Study on the Bearing Characteristics of Composite Foundations with Permeable Concrete Piles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Best Mix Ratio Design of Permeable Concrete Piles
2.1. Experiment Method
2.1.1. Experiment Material
2.1.2. Experiment Design
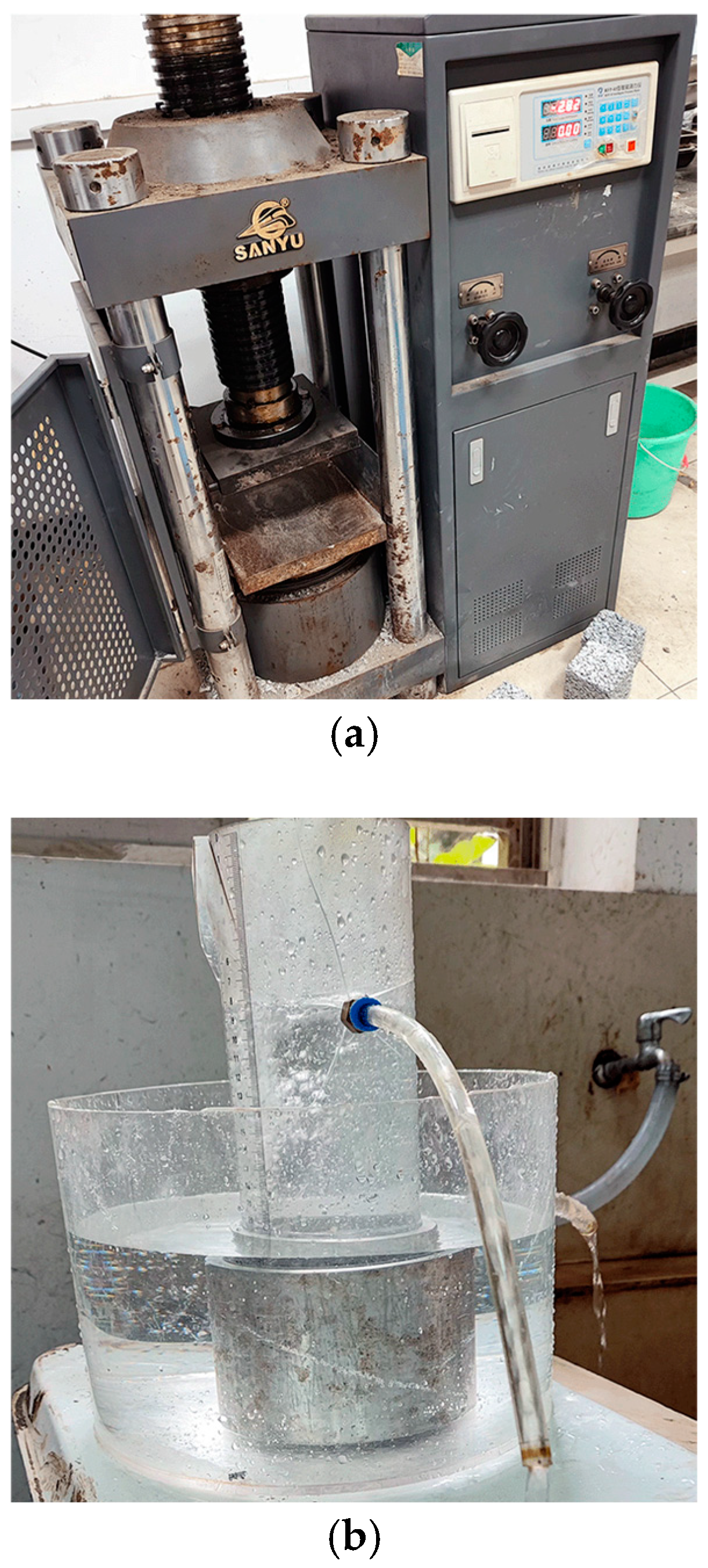
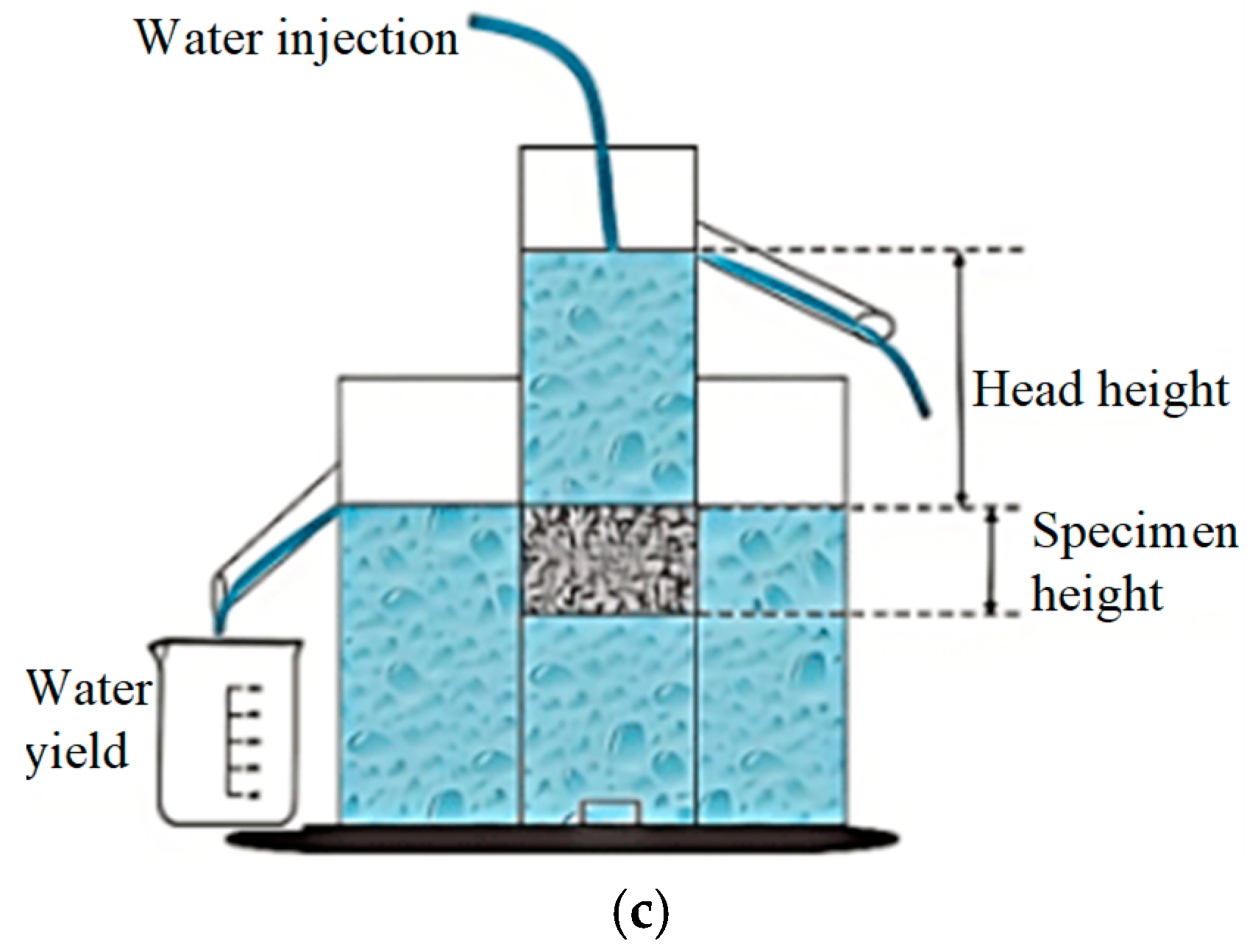
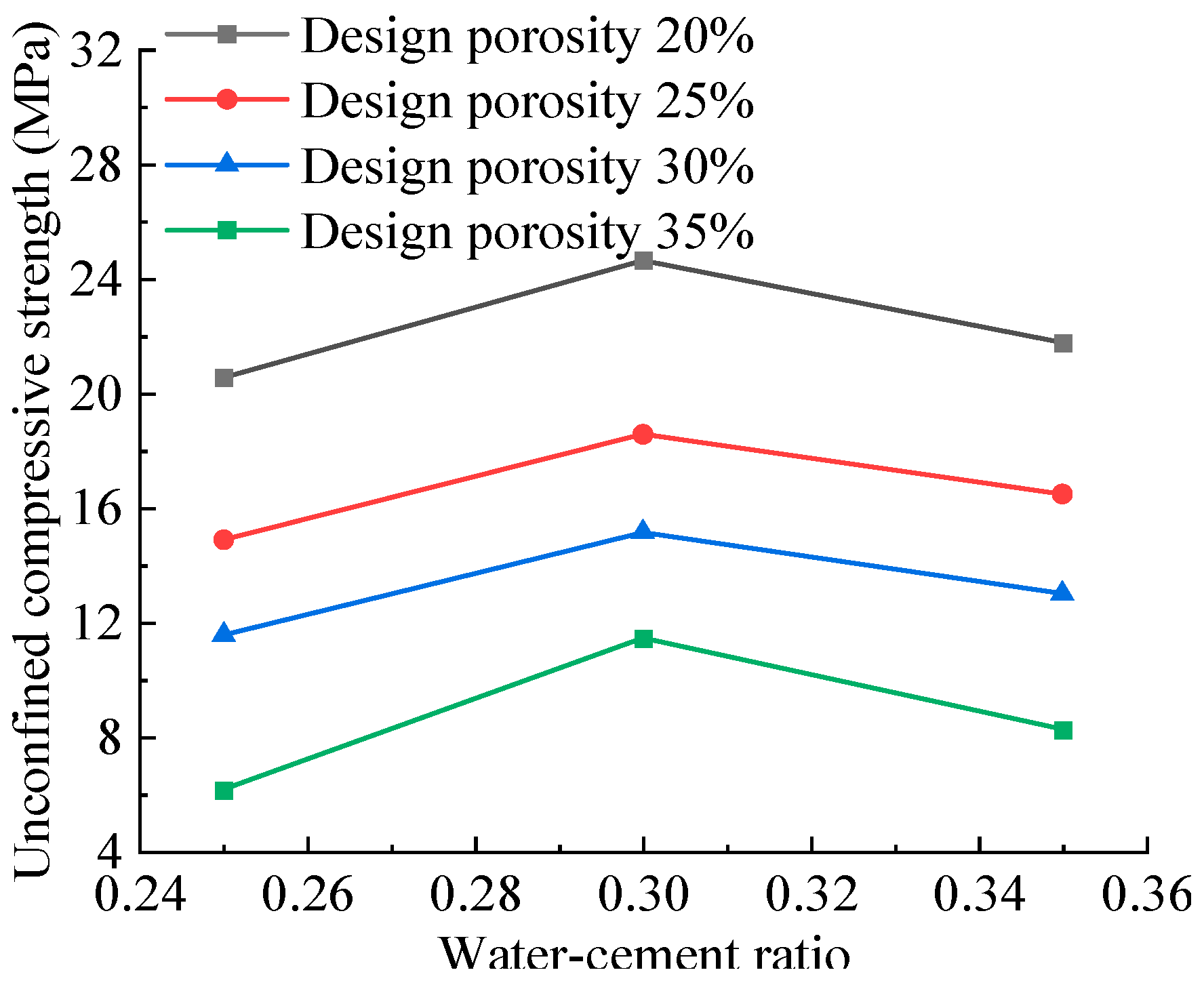
2.1.3. Test Method
2.2. Experiment Results
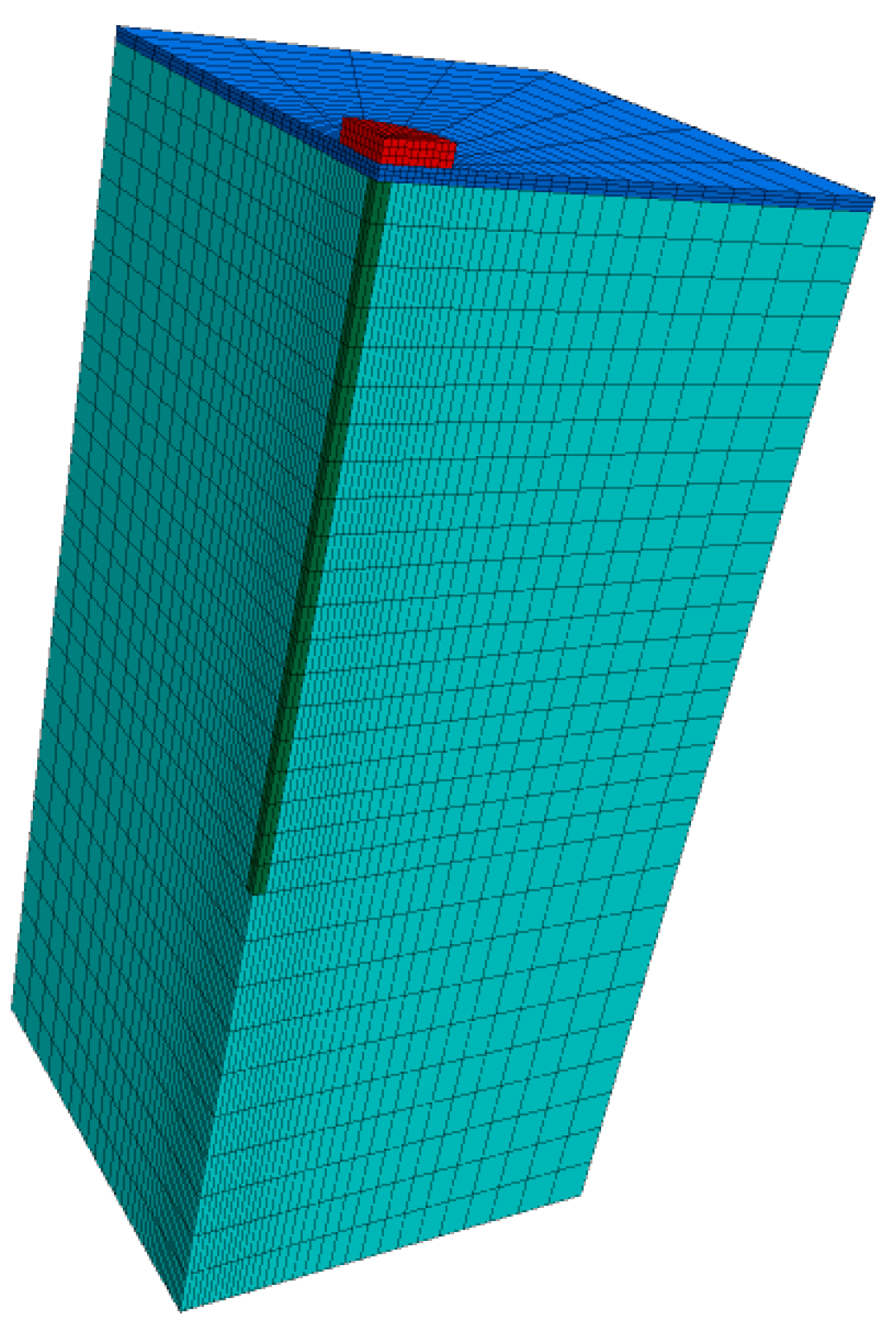
2.3. Determination of Optimal Mix Proportion
3. Numerical Simulation of Composite Foundations with Permeable Concrete Piles
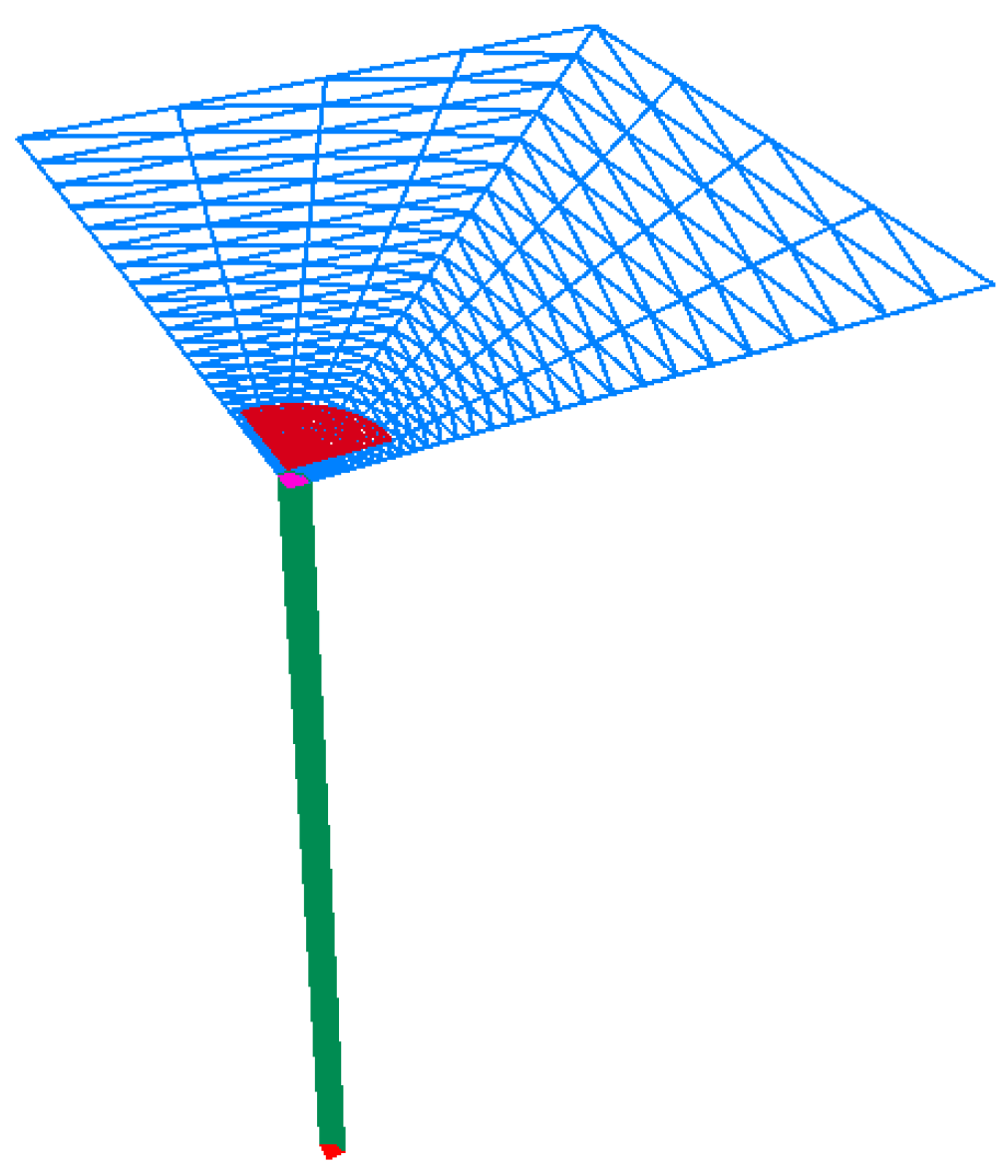
3.1. Model Establishment
3.2. Parameter Selection
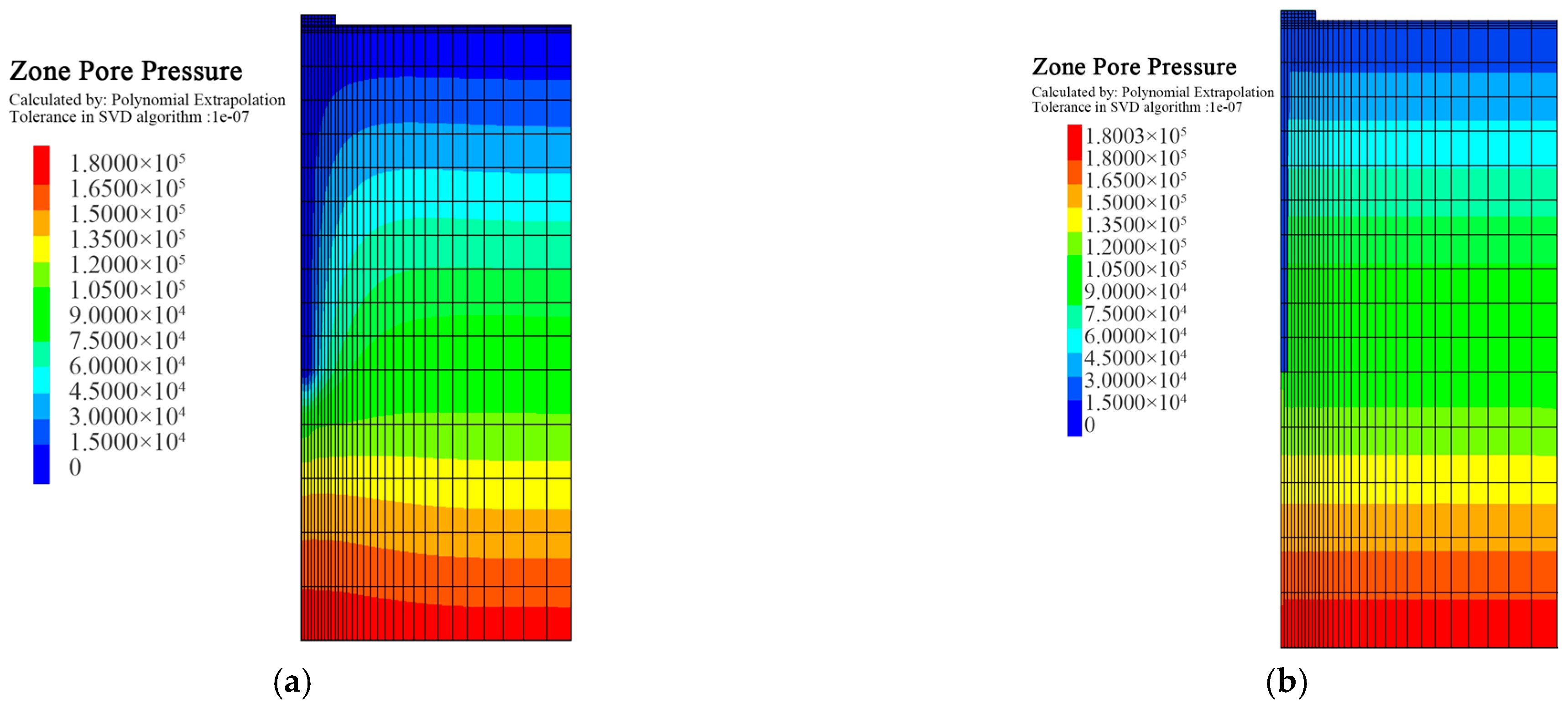
3.3. Pore Pressure Setup
4. Results and Discussions
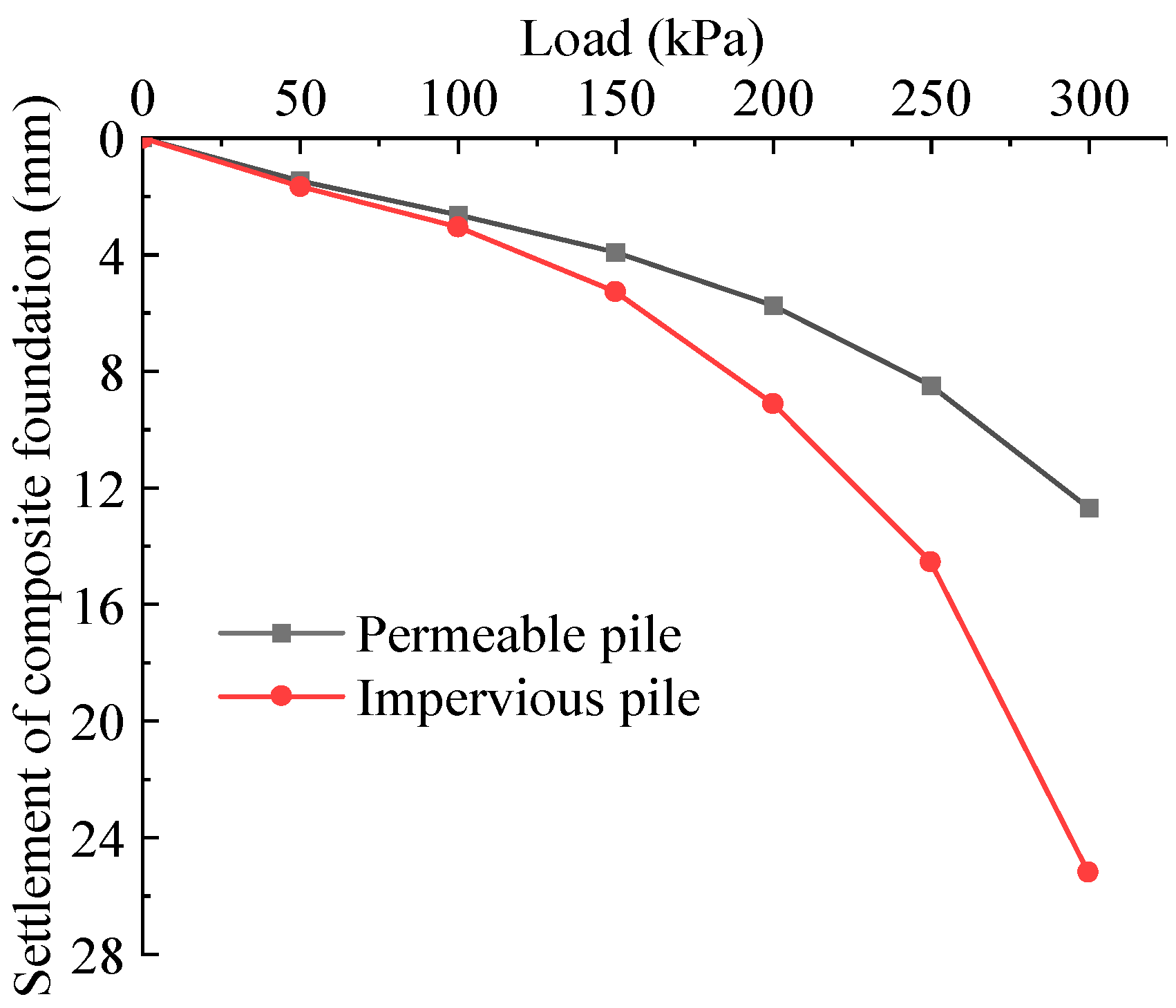
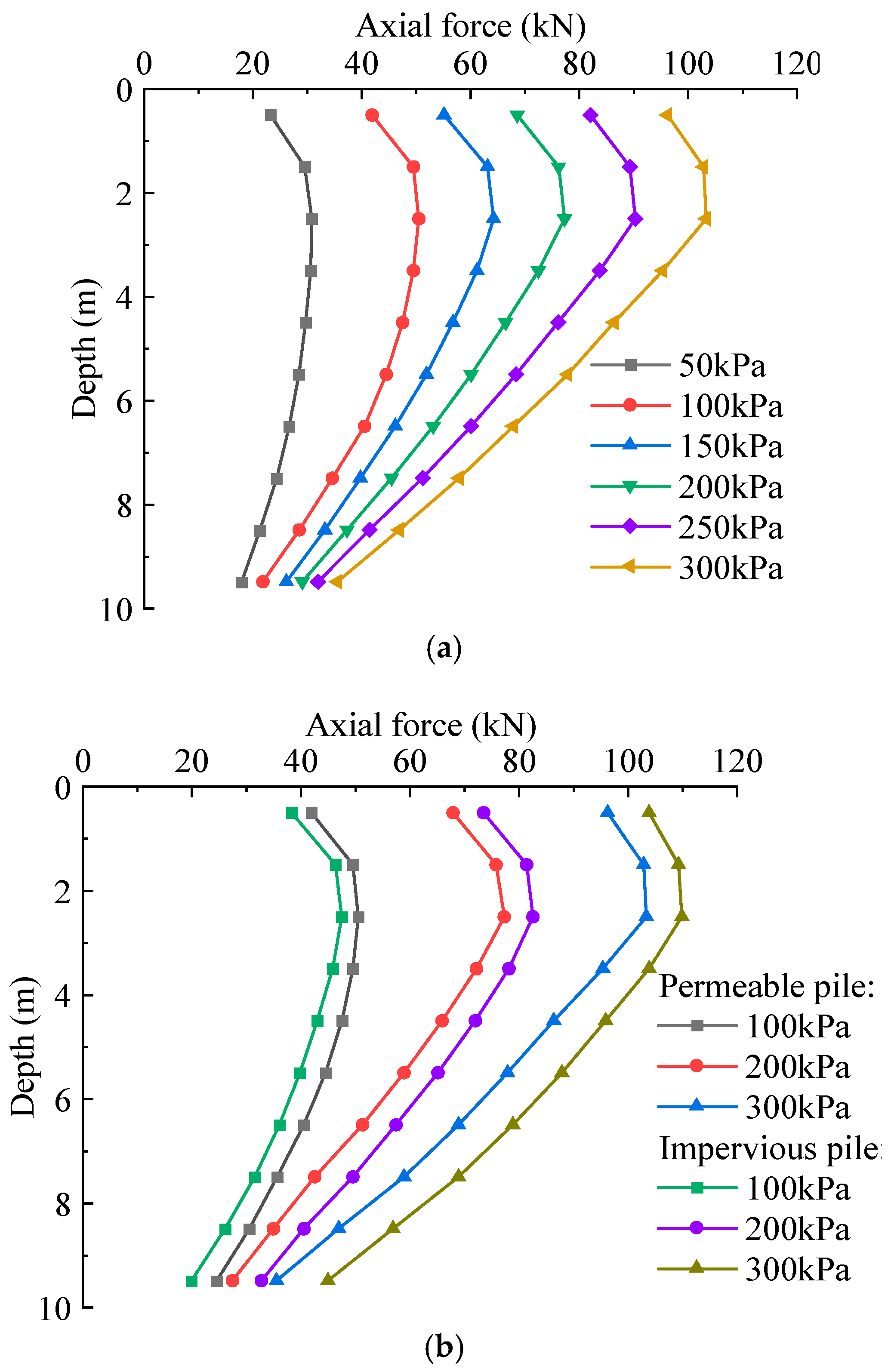
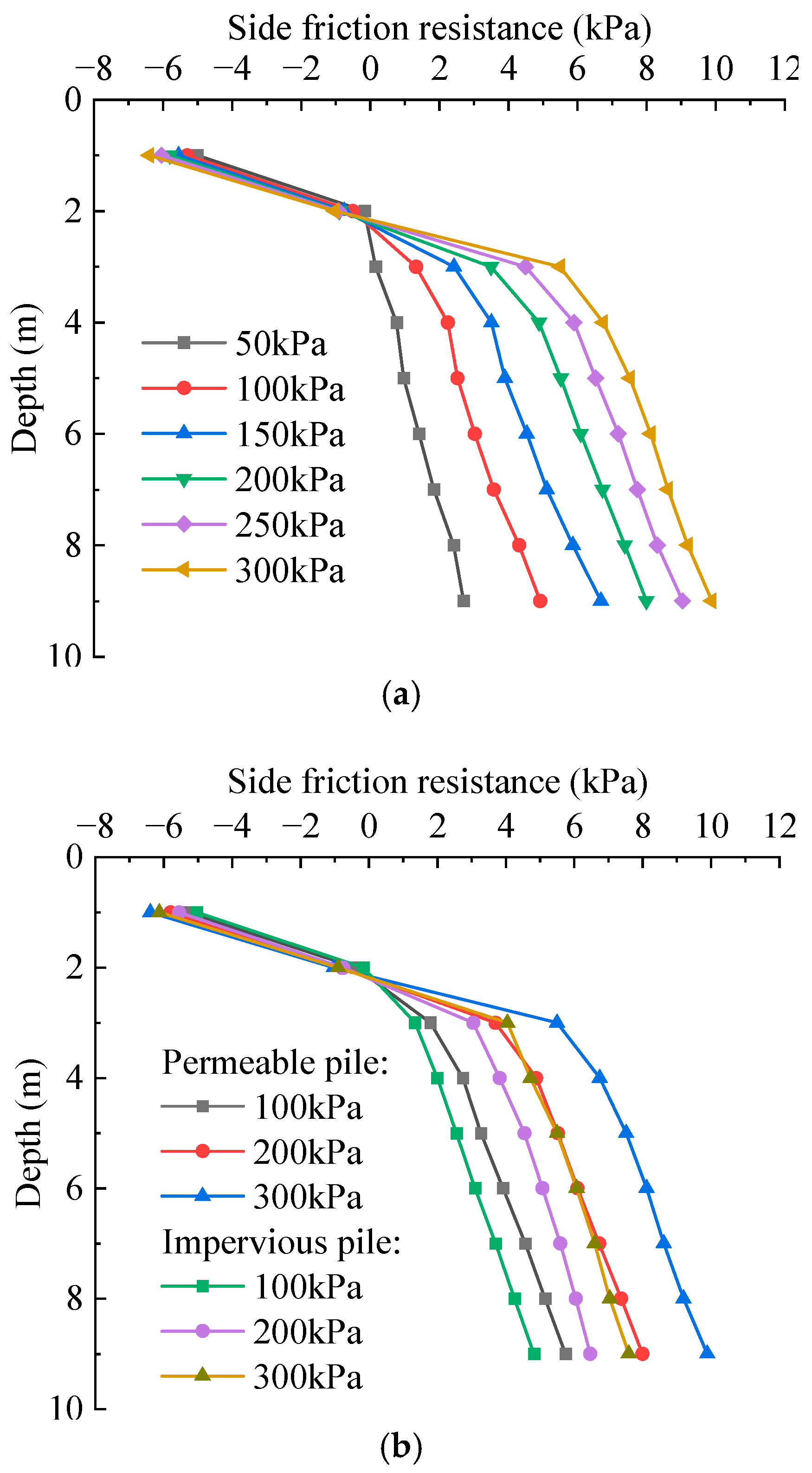
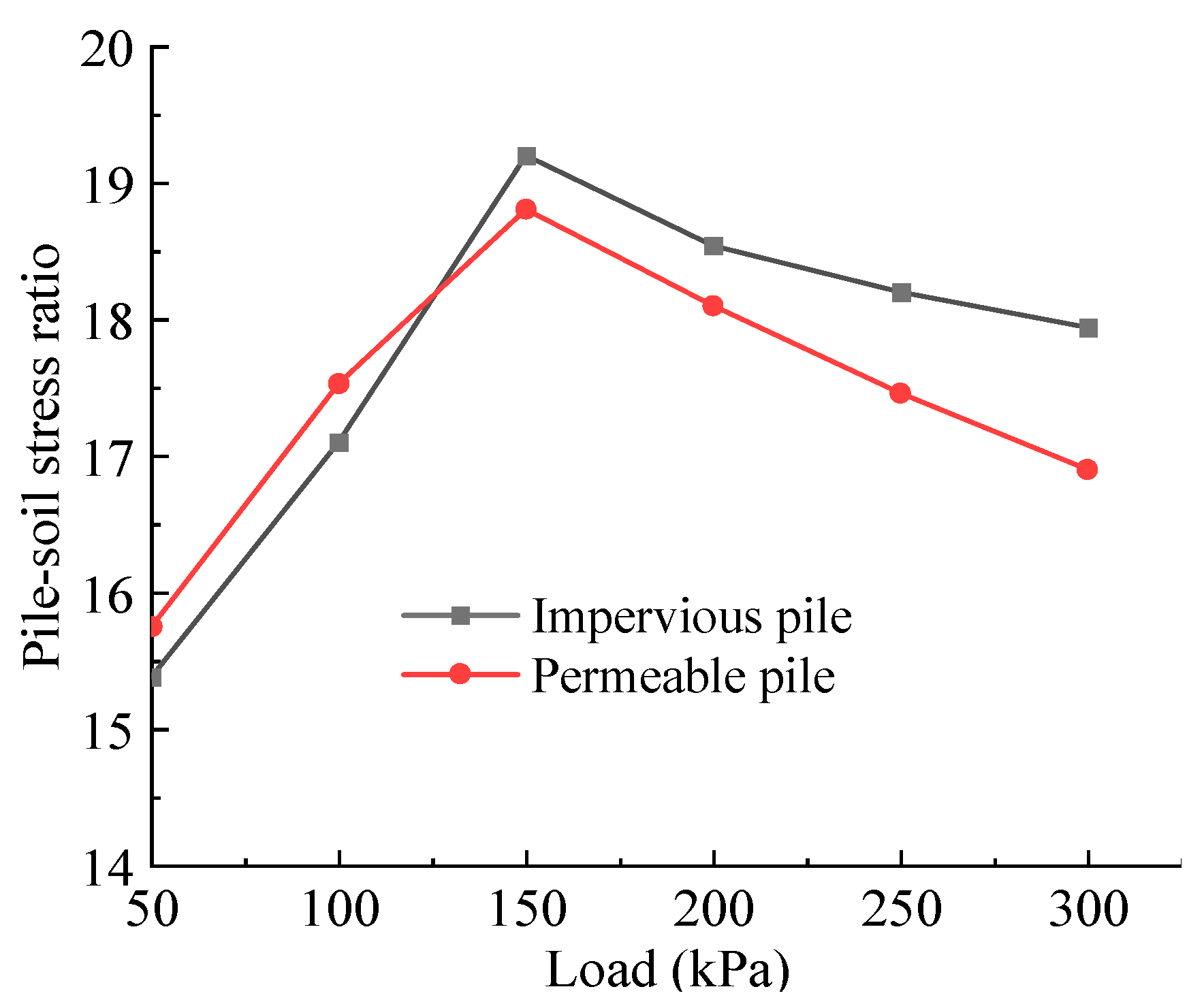
4.1. Comparison of Bearing Characteristics of Permeable and Impermeable Piles
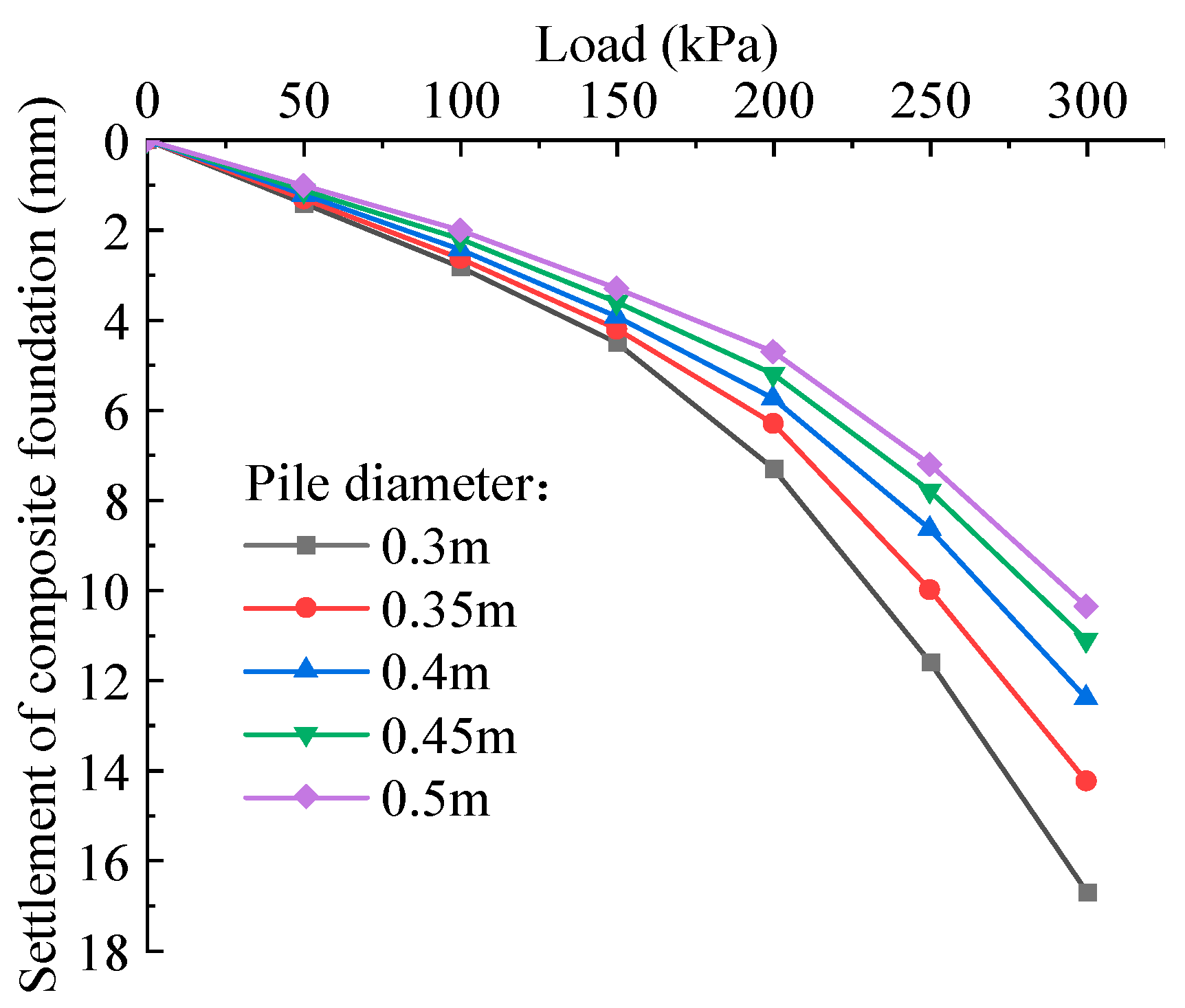
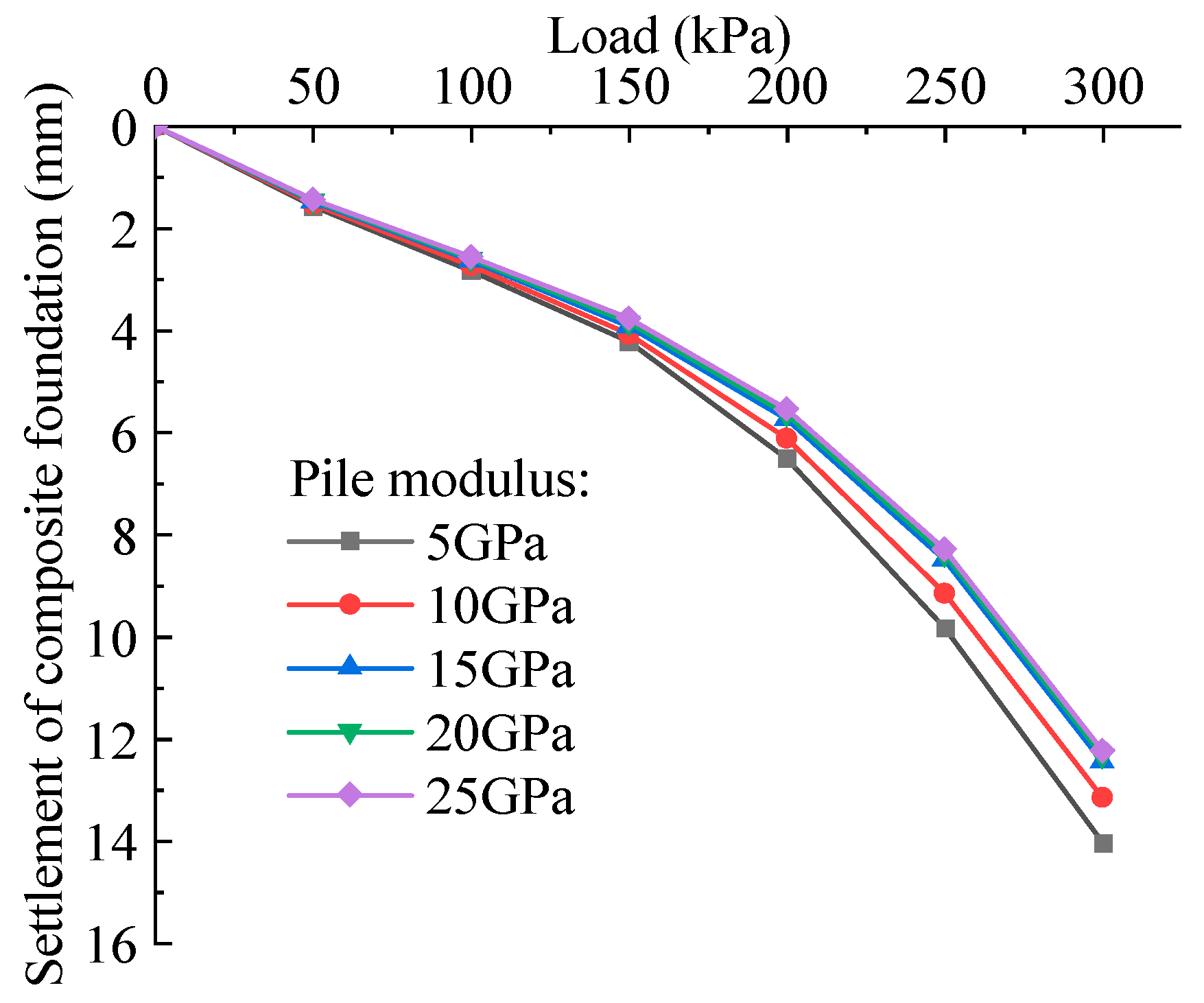
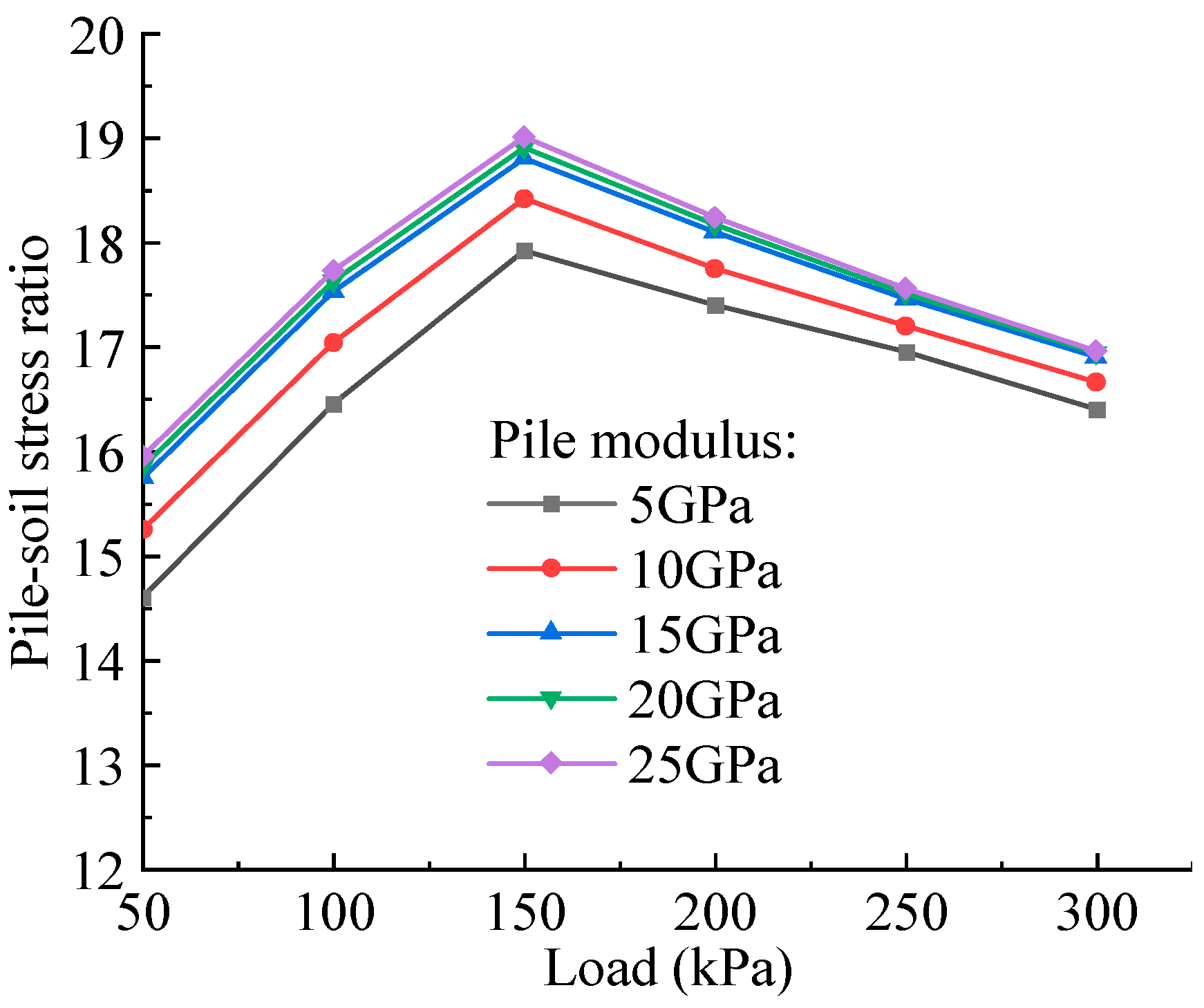
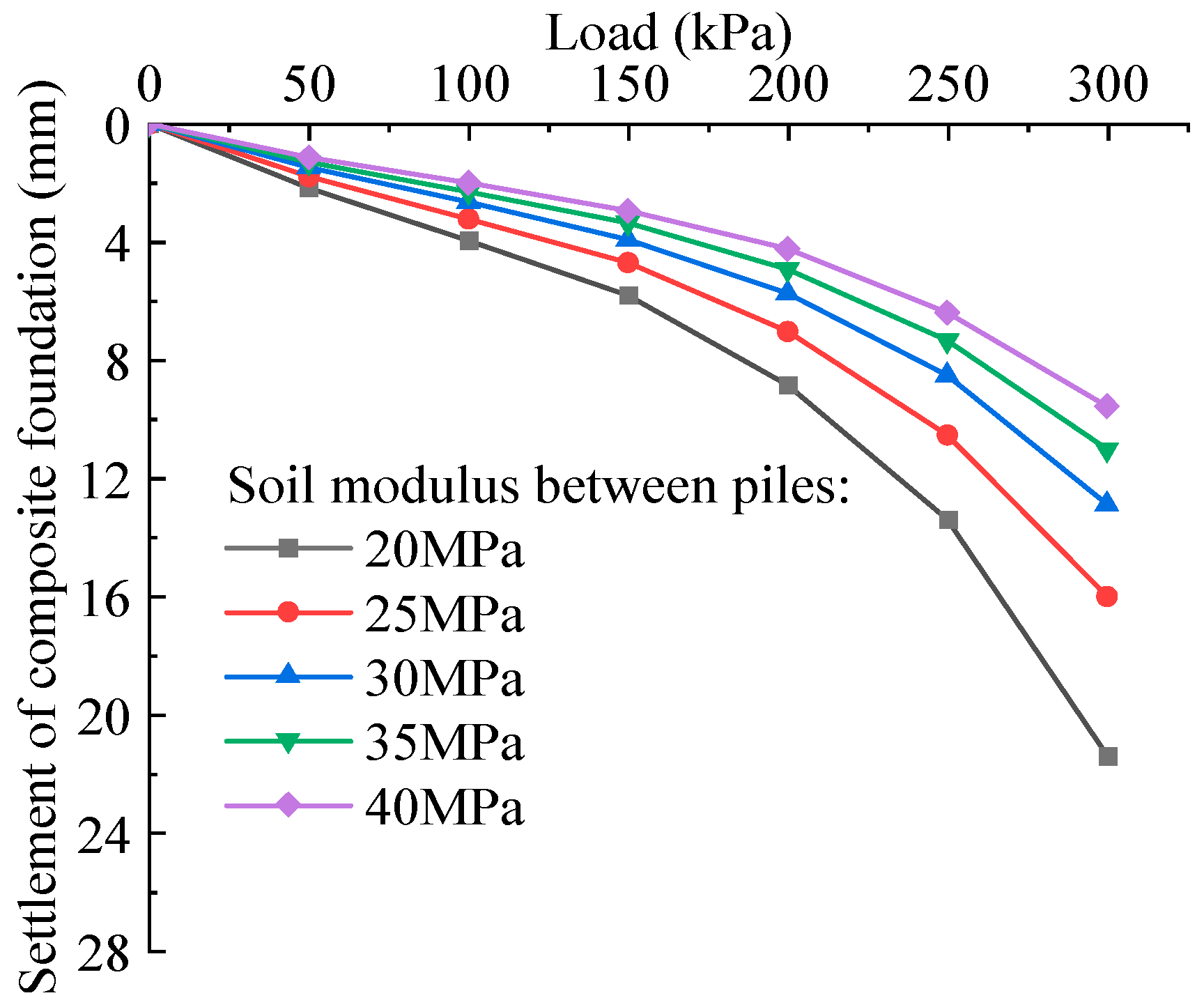
