Sward Diversity Modulates Soil Carbon Dynamics After Ploughing Temporary Grassland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Experimental Layout and Treatments
2.3. CO2 Measurements
2.4. Flux Calculations
2.5. Above- and Belowground Sampling
2.6. Adding Straw
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biomass, Carbon, and Nitrogen
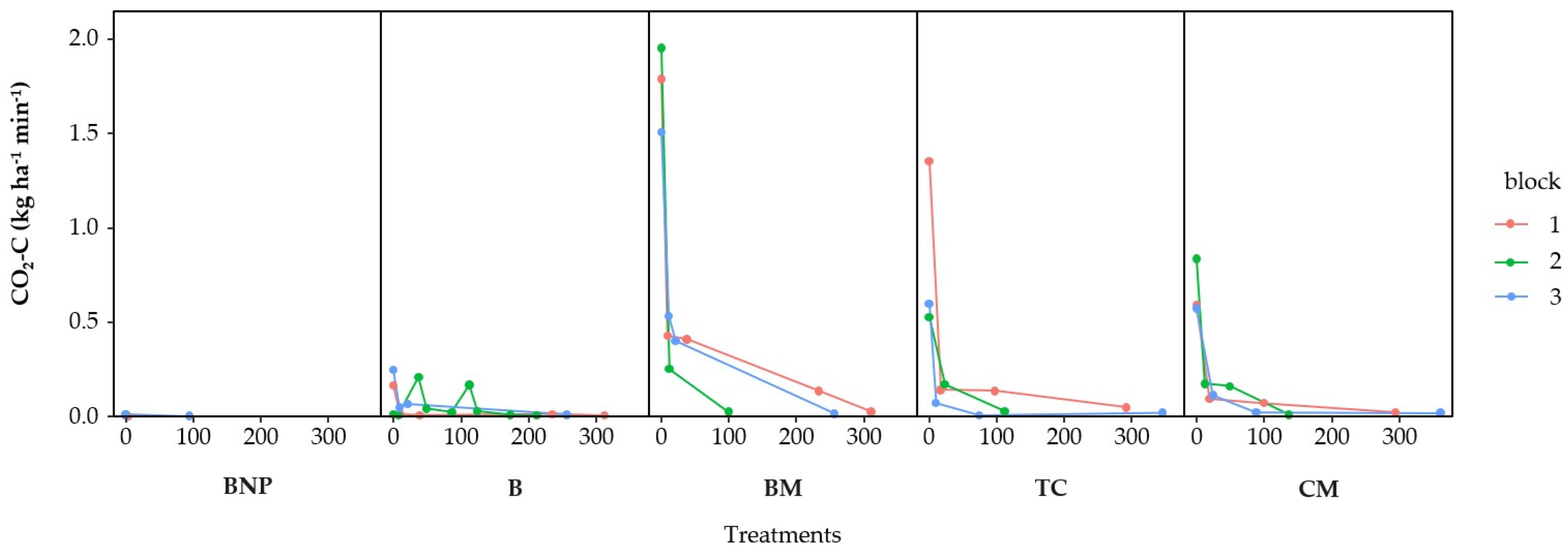
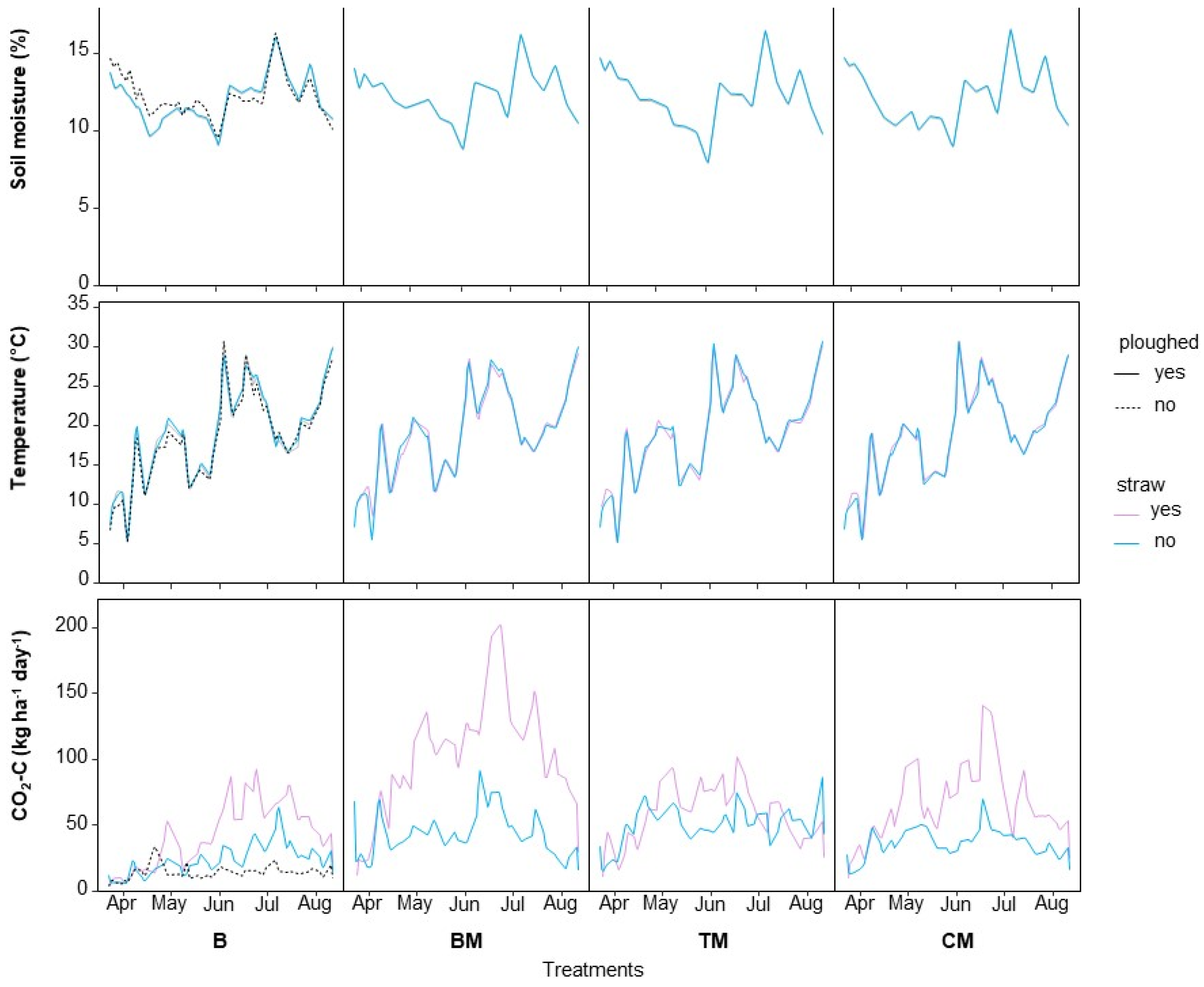
3.2. CO2 Fluxes
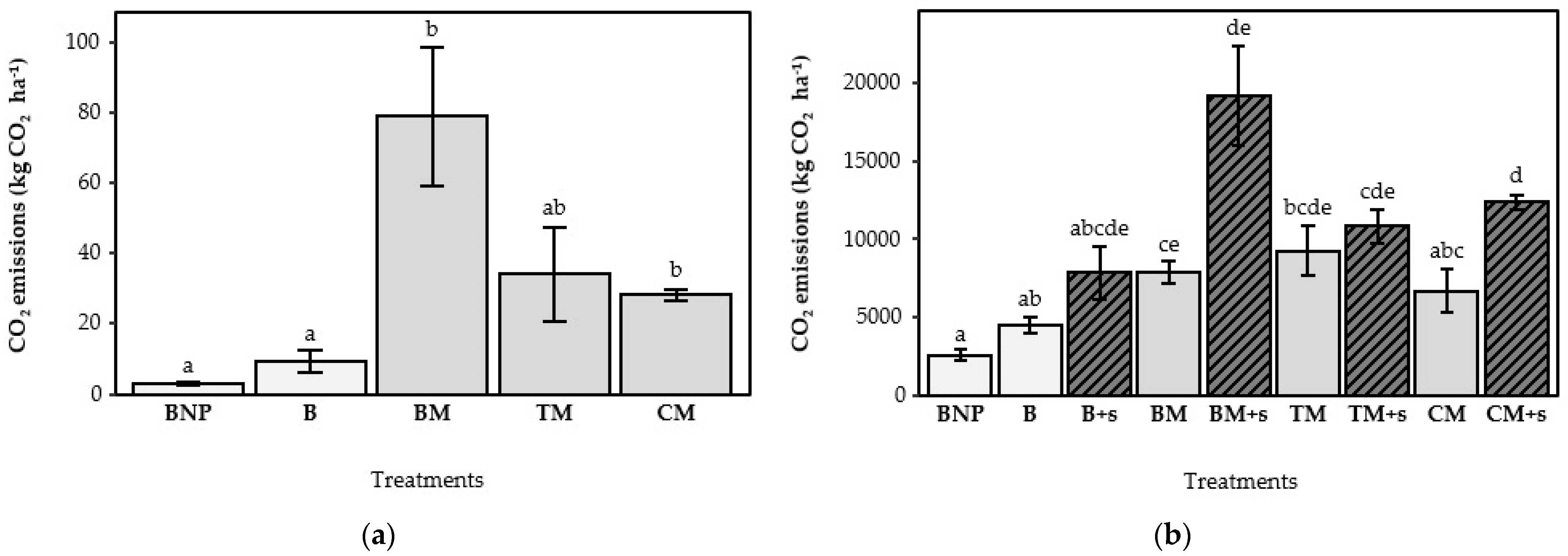
3.3. Accumulated CO2-Losses
4. Discussion
4.1. Biomass, C, and N Yield
4.2. Impact of Soil Disturbance and Vegetation on CO2 Emissions After Ploughing
4.3. The Effect of Adding Straw on CO2 Losses
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Power, A.G. Ecosystem Services and Agriculture: Tradeoffs and Synergies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2959–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesbahi, G.; Michelot-Antalik, A.; Goulnik, J.; Plantureux, S. Permanent Grassland Classifications Predict Agronomic and Environmental Characteristics Well, but Not Ecological Characteristics. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeffner, K.; Beylich, A.; Chabbi, A.; Cluzeau, D.; Dascalu, D.; Graefe, U.; Guzmán, G.; Hallaire, V.; Hanisch, J.; Landa, B.B.; et al. Legacy Effects of Temporary Grassland in Annual Crop Rotation on Soil Ecosystem Services. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Cotrufo, M.F. Grassland Soil Carbon Sequestration: Current Understanding, Challenges, and Solutions. Science 2022, 377, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loges, R.; Bunne, I.; Reinsch, T.; Malisch, C.; Kluß, C.; Herrmann, A.; Taube, F. Forage Production in Rotational Systems Generates Similar Yields Compared to Maize Monocultures but Improves Soil Carbon Stocks. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 97, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Carbon sequestration. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.B.; Gifford, R.M. Soil Carbon Stocks and Land Use Change: A Meta Analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussana, J.-F.; Loiseau, P.; Vuichard, N.; Ceschia, E.; Balesdent, J.; Chevallier, T.; Arrouays, D. Carbon Cycling and Sequestration Opportunities in Temperate Grasslands. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 20, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meersmans, J.; Martin, M.P.; Lacarce, E.; Orton, T.G.; de Baets, S.; Gourrat, M.; Sab, N.P.A.; Wetterlind, J.; Bispo, A.; Quine, T.A.; et al. Estimation of soil carbon input in France: An inverse modelling approach. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, R.M.; Bingham, I.J.; Baddeley, J.A.; Watson, C.A. The Role of Plants and Land Management in Sequestering Soil Carbon in Temperate Arable and Grassland Ecosystems. Geoderma 2005, 128, 130–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsler, D.; Geisseler, D.; Loges, R.; Taube, F.; Ludwig, B. Temporal Dynamics of Soil Organic Matter Composition and Aggregate Distribution in Permanent Grassland after a Single Tillage Event in a Temperate Climate. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 126, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necpálová, M.; Li, D.; Lanigan, G.; Casey, I.A.; Burchill, W.; Humphreys, J. Changes in Soil Organic Carbon in a Clay Loam Soil Following Ploughing and Reseeding of Permanent Grassland under Temperate Moist Climatic Conditions. Grass Forage Sci. 2014, 69, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsch, T.; Loges, R.; Kluß, C.; Taube, F. Effect of Grassland Ploughing and Reseeding on CO2 Emissions and Soil Carbon Stocks. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellinga, T.V.; van den Pol-van Dasselaar, A.; Kuikman, P.J. The impact of grassland ploughing on CO2 and N2O emissions in the Netherlands. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2004, 70, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Balvert, S.F.; Wise, B.; Welten, B.; Ledgard, S.F.; de Klein, C.A.M.; Lindsey, S.; Judge, A. Using Alternative Forage Species to Reduce Emissions of the Greenhouse Gas Nitrous Oxide from Cattle Urine Deposited onto Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbeiss, S.; Beßler, H.; Engels, C.; Temperton, V.M.; Buchmann, N.; Roscher, C.; Kreutziger, Y.; Baade, J.; Habekost, M.; Gleixner, G. Plant diversity positively affects short-term soil carbon storage in experimental grasslands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 2937–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, H.; Reinsch, T.; Kluß, C.; Taube, F.; Loges, R. Does the Admixture of Forage Herbs Affect the Yield Performance, Yield Stability and Forage Quality of a Grass Clover Ley? Sustainability 2020, 12, 5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.; McAree, C.; Mulville, W.; Sullivan, T. The Problem of Agricultural ‘Diffuse’ Pollution: Getting to the Point. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 700–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, A.J.; Cameron, K.C.; Di, H.J.; Edwards, G.R.; Clough, T.J. Nitrate Leaching Losses Are Lower from Ryegrass/White Clover Forages Containing Plantain than from Ryegrass/White Clover Forages under Different Irrigation. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 62, 150–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loza, C.; Reinsch, T.; Loges, R.; Taube, F.; Gere, J.I.; Kluß, C.; Hasler, M.; Malisch, C.S. Methane Emission and Milk Production from Jersey Cows Grazing Perennial Ryegrass–White Clover and Multispecies Forage Mixtures. Agriculture 2021, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, J.; Mortensen, T.; Søegaard, K. Root Biomass and Carbon Storage in Differently Managed Multispecies Temporary Grasslands. Grassl. Sci. Eur. 2012, 17, 610–612. Available online: https://orgprints.org/id/eprint/22043/ (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Kagiya, N.; Reinsch, T.; Taube, F.; Salminen, J.-P.; Kluß, C.; Hasler, M.; Malisch, C.S. Turnover Rates of Roots Vary Considerably across Temperate Forage Species. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Eisenhauer, N.; Sierra, C.A.; Bessler, H.; Engels, C.; Griffiths, R.I.; Mellado-Vázquez, P.G.; Malik, A.A.; Roy, J.; Scheu, S.; et al. Plant Diversity Increases Soil Microbial Activity and Soil Carbon Storage. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Meena, R.S.; Lal, R.; Singh Yadav, G.; Mitran, T.; Meena, B.L.; Dotaniya, M.L.; EL-Sabagh, A. Role of Legumes in Soil Carbon Sequestration. In Legumes for Soil Health and Sustainable Management; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2018; pp. 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyda, A.; Wizemann, H.-D.; Ingwersen, J.; Eshonkulov, R.; Högy, P.; Demyan, M.S.; Kremer, P.; Wulfmeyer, V.; Streck, T. Carbon Fluxes and Budgets of Intensive Crop Rotations in Two Regional Climates of Southwest Germany. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 276, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P.; Rengel, Z. Nutrient Cycling in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Marschner, P., Rengel, Z., Eds.; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Feger, K.H. Book Review: Hans-Peter Blume, Rainer Horn, Sören Thiele-Bruhn: Handbuch Des Bodenschutzes: Bodenökologie Und Bodenbelastung–Vorbeugende Und Abwehrende Schutzmaßnahmen. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2011, 174, 690–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, A.B.; Augustenborg, C.A.; Hepp, S.; Lanigan, G.; Hochstrasser, T.; Kammann, C.; Müller, C. Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Spring Ploughing of Grassland in Ireland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DWD. Temperatur: Langjährige Mittelwerte 1991–2020. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/klimadatendeutschland/mittelwerte/temp_8110_akt_html.html?view=%0AnasPublication&nn=16102Dtsch.Wetterd (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Reinsch, T.; Loges, R.; Kluß, C.; Taube, F. Renovation and Conversion of Permanent Grass-Clover Swards to Pasture or Crops: Effects on Annual N2O Emissions in the Year after Ploughing. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.L.; Mosier, A.R. Improved Soil Cover Method for Field Measurement of Nitrous Oxide Fluxes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panettieri, M.; Guigue, J.; Chemidlin Prevost-Bouré, N.; Thévenot, M.; Lévêque, J.; Le Guillou, C.; Maron, P.-A.; Santoni, A.-L.; Ranjard, L.; Mounier, S.; et al. Grassland-Cropland Rotation Cycles in Crop-Livestock Farming Systems Regulate Priming Effect Potential in Soils through Modulation of Microbial Communities, Composition of Soil Organic Matter and Abiotic Soil Properties. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 299, 106973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flessa, H.; Wild, U.; Klemish, M.; Pfadenhauer, J. Nitrous Oxide and Methane Fluxes from Organic Soils under Agriculture. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 1998, 49, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drösler, M.; Schaller, L.; Kantelhardt, J.; Schweiger, M.; Fuchs, D.; Tiemeyer, B.; Augustin, J.; Wehrhan, M.; Förster, C.; Bergmann, L.; et al. Beitrag von Moorschutzund-Revitalisierungsmaßnahmen Zum Klimaschutz Am Beispiel von Naturschutzgroßprojekten. Nat. Und Landsch. 2012, 87, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, L.-P.; Lemke, R.L.; Knight, J.D.; Bedard-Haughn, A. Carbon Input from 13C-Labeled Crops in Four Soil Organic Matter Fractions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Kozak, M.; Piepho, H.p. What’s Normal Anyway? Residual Plots Are More Telling than Significance Tests When Checking ANOVA Assumptions. J. Agron. Crop. Sci 2018, 204, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Multiple Comparisons Using R., 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Boller, B.; Greene, S.L. Fodder Crops and Amenity; Boller, B., Posselt, U.K., Veronesi, F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, E.Ø.; Abalos, D.; Rasmussen, J. Well-Designed Multi-Species Grassland Mixtures Enhance Both Soil Carbon Inputs and Aboveground Productivity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 385, 109578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, L.M.; Barry, K.E.; Mommer, L.; van Ruijven, J. Focusing on Individual Plants to Understand Community Scale Biodiversity Effects: The Case of Root Distribution in Grasslands. Oikos 2021, 130, 1954–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Sørensen, P.; Li, X.; Olesen, J.E. Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization Differ between Incorporated Shoots and Roots of Legume versus Non-Legume Based Cover Crops. Plant Soil 2020, 446, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böldt, M.J.; Smit, H.P.J.; Loges, R.; Taube, F.; Kluß, C.; Reinsch, T. Evaluating Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Low Input Systems Using Different Cover Crop Strategies over the Winter Period. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietola, L.; Alakukku, L. Root Growth Dynamics and Biomass Input by Nordic Annual Field Crops. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 108, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redin, M.; Recous, S.; Aita, C.; Chaves, B.; Pfeifer, I.C.; Bastos, L.M.; Pilecco, G.E.; Giacomini, S.J. Root and Shoot Contribution to Carbon and Nitrogen Inputs in the Topsoil Layer in No-Tillage Crop Systems under Subtropical Conditions. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2018, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Beule, L.; Zang, H.; Pfeiffer, B.; Ma, S.; Karlovsky, P.; Dittert, K. The Potential of Ryegrass as Cover Crop to Reduce Soil N2O Emissions and Increase the Population Size of Denitrifying Bacteria. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2021, 72, 1447–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reicosky, D.C.; Archer, D.W. Moldboard Plow Tillage Depth and Short-Term Carbon Dioxide Release. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reicosky, D. Tillage-Induced CO2 Emission from Soil. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1997, 49, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oram, N.J.; Ravenek, J.M.; Barry, K.E.; Weigelt, A.; Chen, H.; Gessler, A.; Gockele, A.; de Kroon, H.; van der Paauw, J.W.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; et al. Below-ground Complementarity Effects in a Grassland Biodiversity Experiment Are Related to Deep-rooting Species. J. Ecol. 2018, 106, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacaldo, R.S.; Volk, T.A.; Briggs, R.D. Carbon Sequestration in Fine Roots and Foliage Biomass Offsets Soil CO2 Effluxes along a 19-Year Chronosequence of Shrub Willow (Salix x dasyclados) Biomass Crops. Bioenergy Res. 2014, 7, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewer, J.; Anderson, M.; Levy, P.E.; Scholtes, B.; Helfter, C.; Parker, J.; Rees, R.M.; Skiba, U.M. The Impact of Ploughing Intensively Managed Temperate Grasslands on N2O, CH4 and CO2 Fluxes. Plant Soil 2017, 411, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, H.P.J.; Reinsch, T.; Kluß, C.; Loges, R.; Taube, F. Very Low Nitrogen Leaching in Grazed Ley-Arable-Systems in Northwest Europe. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y. Priming Effects: Interactions between Living and Dead Organic Matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Senbayram, M.; Blagodatsky, S.; Myachina, O.; Dittert, K.; Lin, X.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil C and N Availability Determine the Priming Effect: Microbial N Mining and Stoichiometric Decomposition Theories. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ning, P.; Liu, J.; Zheng, W.; Tian, X.; Shi, J.; Xu, M.; Liang, Z.; Shar, A.G. Effect of Different Straw Return Modes on Soil Bacterial Community, Enzyme Activities and Organic Carbon Fractions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, M.; Cui, J.; Li, B.; Fang, C. Effects of Straw Carbon Input on Carbon Dynamics in Agricultural Soils: A Meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabro, J.D.; Sainju, U.; Stevens, W.B.; Evans, R.G. Carbon Dioxide Flux as Affected by Tillage and Irrigation in Soil Converted from Perennial Forages to Annual Crops. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bimüller, C.; Kreyling, O.; Kölbl, A.; von Lützow, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization in Hierarchically Structured Aggregates of Different Size. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Frank, D.A. Short Sampling Intervals Reveal Very Rapid Root Turnover in a Temperate Grassland. Oecologia 2008, 157, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, D.; Collins, C.D.; Clark, J.M.; Sizmur, T. Soil Organic Matter Storage in Temperate Lowland Arable, Grassland and Woodland Topsoil and Subsoil. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, C.A.; Trumbore, S.E.; Davidson, E.A.; Vicca, S.; Janssens, I. Sensitivity of Decomposition Rates of Soil Organic Matter with Respect to Simultaneous Changes in Temperature and Moisture. J. Adv. Model Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation (mm) | |||||||||||||
| 2020 | 80 | 130 | 36 | 14 | 26 | 60 | 79 | 62 | 12 | 61 | 17 | 60 | 637 |
| Long-term | 67 | 51 | 52 | 38 | 50 | 64 | 83 | 78 | 62 | 74 | 65 | 71 | 754 |
| Temperature (°C) | |||||||||||||
| 2020 | 5.7 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 9.0 | 11.2 | 16.6 | 15.8 | 19.7 | 14.8 | 11.3 | 7.9 | 4.4 | 10.6 |
| Long-term | 1.7 | 2.2 | 4.3 | 8.1 | 12.0 | 15.3 | 17.8 | 17.6 | 14.3 | 10.0 | 5.8 | 2.9 | 9.3 |
| Treatment | Species Composition | |
|---|---|---|
| Binary mixture (BM) | Ryegrass (Lolium perenne) | |
| White clover (Trifolium repens) | ||
| Tertiary mixture (TM) | Ryegrass (Lolium perenne) | |
