Study of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Based on Geometrical and Hemodynamic Characteristics: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Search
3. Current Risk Stratification Methods
4. Relationship Between LAA and Stroke
4.1. Geometric Characteristics of Left Atrial Appendage
4.2. Hemodynamic Characteristics of Left Atrial Appendage
5. Diagnostic Methods and Techniques
5.1. Invasive Imaging Modalities
5.1.1. Transesophageal Echocardiography
5.1.2. Intracardiac Echocardiography (ICE)
5.2. Non-Invasive Imaging Modalities
5.2.1. Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
5.2.2. Cardiac Computed Tomography (CCT)
5.2.3. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
5.3. Computer Aided Diagnosis
5.3.1. Computational Fluid Dynamics
5.3.2. Artificial Intelligence
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Literature Review on Risk Stratification
| Study | Number of Study | Sample Size | Risk Score Characteristics | Evaluating Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [51] | 12 | 205,939 | CHADS2/CHA2DS2-VASc | CHADS2: RR = 3.36 (2.93–3.85) CHA2DS2-VASc: RR = 5.15(3.85–6.88) |
| [52] | 6 | 31,539 | CHADS2/CHA2DS2-VASc | RR |
| [143] | 19 | 714,672 | CHADS2 | Odds ratio |
| [53] | 10 | 166,017 | CHA2DS2-VASc | The summary annual risk of stroke = 1.61% |
| [24] | 6 | 9845 | CHADS2/CHA2DS2-VASc | CHADS2: DOR = 2.86 (1.79–4.55) AUC = 0.6728 CHA2DS2-VASc: DOR = 2.8 (1.83–4.28) AUC = 0.6655 |
| [26] | 19 | 846,748 | CHA2DS2-VASc | C-statistic = 0.64–0.71 |
| [27] | 6 | 363,432 | CHA2DS2-VASc/ATRIA | CHA2DS2-VASc: C-statistic = 0.63 ATRIA: C-statistic = 0.66 |
| [30] | 7 | 18,694 | ORBIT/HAS-BLED | ORBIT: C-statistic = 0.65 (0.60–0.69) HAS-BLED: C-statistic = 0.63 (0.60–0.67) |
| [22] | 50 | 669,217 | ATRIA/ATRIA bleeding/CHADS2/CHA2DS2-VASc/HAS-BLED/ORBIT | CHADS2: C-statistic = 0.64 (0.63–0.65) CHA2DS2-VASc: C-statistic = 0.62 (0.61–0.64) HAS-BLED: C-statistic = 0.62 (0.58–0.66) |
| [144] | 9 | 101,118 | HAS-BLED/ATRIA/ORBIT | odds ratio |
| [145] | 18 | 321,888 | ABC-bleeding score/ATRIA/HAS-BLED/ORBIT/ | Odds ratio/sensitivity and specificity analysis |
| [146] | 15 | 6223 | CHA2DS2-VASc | Odds ratio/I2/sensitivity analysis |
| [23] | 39 | 10,000+ | HAS- BLED/ORBIT/ATRIA/CHA2DS2-VASc/CHADS2/ABC | HAS-BLED: 0.63 [0.61, 0.65] ORBIT: 0.63 [0.60, 0.67] ATRIA: 0.63 [0.60, 0.66] CHADS2: 0.61 [0.57, 0.65] CHA2DS2-VASc: 0.61 [0.57, 0.66] ABC: 0.65 [0.58, 0.72] |
| [25] | 110 | 6,627,101 | CHA2DS2-VASc/CHADS2/ATRIA/Framingham/The ABC stroke risk score | CHA2DS2-VASc: 0.644 [0.635–0.653] CHADS2: 0.658 (0.644–0.672) ATRIA: 0.683 (0.658–0.708) The ABC stroke risk score: 0.678 (0.658–0.697) |
| [28] | 19 | 592,009 | CHA2DS2-VASc | c-statistic = 0.66 (0.63–0.69) |
| [29] | 28 | 639,450 | CHA2DS2-VASc | c-statistic = 0.66 (0.62–0.70) |
| [31] | 17 | 305,498 | HAS-BLED/ORBIT | HAS-BLED: 0.63 (0.60–0.66) ORBIT: 0.61 (0.59–0.63) |
| [11] | 12 | 12,510 | ABC stroke/CHA2DS2-VASc/ABC bleeding | ABC stroke: c-statistic = 0.67 (0.65–0.68) CHA2DS2-VASc: c-statistic = 0.64 (0.60–0.67) ABCbleeding: c-statistic = 0.66 (0.61–0.70) |
| [32] | 14 | – | HAS-BLED/ORBIT/ABC bleeding | HAS-BLED: 0.63 (0.61–0.65) ORBIT: 0.65 (0.62–0.68) ABC bleeding: 0.68 (0.61–0.75) |
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Si, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lip, G.Y. Prevalence, incidence, and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation in China: New insights into the global burden of atrial fibrillation. Chest 2015, 147, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, R.B.; Yin, X.; Gona, P.; Larson, M.G.; Beiser, A.S.; McManus, D.D.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Lubitz, S.A.; Magnani, J.W.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. 50 year trends in atrial fibrillation prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and mortality in the framingham heart study: A cohort study. Lancet 2015, 386, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizhanov, K.A.; Abzaliyev, K.B.; Baimbetov, A.K.; Sarsenbayeva, A.B.; Lyan, E. Atrial fibrillation: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and clinical complications (literature review). J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2023, 34, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.Y.; Gupta, D.; Lip, G.Y.H. Atrial fibrillation and the prothrombotic state: Revisiting virchow’s triad in 2020. Heart 2020, 106, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Seo, J.; Uhm, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Sung, J.; Pak, H.; Lee, M.; Joung, B. Why Is Left Atrial Appendage Morphology Related to Strokes? An Analysis of the Flow Velocity and Orifice Size of the Left Atrial Appendage. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2015, 26, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Sheitt, H.; Bristow, M.S.; Lydell, C.; Howarth, A.G.; Heydari, B.; Prato, F.S.; Drangova, M.; Thornhill, R.E.; Nery, P.; et al. Left atrial vortex size and velocity distributions by 4D flow MRI in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: Associations with age and CHA2DS2-VASc risk score. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 51, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Writing Group Members; Lloyd-Jones, D.; Adams, R.J.; Brown, T.M.; Carnethon, M.; Dai, S.; De Simone, G.; Ferguson, T.B.; Ford, E.; Furie, K.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, e46–e215. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-J.; Wolf, P.A.; Kelly-Hayes, M.; Beiser, A.S.; Kase, C.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; D’Agostino, R.B. Stroke severity in atrial fibrillation. Stroke 1996, 27, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulli, D.A.; Stanko, H.; Levine, R.L. Atrial fibrillation is associated with severe acute ischemic stroke. Neuroepidemiology 2003, 22, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Ali, M.; Shahid, I. Meta-analysis on performance of ABC and GARFIELD-AF compared to CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED in anticoagulated atrial fibrillation patients. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2024, 60, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; He, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Hong, K. The HAS-BLED score for predicting major bleeding risk in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2015, 38, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biase, L.; Santangeli, P.; Anselmino, M.; Mohanty, P.; Salvetti, I.; Gili, S.; Horton, R.; Sanchez, J.E.; Bai, R.; Mohanty, S.; et al. Does the left atrial appendage morphology correlate with the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation? results from a multicenter study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dueñas-Pamplona, J.; García, J.G.; Castro, F.; Muñoz-Paniagua, J.; Goicolea, J.; Sierra-Pallares, J. Morphing the left atrium geometry: A deeper insight into blood stasis within the left atrial appendage. Appl. Math. Model. 2022, 108, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, M.; et al. Stroke risk evaluation for patients with atrial fibrillation: Insights from left atrial appendage with fluid-structure interaction analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 148, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, D.; Monteleone, A.; Musotto, G.; Bosi, G.M.; Burriesci, G. Effect of the alterations in contractility and morphology produced by atrial fibrillation on the thrombosis potential of the left atrial appendage. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 586041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedula, V.; George, R.; Younes, L.; Mittal, R. Hemodynamics in the left atrium and its effect on ventricular flow patterns. J. Biomech. Eng. 2015, 137, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas-Pamplona, J.; García, J.G.; Sierra-Pallares, J.; Ferrera, C.; Agujetas, R.; López-Mínguez, J.R. A comprehensive comparison of various patient-specific CFD models of the left atrium for atrial fibrillation patients. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, H.; Liu, X.; Qian, J.; Cai, S.; Fan, H.; Gao, Q. LAFlowNet: A dynamic graph method for the prediction of velocity and pressure fields in left atrium and left atrial appendage. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 136, 108896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Lin, H.; Qian, J.; Liu, X.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Fan, H.; Zheng, Z. A deep learning model for efficient end-to-end stratification of thrombotic risk in left atrial appendage. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferez, X.M.; Mill, J.; Juhl, K.A.; Acebes, C.; Iriart, X.; Legghe, B.; Cochet, H.; De Backer, O.; Paulsen, R.R.; Camara, O. Deep learning framework for real-time estimation of in-silico thrombotic risk indices in the left atrial appendage. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 694945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, M.; Farcomeni, A.; Romiti, G.F.; Di Rocco, A.; Placentino, F.; Diemberger, I.; Lip, G.Y.; Boriani, G. Association between clinical risk scores and mortality in atrial fibrillation: Systematic review and network meta-regression of 669,000 patients. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cai, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W. Diagnostic Accuracy of the HAS-BLED Bleeding Score in VKA- or DOAC-Treated Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 757087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.D.; Shen, X.L.; Zhao, R.; Li, G.F.; Wu, Y.L.; Tao, X.X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.J.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.T.; et al. Predictive role of CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc scores on stroke and thromboembolism in patients without atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Endt, V.H.W.; Milders, J.; de Vries, B.B.L.P.; Trines, S.A.; Groenwold, R.H.H.; Dekkers, O.M.; Trevisan, M.; Carrero, J.J.; van Diepen, M.; Dekker, F.W.; et al. Comprehensive comparison of stroke risk score performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis among 6 267 728 patients with atrial fibrillation. Europace 2022, 24, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Doorn, S.; Debray, T.P.A.; Kaasenbrood, F.; Hoes, A.W.; Rutten, F.H.; Moons, K.G.M.; Geersing, G. Predictive performance of the CHA2DS2-VASc rule in atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Fu, L.; Ding, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, Z.; Hu, J.; Hong, K. Meta-analysis of ATRIA versus CHA2DS2-VASc for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in patients with atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 227, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, T.J.; Usman, M.S.; Shahid, I.; Ahmed, J.; Khan, S.U.; Ya’qoub, L.; Rihal, C.S.; Alkhouli, M. Utility of the CHA2DS2-VASc score for predicting ischaemic stroke in patients with or without atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, J.; Zaheer, Z.; Yasmin, F.; Ahmed, A.; Hamza, M.; Cheema, H.A.; Akbar, U.A.; Aamir, M.; Dhama, K.; Saeed, S.; et al. Abstract 17712: The Discrimination Ability of the CHA2DS2-VASc Score for Predicting Ischemic Stroke in Patients With and Without Atrial Fibrillation: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Circulation 2023, 148 (Suppl. S1), A17712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Yu, J.; Lip, G.Y.; Hong, K. Comparing the ORBIT and HAS-BLED bleeding risk scores in anticoagulated atrial fibrillation patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 109703–109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; He, W.; Guo, L. HAS-BLED vs. ORBIT scores in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 9, 1042763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Zhu, W.; Guo, S.; Hong, H. Predictive performance of HAS-BLED, ORBIT, ABC, and DOAC scores for major bleeding in atrial fibrillation patients on DOACs. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 128, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, M.I.; Mill, J.; Fernandez-Quilez, A.; Olivares, A.L.; Silva, E.; de Potter, T.; Camara, O. Joint Analysis of Morphological Parameters and In Silico Haemodynamics of the Left Atrial Appendage for Thrombogenic Risk Assessment. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2022, 2022, 9125224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masci, A.; Barone, L.; Dedè, L.; Fedele, M.; Tomasi, C.; Quarteroni, A.; Corsi, C. The Impact of Left Atrium Appendage Morphology on Stroke Risk Assessment in Atrial Fibrillation: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Study. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-C.; Shin, J.; Ban, J.-E.; Choi, J.-I.; Park, S.-W.; Kim, Y.-H. Left atrial appendage: Morphology and function in patients with paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 29, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, M.; Kawasaki, M.; Tanaka, R.; Ono, K.; Watanabe, T.; Hirose, T.; Nagaya, M.; Noda, T.; Watanabe, S.; Minatoguchi, S. Left atrial appendage emptying fraction assessed by a feature-tracking echocardiographic method is a determinant of thrombus in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, N.; Park, H.-C.; Mao, Y.; Hong, S.J.; Lee, Y.; Spragg, D.D.; Calkins, H.; Trayanova, N.A. Slow blood-flow in the left atrial appendage is associated with stroke in atrial fibrillation patients. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Fang, R.; Li, Z.-Y. Evaluation of Stroke Risk in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Using Morphological and Hemodynamic Characteristics. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 842364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Villalba, M.; Rossini, L.; Gonzalo, A.; Vigneault, D.; Martinez-Legazpi, P.; Durán, E.; Flores, O.; Bermejo, J.; McVeigh, E.; Kahn, A.M.; et al. Demonstration of patient-specific simulations to assess left atrial appendage thrombogenesis risk. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 596596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, G.M.; Cook, A.; Rai, R.; Menezes, L.J.; Schievano, S.; Torii, R.; Burriesci, G. Computational fluid dynamic analysis of the left atrial appendage to predict thrombosis risk. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, M.; Zingaro, A.; Dede’, L.; Quarteroni, A.M. Impact of atrial fibrillation on left atrium haemodynamics: A computational fluid dynamics study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 150, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: The euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gage, B.; Waterman, A.; Shannon, W.; Boechler, M.; Rich, M.; Radford, M. Validation of clinical classification schemes for predicting stroke: Results from the national registry of atrial fibrillation. ACC Curr. J. Rev. 2001, 10, 2864–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, Z.; Lindbäck, J.; Alexander, J.H.; Hanna, M.; Held, C.; Hylek, E.M.; Lopes, R.D.; Oldgren, J.; Siegbahn, A.; Stewart, R.A.; et al. The ABC (age, biomarkers, clinical history) stroke risk score: A biomarker-based risk score for predicting stroke in atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, P.W.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Levy, D.; Belanger, A.M.; Silbershatz, H.; Kannel, W.B. Prediction of coronary heart disease using risk factor categories. Circulation 1998, 97, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Nieuwlaat, R.; De Vos, C.B.; Crijns, H.J.; Lip, G.Y. A novel user-friendly score (has-bled) to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation: The euro heart survey. Chest 2010, 138, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.C.; Go, A.S.; Chang, Y.; Borowsky, L.; Pomernacki, N.K.; Singer, D.E. Comparison of risk stratification schemes to predict thromboembolism in people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, Z.; Oldgren, J.; Lindbäck, J.; Alexander, J.H.; Connolly, S.J.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Held, C.; Hylek, E.M.; Lopes, R.D.; et al. The novel biomarker-based ABC (age, biomarkers, clinical history)-bleeding risk score for patients with atrial fibrillation: A derivation and validation study. Lancet 2016, 387, 2302–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.C.; Simon, D.N.; Thomas, L.E.; Hylek, E.M.; Gersh, B.J.; Ansell, J.E.; Kowey, P.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Chang, P.; Fonarow, G.C.; et al. The ORBIT bleeding score: A simple bedside score to assess bleeding risk in atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 3258–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Zhang, A.-D.; Lu, H.-Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, F.-F.; Li, Z.-C. Chads2 versus cha2ds2-vasc score in assessing the stroke and thromboembolism risk stratification in patients with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. JGC 2013, 10, 258. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.-G.; Xiong, Q.-M.; Hong, K. Meta-Analysis of CHADS2 versus CHA2DS2-VASc for Predicting Stroke and Thromboembolism in Atrial Fibrillation Patients Independent of Anticoagulation. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2015, 42, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Chen, S.; Senoo, K.; Proietti, M.; Hong, K.; Lip, G.Y. The CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc scores for predicting ischemic stroke among East Asian patients with atrial fibrillation: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 195, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joundi, R.A.; Cipriano, L.E.; Sposato, L.A.; Saposnik, G.; on behalf of the Stroke Outcomes Research Working Group. Ischemic Stroke Risk in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and CHA2DS2-VASc Score of 1. Stroke 2016, 47, 1364–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Chen, S.; Jiang, X.; Liao, J.; Chen, W.; Zou, L.; Su, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, Y.; et al. Left Atrial Appendage Thrombus in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation before Catheter Ablation and Cardioversion: Risk Factors beyond the CHA2DS2-VASc Score. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, T.; Shantsila, E.; Lip, G.Y. Mechanisms of thrombogenesis in atrial fibrillation: Virchow’s triad revisited. Lancet 2009, 373, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelieva, I.; Bajpai, A.; Camm, A.J. Stroke in atrial fibrillation: Update on pathophysiology, new antithrombotic therapies, and evolution of procedures and devices. Ann. Med. 2007, 39, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; DI Biase, L.; Horton, R.P.; Nguyen, T.; Morhanty, P.; Natale, A. Left atrial appendage studied by computed tomography to help planning for appendage closure device placement. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2010, 21, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Villarreal, A. Relationship between left atrial appendage morphology and thrombus formation in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic mitral valve disease. Cirugía Card. En México 2024, 4, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Abanador-Kamper, N.; Bepperling, J.; Seyfarth, M.; Haage, P.; Kamper, L. Impact of left atrial appendage morphology on thrombus formation in TAVI patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Takatsuki, S.; Inagawa, K.; Katsumata, Y.; Nishiyama, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Fukumoto, K.; Aizawa, Y.; Tanimoto, Y.; Tanimoto, K.; et al. Anatomical characteristics of the left atrial appendage in cardiogenic stroke with low CHADS2 scores. Heart Rhythm. 2013, 10, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, M.; Muuronen, A.; Arponen, O.; Mustonen, P.; Hedman, M.; Jäkälä, P.; Vanninen, R.; Taina, M. Left atrial appendage morphology in patients with suspected cardiogenic stroke without known atrial fibrillation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurram, I.M.; Dewire, J.; Mager, M.; Maqbool, F.; Zimmerman, S.L.; Zipunnikov, V.; Beinart, R.; Marine, J.E.; Spragg, D.D.; Berger, R.D.; et al. Relationship between left atrial appendage morphology and stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2013, 10, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghi, S.; Chang, A.D.; Akiki, R.; Collins, S.; Novack, T.; Hemendinger, M.; Schomer, A.; Mac Grory, B.; Cutting, S.; Burton, T.; et al. The left atrial appendage morphology is associated with embolic stroke subtypes using a simple classification system: A proof of concept study. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2020, 14, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słodowska, K.; Szczepanek, E.; Dudkiewicz, D.; Hołda, J.; Bolechała, F.; Strona, M.; Lis, M.; Batko, J.; Koziej, M.; Hołda, M.K. Morphology of the left atrial appendage: Introduction of a new simplified shape-based classification system. Heart Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongcharoen, W.; Tsao, H.; Wu, M.; Tai, C.; Chang, S.; Lin, Y.; Lo, L.; Chen, Y.; Sheu, M.; Chang, C.; et al. Morphologic Characteristics of the Left Atrial Appendage, Roof, and Septum: Implications for the Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2006, 17, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Seo, Y.; Kawamatsu, N.; Sato, K.; Sugano, A.; Machino-Ohtsuka, T.; Kawamura, R.; Nakajima, H.; Igarashi, M.; Sekiguchi, Y.; et al. Complex left atrial appendage morphology and left atrial appendage thrombus formation in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adukauskaite, A.; Barbieri, F.; Senoner, T.; Plank, F.; Knoflach, M.; Boehme, C.; Hintringer, F.; Mueller, S.; Bauer, A.; Feuchtner, G.; et al. Left atrial appendage morphology and left atrial wall thickness are associated with cardio-embolic stroke. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedios, S.; Koutalas, E.; Kornej, J.; Rolf, S.; Arya, A.; Sommer, P.; Husser, D.; Hindricks, G.; Bollmann, A. Cardiogenic stroke despite low cha2ds2-vasc score: Assessing stroke risk by left atrial appendage anatomy (ask LAA). J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2015, 26, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Gao, Q.; Wei, R.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Yao, Y.; Fan, H.; Zheng, Z. Fractal geometry illustrated left atrial appendage morphology that predicted thrombosis and stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 779528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Li, Q.; Xia, Z.; Yan, S.; Wei, Y.; Hong, K.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, X. Risk factors of thromboembolism in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients with low CHA2DS2-VASc score. Medicine 2019, 98, e14549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.-Q. Value of left atrial diameter with cha2ds2-vasc score in predicting left atrial/left atrial appendage thrombosis in non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Arq. Bras. De Cardiol. 2021, 116, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Xi, S.; Gan, T.; Zhao, L. Independent risk factors of atrial thrombosis in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and low cha 2 ds 2-vasc scores. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao= J. South. Med. Univ. 2021, 41, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Rong, W.; He, B.; Zhao, L. Risk factors for left atrial thrombus or spontaneous echo contrast in non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients with low CHA2DS2-VASc score. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2022, 53, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Nordsletten, D.A.; Williams, S.E.; Aslanidi, O.; de Vecchi, A. Imaging and biophysical modelling of thrombogenic mechanisms in atrial fibrillation and stroke. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 9, 1074562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, B.; Furie, B.C. Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M. Remodeling the blood coagulation cascade. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2003, 16, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ling, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Tong, Q.; Qian, Y. Finding low CHA2DS2-VASc scores unreliable? Why not give morphological and hemodynamic methods a try? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 9, 1032736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkiran, A.; Amier, R.P.; Hofman, M.B.M.; van der Geest, R.J.; Robbers, L.F.H.J.; Hopman, L.H.G.A.; Mulder, M.J.; van de Ven, P.; Allaart, C.P.; van Rossum, A.C.; et al. Altered left atrial 4D flow characteristics in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in the absence of apparent remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdian, E.; Dubowitz, D.J.; Mauger, C.A.; Wang, A.; Young, A.A. WSSNet: Aortic Wall Shear Stress Estimation Using Deep Learning on 4D Flow MRI. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 769927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Park, H.-C.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.-G. Comparison of morphologic features and flow velocity of the left atrial appendage among patients with atrial fibrillation alone, transient ischemic attack, and cardioembolic stroke. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 119, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, N.; Kato, K.; Ejima, K.; Sato, H.; Fukushima, K.; Saito, C.; Hayashi, K.; Arai, K.; Manaka, T.; Ashihara, K.; et al. Correlation between left atrial appendage morphology and flow velocity in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, N.; Akdemir, O.; Turgut, B.; Demir, M.; Ekuklu, G.; Vural, Ö.; Özbay, G.; Utku, U. Hypercoagulopathy in stroke patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: Hematologic and cardiologic investigations. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2006, 12, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, J.G.; Jeske, W.; Wilber, D.J. Acute onset human atrial fibrillation is associated with local cardiac platelet activation and endothelial dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1790–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, F.; Roldán, V.; Climent, V.E.; Ibáñez, A.; García, A.; Marco, P.; Sogorb, F.; Lip, G.Y.H. Plasma von willebrand factor, soluble thrombomodulin, and fibrin D-dimer concentrations in acute onset non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation. Heart 2004, 90, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, J.W.; Teoh, H.; Verma, S. Endothelial cell control of thrombosis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2015, 15, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, R.J.; Nakagawa, T.; Johnson, R.J.; Thurman, J.M. The role of endothelial cell injury in thrombotic microangiopathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Joung, B.; Uhm, J.-S.; Shim, C.Y.; Hwang, C.; Lee, M.H.; Pak, H.-N. High left atrial pressures are associated with advanced electroanatomical remodeling of left atrium and independent predictors for clinical recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhart, M.; Lewalter, T.; Mittmann-Braun, E.L.; Karbach, N.C.; Andrié, R.P.; Hammerstingl, C.; Fimmers, R.; Kreuz, J.; Nickenig, G.; Schrickel, J.W.; et al. Left atrial pressure as predictor for recurrence of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2013, 38, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, W.J.; Weintraub, R.M.; Waksmonski, C.A.; Haering, J.M.; Rooney, P.S.; Maslow, A.D.; Johnson, R.G.; Douglas, P.S. Accuracy of transesophageal echocardiography for identifying left atrial thrombi: A prospective, intraoperative study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1995, 123, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Bogush, N.; Caceres, J.D.; Msaouel, P.; Tobis, J.M. Diagnostic accuracy of transesophageal echocardiogram for the detection of patent foramen ovale: A meta-analysis. Echocardiography 2014, 31, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoneim, S.S.; Mulvagh, S.L. Techniques to improve left atrial appendage imaging. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2014, 7, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, Y.; Bernards, J.; Mekeirele, M.; Hoffmann, B.; Raes, M.; Malbrain, M. Hemodynamic monitoring: To calibrate or not to calibrate? part 1–calibrated techniques. Anestezjol. Intensywna Ter. 2019, 47, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Ren, S.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, C.; Tan, X.; Pan, Y.; Sun, F.; Ren, W. Real-time 3D echocardiographic transilluminated imaging combined with artificially intelligent left atrial appendage measurement for atrial fibrillation interventional procedures. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1043551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkowski, M.M.; Jubele, K.; Marín, F.; Gandjbakhch, E.; Ptaszynski, P.; Merino, J.L.; Lenarczyk, R.; Potpara, T.S. Diagnosis and management of left atrial appendage thrombus in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing cardioversion or percutaneous left atrial procedures: Results of the European heart rhythm association survey. EP Eur. 2020, 22, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobrino, A.; Tzikas, A.; Freixa, X.; Pulido, A.; Chan, J.; Garceau, P.; Ibrahim, R.; Basmadjian, A.J. Intra-procedural imaging of the left atrial appendage: Implications for closure with the Amplatzer™ cardiac plug. Arch. Cardiol. Mex. 2014, 84, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Brown, A. Transesophageal echocardiography: Implications for the critical care nurse. Crit. Care Nurse 1994, 14, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Nam, J.E.; Choe, K.O.; Choi, E.Y.; Shim, C.Y.; Choi, B.W. Thrombus in the left atrial appendage in stroke patients: Detection with cardiac CT angiography—A preliminary report. Radiology 2008, 249, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Husain, S.A.; Kelesidis, I.; Sanz, J.; Medina, H.M.; Garcia, M.J. Detection of left atrial appendage thrombus by cardiac computed tomography in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Seo, Y.; Ishizu, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Machino, T.; Harimura, Y.; Kawamura, R.