XClinic Sensors: Validating Accuracy in Measuring Range of Motion Across Trauma Conditions
Abstract
1. Background
Objective
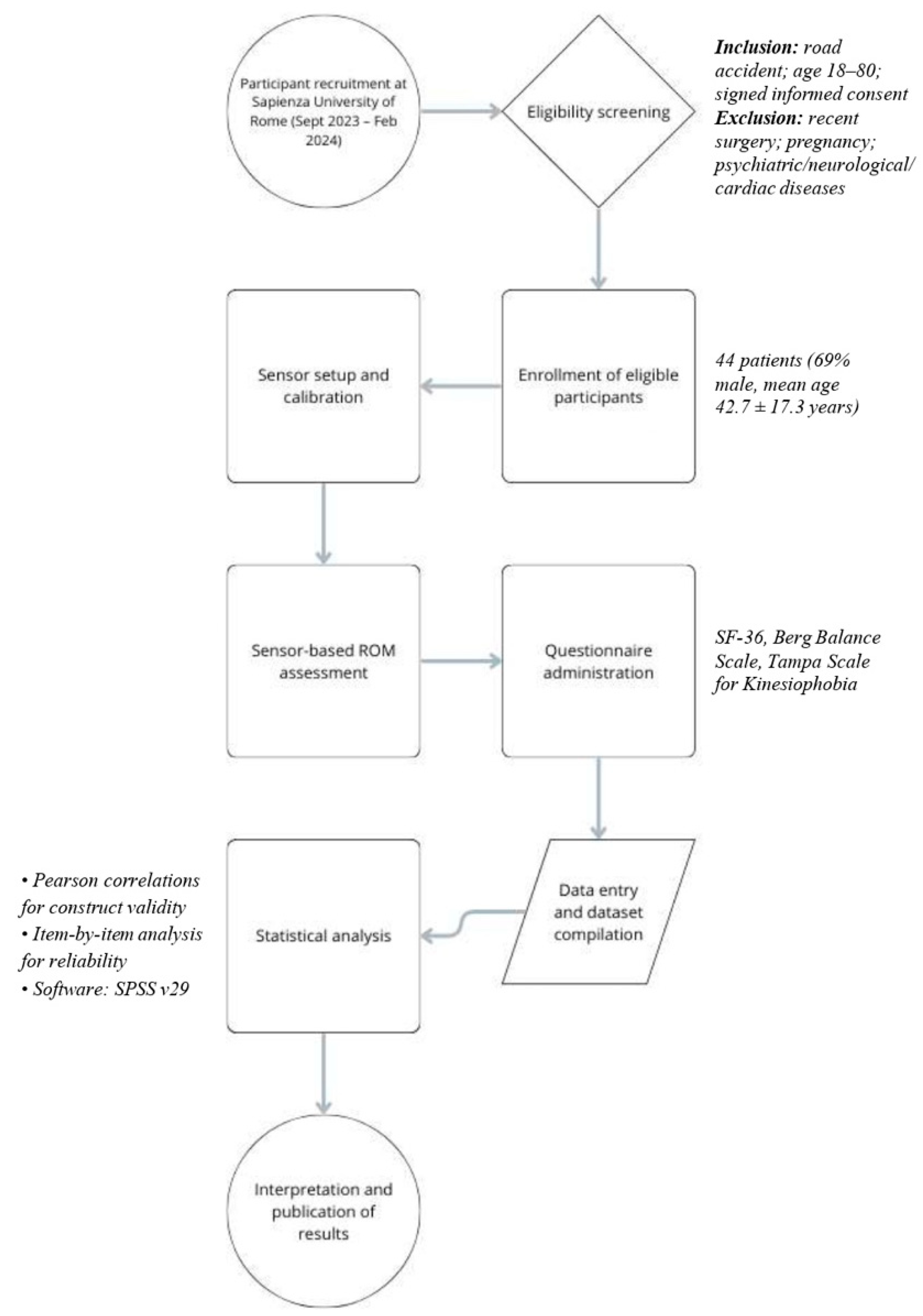
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection
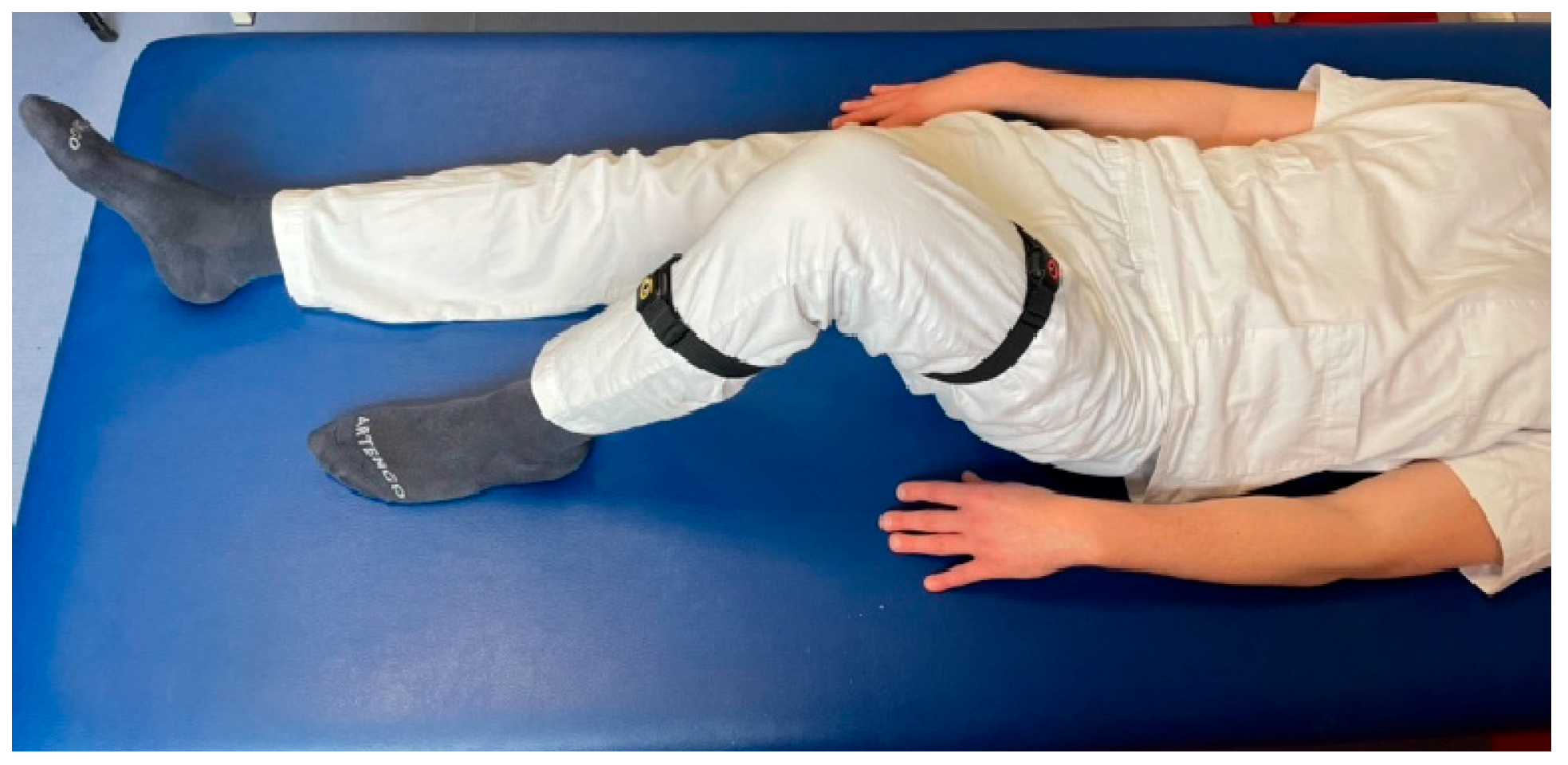
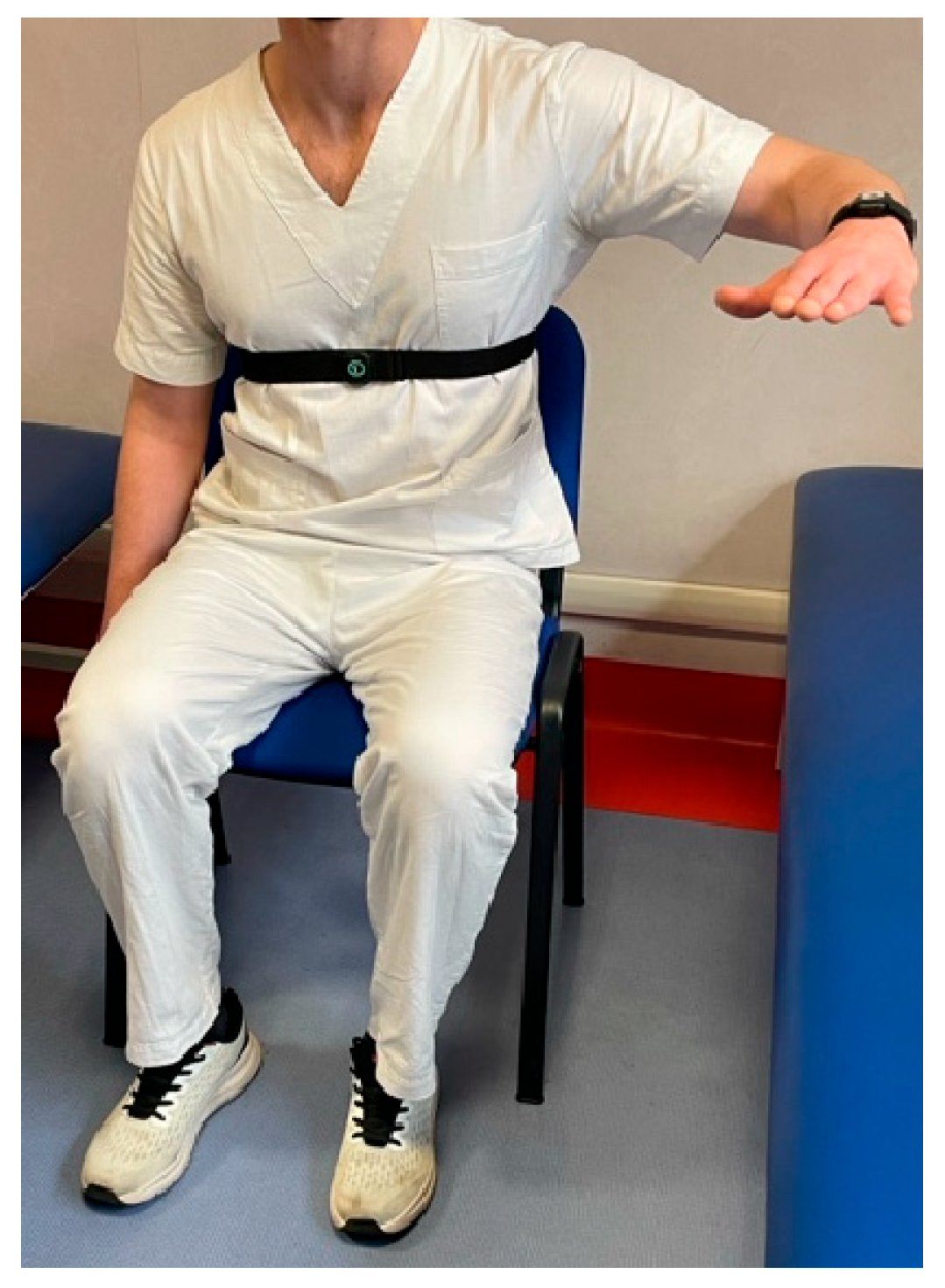
- Hip: flexion (with a flexed knee), extension, abduction, adduction, internal rotation, and external rotation.
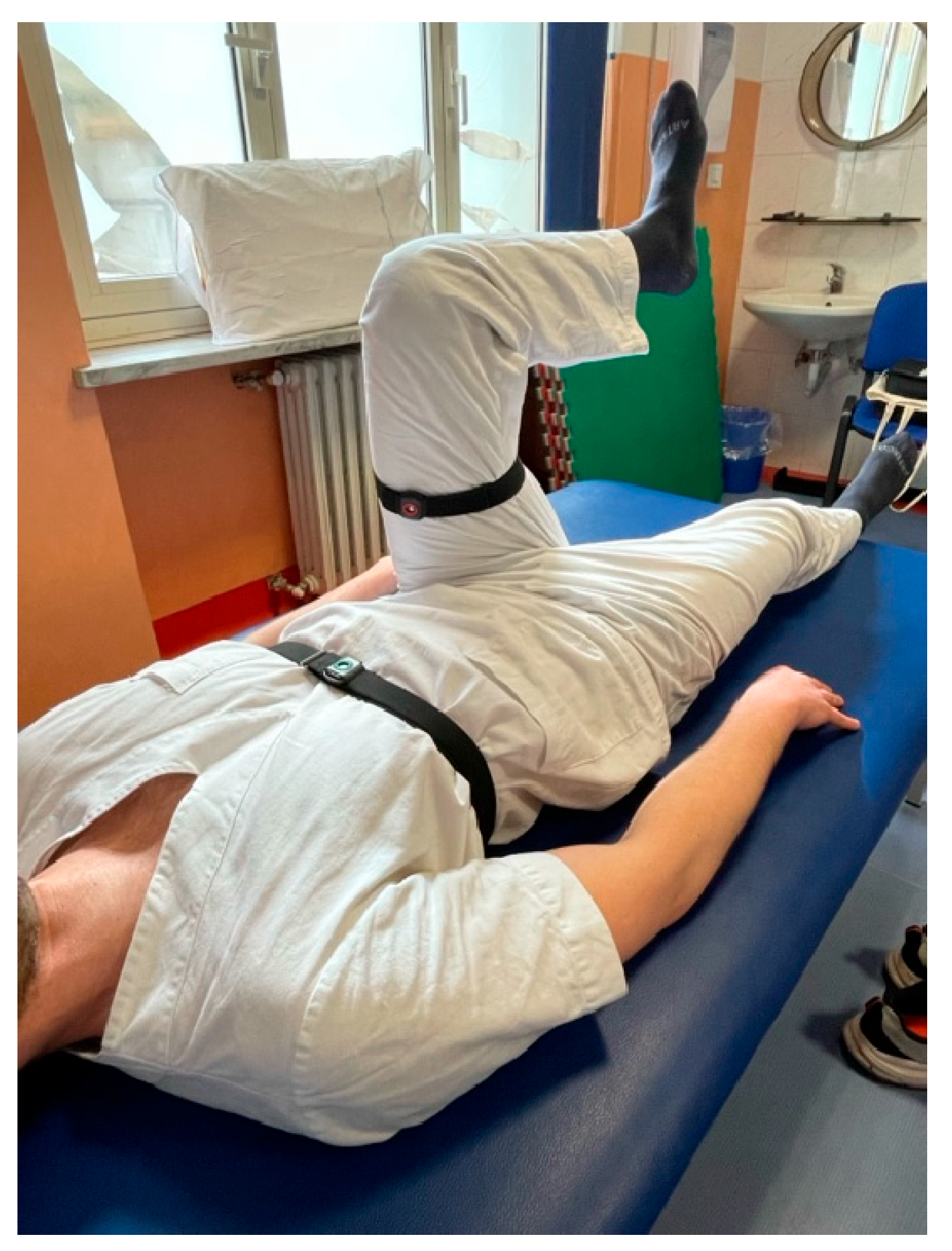
- Knee: flexion and extension.
- Ankle: plantar flexion, dorsiflexion, inversion, and eversion.
2.3. Evaluation Using Sensors
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Sample
3.2. Item-by-Item Analysis
3.3. Construct Validity
4. Discussion
5. Medico-Legal Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abedi, M.; Gane, E.; Aplin, T.; Zerguine, H.; Johnston, V. Barriers and Facilitators Associated with Return to Work Following Minor to Serious Road Traffic Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review. J. Occup. Rehabil. 2022, 32, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenezi, E.Z.; AlQahtani, A.M.; Althunayan, S.F.; Alanazi, A.S.; Aldosari, A.O.; Alharbi, A.M.; Alanazi, S.T.; Alanazi, S.S.S.; Tubayqi, H.G.A.; Taheri, T.A. Prevalence and Determinants of Road Traffic Accidents in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e51205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, B.H.; Chen, W.S.; Lee, S.W.H. Global burden of road traffic accidents in older adults: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2017, 72, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalay, Y.A.; Alemie, B.W.; Gelaw, B.; Gelaw, K.A. Epidemiology of road traffic accidents and its associated factors among public transportation in Africa: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1511715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, W.; van den Brande, R.; Polinder, S.; Brazinova, A.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Lingsma, H.F.; Maas, A.I.R. Epidemiology of traumatic brain injury in Europe. Acta Neurochir. 2015, 157, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaie, M.; Joulani, M.; Ranjbar Hameghavandi, M.H.; Asgardoon, M.H.; Nojomi, M.; O’Reilly, G.M.; Gholami, M.; Ghodsi, Z.; Rahimi-Movaghar, V. Risk of permanent medical impairment after road traffic crashes: A systematic review. Chin. J. Traumatol. Zhonghua Chuang Shang Za Zhi 2023, 26, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, M.A.; Gater, D.R.; Channell, I. Psychosocial Consequences of Spinal Cord Injury: A Narrative Review. