Abstract
Background: In this study, we surveyed the prevalence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen (HBsAg) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody (anti-HCV) among inpatients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and analyzed the correlated factors. Methods: We conducted a retrospective data collection of the HIV-infected inpatients in our hospital from January 2010 to December 2020. We utilized multivariate logistic regression to identify the correlated factors. Results: The proportion of patients screened for HBsAg was 81.8%, which increased from 66.7% in 2010 to 85.7% in 2020. The proportion of patients with anti-HCV screening was 73.9%, which increased from 58.3% in 2010 to 86.7% in 2020. The prevalence of HBsAg positivity was 10.9%, which decreased from 15.0% in the period of 2010–2015 to 9.0% during 2016–2020. Positive anti-HCV was identified in 4.1% of cases. Compared to 4.8% in the period of 2010–2015, there was a similar prevalence of anti-HCV at 3.1% during 2016–2020. Among the HBsAg-positive cases, HBV deoxyribonucleic acid was screened in 70.8% of cases. Among the anti-HCV positive cases, HCV ribonucleic acid (RNA) was screened in 90% of cases. Albumin < 30 g/L, thrombocytopenia and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > 40 U/L were associated with HBsAg positivity. AST > 40 U/L and higher CD4-positive T lymphocyte counts were associated with HIV/HCV coinfection. Conclusions: The routine screening for both HBV and HCV among HIV-positive inpatients has been greatly improved in the past decade. However, screening for the complete HBV serological markers in HIV-positive inpatients and HCV genotyping among HCV RNA-positive cases leaves much to be desired. A concerted effort should be made to improve HBV vaccine compliance in the HIV-positive population and provide direct-acting antiviral therapies to HCV RNA-positive patients.
1. Introduction
In the past 30 years, China has successfully reduced the hepatitis B virus (HBV) endemicity from high to intermediate through HBV vaccination. However, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/HBV coinfection remains an urgent concern, because most of the current HIV-positive individuals were predominantly born before the time of routine HBV immunization in China. Compared to an HBV infection chronicity rate of less than 5% among HIV-negative adults, there was a more than 10% chronicity among HIV-positive adults [1,2]. Spontaneous acute hepatitis C virus (HCV) resolution was observed in only 14.4–23% of infections in HIV-positive patients [3,4]. Patients with HBV or HCV coinfection were susceptible to liver damage [5,6]. Compared with HIV-mono-infected patients, HBV- or HCV-coinfected patients had an accelerated progression of cirrhosis and higher liver-related death and all-cause death rates [7,8]. A poorer increase in the CD4-positive T lymphocyte (CD4+T) cell count after antiretroviral therapy (ART) was found among HBV/HIV-coinfected patients [9]. Among the HIV seropositive population, the prevalence of HBV or HCV infection was higher than in the HIV-negative population [10,11]. The percentage of HBV coinfection was 20–30% in sub-Saharan Africa and Asia, while it was only 5–10% in North America, Europe and Australia [12]. The HBV co-infection rate was higher in southern China (14.18%) and western China (10.73%), while it was lower in northern China (6.36%) [13]. The prevalence of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) was higher among individuals aged ≥40 years than individuals aged ≤40 years [14]. There was a moderate HBV coinfection decrease in China in 2015 compared to 2007 [15]. In recent years, a distinct decrease in the hepatitis C virus antibody (anti-HCV) in the HIV-positive population was observed [14,15]. Intravenous drug users (IVDUs) and men who have sex with men (MSM) had a high prevalence of HCV/HIV coinfection [4,16]. Among HIV-positive individuals with African ancestry in the United Kingdom, the prevalence of anti-HCV and HCV ribonucleic acid (RNA) were 1.3% and 0.17%, respectively [17]. The prevalence of HCV/HIV coinfection was 29.6% in Nepal [16]. Importantly, the practice of HBsAg testing among the HIV-positive population showed notable regional differences, with only 0.7% in Kenya compared to 96.0% in South Africa [18]. Although HBV and HCV are routinely tested for when starting ART in China, they are not routinely tested for among HIV-positive inpatients. Among HIV/HBV-coinfected patients undergoing ART, the seroconversion and reappearance of HBsAg or hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg) were frequently observed [19,20]. The reactivation incidence of a former HBV infection [21] and the HBV incidence were observed among followed-up individuals receiving HIV care [22]. The recently acquired HCV infection (RAHC) incidence was also found among MSM with HIV [23,24]. The routine examination for HCV infection among inpatients was recommended [25]. In order to achieve the global strategy aiming to eliminate HBV and HCV by 2030 [26], we conducted a retrospective study of the screening for HBV and HCV infection among HIV-positive inpatients and evaluated the correlated characteristics.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
We retrospectively collected the records of HIV-positive inpatients at the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University (a tertiary hospital with 3933 beds in Shenyang, Liaoning, China) from 1 January 2010 to 31 December 2020. The Clinical Research Ethics Committee of China Medical University approved this study.
