Exploration of the Pulsation Characteristics of a Bubble Adjacent to the Structure with Multiple Air Bubble Adhesions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Methods
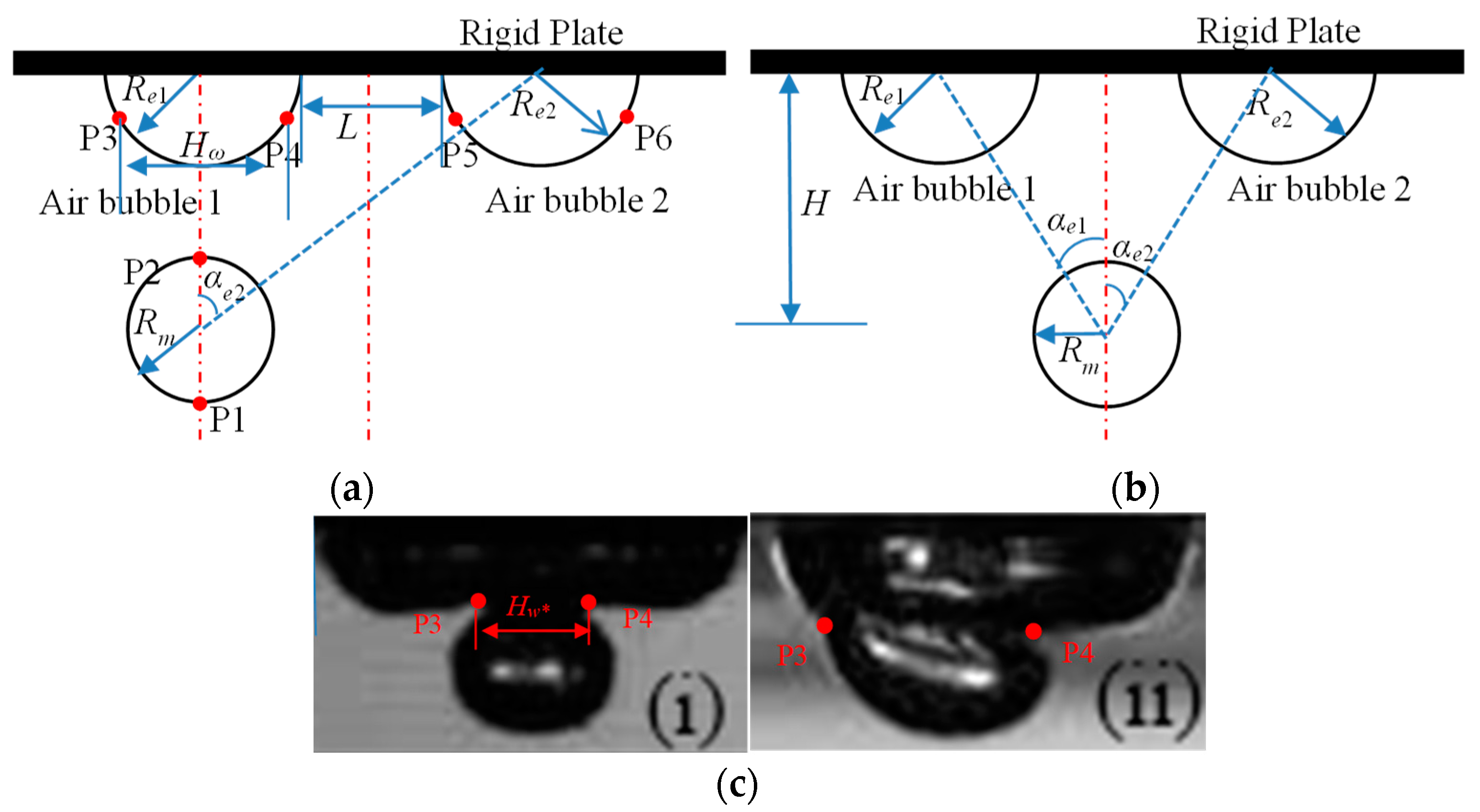
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Layout I: Bubble Movement Characteristics Directly below Unilateral Air Bubble
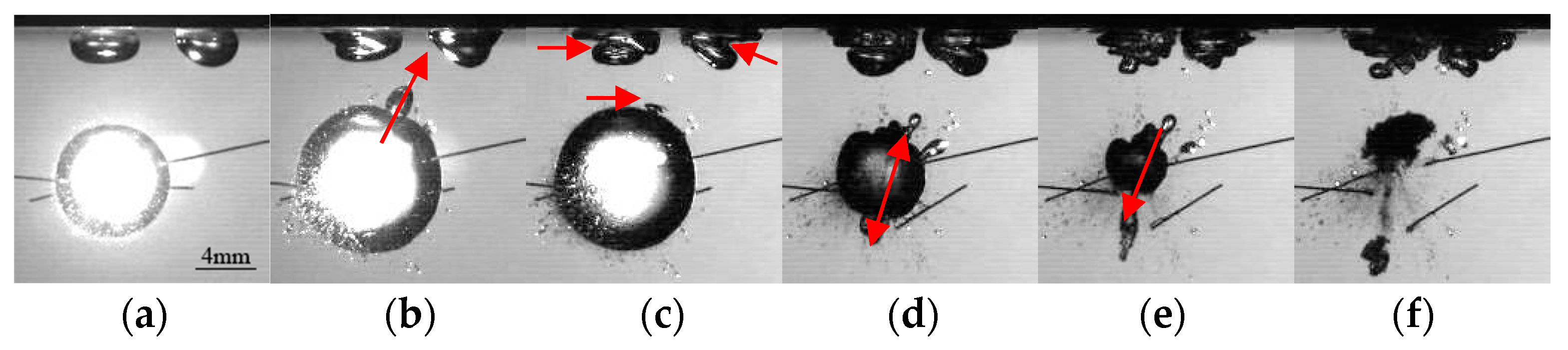
3.1.1. Reverse Jets in an Inclined Direction