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefifard, M.; Toloui, A.; Ahmadzadeh, K.; Gubari, M.I.M.; Madani Neishaboori, A.; Amraei, F.; Safari, S.; Baratloo, A.; Rahimi-Movaghar, V.; Hosseini, M. Risk Factors for Road Traffic Injury-Related Mortality in Iran; a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2021, 9, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakenridge, C.L.; Smits, E.J.; Gane, E.M.; Andrews, N.E.; Williams, G.; Johnston, V. Effectiveness of Interventions on Work Outcomes After Road Traffic Crash-Related Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Occup. Rehabil. 2025, 35, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health of Survivors and Long Term Disability—European Commission [WWW Document]. Available online: https://road-safety.transport.ec.europa.eu/european-road-safety-observatory/statistics-and-analysis-archive/post-impact-care/health-survivors-and-long-term-disability_en (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Montella, A.; Aria, M.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Mauriello, F. Analysis of powered two-wheeler crashes in Italy by classification trees and rules discovery. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2012, 49, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.; Järbrink, K.; Divakar, U.; Bajpai, R.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J. The humanistic and economic burden of chronic wounds: A systematic review. Wound Repair Regen. 2019, 27, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.M.; Plinsinga, M.L.; Brakenridge, C.L.; Smits, E.J.; Aplin, T.; Johnston, V. The Impact of Musculoskeletal Injuries Sustained in Road Traffic Crashes on Work-Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heron-Delaney, M.; Kenardy, J.; Charlton, E.; Matsuoka, Y. A systematic review of predictors of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) for adult road traffic crash survivors. Injury 2013, 44, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoborec, S.; Ruseckaite, R.; Ayton, D.; Evans, S. Biopsychosocial factors associated with non-recovery after a minor transport-related injury: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriero, G.; Carda, S.; Moslavac, S.; Rabini, A. Technological advances in instrumental assessment in rehabilitation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 264067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Gervasi, M.; Giustino, V.; Figlioli, F.; Canzone, A.; Drid, P.; Thomas, E.; Messina, G.; Vicari, D.S.S.; Palma, A.; et al. The