Deep-Space Background Low-Light Image Enhancement Method Based on Multi-Image Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a low-light image enhancement method for deep-space background based on multi-image fusion, which effectively solves the problem of Earth halo interference and color distortion through the steps of calculating segmentation thresholds and binarization processing, calculating halo ranges, extracting and separating halos, contouring analysis, and region optimization, and mask generation;
- We design an adaptive enhancement module based on luminance distribution detection, which effectively suppresses and eliminates the noise and artifacts introduced in the image during the preprocessing of RetinexFormer;
- We design an edge detection extension module, which extends the edges by expansion and intersection detection, effectively avoiding incomplete extraction of the target region and solving the problem of incomplete satellite target region;
- By combining the features of different regions, the extraction of the satellite target region, the Earth region, and the deep-space background is realized, which significantly improves the detailed visibility of the satellite target while ensuring high fidelity of the Earth region.
2. Related Work
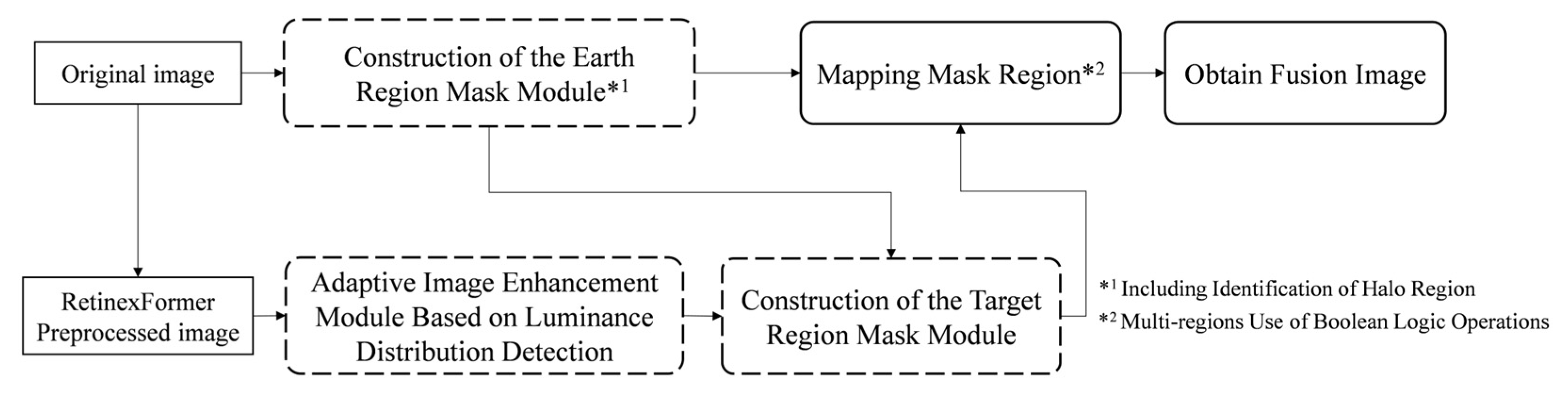
3. Method
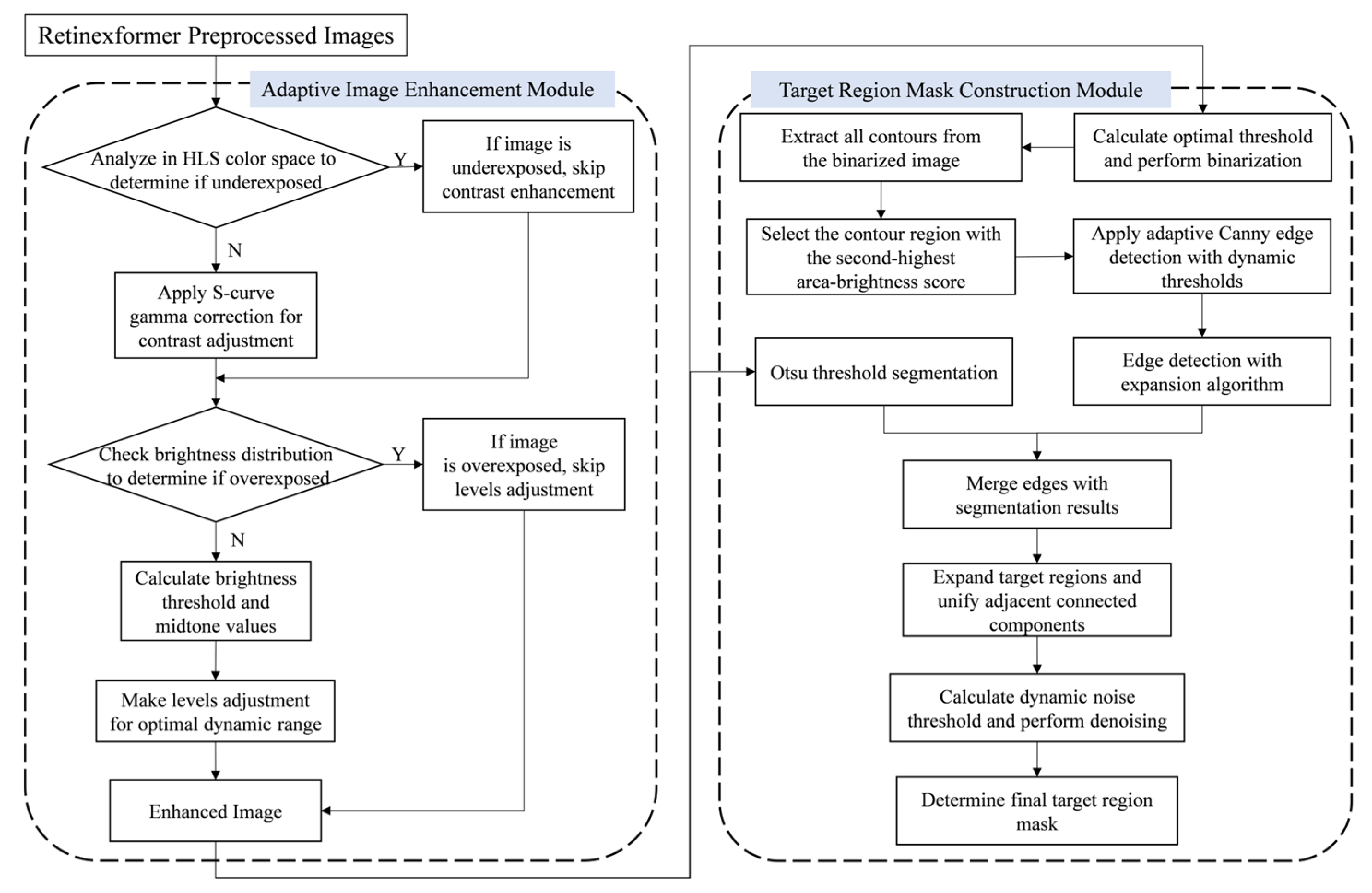
3.1. Enhancement of Single Satellite Images
- Contrast enhancement based on segmented exponential function
- 2.
- Detecting luminance distribution and adjusting dynamic threshold
- 3.
- Extraction of satellite target area
- 4.
