Biomechanical and Clinical Validation of a Modulus-Graded Ti-Nb-Sn Femoral Stem for Suppressing Stress Shielding in Total Hip Arthroplasty
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
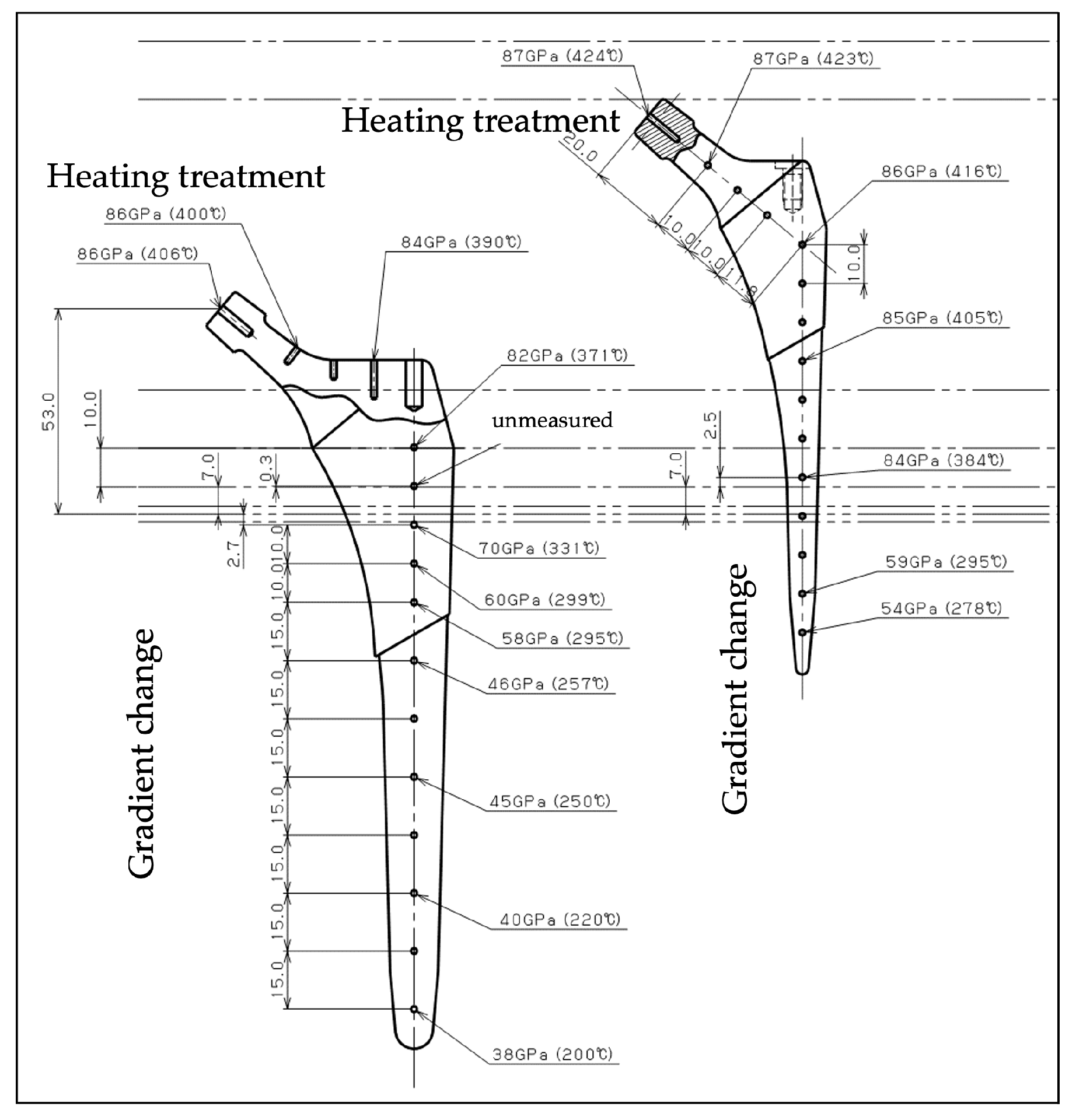
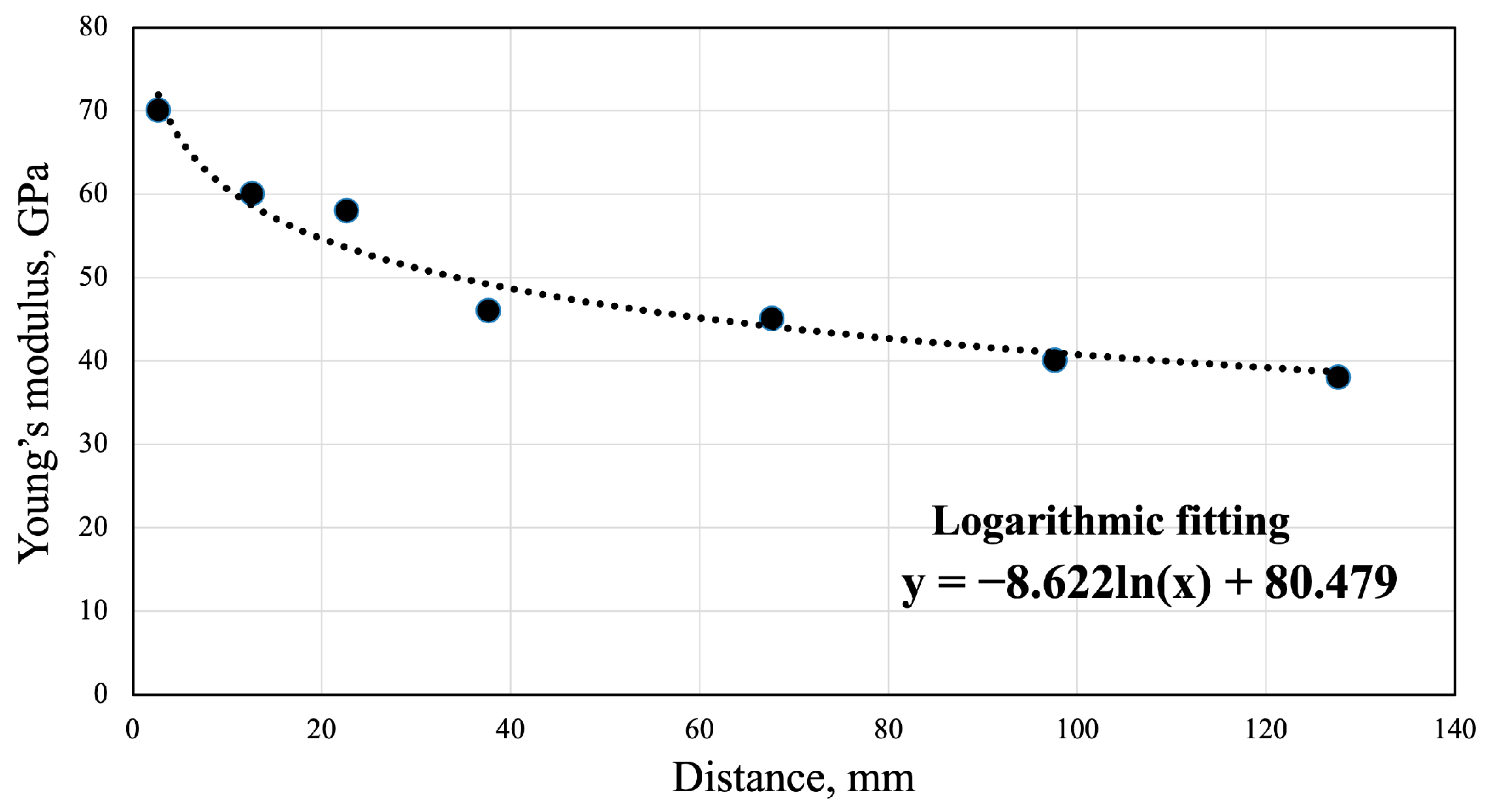
2.1. Construction of Gradient Young’s Modulus FEM
2.2. Bone Mineral Density-Reflected Bone Modeling
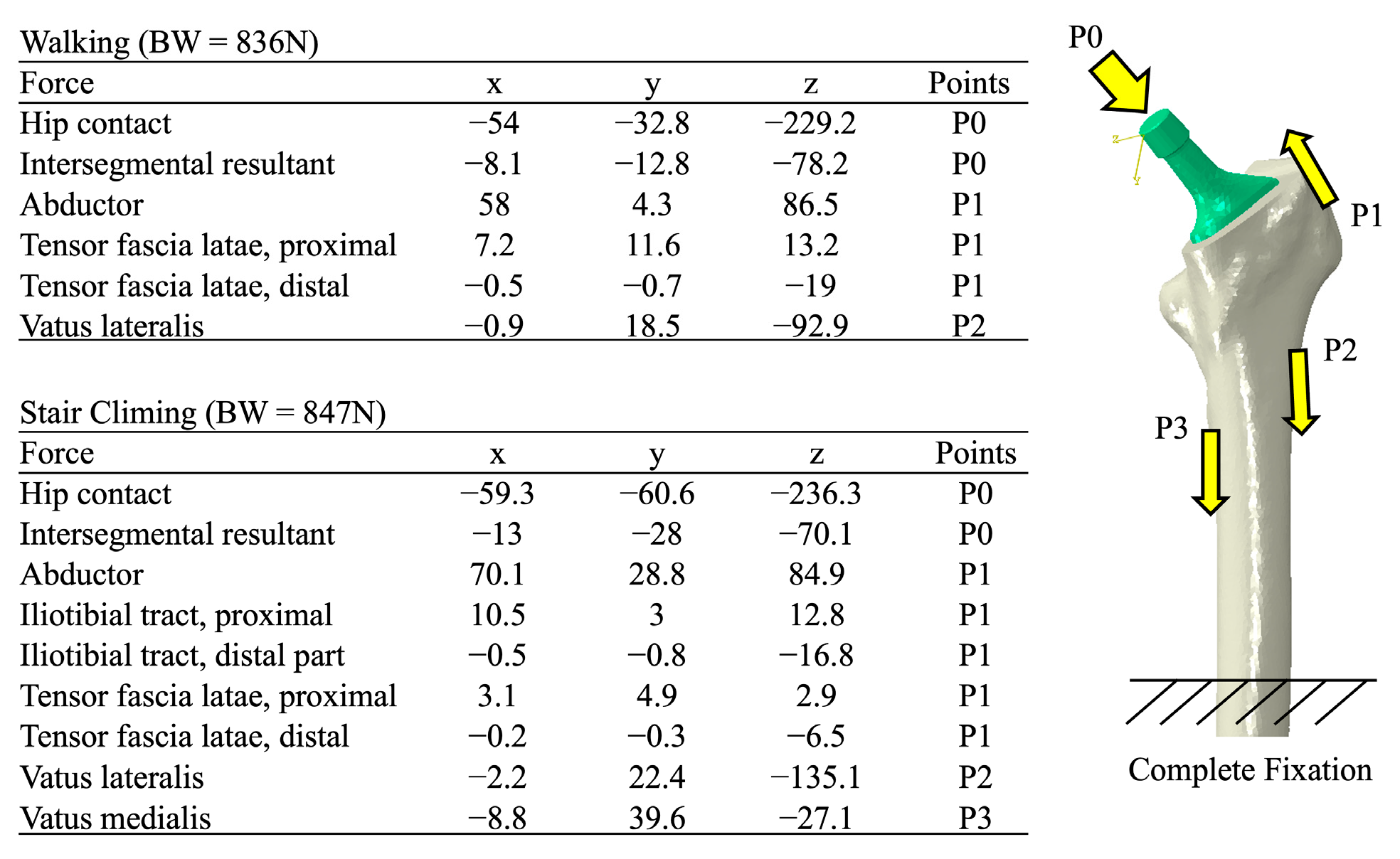
2.3. Boundary and Loading Conditions
2.4. Assessment of Clinical Image
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
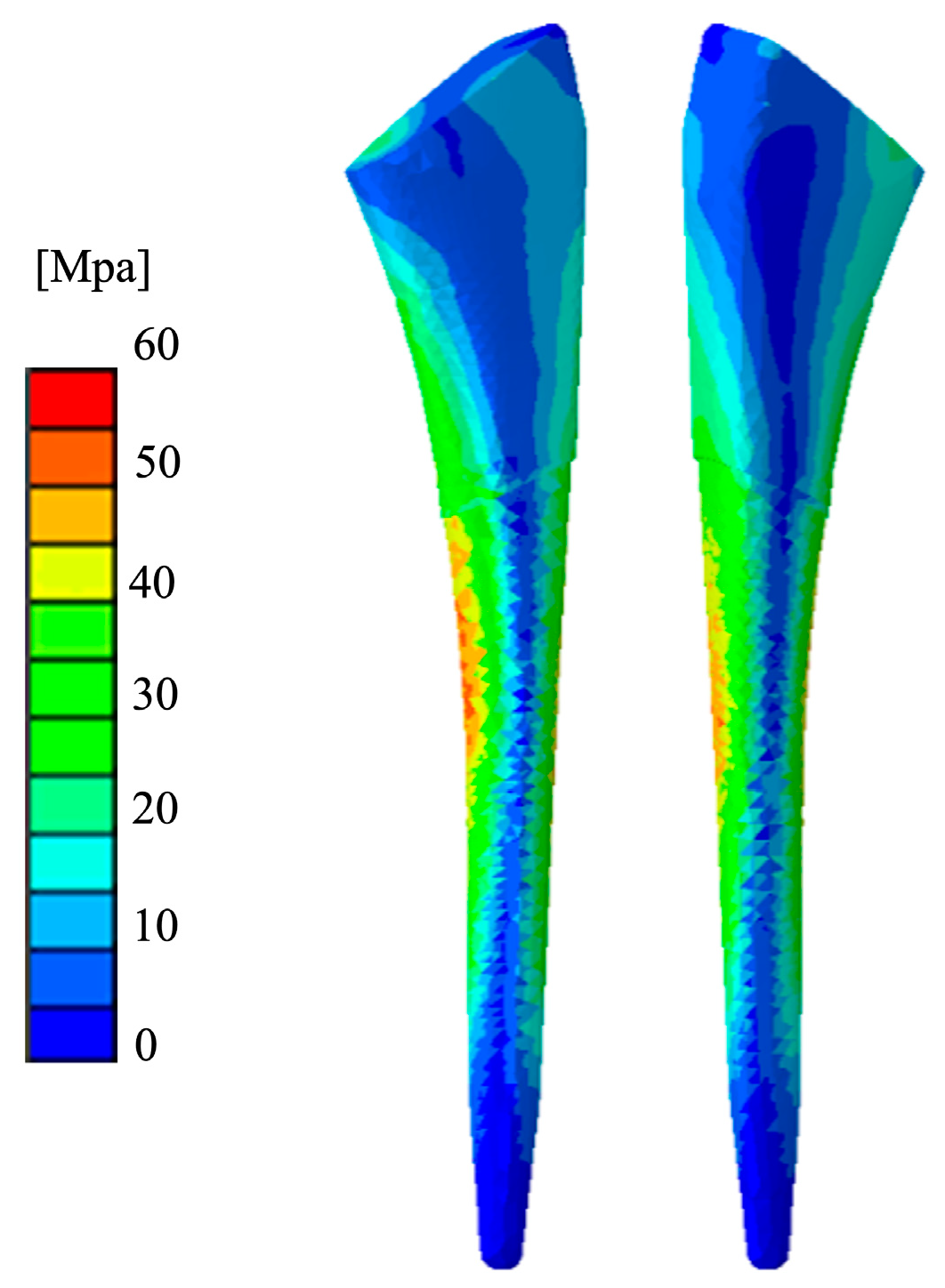
3.1. Mechanical Stress Distribution
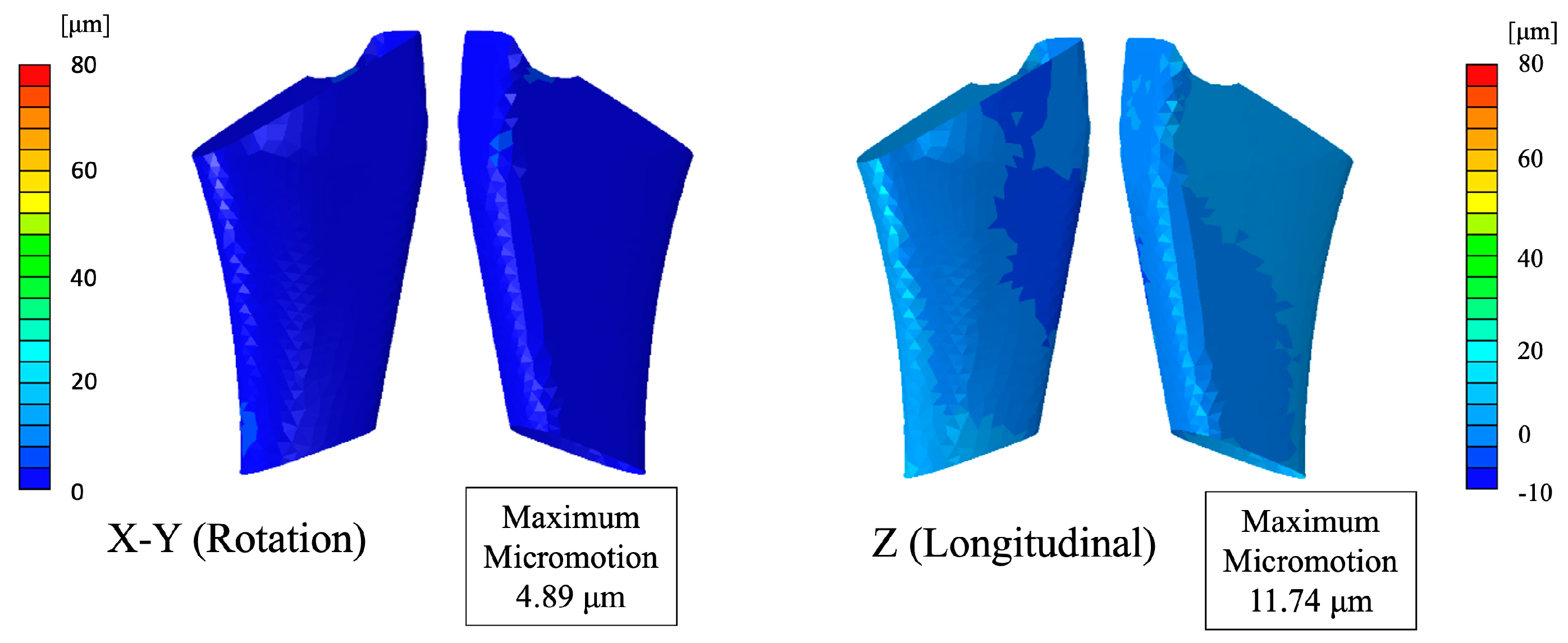
3.2. Micromotion Assessment
3.3. Clinical Image Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| THA | Total hip arthroplasty |
| FEM | Finite element model |
| Ti-Nb-Sn | Ti-33.6%Nb-4Sn |
| CT | Computed tomography |
References
- Amendola, R.L.; Goetz, D.D.; Liu, S.S.; Callaghan, J.J. Two- to 4-Year Followup of a Short Stem THA Construct: Excellent Fixation, Thigh Pain a Concern. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanto, M.; Fukunishi, S.; Fukui, T.; Nishio, S.; Fujihara, Y.; Okahisa, S.; Takeda, Y.; Yoshiya, S.; Tachibana, T. Radiological Evaluation of the Relationship Between Cortical Hypertrophy and Stress Shielding After Total Hip Arthroplasty Using a Cementless Stem. Arthroplast. Today 2020, 6, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, T.; Nakano, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Momose, T.; Sobajima, A.; Takahashi, J.; Nakata, K.; Nawata, M. Relationship between Stress Shielding and Optimal Femoral Canal Contact Regions for Short, Tapered-Wedge Stem Analyzed by 2D and 3D Systems in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engh, C.A., Jr.; Young, A.M.; Engh, C.A., Sr.; Hopper, R.H., Jr. Clinical consequences of stress shielding after porous-coated