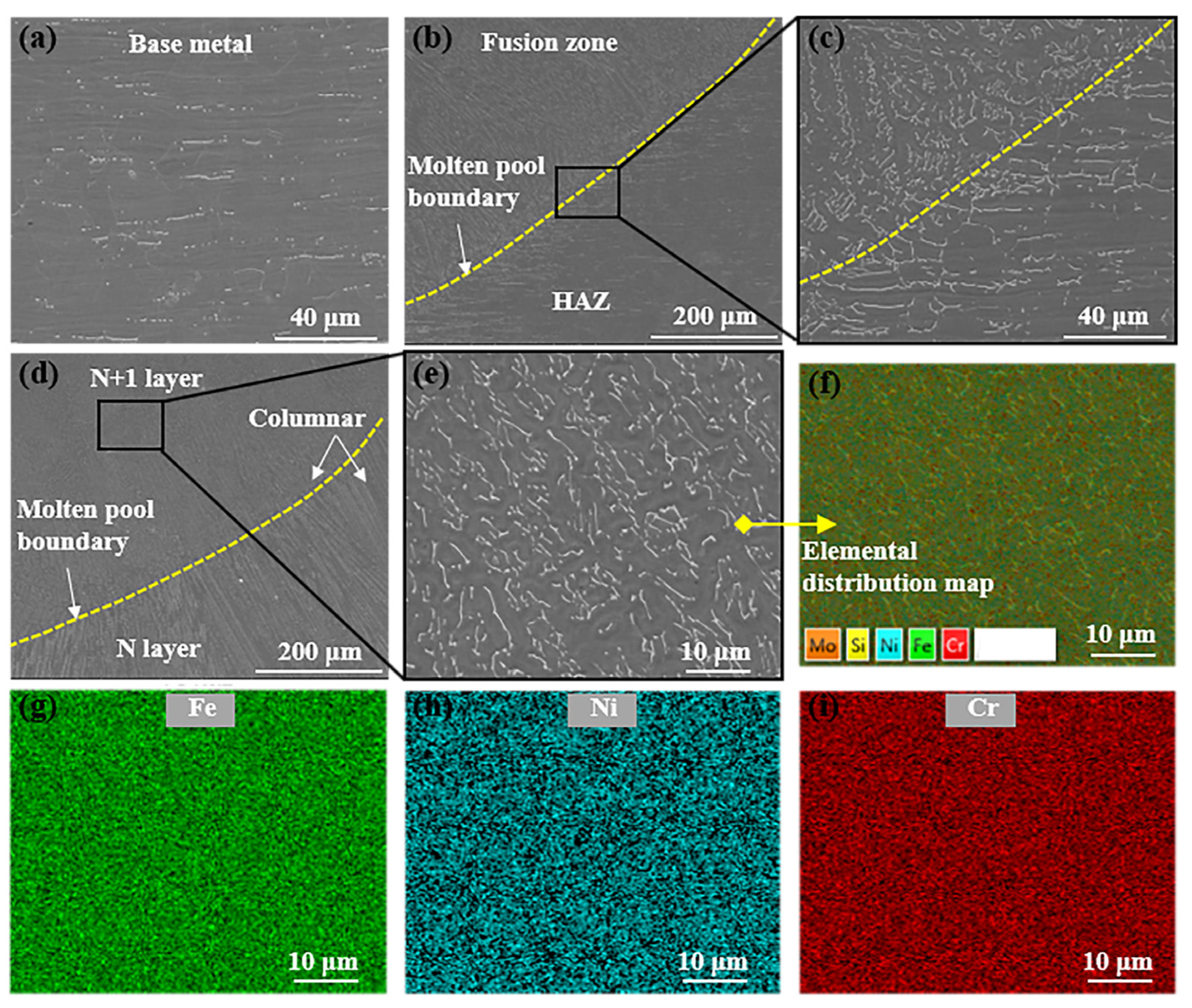
3.2. Microstructural Characteristics
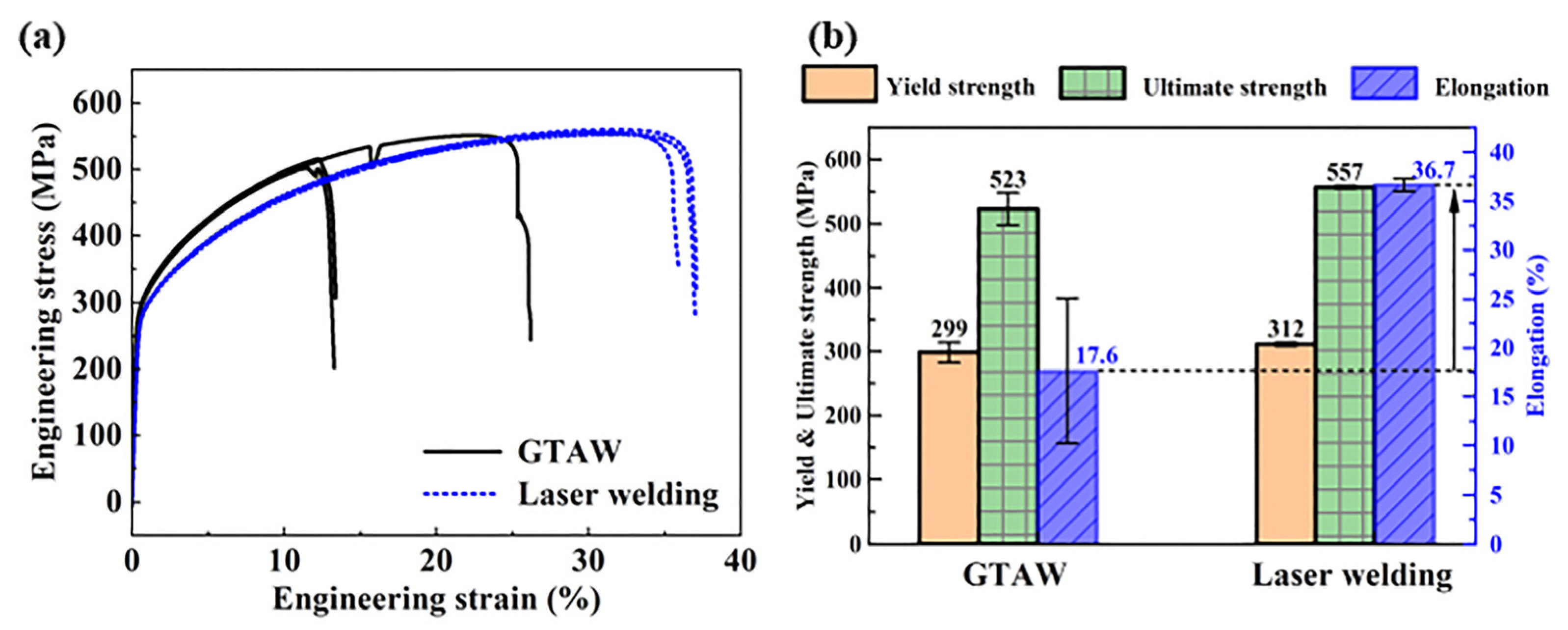
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The width of the FZ and HAZ using GTAW was much wider than that obtained using laser welding. Discontinuous insufficient fusion was detected in the GTAW joints, and the laser-welded joints presented full welds without visible defects.
- (2)
- Compared with GTAW, there are much bigger equiaxed grain regions located in the FZs of the laser-welded samples. Fewer ferrites penetrated into the boundary of the austenite phase and the homogeneous elemental distribution in the HAZ, indicating few elemental segregations.
- (3)
- Elongations of the samples welded by GTAW and laser welding were 17.6% and 36.7%, respectively. The increase in the elongation in laser welding was due to the combined effect of full welds without visible defects and a homogeneous elemental distribution in the HAZs, which resulted in fractures occurring in the 316L stainless-steel base material.