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Tada, H.; Aonuma, K. Analysis of the left atrial appendage by three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutt, E.G.; Klein, D.H.; Mattrey, R.M.; Riess, J.G. Injectable microbubbles as contrast agents for diagnostic ultrasound imaging: The key role of perfluorochemicals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2003, 42, 3218–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Shen, J.X.; Xue, F.H.; Cheng, H.D.; Qu, X.F. A computer-aided diagnostic algorithm improves the accuracy of transesophageal echocardiography for left atrial thrombi: A single-center prospective study. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akella, K.; Murtaza, G.; Turagam, M.; Sharma, S.; Madoukh, B.; Amin, A.; Gopinathannair, R.; Lakkireddy, D. Evaluating the role of transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) or intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) in left atrial appendage occlusion: A meta-analysis. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2021, 60, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desimone, C.V.; Asirvatham, S.J. Ice imaging of the left atrial appendage. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2014, 25, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, J.; Stec, S.; Pilichowska-Paszkiet, E.; Zaborska, B.; Sikora-Frac, M.; Kryski, T.; Michaowska, I.; Łopatka, R.; Kuakowski, P. Intracardiac echocardiography for detection of thrombus in the left atrial appendage: Comparison with transesophageal echocardiography in patients undergoing ablation for atrial fibrillation: The action-ice i study. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2013, 6, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Winoker, J.S.; Roberts, S.C.; Msaouel, P.; Zaman, M.O.; Gevorgyan, R.; Tobis, J.M. Accuracy of conventional transthoracic echocardiography for the diagnosis of intracardiac right-to-left shunt: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Echocardiography 2014, 31, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.D.; Steinberg, M.; Showler, A.; Burry, L.; Bhatia, R.S.; Tomlinson, G.A.; Bell, C.M.; Morris, A.M. Diagnostic accuracy of transthoracic echocardiography for infective endocarditis findings using transesophageal echocardiography as the reference standard: A meta-analysis. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2017, 30, 639–646.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Nanda, N.C. Is it time to move on from two-dimensional transesophageal to three-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography for assessment of left atrial appendage? review of existing literature. Echocardiography 2012, 29, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakus, G.; Kodali, V.; Inamdar, V.; Nanda, N.C.; Suwanjutah, T.; Pothineni, K.R. Comparative assessment of left atrial appendage by transesophageal and combined two-and three-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography. Echocardiography 2008, 25, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, A.; Cantré, D.; Beller, E.; Streckenbach, F.; Öner, A.; Ince, H.; Weber, M.-A.; Meinel, F.G. Cardiac CT: Why, when, and how: Update 2019. Der Radiol. 2019, 59 (Suppl. 1), 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M. Left ventricular thrombus in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Intern. Med. 2019, 58, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontone, G.; Andreini, D.; Bartorelli, A.L.; Cortinovis, S.; Mushtaq, S.; Bertella, E.; Annoni, A.; Formenti, A.; Nobili, E.; Trabattoni, D.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of coronary computed tomography angiography: A comparison between prospective and retrospective electrocardiogram triggering. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, R.; Osende, J.I.; Fayad, Z.A.; Fallon, J.T.; Fuster, V.; Mizsei, G.; Dickstein, E.; Drayer, B.; Badimon, J.J. In vivo noninvasive detection and age definition of arterial thrombus by MRI. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, L.D.; Horne, B.D.; Anderson, J.L.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Whisenant, B.K. Usefulness of left atrial appendage volume as a predictor of embolic stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 112, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajiah, P.S.; François, C.J.; Leiner, T. Cardiac MRI: State of the art. Radiology 2023, 307, e223008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Xiao, J.; Hu, Z.; Kwan, A.C.; Fan, Z. Imaging of left heart intracardiac thrombus: Clinical needs, current imaging, and emerging cardiac magnetic resonance techniques. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 16, 17539447221107737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohrs, O.K.; Ruebesam, D.; Peters, J. Computed tomography in a patient after percutaneous left atrial appendage transcatheter occlusion (PLAATO). Heart 2006, 92, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulat, G.; McCarthy, P.; Markl, M. 4D flow with MRI. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 22, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, M.; Khatir, Z.; Khan, A.; Bissell, M. The impact of 4D-Flow MRI spatial resolution on patient-specific CFD simulations of the thoracic aorta. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, M.; Frydrychowicz, A.; Kozerke, S.; Hope, M.; Wieben, O. 4D flow MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 1015–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, M.; Lee, D.C.; Ng, J.; Carr, M.; Carr, J.; Goldberger, J.J. Left atrial 4-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging: Stasis and velocity mapping in patients with atrial fibrillation. Investig. Radiol. 2016, 51, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, F.M.; Grieve, S.M. Spatial resolution and velocity field improvement of 4D-flow MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wåhlin, A.; Ambarki, K.; Birgander, R.; Wieben, O.; Johnson, K.; Malm, J.; Eklund, A. Measuring pulsatile flow in cerebral arteries using 4D phase-contrast MR imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, X.; Mill, J.; Juhl, K.A.; Olivares, A.; Jimenez-Perez, G.; Paulsen, R.R.; Camara, O.T. Deep learning surrogate of computational fluid dynamics for thrombus formation risk in the left atrial appendage. In Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart. Multi-Sequence CMR Segmentation, CRT-EPiggy and LV Full Quantification Challenges; Pop, M., Sermesant, M., Camara, O., Zhuang, X., Li, S., Young, A., Mansi, T., Suinesiaputra, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparotti, E.; Fanni, B.M.; Del Pia, E.; Capellini, K.; Danielli, F.; Berti, F.; Clemente, A.; Berti, S.; Pennnati, G.; Petrini, L.; et al. Computational fluid dynamic simulation to evaluate the device-related effects after left atrial appendage occlusion. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, Paris, France, 3–5 May 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Masci, A.; Dalessandro, N.; Scivoletto, A.; Severi, S.; Ansaloni, F.; Monte, A.D.; Tomasi, C.; Fabbri, C.; Corsi, C. Endocardial left atrial appendage occlusion in atrial fibrillation: Computational fluid dynamics simulations to assess stroke risk. EP Eur. 2021, 23 (Suppl. S3), euab116–euab173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodrati-Misek, M.; Schlöglhofer, T.; Gross, C.; Maurer, A.; Zimpfer, D.; Beitzke, D.; Zonta, F.; Moscato, F.; Schima, H.; Aigner, P. Left atrial appendage occlusion in ventricular assist device patients to decrease thromboembolic events: A computer simulation study. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1010862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mill, J.; Agudelo, V.; Olivares, A.L.; Pons, M.I.; Silva, E.; Nuñez-Garcia, M.; Morales, X.; Arzamendi, D.; Freixa, X.; Noailly, J.; et al. Sensitivity analysis of in silico fluid simulations to predict thrombus formation after left atrial appendage occlusion. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäck, S.; Lantz, J.; Skoda, I.; Henriksson, L.; Persson, A.; Karlsson, L.O.; Carlhäll, C.-J.; Ebbers, T. Comprehensive left atrial flow component analysis reveals abnormal flow patterns in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2024, 326, H511–H521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon-Murphy, D.; Marlevi, D.; Ruijsink, B.; Qureshi, A.; Chubb, H.; Kerfoot, E.; O’Neill, M.; Nordsletten, D.; Aslanidi, O.; de Vecchi, A. Modeling left atrial flow, energy, blood heating distribution in response to catheter ablation therapy. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Albers, G.W.; Chatzikonstantinou, A.; De Marchis, G.M.; Ferrari, J.; George, P.; Katan, M.; Knoflach, M.; Kim, J.S.; Li, L.; et al. Validation and comparison of imaging-based scores for prediction of early stroke risk after transient ischaemic attack: A pooled analysis of individual-patient data from cohort studies. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, T.; Al-Issa, A.; Pourmorteza, A.; McVeigh, E.R.; Wada, S.; Ashikaga, H. A computational framework for personalized blood flow analysis in the human left atrium. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 3284–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, P.; Kelion, A.; Hyde, T.; Barnes, E.; Rahbi, H.; Beale, A.; Ramcharitar, S. CT coronary angiography with HeartFlow®: A user’s perspective. Br. J. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Lu, Y.; Li, B.; Gao, Q.; Xu, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Segmentation of cardiac tissues and organs for CCTA images based on a deep learning model. Front. Phys. 2023, 11, 1266500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Cui, X.; Jiang, F.; Chen, N.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, S.; Zou, J. Using machine learning to predict atrial fibrillation diagnosed after ischemic stroke. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 347, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, S.-H.; Wang, T.-H.; Lan, T.-Y.; Tseng, V.S.; Tsao, H.-M.; Wang, H.-H.; Tang, G.-J. Deep learning-based automatic left atrial appendage filling defects assessment on cardiac computed tomography for clinical and subclinical atrial fibrillation patients. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.; Daniel; Ferez, X.M.; Rey, O.C. Geometrical Deep Learning for the Estimation of Residence Time in the Left Atria. In International Workshop on Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, W.-S.; Schellingerhout, D.; Lee, H.; Lee, K.-J.; Kim, C.K.; Kim, B.J.; Chung, J.-W.; Lim, J.-S.; Kim, J.-T.; Kim, D.-H.; et al. Deep learning-based automatic classification of ischemic stroke subtype using diffusion-weighted images. J. Stroke 2024, 26, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, N.; Paheding, S.; Elkin, C.P.; Devabhaktuni, V. U-net and its variants for medical image segmentation: A review of theory and applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82031–82057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, B. Interpretable graph convolutional network of multi-modality brain imaging for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), IEEE, Kolkata, India, 28–31 March 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Chan, Y.H.; Girish, D.; Rajapakse, J.C. IMG-GCN: Interpretable modularity-guided structure-function interactions learning for brain cognition and disorder analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Marrakesh, Morocco, 7–11 October 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 470–480. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Chan, Y.H.; Girish, D.; Rajapakse, J.C.; Han, W.; Kang, X.; He, W.; Jiang, L.; Li, H.; Xu, B. A new method for disease diagnosis based on hierarchical BRB with power set. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ng, C.Y.; Li, G.; Liu, T. Meta-analysis of CHADS2 Score in Predicting Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yu, P.; Cui, W.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Zeng, C. Comparison of HAS-BLED with other risk models for predicting the bleeding risk in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation A PRISMA-compliant article. Medicine 2020, 99, e20782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Xie, Q.; Ma, L.; Hu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, G.; Cui, Y. Accuracy of HAS-BLED and other bleeding risk assessment tools in predicting major bleeding events in atrial fibrillation: A network meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Guo, Z.H.; Zhang, H.B. CHA2DS2-VASc Score as a Predictor for Left Atrial Thrombus or Spontaneous Echo Contrast in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2679539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


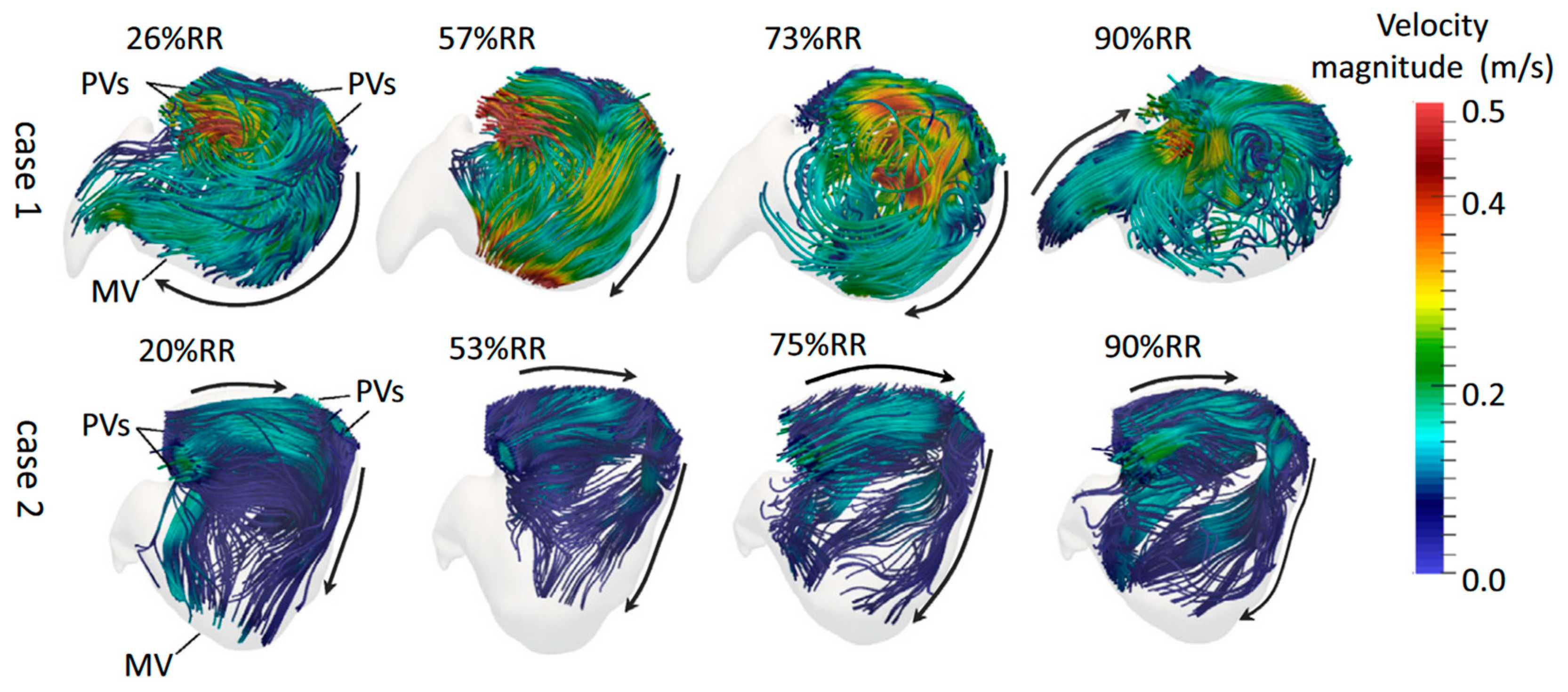
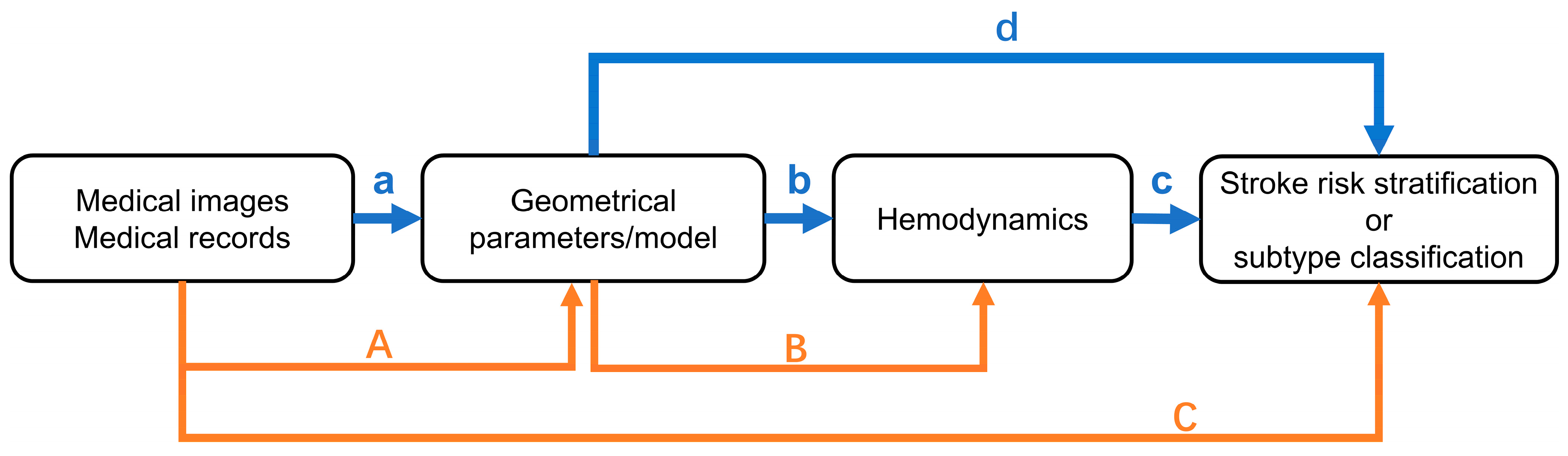
| Stroke Risk Stratification | CHADS2 | Framingham | CHA2DS2-VASc | ABC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk factors | Patient Characteristics | Age | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Sex | ✓ | |||||
| Comorbidities | Diabetes | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Hypertension | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Vascular Diseases | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Heart Failure | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Prior Stroke/TIA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Prior Thromboembolism | ✓ | |||||
| Biomarkers | NT-ProBNP | ✓ | ||||
| Hs-CTnI | ✓ | |||||
| C-statistic range [mean value] | 0.61–0.67 [0.645] | 0.633 [0.633] | 0.61–0.71 [0.644] | 0.6–0.8 [0.642] | ||
| References | [22,23,24,25] | [25] | [11,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] | [11,23,25] | ||
| Stroke Risk Stratification | HAS-BLED | ATRIA | ORBIT | ABS-Bleeding | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk factors | Patient Characteristics | Age | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Comorbidities | Drug/Alcohol Use | ✓ | ||||
| Hypertension | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Abnormal renal of liver function | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Anemia | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Previous Stroke | ✓ | |||||
| Labile INR | ✓ | |||||
| Bleeding history or predisposition | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Biomarkers | Hemoglobin | ✓ | ||||
| cTn-hs | ✓ | |||||
| GDF-15 or cystatin C/CKD-EPI | ✓ | |||||
| C-statistic range [mean value] | 0.62–0.63 [0.628] | 0.63–0.683 [0.651] | 0.61–0.65 [0.635] | 0.66–0.68 [0.67] | ||
| References | [22,23,30,31,32] | [22,23,25,27] | [22,23,25,27] | [11,32] | ||
| LAA Hemodynamic Index | Definition | Relation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Velocity | - | N | [15,33,34] |
| Vortex size | - | P | [7] |
| Vorticity | - | N | [34] |
| Ejection fraction | N | [35,36] | |
| TAWSS | N | [19,20,33,37] | |
| OSI | P | [19,20,33] | |
| ECAP | P | [19,20,37] | |
| RRT | P | [19,20,38] | |
| Kinetic energy | N | [34,39] | |
| SSR | - | N | [40] |
| AS | P | [41] | |
| M4 | the fourth moment of the blood age probability distribution | P | [14] |
| AI Task | Reference | Neural Network | Input | Output | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | [135] | U-net | CCT | Felling defects area | AUC = 0.979 ICC ≥ 0.895 |
| A | [133] | 3D-Unet | CCTA | LV, Aorta, LA, LAA and Myoc | DSC = 0.882–0.961 |
| B | [21] | PCA-FCN/U-net/GDL | 2D mapping of the 3D geometrical model for PCA-FCN U-net and point clouds of 3D geometrical | ECAP | GDL has the best performance MAE = 0.5 |
| B | [136] | GDL/U-net | 3D point clouds for GDL and mesh information for U-net | RRT | NRMSE = 0.08 for both two NNs |
| B | [20] | GDL | 3D point clouds | TAWSS/OSI/ECAP/RRT | MAE = 0.784 |
| B | [19] | GDL | 3D point clouds | Velocity and Pressure | NMAE = 5.7% for pressure and 10.35% for velocity |
| C | [134] | DNN | Medical record | risk score for post-stroke AF | AUC = 0.922 |
| C | [137] | U-net EfficientNetV2 | MRI with AF information | Stroke subtype | percentage agreement with expert consensus = 72.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Gao, Q. Study of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Based on Geometrical and Hemodynamic Characteristics: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094633
Liu X, Gao Q. Study of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Based on Geometrical and Hemodynamic Characteristics: A Review. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094633
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoyu, and Qi Gao. 2025. "Study of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Based on Geometrical and Hemodynamic Characteristics: A Review" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094633
APA StyleLiu, X., & Gao, Q. (2025). Study of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Based on Geometrical and Hemodynamic Characteristics: A Review. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094633