3.1.2. The Oblique Directional Midsection Splitting
3.1.3. Jet towards the Boundary
3.2. Layout II: Bubble Motion Characteristics on the Symmetry Axis of Two Air Bubbles
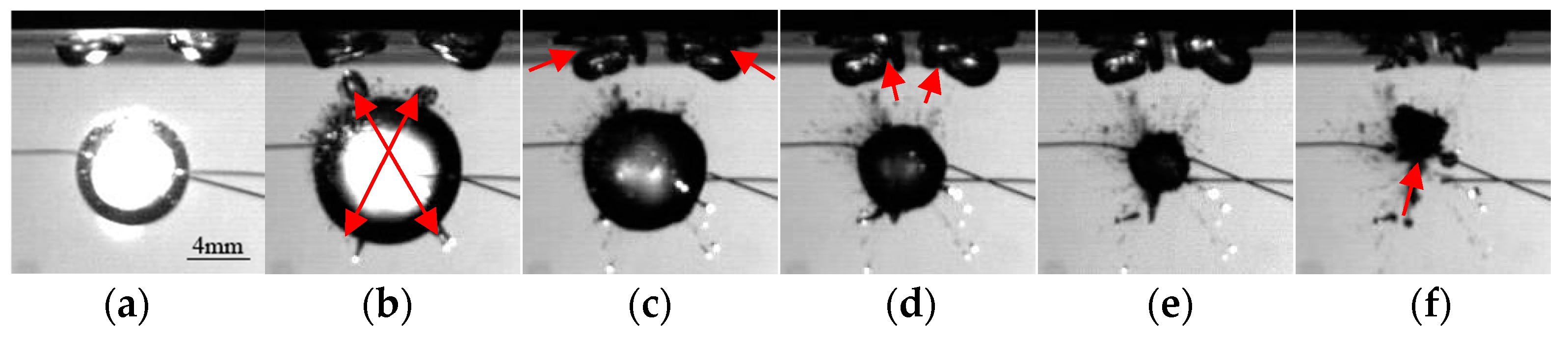
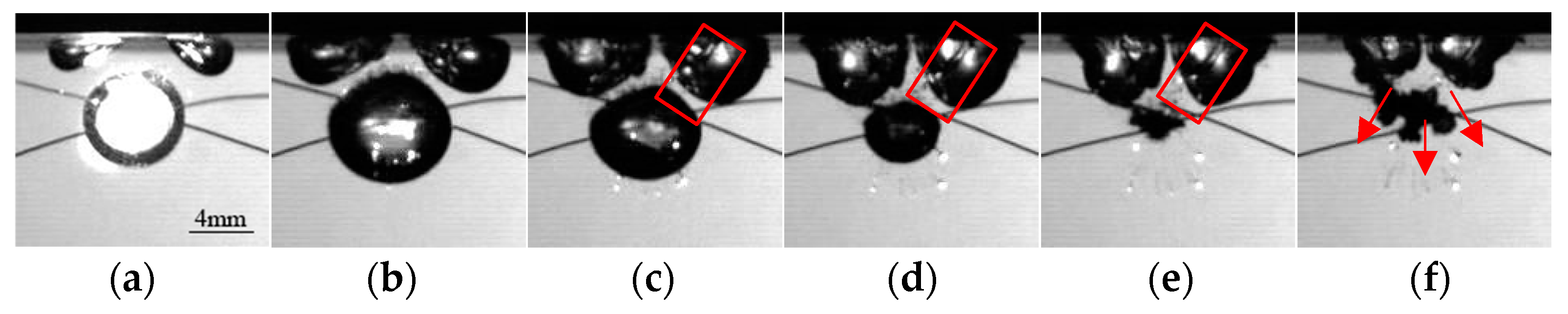
3.2.1. Jet towards the Boundary
3.2.2. Multidirectional Jet
3.2.3. Jets Departing from the Boundary
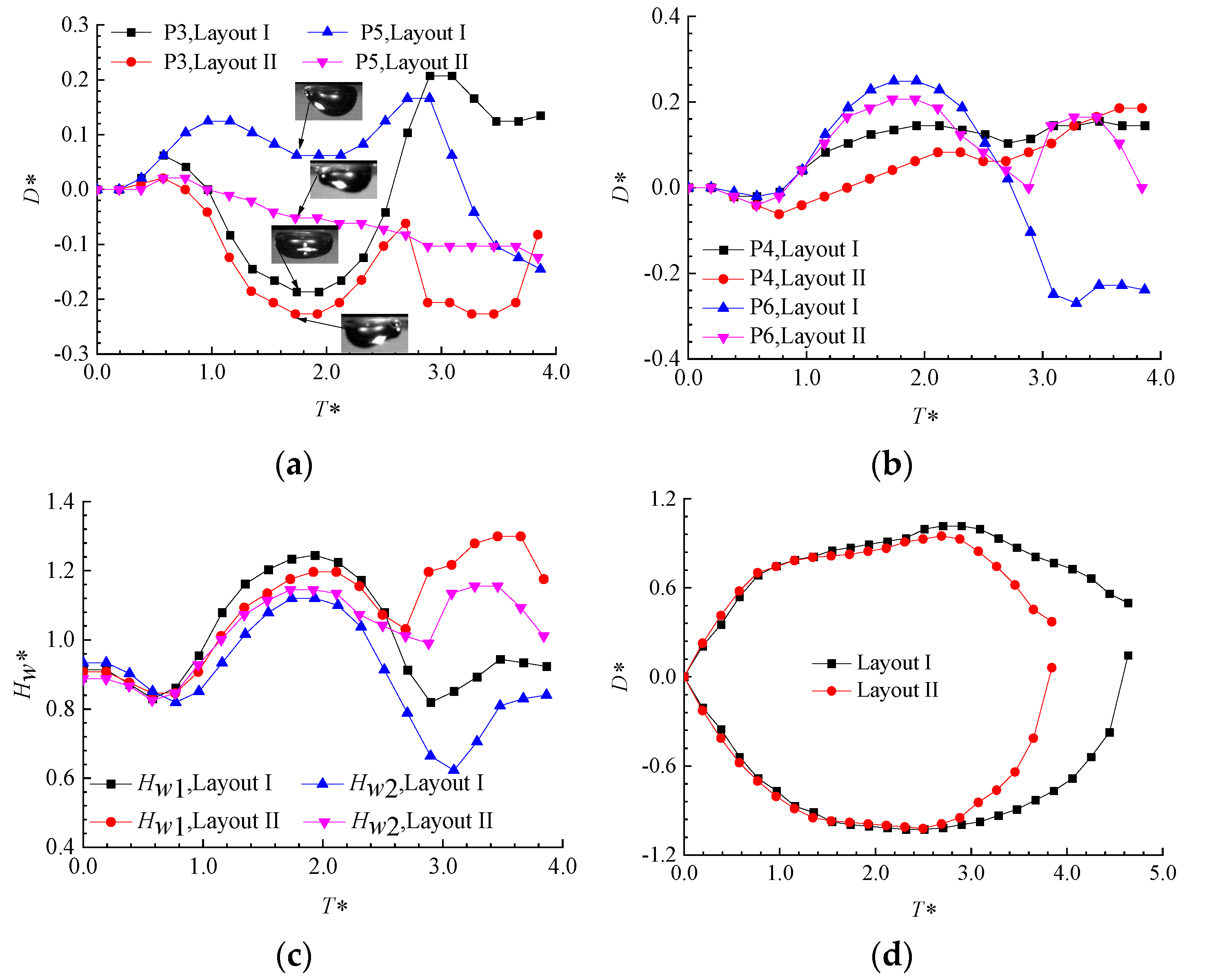