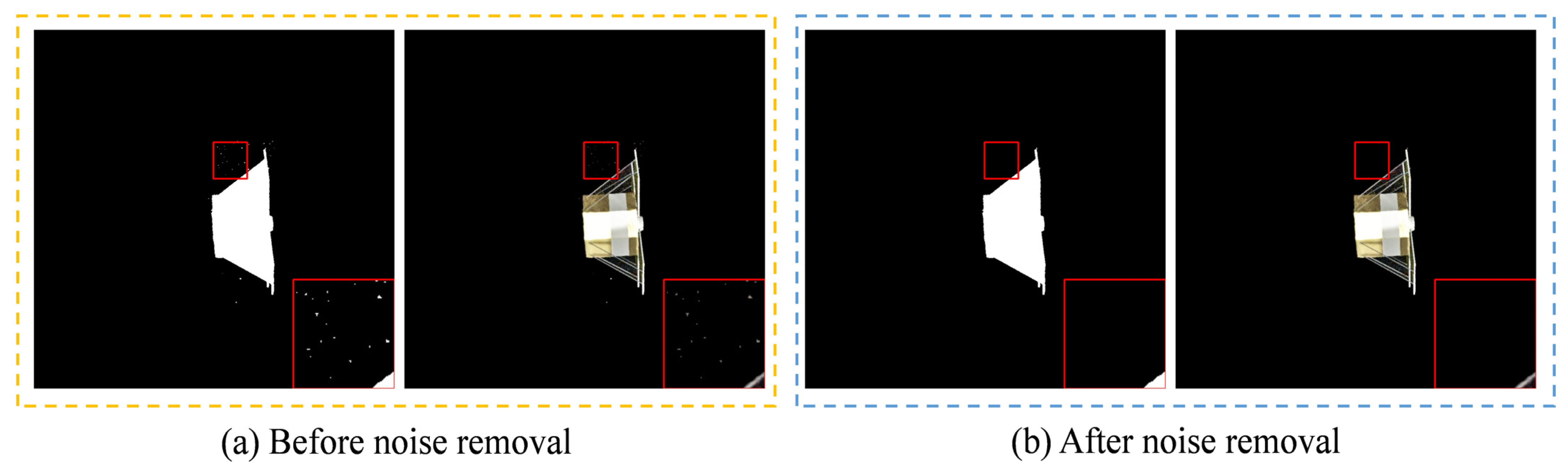
- Target areas merging and noise removal
3.2. Enhancement of Satellite Images Containing Celestial Bodies
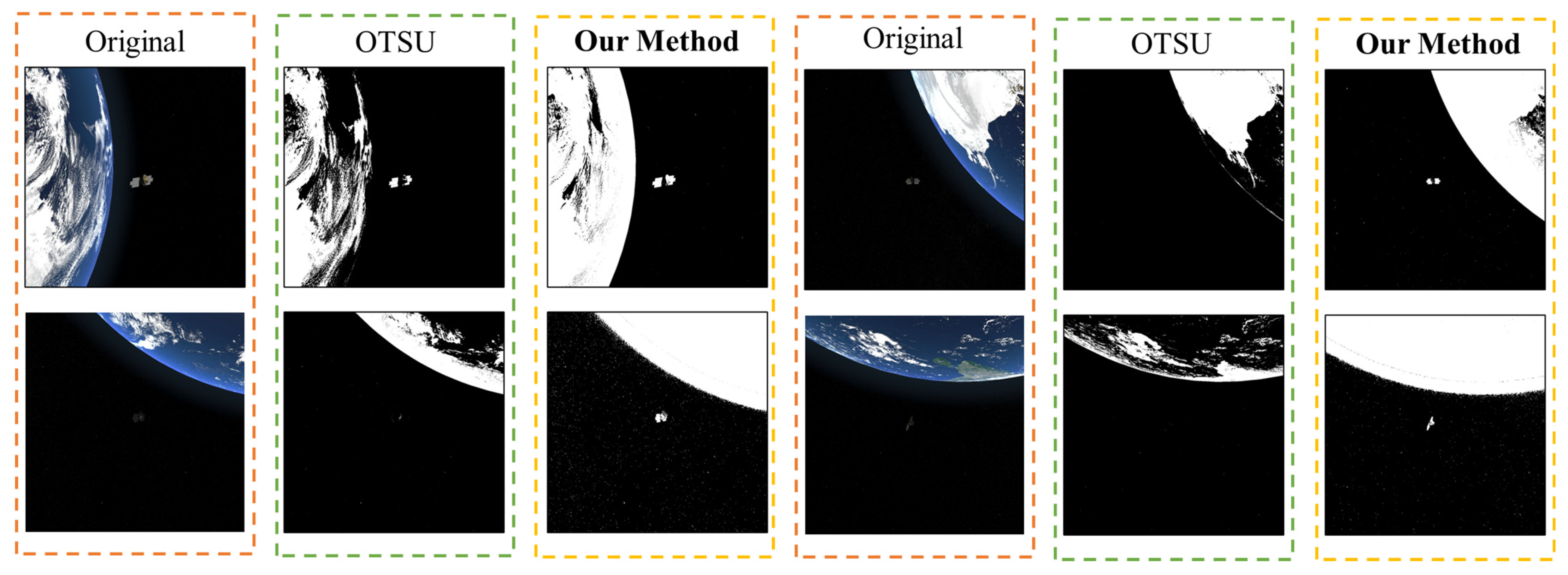
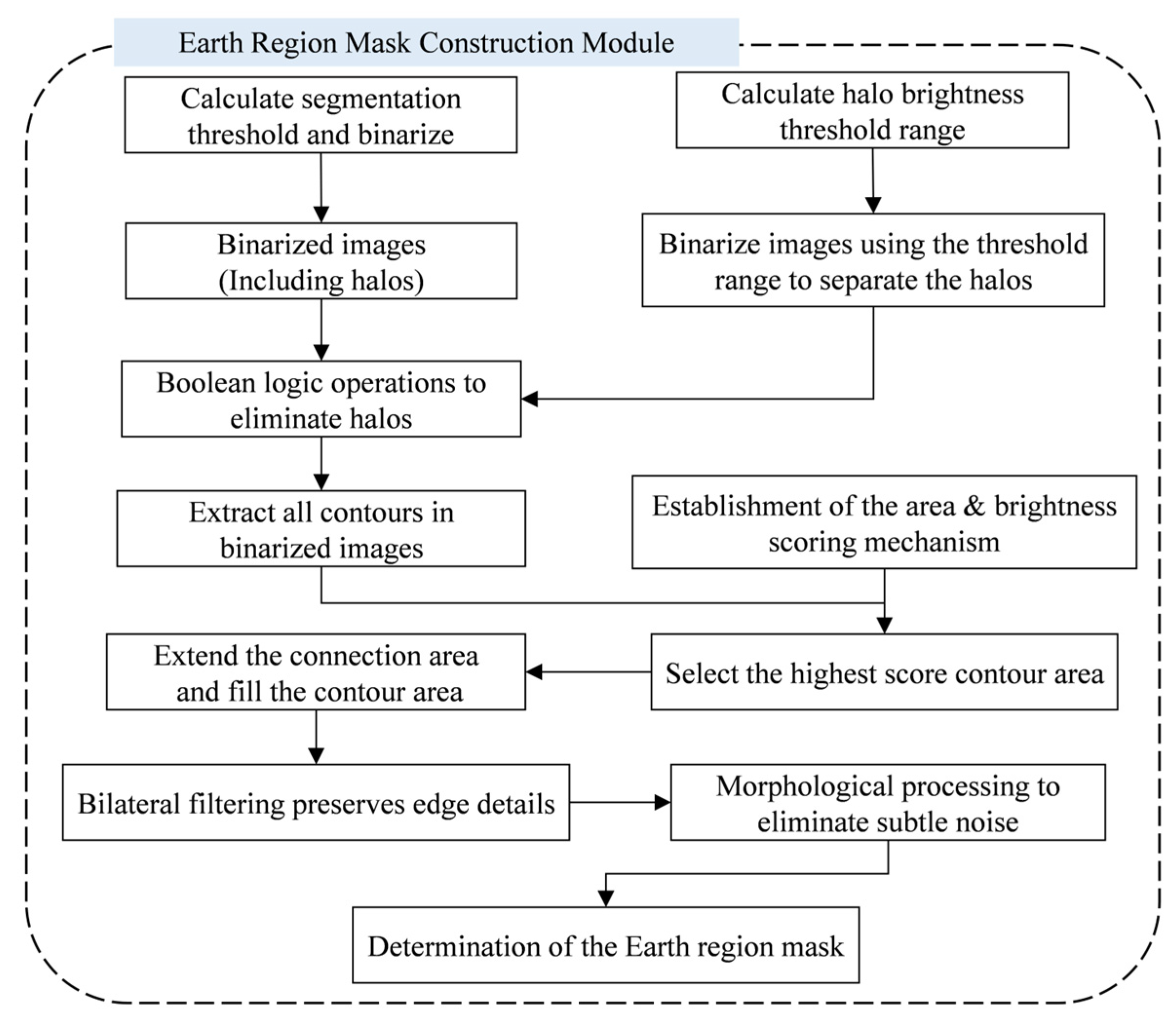
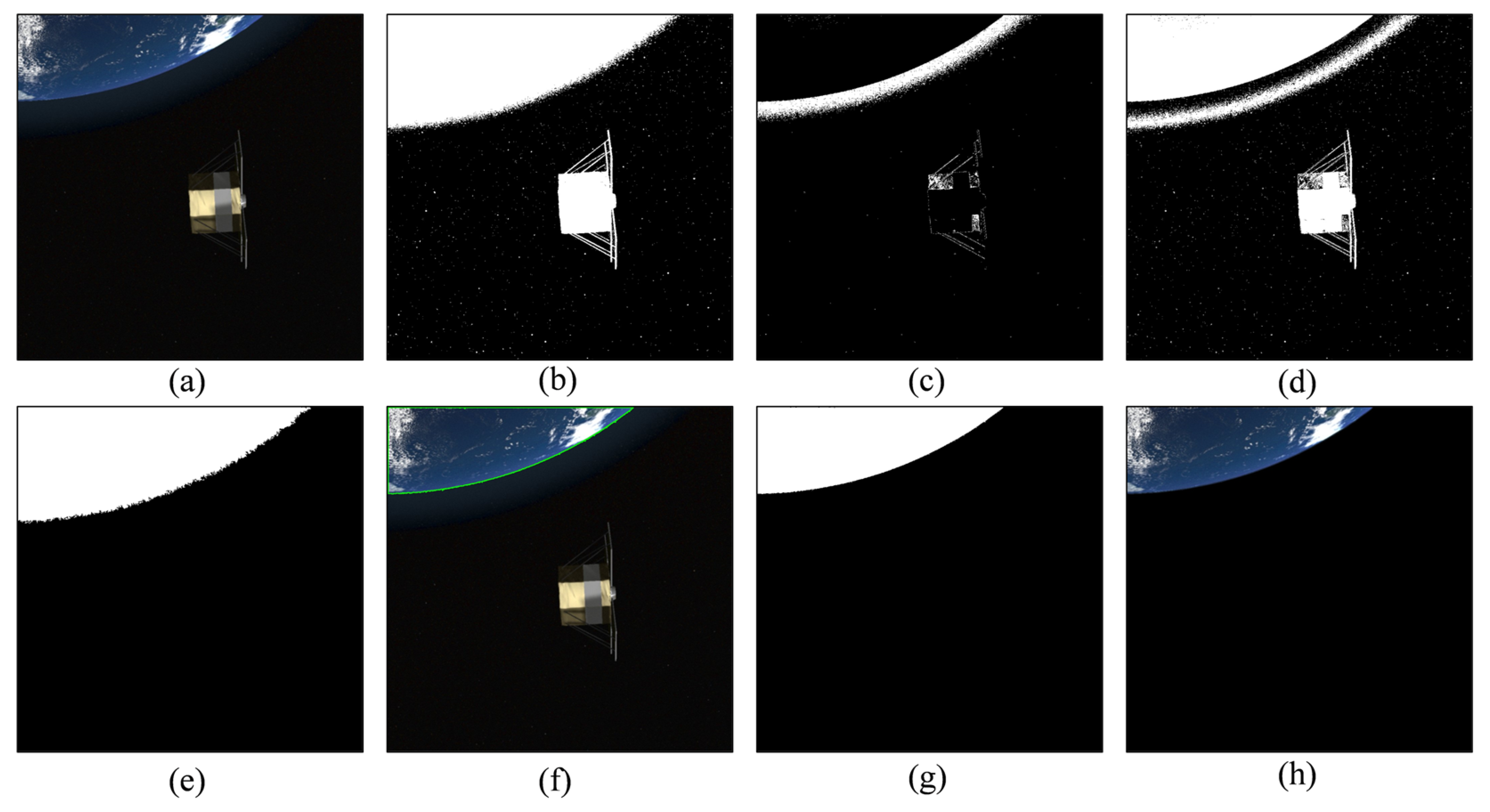
3.2.1. Extract the Earth Region
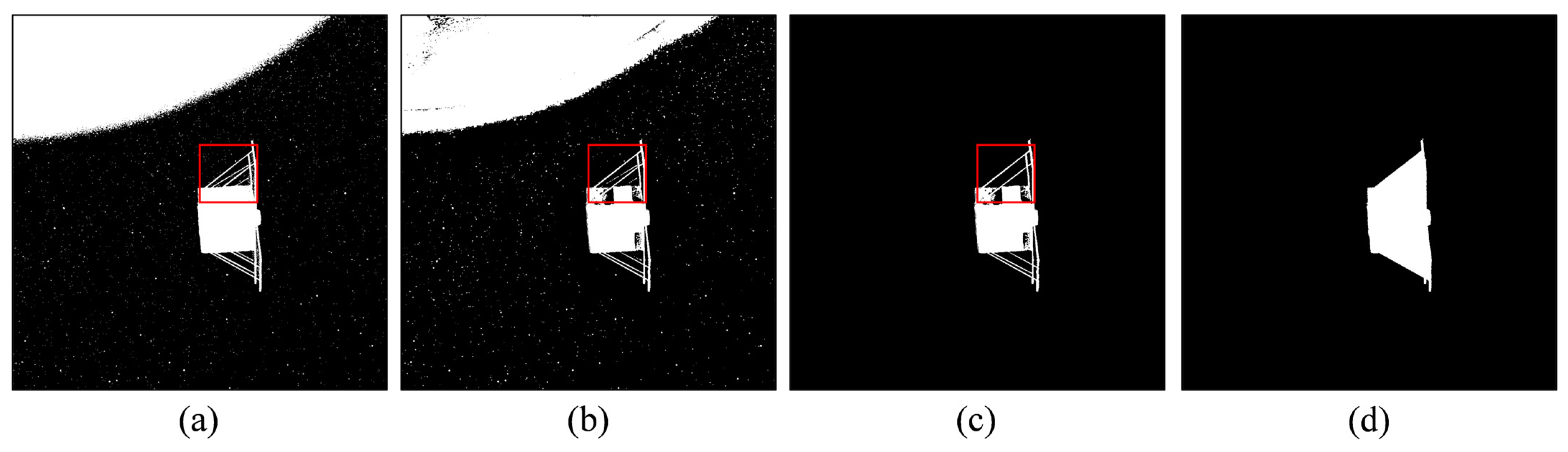
- Calculate segmentation threshold and binarization
- The black area is entirely encircled by the white area, and its area is less than 50% of the white area;
- The region is located at the edge of the image, i.e., at least one point of its outline is located at the left, right, top, or bottom edge of the image.
- 2.
- Suppressing the halo effect
- 3.
- Contour analysis and region optimization
- 4.
- Post-processing and mask generation
3.2.2. Extract Satellite Target Area
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset Selection
4.2. Experimental Details
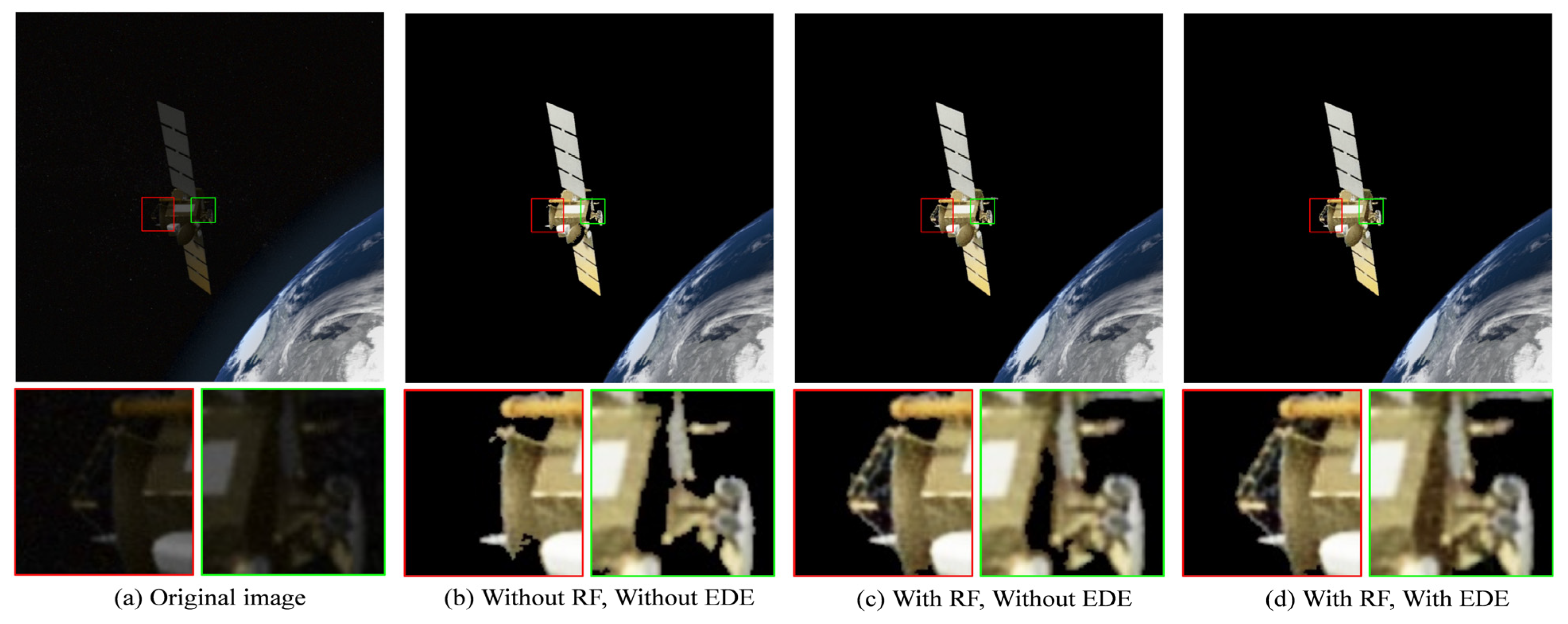
4.3. Ablation Study
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
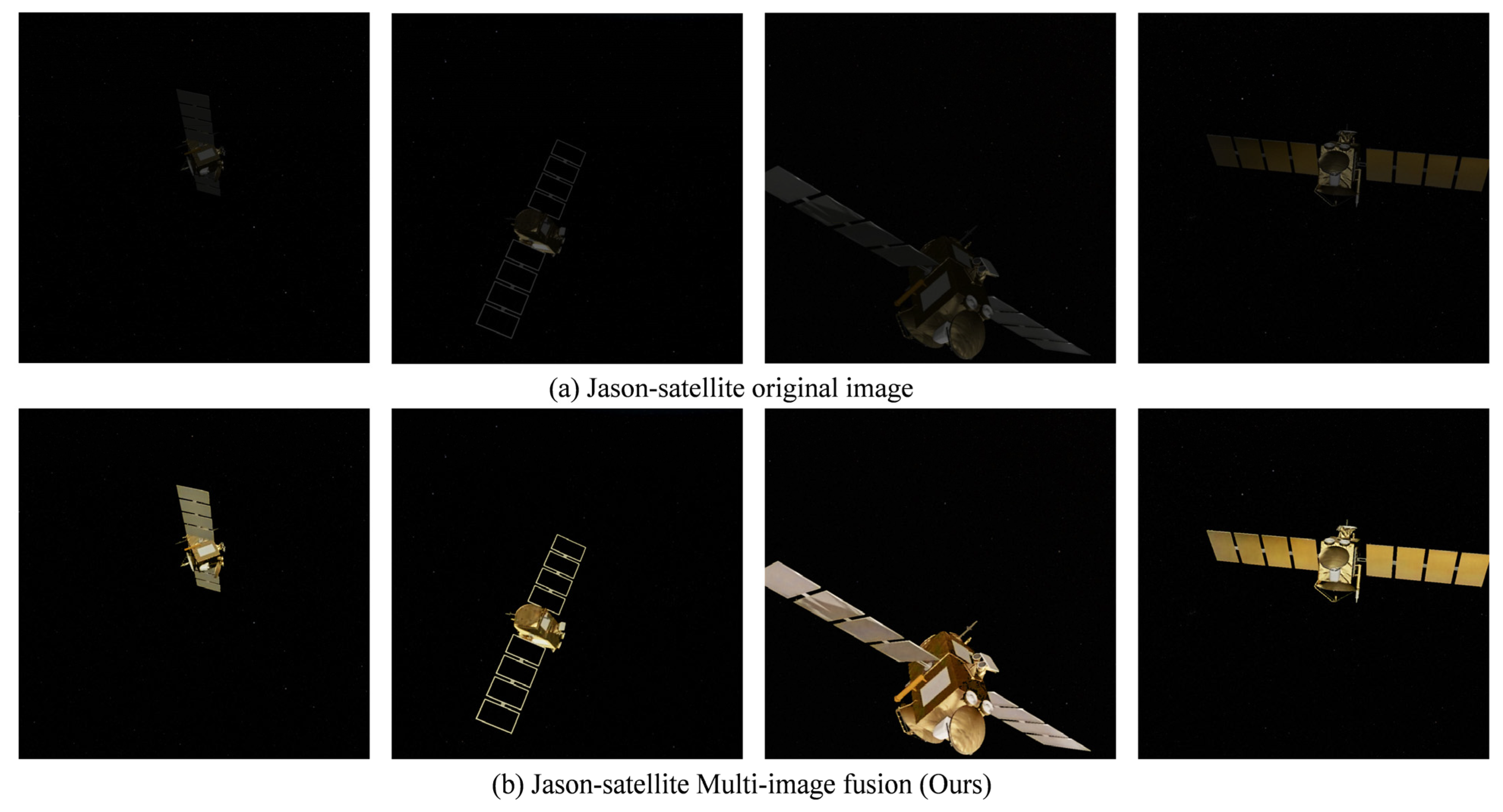
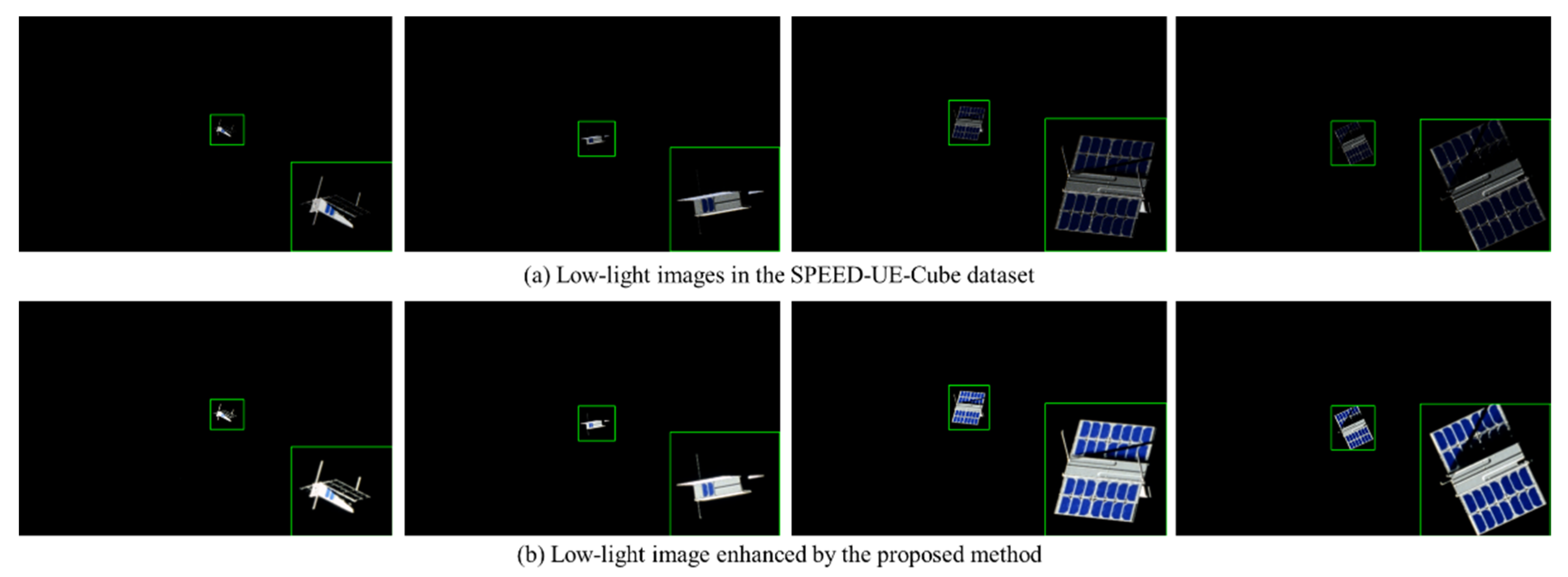
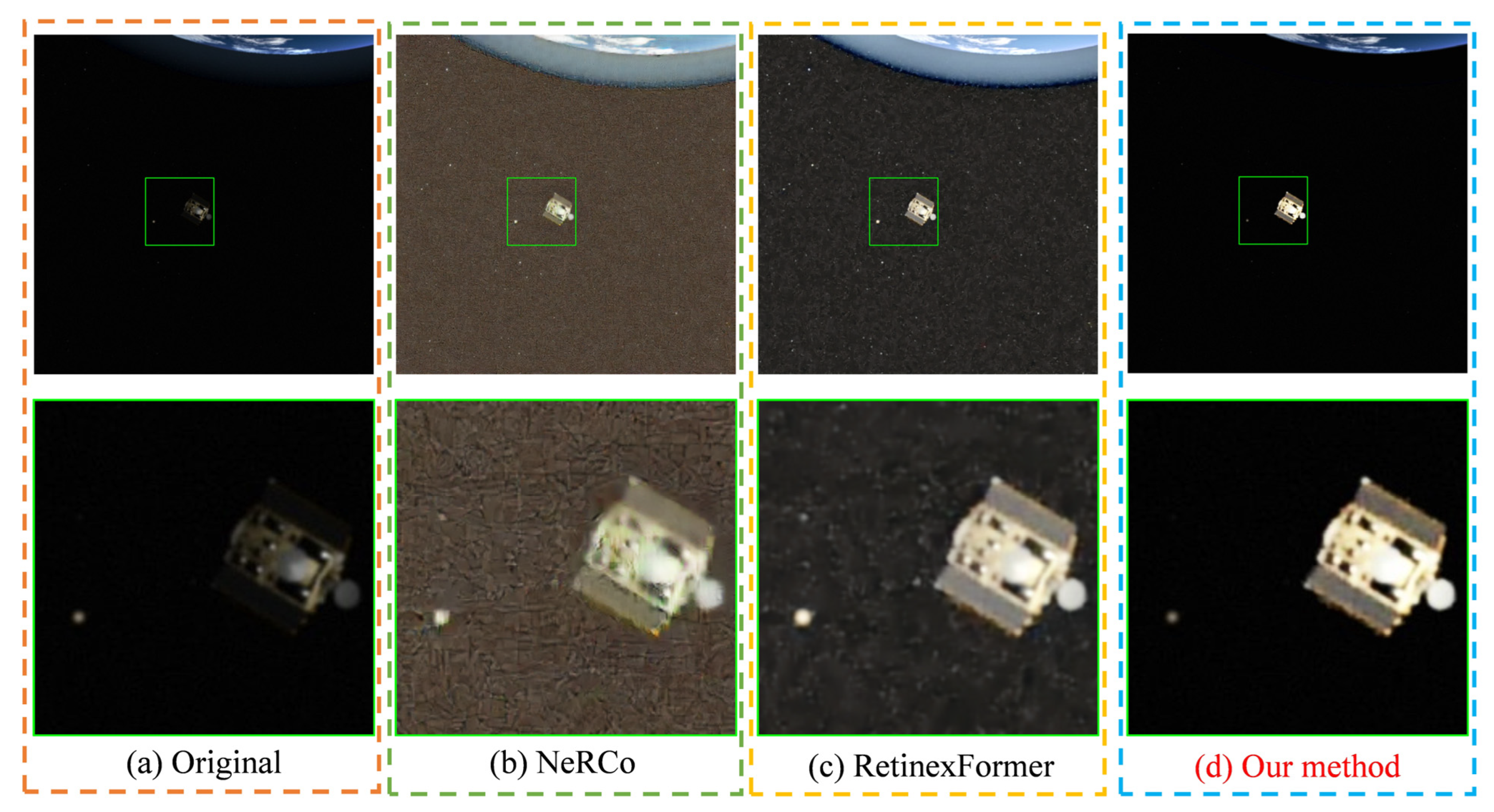
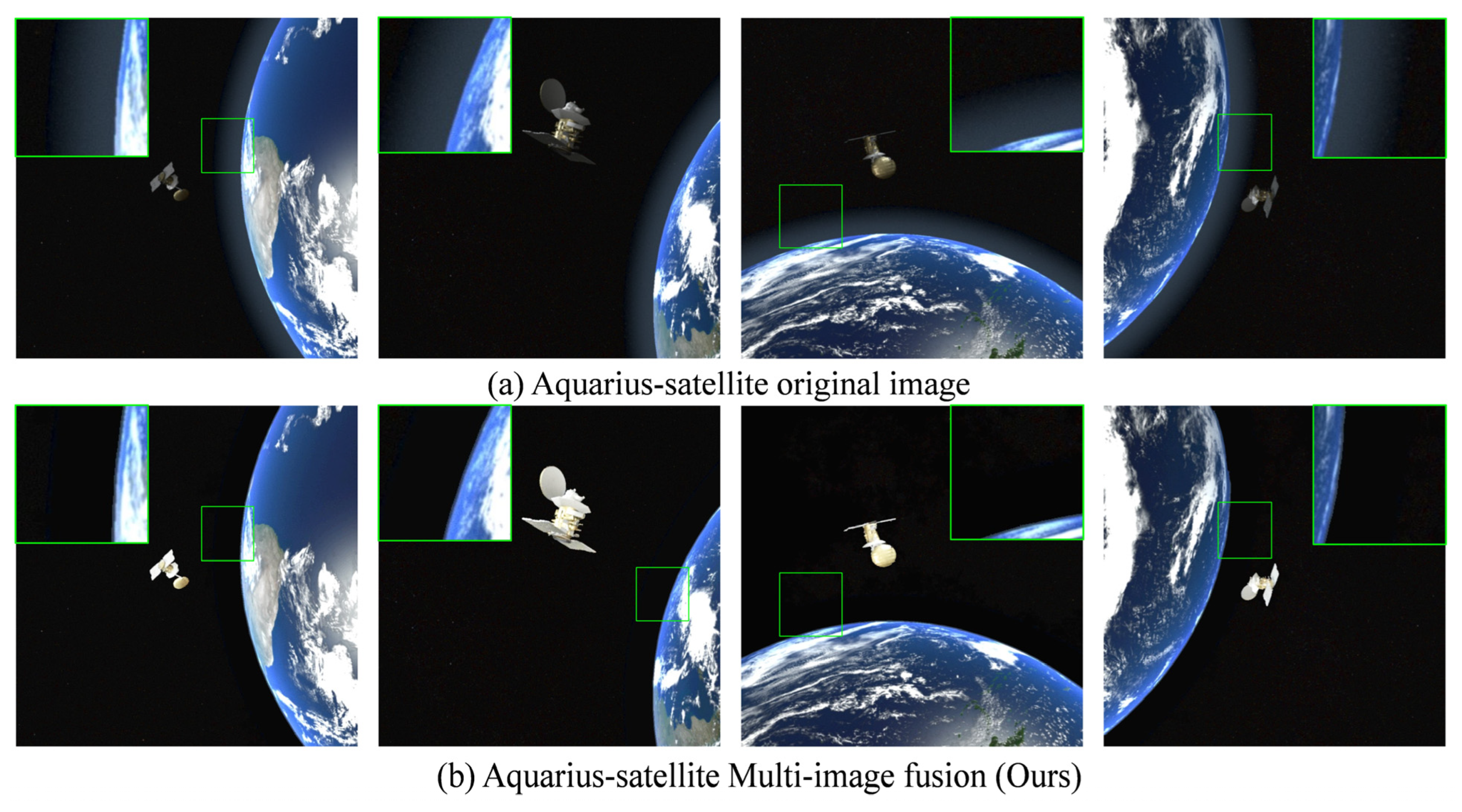
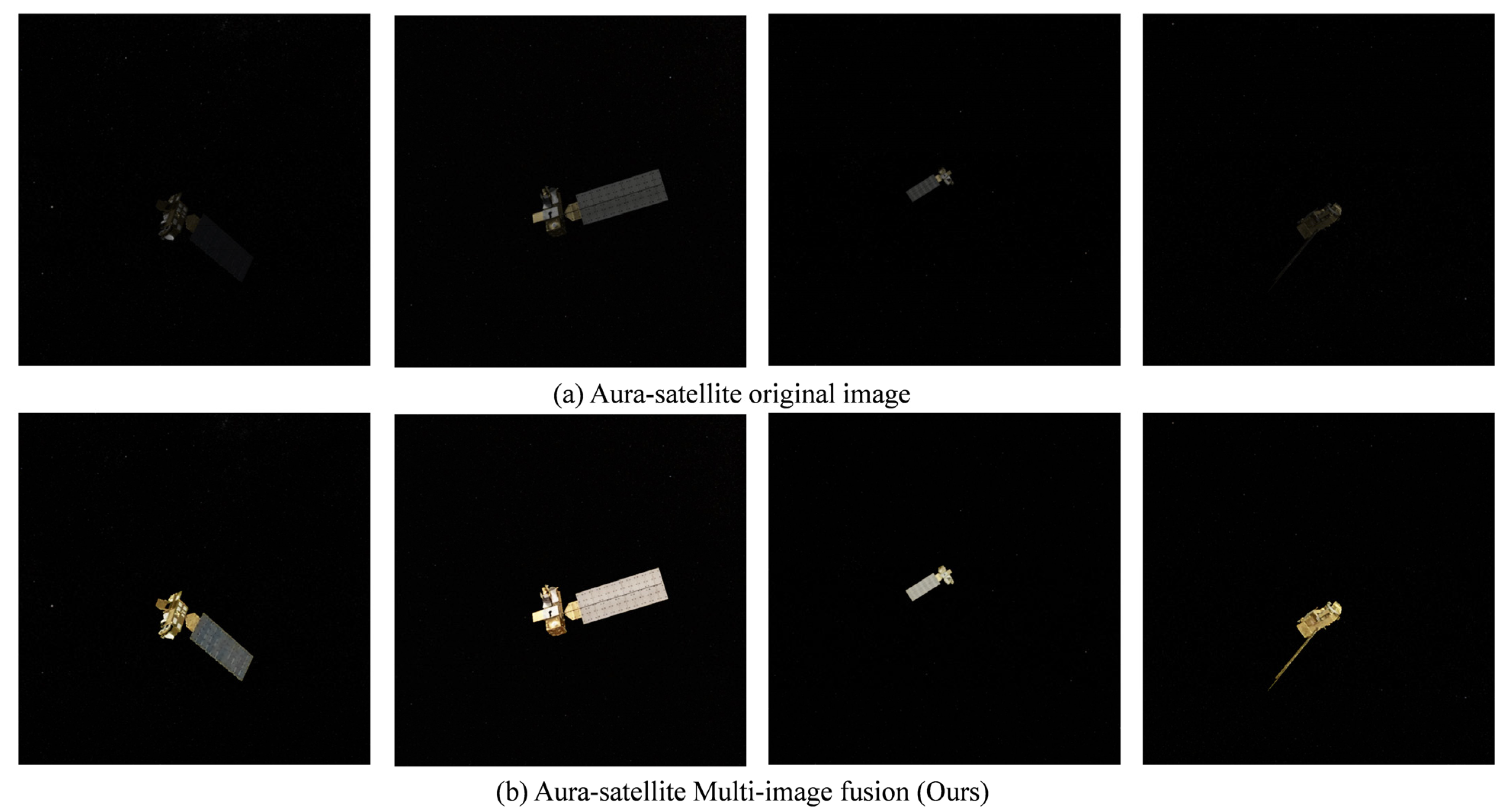
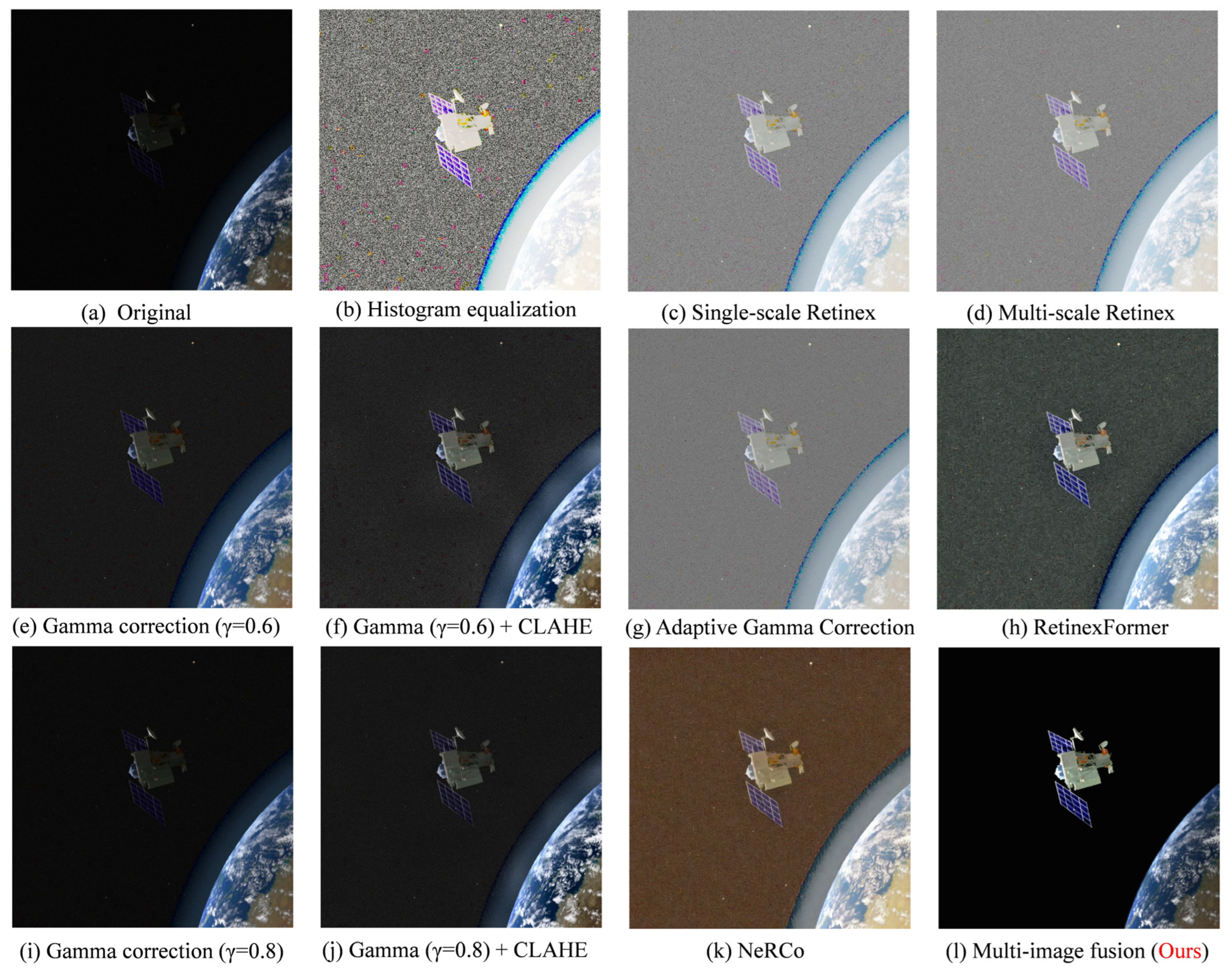
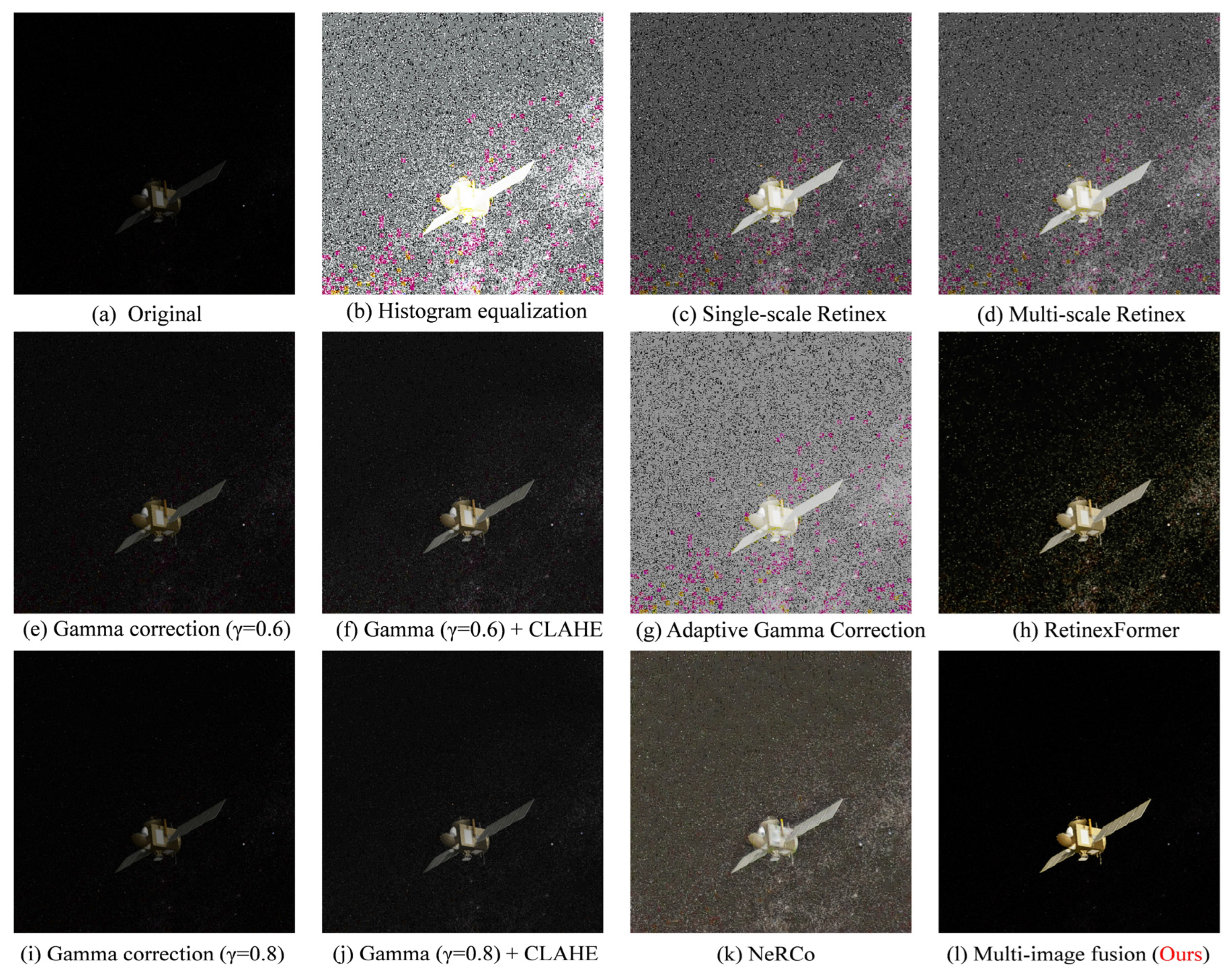
4.5. Visualization (Qualitative Comparison)
4.6. Quantitative Evaluation
4.7. Efficiency Analysis
4.7.1. Computational Complexity Analysis
4.7.2. Runtime Test
- CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8368 CPU @ 2.40 GHz;
- GPU: NVIDIA RTX 4090, 24 GB VRAM;
- Operating system: Ubuntu 20.04.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, B.-Z.; Cai, G.-P.; Liu, Y.-M.; Liu, P. Motion Prediction of a Non-Cooperative Space Target. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Niu, W.; Li, Y.; Ren, C.; Peng, X.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Z. Dim and Small Space-Target Detection and Centroid Positioning Based on Motion Feature Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Dong, J. TYCOS: A Specialized Dataset for Typical Components of Satellites. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musallam, M.A.; Gaudilliere, V.; Ghorbel, E.; Al Ismaeil, K.; Perez, M.D.; Poucet, M.; Aouada, D. Spacecraft Recognition Leveraging Knowledge of Space Environment: Simulator, Dataset, Competition Design and Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing Challenges (ICIPC), Anchorage, AK, USA, 19–22 September 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, P.-Y.; Sun, S.-L.; Lin, C.-Q.; Liu, G.-R. Space Moving Target Detection and Tracking Method in Complex Background. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 91, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.S. Dynamic Histogram Equalization for Contrast Enhancement for Digital Images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 89, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Kabir, M.H.; Dewan, M.A.A.; Chae, O. A Dynamic Histogram Equalization for Image Contrast Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T.; Tjahjadi, T. Contextual and Variational Contrast Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 3431–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Al-Quaderi, G.D.; Shoyaib, M. An Adaptive Gamma Correction for Image Enhancement. J. Image Video Proc. 2016, 2016, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jung, C.; Ke, P.; Song, H.; Hwang, J. Automatic Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization with Dual Gamma Correction. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 11782–11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Jobson, D.J.; Woodell, G.A. Retinex Processing for Automatic Image Enhancement. J. Electron. Imaging 2004, 13, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Parihar, A.S.; Singh, K. A Study on Retinex Based Method for Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC), Coimbatore, India, 19–20 January 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 619–624. [Google Scholar]
- Zotin, A. Fast Algorithm of Image Enhancement Based on Multi-Scale Retinex. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 131, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Bian, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Timofte, R.; Zhang, Y. Retinexformer: One-Stage Retinex-Based Transformer for Low-Light Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 12504–12513. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Ding, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Implicit Neural Representation for Cooperative Low-Light Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 12918–12927. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep Retinex Decomposition for Low-Light Enhancement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04560. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.-P.; Ding, X. A Weighted Variational Model for Simultaneous Reflectance and Illumination Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2782–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-Light Image Enhancement via Illumination Map Estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J. Beyond Brightening Low-Light Images. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1013–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Kindling the Darkness: A Practical Low-Light Image Enhancer. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 15–19 October 2019; ACM: Nice, France, 2019; pp. 1632–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Do, M.N.; Koltun, V. Seeing Motion in the Dark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3185–3194. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Yue, X. An Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm Based on Multilevel Threshold Image Segmentation Using the Otsu Method. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 113, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekehravani, E.A.; Babulak, E.; Masoodi, M. Implementing Canny Edge Detection Algorithm for Noisy Image. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2020, 9, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, K.A.M.; Jambek, A.B. Analysis of Image Processing Using Morphological Erosion and Dilation. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; Volume 2071, p. 012033. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Tan, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, C. Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Based on Joint Bilateral Filter and Local Gradient Energy. Inf. Sci. 2021, 569, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisantal, M.; Sharma, S.; Park, T.H.; Izzo, D.; Märtens, M.; D’Amico, S. Satellite Pose Estimation Challenge: Dataset, Competition Design, and Results. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 4083–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Märtens, M.; Lecuyer, G.; Izzo, D.; D’Amico, S. SPEED+: Next-Generation Dataset for Spacecraft Pose Estimation across Domain Gap. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO), Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.H.; D’Amico, S. Rapid Abstraction of Spacecraft 3D Structure from Single 2D Image. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2024 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2024; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Orlando, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, Z.; Park, T.H.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Razel-Rezai, R.; Graves, R.; Saarela, O.; Teramoto, R.; Vemulapalli, K.; D’Amico, S. SPEED-UE-Cube: A Machine Learning Dataset for Autonomous, Vision-Based Spacecraft Navigation. In Proceedings of the 46th Rocky Mountain AAS Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference, Breckenridge, CO, USA, 2–7 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.