2.2. Study Design
Clinical and laboratory data were acquired from the cases’ medical records, which were implemented by three authors simultaneously. We analyzed the trend of the screening rates for HBsAg and anti-HCV among the inpatients. We also described the distribution modes of the HBV serological markers among the cases with complete serological results. We reported the data of HBV deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) detection for the HBsAg-positive samples, HCV RNA detection among the anti-HCV positive cases, and HCV genotyping among the cases with positive HCV RNA. We analyzed the factors that might be categorical variables of HBsAg and HCV/HIV co-infection, including the following: age; sex; education level; local residence in Shenyang (or not); body mass index (BMI); World Health Organization (WHO) HIV clinical stage classification; death during hospitalization (or not); ART status before admission; CD4+T cell count; hemoglobin (HB); platelet (PLT) count; glutamic alanine transaminase (ALT); aspartate aminotransferase (AST); alkaline phosphatase (ALP); gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT); total bilirubin (TBIL); serum albumin (ALB); serum creatinine (Scr); prothrombin time (PT); and serum sodium concentration.
2.3. Definitions
The complete HBV serological markers consisted of HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb), HBeAg, hepatitis B e antibody (HBeAb), and hepatitis B core antibody (HBcAb), which were quantified by a chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) using an “Alinity” instrument (Abbott Laboratories, Lake Forest, IL, USA). The isolated HBsAb was defined as positive HBsAb with negative HBsAg, HBeAg, HBeAb, and HBcAb. The isolated HBcAb was defined as positive HBcAb with negative HBsAg and HBsAb. HCV coinfection was defined as HIV positivity in individuals with both positive anti-HCV and positive HCV RNA. Thrombocytopenia was defined as a platelet count of less than 100,000/μL. Abdominal ultrasound examination or computed tomography scans were the diagnostic procedures used to assess liver cirrhosis or fatty liver disease. Alcohol consumption was defined as patients who drank more than 40 g (20 g for female patients) of alcohol per day for more than 5 years.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The data were illustrated as numbers and percentages. We compared the conditions between the HBsAg-positive patients and HBsAg-negative patients and between the HIV/HCV-coinfected patients and HIV-mono-infected patients, respectively. The proportions of the categorical variables were compared using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression models were employed to assess the factors associated with HIV/HBV coinfection and HIV/HCV coinfection, respectively. The odds ratios (OR), adjusted odds ratios (AOR), and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were displayed. Variables with p < 0.10 in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate logistic models. Only variables with p < 0.05 were retained in the final multivariate models. The data were analyzed using the SPSS software for Windows version 22.0 (Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
3.1. The Prevalence of Screening for HBsAg and Anti-HCV among Inpatients with HIV Infection
In total, 1002 hospitalized HIV-infected cases were enrolled in this study, including 916 men (91.4%) and 86 women (8.6%) (Supplementary Table S1). There were 489 (48.8%) cases representing Shenyang local residents and 513 (51.2%) patients from different cities around Shenyang. The median age was 39 years (range: 8–86 years). HIV was sexually transmitted in 881 patients (88.0%), and 541 patients (54.0%) were MSM. The causes of hospital admission in 662 cases (66.1%) were AIDS-related illnesses (at WHO clinical stages III–IV). There were 766 cases (76.4%) whose CD4+T count was <200 cells/µL. There were 325 patients (32.4%) who received ART prior to admission. A total of 248 patients had underlying medical conditions, including hyperlipemia (146 patients), hypertension (62 patients), and diabetes (57 patients). There were 62 cases with alcohol consumption history and 81 cases with fatty livers. All HIV-positive inpatients were Chinese, with Han nationality accounting for 84.5% and other ethnic groups accounting for 15.5%. The HIV inpatients came from our own HIV care clinic and different cities around Shenyang. There were 51 cases who died during hospitalization. Here, we provide a table (Supplementary Table S2) comparing all the data between the sex groups. The results showed that there was no difference in the positivity for HBsAg, the positivity for anti-HCV, and hospitalization mortality between the male and female HIV-positive inpatients.
