Abstract
It was recently reported that implant osseointegration is affected by surface wettability. The relationship between hydrophilicity and cell adhesion was corroborated by numerous in vivo studies. Concentrated alkali improves the biocompatibility of pure titanium. Research was conducted on the mechanism by which this treatment increases hydrophilicity. In the present study, we used atmospheric pressure plasma processing to enhance the hydrophilicity of the material surface. The aim was to assess its influences on the initial adhesion of the material to rat bone marrow and subsequent differentiation into hard tissue. Superhydrophilicity was induced on a pure titanium surface with a piezobrush, a simple, compact alternative to the conventional atmospheric pressure plasma device. No structural change was confirmed by Scanning electron microscope (SEM) or scanning probe microscopy (SPM) observation. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis presented with hydroxide formation and a reduction in the C peak. A decrease in contact angle was also observed. The treated samples had higher values for in vitro bovine serum albumin (BSA) adsorption, rat bone marrow (RBM) cell initial adhesion, alkaline phosphatase activity (ALP) activity tests, and factors related to bone differentiation than the untreated control. The present study indicated that the induction of superhydrophilicity in titanium via atmospheric pressure plasma treatment with a piezobrush affects RBM cell adhesion and bone differentiation without altering surface properties.
1. Introduction
Concerted efforts are being made among material scientists and clinicians worldwide to improve the performance of dental implants by accelerating and maintaining their integration into hard and soft tissues and/or expanding their coverage [1]. The surface properties of the implant material affect the speed and extent of its osseointegration. Recently, Vandrovcova et al. reported that surface-modifying materials could substantially improve cell adhesion, growth, and osteogenic differentiation. In this way, they could promote implant integration into bone and maintain its secondary stability [2].
Osseointegration is the rapid, direct incorporation of bone into an implant. It is an important factor in functional implant loading. Several approaches and strategies have been devised to enhance osseointegration and stabilize implants [3,4] For example, chemical or mechanical abrasion of the implant surface significantly improved bone bonding [5,6,7] compared to untreated implant surfaces. It is believed that these treatments induce the adsorption of fibronectin or other proteins on the implant surface which, in turn, triggers osteoblasts to form focal adhesions via an integrin-mediated mechanism [8,9].
Titanium has been widely used as an implant material because of its biocompatibility. Moreover, the thin surface oxide layer it produces has excellent corrosion resistance [10]. Several titanium surface modification strategies have been tested. They focused on the surface properties of biomaterials in order to enhance dental implant osseointegration [10,11,12]. Sterilization is the final step in surface modification as the biomaterial must be aseptic prior to its implantation. Depending on the biomedical device or material, secondary cleaning or sterilization may be performed at the clinical site [13]. The biomaterial may be subjected to several uncontrolled washing and/or sterilization steps. When the implant device is approved for reuse, the key steps in its reconditioning are cleaning and sterilization. However, these processes may alter its initial surface properties [14]. Therefore, material surface cleaning is a vital component of the surface treatment strategy.
Plasma biology is a new interdisciplinary research area [15]. The scope of applications for physical plasma is expanding. At present, it is being used to functionalize biomaterial surfaces, improve their biocompatibility, and enhance their bioequivalent coatings [16,17,18]. The relationship between plasma treatment of implant material surfaces and hard tissue differentiation has been reported in several papers [19,20,21,22]. For past decades, several techniques have been used for generating plasmas at atmospheric pressure and with a temperature close to ambient, such as Radio-frequency plasmas (RF) [23], Dielectric barrier discharges (DBD) plasmas [24], Corona discharge plasmas [24,25,26], and Gliding arc discharge plasmas [27]. The general advantage of these techniques is that the formation of a large number of reactive species could be obtained which was used for the treatment of surface, gases and aqueous solutions. Meanwhile, the miniaturization of the generator employed to create plasma has always been an important subject of research. The aim of these technologies, such as Piezoelectric direct discharge plasmas [28,29], is to generate plasmas as “thin and small” as possible in terms of clinical application. However, the devices performing plasma processing are very large and may be impractical for clinical application. In contrast, the plasma apparatus used in the present study was comparatively small and easy to use.
The aim of the present study was to investigate the mechanism by which piezobrush plasma treatment of a pure titanium surface affects its initial adhesion and ability to induce hard tissue differentiation in rat bone marrow cells. The results of this study may prove to be invaluable in the fields of dentistry and prosthodontics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
Titanium disks (diameter: 15 mm; thickness: 1 mm) of commercially pure grade 2 titanium were prepared by machining (Daido Steel, Osaka, Japan). The disks were polished with abrasive SiC paper (Nos. 1000 and 1500), ultrasonically rinsed in acetone, ethanol, and distilled water for 10 min each, and air-dried. A Piezobrush® PZ2 (Relyon Plazma GmbH, Regensburg, Germany) was used to coat the disks by using active gas in atmospheric-pressure, low-temperature plasma treatment under irradiation at 0.2 MPa for 30 s at 10 mm. The disks of the test group were subjected to plasma treatment whereas the control disks were untreated.
2.2. Characterization of Materials
The surfaces of the plasma-treated samples were observed under a scanning electron microscope (SEM, S-4800; Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) and a scanning probe microscope (SPM, SPM-9600, SHIMADZU). The chemical composition of the surface coating was analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Kratos analytical axis ultra DLD electron spectrometer; Kratos Instruments, Manchester, UK) with a monochromatic Al Kα X-ray source. Each sample was etched with Ar ions for 2 min (evaporation rate: 5 nm min−1) to remove surface contaminants.
Contact angle measurements in ultrapure water were performed at room temperature using a video contact angle measurement system (VSA 2500 XE; AST Products, Tokyo, Japan).
2.3. Protein Adsorption Assay
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) fraction V (Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL, USA) was used as a model protein. A protein solution (300 µL, 1 mg mL−1 protein in saline) was pipetted onto each sample. After incubation for 1, 3, 6, or 24 h at 37 °C, the nonadherent proteins were removed and mixed with bicinchoninic acid (BCA; Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL, USA) at 37 °C for 1 h. The released and total quantities of inoculated BSA were quantified in a microplate reader at 562 nm.
2.4. Cell Culture
Rat bone marrow (RBM) cells were isolated from the femurs of 8-week Sprague-Dawley rats. This study was approved by the Guidelines for Animal Experimentation of Osaka Dental University (Approval No. 18-03007). The rats were euthanized by 4% isoflurane inhalation and their bones were aseptically excised from their hind limbs. The proximal ends of the femurs and the distal ends of the tibiae were clipped and flushed with Eagle’s minimal essential medium (MEM; Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Osaka, Japan). A 21-gauge needle (Terumo, Tokyo, Japan) was used to aspirate the bone marrow. The marrow pellets were dispersed by trituration. Cell suspensions from all bones were combined in one centrifuge tube. The RBM cells were cultured in 75-cm2 Falcon culture flasks (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) at 37 °C under a 5% CO2 atmosphere in a growth medium containing MEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA), penicillin (500 U mL−1; Cambrex Bio Science, Walkersville, MD, USA), and Fungizone (1.25 μg mL−1; Cambrex Bio Science, Walkersville, MD, USA). When the cells reached confluence, they were removed from the flask by trypsinization, washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), resuspended in culture medium, and seeded at a density of 4 × 104 cm−2 in 24-well Falcon tissue culture plates (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) containing either a test or a control titanium disk.
2.5. Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion was measured with a Cell Titer-Blue Cell viability assay kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. RBM cells were seeded onto the samples at a density of 4 × 104 cm−2 and allowed to attach for 1, 3, 6, or 24 h. At each time point, the nonadherent cells were removed by rinsing with PBS. CellTiter-Blue Reagent (50 µL) and PBS (250 µL) were then added to each well. After incubation at 37 °C for 1 h, the solution was removed and 3 × 100 μL (triplicates) of it was transferred to a new Falcon 96-well tissue culture plate (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Absorbances of the remaining solution were measured at OD560/590.
2.6. Cell Morphology
RBM were seeded onto the samples at a density of 4 × 104 cm Samples with attached cells were washed with PBS, fixed by incubation with 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min at room temperature, and permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 30 min at room temperature after 6 h. Cells were incubated with Blocking One reagent (Nacalai Tesque, Kyoto, Japan) for 30 min at room temperature and stained with Alexa Fluor 488-phalloidin (Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) at 37 °C in the dark for 1 h. F-actin and the cell nuclei were visualized by confocal laser scanning microscopy (LSM700; Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
2.7. RT-PCR Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from the cells and cDNA was synthesized from 1 µg RNA using a high-capacity cDNA archive kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) after 3, 7, 14, and 21 d. Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), ALP, bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2), and bone gamma-carboxyglutamate (gla) protein (Bglap) mRNA expression were evaluated by qRT-PCR on a StepOne Plus Real-Time RT-PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Taqman Fast Universal PCR Master mix (10 µL), 1 µL primer probe set (20 × Taqman Gene Expression Assays), sample cDNA (2 µL), and 7 µL diethylpyrocarbonate-treated water (Nippongene, Toyama, Japan) were added to each well of a fast 96-well reaction plate (0.1-mL well volume; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The plate was subjected to 40 reaction cycles of 95 °C for 1 s and 60 °C for 20 s. The target gene expression level was calculated relative to the negative control group by the 2−ΔΔCt method.
2.8. ALP Activity
RBM cells at 7 and 14 d culture were washed with PBS and lysed with 200 µL of 0.2% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The lysate was transferred to a microcentrifuge tube containing a hardened 5-mm steel ball. The tube was agitated on a shaker (Mixer Mill Type MM 301; Retsch GmbH, Haan, Germany) at 29 Hz for 20 s to homogenize the contents. ALP activity was measured with an alkaline phosphatase luminometric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The reaction was terminated by adding 3 N NaOH until a final concentration of 0.5 N NaOH was achieved. Then p-nitrophenol production was determined on a microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). DNA content was measured with a PicoGreen dsDNA assay kit (Invitrogen/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The amount of ALP was normalized to the amount of DNA in the cell lysate.
2.9. Mineralization
Mineralization was assessed with a calcium E-test kit (Wako Pure Chemical Industries Ltd., Osaka, Japan). At each time point (21 or 28 d culture), 1 mL calcium E-test reagent and 2 mL buffer were added to 50 µL of the medium. Absorbance of the reaction products was measured at 610 nm in a 96-microplate reader (SpectraMax M5; Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). The calcium ion concentration was calculated from the absorbance value relative to a standard curve.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
All samples were prepared in triplicate. All data are means ± SD. Statistical significance was determined with a paired two-tailed Student’s t-test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Sample Preparation
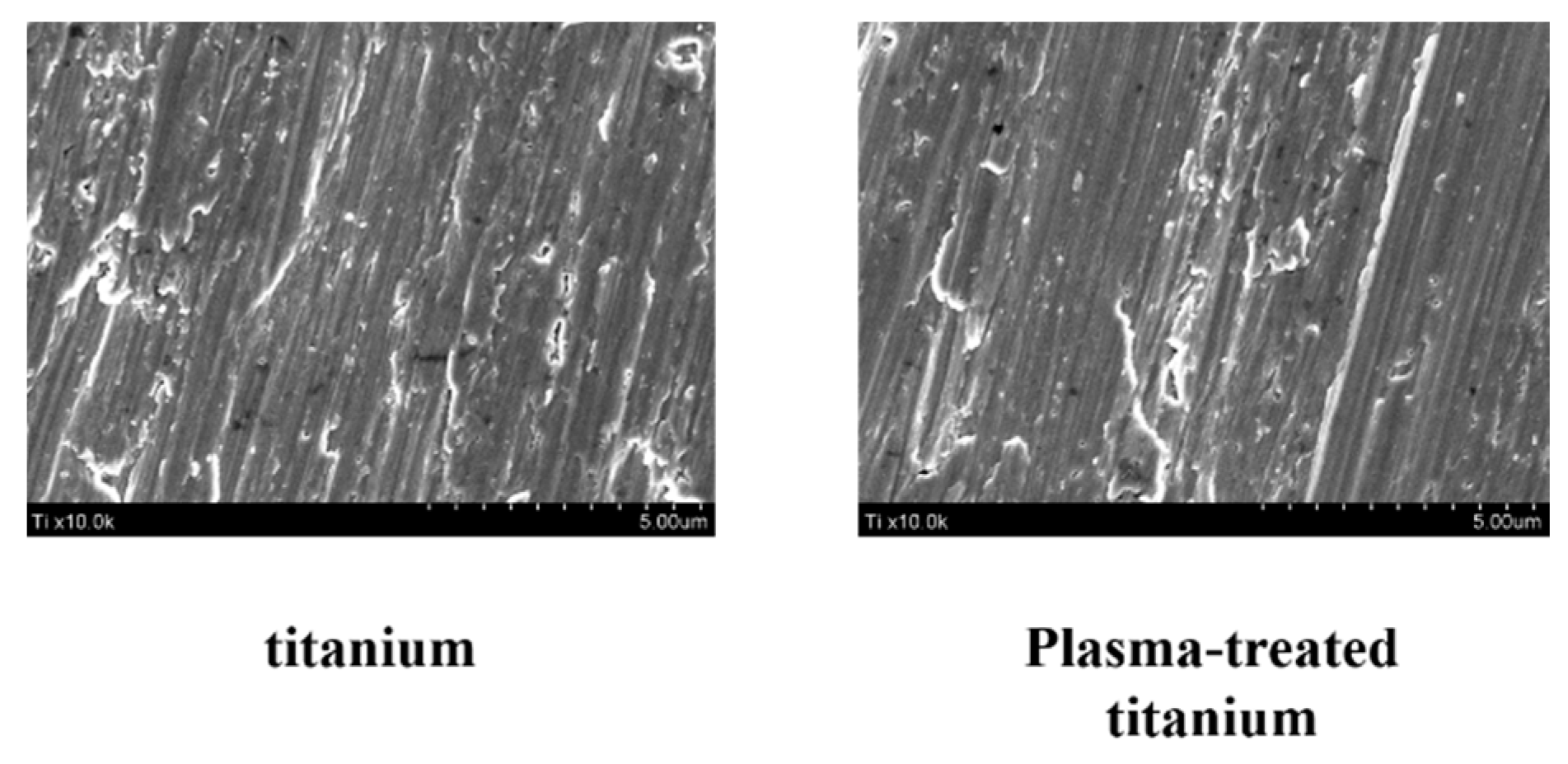
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) disclosed no structural changes on the titanium disk surface after plasma irradiation (Figure 1).
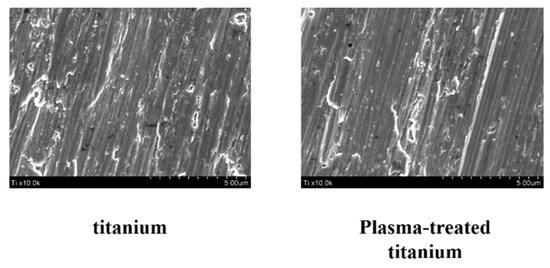
Figure 1.
Surface morphology of titanium and plasma-modified titanium by SEM. SEM disclosed no structural changes on the titanium disk surface after plasma irradiation.
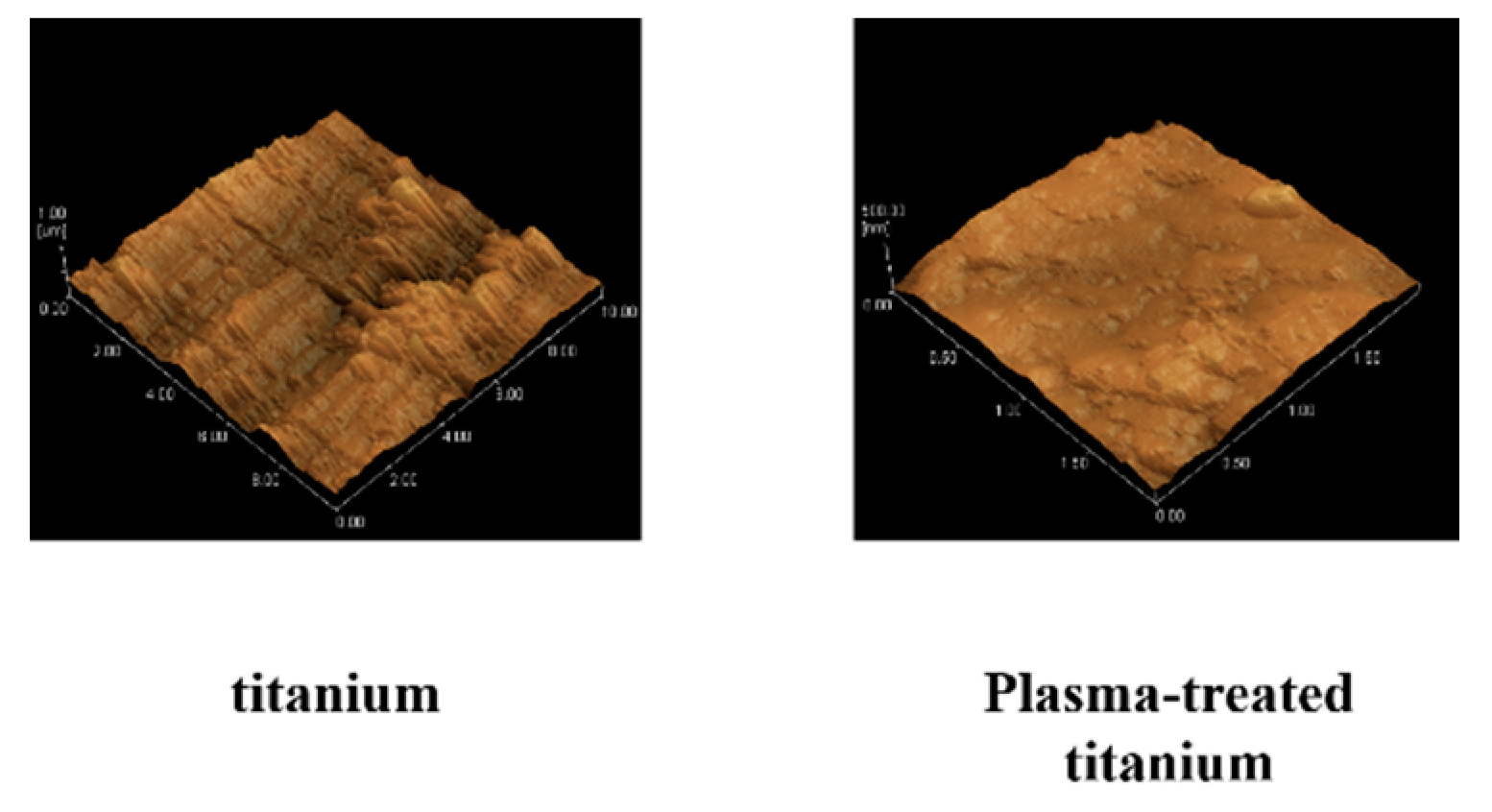
No changes in surface roughness were detected on the test disks observed by scanning probe microscopy (SPM) (Figure 2).
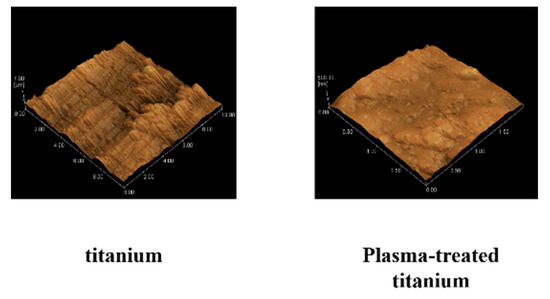
Figure 2.
Scanning probe microscopy of titanium and plasma-modified titanium. No changes in surface roughness (titanium; Ra = 7.5, plasma-modified titanium; Ra = 8.2) were detected on the test disks observed by scanning probe microscopy (SPM) (Figure 2).
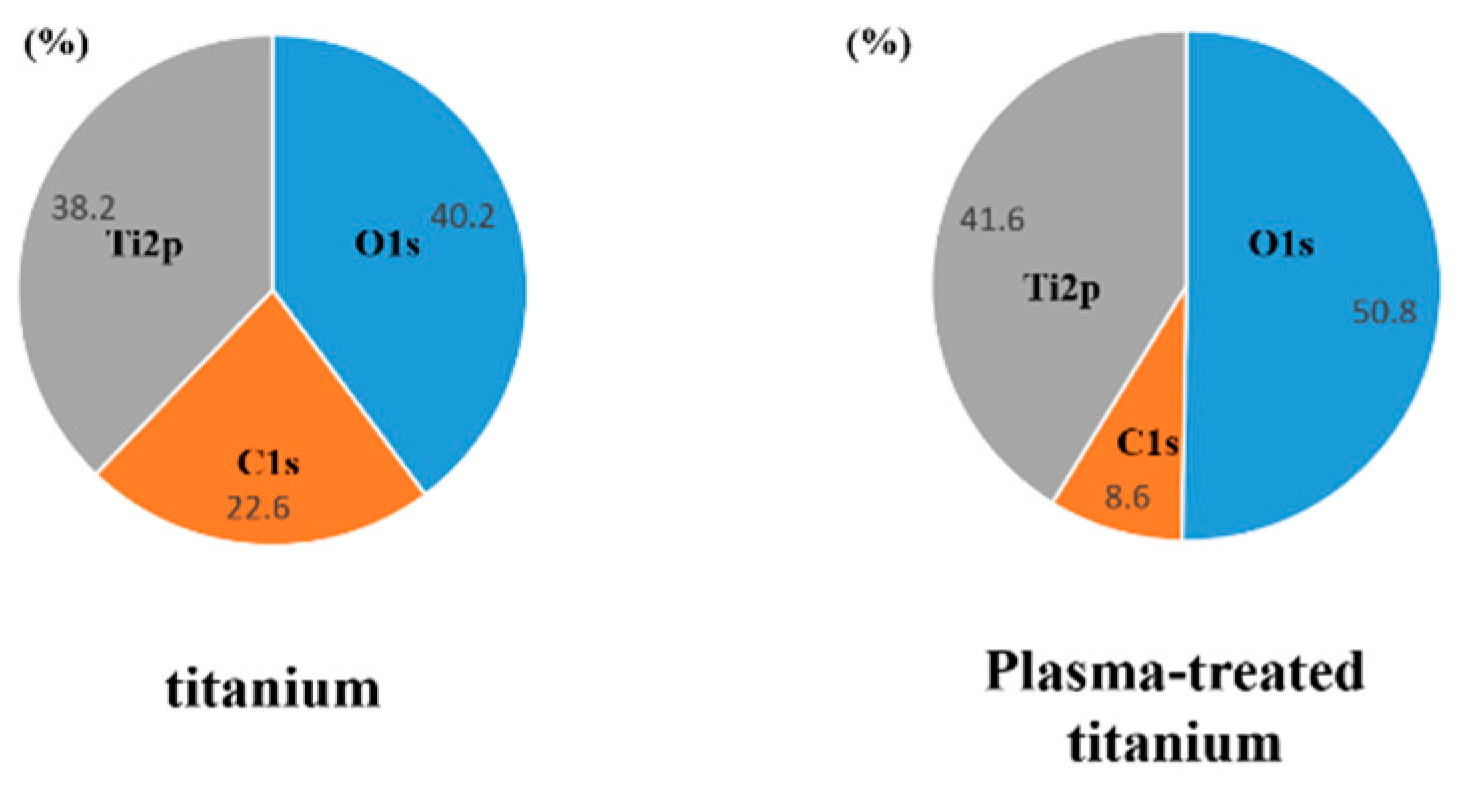
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) revealed that the intensity of the O1s peaks increased while that of the C1s peaks decreased in response to plasma irradiation (Figure 3).
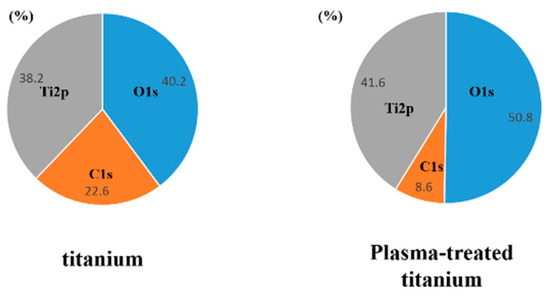
Figure 3.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of titanium and plasma-modified titanium. It showed the intensity of the O1s peaks increased while that of the C1s peaks decreased in response to plasma irradiation.
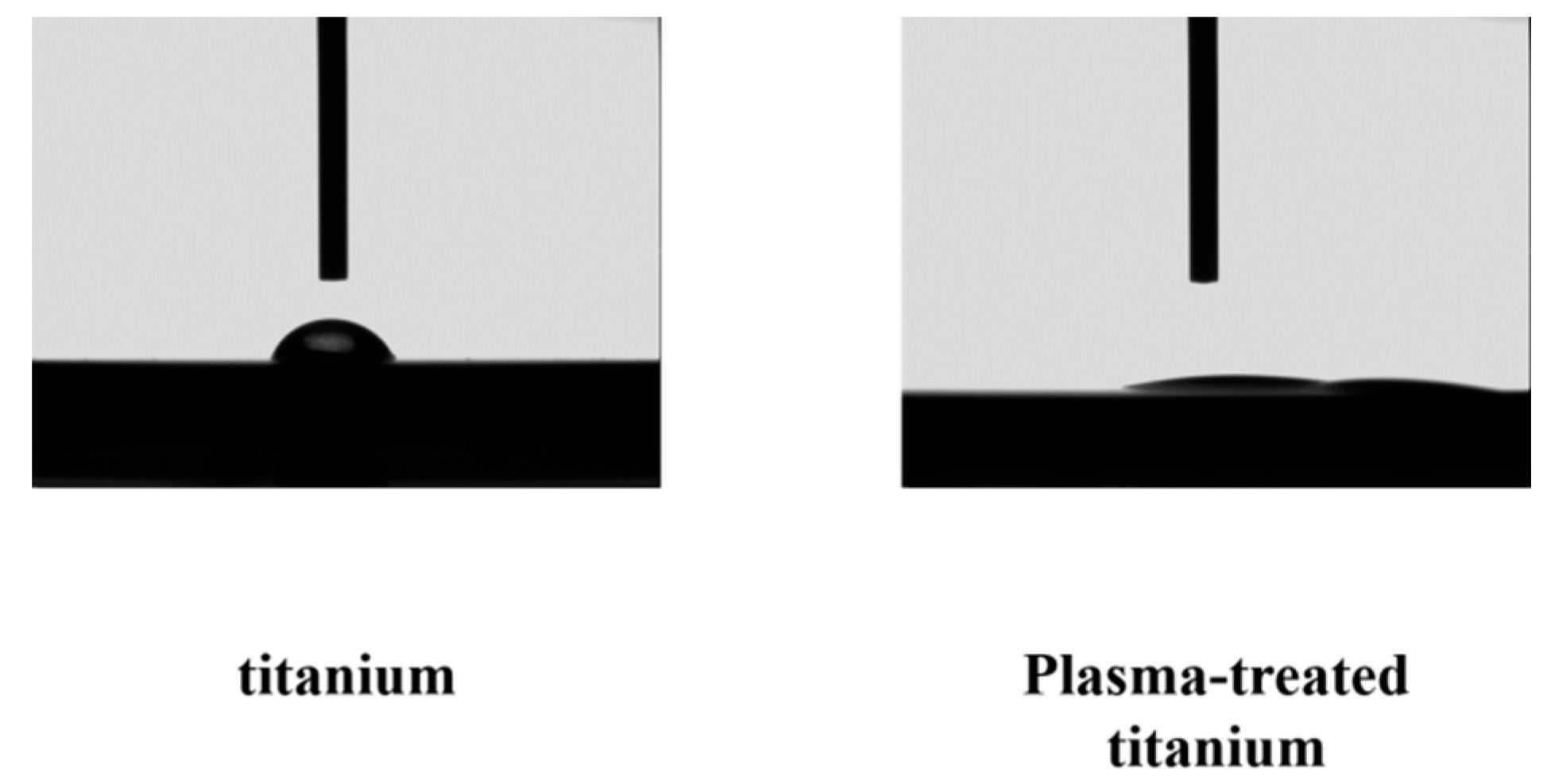
There was a clear difference between the contact angle of the plasma-treated titanium disks (titanium; 32°, plasma-modified titanium; 0) and those of the untreated disks (Figure 4).
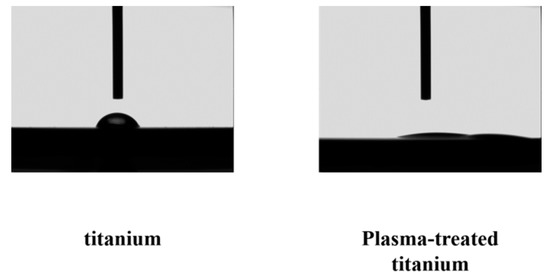
Figure 4.
Contact angle of titanium and plasma-modified titanium. There was a clear difference between the contact angles (titanium; 32°, plasma-modified titanium; 0°) of the plasma-treated titanium disks and those of the titanium disks (Figure 4).
3.2. Protein Adsorption
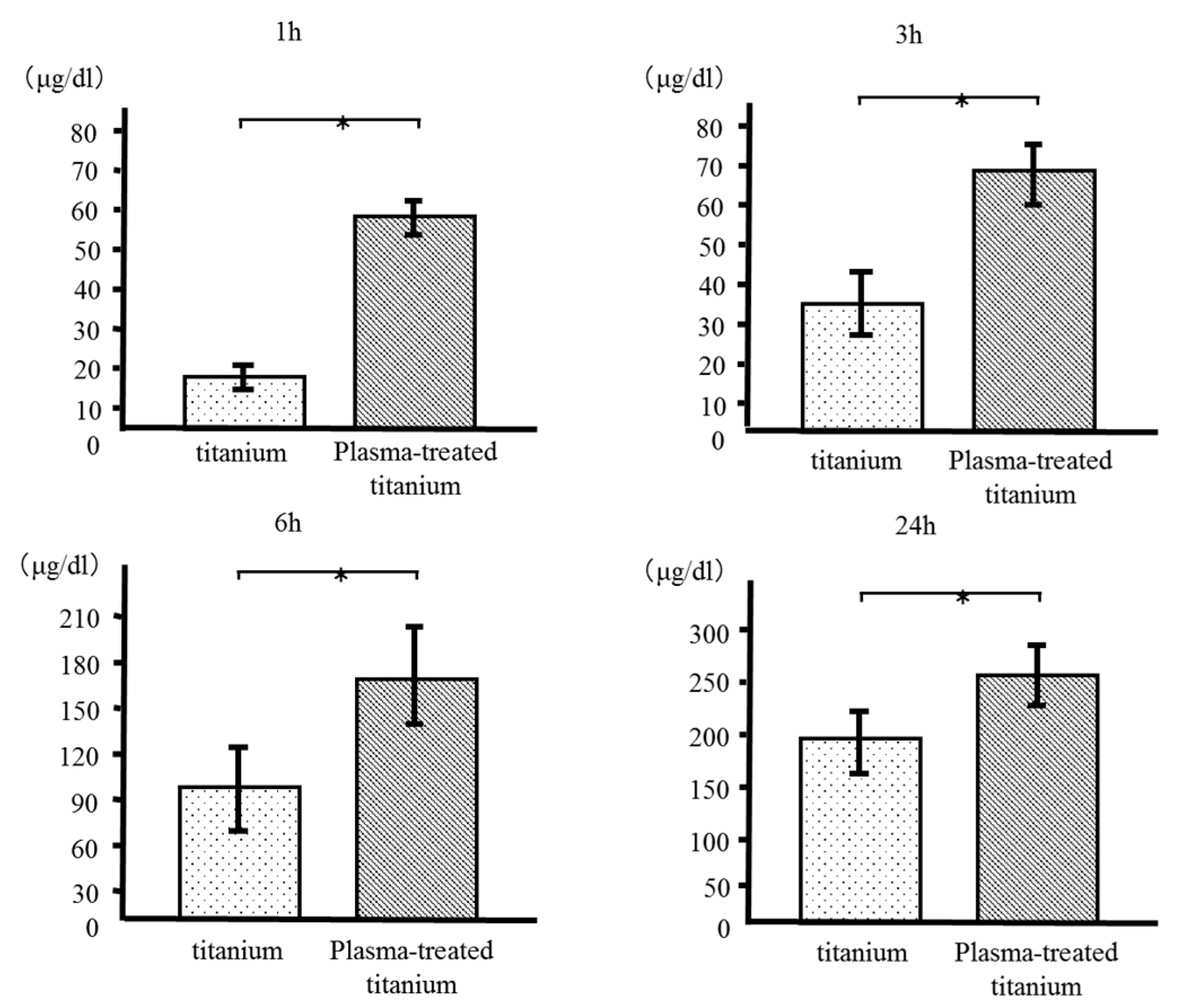
We measured the quantity of bovine serum albumin (BSA) adsorbed to the plasma-treated and untreated titanium disk surfaces after incubation for 1, 3, 6, and 24 h. More BSA was adsorbed to the plasma-treated than the control disks at every time point. (Figure 5).
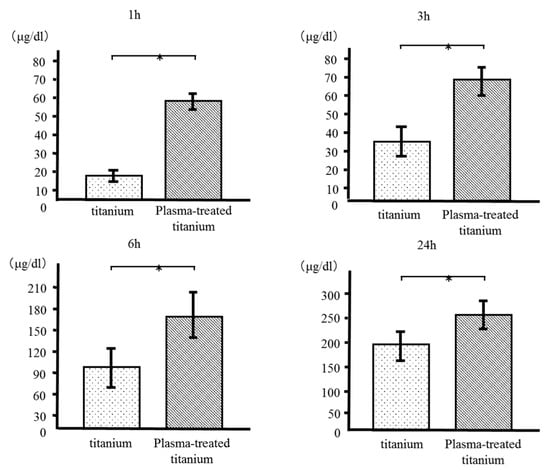
Figure 5.
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) adsorption of titanium and plasma-modified titanium. More BSA was adsorbed to the plasma-treated than the titanium disks at every time point.
3.3. Cell Adhesion and Morphology
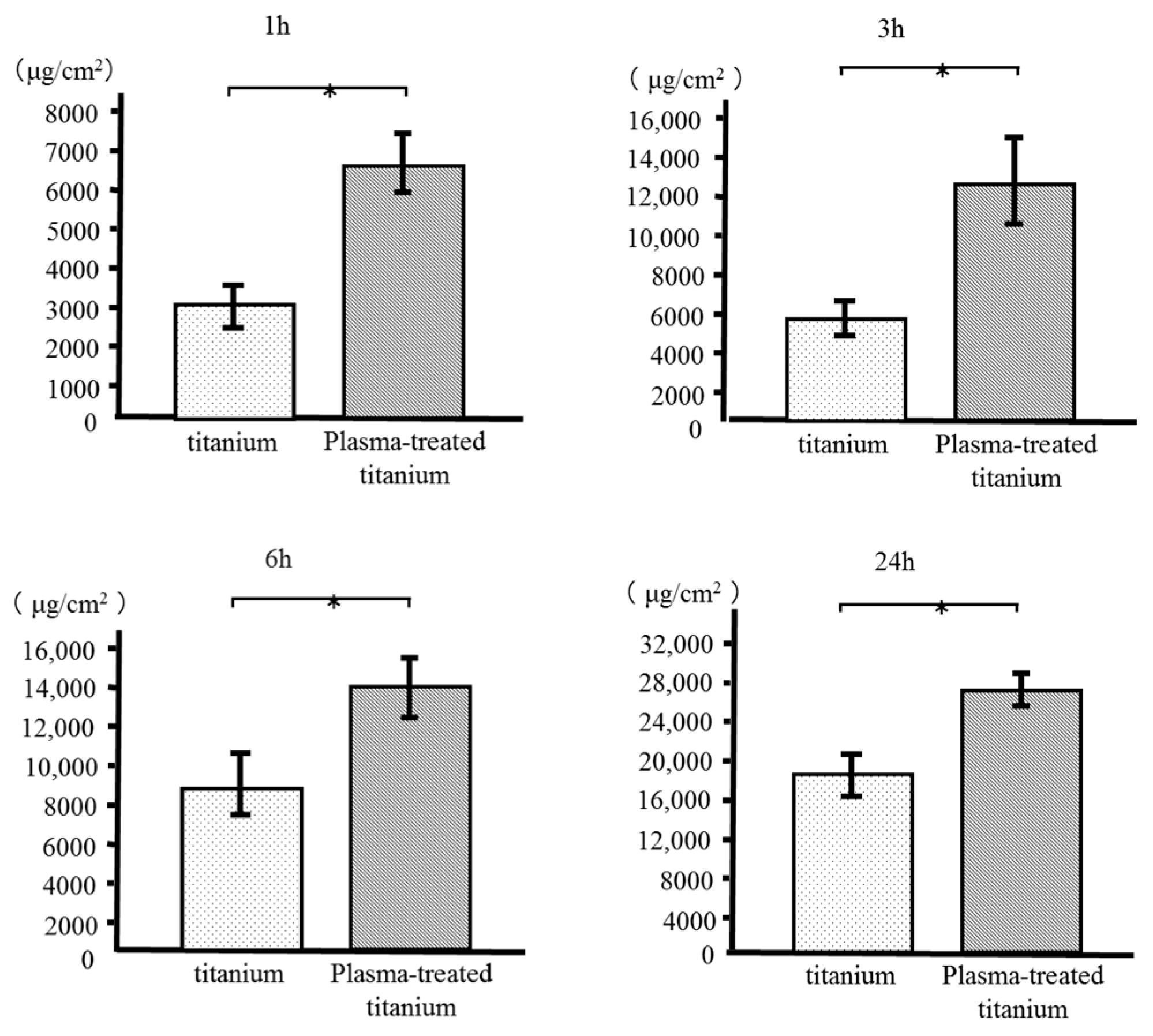
RBM cell adhesion to the sample disks was evaluated after 1, 3, 6, and 24 h incubation. Plasma-treated titanium disks showed greater RBM cell adhesion than the untreated disk surfaces at every time point (Figure 6).
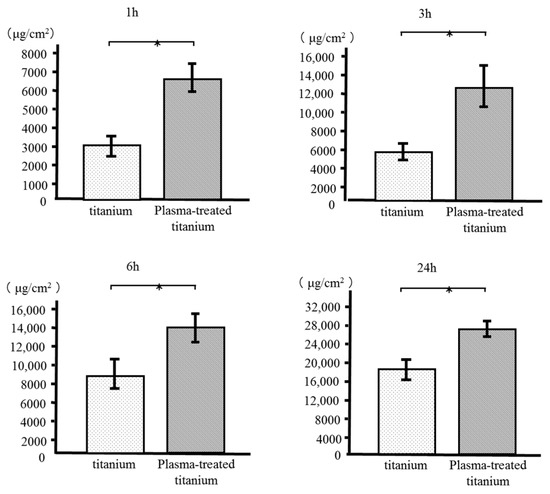
Figure 6.
Rat bone marrow (RBM) cell adhesion of titanium and plasma-modified titanium. Plasma-treated titanium disks showed greater RBM cell adhesion than the titanium disk surfaces at every time point.
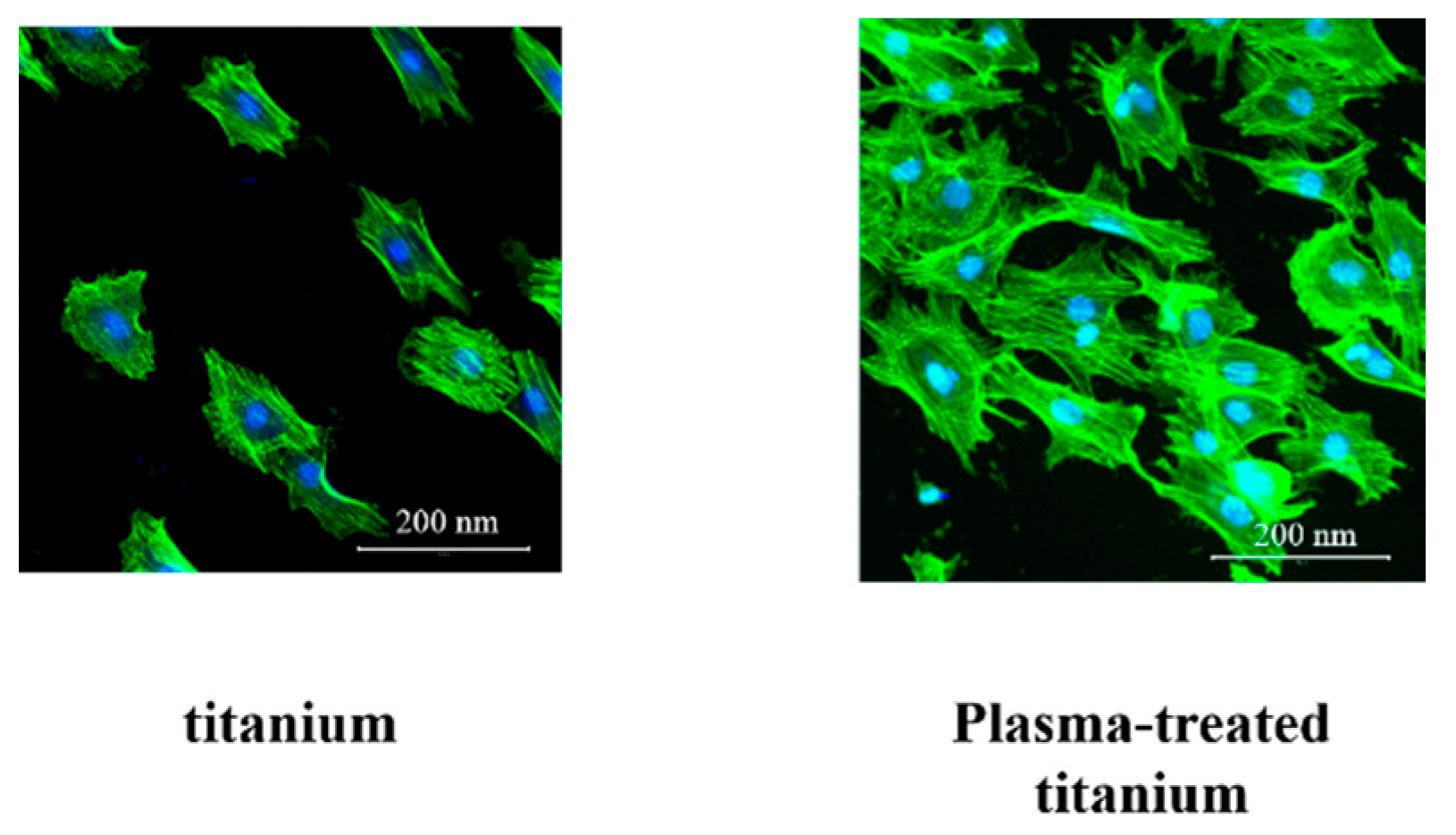
Cell morphology was observed using Alexa Fluor 488-phalloidin and 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining after 24 h incubation. The RBM cells adhering to plasma-treated titanium showed greater F-actin expression and more filopodia and lamellipodia than those on the untreated titanium surface (Figure 7).
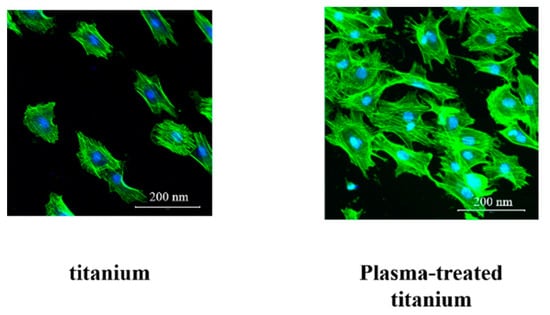
Figure 7.
RBM cell morphology of titanium and plasma-modified titanium. The RBM cells adhering to plasma-treated titanium showed greater F-actin expression and more filopodia and lamellipodia than those on the titanium surface.
3.4. qRT-PCR Analysis
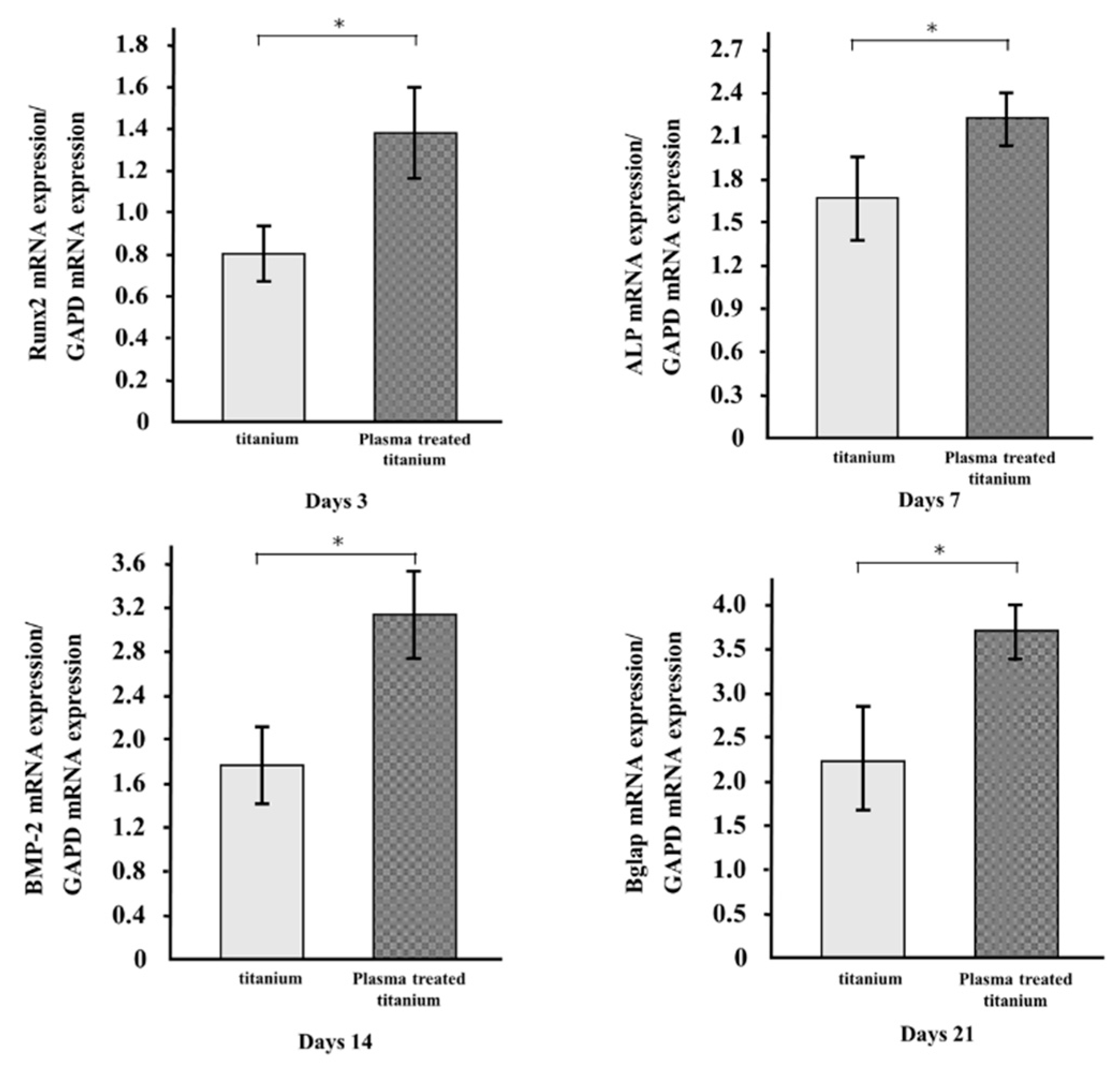
The mRNA expression levels of osteogenesis-related genes, including Runx2, ALP, BMP-2, and Bglap in RBM grown on the specimens for 3, 7, 14, and 21 d, were evaluated by qRT-PCR. All genes in the cells grown on plasma-treated titanium disk surfaces were upregulated compared to those in the cells on untreated titanium (Figure 8).
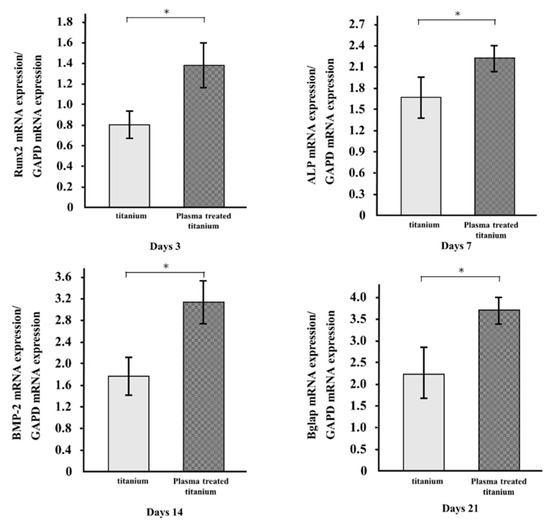
Figure 8.
qRT-PCR analysis of titanium and plasma-modified titanium. All genes in the cells grown on plasma-treated titanium disk surfaces were upregulated compared to those in the cells on titanium disk.
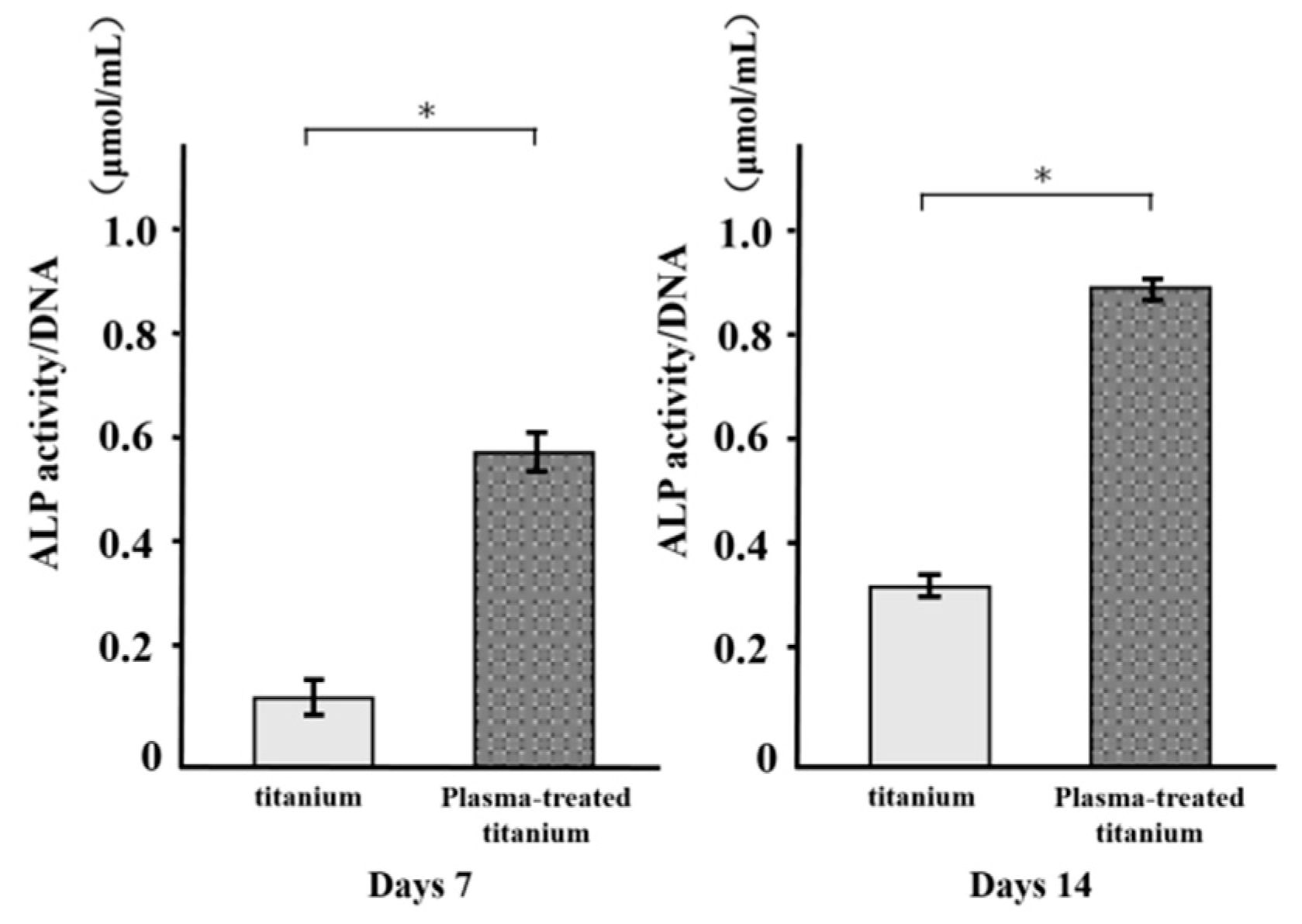
3.5. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity
ALP activity was measured in RBM cells grown on various disks for 7 d and found to increase with time. There were major differences in ALP activity between the plasma-treated and untreated titanium surfaces at days 7 and 14 (Figure 9). ALP was upregulated in the former relative to the latter.
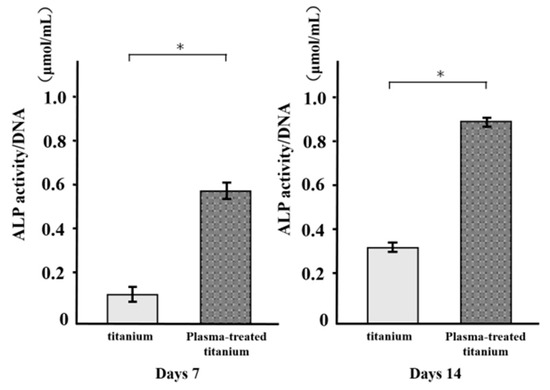
Figure 9.
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) activity of titanium and plasma-modified titanium. There were major differences in ALP activity between the plasma-treated and titanium surfaces at days 7 and 14.
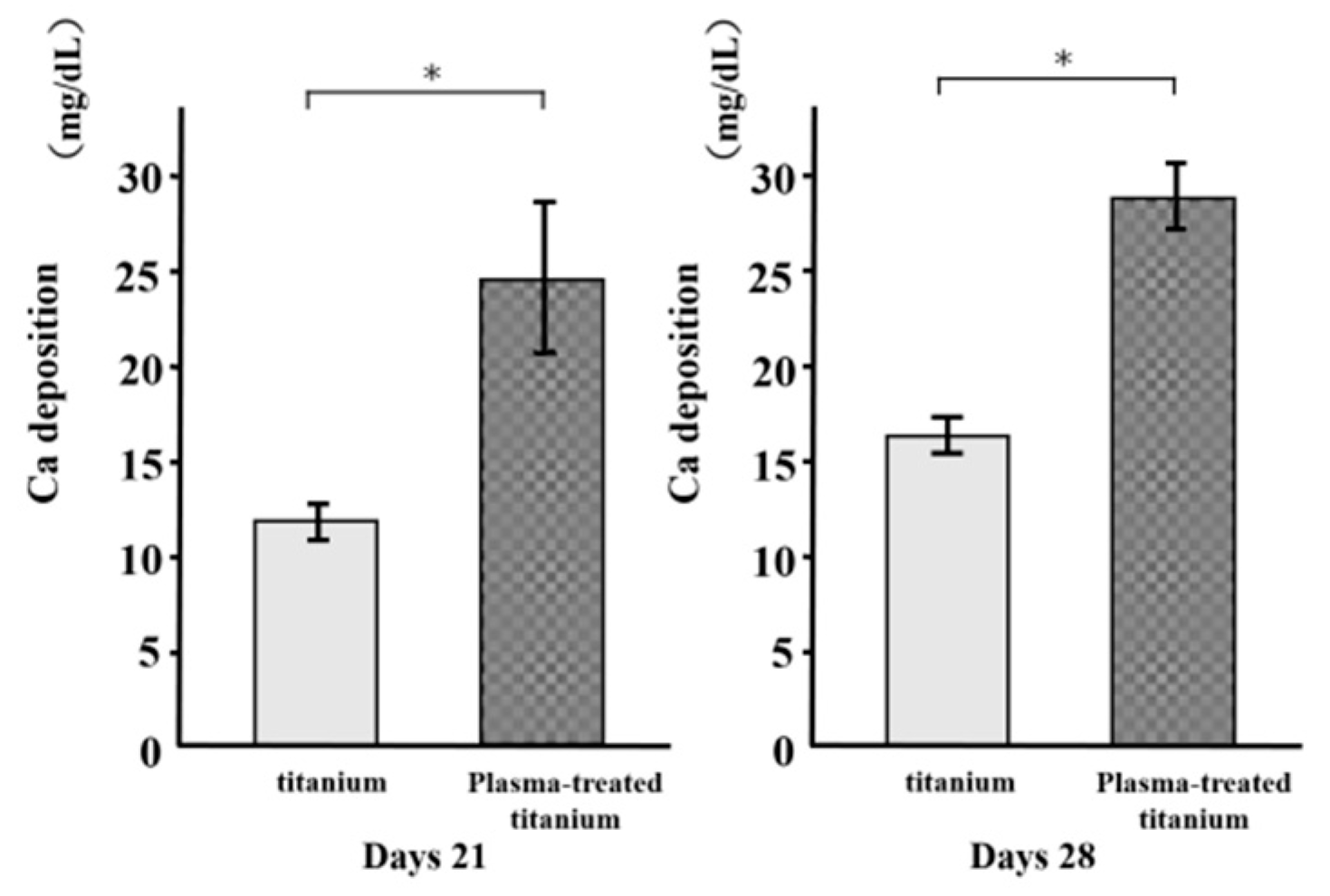
3.6. Mineralization
As a metric of osteogenic differentiation, calcium deposition was evaluated for the cells on the various surfaces at 21 and 28 d culture (Figure 10). Mineralization was greater in the cells on the plasma-treated specimens than the untreated specimens.
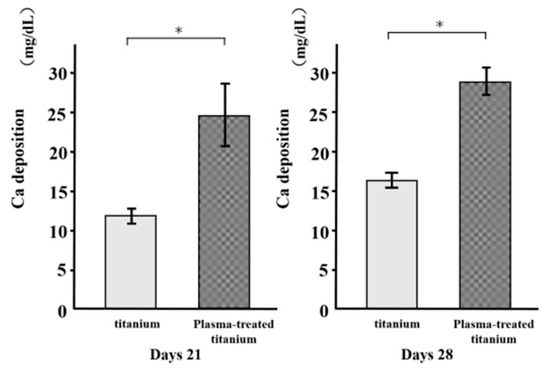
Figure 10.
Calcium deposition of titanium and plasma-modified titanium. Mineralization was greater in the cells on the plasma-treated specimens than the untreated titanium disk.
4. Discussion
The aim of this study was to establish whether RBM cells respond differently to titanium implants that have undergone surface modification by plasma treatment. The results showed that adhesion and osteogenic differentiation increased in cells grown on plasma-treated disks compared to those raised on untreated disks. Titanium disks modified by plasma treatment promoted RBM cell adhesion and osteogenic differentiation.
Titanium implant surface properties, such as chemistry, wettability, and morphology, affect osteoblast proliferation, extracellular matrix and local factor production, and stimulation of the osteogenic microenvironment [30,31]. Thus, it is important to understand how material surface cleaning affects these physicochemical properties [32]. The optimal surface characteristics for clinically placed dental implants and orthopedic endoprostheses have not yet been determined. However, it is clear that removing contaminants from the material surface and imparting hydrophilicity to it are both useful [33,34,35]. In the present study, we investigated changes in titanium surfaces treated with atmospheric-pressure, low-temperature plasma. The device generating these conditions utilizes mechanical piezoelectric resonance to amplify electrical energy and generate high voltage. In this way, it ionizes the active gas or the surrounding atmosphere and produces plasma. Conventional plasma devices require vacuum and processing is both constrained and costly. In contrast, the piezobrush device used in the present study was compact and readily generated plasma. Therefore, it is suitable for chairside use in dentistry.
There were no perceivable differences in the SEM or SPM analysis between the untreated surface and that treated with atmospheric low-temperature plasma. On the other hand, the contact angle experiment test disclosed that atmospheric low-temperature plasma treatment increased the wettability of the titanium relative to that of the control [36,37]. Atmospheric-pressure, low-temperature plasma treatment introduces hydrophilic functional groups to resinous organic materials and inactive inorganic substances such as zirconia and titanium [38]. Adhesion between cells and proteins increases with wettability. The XPS analysis revealed that the atmospheric pressure, low-temperature plasma treatment effectively removes the carbon content derived from organic contaminants on the material surface. Under atmospheric pressure, low-temperature plasma, high-energy ions collide with the sample surface, dissociate the carbon bonds in the organic contaminants, and cause them to volatilize. Analysis of the surface of the pure titanium material showed that low-temperature, atmospheric-pressure plasma treatment cleaned it, increased its hydrophilicity, and improved its biocompatibility.
In the in vitro culture media and in vivo biological fluids, all implant surfaces are immediately covered with a layer of protein. This interface modulates a cascade of cellular responses and behaviors [38]. To examine the relationships among implant surface properties, opsonization, and phagocytosis in vivo, phagocytic experiments were conducted on a cell line grown in a culture medium supplemented with BSA and human opsonizing serum factors [39]. Albumin is the most abundant plasma protein. It inhibits the adsorption of proteins that stimulate inflammation and bacterial colonization [39,40]. In the present study, the test group adsorbed more albumin than the control group. Indirect improvement of surface topography could involve the adsorption of proteins or ions that act as bridges between the nanostructured surface and the cells [41]. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is to compare RBM cell proliferation on plasma-treated titanium surfaces with that on unprocessed controls. Plasma treated titanium surface enhances the adhesion of cells such as osteoblasts and fibroblasts. Thus, it was proposed that altered material surface energy may promote tissue growth because it increases the adsorption of certain proteins relative to materials with microscale features [41]. The adsorption of certain proteins may, in turn, induce cell adhesion on the implant surface and perform other functions. Numerous studies demonstrated that the stimulation of cell adhesion and proliferation on modified surfaces could be beneficial for various therapeutic bladder, bone, vasculature, and nervous system applications [16,17,18].
The RBM cells on plasma-treated titanium surfaces presented with greater ALP activity, calcium deposition, and bone formation-related gene expression than those on the untreated control surfaces. ALP activity is a marker of bone differentiation at the early stages, bone formation, and osteoblast activity [42]. There were significant differences between plasma-treated and untreated titanium implant surfaces in terms of the expression levels of osteoblast-specific markers. Furthermore, plasma-treated surfaces upregulated ALP, Bglap, BMP-2 and Runx2 (important transcription factors mediating osteoblast differentiation) in RBM cells. Plasma treatment maintains the viability of adherent stromal cells and promotes their differentiation into osteoblasts.
According to the experimental results, low-temperature, atmospheric-pressure plasma treatment removes contaminants from pure titanium metal surfaces, increases its hydrophilicity, enhances the initial adhesion of protein and rat bone marrow cells, and induces hard tissue differentiation. The piezobrush plasma device used in the present study is invaluable to clinicians because it is smaller and easier to operate than conventional plasma devices. Moreover, the findings of the in vitro efficacy assays performed in the present study suggest that this novel technology could be highly useful in dental practice.
5. Conclusions
The present study clarified that low-temperature, atmospheric-pressure plasma treatment imparts hydrophilicity to the surface of pure titanium metal and removes contaminants from it. The results also disclosed that plasma treatment induces the initial adhesion of rat bone marrow cells and proteins to the material surface and may trigger hard tissue formation. It is expected that this technology will be extensively applied in clinical settings because it is compact and easy to use.
Author Contributions
S.K. and H.N. conceived and designed the experiments. D.U. performed the experiments. D.U., S.H. and J.O. analyzed the data and D.U. and S.K. wrote the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (18K09713). We thank Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript and helping us draft the abstract.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Seiji Takao and the members of the Department of Removable Prosthodontics and Occlusion for their kind advice and assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wadamoto, M.; Akagawa, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kubo, T. The three-dimensional bone interface of an osseointegrated implant. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1996, 76, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandrovcova, M.; Bacakova, L. Adhesion, growth and differentiation of osteoblasts on surface-modified materials developed for bone implants. Physiol. Res. 2011, 60, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buser, D.; Broggini, N.; Wieland, M.; Schenk, R.K.; Denzer, A.J.; Cochran, D.L.; Hoffmann, B.; Lussi, A.; Steinemann, S.G. Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.; Sennerby, L.; Meredith, N. Influence of implant taper on the primary and secondary stability of osseointegrated titanium implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 4, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T.; Linder, E.; Lang, N.P.; Lindhe, J. Early bone formation adjacent to rough and turned endosseous implant surfaces. An experimental study in the dog. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 4, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberktsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Oral implants surfaces: Part 1—Review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, L.F.; Zhou, Y.; Takebe, J.; Guo, J.; Abron, A.; Holmén, A.; Ellingsen, J.E. Fluoride modification effects on osteoblast behavior and bone formation at TIO2 grit-blasted c.p. titanium endosseous implants. Biomaterials 2006, 6, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, G.; Burridge, K. Formation of focal adhesions by osteoblasts adhering to different substrata. Exp. Cell Res. 1994, 1, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpadi, K.L.; Chang, P.L.; Bellis, S.L. Hydroxylapatite binds more serum proteins, purified integrins, and osteoblast precursor cells than titanium or steel. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 2, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Dimitriou, R.; Parvizi, Z.; Babis, G.C. Biology of implant osseointegration. J. Musculoskel. Neuron. Interact. 2009, 9, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, F.; Wieland, M.; Schwarz, Z.; Zhao, G.; Rupp, F.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Schedle, A.; Broggini, N.; Bornstein, M.M.; Buser, D.; et al. Potential of chemically modified hydrophilic surface characteristic to support tissue integration of titanium dental implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2009, 88B, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. Underlying mechanisms at the bone-biomaterial interface. J. Cell Biochem. 1994, 56, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemo, B.; Lausmaa, J. Biomaterial and implant surface—On the role of cleanliness, contamination, and preparation procedures. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 1988, 22, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.Y.; Dean, D.D.; Chran, D.L.; Simpson, J.; Boyan, B.D.; Schwarz, Z. Proliferation, differentiation, and protein synthesis of human osteoblast-like cells (MG63) cultured on previously used titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1996, 7, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Gutsol, A.; Shekhter, A.B.; Vasilets, V.N.; Fridman, A. Applied plasma medicine. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, K.; Finke, B.; Ohl, A.; Lüthen, F.; Bergemann, C.; Nebe, B.; Rychly, J.; Walschus, U.; Schlosser, M.; Liefeith, K.; et al. Capability of differently charged plasma polymer coatings for control of tissue interactions with titanium surfaces. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Finke, B.; Luthen, F.; Jesswein, H.; Ihrke, R.; Ohl, A.; Weltmann, K.D.; Diener, A.; Rychly, J.; Nebe, J.B. Similarities between plasma amino functionalized PEEK and titanium surfaces concerning enhancement of osteoblast cell adhesion. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 905–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, K.; Finke, B.; Polak, M.; Lüthen, F.; Nebe, B.; Rychly, J.; Bader, R.; Lukowski, G.; Walschus, U.; Schlosser, M.; et al. Gas-discharge plasma-assisted functionalization of titanium implant surfaces. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2010, 638–642, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettlich, H.J.; Otterbach, F.; Mittermayer, C.; Kaufmann, R.; Klee, D. Plasma-induced surface modifications on suicone intraocular lenses: Chemical analysis and in vitro characterization. Biomaterials 1991, 12, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.W.K.; Chan, R.Y.L.; Lam, K.O.; Wu, S.L.; Liu, X.M.; Chung, C.Y.; Paul, K.; Chu, W.; Lu, W.; Chan, D.; et al. In vitro and in vivo characterization of novel plasma treated nickel titanium shape memory alloy for orthopedic implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, P.L., Jr.; Cobb, C.M.; French, A.A.; Love, J.W.; Drisko, C.L.; Killoy, W.J. Effects of an air-powder abrasive system on plasma-sprayed titanium implant surfaces: An in vitro evaluation. J. Oral Implantol. 1989, 15, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Le, L.; Guehennec, A.; Soueidan, P.; Layrolle, Y.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffels, E.; FLikweert, A.J.; Stoffels, W.W.; Kroesen, G.M.W. Plasma needle: A non-destructive atmospheric plasma source for fine surface treatment of (bio)materials. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2002, 11, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, A.; Chirokov, A.; Gutsol, A. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure discharges. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, R1–R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Lawless, P.A.; Yamamoto, T. Corona discharge processes. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1991, 19, 1152–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellakhal, N.; Draou, K.; Brisset, J.L. Electrochemical investigation of copper oxide films formed by oxygen plasma treatment. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1997, 27, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernichowski, A. Gliding arc. Applications to engineering and environmental control. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschke, M. Piezoelectric Low Voltage Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Sources. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2009, 49, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.J.; David, B.G. Piezoelectric transformers for low-voltage generation of gas discharges and ionic winds in atmospheric air. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 243–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, F.; Scheideler, L.; Olshanska, N.; de Wild, M.; Wieldan, M.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Enhancing surface free energy and hydrophilicity through chemical modification of microstructured titanium implant surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 76, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Schwarz, Z.; Wieland, M.; Rupp, F.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Cochran, D.L.; Boyan, B.D. High surface energy enhances cell response to titanium substrate microstructure. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2005, 74A, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.K.; Chen, J.Y.; Wang, L.P.; Huang, N. Plasma-surface modification of biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2002, 36, 143–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiewetter, K.; Schwartz, Z.; Hummert, T.W.; Cochran, D.L.; Simson, J.; Dean, D.D.; Boyan, B.D. Surface roughness modulates the local production of growth factors and cytokines by osteoblast-like MG-63 cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 32, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimbo, R.; Sawase, T.; Baba, K.; Kurogi, T.; Shibata, Y.; Atsuta, M. Enhanced initial cell responses to chemically modified anodized titanium. Clin. Implant Dent. Rel. Res. 2008, 10, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foest, R.; Kindel, E.; Ohl, A.; Stieber, M.; Weltmann, K.M. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure discharges for surface modification. Plasma Phys. Contr. Fusion 2005, 47, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duske, K.; Koban, I.; Kindel, E. Atmospheric plasma enhances wettability and cell spreading on dental implant metals. J. Clin. Periodont. 2012, 39, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.; Granato, R.; Suzuki, M. Biomechanical and histomorphometric analysis of etched and non-etched resorbable blasting media processed implant surfaces: An experimental study in dogs. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 3, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mei, S.; Chu, P.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. The influence of hierarchical hybrid micro/nano-textured titanium surface with titania nanotubes on osteoblast functions. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5072–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roser, M.; Fischer, D.; Kissel, T. Surface-modified biodegradable albumin nano-and microspheres. II: Effect of surface charges on in vitro phagocytosis and biodistribution in rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 46, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, P.; Farrar, D.; Perry, C.C. Interpretation of protein adsorption: Surface-induced conformational changes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8168–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, C.; De Filippis, C.; Jenkins, M.; Tunstell, A.; Rhodes, N.; Williams, D. Albumin-binding surfaces: In vitro activity. J. Biomater. Sci. 1998, 9, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, C.; Schneider, G.B.; Zaharias, R.; Seabold, D.; Stanford, C. Effects of implant surface microtopography on osteoblast gene expression. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).