Abstract
Geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol, molecules with the same odor characteristics, are mainly responsible for the smell of soil and cause odor problems worldwide in drinking water supplies. However, the effect of these odor molecules on human brain function is still unclear. The present investigation aimed to evaluate the effect of inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol on human electroencephalographic (EEG) activity in order to understand whether their action on brain wave activity is the same or different. A total of 20 healthy volunteers (10 women and 10 men) were selected to determine the EEG power spectrum changes. The EEG data were recorded from 32 channels according to the International 10–20 system and 25 EEG power spectrum indices were analyzed. The inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol exhibited different EEG activity by producing changes in different EEG indicators as well as brain regions. In both genders, significant changes in EEG power spectra were observed during the inhalation of geosmin when compared with 2-methylisoborneol. Absolute waves such as beta, fast alpha, low beta, high beta, and gamma significantly decreased, particularly in the centro-parietal (Cp6) region, due to the exposure to geosmin. According to gender variation, geosmin produced significant changes in the absolute low beta and high beta waves at the Cp6 region in women. In the case of 2-methylisoborneol, a significant increase in absolute alpha and absolute fast alpha activity was observed at the F8 region in men. However, there were no significant changes in absolute waves for men and women during the inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol. Although both components are responsible for soil smell, they exhibit significantly different EEG activity according to gender.
1. Introduction
The soil smell is mainly characterized by two odor molecules, geosmin (C12H22O, trans-1,10-dimethyl-trans-9 decalol) and 2-methylisoborneol (C11H20O, 1,2,7,7-tetramethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol). These odor molecules possess earthy and musty smell characteristics and are mainly found in soil [1]. In addition, they have been found in drinking water and various fruits and vegetables, even after various industrial processing treatments [2]. Geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol are microbial metabolites produced by actinobacteria, cyanobacteria, proteobacteria, and some fungi. Actinobacteria are the main producers of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in the soil, whereas cyanobacteria are the major producers of these odor molecules in aquatic environments [3,4,5].
Geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol are not a public health concern, but the presence of unpleasant tastes and odors in drinking water and food products is an important global problem. Furthermore, very low threshold concentrations of these molecules and their persistence despite common water purification processes are major problems. The odor threshold concentrations for geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol can range from 4 to 20 ng/L [6]. Humans can smell these odor molecules at very low concentrations (<10 parts per trillion) in water [7]. Many people like the odor of soil mixed with rain because it brings a lot of nostalgic memories. The smell of water can affect the psychophysiological conditions of human beings. Haese et al. [8] reviewed the tastes and odor of water based on sensory profiles, chemical measurements, and electrophysiological responses. In general, odors play an important role in emotions and the memory process. Furthermore, Zucco et al. [9] stated that even unnoticed odors may affect mental states. The influence of odor molecules on the autonomic nervous system is mainly through direct connections between odors and olfactory receptors, and their effect on brain states is via the subjective effects of odor perception [10].
A number of studies are being conducted to evaluate the olfactory stimulation effects on humans in order to understand whether odors can produce functional changes such as relaxation and excitation states in the brain [11]. The effect of odors on brain state can be measured by electroencephalography (EEG) through changes in brain wave activity. EEG is the most effective method for noninvasively investigating electrophysiological changes in the brain and is capable of exhibiting the central nervous system’s responses over time. Previously, several authors have used the EEG technique to determine brain wave changes during the inhalation of odor molecules [12,13,14]. It was also reported that EEG activity significantly changed in subjects who did not perceive the presence of odor molecules when compared with odor controls [15]. In addition, gender plays a major role in the detection, perception, and their cognitive implications of olfactory process with respect to different odors. In a similar way, various odorants produced different EEG activity according to gender. Previous studies have suggested that even isomers of odor molecules (carvone, linalool, and limonene) possess different odor qualities and intensities for humans [11,16,17].
To date, there has been no study in relation to the inhalation of gesomin and 2-methylisoborneol odors on human EEG activity. Based on the above knowledge, the present study was carried out to investigate the effect of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol on human EEG activity in order to understand whether odor molecules with the same type of odor characteristics exhibit the same EEG activity or different.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
Geosmin (CAS No. 16423-19-1) and 2-methylisoborneol (CAS No. 2371-42-8) were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). The purchased chemicals were stored at 4 °C until use in the EEG study.
2.2. Subjects
The present study followed the Declaration of Helsinki on Biomedical Research Involving Human Subjects. The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee from the Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, South Korea. Twenty healthy subjects (10 men and 10 women) aged 20–30 years participated in this study. Individuals with olfactory diseases, mental or physical illness, and those taking medication or abusing drugs were not included in the study. Informed consent was obtained from all the subjects before participation.
2.3. Experimental Design
A single group pretest and posttest experimental design was used in the study (20 subjects). The subjects were told that the purpose of the study was to evaluate the effect of inhalation of odor molecules on EEG activity. During the EEG recordings, the subjects were instructed to sit quietly, keep their eyes closed, and breathe normally but remain awake. After the EEG recordings, the subjects were asked to give their preference and impression of the odors of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol.