Influence of Ankle Mobility and Foot Stability on Jumping Ability and Landing Mechanics: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeoto, G.; Ruotolo, I.; Sellitto, G.; Amadio, E.; Di Sipio, E.; La Russa, R.; Volonnino, G.; Frati, P. The Innovative XClinic Tool: A Pilot Study Validating Its Precision in Measuring Range of Motion in Healthy Individuals. Sensors 2025, 25, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, W.; O’Reilly, M.; Argent, R.; Caulfield, B. Reliability, Validity and Utility of Inertial Sensor Systems for Postural Control Assessment in Sport Science and Medicine Applications: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 783–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riabilitazione Digitale per Centri di Fisioterapia—Ferrox [WWW Document]. Available online: https://www.ferrox.it/riabilitazione-digitale/ (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Szabo, D.A.; Neagu, N.; Teodorescu, S.; Apostu, M.; Predescu, C.; Pârvu, C.; Veres, C. The Role and Importance of Using Sensor-Based Devices in Medical Rehabilitation: A Literature Review on the New Therapeutic Approaches. Sensors 2023, 23, 8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeoto, G.; Marquez, M.A.; Ottone, L.; Sellitto, G.; Panuccio, F.; Gonzàlez-Bernal, J.; Tofani, M.; Berardi, A. Intermittent Catheterization Adherence Scale (ICAS): Italian Translation, Cultural Adaptation and Validation [WWW Document]. 2022. Available online: https://www.signavitae.com/articles/10.22514/sv.2021.145 (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Marquez, M.A.; Speroni, A.; Galeoto, G.; Ruotolo, I.; Sellitto, G.; Tofani, M.; González-Bernal, J.; Berardi, A. The Moorong Self Efficacy Scale: Translation, Cultural Adaptation, and Validation in Italian; Cross-Sectional Study in People with Spinal Cord Injury. Spinal Cord Ser. Cases 2022, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotolo, I.; Sellitto, G.; Berardi, A.; Simeon, R.; Panuccio, F.; Amadio, E.; Ugolini, A.; Fabbrini, G.; Galeoto, G. Psychometric properties of the Parkinson’s disease Questionnaire-39 and its short form Parkinson’s disease Questionnaire-8: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2024, 123, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, A.; Tofani, M.; Colalelli, F.; Valente, D.; Sellitto, G.; Ruotolo, I.; Galeoto, G. The psychometric properties of the Italian version of the PEDro Scale. Gazz. Medica Ital.