3.3. Displacement Pattern Variations in Individual Bubble Measurement Points
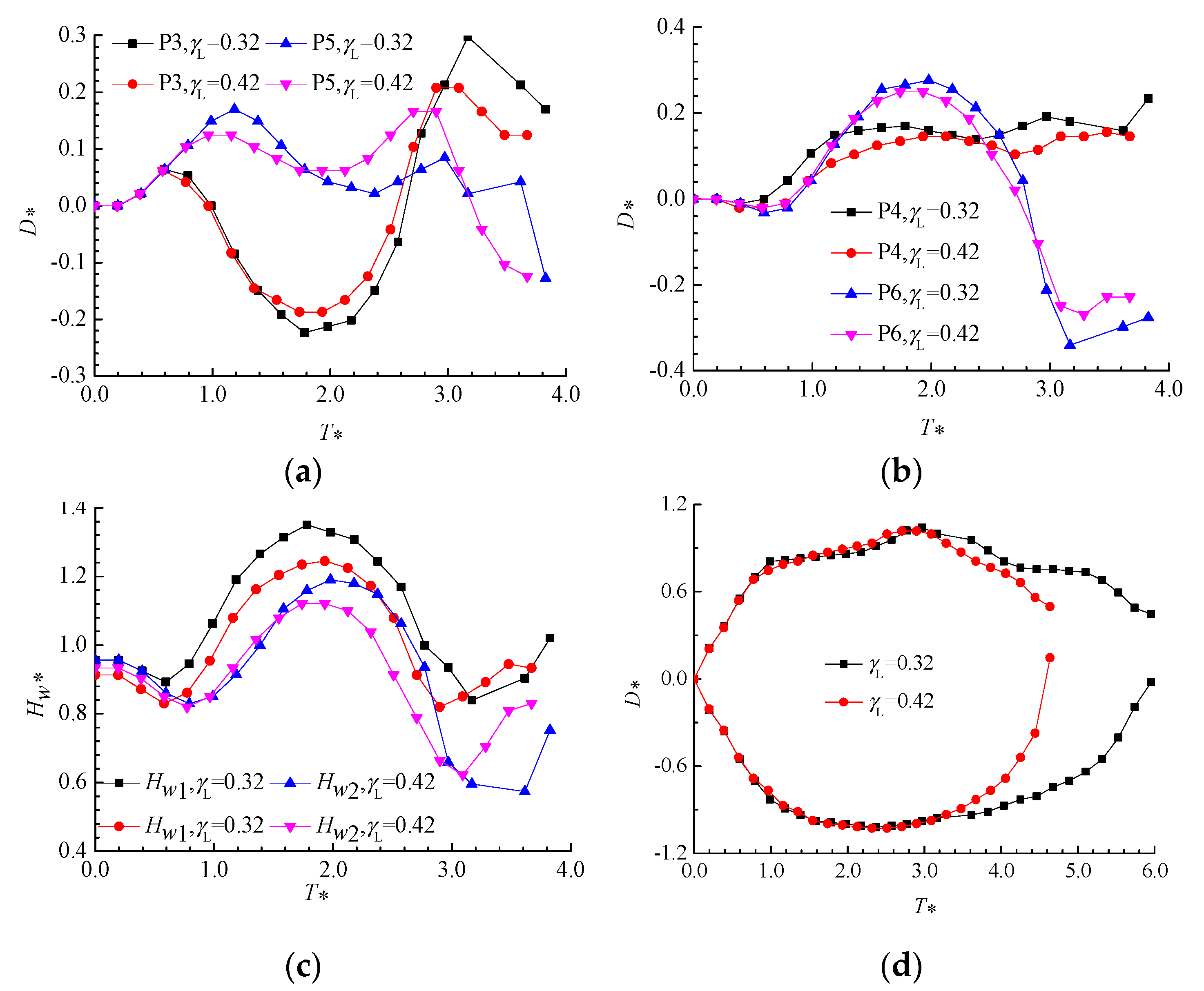
3.3.1. Displacement Variation Patterns of Measurement Points for Layout I
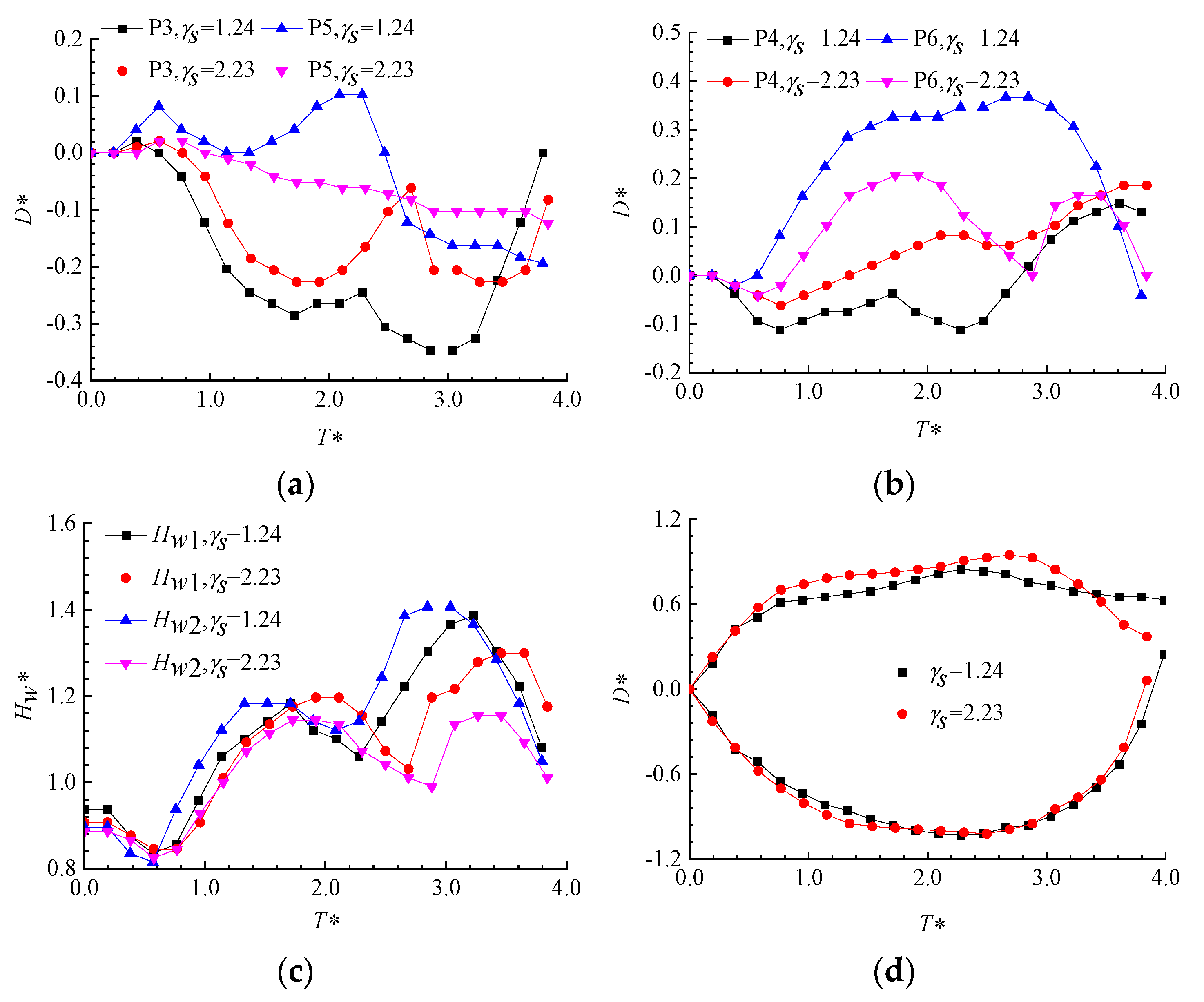
3.3.2. Displacement Variation Patterns of Measurement Points for Layout II
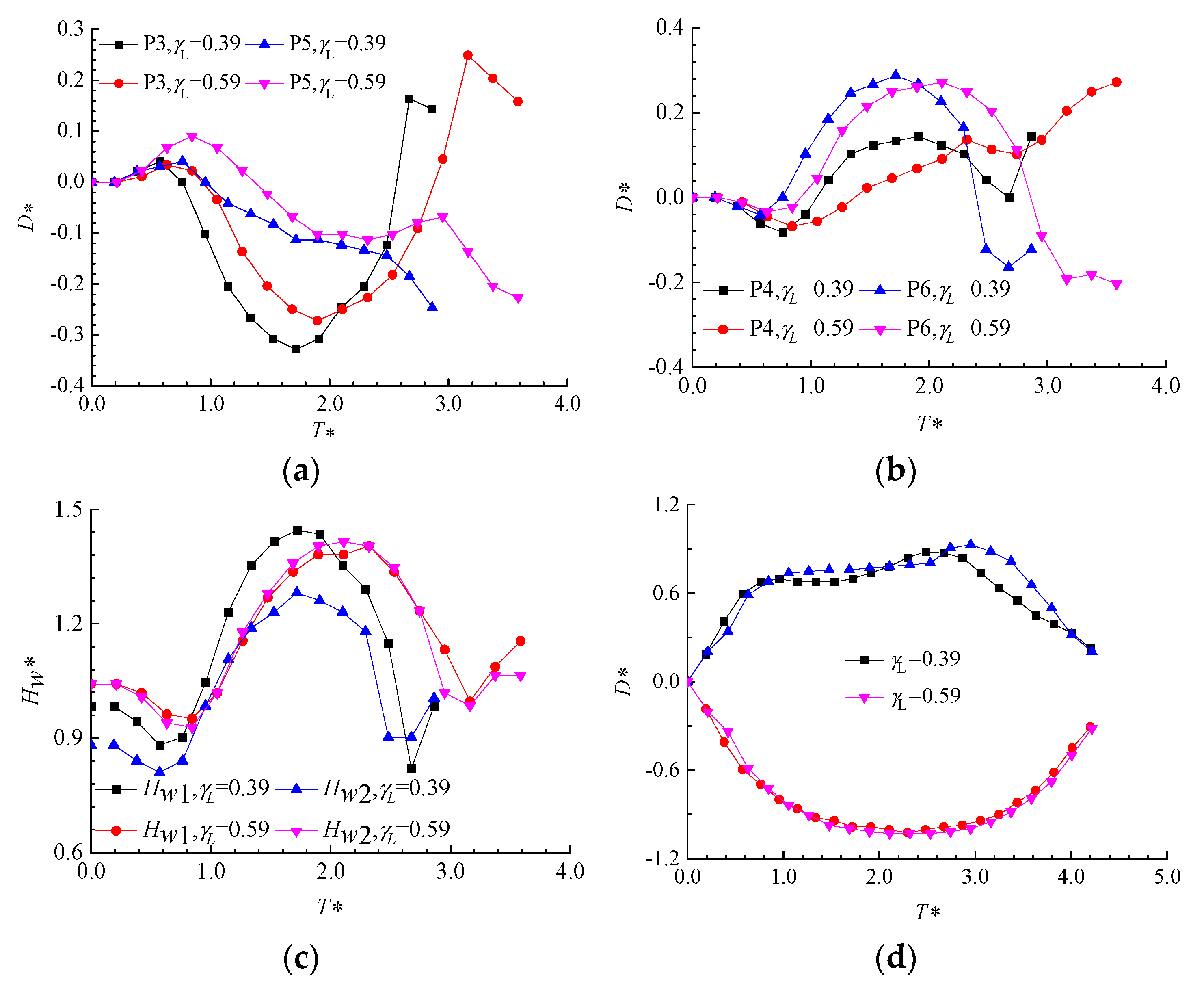
3.3.3. Comparison of Displacement Changes at Various Measurement Points When the Bubble Is Generated at Different Positions