The proportion of patients screened for HBsAg was 81.8% (820/1002), which increased from 66.7% in 2010 to 85.7% in 2020 overall (p = 0.045) (Figure 1). Among the 820 individuals tested, 89 (10.9%) cases were HBsAg-positive, and 37.1% (33/89) of these patients were aware of their HBV-infected condition before hospitalization. The HBsAg prevalence was 12.5% (52/415) in the 30–50-year age group and 11.6% (20/172) in the <30-year age group, while it was only 7.3% (17/233) in the >50-year age group (p > 0.05). For the HBsAg-positive samples, HBV DNA was detected in 70.8% (63/89) of cases, including 46 cases with HBV DNA beyond 10,000 IU/mL, 13 cases with between 100 IU/mL and 10,000 IU/mL, and 4 cases with under 100 IU/mL. Compared to the 15.0% prevalence of HBsAg in the period of 2010–2015, there was a moderate decrease to 9.0% during the 2016–2020 period (p = 0.01). At discharge, 95.5% (85/89) of the HBsAg-positive cases received ART containing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) or tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) (Figure 2).
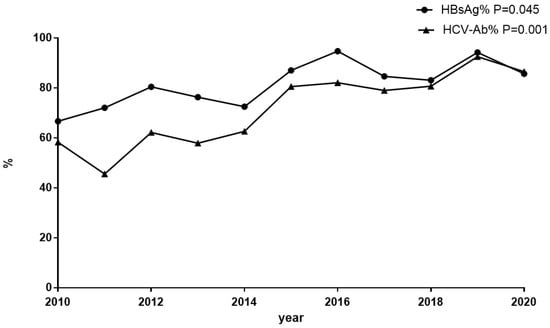
Figure 1.
Trend analysis based on a linear-by-linear association test for the screening proportions of HBsAg and anti-HCV. The screening proportions of HBsAg and anti-HCV showed an ascending trend among the HIV-positive inpatients in the past several years. HBsAg: the screening proportion of HBsAg among HIV-positive inpatients. HCV-Ab: the screening proportion of anti-HCV among HIV-positive in patients.
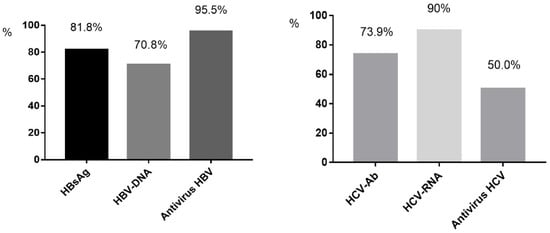
Figure 2.
The proportion of HIV-positive inpatients accepting screening and anti-virus treatment. HBsAg: the screening proportion of HBsAg among HIV-positive inpatients. HCV-Ab: the screening proportion of anti-HCV among HIV-positive in patients. HBV-DNA: the screening proportion of HBV-DNA among HBV/HIV co- infected inpatients. HCV-RNA: the screening proportion of HCV-RNA among anti-HCV- positive inpatients with HIV infection. Antivirus HBV: the proportion of anti- HBV treatment among HBV/HIV co- infected patients. Antivirus HCV: the proportion of anti-HCV treatment among HCV/HIV co-infected inpatients.
The percentage of patients screened for anti-HCV was 73.9% (740/1002), which increased from 58.3% in 2010 to 86.6% in 2020 overall (p = 0.001) (Figure 1). Positive anti-HCV was found in 4.1% (30/740) of cases. The positive anti-HCV prevalence was 5.5% (11/201) in the >50-year age group and 4.4% (16/362) in the 30–50-year age group, while it was only 1.9% (3/161) in the <30-year age group (p > 0.05). Compared to 4.8% in the period of 2010–2015, there was a similar 3.1% prevalence of anti-HCV during 2016–2020 (p > 0.05). Of the anti-HCV-positive cases, HCV RNA was detected in 90.0% (27/30), and nine of these tested negative for HCV RNA. Among 18 cases with positive HCV RNA (HIV/HCV coinfection), 4 cases were tested for genotypes. At discharge, 50% (9/18) of the HCV RNA-positive cases received anti-HCV therapy (Figure 2). No patients had HCV/HBV/HIV tri-infection.
