Characterization and Energy Performance of Rice Husk Fiber Insulation Applied by the Blowing Technique in an Industrialized Modular Housing System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
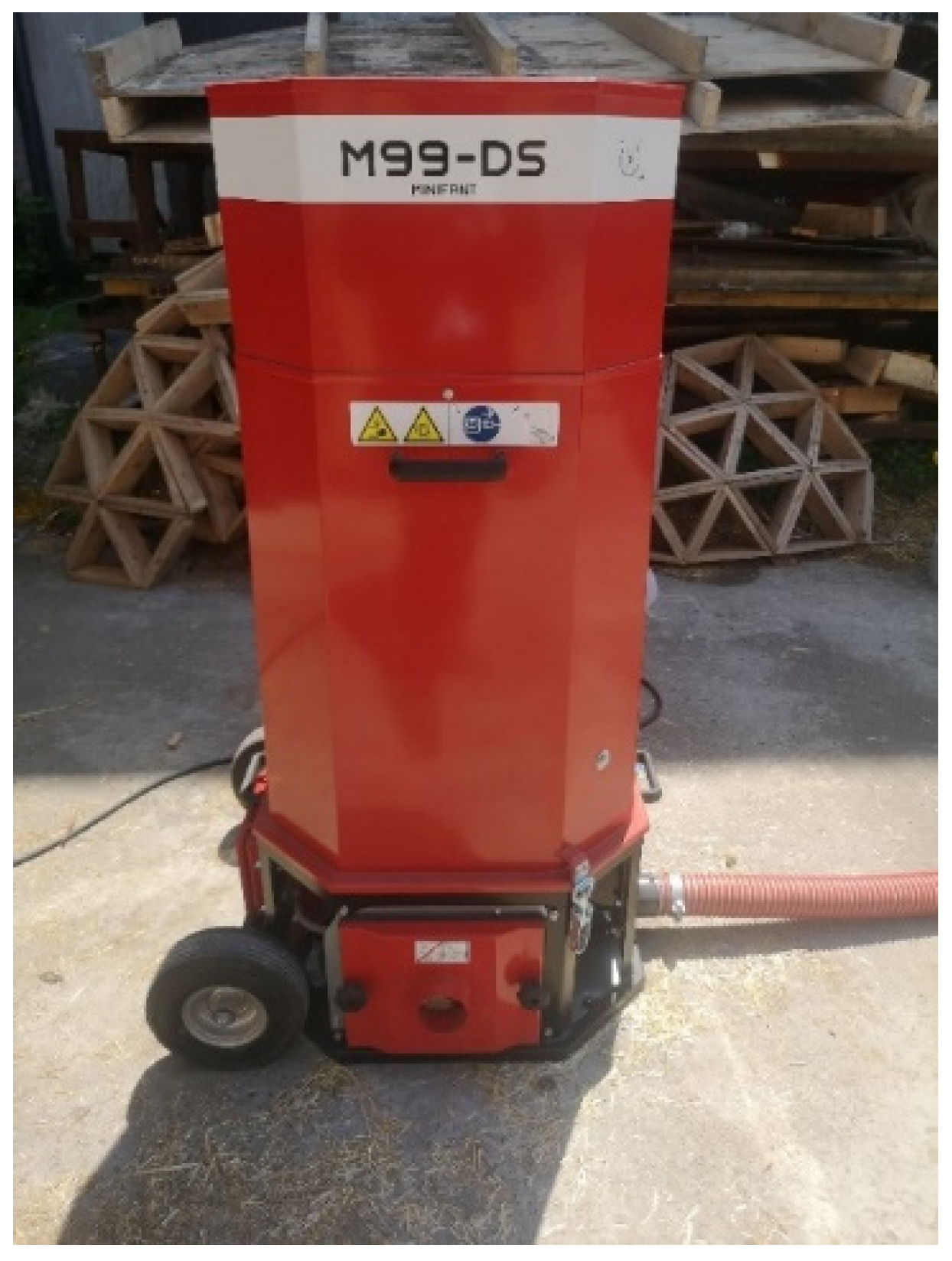
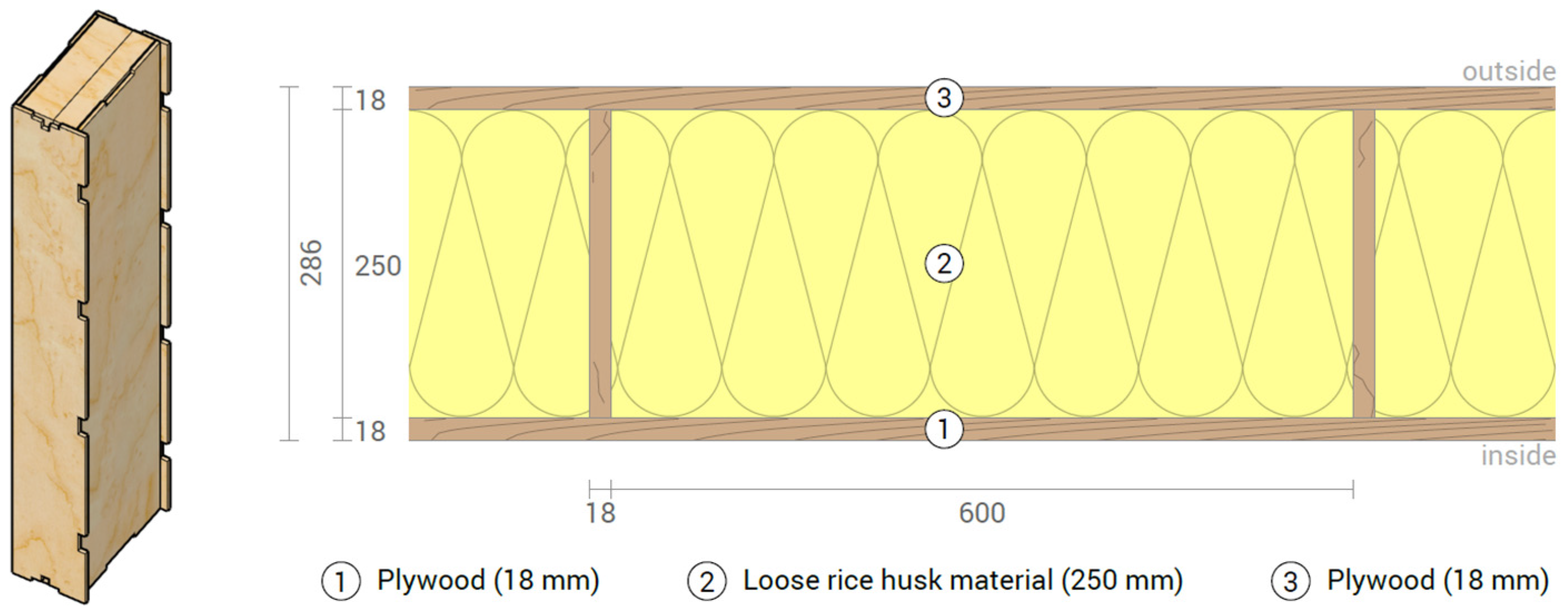
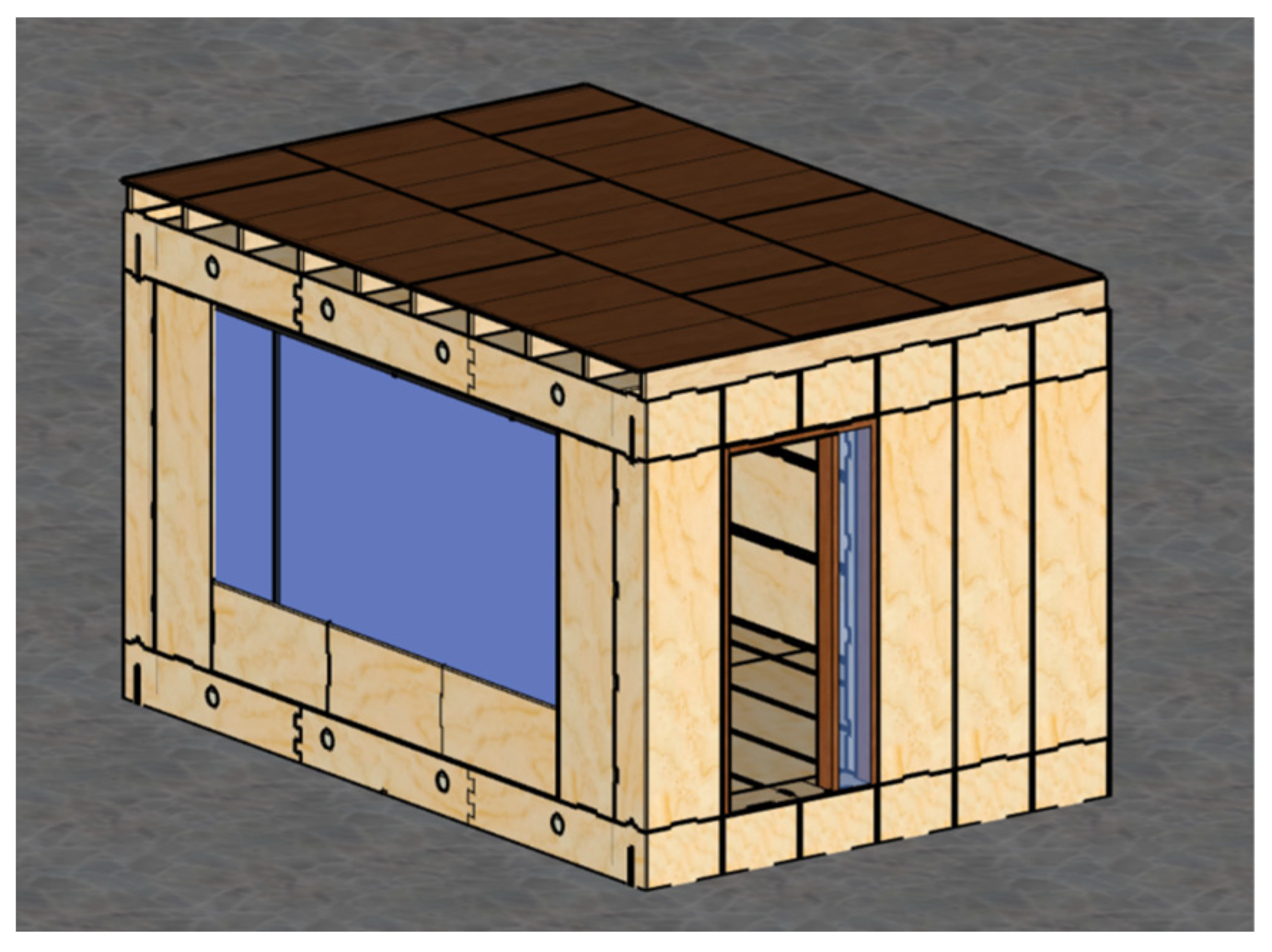
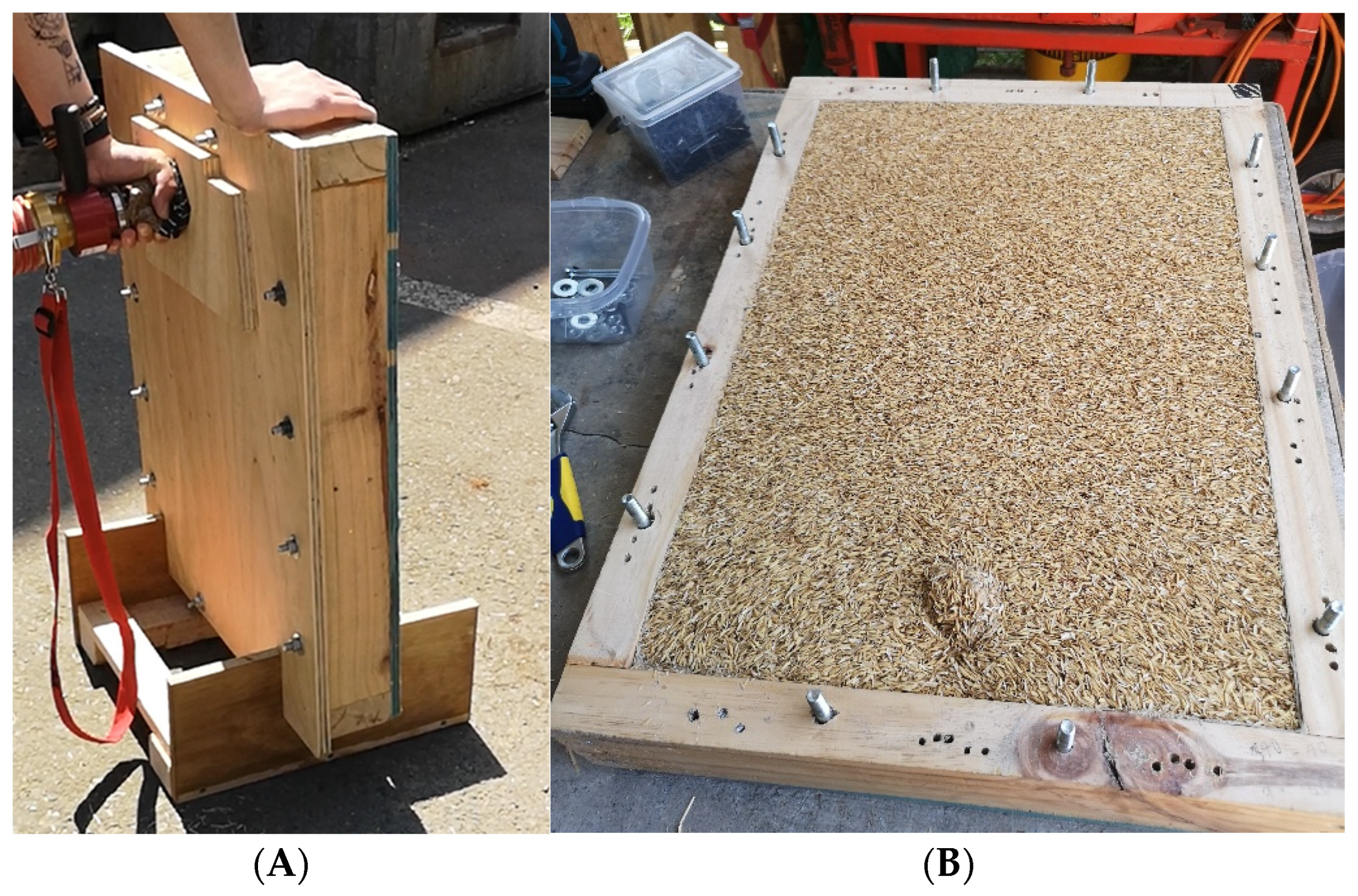
2.1. Sample Preparation and Material Application
2.2. Physical Characterization
2.2.1. Thermal Stability
2.2.2. Thermal Conductivity
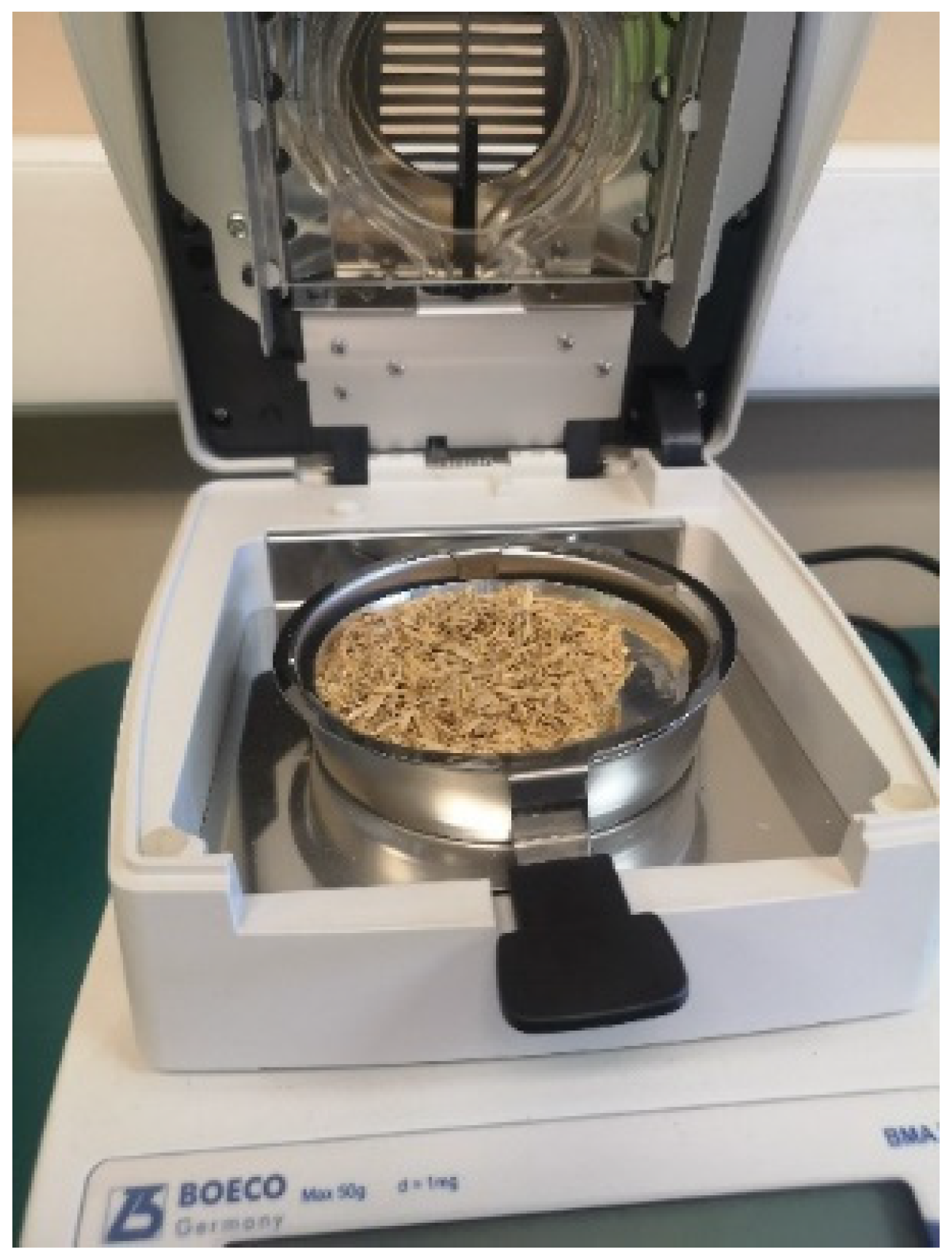
2.2.3. Density and Moisture
2.2.4. Surface Analysis
2.3. Fire Behavior
2.3.1. Fire Reaction Test
2.3.2. Smoldering Combustion Analysis Test
2.4. Thermal Performance of the Insulating Envelope and Energy Simulation
2.4.1. Thermal Inertia
2.4.2. Energy Simulation
Scenario Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Application Results
3.2. Physical Characterization
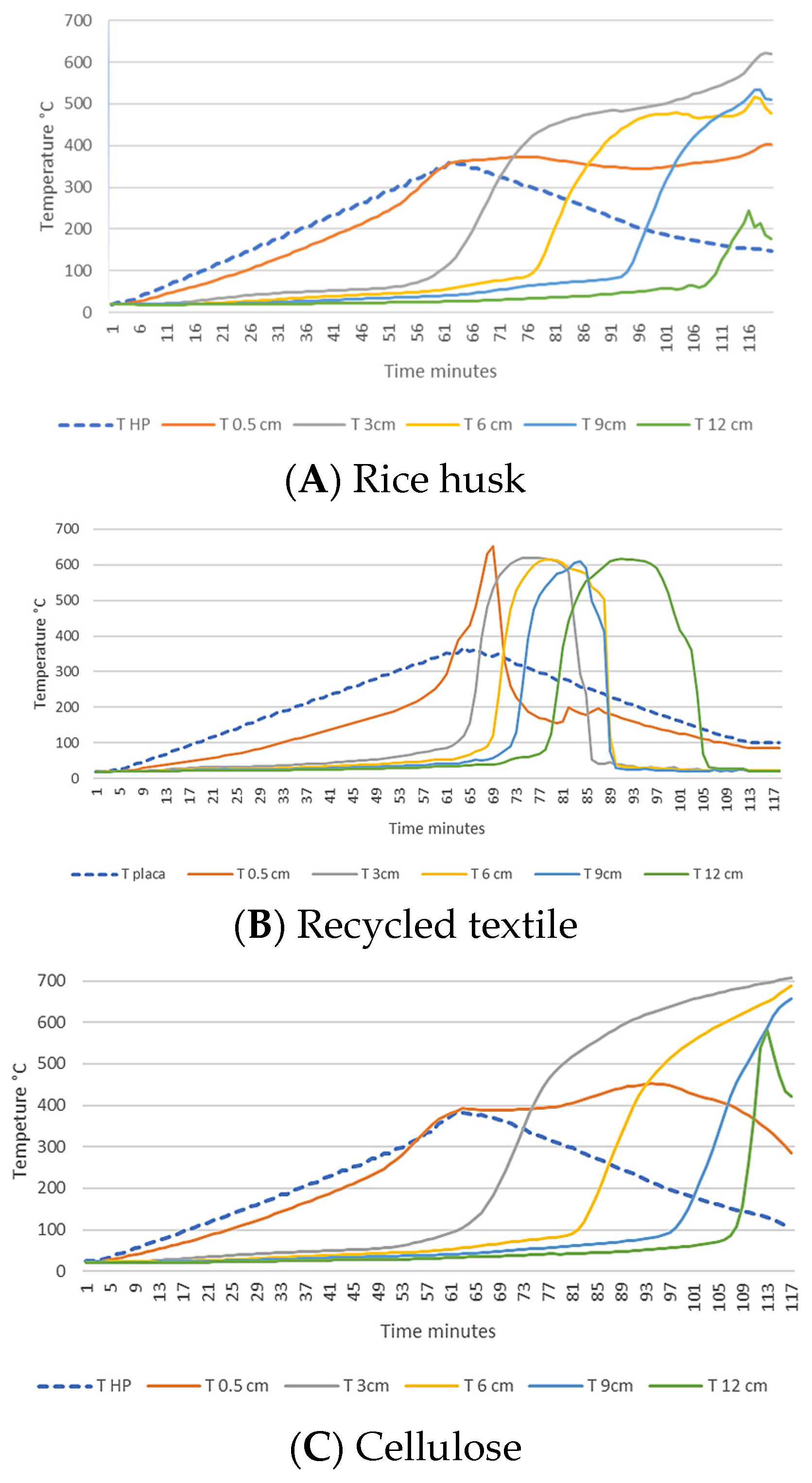
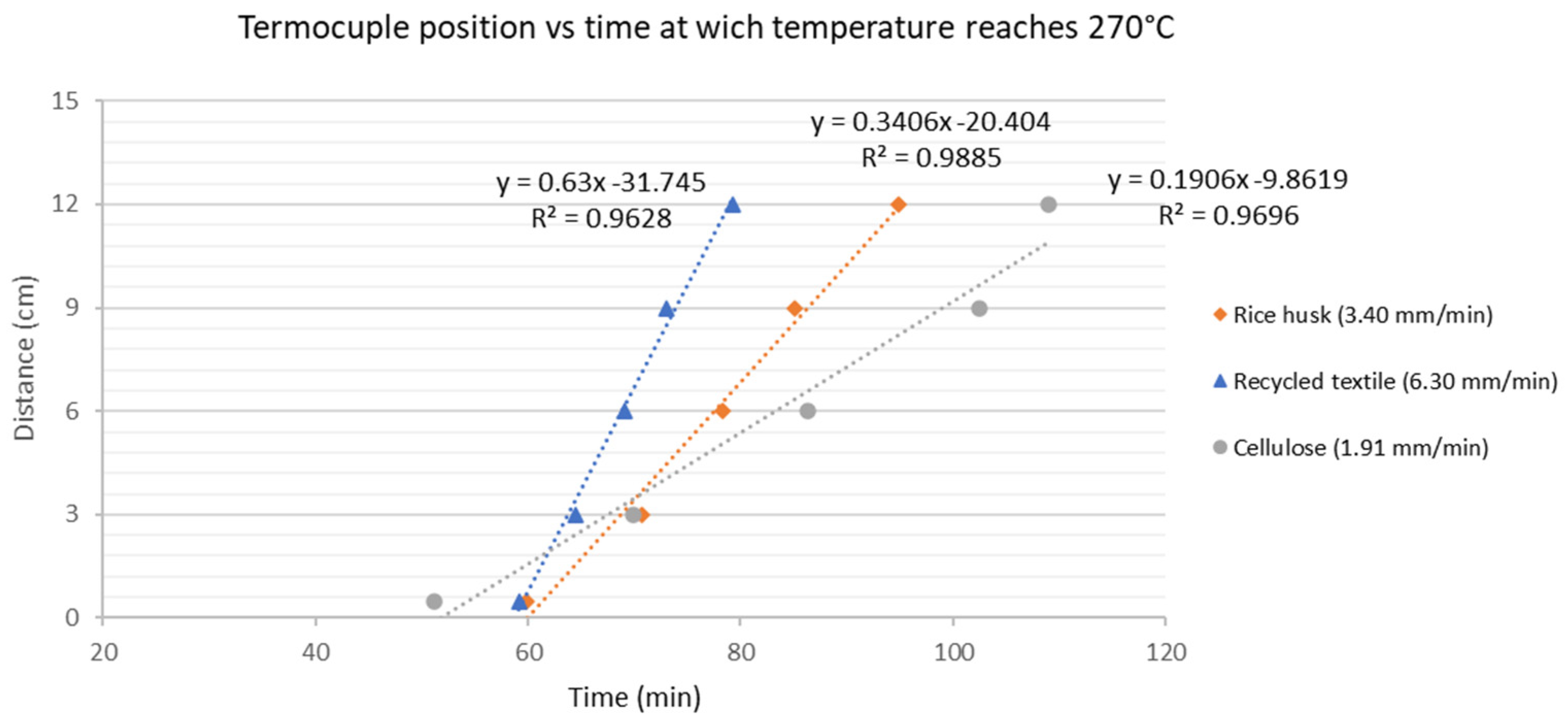
3.2.1. Thermal Stability Analysis
3.2.2. Thermal Conductivity Results
3.2.3. Density and Moisture Content Results
3.2.4. Surface Morphology Analysis
3.3. Fire Behavior
3.3.1. Fire Reaction Test Results
3.3.2. Smoldering Combustion Performance
3.4. Thermal Performance of the Insulating Envelope and Energy Simulation
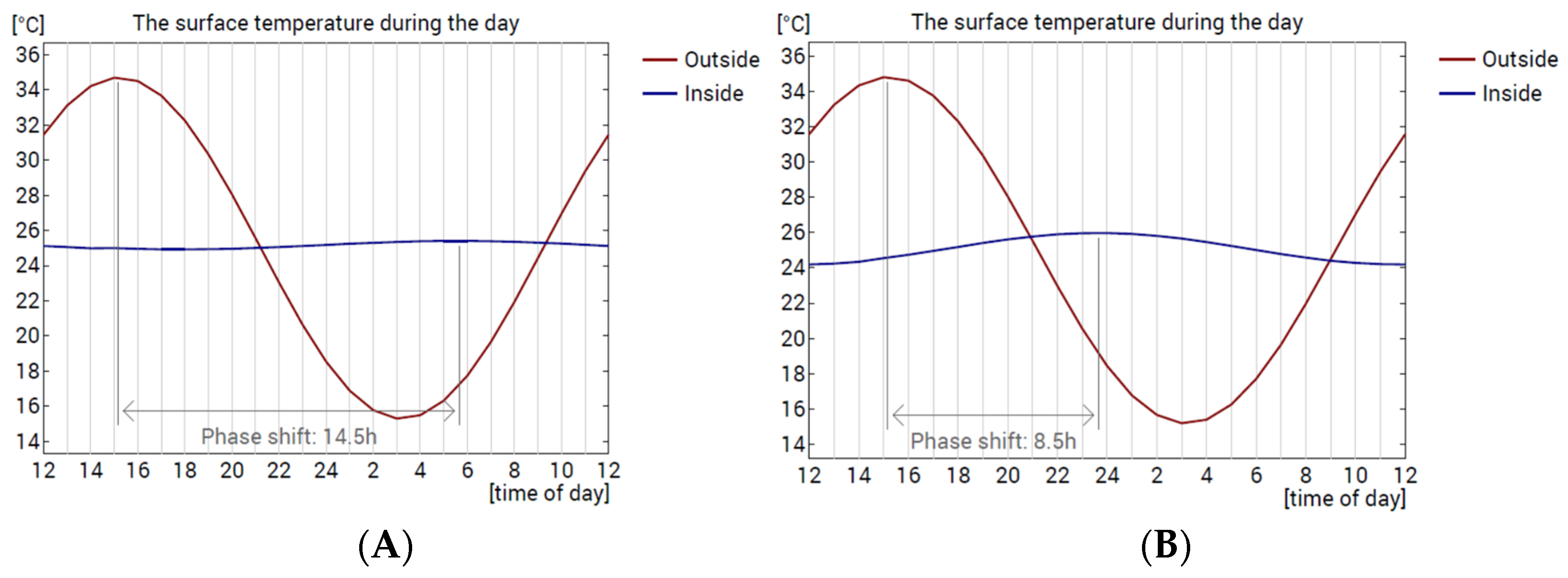
3.4.1. Thermal Inertia Results
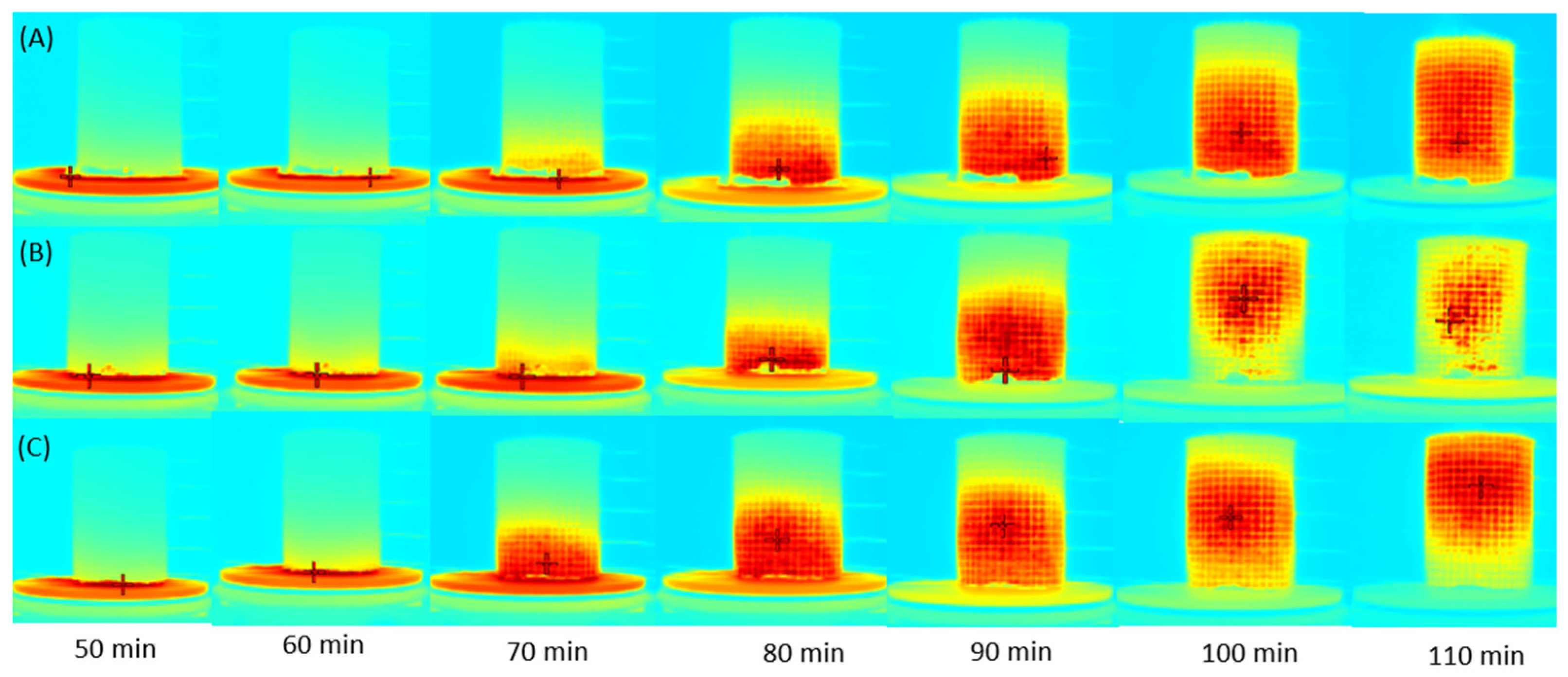
3.4.2. Energy Simulation Results
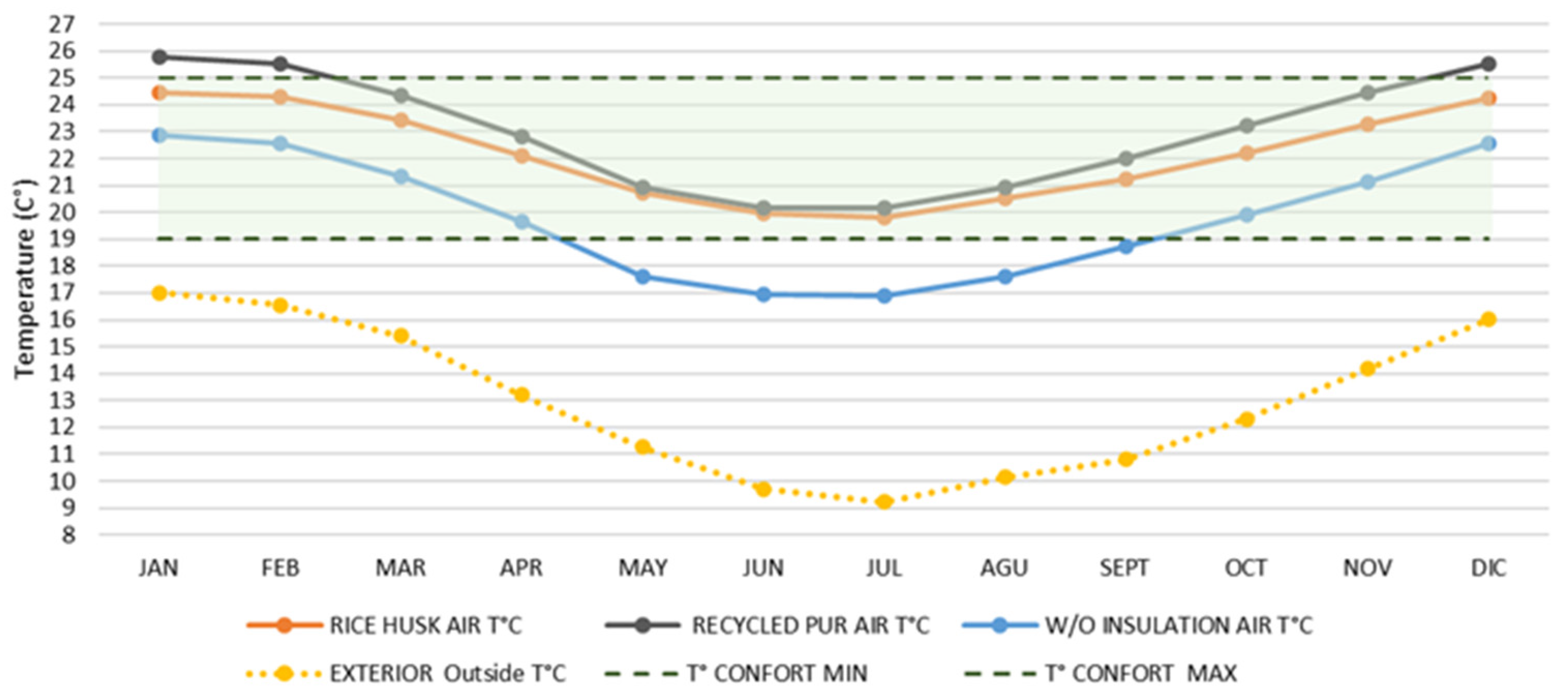
Temperature Homogeneity
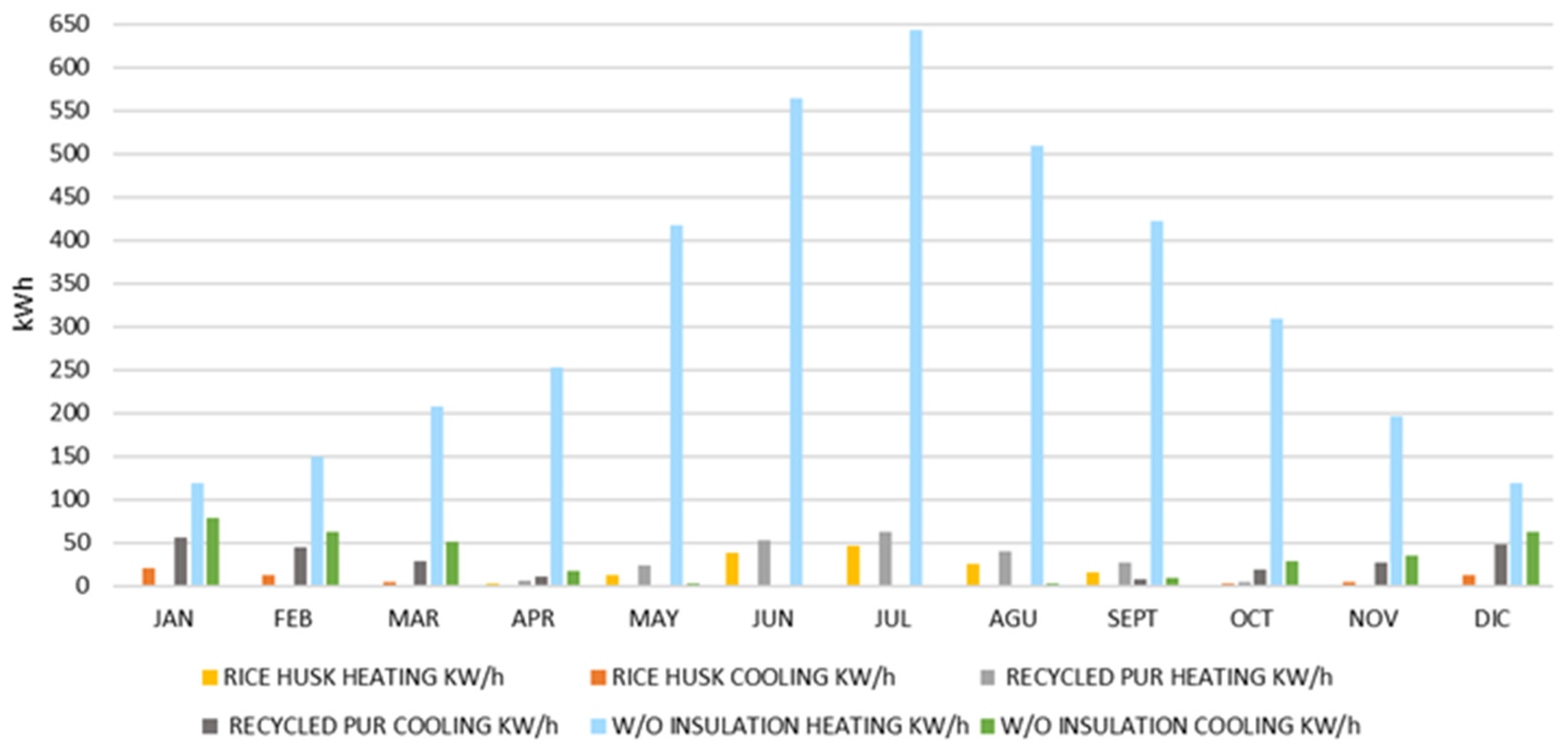
Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasilca, I.S.; Nen, M.; Chivu, O.; Radu, V.; Simion, C.P.; Marinescu, N. The management of environmental resources in the construction sector: An empirical model. Energies 2021, 14, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikmen, N.; Ozkan, S.T.E. Unconventional Insulation Materials; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korjenic, A.; Petránek, V.; Zach, J.; Hroudová, J. Development and performance evaluation of natural thermal-insulation materials composed of renewable resources. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 2518–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangmesh, B.; Patil, N.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Gowrishankar, T.P.; Selvakumar, K.K.; Jyothi, M.S.; Jyothilakshmi, R.; Kumar, S. Development of sustainable alternative materials for the construction of green buildings using agricultural residues: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajabli, H.; Zoubir, A.; Elotmani, R.; Louzazni, M.; Kandoussi, K.; Daya, A. Review on Eco-friendly insulation material used for indoor comfort in building. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 185, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hua, J.; Liu, Y.; Osman, A.I.; Farghali, M.; Huang, L.; et al. Biomaterials technology and policies in the building sector: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 715–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, L.; Mahlia, T.I.; Rismanchi, B.; Ng, H.M.; Hasan, M.H.; Metselaar, H.S.C.; Muraza, O.; Aditiya, H.B. A review on insulation materials for energy conservation in buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 1352–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Bhat, G. Environmentally-friendly thermal and acoustic insulation materials from recycled textiles. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Rahman, A.N.M.R.; Zhang, J. Trends in rice research: 2030 and beyond. Food Energy Secur. 2023, 12, e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Bahrami, A.; Pech-Canul, M.I.; González, L.A. Review on the physicochemical treatments of rice husk for production of advanced materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 899–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Neira, K.; Cárdenas-Ramírez, J.P.; Rojas-Herrera, C.J.; Haurie, L.; Lacasta, A.M.; Torres Ramo, J.; Sánchez-Ostiz, A. Assessment of Elaboration and Performance of Rice Husk-Based Thermal Insulation Material for Building Applications. Buildings 2024, 14, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, H.; Zou, S.; Zhang, G. Experimental research on a feasible rice husk/geopolymer foam building insulation material. Energy Build. 2020, 226, 110358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, C.; Belloni, E.; Lascaro, E.; Merli, F.; Ricciardi, P. Rice husk panels for building applications: Thermal, acoustic and environmental characterization and comparison with other innovative recycled waste materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, B.; Tadeu, A.; António, J.; Almeida, J.; de