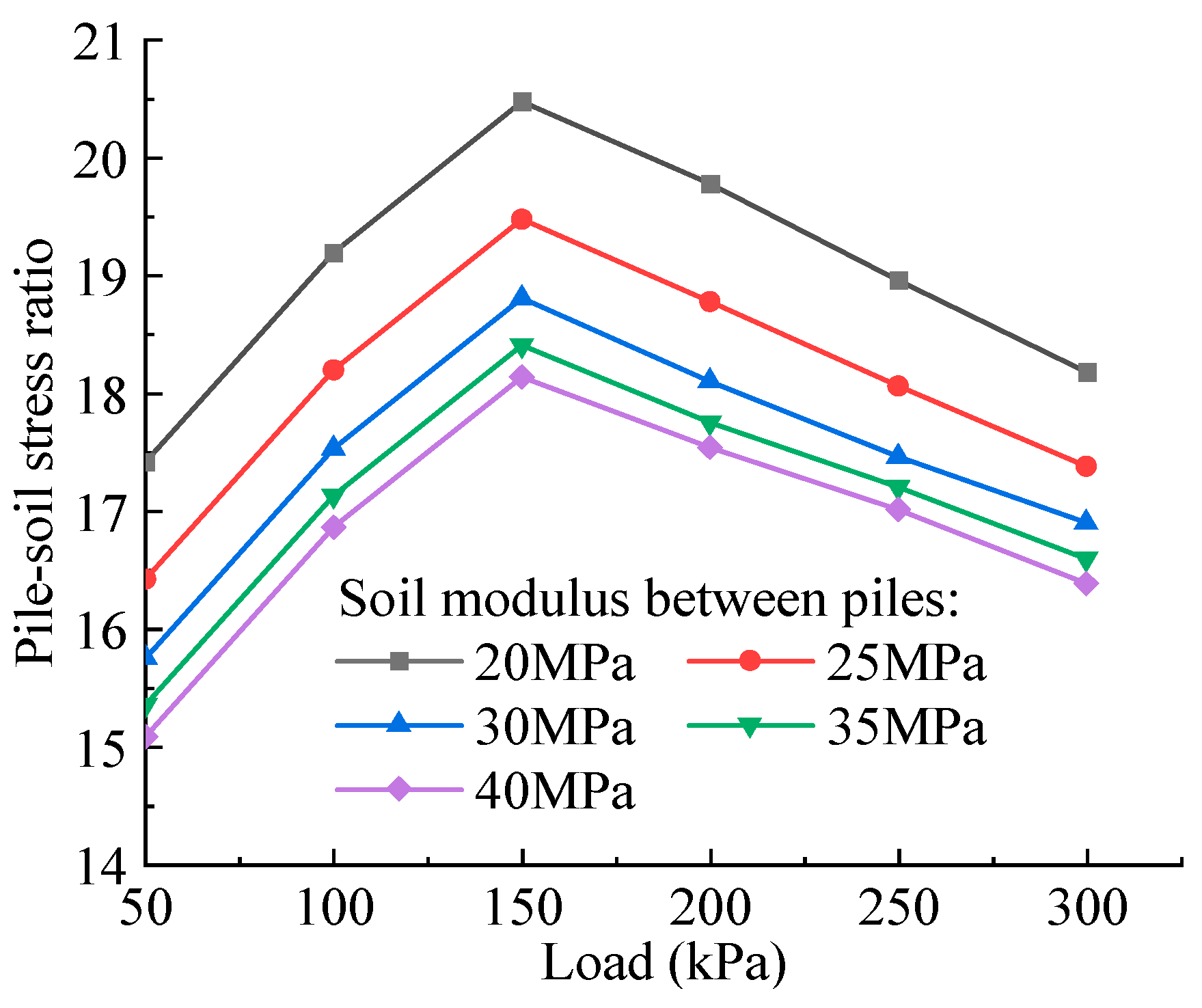
4.2. Influence of the Parameters of Pile
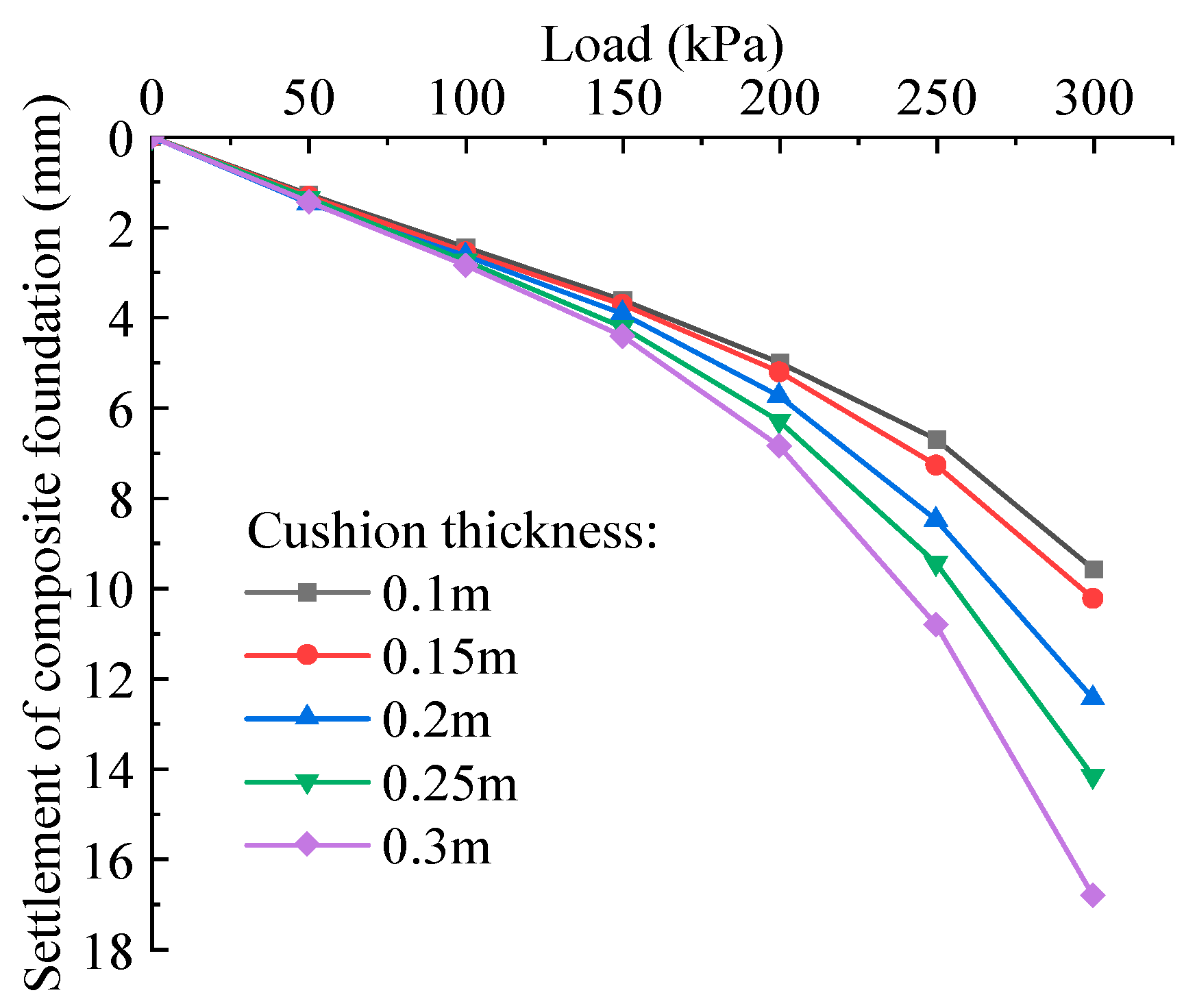
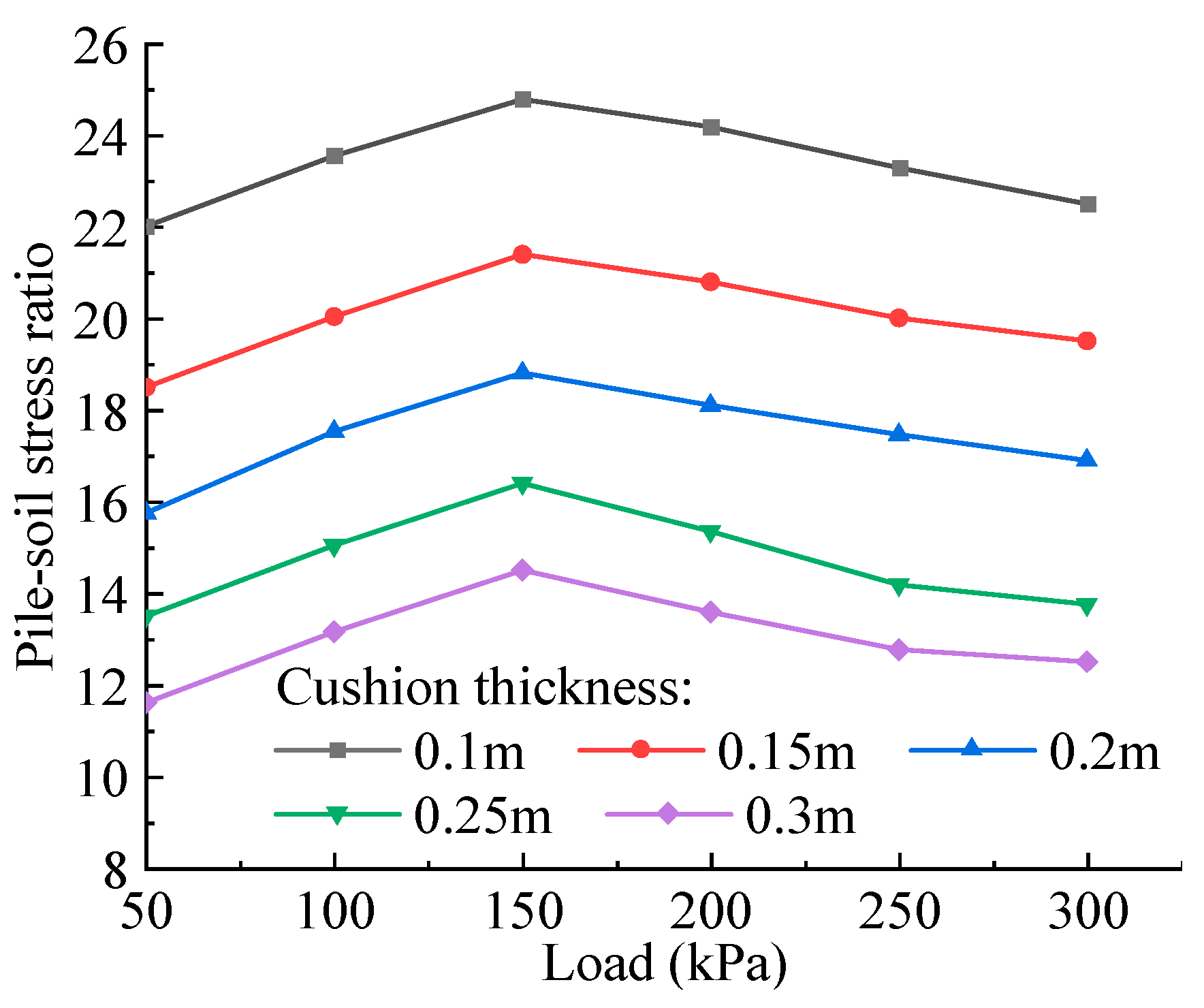
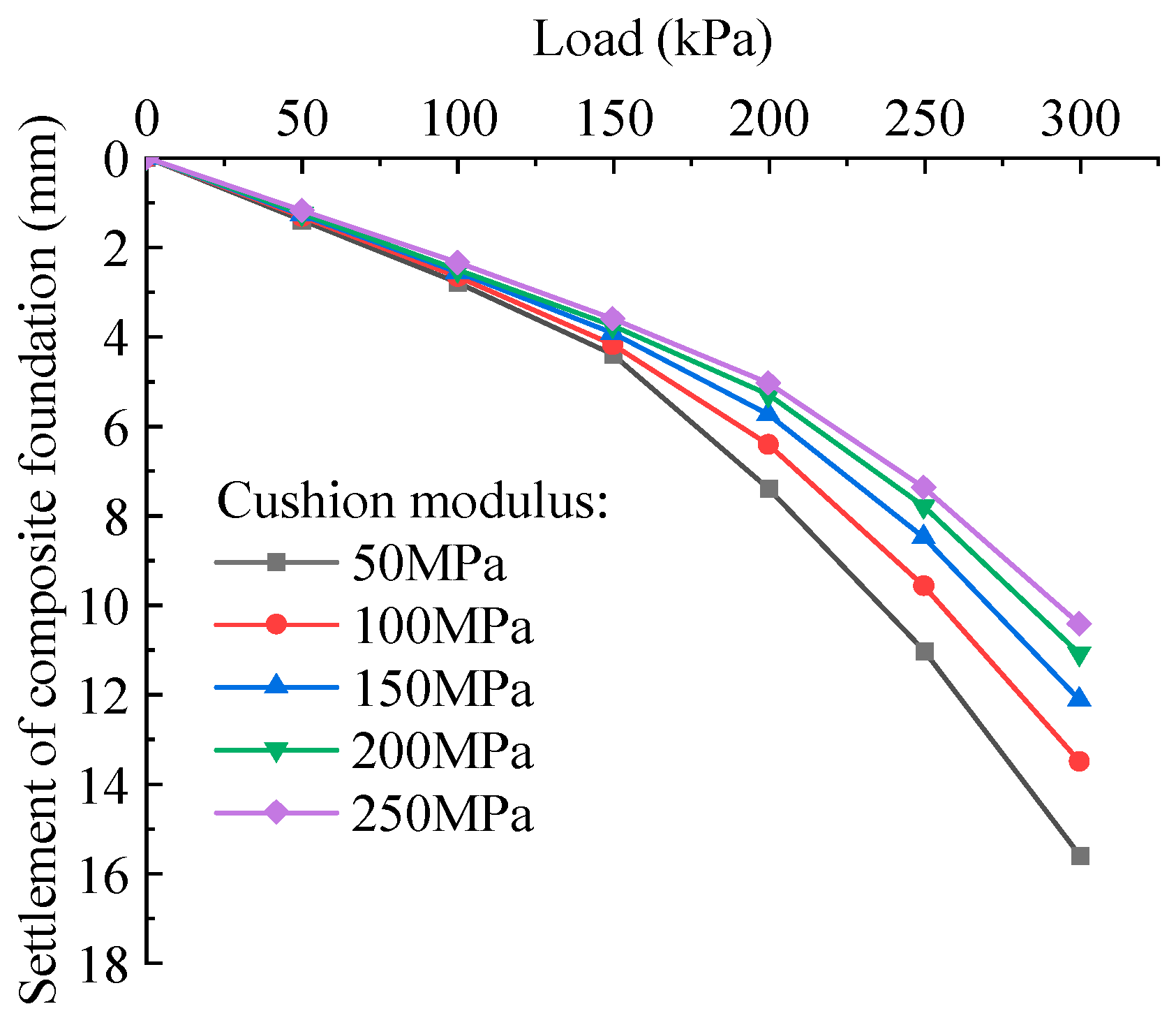
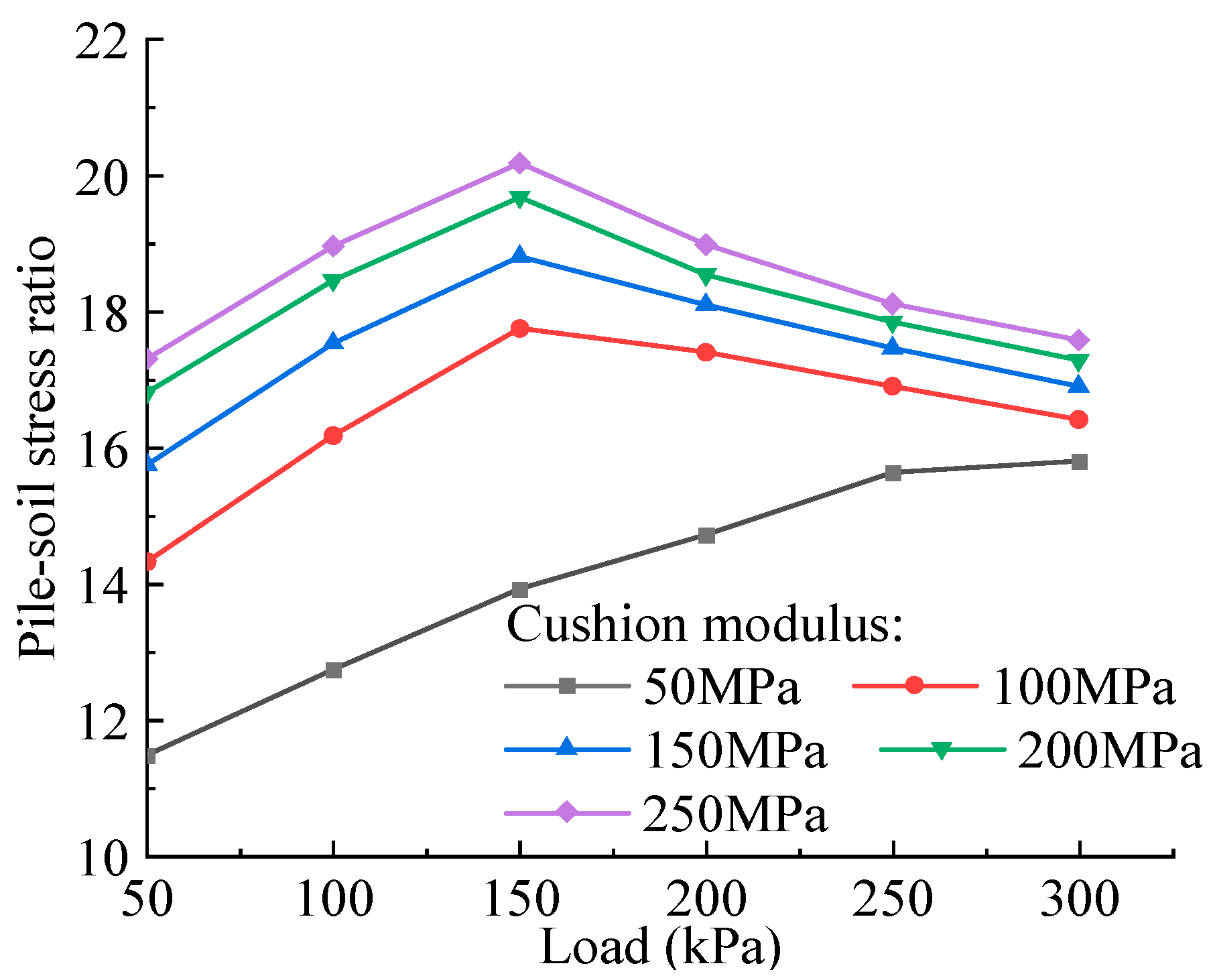
4.3. Influence of the Parameters of Cushion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monkul, M.M.; Yamamuro, J.A. Influence of silt size and content on liquefaction behavior of sands. Can. Geotech. J. 2011, 48, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Huang, H.; Bi, H. Land subsidence in the modern Yellow River Delta based on InSAR time series analysis. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Lu, Q.R.; Chen, S.J.; Dai, R.H.; Gao, J.H. Research progress of soft soil foundation treatment technology. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 455, 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.T.; Kang, W.L.; Yuan, Z.; Liang, J.X.; Zhao, W.F. Experimental study of the bearing capacity of a drainage pipe pile under vacuum consolidation. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2022, 23, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uba, B.U.; Cheng, G.Y. CFG Pile Composite Foundation: Its Engineering Applications and Research Advances. J. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5343472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.P.; Zhang, K.N.; Fu, L.M.; Liu, J.; He, J. Performance of cement–soil pile composite foundation with lateral constraint. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 4693–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.H.; Li, L.X. Vertical load transfer behavior of composite foundation and its responses to adjacent excavation: Centrifuge model test. Geotech. Test. J. 2021, 44, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.B.; Hong, B.N.; Qiu, G.F. Research on cushion action mechanism of CFG pile composite foundation for expressway. Rock Soil Mech. 2004, 15, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Dai, Z.H. Finite element analysis of functions of cushion of cement flyash gravel pile composite foundation. Rock Soil Mech. 2005, 79, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Zhuge, Y. Optimum mix design of enhanced permeable concrete—An experimental investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2664–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behlul, O.F.; Seyma, S.; Yusa, S. The effects of aggregate and fiber characteristics on the properties of pervious concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 356, 129294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.S.; Murugan, M. A review of factors influencing performance of pervious concrete. Seeni Bright. Singh Madasamy Murugan 2021, 73, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.L.; Luo, Z.B.; Khan, M.B.E. Impact of aggregate type and size and mineral admixtures on the properties of pervious concrete: An experimental investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.J.; Kang, M. Properties of pervious concrete with steel slag as aggregates and different mineral admixtures as binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ 52-2006; Standard for Quality and Testing Methods of Sand and Stone for Ordinary Concrete. China Architecture& Building Press: Beijing, China, 2006.