3.2. Distribution of HBV Serological Markers among Cases with Complete Serological Results
There were 487 cases with complete HBV serological markers, and 47 cases (9.7%) were HBsAg-positive. Among the 47 HBsAg-positive cases, 48.9% (23/47) of cases were HBeAg-positive. Isolated HBsAb positivity among the inpatients with HIV infection was 26.5% (129/487). The highest isolated HBsAb prevalence was 40.6% (43/106) in the <30-year age group. The lowest isolated HBsAb prevalence was 16.2% (24/148) in the >50-year age group. Among the 440 HBsAg-negative cases, 43.9% (193/440) of cases were HBcAb-positive, including 92 cases with isolated HBcAb. The rate of negative results for all the HBV serological tests among the inpatients with HIV infection was 24.2% (118/487) (Table 1).

Table 1.
The distribution of different modes of HBV serological markers among HIV-positive inpatients.
3.3. Clinical Characteristics at Baseline among HIV/HBV-Coinfected Patients
Among the HBsAg-positive participants, 11.2% (10/89) of cases had cirrhosis (4 cases of Child–Pugh class B and 6 cases of Child–Pugh class C). Compared with the patients with HIV monoinfection, the cases with HBV coinfection were more likely to have thrombocytopenia (p = 0.001), ALB < 30 g/L (p = 0.036), ALT > 50 U/L (p = 0.038), AST > 40 U/L (p = 0.001), ALP > 100 U/L (p = 0.002), and PT > 13.7 S (p = 0.003) (Table 2). The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that thrombocytopenia (p = 0.001), ALB < 30g/L (p = 0.024), and AST > 40 U/L (p = 0.004) were characteristic of the HBsAg-positive cases (Table 3).

Table 2.
The baseline clinical features of HBV/HIV- or HCV/HIV-coinfected inpatients.

Table 3.
Factors associated with HBV or HCV coinfection in HIV-positive inpatients.
3.4. Clinical Characteristics at Baseline among HIV/HCV-Coinfected Patients
Among the 18 HIV/HCV-coinfected patients, two cases had cirrhosis of Child–Pugh class A, and 55.6% (10/18) of the patients were aware of their HCV-infected status before hospitalization. Compared with the patients with HIV monoinfection, the patients with HCV coinfection were more likely to present with ALT > 50 U/L (p = 0.018), AST > 40 U/L (p < 0.022), ALP > 100 U/L (p = 0.014), and an age of < 30 years (p = 0.047), while they were less likely to have CD4+T counts of <200 cells/µL (p = 0.001) (Table 2). The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that AST > 40 U/L (p = 0.013) and higher CD4+T counts (p = 0.001) were characteristics of the HCV RNA-positive cases (Table 3).
4. Discussion
The screening for both HBV and HCV among HIV-positive inpatients at our hospital has greatly improved in the past decade, but it still falls short of the 2030 target of the diagnosis of viral hepatitis B and C in 90% of cases [26]. As one of the populations most affected by HBV and HCV infection, testing for HBV and HCV in the HIV-positive population was recommended [26]. The practice of HBsAg testing among the HIV population varies widely across countries, remaining below 50% in most countries across sub-Saharan Africa [18]. Although we observed that HBsAg screening has increased considerably over time, the screening for the complete HBV serological markers leaves much room for improvement, which is considered as the optimal HBV screening strategy for China within the next 10 years [27].
The HBsAg-positive rate was 10.9% in this study, which is higher than the 6.1–7.43% rate among the general population [28,29]. In this study, no statistically relevant age difference in the HBsAg prevalence was found, whereas the highest HBsAg prevalence was previously reported in patients who were 41–50 years old [28]. Isolated HBsAb positivity in this study was 26.5%, which was higher than the rate of 7.7% in the HIV-positive population [30] and similar to the rate of 27% in the general population [28,31].
Considering the high prevalence of occult hepatitis B in HIV-positive patients [32], detecting HBV DNA is necessary, especially for the HBsAg-negative patients with positive HBcAb [33]. There is a higher HBV DNA load and HBeAg percentage among coinfected individuals compared to HBV-mono-infected cases [34]. The prevalence of HBeAg among the HBsAg-positive cases in this study was 48.9%, which was previously reported as ranging from 24.4% to 48.5% in the HIV-positive population [34,35] and higher than the rate of 31.04% in the general population [28].
The prevalence of isolated HBcAb can be high in HCV- or HIV-infected patients and other types of immunocompromised patients. Isolated HBcAb positivity rate was 18.9% in this study, which is within the previously reported range of 7% to 40%. Thrombocytopenia, ALB < 30 g/L, and AST > 40 U/L were the correlated characteristics of HBsAg positivity in this study. Higher ALT levels and lower PLT counts were correlated with advanced fibrosis among HIV/HBV-coinfected patients [36]. The PT and international normalized ratios were reported to be significantly high among coinfected individuals [34]. HIV/HBV-coinfected patients are associated with lower CD4+T cell counts [37]. HBV/HIV coinfection, especially in cases with low nadir CD4+T cell counts, is associated with increased liver disease progression and liver-related mortality [38].