4. Conclusions
- For spatial Layout I, the experiments observed that a bubble directly below a single air bubble produces a jet directed towards the distant air bubble. The oscillating bubble undergoes a tearing phenomenon in the direction towards the lower left, which is caused by the vectorial summation of the repulsive forces exerted by the two adhering air bubbles on the oscillating bubble. Compared to Layout II, the bubble only exhibits off-axis migration and jet direction in Layout I. There is an inclination angle between the other air bubbles and the bubble.
- For spatial Layout I, when the air bubble spacing γL is fixed, the displacement of the air bubble directly above the bubble is proportional to the distance parameter γs, and this also causes varying degrees of lateral displacement in the two air bubbles, with the lateral displacement of air bubble 2 being more significant.
- For spatial Layout I, when the distance parameter γs is constant, the positive pressure exerted by the bubble on air bubble 1 directly above is proportional to the air bubble spacing γL, and the displacement of the outer endpoint of air bubble 2 increases with the increase in γL.
- For spatial layout II, when the air bubble spacing γL is fixed, the displacement of the middle of the air bubbles on both sides increases as the distance parameter decreases. The closer the bubble is to the air bubbles, the more significant the pressure on the air bubbles and the greater the displacement variation. At the same time, the two air bubbles undergo lateral displacements in opposite directions, with the displacement magnitudes changing symmetrically.