- CJJ/T 135-2009; Technical Code for Pervious Cement Concrete Pavements. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 50081-2019; Standard for Test Methods of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Concrete. China Architecture& Building Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Sriravindrarajah, R.; Wang, N.D.H.; Ervin, L.J.W. Mix Design for Pervious Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2012, 6, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Wen, P.; Wang, M.H.; Zhao, J.X. Comprehensive performance evaluation of low-carbon modified asphalt based on efficacy coefficient method. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, H.; Han, L.; Yu, L.Y.; Zhang, Q. Risk analysis on swell–shrink capacity of expansive soils with efficacy coefficient method and entropy coefficient method. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 99, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Wang, L.J.; Hao, L.; Su, Z.L. Optimization of coarse aggregate content based on efficacy coefficient method. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2011, 26, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Yan, Y.H.; Cui, X.Q. Optimization of self-insulating regenerated concrete mix ratio based on total efficacy coefficient method. Sichuan Build. Sci. Res. 2017, 43, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Du, G.; Xia, H.; Sun, C. Model Test and Numerical Simulation Study on Bearing Characteristics of Pervious Concrete Pile Composite Foundation. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.Q. Discussion on China’s Soft Soil Zoning and Its Statistical Characteristics of Parameters. Master’s Thesis, Railway University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itasca Consulting Group, Inc. FLAC3D (Fast Largrangian Analysis of Continua in 3 Dimention) User Manuals; Version 5.0; Itasca Consulting Group, Inc.: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2012; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50783-2012; Technical Specifications for Composite Foundation. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2012.







| Particle Size (mm) | Apparent Density (kg/m3) | Bulk Density (kg/m3) | Water Absorption Rate (%) | Crush Value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.75–9.50 | 2700 | 1520 | 0.6 | 8.7 |
| Serial Number | Water–Cement Ratio | Design Porosity (%) | Efficacy Coefficient (Compressive Strength) | Efficacy Coefficient (Permeability Coefficient) | Total Coefficient of Efficacy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-1 | 0.25 | 20 | 0.83 | 0.46 | 0.62 |