-Arch. Per Le Sci. Mediche 2022, 181, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeoto, G.; De Santis, R.; Marcolini, A.; Cinelli, A.; Cecchi, R. II consenso informato in Terapia Occupazionale: Proposta di una modulistica. G. Ital. Med. Lav. Ergon. 2016, 38, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeoto, G.; Mollica, R.; Astorino, O.; Cecchi, R. Il consenso informato in fisioterapia: Proposta di una modulistica. G. Ital. Med. Lav. Ergon. 2015, 37, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Apolone, G.; Mosconi, P. The Italian SF-36 Health Survey: Translation, validation and norming. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1998, 51, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, F.; Caselli, S.; Susassi, S.; Cavallini, P.; Tennant, A.; Franceschini, M. Is the Berg Balance Scale an internally valid and reliable measure of balance across different etiologies in neurorehabilitation? A revisited Rasch analysis study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticone, M.; Giorgi, I.; Baiardi, P.; Barbieri, M.; Rocca, B.; Bonezzi, C. Development of the Italian version of the Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia (TSK-I): Cross-cultural adaptation, factor analysis, reliability, and validity. Spine 2010, 35, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COSMIN. COSMIN—Improving the Selection of Outcome Measurement Instruments [WWW Document]. Available online: https://www.cosmin.nl/ (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Mohamad, I. Gender disparities in rural motorcycle accidents: A neural network analysis of travel behavior impact. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2025, 210, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enseki, K.R.; Bloom, N.J.; Harris-Hayes, M.; Cibulka, M.T.; Disantis, A.; Di Stasi, S.; Malloy, P.; Clohisy, J.C.; Martin, R.L. Hip Pain and Movement Dysfunction Associated With Nonarthritic Hip Joint Pain: A Revision. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2023, 53, CPG1–CPG70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Chebil, B.; Cockroft, J.; Bianchini, E.; Romijnders, R.; Maetzler, W. Changes in Coordination and Its Variability with an Increase in Functional Performance of the Lower Extremities. Biosensors 2023, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Neptune, R.R.; Kautz, S.A. The relationships between muscle, external, internal and joint mechanical work during normal walking. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, D.A. Kinesiology of the Hip: A Focus on Muscular Actions. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2010, 40, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.