In this study, we observed that anti-HCV screening has increased considerably over time, a finding analogous to that of a previous report [25]. The rate of anti-HCV positivity was only 4.1% in this study, which is higher than the rate of 0.88–3.0% in the general population [26,29]. Most of the HIV-positive cases in our study were due to sexual transmission and had a lower HCV infection rate than IVDUs and former plasma donors. Screening for anti-HCV alone among HIV-infected patients was not enough. In total, 90% of anti-HCV-positive cases were screened for HCV RNA in this study, while HCV genotyping leaves much to be desired. Moreover, we should also pay attention to the high rate of occult hepatitis C in HIV-positive patients with IVDU [39]. Higher AST levels and higher CD4+T cell counts were found among the HIV/HCV-coinfected inpatients, because the abnormal liver tests were the main cause of hospital admission for a number of HIV/HCV-coinfected patients. An AST >40 IU/L was correlated with HCV co-infection [40]. An age >35 years, alcohol abuse, and a decrease in the CD4 cell count were identified as risk factors for fibrosis progression in HIV/HCV-coinfected patients [41]. Persistently normal aminotransferases in HIV/HCV-coinfected patients undergoing antiretroviral therapy only show minimal liver cirrhosis development [42]. Furthermore, the improvements in anti-HCV and HIV testing among general outpatients and inpatients resulted in the earlier discovery of HIV/HCV-coinfected cases.
The limitations of our study were the small sample size and the lack of follow-up detection. Therefore, the HBV or HCV incidence rates were not obtained during long-term follow-up. Additionally, we only enrolled inpatients at our hospital, which allowed us to collect detailed information from their medical records. This study highlighted the necessity of the frequent monitoring of complete HBV serum markers and HBV DNA among the HIV-positive population. Despite being on ART including lamivudine and tenofovir, HBV viremia was still found in 28.6% of HIV/HBV-coinfected patients [43]. Although the immunogenicity of the HBV vaccination in HIV-infected patients is inferior to that among the HIV-seronegative population, this could be notably improved by a double dose of the HBV vaccine [44]. Among cases with isolated HBcAb, monitoring and vaccination should also be recommended [45,46]. Indeed, poor vaccine compliance was identified among the HIV-infected population, which was associated with a lack of insurance coverage and low educational level [47]. For the anti-HCV-positive cases, HCV RNA and HCV genotyping should be recommended. The Direct acting antiviral agents (DAA) achieved an identical efficacy between patients with HCV monoinfection and patients with HIV/HCV coinfection.
5. Conclusions
The viral hepatitis epidemic in HIV-positive populations continues to be a concern. The feasible practice recommendations include the integration of screening for HBV or HCV serological markers with routine physical examinations, professional training of healthcare workers, education of the general population, budgeting of the Chinese health-care system, and expansion of the mechanism of linkage-to-care [48]. HBV vaccination is recommended for people living with HIV for preventing horizontal transmission of HBV. It is crucial to keep TDF or TAF in the anti-HIV regimen among HIV/HBV coinfected cases, even in those with a clinically cured HBV infection. Importantly, optimizing the provision of DAA to HIV/HCV coinfected patients, monitoring for the recurrence and reinfection of HCV, and tracking RAHC incidence may eliminate some of the barriers to achieving HCV eradication.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm11226620/s1, Table S1: The demographic and clinical features of HIV-positive inpatients; Table S2: Comparison of the baseline clinical features between male inpatients and female inpatients with HIV infection.