2.4. EEG Recordings
A QEEG-64FX system was used to record the EEG readings (LAXTHA Inc., Daejeon, Korea). The EEG recordings were made using an electrode cap from 32 channels placed at the Fp1, Fp2, F3, F4, C3, C4, P3, P4, O1, O2, F7, F8, T7, T8, P7, P8, Afz, Cz, Fz, Pz, Fpz, Oz, Af3, Af4, Fc1, Fc2, Fc5, Fc6, Cp1, Cp2, Cp5, and Cp6 regions according to the International 10–20 System (Figure 1). The electrodes were referenced to the ipsilateral earlobe electrodes. The EEG sampling rate of the measured subjects was 250 Hz, filtered in the range of 2.5–50 Hz, and the readings were stored in a computer by 24-bit analog-to-digital conversion. The electrodes (silver/silver chloride) were applied over an elastic cap with plastic electrode holders. The ECI electrode gel (Electro-gel™, Electro-Cap International Inc., Eaton, OH, USA) was applied to each electrode to connect with the surface of the scalp in order to drop the electric resistance of the scalp below 5 kΩ.
Figure 1.
The electrode placement sites according to the International 10–20 system, with modified combinatorial nomenclature.
2.5. Fragrance Administration
Geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol (10% w/v) were dissolved in dipropylene glycol and used as fragrance stimuli. The EEG recording room was maintained with a constant temperature (24 °C) and humidity (50%). The undiluted geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol (10 μL) was added on the perfumer’s paper strip and then placed about 3 cm in front of the subject’s nose. The EEG was recorded 45 s before and 45 s during the exposure of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol. The baseline EEG readings were recorded at eye-closed state for each condition. First, the EEG was recorded before and during the exposure of geosmin. After resting for 3 min, the EEG was again recorded before and during the exposure of 2-methylisoborneol.
2.6. Data Analysis