-S.; Tikoft, E.; O’Sullivan, P.; Smith, A.; Campbell, A.; Caneiro, J.P.; Kent, P. The Relationship Between Changes in Movement and Activity Limitation or Pain in People With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2021, 51, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanyshyn, D.J.; Engsberg, J.R. Right to left differences in the ankle joint complex range of motion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1994, 26, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, P.; McGill, B. The relationship between experience of knee pain and physical activity participation: A scoping review of quantitative studies. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2023, 10, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portegijs, E.; Edgren, J.; Salpakoski, A.; Kallinen, M.; Rantanen, T.; Alen, M.; Kiviranta, I.; Sihvonen, S.; Sipilä, S. Balance confidence was associated with mobility and balance performance in older people with fall-related hip fracture: A cross-sectional study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 2340–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleem, M.K.; Alkhars, A.M.; Alalwan, H.A.; Almutairi, A.; Alonayzan, A.; AlYaeesh, I.A. Kinesiophobia Post Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Study. Cureus 2021, 13, e15991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, I.; Fazzi, L.; Griffo, G. Human rights, UN convention, and the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health: Collecting data on persons with disabilities? Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, S159–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingravallo, F.; Cerquetti, I.; Vignatelli, L.; Albertini, S.; Bolcato, M.; Camerlingo, M.; Corbi, G.; De Leo, D.; De Nicolò, A.; De Stefano, F.; et al. Medico-legal assessment of personal damage in older people: Report from a multidisciplinary consensus conference. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2020, 134, 2319–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Tanaka, T.; Hirota, Y.; Kawamura, H.; Miura, H.; Sugioka, Y.; Inoue, H.; Kurosaka, M.; Yamashita, T.; Shirata, K.; et al. Factors Associated with Functional Limitation in Stair Climbing in Female Japanese Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 16, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Average ± SD | N° (%) | |
| Age | 42.7 ± 17.3 | 44 |
| Gender | ||
| Male N (%) | 30 (69) | |
| Kind of Damage N (%) | ||
| Motorcycle accident | 21 (47.73) | |
| Car accident | 9 (20.45) | |