-C.; Cheng, F.-C.; Chiu, Y.-S. Efficient Contrast Enhancement Using Adaptive Gamma Correction with Weighting Distribution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 22, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, J.; Xuan, Z.; Yang, R.; Hao, Y.; Zou, F.; Lin, F.; Han, S. R2rnet: Low-Light Image Enhancement via Real-Low to Real-Normal Network. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2023, 90, 103712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]








| Dataset | SPEED | SPEED+ | SPE3R | SPEED-UE-Cube | SPARK 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scene | Synthetic | Synthetic and real | Synthetic | Synthetic | Synthetic |
| Illumination | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| BGD Noise 1 | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Bit Depth | 8 | 8 | 24 | 32 | 24 |
| Resolution | 1920 × 1200 | 1920 × 1200 | 256 × 256 | 1920 × 1200 | 1024 × 1024 |
| Categories | 4 | 4 | 64 | 1 | 11 |
| Application | Pose estimation | Pose estimation | Pose estimation and 3D Reconstruction | Pose estimation | Pose estimation |
| Parameters | Value | Basis for Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Exponential parameter p | 1.6 | Experimentally determined index parameters that balance contrast and detail retention. |
| Segment threshold m | 155 | Determined from the brightness characteristics of the target and background in satellite images. |
| OTSU grayscale limit range | [20, 50] | Experiments show that satellite image noise is mostly concentrated in the low gray area, and limiting the range can improve the threshold stability. |
| Percentage of regional expansion | 5% | Balancing target integrity protection with over-extension risk. |
| Density thresholds | 0.8 | Ensure that the selection area has a compact form to avoid loose noise interference. |
| Satellite Name | Metrics | SSR 1 | Gamma (γ = 0.6/0.8) 2 | Gamma + CLAHE (γ = 0.6/0.8) | NeRCo | Retineformer | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcrimSat | PSNR ↑ | 28.98 | 27.52 (31.17 3) | 27.59 (27.58) | 27.80 | 27.46 | 36.67 3 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.1041 | 0.5102 (0.8321) | 0.3272 (0.5176) | 0.2012 | 0.2097 | 0.8724 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.821 | 0.288 (0.096) | 0.488 (0.289) | 0.804 | 0.747 | 0.117 | |
| Aquarius | PSNR ↑ | 28.92 | 27.60 (31.38) | 27.59 (27.79) | 27.98 | 27.54 | 37.87 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.1078 | 0.5046 (0.8330) | 0.2904 (0.4844) | 0.2066 | 0.2225 | 0.9003 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.841 | 0.314 (0.104) | 0.535 (0.307) | 0.819 | 0.761 | 0.097 | |