- (4)
- The results show that laser welding is more suitable than GTAW for welding multi-layer 316L stainless-steel sheets with B610CF high-strength steel plates for the fabrication and repair of hydro plant bellows.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, P.; Ma, J.; Fang, Y.; Xu, B.; Qiu, L.; Liu, W. Effect of repeated weld repairs on microstructure and mechanical properties of heat-affected zone in CA6NM stainless steel. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4527917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.; Kuijper, M.; Helferty, H.; Girardin, C.; Allen, M. Extended producer responsibility for fossil fuels. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 011005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, A.; Ganesan, U.; Sundararajan, R. Key parameters that affect the fatigue life of metal bellows-type expansion joint: Another look. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 108400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhede, S.D.; Gawande, S.H. Design and analysis aspect of metal expansion bellows: A review. Forces Mech. 2023, 13, 100244. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Lei, Y.; Ding, J.; Li, K.; Guo, F. Residual stress analysis and measurement in multi-layer bellows. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 72, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, L. Deformation behaviors of four-layered U-shaped metallic bellows in hydroforming. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 33, 3479–3494. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Wan, Z.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y. Effect of residual stress on the axial buckling behaviour of the hydraulic-formed bellows. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 2025, 215, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, B.; Aday, X. Impact of strain on the corrosion resistance of 304 stainless steel welded joints using electrochemical methods and numerical modeling of stress corrosion. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2025, 20, 100910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y. On the Si content prediction for submerged arc welded metal via calphad technique: A brief discussion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.S.; Rao, C.S.; Rao, D.N. Study on weld quality characteristics of micro plasma arc welded austenitic stainless steels. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Huo, S.; Ren, J. Mathematical description and mechanical characteristics of reinforced S-shaped bellows. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 2019, 175, 103931. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Liu, P.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Microstructures and properties of a novel 115 mm thick 08Cr9W3Co3VNbCuBN heat-resistant steel tube joints welded by shielded metal arc welding. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 2023, 202, 104918. [Google Scholar]
- Mazar Atabaki, M.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Kovacevic, R. Pore formation and its mitigation during hybrid laser/arc welding of advanced high strength steel. Mater. Des. 2015, 67, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, Z.; Zeng, J.; Feng, J.; Su, X.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Xia, G. Laser-arc hybrid welding of 25 mm high strength steel sections. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 182, 112193. [Google Scholar]