| Domestic accident | 1 (2.27) | |
| Hospital accident | 1 (2.27) | |
| Workplace accident | 5 (11.36) | |
| Fall | 1 (2.27) | |
| Pedestrian accident | 6 (13.64) | |
| Event location N (%) | ||
| Road | 37 (84.09) | |
| Hospital | 6 (13.64) | |
| Work | 1 (2.27) | |
| Upper limb involved | 13 (66) | |
| Lower limb involved | 37 (23) | |
| Other involved districts | 6 (11) | |
| Years since the damage N (%) | ||
| <1 | 27 (61.36) | |
| >1 | 17 (38.64) | |
| Left | Right | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extrarotation | Intrarotation | Adduction | Abduction | Flexion | Exention | Mean Left Deficit | Extrarotation | Intrarotation | Adduction | Abduction | Flexion | Exention | Mean Right Deficit | ||
| Left | Extrarotation | 1 | 0.727 ** | 0.326 | 0.335 | 0.283 | 0.068 | −0.663 ** | 0.279 | 0.261 | −0.104 | 0.116 | 0.243 | 0.224 | −0.168 |
| Intrarotation | 0.727 ** | 1 | 0.380 * | 0.308 | 0.231 | 0.045 | −0.615 ** | 0.098 | 0.083 | −0.138 | 0.020 | 0.120 | 0.075 | −0.015 | |
| Adduction | 0.326 | 0.380 * | 1 | 0.411 * | 0.631 ** | 0.246 | −0.784 * | 0.233 | 0.093 | 0.361 * | 0.207 | 0.181 | 0.094 | −0.251 | |
| Abduction | 0.335 | 0.308 | 0.411 * | 1 | 0.578 ** | −0.009 | −0.570 ** | 0.108 | −0.073 | 0.066 | 0.363 * | 0.135 | −0.194 | −0.095 | |
| Flexion | 0.283 | 0.231 | 0.631 ** | 0.578 ** | 1 | 0.424 * | −0.754 ** | 0.242 | 0.165 | 0.438 * | 0.310 | 0.488 ** | 0.137 | −0.389 * | |
| Extention | 0.068 | 0.045 | 0.246 | −0.009 | 0.424 * | 1 | −0.484 ** | 0.222 | 0.225 | 0.428 * | 0.195 | 0.330 | 0.365 * | −0.387 * | |
| Mean Left Deficit | −0.663 ** | −0.615 ** | −0.784 ** | −0.570 ** | −0.754 ** | −0.484 ** | 1 | −0.168 | −0.015 | −0.251 | −0.095 | −0.095 | −0.389 * | 0.412 * | |
| Right | Extrarotation | 0.279 | 0.098 | 0.233 | 0.108 | 0.242 | 0.222 | −0.352 * | 1 | 0.743 ** | 0.627 ** | 0.639 ** | 0.499 ** | 0.321 | −0.820 ** |
| Intrarotation | 0.261 | 0.083 | 0.093 | −0.073 | 0.165 | 0.225 | −0.248 | 0.743 ** | 1 | 0.620 ** | 0.587 ** | 0.449 * | 0.293 | −0.790 ** | |
| Adduction | −0.104 | −0.138 | 0.361* | 0.066 | 0.438 * | 0.428 * | −0.352 * | 0.627 ** | 0.620 ** | 1 | 0.676 ** | 0.682 ** | 0.345 | −0.874 ** | |
| Abduction | 0.116 | 0.020 | 0.207 | 0.363 * | 0.310 | 0.195 | −0.353 * | 0.639 ** | 0.587 ** | 0.676 ** | 1 | 0.593 ** | 0.201 | −0.817 ** | |
| Flexion | 0.243 | 0.120 | 0.181 | 0.135 | 0.488 ** | 0.330 | −0.417 * | 0.499 ** | 0.449 * | 0.682 ** | 0.593 ** | 1 | 0.600 ** | −0.797 ** | |
| Extention | 0.224 | 0.075 | 0.094 | −0.194 | 0.137 | 0.365 * | −0.263 | 0.321 | 0.293 | 0.345 | 0.201 | 0.600 ** | 1 | −0.484 ** | |