Brito, J. Mechanical, thermal and acoustic behaviour of polymer-based composite materials produced with rice husk and expanded cork by-products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, A.; Faria, P.; Silva, V.; Brás, A. Rice husk-earth based composites: A novel bio-based panel for buildings refurbishment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraj, R.; Lacoste, C.; Lacroix, P.; Bergeret, A. Sustainable thermal insulation biocomposites from rice husk, wheat husk, wood fibers and textile waste fibers: Elaboration and performances evaluation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 135, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, A.M.; Romero, M.L.; Serra, E.; Guerrero, J.C.; Perez, R. Sustainable insulation panel for buildings made of rice husks and posidonia. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 445, 137983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, M.; Navarro, A.; Avellaneda, J.; Lacasta, A.M. Characterization of thermal insulation materials developed with crop wastes and natural binders. World Barcelona 2014, 28, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Kolb, T.; Rüther, N.; Meinlschmidt, P.; Chen, H.; Yan, L. Physical, Mechanical, thermal and fire behaviour of recycled aggregate concrete block wall system with rice husk insulation. Energy Build. 2024, 320, 114560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Garrido, A.J.; Navarro, I.J.; García, J.; Yepes, V. A systematic literature review on modern methods of construction in building: An integrated approach using machine learning. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 73, 106725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Herrera, C.; Martínez-Soto, A.; Avendaño-Vera, C.; Carrasco, R.C.; Barbato, N.R. Industrialized Construction: A Systematic Review of Its Benefits and Guidelines for the Development of New Constructive Solutions Applied in Sustainable Projects. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.H.N.; Moon, H.; Ahn, Y. Critical Review of Trends in Modular Integrated Construction Research with a Focus on Sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvoisin, J.; Halstenberg, F.; Buchert, T.; Stark, R. A systematic literature review on modular product design. J. Eng. Des. 2016, 27, 488–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Systems Lab. Available online: https://www.wikihouse.cc/blocks/skylark-250 (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- Quidel, G.R.; Acuña, M.J.S.; Herrera, C.J.R.; Neira, K.R.; Cárdenas-Ramírez, J.P. Assessment of Modular Construction System Made with Low Environmental Impact Construction Materials for Achieving Sustainable Housing Projects. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Soto, A.; Jimenez-Gallardo, C.; Villarroel-Lopez, A.; Reyes-Riveros, A.; Höhl, J. Toward Sustainable Indoor Environments: Assessing the Impact of Thermal Insulation Measures on Air Quality in Buildings—A Case Study in Temuco, Chile. Sustainability 2024, 16, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, H.; Ozarisoy, B. An Analysis of the Development of Modular Building Design Elements to Improve Thermal Performance of a Representative High Rise Residential Estate in the Coastline City of Famagusta, Cyprus. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, M.; Rojas, C.; Cárdenas-Ramírez, J.P. Characterization of a Thermal Insulating Material Based on a Wheat Straw and Recycled Paper Cellulose to Be Applied in Buildings by Blowing Method. Sustainability 2023, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Herrera, C.; Martínez-Soto, A.; Avendaño-Vera, C.; Cárdenas-R, J.P. Characterization and utilization of sawdust waste generated from advanced manufacture for its application as a thermal insulation in sustainable buildings using the blowing technique. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 88, 109217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javier, R.H.C.; Karin, R.N.; Pablo, C.-R.J. Valorization of Wheat Crop Waste in Araucanía, Chile: Development of Prototype of Thermal Insulation Material for Blowing Technique and Geographical Analysis. Buildings 2023, 13, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, T.; Fischer, H.; Korjenic, A. Chopped Straw as an Insulation Material: The Influence of Different Blow-In Technologies and Flame Retardants on Hygrothermal Properties. Buildings 2023, 13, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, M.; Vera, M.; Parra, K.; Rojas, C.; Cárdenas, J.P. Potential of the Residual Fibers of Pisum Sativum (PS), for use in a Development of a Thermal Insulator Material. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.; Cea, M.; Iriarte, A.; Valdés, G.; Navia, R.; Cárdenas-R, J.P. Thermal insulation materials based on agricultural residual wheat straw and corn husk biomass, for application in sustainable buildings. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2019, 20, e00102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.R.; Lemus, M.C.; Diaz, F.E.R.; Ramirez, J.P.C. Physical, chemical and mechanical characterization of a prototype insulating material based on eucalyptus bark fiber. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2018, 16, 2441–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravena, M.; Almonacid-Muñoz, L.; Rojas-Herrera, C.; Herrera, H.; Cárdenas-Ramírez, J.P.; Veliz Reyes, A.; Sagredo-Saez, C. Evaluation of the Thermal Insulation Potential of Post-Harvest Blocks Using the Native Strain of the Edible Mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus. Buildings 2024, 14, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 442-1981; IEEE Guide for Soil Thermal Resistivity Measurements. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1980; pp. 1–16.
- D5334-00; Standard Test Method for Determination of Thermal Conductivity of Soil and Soft Rock by Thermal Needle Probe Procedure. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- UNE 23-725-90-2-3; Principle of the Method [in Spanish]. Spanish Association for Standardization (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 1990.