| Aura | PSNR ↑ | 28.75 | 27.53 (31.89) | 27.52 (27.71) | 27.76 | 27.54 | 35.65 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0805 | 0.4871 (0.8292) | 0.2580 (0.4482) | 0.1132 | 0.2006 | 0.7946 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.834 | 0.317 (0.111) | 0.532 (0.315) | 0.829 | 0.748 | 0.245 | |
| Calipso | PSNR ↑ | 28.88 | 27.60 (32.33) | 27.57 (27.72) | 27.97 | 27.67 | 36.95 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0705 | 0.4635 (0.8177) | 0.2600 (0.4438) | 0.1672 | 0.2050 | 0.8107 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.869 | 0.339 (0.119) | 0.541 (0.321) | 0.837 | 0.770 | 0.233 | |
| CloudSat | PSNR ↑ | 31.62 | 31.44 (35.13) | 30.08 (30.58) | 27.77 | 31.87 | 38.05 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.2077 | 0.5870 (0.8970) | 0.2873 (0.3783) | 0.1086 | 0.5463 | 0.9021 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.665 | 0.241 (0.073) | 0.327 (0.217) | 0.676 | 0.357 | 0.040 | |
| CubeSat | PSNR ↑ | 28.82 | 27.59 (31.81) | 27.61 (27.66) | 27.89 | 27.54 | 35.61 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0734 | 0.4810 (0.8214) | 0.2835 (0.4611) | 0.1899 | 0.2235 | 0.7820 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.860 | 0.324 (0.112) | 0.529 (0.318) | 0.836 | 0.758 | 0.233 | |
| Jason | PSNR ↑ | 28.43 | 27.61 (32.68) | 27.50 (27.60) | 27.91 | 27.82 | 37.34 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0724 | 0.4495 (0.8154) | 0.2494 (0.4123) | 0.1415 | 0.2081 | 0.8863 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.850 | 0.334 (0.125) | 0.513 (0.321) | 0.809 | 0.691 | 0.126 | |
| Sentinel-6 | PSNR ↑ | 28.76 | 27.58 (32.52) | 27.55 (27.69) | 27.84 | 27.85 | 36.87 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0710 | 0.4559 (0.8142) | 0.2556 (0.4323) | 0.1578 | 0.2155 | 0.8235 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.886 | 0.350 (0.124) | 0.549 (0.336) | 0.863 | 0.757 | 0.229 | |
| Terra | PSNR ↑ | 28.92 | 27.52 (31.79) | 27.53 (27.70) | 27.87 | 27.57 | 36.70 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0917 | 0.4860 (0.8276) | 0.2676 (0.4504) | 0.1827 | 0.2063 | 0.8866 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.854 | 0.322 (0.115) | 0.537 (0.323) | 0.845 | 0.754 | 0.100 | |
| TRMM | PSNR ↑ | 28.92 | 27.49 (32.17) | 27.55 (27.70) | 27.91 | 27.57 | 37.42 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0862 | 0.4675 (0.8186) | 0.2637 (0.4454) | 0.1667 | 0.1998 | 0.8727 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.877 | 0.338 (0.121) | 0.542 (0.325) | 0.852 | 0.778 | 0.160 |