| PC-2 | 0.25 | 25 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.61 |
| PC-3 | 0.25 | 30 | 0.47 | 0.84 | 0.63 |
| PC-4 | 0.25 | 35 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 0.50 |
| PC-5 | 0.3 | 20 | 1.00 | 0.40 | 0.63 |
| PC-6 | 0.3 | 25 | 0.75 | 0.52 | 0.63 |
| PC-7 | 0.3 | 30 | 0.61 | 0.72 | 0.67 |
| PC-8 | 0.3 | 35 | 0.46 | 0.91 | 0.65 |
| PC-9 | 0.35 | 20 | 0.88 | 0.35 | 0.55 |
| PC-10 | 0.35 | 25 | 0.67 | 0.48 | 0.56 |
| PC-11 | 0.35 | 30 | 0.53 | 0.62 | 0.57 |
| PC-12 | 0.35 | 35 | 0.34 | 0.80 | 0.52 |
| Cement (kg/m3) | Coarse Bone Material (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) | Water Reducing Agent (kg/m3) |
| 219.72 | 1502.1 | 66.42 | 2.00 |
| Category | Density (ρ/g∙cm−3) | E (MPa) | v | c (kPa) | φ (°) | Permeability Coefficient (k/cm∙s−1) | Porosity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cap | 2.4 | 2.0 × 104 | 0.20 | - | - | - | - |
| Cushion | 2.0 | 150 | 0.30 | 0 | 35 | 5.0 × 10−3 | 0.50 |
| Soil | 1.9 | 20 | 0.35 | 30 | 17 | 1.0 × 10−6 | 0.65 |
| Pile | 2.1 | 1.5 × 104 | 0.20 | - | - | 0.611 | 0.30 |
| Interface Name | kn (GPa/m) | ks (GPa/m) | c (kPa) | f (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pile cap–cushion | 3310 | 3310 | / | / |
| Cushion–pile | 2150 | 2150 | / | / |
| Cushion–soil | 580 | 580 | / | / |
| Pile–soil | 1440 | 1440 | 21 | 11.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Bian, X.; Zhou, H. Study on the Bearing Characteristics of Composite Foundations with Permeable Concrete Piles. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094835
Liu H, Yang S, Bian X, Zhou H. Study on the Bearing Characteristics of Composite Foundations with Permeable Concrete Piles. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094835
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hui, Sifan Yang, Xiaoya Bian, and Heng Zhou. 2025. "Study on the Bearing Characteristics of Composite Foundations with Permeable Concrete Piles" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094835
APA StyleLiu, H., Yang, S., Bian, X., & Zhou, H. (2025). Study on the Bearing Characteristics of Composite Foundations with Permeable Concrete Piles. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094835