- Rosa, A.C.; Teixeira, I.; Lacasta, A.M.; Haurie, L.; Soares, C.A.; Tam, V.W.; Haddad, A. Experimental Design for the Propagation of Smoldering Fires in Corn Powder and Cornflour. Eng 2022, 4, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, M.; Lacasta, A.M.; Navarro, A.; Giraldo, M.P.; Lesar, B. Improvement of fire reaction and mould growth resistance of a new bio-based thermal insulation material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, P.L.; Rouilly, A.; Vandenbossche, V.; Raynaud, C. A review on the properties of cellulose fibre insulation. Build. Environ. 2016, 96, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadded, A.; Benltoufa, S.; Fayala, F.; Jemni, A. Thermo physical characterisation of recycled textile materials used for building insulating. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 5, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN 4108-10; Thermal Insulation and Energy Economy in Buildings–Part 10: Application-Related Requirements for Thermal Insulation Materials. Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN): Berlin, Germany, 2015.
- DIN EN ISO 6946:2017; Building Components and Building Elements–Thermal Resistance and Thermal Transmittance–Calculation Methods. Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN): Berlin, Germany, 2017.
- DesignBuilder LATAM; Official Website. Available online: https://designbuilder-lat.com (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- NTM 011/2:2014; Thermal Insulation–Requirements for the Application of Insulation Materials [in Spanish, Draft Standard]. Instituto Nacional de Normalización (INN): Santiago, Chile, 2014.
- Cintura, E.; Nunes, L.; Esteves, B.; Faria, P. Agro-industrial wastes as building insulation materials: A review and challenges for Euro-Mediterranean countries. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalife, E.; Sabouri, M.; Kaveh, M.; Szymanek, M. Recent Advances in the Application of Agricultural Waste in Construction. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas Herrera, C.J.; Rodríguez Neira, K.; Cárdenas-Ramírez, J.P. Evaluation of Two Chilean Native Macroalgae: ‘Pelillo’ (Gracilaria chilensis) and ‘Lamilla’ (Ulva sp.) for Thermal Insulation Application. Buildings 2023, 13, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorik, F.; Zach, J.; Lehto, M.; Kymäläinen, H.R.; Kuisma, R.; Jallinoja, M.; Illikainen, K.; Alitalo, S. Hygrothermal properties of advanced bio-based insulation materials. Energy Build. 2021, 253, 111528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Trabelsi, A.; El Mankibi, M. A review on the properties of straw insulation for buildings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 330, 127215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrez, I.; Hachem, H.; Jemni, A. Thermal insulation potential of wood-cereal straws/plaster composite. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavoni, S.; D’Alessandro, F.; Bianchi, F.; Asdrubali, F. Insulation materials for the building sector: A review and comparative analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 988–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charai, M.; Sghiouri, H.; Mezrhab, A.; Karkri, M. Thermal insulation potential of non-industrial hemp (Moroccan cannabis sativa L.) fibers for green plaster-based building materials. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 292, 126064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padre, T.Y.; Casas, L. Construcción + PDA: Temuco y Padre Las Casas; Ministerio de Vivienda y Urbanismo (MINVU): Santiago, Chile, 2018; ISBN 978-956-398-525-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kośny, J.; Thakkar, J.; Kamidollayev, T.; Sobkowicz, M.J.; Trelles, J.P.; Schmid, C.; Phan, S.; Annavajjala, S.; Horwath, P. Dynamic Thermal Performance Analysis of PCM Products Used for Energy Efficiency and Internal Climate Control in Buildings. Buildings 2023, 13, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Parameters for Energy Simulation in DesignBuilder | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Tipe | Characteristics |
| Activity | Residential | 0.02 (people/m2)—residential, residential occ schedule |
| Construction | Project template | Walls, roofs, and floors of Skylar 250 system have model infiltration of 0.7 (ac/h) |
| Opening | Project template | 30% wall to window ratio—double glazing, clear, 6 mm/6 mm |
| Lighting energy | Project template | 5.00 W/m2—100 lux |
| HVAC | ON, heating COP 0.5 and cooling COP 4.5, fuel electricity from grid | |
| Thermal Conductivity [W/mK] | AVG | SD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement (M) | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | ||
| Sample 1 | 0.040 | 0.035 | 0.037 | 0.041 | 0.038 | 0.0028 |
| Sample 2 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.042 | 0.040 | 0.041 | 0.0008 |
| Sample 3 | 0.040 | 0.041 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.0005 |
| Sample 4 | 0.041 | 0.040 | 0.041 | 0.038 | 0.040 | 0.0014 |
| 0.040 | 0.0014 | |||||
| Property | Unit | Wall M Rice Husk | Wall M Recycled PUR |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-value | W/m2K | 0.17 | 0.201 |
| Time lag | h | 14.50 | 8.50 |
| Decrement factor | _ | 40.30 | 11 |
| Heat storage capacity (whole component) | KJ/m2K | 98 | 69 |
| Thermal capacity of inner layers | KJ/m2K | 49 | 34 |
| Scenario | Heating Demand (kWh-year) | Cooling Demand (kWh-year) | Heating Demand (kWh/m2-year) | Cooling Demand (kWh/m2-year) | Total Demand (kWh/m2-year) | CO2 Emissions (kg eq-year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice husk insulation | 140.96 | 55.35 | 9.56 | 3.75 | 13.31 | 1956.81 |
| Recycled PUR insulation | 217.00 | 241.00 | 14.71 | 16.34 | 31.05 | 2116.04 |
| Without Insulation | 3909.14 | 350.06 | 265.03 | 23.73 | 288.76 | 4418.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez Neira, K.; Rojas-Herrera, C.J.; Cárdenas-Ramírez, J.P.; Torres Ramo, J.; Sánchez-Ostiz, A. Characterization and Energy Performance of Rice Husk Fiber Insulation Applied by the Blowing Technique in an Industrialized Modular Housing System. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4602. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094602
Rodríguez Neira K, Rojas-Herrera CJ, Cárdenas-Ramírez JP, Torres Ramo J, Sánchez-Ostiz A. Characterization and Energy Performance of Rice Husk Fiber Insulation Applied by the Blowing Technique in an Industrialized Modular Housing System. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4602. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094602
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez Neira, Karin, Carlos Javier Rojas-Herrera, Juan Pablo Cárdenas-Ramírez, Joaquín Torres Ramo, and Ana Sánchez-Ostiz. 2025. "Characterization and Energy Performance of Rice Husk Fiber Insulation Applied by the Blowing Technique in an Industrialized Modular Housing System" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4602. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094602
APA StyleRodríguez Neira, K., Rojas-Herrera, C. J., Cárdenas-Ramírez, J. P., Torres Ramo, J., & Sánchez-Ostiz, A. (2025). Characterization and Energy Performance of Rice Husk Fiber Insulation Applied by the Blowing Technique in an Industrialized Modular Housing System. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4602. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094602