| Satellite Name | Metrics | SSR | Gamma (γ = 0.6/0.8) | Gamma + CLAHE (γ = 0.6/0.8) | NeRCo | Retineformer | Ours 1 | Ours_BGD 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcrimSat | PSNR ↑ | 28.81 | 27.57 (37.45) | 30.14 (28.04) | 27.55 | 28.98 | 39.67 3 | 52.46 3 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0242 | 0.3202 (0.7539) | 0.2103 (0.3406) | 0.0225 | 0.2126 | 0.5550 | 0.9934 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.880 | 0.370 (0.133) | 0.450 (0.343) | 0.887 | 0.590 | 0.255 | 0.012 | |
| Aquarius | PSNR ↑ | 29.07 | 30.13 (40.85) | 26.69 (28.94) | 27.59 | 37.42 | 44.11 | 52.44 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0236 | 0.2954 (0.7809) | 0.1380 (0.2445) | 0.0139 | 0.6357 | 0.8165 | 0.9952 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.970 | 0.545 (0.195) | 0.645 (0.467) | 0.940 | 0.409 | 0.173 | 0.010 | |
| Aura | PSNR ↑ | 29.24 | 30.18 (40.28) | 27.10 (29.07) | 27.57 | 35.59 | 42.84 | 51.01 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0116 | 0.2868 (0.7846) | 0.1305 (0.2415) | 0.0129 | 0.5581 | 0.7982 | 0.9927 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.916 | 0.469 (0.167) | 0.567 (0.400) | 0.875 | 0.471 | 0.270 | 0.013 | |
| Calipso | PSNR ↑ | 30.12 | 31.21 (42.05) | 27.11 (29.75) | 27.50 | 39.13 | 45.58 | 55.71 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0650 | 0.3475 (0.8099) | 0.1392 (0.2411) | 0.0096 | 0.7099 | 0.8628 | 0.9960 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.971 | 0.573 (0.190) | 0.673 (0.478) | 0.965 | 0.399 | 0.169 | 0.009 | |
| CloudSat | PSNR ↑ | 33.22 | 33.87 (41.84) | 31.04 (31.86) | 27.55 | 35.46 | 42.92 | 53.88 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.1633 | 0.5142 (0.8807) | 0.1697 (0.2572) | 0.0076 | 0.5945 | 0.8462 | 0.9522 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.698 | 0.272 (0.082) | 0.335 (0.222) | 0.816 | 0.337 | 0.480 | 0.006 | |
| CubeSat | PSNR ↑ | 30.32 | 31.28 (42.23) | 27.03 (29.83) | 27.55 | 39.00 | 45.94 | 58.73 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0711 | 0.3525 (0.8099) | 0.1414 (0.2418) | 0.0085 | 0.7036 | 0.8651 | 0.9986 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.962 | 0.553 (0.182) | 0.649 (0.461) | 0.971 | 0.407 | 0.169 | 0.005 | |
| Jason | PSNR ↑ | 30.19 | 30.63 (40.94) | 27.14 (29.46) | 27.49 | 36.72 | 43.80 | 53.83 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0169 | 0.2994 (0.7962) | 0.1288 (0.2386) | 0.0102 | 0.6144 | 0.8270 | 0.9946 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.919 | 0.486 (0.170) | 0.584 (0.409) | 0.891 | 0.458 | 0.264 | 0.011 | |