Author Contributions
C.L., Y.W. (Ying Wen) and S.L. were responsible for the data collection, statistical analysis, and article revision. Y.Z., Y.W. (Yu Wang), W.W., X.L., C.S. and P.L. participated in the clinical diagnosis and treatment. Y.W. (Ying Wen) took part in the design, writing, and revision of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the “double first-class” university and discipline construction funds of China Medical University (3110119068 to Ying Wen). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection, or analysis.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by The Clinical Research Ethics Committee of China Medical University (protocol code2019-235-2 and date of approval 23 October 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request to the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their sincere thanks to all the participants of the study. The authors also thank Qing Hai Hu from the Key Laboratory of AIDS Immunology of the Ministry of Health and Department of Laboratory Medicine in the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University for the statistical assistance received.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| HBsAg | hepatitis B surface antigen |
| anti-HCV | hepatitis C virus antibody |
| HBV | hepatitis B virus |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HCV | hepatitis C virus |
| IVDUs | intravenous drug user |
| MSM | men who have sex with men |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| ART | antiretroviral therapy |
| HBeAg | hepatitis B e-antigen |
| RAHC | recently acquired HCV infection |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| BMI | body mass index |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| HB | hemoglobin |
| PLT | platelet |
| ALT | glutamic alanine transaminase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| GGT, | gamma-glutamyltransferase |
| TBIL | total bilirubin |
| ALB | albumin |
| Scr | serum creatinine |
| PT | prothrombin time |
| HBsAb | hepatitis B surface antibody |
| HBeAb | hepatitis B e antibody |
| HBcAb | hepatitis B core antibody |
| CLIA | chemiluminescence immunoassay |
| OR | odds ratios |
| AOR | adjusted odds ratios |
| CI | confidence intervals |
| OBI | occult hepatitis B |
| OCI | occult hepatitis C |
| TDF | tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
| TAF | tenofovir alafenamide |
| DAAs | direct-acting antiviral therapies |
References
- Shahriar, S.; Araf, Y.; Ahmad, R.; Kattel, P.; Sah, G.S.; Rahaman, T.I.; Sadiea, R.Z.; Sultana, S.; Islam, M.S.; Zheng, C.; et al. Insights Into the Coinfections of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Hepatitis B Virus, Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Hepatitis C Virus, and Hepatitis B Virus-Hepatitis C Virus: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 780887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodsworth, N.J.; Cooper, D.A.; Donovan, B. The influence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection on the development of the hepatitis B virus carrier state. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 163, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausen, L.N. Factors associated with resolution and progression of HIV/hepatitis C virus infection. Dan. Med. J. 2014, 61, B4838. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidbauer, C.; Chromy, D.; Schmidbauer, V.; Bauer, D.; Apata, M.; Nguyen, D.; Mandorfer, M.; Simbrunner, B.; Rieger, A.; Mayer, F.; et al. Epidemiological trends in HCV transmission and prevalence in the Viennese HIV+ population. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2020, 40, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, R.; Núñez, M.; Mendoza, J.L.; Soriano, V. Rate and risk factors of liver toxicity in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. Med. Clin. 2001, 117, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, A.; Riva, A.; Falvella, F.S.; Oreni, M.L.; Cattaneo, D.; Cheli, S.; Renisi, G.; Di Cristo, V.; Lupo, A.; Clementi, E.; et al. Clinical and genetic factors associated with increased risk of severe liver toxicity in a monocentric cohort of HIV positive patients receiving nevirapine-based antiretroviral therapy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, E.; Roussillon, C.; Salmon-Céron, D.; Georget, A.; Hénard, S.; Huleux, T.; Gueit, I.; Mortier, E.; Costagliola, D.; Morlat, P.; et al. Liver-related deaths in HIV-infected patients between 1995 and 2010 in France: The Mortavic 2010 study in collaboration with the Agence Nationale de Recherche sur le SIDA (ANRS) EN 20 Mortalité 2010 survey. HIV Med. 2015, 16, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhu, Q.; Deng, L.; Lan, G.; Johnson, A.; Chen, H.; Shen, Z.; Li, J.; Xing, H.; Ruan, Y.; et al. Treatment outcomes of HIV patients with hepatitis B and C virus co-infections in Southwest China: An observational cohort study. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, A.; Ochola, E.; Oreni, L.; Vassalini, P.; Rizzardini, G.; Galli, M. Hepatitis B and HIV coinfection in Northern Uganda: Is a decline in HBV prevalence on the horizon? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafeero, H.M.; Ndagire, D.; Ocama, P.; Kudamba, A.; Walusansa, A.; Sendagire, H. Prevalence and predictors of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in east Africa: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies published from 2005 to 2020. Arch. Public Health 2021, 79, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, L.; Easterbrook, P.; Gower, E.; McDonald, B.; Sabin, K.; McGowan, C.; Yanny, I.; Razavi, H.; Vickerman, P. Prevalence and burden of HCV co-infection in people living with HIV: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayana, D.A.; Mulu, A.; Mihret, A.; Seyoum, B.; Aseffa, A.; Howe, R. Hepatitis B virus seromarkers among HIV infected adults on ART: An unmet need for HBV screening in eastern Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, M.H.; Zhai, X.J. Prevalence of HBV co-infection in HIV-positive population in China: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi 2021, 42, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Deng, M. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevalence among people living with HIV/AIDS in China: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Ou, W.; Li, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Shao, Y. Changing Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Coinfection in a Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Population in China: Results From the Third and Fourth Nationwide Molecular Epidemiologic Surveys. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2021, 73, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, K.C.; Poudel-Tandukar, K. High prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus in people living with HIV in Kathmandu, Nepal. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, R.; Patel, N.; Fox, J.; Cosgrove, C.; Pett, S.L.; Burns, F.; Ustianowski, A.; Rosenvinge, M.; Bhagani, S.; Dusheiko, G.; et al. Prevalence of HIV/hepatitis B and HIV/hepatitis C coinfection among people of East, South, Central and West African ancestry in the United Kingdom. AIDS 2021, 35, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffie, P.A.; Egger, M.; Vinikoor, M.J.; Zannou, M.; Diero, L.; Patassi, A.; Kuniholm, M.H.; Seydi, M.; Bado, G.; Ocama, P.; et al. Trends in hepatitis B virus testing practices and management in HIV clinics across sub-Saharan Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.K.; Vigil, K.J.; Parisot, P.; Go, G.; Vu, T.; Li, X.; Hansen, L.; Taylor, B.S. Incidence and Predictors of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Clearance in HIV Patients: A Retrospective Multisite Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, A.L.; Corrêa, M.C. Evolution of hepatitis B serological markers in HIV coinfected patients: A case study. Rev. Saude Publica 2017, 51, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloquel, B.; Jeulin, H.; Burty, C.; Letranchant, L.; Rabaud, C.; Venard, V. Occult hepatitis B infection in patients infected with HIV: Report of two cases of hepatitis B reactivation and prevalence in a hospital cohort. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msomi, N.; Naidoo, K.; Yende-Zuma, N.; Padayatchi, N.; Govender, K.; Singh, J.A.; Abdool-Karim, S.; Abdool-Karim, Q.; Mlisana, K. High incidence and persistence of hepatitis B virus infection in individuals receiving HIV care in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Serna, A.; Macias, J.; Palacios, R.; Gómez-Ayerbe, C.; Tellez, F.; Rivero-Juárez, A.; Fernandez, M.; Santos, J.; Real, L.M.; Gonzalez-Domenech, C.M.; et al. Incidence of recently acquired hepatitis C virus infection among HIV-infected patients in southern Spain. HIV Med. 2021, 22, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, L.J.; Cooke, G.S.; Smith, C.; Stingone, C.; Ghosh, I.; Dakshina, S.; Jain, L.; Waters, L.J.; Mahungu, T.; Ferro, F.; et al. Decline in Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Incidence in Men Who Have Sex with Men Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Progress to HCV Microelimination in the United Kingdom? Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2021, 72, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xu, H.; Hu, Y.; Shang, J.; Jiang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; et al. Hepatitis C screening in hospitals: Find the missing patients. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Draft Global Health Sector Strategies Viral Hepatitis 2016–2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/strategy2016-2021/ghss-hep/en/ (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- Su, S.; Wong, W.C.; Zou, Z.; Cheng, D.D.; Ong, J.J.; Chan, P.; Ji, F.; Yuen, M.F.; Zhuang, G.; Seto, W.K.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of universal screening for chronic hepatitis B virus infection in China: An economic evaluation. Lancet. Glob. Health 2022, 10, e278–e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Xu, H.; Sui, D.; Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Niu, J. A retrospective serological survey of hepatitis B virus infection in Northeast China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qi, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhao, P.; Guo, H.; Jiao, J.; Zhou, C.; et al. Epidemiology of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Infections and Benefits of Programs for Hepatitis Prevention in Northeastern China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2016, 62, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, T.; Gou, Y.; Wei, B.; Tao, C. High prevalence of syphilis, HBV, and HCV co-infection, and low rate of effective vaccination against hepatitis B in HIV-infected patients in West China hospital. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Shen, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, D.; Liu, M. Seroepidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection in 2 million men aged 21–49 years in rural China: A population-based, cross-sectional study. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.H.; Meier-Stephenson, V.; Genetu, M.; Damtie, D.; Abate, E.; Alemu, S.; Aleka, Y.; Van Marle, G.; Fonseca, K.; Coffin, C.S.; et al. Prevalence and genetic variability of occult hepatitis B virus in a human immunodeficiency virus positive patient cohort in Gondar, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, R.R.; Mathur, A.; Mathur, D.; Udawat, H.P.; Nepalia, S.; Nijhawan, S.; Mathur, A. Prevalence of occult hepatitis B & C in HIV patients infected through sexual transmission. Trop. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Dig. Dis. Found. 2007, 28, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Demosthenes, J.P.; Sachithanandham, J.; Fletcher, G.J.; Zachariah, U.G.; Varghese, G.M.; John Daniel, H.D.; Jeyaseelan, L.; Abraham, P.; Kannangai, R. Characteristics of treatment-naïve HBV-infected individuals with HIV-1 coinfection: A cross-sectional study from South India. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 37, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lô, G.; Sow-Sall, A.; Diop-Ndiaye, H.; Mandiouba, N.C.; Thiam, M.; Diop, F.; Ndiaye, O.; Gueye, S.B.; Seck, S.M.; Dioura, A.A.; et al. Prevalence of hepatitis B markers in Senegalese HIV-1-infected patients. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Wahed, A.S.; King, W.C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Khalili, M.; Sulkowski, M.; Chung, R.T.; Jain, M.K.; Lisker-Melman, M.; Wong, D.K.; et al. Spectrum of Liver Disease in Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Patients Co-infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): Results of the HBV-HIV Cohort Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, C.L.; Smeaton, L.; Saulynas, M.; Hwang, H.; Saravanan, S.; Kulkarni, S.; Hakim, J.; Nyirenda, M.; Iqbal, H.S.; Lalloo, U.G.; et al. Characterization of HIV-HBV coinfection in a multinational HIV-infected cohort. AIDS 2013, 27, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, C.L.; Seaberg, E.C.; Skolasky, R., Jr.; Phair, J.; Visscher, B.; Muñoz, A.; Thomas, D.L. HIV-1, hepatitis B virus, and risk of liver-related mortality in the Multicenter Cohort Study (MACS). Lancet 2002, 360, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donyavi, T.; Bokharaei-Salim, F.; Khanaliha, K.; Sheikh, M.; Bastani, M.N.; Moradi, N.; Babaei, R.; Habib, Z.; Fakhim, A.; Esghaei, M. High prevalence of occult hepatitis C virus infection in injection drug users with HIV infection. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggorowati, N.; Yano, Y.; Heriyanto, D.S.; Rinonce, H.T.; Utsumi, T.; Mulya, D.P.; Subronto, Y.W.; Hayashi, Y. Clinical and virological characteristics of hepatitis B or C virus co-infection with HIV in Indonesian patients. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavini, M.; Angeli, E.; Mainini, A.; Zerbi, P.; Duca, P.G.; Gubertini, G.; Vago, L.; Fociani, P.; Giorgi, R.; Cargnel, A. Risk factors for fibrosis progression in HIV/HCV coinfected patients from a retrospective analysis of liver biopsies in 1985–2002. HIV Med. 2006, 7, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, F.H.; Ferreira, L.E.; Silva, A.E.; Ferraz, M.L. Liver fibrosis progression in HIV/hepatitis C virus coinfected patients with normal aminotransferases levels. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2012, 45, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmann, L.; Picone, C.M.; Gouvêa, M.S.G.; Ferreira, P.R.A.; Viana, M.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Cassenote, A.J.F.; Segurado, A.C. Hepatitis B viremia in HIV-coinfected individuals under antiretroviral therapy. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Braz. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2019, 23, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Hong, S.; Im, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Baek, J.H.; Kwon, H.Y. Systematic review and meta-analysis of immune response of double dose of hepatitis B vaccination in HIV-infected patients. Vaccine 2020, 38, 3995–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretto, F.; Catherine, F.X.; Esteve, C.; Blot, M.; Piroth, L. Isolated Anti-HBc: Significance and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piroth, L.; Launay, O.; Michel, M.L.; Bourredjem, A.; Miailhes, P.; Ajana, F.; Chirouze, C.; Zucman, D.; Wendling, M.J.; Nazzal, D.; et al. Vaccination Against Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) in HIV-1-Infected Patients with Isolated Anti-HBV Core Antibody: The ANRS HB EP03 CISOVAC Prospective Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsachouridou, O.; Georgiou, A.; Naoum, S.; Vasdeki, D.; Papagianni, M.; Kotoreni, G.; Forozidou, E.; Tsoukra, P.; Gogou, C.; Chatzidimitriou, D.; et al. Factors associated with poor adherence to vaccination against hepatitis viruses, streptococcus pneumoniae and seasonal influenza in HIV-infected adults. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cui, F. Expanded screening for chronic hepatitis B virus infection in China. Lancet. Glob. Health 2022, 10, e171–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).