total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2003, 417, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusano, T.; Seki, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Takegami, Y.; Osawa, Y.; Ishiguro, N. Preoperative Canal Bone Ratio is Related to High-Degree Stress Shielding: A Minimum 5-Year Follow-Up Study of a Proximally Hydroxyapatite-Coated Straight Tapered Titanium Femoral Component. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1764–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, R. The various stress patterns of press-fit, ingrown, and cemented femoral stems. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1990, 261, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rietbergen, B.; Huiskes, R.; Weinans, H.; Sumner, D.R.; Turner, T.M.; Galante, J.O. ESB Research Award 1992. The mechanism of bone remodeling and resorption around press-fitted THA stems. J. Biomech. 1993, 26, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, H. Epidemiology of periprosthetic femur fracture around a total hip arthroplasty. Injury 2007, 38, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Yoo, J.J. Does Proximally Coated Single-Wedge Cementless Stem Work Well in Dorr Type C Femurs? Minimum 10-year Followup. Indian J. Orthop. 2019, 53, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubosaka, M.; Hayashi, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Takayama, K.; Kuroda, R.; Matsumoto, T. Patients with a Dorr type C femoral bone require attention for using a Summit cementless stem: Results of total hip arthroplasty after a minimum follow-up period of 5 years after insertion of a Summit cementless stem. J. Orthop. Sci. 2018, 23, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, L.D.; Faugere, M.C.; Mackel, A.M.; Gruen, T.A.; Bognar, B.; Malluche, H.H. Structural and cellular assessment of bone quality of proximal femur. Bone 1993, 14, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huiskes, R.; Hollister, S.J. From structure to process, from organ to cell: Recent developments of FE-analysis in orthopaedic biomechanics. J. Biomech. Eng. 1993, 115, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, J.Y.; Ashman, R.B.; Turner, C.H. Young’s modulus of trabecular and cortical bone material: Ultrasonic and microtensile measurements. J. Biomech. 1993, 26, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamako, G.; Janssen, D.; Hanada, S.; Anijs, T.; Ochiai, K.; Totoribe, K.; Chosa, E.; Verdonschot, N. Improving stress shielding following total hip arthroplasty by using a femoral stem made of β type Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn with a Young’s modulus gradation. J. Biomech. 2017, 63, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghavi, S.A.; Tamaddon, M.; Garcia-Souto, P.; Moazen, M.; Taylor, S.; Hua, J.; Liu, C. A novel hybrid design and modelling of a customised graded Ti-6Al-4V porous hip implant to reduce stress-shielding: An experimental and numerical analysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1092361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, S.; Masahashi, N.; Jung, T.K.; Yamada, N.; Yamako, G.; Itoi, E. Fabrication of a high-performance hip prosthetic stem using β Ti-33.6Nb-4Sn. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 30, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Mori, Y.; Kamimura, M.; Koguchi, M.; Kurishima, H.; Koyama, T.; Mori, N.; Masahashi, N.; Hanada, S.; Itoi, E.; et al. β-type TiNbSn Alloy Plates with Low Young Modulus Accelerates Osteosynthesis in Rabbit Tibiae. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2022, 480, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Fujisawa, H.; Kamimura, M.; Kogure, A.; Tanaka, H.; Mori, N.; Masahashi, N.; Aizawa, T. Acceleration of Fracture Healing in Mouse Tibiae Using Intramedullary Nails Composed of β-Type TiNbSn Alloy with Low Young’s Modulus. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2021, 255, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, A.; Mori, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Kamimura, M.; Masahashi, N.; Hanada, S.; Itoi, E. Effects of elastic intramedullary nails composed of low Young’s modulus Ti-Nb-Sn alloy on healing of tibial osteotomies in rabbits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Kamimura, M.; Ito, K.; Koguchi, M.; Tanaka, H.; Kurishima, H.; Koyama, T.; Mori, N.; Masahashi, N.; Aizawa, T. A Review of the Impacts of Implant Stiffness on Fracture Healing. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, D.; Yamada, N.; Mori, Y.; Oyama, M.; Ohtsu, S.; Kuwahara, Y.; Baba, K.; Tanaka, H.; Aizawa, T.; Hanada, S.; et al. Mid-term results of a new femoral prosthesis using Ti-Nb-Sn alloy with low Young’s modulus. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, K.; Mori, Y.; Chiba, D.; Kuwahara, Y.; Kurishima, H.; Tanaka, H.; Kogure, A.; Kamimura, M.; Yamada, N.; Ohtsu, S.; et al. TiNbSn stems with gradient changes of Young’s modulus and stiffness reduce stress shielding compared to the standard fit-and-fill stems. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, C.K. Femoral Stems with Porous Lattice Structures: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 772539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, T.; Mori, Y.; Kamimura, M.; Tanaka, H.; Tome, R.; Ito, K.; Koguchi, M.; Mori, N.; Aizawa, T. TiNbSn alloy plates with low Young’s modulus modulates interfragmentary movement and promote osteosynthesis in rat femur. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2025, 161, 106820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, M.O.; Bergmann, G.; Kassi, J.P.; Claes, L.; Haas, N.P.; Duda, G.N. Determination of muscle loading at the hip joint for use in pre-clinical testing. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancourt, D.; Shirazi-Adl, A.; Drouin, G.; Paiement, G. Friction properties of the interface between porous-surfaced metals and tibial cancellous bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 1503–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefzy, M.S.; Singh, S.P. Comparison between two techniques for modeling interface conditions in a porous coated hip endoprosthesis. Med. Eng. Phys. 1997, 19, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccini, R.; Baleani, M.; Viceconti, M. Selection of the best element type in the finite element analysis of hip prostheses. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2000, 24, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charnley, J. The long-term results of low-friction arthroplasty of the hip performed as a primary intervention. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1972, 54, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engh, C.A.; Bobyn, J.D.; Glassman, A.H. Porous-coated hip replacement. The factors governing bone ingrowth, stress shielding, and clinical results. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1987, 69, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruen, T.A.; McNeice, G.M.; Amstutz, H.C. “Modes of failure” of cemented stem-type femoral components: A radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1979, 141, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.; de Vries, E.; Matthews, D.; van der Heide, E.; Janssen, D. The effect of coating characteristics on implant-bone interface mechanics. J. Biomech. 2024, 163, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, C.; Kim, I.Y. Comparison of different hip prosthesis shapes considering micro-level bone remodeling and stress-shielding criteria using three-dimensional design space topology optimization. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, M.; Trentadue, B. Evaluation of Rotational Stability and Stress Shielding of a Stem Optimized for Hip Replacements-A Finite Element Study. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, M.; Solarino, G.; Giannini, G.; De Giosa, G.; Tucci, M.; Trentadue, B. A Finite Element Analysis Study of Influence of Femoral Stem Material in Stress Shielding in a Model of Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty: Ti-6Al-4V versus Carbon Fibre-Reinforced PEEK Composite. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Ike, H.; Fujimaki, H.; Saito, T. Comparison of mechanical stress and change in bone mineral density between two types of femoral implant using finite element analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 1731–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyland, M.; Checa, S.; Kendoff, D.; Duda, G.N. Anatomic grooved stem mitigates strain shielding compared to established total hip arthroplasty stem designs in finite-element models. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wu, X.D.; Wan, Y.; Liao, J.; Cheng, Q.; Tian, M.; Bai, Z.; Huang, W. Femoral Stress Changes after Total Hip Arthroplasty with the Ribbed Prosthesis: A Finite Element Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6783936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.G.; Chevalier, Y.; Liu, F.; Hua, X.; Schreiner, A.; Jansson, V.; Schmidutz, F. Metaphyseal anchoring short stem hip arthroplasty provides a more physiological load transfer: A comparative finite element analysis study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, J.I.; Rack, H.J. Metastable beta titanium alloys for orthopedic applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2005, 7, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopova, I.; Strasky, J.; Harcuba, P.; Landa, M.; Janecek, M.; Bacakova, L. Newly developed