| Sentinel-6 | PSNR ↑ | 29.88 | 31.03 (41.78) | 27.07 (29.60) | 27.56 | 39.18 | 45.14 | 53.39 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0710 | 0.3500 (0.8058) | 0.1446 (0.2464) | 0.0138 | 0.7073 | 0.8477 | 0.9929 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.984 | 0.587 (0.192) | 0.686 (0.494) | 0.977 | 0.363 | 0.139 | 0.012 | |
| Terra | PSNR ↑ | 29.95 | 30.92 (41.33) | 27.31 (29.62) | 27.52 | 37.42 | 44.19 | 53.80 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0423 | 0.3253 (0.8039) | 0.1343 (0.2407) | 0.0113 | 0.6425 | 0.8363 | 0.9940 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.933 | 0.512 (0.174) | 0.610 (0.430) | 0.912 | 0.434 | 0.231 | 0.010 | |
| TRMM | PSNR ↑ | 29.80 | 30.47 (40.88) | 26.73 (29.24) | 27.56 | 38.19 | 44.02 | 50.79 |
| SSIM ↑ | 0.0444 | 0.3222 (0.7922) | 0.1443 (0.2492) | 0.0149 | 0.6686 | 0.8233 | 0.9909 | |
| LPIPS ↓ | 0.986 | 0.573 (0.195) | 0.670 (0.486) | 0.966 | 0.380 | 0.149 | 0.016 |
| Resolution | Metric | AcrimSat | Aquarius | Aura | Calipso | CloudSat | CubeSat | Jason | Sentinel-6 | Terra | TRMM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 256 × 256 | Time (ms) | 71.65 | 61.92 | 73.77 | 69.14 | 67.89 | 71.84 | 69.50 | 57.45 | 68.28 | 67.99 |
| Frame rate (FPS) | 13.96 | 16.15 | 13.55 | 14.46 | 14.73 | 13.92 | 14.39 | 17.41 | 14.65 | 14.71 | |
| 512 × 512 | Time (ms) | 87.12 | 94.85 | 95.53 | 92.51 | 86.31 | 92.01 | 89.06 | 86.07 | 82.51 | 93.83 |
| Frame rate (FPS) | 11.48 | 10.54 | 10.47 | 10.81 | 11.59 | 10.87 | 11.23 | 11.62 | 12.12 | 10.66 | |
| 1024 × 1024 | Time (ms) | 188.25 | 189.84 | 184.89 | 183.39 | 184.22 | 195.37 | 194.13 | 185.04 | 178.80 | 192.84 |
| Frame rate (FPS) | 5.31 | 5.27 | 5.41 | 5.45 | 5.43 | 5.12 | 5.15 | 5.40 | 5.59 | 5.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, F.; Kang, C. Deep-Space Background Low-Light Image Enhancement Method Based on Multi-Image Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094837
Han F, Liu Q, Wang H, Ren Z, Zhou F, Kang C. Deep-Space Background Low-Light Image Enhancement Method Based on Multi-Image Fusion. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094837
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Feixiang, Qing Liu, Huawei Wang, Zeyue Ren, Feng Zhou, and Chanchan Kang. 2025. "Deep-Space Background Low-Light Image Enhancement Method Based on Multi-Image Fusion" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094837
APA StyleHan, F., Liu, Q., Wang, H., Ren, Z., Zhou, F., & Kang, C. (2025). Deep-Space Background Low-Light Image Enhancement Method Based on Multi-Image Fusion. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094837