| White clover (Trifolium repens) | ||
| Red clover (Trifolium pratens) | ||
| Complex mixture (CM) | Ryegrass (Lolium perenne) | |
| White clover (Trifolium repens) | ||
| Red clover (Trifolium pratens) | ||
| Chicory (Cichorium intybus) | ||
| Caraway (Carum carvi) | ||
| Sheep’s burnet (Sanguisorba minor) | ||
| Birdsfoot trefoil (Lotus corniculates) | ||
| Ribwort plantain (Plantago lanceolata) | ||
| Treatment | Biomass | C | N | C/N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t DM ha−1) | (t ha−1) | (kg ha−1) | |||
| Aboveground biomass | |||||
| BM | 1.06 b ± 0.16 | 0.47 b ± 0.07 | 33.30 b ± 6.4 | 14.3 ± 1.2 | |
| TM | 1.01 b ± 0.04 | 0.43 b ± 0.02 | 32.80 b ± 1.2 | 13.2 ± 0.4 | |
| CM | 0.72 b ± 0.06 | 0.30 b ± 0.04 | 21.60 b ± 1.4 | 13.8 ± 1.1 | |
| B | - | - | - | - | |
| BNP | - | - | - | - | |
| Belowground biomass | |||||
| BM | 13.50 c ± 0.9 | 6.54 c ± 0.41 | 242.00 c ± 15.3 | 27.1 a ± 0.0 | |
| TM | 11.00 c ± 2.6 | 5.33 c ± 1.24 | 210.00 c ± 48.7 | 25.5 c ± 0.0 | |
| CM | 13.70 c ± 1.6 | 6.52 c ± 0.74 | 225.00 c ± 25.4 | 29.0 b ± 0.0 | |
| B | 0.92 a ± 0.51 | 0.44 a ± 0.25 | 16.90 a ± 8.9 | 27.5 ab ± 0.5 | |
| BNP | 2.13 b ± 0.76 | 1.14 b ± 0.27 | 39.00 b ± 14.4 | 26.0 ac ± 0.6 | |
| Total | |||||
| BM | 14.56 | 7.00 b ± 0.34 | 275.00 b ± 8.9 | 25.4 a ± 0.4 | |
| TM | 12.01 | 5.77 b ± 1.26 | 242.00 b ± 49.8 | 23.7 c ± 0.3 | |
| CM | 14.42 | 6.82 b ± 0.75 | 246.00 b ± 25.5 | 27.7 b ± 0.2 | |
| B | 0.92 | 0.44 a ± 0.25 | 16.90 a ± 14.4 | 27.5 ab ± 0.5 | |
| BNP | 2.13 | 1.15 a ± 0.25 | 39.00 a ± 8.9 | 26.0 a ± 0.6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smit, H.P.J.; Anders, H.; Kluß, C.; Taube, F.; Loges, R.; Poyda, A. Sward Diversity Modulates Soil Carbon Dynamics After Ploughing Temporary Grassland. Agriculture 2025, 15, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080888
Smit HPJ, Anders H, Kluß C, Taube F, Loges R, Poyda A. Sward Diversity Modulates Soil Carbon Dynamics After Ploughing Temporary Grassland. Agriculture. 2025; 15(8):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080888
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmit, Hendrik P. J., Hanna Anders, Christof Kluß, Friedhelm Taube, Ralf Loges, and Arne Poyda. 2025. "Sward Diversity Modulates Soil Carbon Dynamics After Ploughing Temporary Grassland" Agriculture 15, no. 8: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080888
APA StyleSmit, H. P. J., Anders, H., Kluß, C., Taube, F., Loges, R., & Poyda, A. (2025). Sward Diversity Modulates Soil Carbon Dynamics After Ploughing Temporary Grassland. Agriculture, 15(8), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15080888