| Mean Right Deficit | −0.168 | −0.015 | −0.251 | −0.095 | −0.389 * | −0.387 * | 0.412 * | −0.820 ** | −0.790 ** | −0.874 ** | −0.817 ** | −0.797 ** | −0.536 ** | 1 | |
| Left | Right | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexion | Estention | Mean Left Deficit | Flexion | Estention | Mean Right Deficit | ||
| Left | Flexion | 1 | 0.222 | −0.555 ** | −0.003 | −0.117 | 0.020 |
| Estention | 0.222 | 1 | −0.899 ** | 0.114 | 0.261 | −0.130 | |
| Mean Left Deficit | −0.555 ** | −0.899 ** | 1 | −0.063 | −0.115 | 0.070 | |
| Right | Flexion | −0.003 | 0.114 | −0.063 | 1 | 0.535 ** | −0.863 ** |
| Estention | −0.117 | 0.261 | −0.115 | 0.535 ** | 1 | −0.844 ** | |
| Mean Right Deficit | 0.020 | −0.130 | 0.070 | −0.863 ** | −0.844 ** | 1 | |
| Left | Right | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plantar Flexion | Dorsal Flexion | Eversion | Inversion | Mean Left Deficit | Plantar Flexion | Dorsal Flexion | Eversion | Inversion | Mean Right Deficit | ||
| Left | Plantar flexion | 1 | 0.153 | 0.482 * | 0.464 * | −0.569 ** | −0.034 | −0.411 * | −0.265 | −0.260 | 0.301 |
| Dorsal flexion | 0.153 | 1 | 0.535 ** | 0.405 * | −0.657 ** | 0.141 | 0.009 | −0.103 | 0.083 | −0.154 0.171 | |
| Eversion | 0.482 * | 0.535 ** | 1 | 0.542 ** | −0.758 ** | 0.006 | −0.454 * | −0.083 | −0.117 | −0.003 | |
| Inversion | 0.464 * | 0.405 * | 0.542 ** | 1 | −0.767 ** | 0.027 | −0.257 | 0.019 | −0.003 | −0.765 ** | |
| Mean Left Deficit | −0.569 ** | −0.657 ** | −0.657 ** | −0.767 ** | 1 | 0.000 | 0.258 | 0.029 | 0.107 | −0.063 | |
| Right | Plantar flexion | −0.034 | 0.141 | 0.006 | 0.027 | 0.000 | 1 | 0.398 * | 0.416 * | 0.693 ** | −0.765 ** |
| Dorsal flexion | −0.411 * | 0.009 | −0.454 * | −0.257 | 0.258 | 0.398 * | 1 | 0.471 * | 0.642 ** | −0.685 ** | |
| Eversion | −0.265 | −0.103 | −0.083 | 0.019 | 0.029 | 0.416 * | 0.471 * | 1 | 0.604 ** | −0.694 ** | |
| Inversion | −0.260 | 0.083 | −0.117 | −0.003 | 0.107 | 0.693 ** | 0.642 ** | 0.604 ** | 1 | −0.903 ** | |
| Mean Right Deficit | 0.301 | −0.154 | 0.171 | −0.003 | −0.063 | −0.765 ** | −0.685 ** | −0.694 ** | −0.903 ** | 1 | |
| Anca | Ginocchio | Caviglia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Media Deficit Sx | Media Deficit Dx | Media Deficit Sx | Media Deficit Dx | Media Deficit Sx | Media Deficit Dx | |
| Physical functioning | 0.003 | −0.362 | −0.068 | −0.503 * | −0.071 | −0.196 |
| Role limitations due to physical health | 0.211 | 0.128 | 0.010 | −0.228 | −0.100 | 0.055 |