Ti-Nb-Zr-Ta-Si-Fe biomedical beta titanium alloys with increased strength and enhanced biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 60, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimpean, A.; Mitran, V.; Ciofrangeanu, C.M.; Galateanu, B.; Bertrand, E.; Gordin, D.M.; Iordachescu, D.; Gloriant, T. Osteoblast cell behavior on the new beta-type Ti-25Ta-25Nb alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, S.; Das, S.; Suwas, S.; Chatterjee, K. Engineering the next-generation tin containing β titanium alloys with high strength and low modulus for orthopedic applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 78, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.P.; Yu, Z.L.; Ren, L.Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.C. Study on Osseointegration Capability of β-Type Ti-Nb-Zr-Ta-Si Alloy for Orthopedic Implants. Materials 2024, 17, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K.; Dai, Y.; Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; Dargusch, M.; Huang, S.; Ma, J.; et al. Impact of scandium on mechanical properties, corrosion behavior, friction and wear performance, and cytotoxicity of a β-type Ti-24Nb-38Zr-2Mo alloy for orthopedic applications. Acta. Biomater. 2021, 134, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, S.; Nag, S.; Nasrazadani, S.; Ukirde, V.; El Bouanani, M.; Mohandas, A.; Nguyen, K.; Banerjee, R. Corrosion resistance and in vitro response of laser-deposited Ti-Nb-Zr-Ta alloys for orthopedic implant applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 94, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.T.; Zhou, H.Y.; Quan, W.J.; Ma, X.; Chon, T.E.; Fernandez, J.; Gusztav, F.; Kovács, A.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. New Insights Optimize Landing Strategies to Reduce Lower Limb Injury Risk. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2024, 5, 0126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