- Doredla, N.; Senthil Kumar, N. Determination of heat input impact on residual stress, microstructure and mechanical characteristics of welded ferrite-pearlite (α-P) steel joints by using taguchi optimization approach. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2025, 11, 100278. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Dilger, K. Thermal cycle method’s applicable conditions for predicting residual stresses in low-strength steel weldments induced by arc welding. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 47, 102260. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Dilger, K. Reliability analysis of thermal cycle method on the prediction of residual stresses in arc-welded ultra-high strength steels. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 185, 108085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Kim, R.E.; He, J.; Lopes, J.G.; Yang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Schell, N.; Kim, H.S.; Oliveira, J.P. Gas tungsten arc welding of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy to 316 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 922, 147664. [Google Scholar]
- de Lima e Silva, L.; Ducommun, N.; Jubin, L.; Mainguy, R.; Thebault, Y.; Andrieu, E.; Blanc, C. Effects of mechanical stress on the corrosion behaviour of an austenitic stainless steel welded joint—Stress corrosion cracking susceptibility. Corros. Sci. 2025, 244, 112629. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Soleimani, M.; Midawi, A.R.H.; Aderibigbe, I.; Zhou, Y.N.; Biro, E. A review on heat affected zone softening of dual-phase steels during laser welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 102, 663–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Pan, J.; Zhong, L.; Cai, Y.; Xing, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, D.; Li, C. All-fiber 3 kW LP02 laser output based on long-period fiber grating for precise welding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 176, 111047. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Arshad, N.I.; Zhang, P.; Hazaimeh, H.M.; Alqahtani, A.M.; Kraiem, N. Experimental study and finite volume modeling of keyhole dynamics, temperature distribution and weld characteristics in laser welding of austenitic stainless steel tube. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 183, 112366. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, H.; Wei, J.; Zhan, X. Role of layer arrangement in microstructure and corrosion behavior for 78-mm thick-plate 316L stainless steel fabricated via narrow gap laser wire filling welding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 1797–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tümer, M.; Schneider-Bröskamp, C.; Enzinger, N. Fusion welding of ultra-high strength structural steels—A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 82, 203–229. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzian, M.; Amne Elahi, M.; Plapper, P. A review: Suppression of the solidification cracks in the laser welding process by controlling the grain structure and chemical compositions. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2023, 7, 100139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Yan, T.; Muneer, W.; Yin, X.; Gao, Q.; Zhan, X. Effect of heat input on LMHMW joint of carbon steel. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Mao, C.; Zhang, M.; Wu, D.; Jiang, H.; Ma, G. Comparative study on microstructure and properties of laser welding and argon arc welding Hastelloy C-276/SS304 with filler wire. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 164, 109565. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Jin, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Yi, H.; Xie, G. A comparative study of the galvanized DP980 steel and 2 GPa PHS welded joint via laser beam welding and cold metal transfer welding. Mater. Lett. 2024, 369, 136726. [Google Scholar]