- For spatial Layout II, when the distance parameter γs is fixed, the displacement of the middle of the air bubbles increases as the spacing parameter decreases. Additionally, the displacement variation in the inner points for the middle of the air bubbles is smaller than that for the outer points.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, W.D. Laser-induced cavitation bubbles for cleaning of solid surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuta, T.; Takemura, F.; Hihara, E.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shoji, M. Generation of micro gas bubbles of uniform diameter in an ultrasonic field. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 548, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-B.; Wu, X.-Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.-G. A method based on potential theory for calculating air cavity formation of an air cavity resistance reduction ship. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2008, 7, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, J.R.; Gibson, D. Cavitation bubbles near boundaries. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1987, 19, 99–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Hong, Z.C.; Zhang, H.; Sahoo, P.K. An investigation of load change of propeller in a four-propulsion vessel using CFD. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2018, 23, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungsiyaphornrat, S.; Klaseboer, E.; Khoo, B.; Yeo, K. The merging of two gaseous bubbles with an application to underwater explosions. Comput. Fluids 2003, 32, 1049–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Wang, Q.X.; Wang, S.P.; Zhang, A.M. Experimental study on interaction and coalescence of synchronized multiple bubbles. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 012103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.N.; Cui, P.; Ren, S.F.; Zhang, A.M. Study on the interactions between two identical oscillation bubbles and a free surface in a tank. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 052104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.B.; Blake, J.R.; Kodama, T.; Shima, A.; Tomita, Y. Interaction of cavitation bubbles with a free surface. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 8225–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, S.W.; Adhikari, D.; Klaseboer, E.; Khoo, B.C. Interactions of multiple spark-generated bubbles with phase differences. Exp. Fluids 2009, 46, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauterborn, W.; Hentschel, W. Cavitation bubble dynamics studied by high speed photography and holography: Part one. Ultrasonics 1986, 24, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timm, E.F.; Hammit, F.G. Bubble collapse adjacent to a rigid wall, a flexible wall, and a second bubble. In Proceedings of the ASME Cavitation Forum, Pittsburgh, Pa, USA, 10-12 May 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.P.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, A.M.; Cui, P. Interaction of clustered air gun bubbles in marine prospecting. Ocean Eng. 2019, 191, 106523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, A.M.; Wang, S.P.; Chen, G.Q.; Li, S. Nonlinear interaction and coalescence features of oscillating bubble pairs: Experimental and numerical study. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 092108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, N.M.T.; Park, J.; Hyun, S.-H.; Jung, R.-T. Impact loads generated by tandem cavitation bubble on solid wall. J. Hydrodyn. 2022, 34, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Niu, Z. Jet and shock wave from collapse of two cavitation bubbles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xu, W.L.; Khoo, B.C. Stratification effect of air bubble on the shock wave from the collapse of cavitation bubble. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 919, A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xu, W.L.; Li, R. Collapse of cavitation bubbles near air bubbles. J. Hydrodyn. 2020, 32, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Zou, J.J.; Chen, Y.; Yan, S.; Li, S.; Zhang A, M. Study on the coupling of heterogeneous double bubbles and jet enhancement effect near rigid wall. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2023, 55, 1605–1617. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.M.; Li, S.M.; Cui, P.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.L. A unified theory for bubble dynamics. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 033323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.J.; Zhang, C.C.; Shen, C.; Wang, L.; Xin, Z.T. Manipulation of bubble collapse patterns near the wall of an adherent gas layer. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 101, 106722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liang, W.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.Y.; Lin, Y.L. Experimental study on the interaction of three linearly arranged spark bubbles with controlled phase differences. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 037105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.R.; Zhong, Q.; Yao, Z.F.; Zi, D.; Xiao, R.F.; Wang, F.J. Deflection of cavitation bubble near the rigid wall with a gas-containing hole. J. Hydrodyn. 2023, 35, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brujan, E.A.; Zhang, A.M.; Liu, Y.L.; Ogasawara, T.; Takahira, H. Jetting and migration of a laser-induced cavitation bubble in a rectangular channel. J. Fluid Mech. 2022, 948, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.B.; Li, B.; Xu, P.; Wakata, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, C.; Zuo, Z.G.; Liu, S.H. Cavitation bubble dynamics in a funnel-shaped tube. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 093313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, G.Y.; Zong, Z. Bubble motion and jet load near elastic-plastic structure under deep-water explosion. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 294, 116750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.K.; Zhang, M.D.; Huang, G.H.; Huang, B. Collapsing behavior of a spark-induced cavitation bubble near the air bubble attached to the tube nozzle. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 253, 111183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Su, K.; