White-Matter Connectivity and General Movements in Infants with Perinatal Brain Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
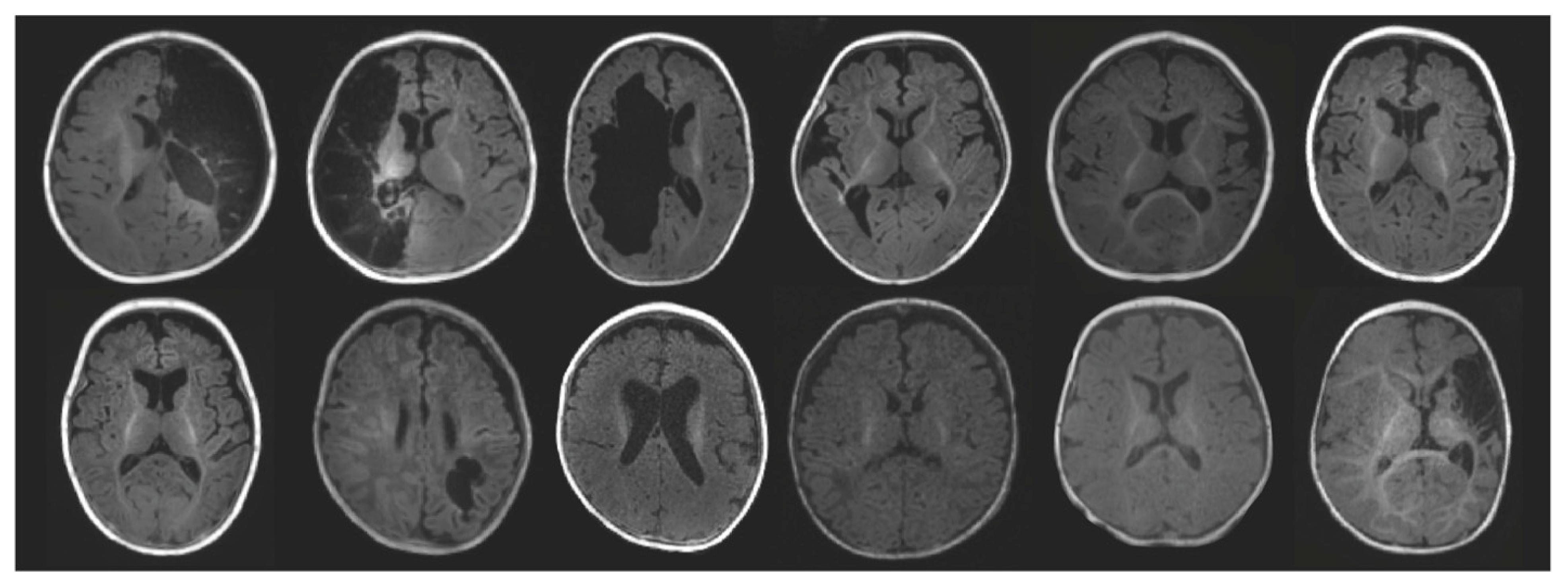
2.1. Participants
2.2. General Movements Assessment
2.3. MRI Acquisition
2.4. MRI Processing and Analysis
2.4.1. Preprocessing
2.4.2. Tractography
2.4.3. TBSS
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Tractography
2.5.2. TBSS
3. Results
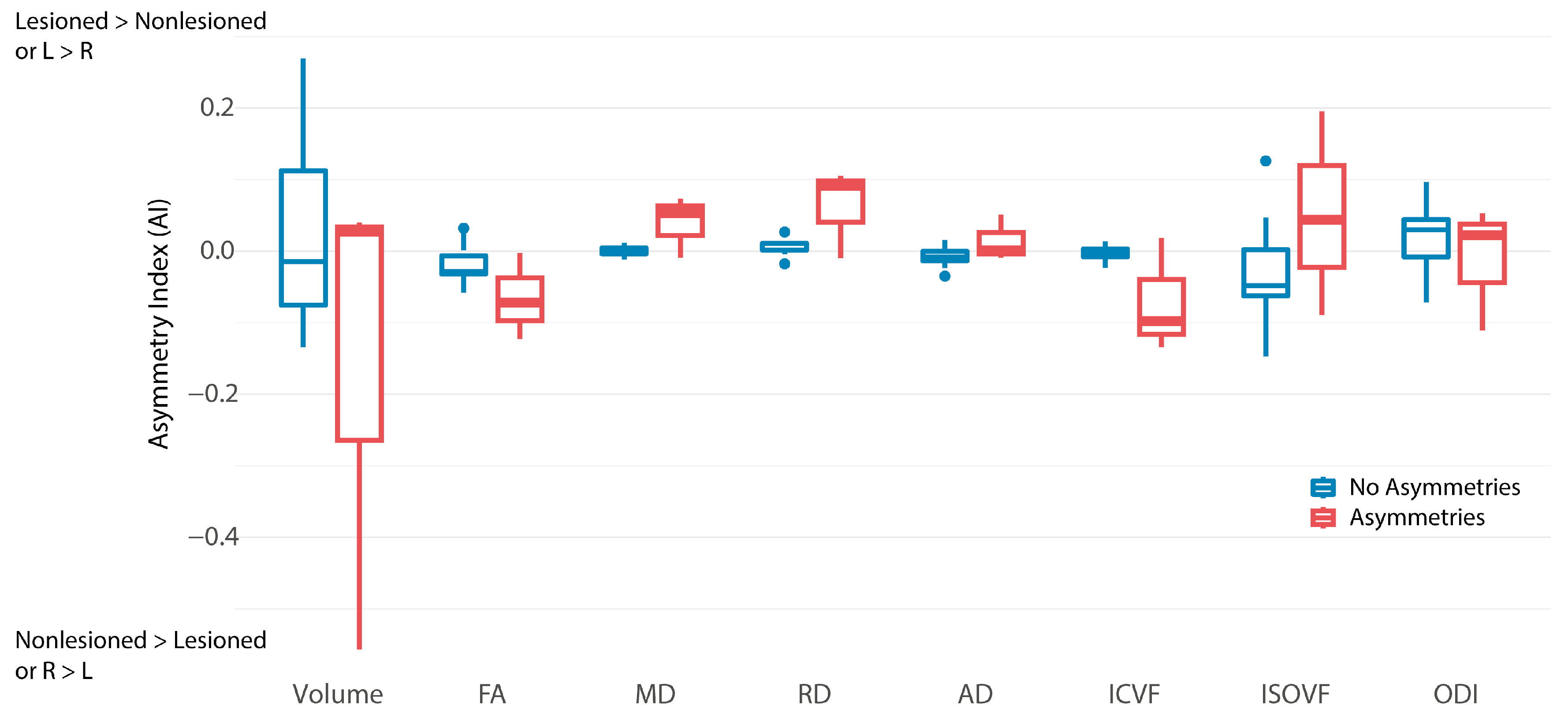
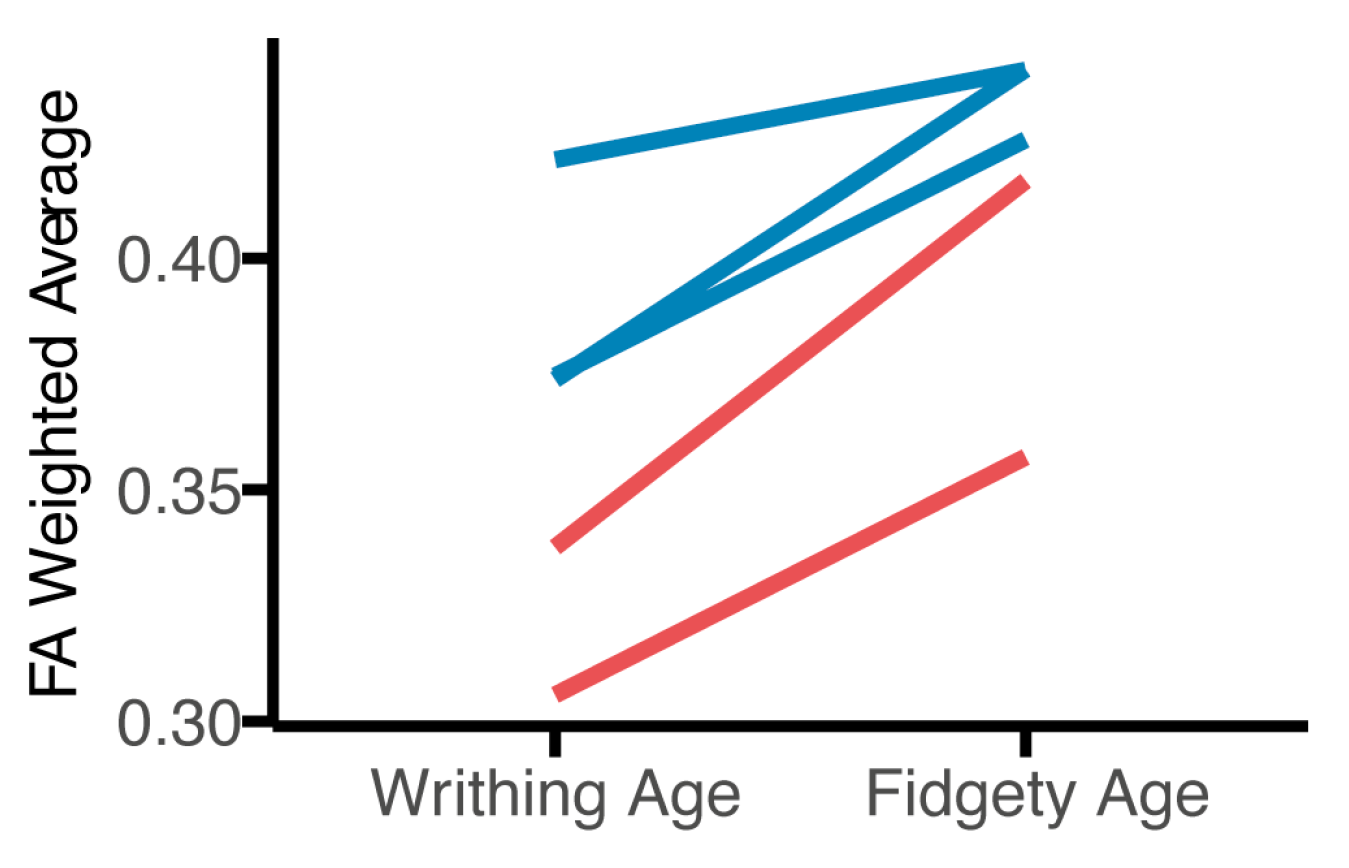
3.1. Tractography
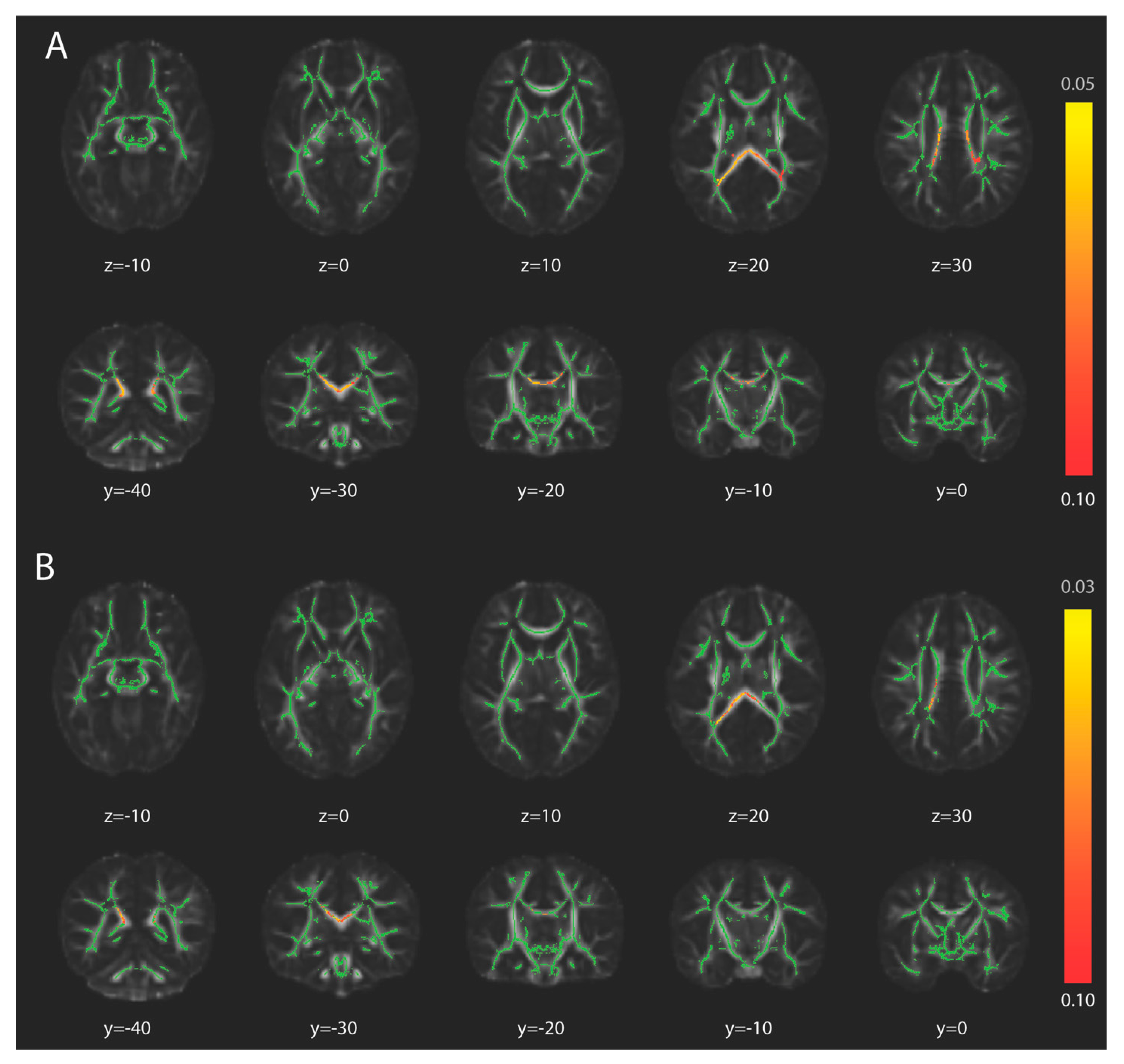
3.2. Tract-Based Spatial Statistics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Dunbar, M.; Kirton, A. Perinatal Stroke. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2019, 32, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herskind, A.; Greisen, G.; Nielsen, J.B. Early identification and intervention in cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2015, 57, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, I.; Morgan, C.; Adde, L.; Blackman, J.; Boyd, R.N.; Brunstrom-Hernandez, J.; Cioni, G.; Damiano, D.; Darrah, J.; Eliasson, A.C.; et al. Early, Accurate Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Cerebral Palsy: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einspieler, C.; Prechtl, H.F. Prechtl’s assessment of general movements: A diagnostic tool for the functional assessment of the young nervous system. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2005, 11, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, A.K.L.; Fitzgerald, T.L.; Doyle, L.W.; Cheong, J.L.Y.; Spittle, A.J. Predictive validity of spontaneous early infant movement for later cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2018, 60, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosanquet, M.; Copeland, L.; Ware, R.; Boyd, R. A systematic review of tests to predict cerebral palsy in young children. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2013, 55, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adde, L.; Rygg, M.; Lossius, K.; Oberg, G.K.; Stoen, R. General movement assessment: Predicting cerebral palsy in clinical practise. Early Hum. Dev. 2007, 83, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechtl, H.F.; Einspieler, C.; Cioni, G.; Bos, A.F.; Ferrari, F.; Sontheimer, D. An early marker for neurological deficits after perinatal brain lesions. Lancet 1997, 349, 1361–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitre, N. Skepticism, cerebral palsy, and the General Movements Assessment. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2018, 60, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einspieler, C.; Bos, A.F.; Krieber-Tomantschger, M.; Alvarado, E.; Barbosa, V.M.; Bertoncelli, N.; Burger, M.; Chorna, O.; Del Secco, S.; DeRegnier, R.A.; et al. Cerebral Palsy: Early Markers of Clinical Phenotype and Functional Outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyton, C.; Einspieler, C.; Fjortoft, T.; Adde, L.; Schreiber, M.D.; Drobyshevsky, A.; Marks, J.D. Correlates of Normal and Abnormal General Movements in Infancy and Long-Term Neurodevelopment of Preterm Infants: Insights from Functional Connectivity Studies at Term Equivalence. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzone, L.; Mugno, D.; Mazzone, D. The General Movements in children with Down syndrome. Early Hum. Dev. 2004, 79, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, D.; Einspieler, C.; Panvequio Aizawa, C.Y.; Mutlu, A.; Yang, H.; Nogolova, A.; Pansy, J.; Nielsen-Saines, K.; Marschik, P.B.; Gen, G.M.S.G. The motor repertoire in 3- to 5-month old infants with Down syndrome. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2017, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschik, P.B.; Soloveichick, M.; Windpassinger, C.; Einspieler, C. General movements in genetic disorders: A first look into Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Dev. Neurorehabil. 2015, 18, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einspieler, C.; Bos, A.F.; Libertus, M.E.; Marschik, P.B. The General Movement Assessment Helps Us to Identify Preterm Infants at Risk for Cognitive Dysfunction. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.L.; Lee, J.E.; Lazar, M.; Field, A.S. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics 2007, 4, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basser, P.J.; Pierpaoli, C. Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J. Magn. Reson. B 1996, 111, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Schneider, T.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Alexander, D.C. NODDI: Practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage 2012, 61, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roze, E.; Harris, P.A.; Ball, G.; Elorza, L.Z.; Braga, R.M.; Allsop, J.M.; Merchant, N.; Porter, E.; Arichi, T.; Edwards, A.D.; et al. Tractography of the corticospinal tracts in infants with focal perinatal injury: Comparison with normal controls and to motor development. Neuroradiology 2012, 54, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Aa, N.E.; Leemans, A.; Northington, F.J.; van Straaten, H.L.; van Haastert, I.C.; Groenendaal, F.; Benders, M.J.; de Vries, L.S. Does diffusion tensor imaging-based tractography at 3 months of age contribute to the prediction of motor outcome after perinatal arterial ischemic stroke? Stroke 2011, 42, 3410–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roze, E.; Van Braeckel, K.N.; van der Veere, C.N.; Maathuis, C.G.; Martijn, A.; Bos, A.F. Functional outcome at school age of preterm infants with periventricular hemorrhagic infarction. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Aa, N.E.; Northington, F.J.; Stone, B.S.; Groenendaal, F.; Benders, M.J.; Porro, G.; Yoshida, S.; Mori, S.; de Vries, L.S.; Zhang, J. Quantification of white matter injury following neonatal stroke with serial DTI. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 73, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumberg, M.S.; Adolph, K.E. Protracted development of motor cortex constrains rich interpretations of infant cognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2023, 27, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.H. The corticospinal system: From development to motor control. Neuroscientist 2005, 11, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, J.; Goodyear, B.; Carlson, H.; Wei, X.C.; Kirton, A. Segmental Diffusion Properties of the Corticospinal Tract and Motor Outcome in Hemiparetic Children With Perinatal Stroke. J. Child. Neurol. 2017, 32, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hayakawa, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Okano, S.; Kanda, T.; Yamori, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Hirota, H. Quantitative diffusion tensor tractography of the motor and sensory tract in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2010, 52, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleyenheuft, Y.; Grandin, C.B.; Cosnard, G.; Olivier, E.; Thonnard, J.L. Corticospinal dysgenesis and upper-limb deficits in congenital hemiplegia: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e1502–e1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, A.; Stinear, C.; Stott, S.; Byblow, W.D. Upper limb function and cortical organization in youth with unilateral cerebral palsy. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyton, C.; Yang, E.; Msall, M.E.; Adde, L.; Stoen, R.; Fjortoft, T.; Bos, A.F.; Einspieler, C.; Zhou, Y.; Schreiber, M.D.; et al. White Matter Injury and General Movements in High-Risk Preterm Infants. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Rueckert, D.; Nichols, T.E.; Mackay, C.E.; Watkins, K.E.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cader, M.Z.; Matthews, P.M.; et al. Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1487–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiote, C.; Sutter, E.; Xenopoulos-Oddsson, A.; Rao, R.; Georgieff, M.; Rudser, K.; Peyton, C.; Dean, D.; McAdams, R.M.; Gillick, B. Study Protocol: Multimodal Longitudinal Assessment of Infant Brain Organization and Recovery in Perinatal Brain Injury. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2022, 34, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einspieler, C.; Prechtl, H.F.; Ferrari, F.; Cioni, G.; Bos, A.F. The qualitative assessment of general movements in preterm, term and young infants—Review of the methodology. Early Hum. Dev. 1997, 50, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kecskemeti, S.; Samsonov, A.; Hurley, S.A.; Dean, D.C.; Field, A.; Alexander, A.L. MPnRAGE: A technique to simultaneously acquire hundreds of differently contrasted MPRAGE images with applications to quantitative T1 mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 1040–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kecskemeti, S.; Samsonov, A.; Velikina, J.; Field, A.S.; Turski, P.; Rowley, H.; Lainhart, J.E.; Alexander, A.L. Robust Motion Correction Strategy for Structural MRI in Unsedated Children Demonstrated with Three-dimensional Radial MPnRAGE. Radiology 2018, 289, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.L.; Skare, S.; Ashburner, J. How to correct susceptibility distortions in spin-echo echo-planar images: Application to diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 870–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraart, J.; Novikov, D.S.; Christiaens, D.; Ades-Aron, B.; Sijbers, J.; Fieremans, E. Denoising of diffusion MRI using random matrix theory. Neuroimage 2016, 142, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellner, E.; Dhital, B.; Kiselev, V.G.; Reisert, M. Gibbs-ringing artifact removal based on local subvoxel-shifts. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Sotiropoulos, S.N. An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Graham, M.S.; Zsoldos, E.; Sotiropoulos, S.N. Incorporating outlier detection and replacement into a non-parametric framework for movement and distortion correction of diffusion MR images. Neuroimage 2016, 141, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I.; Flitney, D.E.; et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 2004, 23 (Suppl. S1), S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierpaoli, C.; Walker, L.; Irfanoglu, M.O.; Barnett, A.; Basser, P.; Chang, L.C.; Koay, C.G.; Pajevic, S.; Rohde, G.; Sarlls, J.; et al. TORTOISE: An integrated software package for processing of diffusion MRI data. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 18th Annual Meeting, Stockholm, Sweden, 1–7 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Irfanoglu, M.O.; Nayak, A.; Jenkins, J.; Pierpaoli, C. TORTOISEv3:Improvements and New Features of the NIH Diffusion MRI Processing Pipeline. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 25th Annual Meeting, Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–27 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Garyfallidis, E.; Brett, M.; Amirbekian, B.; Rokem, A.; van der Walt, S.; Descoteaux, M.; Nimmo-Smith, I.; Dipy, C. Dipy, a library for the analysis of diffusion MRI data. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pines, A.R.; Cieslak, M.; Larsen, B.; Baum, G.L.; Cook, P.A.; Adebimpe, A.; Dávila, D.G.; Elliott, M.A.; Jirsaraie, R.; Murtha, K.; et al. Leveraging multi-shell diffusion for studies of brain development in youth and young adulthood. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2020, 43, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, R.H.J.; Wassermann, D.; Deriche, R. The Dmipy Toolbox: Diffusion MRI Multi-Compartment Modeling and Microstructure Recovery Made Easy. Front. Neuroinform. 2019, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournier, J.D.; Smith, R.; Raffelt, D.; Tabbara, R.; Dhollander, T.; Pietsch, M.; Christiaens, D.; Jeurissen, B.; Yeh, C.H.; Connelly, A. MRtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation. Neuroimage 2019, 202, 116137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurissen, B.; Tournier, J.D.; Dhollander, T.; Connelly, A.; Sijbers, J. Multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution for improved analysis of multi-shell diffusion MRI data. Neuroimage 2014, 103, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, J.D.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. Robust determination of the fibre orientation distribution in diffusion MRI: Non-negativity constrained super-resolved spherical deconvolution. Neuroimage 2007, 35, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhollander, T.; Mito, R.; Raffelt, D.; Connelly, A. Improved white matter response function estimation for 3-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 27th Annual Meeting, Montréal, QC, Canada, 11–16 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserthal, J.; Neher, P.; Maier-Hein, K.H. TractSeg—Fast and accurate white matter tract segmentation. Neuroimage 2018, 183, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserthal, J.; Neher, P.F.; Hirjak, D.; Maier-Hein, K.H. Combined tract segmentation and orientation mapping for bundle-specific tractography. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, G.; Janke, A.L.; Budge, M.M.; Smith, D.; Pruessner, J.; Collins, D.L. Symmetric atlasing and model based segmentation: An application to the hippocampus in older adults. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2006, 9, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avants, B.B.; Tustison, N.J.; Song, G.; Cook, P.A.; Klein, A.; Gee, J.C. A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S. A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med. Image Anal. 2001, 5, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Nichols, T.E. Threshold-free cluster enhancement: Addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, J.A. Corticospinal tract development and its plasticity after perinatal injury. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, T.H.; Eyre, J.A. Maturation of corticospinal tracts assessed by electromagnetic stimulation of the motor cortex. Arch. Dis. Child. 1988, 63, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, J.A.; Smith, M.; Dabydeen, L.; Clowry, G.J.; Petacchi, E.; Battini, R.; Guzzetta, A.; Cioni, G. Is hemiplegic cerebral palsy equivalent to amblyopia of the corticospinal system? Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemanich, S.T.; Mueller, B.A.; Gillick, B.T. Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging quantifies corticospinal tract microstructural organization in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 4888–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.M.; Vandewouw, M.M.; Mossad, S.I.; Morgan, B.R.; Lee, W.; Smith, M.L.; Sled, J.G.; Taylor, M.J. White matter microstructural differences identified using multi-shell diffusion imaging in six-year-old children born very preterm. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 23, 101855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.E.; Thompson, D.K.; Chen, J.; Leemans, A.; Adamson, C.L.; Inder, T.E.; Cheong, J.L.; Doyle, L.W.; Anderson, P.J. Axon density and axon orientation dispersion in children born preterm. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 3080–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacaru, C.; Braimah, A.; Kline-Fath, B.; Parikh, N.; Merhar, S. Diffusion Tensor Imaging to Predict Neurodevelopmental Impairment in Infants after Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury. Am. J. Perinatol. 2024, 41, e1740–e1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, M.V.; Weber, P.D.; Felderhoff-Mueser, U.; Huening, B.M.; Dathe, A.K. A Simple MRI Score Predicts Pathological General Movements in Very Preterm Infants with Brain Injury-Retrospective Cohort Study. Children 2024, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadders-Algra, M. Neural substrate and clinical significance of general movements: An update. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2018, 60, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanold, P.O. Subplate neurons: Crucial regulators of cortical development and plasticity. Front. Neuroanat. 2009, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruen, J.; Bauer, T.; Rüber, T.; Schultz, T. Deep learning based tractography with TractSeg in patients with hemispherotomy: Evaluation and refinement. NeuroImage Clin. 2025, 45, 103738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, K.; Kline, J.E.; Altaye, M.; Kline-Fath, B.M.; Parikh, N.A.; Cincinnati Infant Neurodevelopment Early Prediction Study, I. Corpus Callosum Abnormalities at Term-Equivalent Age Are Associated with Language Development at 2 Years’ Corrected Age in Infants Born Very Preterm. J. Pediatr. Clin. Pract. 2024, 11, 200101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshe, Y.H.; Ben Bashat, D.; Hananis, Z.; Teicher, M.; Artzi, M. Utilizing the TractSeg Tool for Automatic Corticospinal Tract Segmentation in Patients with Brain Pathology. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 21, 15330338221131387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Infants with Perinatal Brain Injury (N = 12) | |
|---|---|
| Sex | 3F, 9M |
| Primary Diagnosis | |
| Ischemic or hemorrhagic perinatal stroke | 6 |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage | 2 |
| PVL | 1 |
| HIE | 3 |
| Lesioned Hemisphere | |
| Left | 4 |
| Right | 4 |
| Bilateral | 4 |
| Preterm/Writhing GMA (N = 5) | |
| Age at Writhing scan, weeks (mean (range)) | 7.4 (5.4–8.4) |
| Age at GMA, weeks post-term (mean (range)) * | 2.8 (−3.7, 5.7) |
| Normal | 0 |
| Poor Repertoire | 5 |
| Cramped-Synchronized | 0 |
| Chaotic | 0 |
| Fidgety GMA (N = 12) | |
| Age at Fidgety scan, weeks (mean (range)) | 19.2 (13.4–29.4) |
| Age at GMA, weeks post-term (mean (range)) * | 15.5 (12.2–18.1) |
| Normal Fidgety | 4 |
| Absent Fidgety | 8 |
| Abnormal Fidgety | 0 |
| Motor Optimality Score (median, range) | (9.5, 7–24) |
| Typically Developing Infants (N = 5) | |
| Sex | 1F, 4M |
| Age at scan–weeks (mean (range)) | 13.7 (6.7–17.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sutter, E.N.; Guerrero-Gonzalez, J.; Casey, C.P.; Dean, D.C., III; de Abreu e Gouvea, A.; Peyton, C.; McAdams, R.M.; Gillick, B.T. White-Matter Connectivity and General Movements in Infants with Perinatal Brain Injury. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040341
Sutter EN, Guerrero-Gonzalez J, Casey CP, Dean DC III, de Abreu e Gouvea A, Peyton C, McAdams RM, Gillick BT. White-Matter Connectivity and General Movements in Infants with Perinatal Brain Injury. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(4):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040341
Chicago/Turabian StyleSutter, Ellen N., Jose Guerrero-Gonzalez, Cameron P. Casey, Douglas C. Dean, III, Andrea de Abreu e Gouvea, Colleen Peyton, Ryan M. McAdams, and Bernadette T. Gillick. 2025. "White-Matter Connectivity and General Movements in Infants with Perinatal Brain Injury" Brain Sciences 15, no. 4: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040341
APA StyleSutter, E. N., Guerrero-Gonzalez, J., Casey, C. P., Dean, D. C., III, de Abreu e Gouvea, A., Peyton, C., McAdams, R. M., & Gillick, B. T. (2025). White-Matter Connectivity and General Movements in Infants with Perinatal Brain Injury. Brain Sciences, 15(4), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040341