The mean power spectrum values [microvolt square (μV2)] were calculated for 25 EEG indices including absolute, relative and ratio values of theta, alpha, beta and gamma waves [17]. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS statistical package 23 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The EEG power spectra before and during the inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol were analyzed by a paired Student’s t-test, with the p value < 0.05 being considered significant. T-mapping of EEG power spectra changes was constructed by Telescan software package (LAXTHA Inc., Daejeon, Korea).
3. Results
In the present study, the earthy odor molecules geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol were used to stimulate the olfactory system via inhalation in order to understand their effect on brain wave activity. The changes of 25 EEG power spectrum values were analyzed from 32 electrode sites located at the prefrontal, frontal, central, temporal, parietal, and occipital regions according to the International 10–20 System. In the results, we presented only significant changes in absolute and ratio values before and during the inhalation of both compounds with the exclusion of relative values (Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3). Figure 2 and Figure 3 illustrate the t-mapping of significant changes of absolute power spectrum values. The results revealed that geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol showed significantly (p < 0.05) different EEG activity in women and men.

Table 1.
Significant changes of EEG power spectra during the inhalation of geosmin in both genders.

Table 2.
Significant changes of EEG power spectra during the inhalation of geosmin in women.

Table 3.
Significant changes of EEG power spectra during the inhalation of 2-methylisoborneol in both genders.
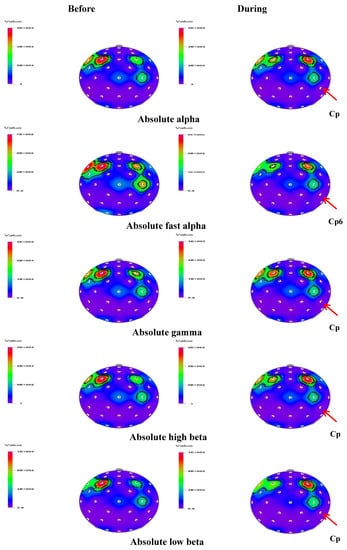
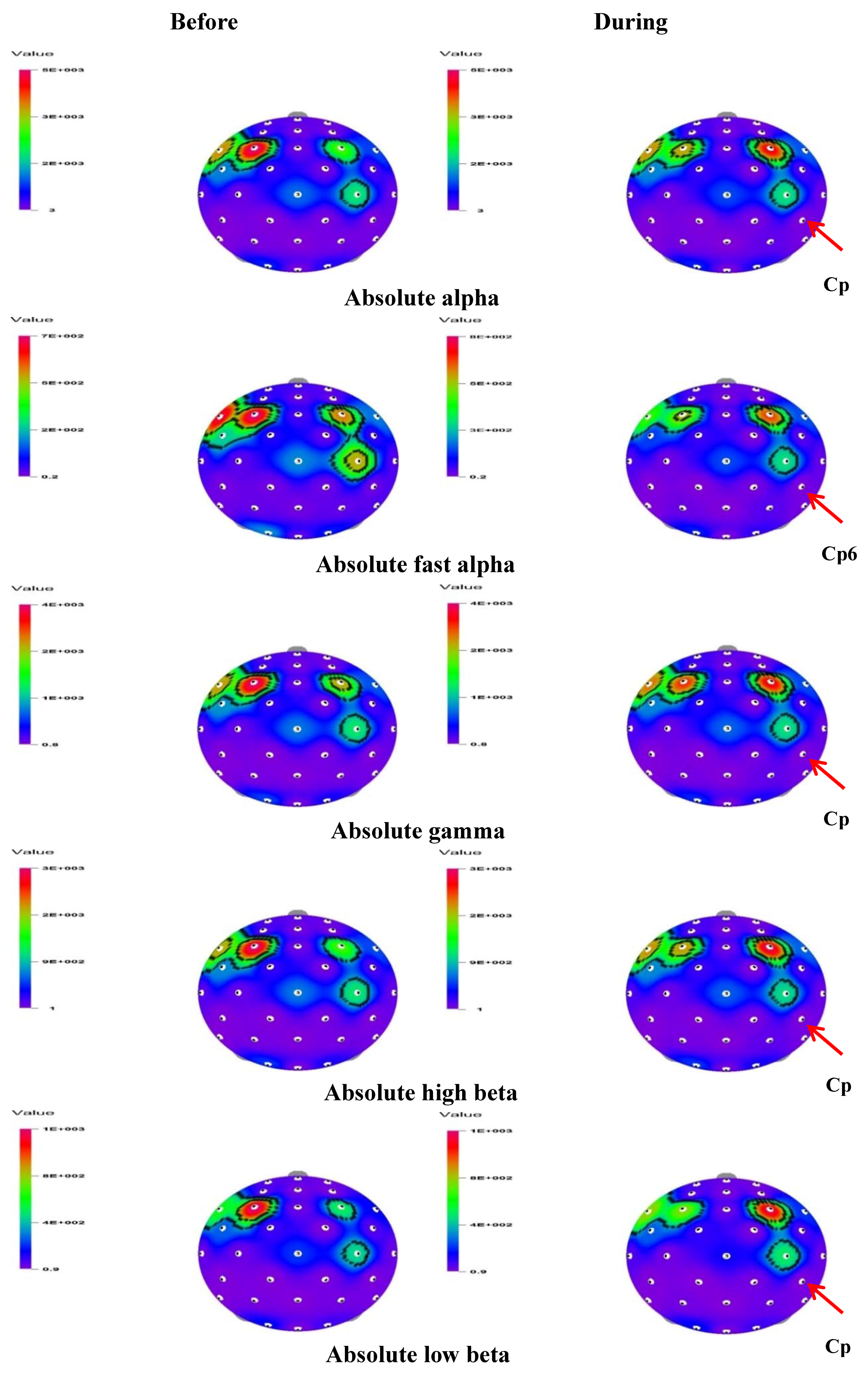
Figure 2.
The t-mapping of EEG changes (absolute waves) before and during the inhalation of geosmin in both genders. Arrows show the significant changes in the region during the inhalation of geosmin.
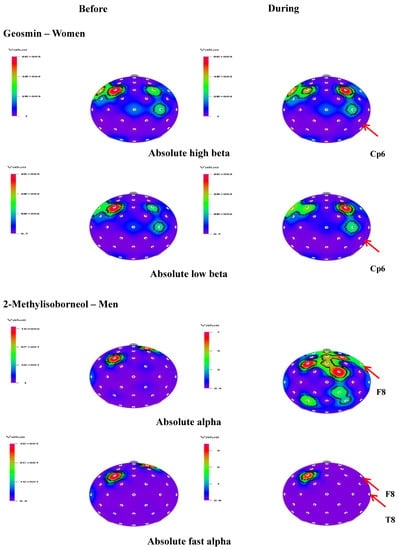
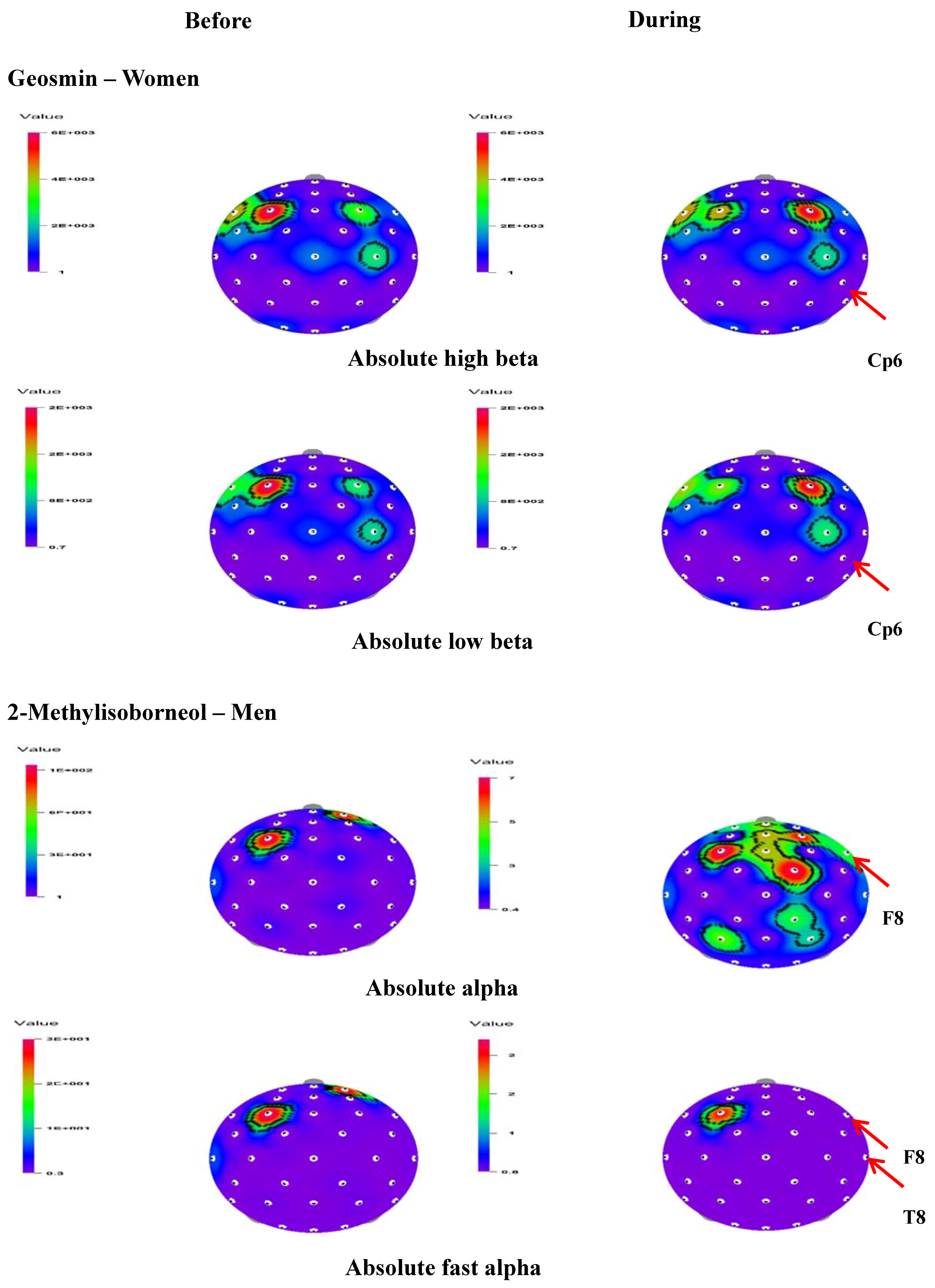
Figure 3.