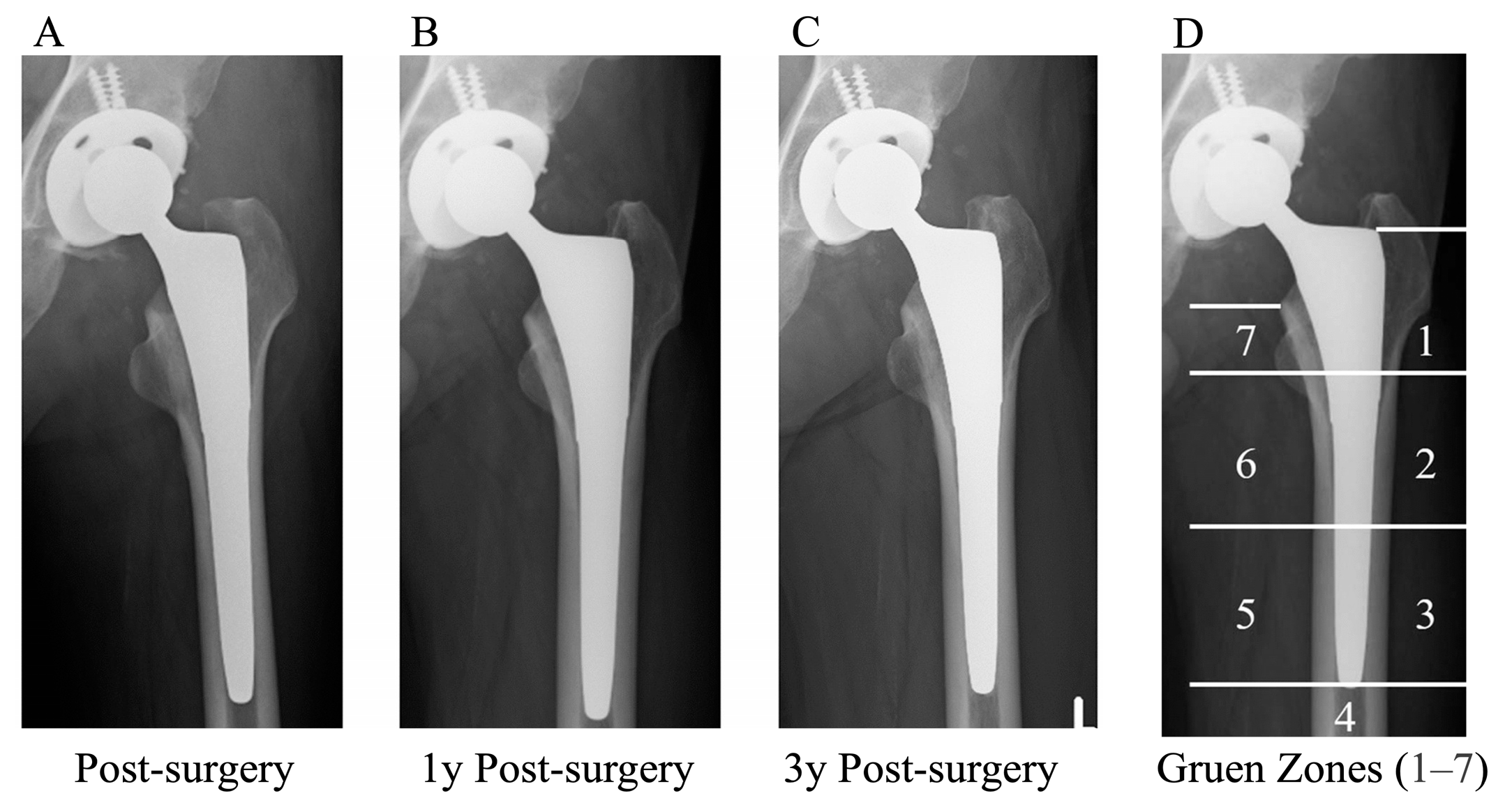
| Engh’s Classification | 1-Year Follow-Up | 3-Year Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|
| n, (ratio) | n, (ratio) | |
| None | 19, (47.5%) | 14, (35%) |
| Grade 1 | 17, (42.5%) | 10, (25%) |
| Grade 2 | 4, (10%) | 16, (40%) |
| Grade 3 | 0, (0%) | 0, (0%) |
| Grade 4 | 0, (0%) | 0, (0%) |
| Gruen Zone | Zone 1 | Zone 2 | Zone 3 | Zone 4 | Zone 5 | Zone 6 | Zone 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stress shielding | 9, (23%) | 0, (0%) | 0, (0%) | 0, (0%) | 0, (0%) | 1, (2.5%) | 21 (53%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mori, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Kurishima, H.; Kanabuchi, R.; Mori, N.; Sasagawa, K.; Aizawa, T. Biomechanical and Clinical Validation of a Modulus-Graded Ti-Nb-Sn Femoral Stem for Suppressing Stress Shielding in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094827
Mori Y, Tanaka H, Kurishima H, Kanabuchi R, Mori N, Sasagawa K, Aizawa T. Biomechanical and Clinical Validation of a Modulus-Graded Ti-Nb-Sn Femoral Stem for Suppressing Stress Shielding in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094827
Chicago/Turabian StyleMori, Yu, Hidetatsu Tanaka, Hiroaki Kurishima, Ryuichi Kanabuchi, Naoko Mori, Keisuke Sasagawa, and Toshimi Aizawa. 2025. "Biomechanical and Clinical Validation of a Modulus-Graded Ti-Nb-Sn Femoral Stem for Suppressing Stress Shielding in Total Hip Arthroplasty" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094827
APA StyleMori, Y., Tanaka, H., Kurishima, H., Kanabuchi, R., Mori, N., Sasagawa, K., & Aizawa, T. (2025). Biomechanical and Clinical Validation of a Modulus-Graded Ti-Nb-Sn Femoral Stem for Suppressing Stress Shielding in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4827. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094827