- Roshith, P.; Arivarasu, M.; Arivazhagan, N.; Srinivasan, A.; Phani Prabhakar, K.V. Investigations on induced residual stresses, mechanical and metallurgical properties of CO2 laser beam and pulse current gas tungsten arc welded SMO 254. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 44, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T228.1-2021; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. National Standard of The People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Khedr, M.; Elsayed, M.; Jaskari, M.; Abdel-Aleem, H.A.; Gaafer, A.M.; Hamada, A. Effect of building orientation on weld characteristics of additively manufactured 316L stainless steel: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 913, 147086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katherasan, D.; Sathiya, P.; Raja, A. Shielding gas effects on flux cored arc welding of AISI 316L (N) austenitic stainless steel joints. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Yan, C.; Ren, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhan, X. Inhomogeneity of microstructure and mechanical properties in the interlayer regions for narrow gap laser wire filling welding of 316L stainless steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 169, 110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNonno, O.; Saville, A.; Benzing, J.; Klemm-Toole, J.; Yu, Z. Solidification behavior and texture of 316L austenitic stainless steel by laser wire directed energy deposition. Mater. Charact. 2024, 211, 113916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yu, C.; Wang, Q.; Niu, F.; Ma, G.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, B. Synchronous-hammer-forging-assisted laser directed energy deposition additive manufacturing of high-performance 316L samples. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 307, 117695. [Google Scholar]
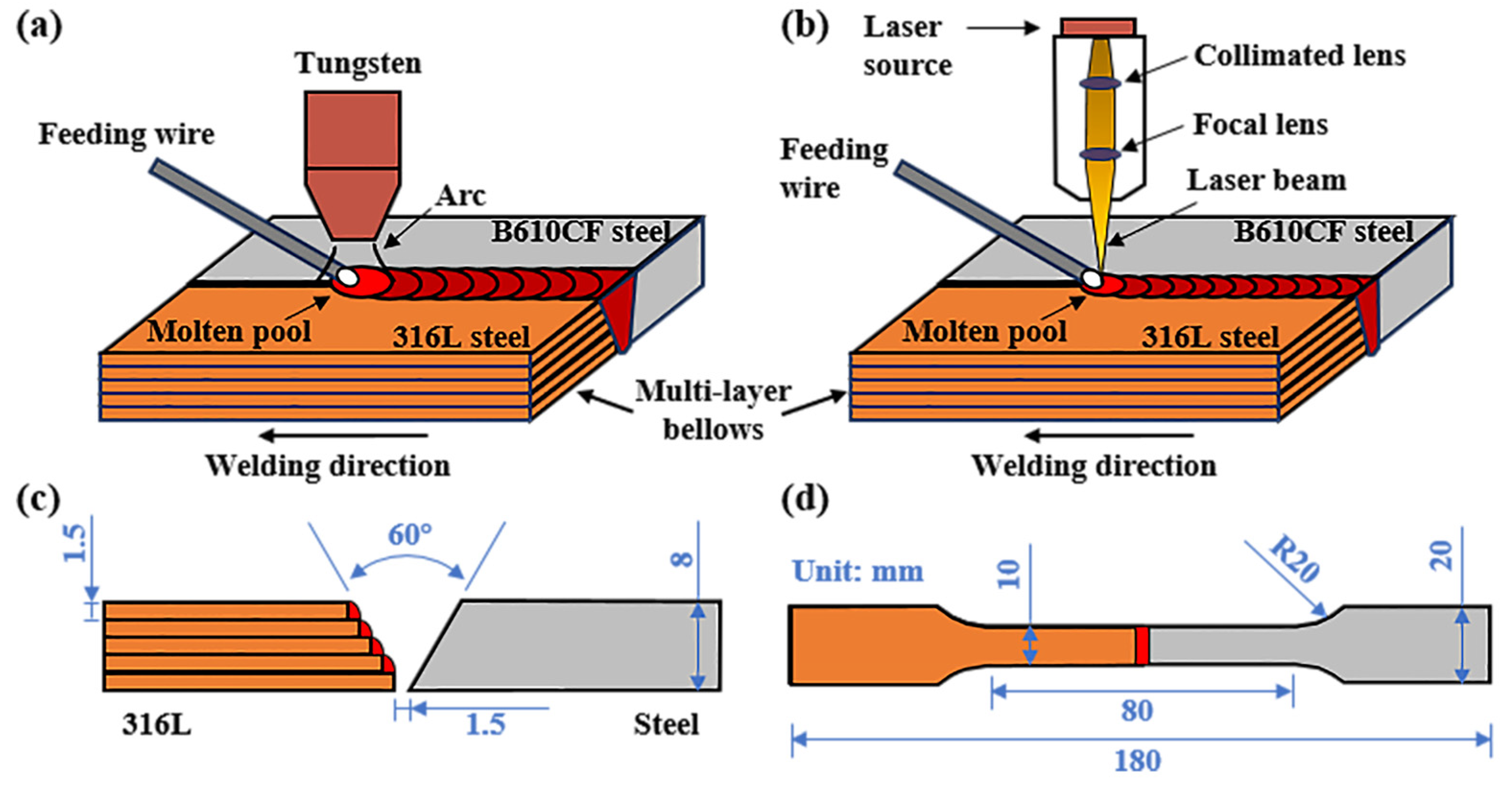



| Material | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316L | <0.03 | <2 | <0.045 | <0.03 | <1 | 16–18 | 10–14 | 2–3 | Balance |
| B610CF | 0.09 | 1.57 | - | - | 0.31 | 0.21 | - | - | Balance |
| Methods | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Laser Power (W) | Diameter of Feeding Wire (mm) | Welding Speed (mm/s) | Wire Feeding Speed (mm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTAW | 13~16 | 80~120 | - | 2.5 | 15~20 | 3~5 |
| Laser welding | - | - | 500~850 | 1.2 | 15~20 | 11~14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, L.; Lv, K.; Liu, Z.; Tu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Bi, G. A Comparative Study of Arc Welding and Laser Welding for the Fabrication and Repair of Multi-Layer Hydro Plant Bellows. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063387
Cao L, Lv K, Liu Z, Tu G, Zhang Y, Hu H, Yang Z, Wang H, Zhang H, Bi G. A Comparative Study of Arc Welding and Laser Welding for the Fabrication and Repair of Multi-Layer Hydro Plant Bellows. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063387
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Lichao, Kaiming Lv, Zhengjun Liu, Guoying Tu, Yi Zhang, Han Hu, Zirui Yang, Huikang Wang, Hao Zhang, and Guijun Bi. 2025. "A Comparative Study of Arc Welding and Laser Welding for the Fabrication and Repair of Multi-Layer Hydro Plant Bellows" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063387
APA StyleCao, L., Lv, K., Liu, Z., Tu, G., Zhang, Y., Hu, H., Yang, Z., Wang, H., Zhang, H., & Bi, G. (2025). A Comparative Study of Arc Welding and Laser Welding for the Fabrication and Repair of Multi-Layer Hydro Plant Bellows. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063387