t-Mapping of EEG changes (absolute waves) before and during the inhalation of geosmin in women and 2-methylisoborneol in women. Arrows show the significant changes in the regions during the inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol.
In both genders, significant changes were observed in 16 and three indices during the inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol, respectively. Table 1 shows significant changes of EEG power spectrum values before and during the inhalation of geosmin in both genders. A significant decrease (p < 0.05) of absolute waves such as fast alpha (4.1374–1.6438 µV2), beta (14.7287–10.4411 µV2), high beta (7.6548–5.3986 µV2), low beta (3.2775–2.1519 µV2), and gamma (9.4893–7.2170 µV2) was observed in both genders, specifically at the centroparietal (Cp6) region during the inhalation of geosmin (Figure 2). Furthermore, relative values of alpha, beta, fast alpha, slow alpha, low beta, and mid beta significantly decreased during the inhalation of geosmin compared to those before inhalation. In addition, the ratio of sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) to theta (RST), the ratio of mid beta to theta (RMT), and the ratio of SMR mid beta to theta (RSMT) significantly decreased during the inhalation of geosmin. Furthermore, spectral edge frequency 50% (SEF50) significantly decreased at the T8 region (12.3871–10.1593 µV2) and relative theta significantly increased at the Af4 region. In the case of 2-methylisoborneol, there was no significant change in absolute wave activity. However, RST (Af4 and Cp5), RMT (Cp5) and RSMT (Cp5 and AF4) significantly decreased during the inhalation of 2-methylisoborneol (Table 3).
In the present study, the effect of inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol on EEG activity according to gender variation was also analyzed. In men, there was no significant change in absolute and relative values during the exposure of geosmin. On the other hand, a significant increase of absolute alpha (3.5391–4.6670 µV2 at F8) and fast alpha (0.4061–0.7929 µV2 at F8 and 0.3116–0.6550 µV2 at T8) activity was observed during the inhalation of 2-mehtylisoborneol (Table 3). The t-mapping of brain wave changes clearly expressed the modification of EEG waves due to the exposure of 2-methylisoborneol in men (Figure 3). In addition to absolute waves, relative alpha, relative slow alpha, and RAHB (3.7485–5.4337 µV2 at Fc6) significantly increased in men during the inhalation of 2-mehtylisoborneol.
In the case of women, significant changes were observed in 18 indices during the inhalation of geosmin and 10 indices during the inhalation of 2-methylisoborneol. The absolute waves, high beta (14.0263–10.5390 µV2), and low beta (5.6537–3.9980 µV2) significantly decreased at the Cp6 region during the inhalation of geosmin (Table 2; Figure 3). The relative values of alpha, beta, gamma, fast alpha, slow alpha, low beta, mid beta, and high beta significantly decreased during the inhalation of geosmin. Additionally, a significant decrease of RST, RMT, RSMT, SEF50, SEF90, and ASEF was observed in women (Table 2). With regards to SEF50 and SEF50 activity, significant changes were observed in 10 and eight regions, respectively. On the other hand, 2-methylisoborneol exhibited changes only in the relative and other ratio values such as alpha, slow alpha, low beta, mid beta, high beta, RST, RMT, RSMT, and SEF90 (Table 3). Among them, RMT values significantly changed in eight regions (O2, F8, Cz, Pz, Af4, Fc2, Cp5, and Cp6). In addition, 2-methylisoborneol odor mainly exhibited changes at Cp5 region for the ratio spectrum values than other regions. Figure 4 illustrates the schematic representation of significant changes of EEG indices during the inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol.