| Role limitations due to emotional problems | 0.254 | 0.110 | 0.054 | −0.244 | −0.074 | 0.034 |
| Energy/fatigue | 0.267 | −0.048 | −0.042 | −0.376 | −0.106 | 0.028 |
| Emotional well-being | 0.125 | −0.221 | −0.063 | −0.380 | −0.068 | −0.063 |
| Social functioning | 0.064 | −0.045 | −0.301 | −0.426 * | −0.024 | −0.119 |
| Pain | −0.101 | −0.286 | −0.376 | −0.497 * | −0.010 | −0.219 |
| General health | 0.085 | −0.068 | −0.208 | −0.296 | 0.082 | 0.070 |
| Health change | 0.275 | 0.084 | 0.094 | −0.128 | 0.398 | 0.080 |
| Anca | Ginocchio | Caviglia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Media Deficit Sx | Media Deficit Dx | Media Deficit Sx | Media Deficit Dx | Media Deficit Sx | Media Deficit Dx | |
| Total score | −0.667 ** | −0.780 ** | −0.259 | −0.366 | −0.360 | −0.273 |
| Anca | Ginocchio | Caviglia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Media Deficit Sx | Media Deficit Dx | Media Deficit Sx | Media Deficit Dx | Media Deficit Sx | Media Deficit Dx | |
| Total score | 0.465 * | 0.205 | 0.213 | −0.045 | 0.198 | 0.242 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruotolo, I.; Sellitto, G.; Galeoto, G.; Valente, D.; Amadio, E.; Berardi, A.; Panuccio, F.; La Russa, R.; Guidoni, U.; Volonnino, G.; et al. XClinic Sensors: Validating Accuracy in Measuring Range of Motion Across Trauma Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4731. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094731
Ruotolo I, Sellitto G, Galeoto G, Valente D, Amadio E, Berardi A, Panuccio F, La Russa R, Guidoni U, Volonnino G, et al. XClinic Sensors: Validating Accuracy in Measuring Range of Motion Across Trauma Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4731. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094731
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuotolo, Ilaria, Giovanni Sellitto, Giovanni Galeoto, Donatella Valente, Emanuele Amadio, Anna Berardi, Francescaroberta Panuccio, Raffaele La Russa, Umberto Guidoni, Gianpietro Volonnino, and et al. 2025. "XClinic Sensors: Validating Accuracy in Measuring Range of Motion Across Trauma Conditions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4731. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094731
APA StyleRuotolo, I., Sellitto, G., Galeoto, G., Valente, D., Amadio, E., Berardi, A., Panuccio, F., La Russa, R., Guidoni, U., Volonnino, G., & Frati, P. (2025). XClinic Sensors: Validating Accuracy in Measuring Range of Motion Across Trauma Conditions. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4731. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094731