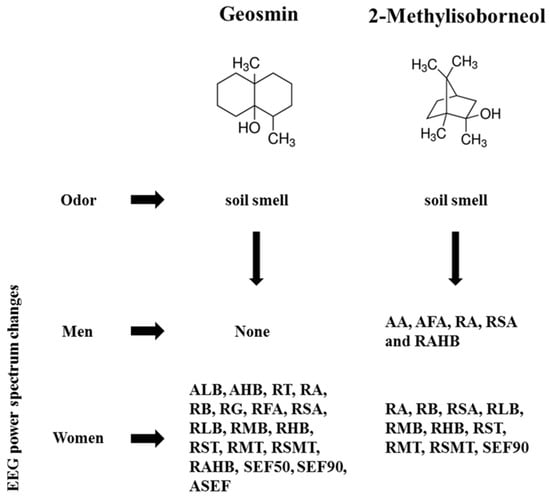
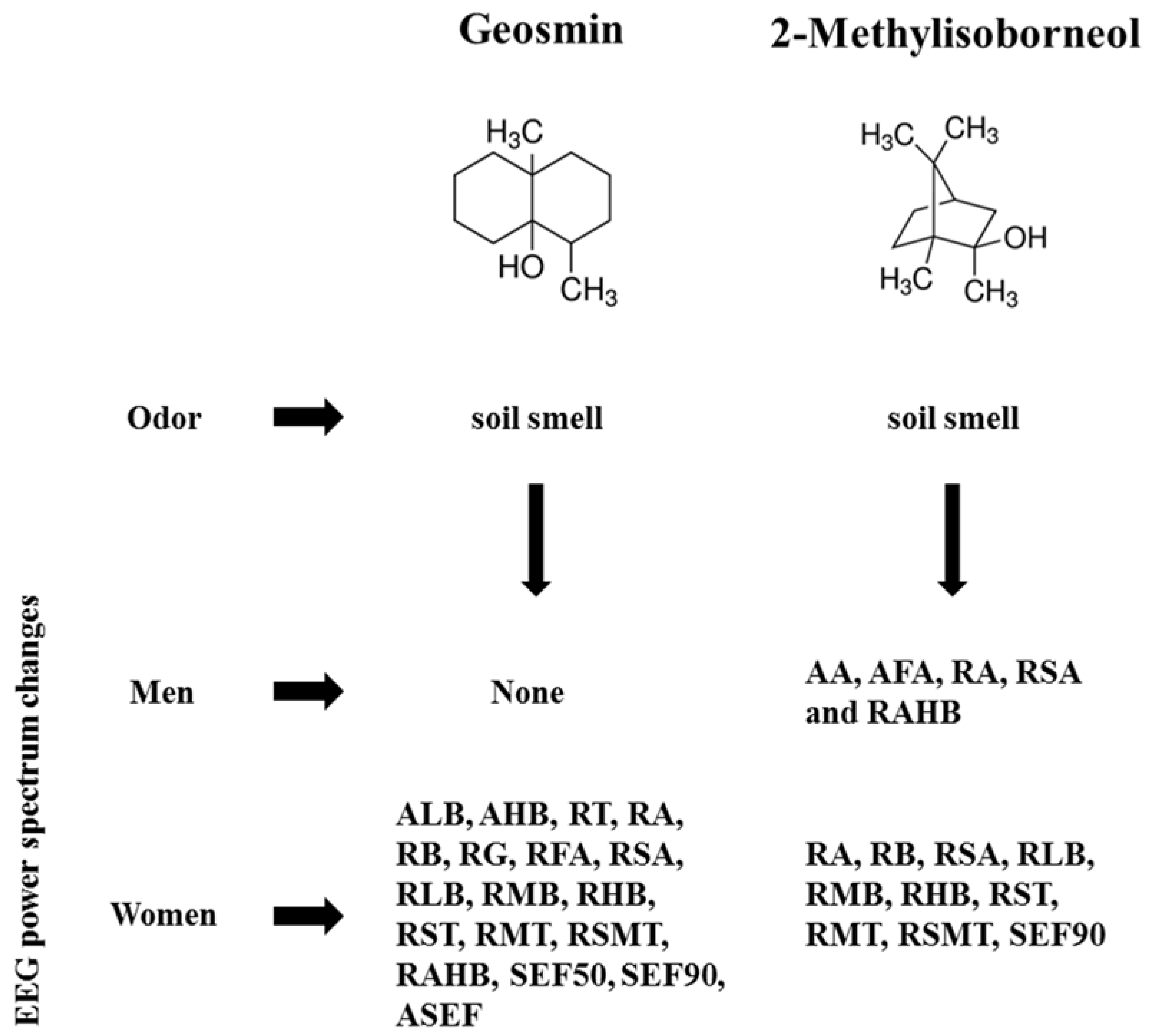
Figure 4.
A schematic representation of inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol on human EEG activity. AA, absolute alpha; AFA, absolute fast alpha; AHB, absolute high beta; ALB, absolute low beta; RT, relative theta; RA, relative alpha; RB, relative beta; RG, relative gamma; RFA, relative fast alpha; RSA, relative slow alpha; RLB, relative low beta; RMB, relative mid beta; RHB, relative high beta; RST, ratio of SMR to theta; RMT, ratio of mid beta to theta; RSMT, ratio of SMR mid beta to theta; RAHB, ratio of alpha to high beta; SEF50, spectral edge frequency 50%; SEF90, spectral edge frequency 90%; ASEF, spectral edge frequency 50% of alpha.
4. Discussion
The characteristic earthy smell of soil is mainly produced from microbial metabolites, geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol. These odor molecules also play an essential role in the taste and odor of the drinking water obtained from surface water [4]. The taste and odor are highly linked with the suitability and safety of drinking water. In addition, humans can easily detect these molecules at very low concentrations due to extremely low levels of odor threshold. According to the odor type (pleasant or unpleasant), the odor molecules significantly affect brain function through the olfactory system. Furthermore, it was reported that odor molecules influenced stress biomarkers, oxidative stress and dopamine in humans. In a positive approach, odor molecules have been used for decreasing mental stress and enhancing relaxation as well as cognitive function [8,18]. In this context, the present study examined the effect of inhalation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol on the human EEG activity in relation to brain functions. In the EEG study, delta (0–4 Hz), theta (4–8 Hz), alpha (8–13 Hz), beta (13–30 Hz), and gamma (30–50 Hz) are the most important brain waves used to understand the role of odors in the psychological and physiological conditions of humans.
In the current study, absolute fast alpha, absolute beta, absolute low beta, absolute high beta, and absolute gamma activity significantly decreased, particularly at the Cp6 region, during the inhalation of geosmin in both genders (Table 2 and Figure 2). In general, increase in alpha wave activity is mainly associated with relaxation and calmness states in the brain. Hence, a decrease in alpha wave activity is highly linked with stress state [13,19,20]. However, absolute waves such as beta, low beta, and high beta significantly decreased at the same region (Cp6) during the inhalation of geosmin. Beta waves play a major role in the enhancement of cognitive performances in humans. An increase in beta activity is associated with alertness and concentration states of brain [21]. In the posterior regions, increase in beta wave activity is highly related to the enhancement of reading speed, reorganization of language, and rhythm-learning task [22,23,24]. Sayowan et al. [25] reported that the beta wave significantly increased at the anterior center and left posterior regions due to the exposure of jasmine oil, and these changes may produce positive psychophysiological effects in humans by enhancing active and fresh feelings. In a recent study, Angelica gigas root essential oil induced significant changes in the absolute low beta activity at the left parietal region [26]. Collectively, beta waves occur when the brain is alert. In the present study, the decrease in beta wave (beta, low beta, and high beta) activity at the Cp6 region due to geosmin exposure might produce the opposite effect—enhancing calmness and relaxation. Sugawara et al. [27] reported that the inhalation of (R)-(–)-linalool produced a significant decrease in beta waves after work when compared with before work.
Furthermore, the results revealed that geosmin affected absolute wave activity only at the Cp6 region in both genders. In addition to absolute waves, ratio values such as RMT, RST, and RSMT significantly decreased at the Cp6 region. The Cp6 region is a parietal region situated between the central and posterior regions of the right hemisphere of the brain. On the other hand, 2-methylisoborneol odor mainly produced changes in the ratio values, RST, RMT, and RSMT, at the Cp5 region. The Cp5 region is the parietal region located in the left hemisphere of the brain. The parietal region is classified into two major functional areas, the anterior zone (somatosensory cortex) and the posterior zone (posterior parietal cortex). This region is mainly responsible for integrating the sensory information from different body parts and recognizing various stimuli [28,29]. Cappelletti et al. [30] suggested that right parietal activation was highly involved in conceptual decisions on numbers and left parietal activation was involved in conceptual decisions on object names. Therefore, the significant decrease of EEG spectra at Cp5 and Cp6 regions due to the exposure of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol might influence the learning memory state of the brain.
In terms of gender variation, geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol showed different EEG activity by producing changes in different power spectra. In men, geosmin did not produce any significant change, even for relative and ratio values. In the case of 2-methylisoborneol, absolute alpha and fast alpha activity significantly increased, especially at the frontal region (F8), in addition to RAHB in men. The frontal region contains various functional zones including the primary motor area and the prefrontal cortex [31]. In the case of women, significant changes in EEG activity were observed during the inhalation of both compounds. In women, absolute low beta and high beta significantly decreased at the Cp6 region during the inhalation of geosmin (Figure 3). Geosmin odor mainly affected the brain waves in the parietal regions (Cp6, P3, and Cp2) when compared to other regions (Table 2). On the other hand, only relative and ratio values (RST, RMT, RSMT, and SEF90) significantly decreased due to the exposure of 2-methylisoborneol in women (Table 3). In a similar way, the odor of supercritical carbon dioxide extract from the Angelica gigas root produced significant changes in EEG activity only in women [26].
Previously, numerous studies have been conducted on gender-dependent brain functions under stimulus and non-stimulus conditions using EEG. Those studies found that women and men showed different EEG activity under various conditions [32,33,34]. Radulescu and Mujica-Parodi [35] stated that women have a better olfactory sensation than men in many species and differences in their sensitivity may be based on biological meanings. Recently, Haehner et al. [36] reported that women easily identified different fragrances (orange, lime, and lemon) and changed their behavior accordingly when compared to men. In our previous studies, isomeric aroma components ((+)-limonene and terpinolene), essential oils from Abies koreana twigs, and Angelica gigas root showed significantly different EEG activity according to gender. Furthermore, women are more sensitive to different odor molecules than men [17,26,37]. In the olfactory bulb, total, neuronal, and non-neuronal cells were higher in the postmortem material of women than in men [12]. When compared with men, higher delta and theta power were observed in women during cognitive performance tasks [38]. Gender differences and reproductive hormones play an important role in the perception of various odor molecules. Women can easily detect and identify different tastes and odors when compared with men [39]. Dalton et al. [40] reported that women’s detection threshold level was lower after repeated exposure to odor molecules. With regards to emotional responses, Robin et al. [41] found that autonomic parameters were not significantly changed between genders. However, Bailenson et al. [42] suggested that women are more highly expressive than men in their facial reactions to emotions. In the brain activity, the left orbitofrontal cortex was more active in women compared with men during the olfactory process; this may be the main advantage women have in the identification of odors [8]. Similar to previous reports, our study also clearly suggests that the odors of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol produced significantly different EEG activity according to gender.
Geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol have different molecular formulas and structural arrangements. They come under the terpenoid group of compounds and are synthetized by terpene synthases. However, both of these components possess similar kind of odor characteristics such as earthy and musty [3]. Odor molecules play a significant role in human behaviors such as emotions, thoughts, and memory by affecting spontaneous brain functions via the olfactory system [43]. In the olfactory process, olfactory receptor cells are responsible for the detection of various odor molecules and they are specifically tuned to distinct odor characteristics. The olfactory receptors detect odors from small molecules, even at very low concentration. Hence, the odor molecules must reach olfactory receptor cells and then the receptors send electrical signals to the brain via the olfactory bulb to perceive a particular smell [44]. Although geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol possess a similar type of smell, their effect on brain wave activity mainly depends on the selectivity and sensitivity of olfactory receptor cells. Furthermore, it was reported that temperature plays an important role in the intensity of odors. At 45 °C, the odor intensity of geosmin, 2-methylisoborneol, and chlorine was higher than at 25 °C [45].
In the present study, fast Fourier transform was used to extract EEG features before and during the inhalation of odor exposure. EEG feature extraction plays a major role in the recognition of patterns. Several techniques have been applied to extract the features from EEG signals, such as time frequency distributions, fast Fourier transform, eigenvector methods, wavelet transform (continuous and discrete), Hilbert Huang transform, the autoregressive method, nonlinear dynamics analysis, and so on [46,47]. However, each of the techniques has specific advantages and disadvantages. Hence, it is important to optimize the EEG feature extraction for understanding brain wave activity such as theta, alpha, beta, and gamma. The results revealed that geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol exhibited some positive psychophysiological functions in humans. However, the current study has some limitations. The eye movement of subjects is one of the major issues during EEG recordings, so we optimized EEG readings many times for each subject. Furthermore, there were variations in the EEG results between individuals. In this study, 10% odor molecules are used as fragrance stimuli; the results may vary when changing the concentration of odor molecules. Moreover, the EEG was recorded for a short duration (45 s before and during the exposure). Hence, it is still unknown whether these odor molecules will exhibit the same effect over a long duration (>1 min) with more participants. In light of these limitations, EEG recordings for a longer duration and different concentrations of odor molecules with placebo control are required in order to understand their exact action on brain functions.
5. Conclusions
The findings of the present study reveal that the geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol exhibited significantly different EEG power spectrum values. In both genders, geosmin produced significant changes in absolute waves, particularly at the Cp6 region. In addition, women are highly sensitive to both compounds compared with men. The changes in absolute alpha and absolute beta wave activity during the inhalation of these earthy odorants are highly linked with the calmness and relaxation states of the brain. The results clearly demonstrate that geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol, though they have similar smell characteristics, produced significantly different EEG activity; these changes might be due to the sensitivity of olfactory receptors, structural arrangements, and gender differences. This is the first report on the EEG activity of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol. Further studies are needed to confirm the exact action of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol odors on brain functions with placebo control.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a research grant from Kangwon National University, Chuncheon and the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE), Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) through the Encouragement Program for The Industries of Economic Cooperation Region (Project No. R0004940).
Author Contributions
Minju Kim, Taehee Kim, and Jai Eun Kim performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Kandhasamy Sowndhararajan wrote the manuscript; Songmun Kim and Jae E. Yang designed the experiment and revised the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liato, V.; Aïder, M. Geosmin as a source of the earthy-musty smell in fruits, vegetables and water: Origins, impact on foods and water, and review of the removing techniques. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parinet, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Serodes, J. Influence of water quality on the presence of off-flavour compounds (geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol). Water Res. 2010, 44, 5847–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suurnäkki, S.; Gomez-Saez, G.V.; Rantala-Ylinen, A.; Jokela, J.; Fewer, D.P.; Sivonen, K. Identification of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in cyanobacteria and molecular detection methods for the producers of these compounds. Water Res. 2015, 68, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, S.B.; Ridal, J.; Boyer, G.L. Taste and odour and cyanobacterial toxins: Impairment, prediction, and management in the Great Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 1779–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; He, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z. Determination of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin produced by Streptomyces sp. and Anabaena PCC7120. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6823–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Xu, Y. Determination of the microbial origin of geosmin in Chinese liquor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2288–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omur-Ozbek, P.; Little, J.; Dietrich, A. Ability of humans to smell geosmin, 2-MIB and nonadienal in indoor air when using contaminated drinking water. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haese, G.; Humeau, P.; De Oliveira, F.; Le Callet, P.; Le Cloirec, P. Tastes and odors of water—quantifying objective analyses: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2455–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucco, G.M.; Paolini, M.; Schaal, B. Unconscious odour conditioning 25 years later: Revisiting and extending Kirk-Smith, Van Toller and Dodd’. Learn. Motiv. 2009, 40, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuberger, E.; Hongratanaworakit, T.; Bohm, C.; Weber, R.; Buchbauer, G. Effects of chiral fragrances on human autonomic nervous system parameters and self-evaluation. Chem. Senses 2001, 26, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowndhararajan, K.; Kim, S. Influence of fragrances on human psychophysiological activity: With special reference to human electroencephalographic response. Sci. Pharm. 2016, 84, 724–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Pinto, A.V.; Santos, R.M.; Coutinho, R.A.; Oliveira, L.M.; Santos, G.B.; Alho, A.T.; Leite, R.E.; Farfel, J.M.; Suemoto, C.K.; Grinberg, L.T.; et al. Sexual dimorphism in the human olfactory bulb: females have more neurons and glial cells than males. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, M.; Osawa, M.; Nishitani, N.; Iwata, M. Effects of incense on brain function: Evaluation using electroencephalograms and event–related potentials. Neuropsychobiology 2009, 59, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, E.; Fukagawa, M.; Okamoto, T.; Ohnuki, K.; Shimizu, K.; Kondo, R. The essential oil of Abies sibirica (Pinaceae) reduces arousal levels after visual display terminal work. Flavour Fragr. J. 2011, 26, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorig, T.S. Beyond self-report: Brain imaging at the threshold of odor perception. Chemosens. Percept. 2012, 5, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoric, M.K.; Adamec, I.; Jerbic, A.B.; Gabelic, T.; Hajnšek, S.; Habek, M. Electroencephalographic response to different odors in healthy individuals: A promising tool for objective assessment of olfactory disorders. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2015, 46, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowndhararajan, K.; Cho, H.; Yu, B.; Kim, S. Effect of olfactory stimulation of isomeric aroma compounds, (+)-limonene and terpinolene on human electroencephalographic activity. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2015, 7, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, F.L.; Silva, V.V.; Dal Pizzol, C.; Spir, L.G.; Praes, C.E.; Maibach, H. Physiological effect of olfactory stimuli inhalation in humans: An overview. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2014, 36, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basar, E. A review of alpha activity in integrative brain function: Fundamental physiology, sensory coding, cognition and pathology. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 86, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayorwan, W.; Siripornpanich, V.; Piriyapunyaporn, T.; Hongratanaworakit, T.; Kotchabhakdi, N.; Ruangrungsi, N. The effects of lavender oil inhalation on emotional states, autonomic nervous system, and brain electrical activity. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2012, 95, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.G.; Lee, B.L.; Chung, W.Y. Mobile healthcare for automatic driving sleep-onset detection using wavelet-based EEG and respiration signals. Sensors 2014, 14, 17915–17936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edagawa, K.; Kawasaki, M. Beta phase synchronization in the frontal-temporalcerebellar network during auditory-to-motor rhythm learning. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penolazzi, B.; Spironelli, C.; Vio, C.; Angrilli, A. Brain plasticity in developmental dyslexia after phonological treatment: A beta EEG band study. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 209, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.; Mueller, H.M. “Too many betas do not spoil the broth”: The role of beta brain oscillations in language processing. Front. Psychol. 2012, 3, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayowan, W.; Siripornpanich, V.; Hongratanaworakit, T.; Kotchabhakdi, N.; Ruangrungsi, N. The effects of jasmine oil inhalation on brain wave activities and emotions. J. Health Res. 2013, 27, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sowndhararajan, K.; Seo, M.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, S. Effect of essential oil and supercritical carbon dioxide extract from the root of Angelica gigas on human EEG activity. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2017, 28, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, Y.; Hara, C.; Aoki, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Masujima, T. Odor distinctiveness between enantiomers of linalool: Difference in perception and responses elicited by sensory test and forehead surface potential wave measurement. Chem. Senses 2000, 25, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuna, B.D.; Eliassen, J.C.; Donoghue, J.P.; Sanes, J.N. Frontal and parietal lobe activation during transitive inference in humans. Cereb. Cortex 2002, 12, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, C.L.R.; Flindall, J.W. Parietal Lobe. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences; Wright, J.D., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 506–510. [Google Scholar]
- Cappelletti, M.; Lee, H.L.; Freeman, E.D.; Price, C.J. The role of right and left parietal lobes in the conceptual processing of numbers. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenemann, P.T. Evolution of the size and functional areas of the human brain. Annu. Rev. Anthropol. 2006, 35, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi-Cabrera, M.; Ramos, J.; Guevara, M.A.; Arce, C.; Gutierrez, S. Gender differences in the EEG during cognitive activity. Int. J. Neurosci. 1993, 72, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jausovec, N.; Jausovec, K. Resting brain activity: Differences between genders. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 3918–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Takizawa, Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Yamaguchi, N. Gender differences in quantitative EEG at rest and during photic stimulation in normal young adults. Clin. Electroencephalogr. 1994, 25, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulescu, A.R.; Mujica-Parodi, L.R. Human gender differences in the perception of conspecific alarm chemosensory cues. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haehner, A.; Maass, H.; Croy, I.; Hummel, T. Influence of room fragrance on attention, anxiety and mood. Flavour Fragr. J. 2017, 32, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Sowndhararajan, K.; Kim, S. Influence of binasal and uninasal inhalations of essential oil of Abies koreana twigs on electroencephalographic activity of human. Behav. Neurol. 2016, 2016, 9250935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kober, S.E.; Reichert, J.L.; Neuper, C.; Wood, G. Interactive effects of age and gender on EEG power and coherence during a short-term memory task in middle-aged adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 40, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L.; Cameron, E.L. Sex differences and reproductive hormone influences on human odor perception. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 97, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, P.; Doolittle, N.; Breslin, P.A.S. Gender-specific induction of enhanced sensitivity to odors. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, O.; Rousmans, S.; Dittmar, A.; Vernet-Maury, E. Gender influence on emotional responses to primary tastes. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 78, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailenson, J.N.; Pontikakis, E.D.; Mauss, I.B.; Gross, J.J.; Jabon, M.E.; Hutcherson, C.A.C.; Nass, C.; John, O. Real-time classification of evoked emotions using facial feature tracking and physiological responses. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2008, 66, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touhara, K.; Vosshall, L.B. Sensing odorants and pheromones with chemosensory receptors. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2009, 71, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoes de Souza, F.M.; Antunes, G. Biophysics of olfaction. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2007, 70, 451–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, A.J.; Dietrich, A.M. Relationship between intensity, concentration, and temperature for drinking water odorants. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fahoum, A.S.; Al-Fraiha, A.A. Methods of EEG signal features extraction using linear analysis in frequency and time-frequency domains. ISRN Neurosci. 2014, 2014, 730218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T. Classification of epilepsy EEG signals using DWT-based envelopeanalysis and neural network ensemble. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).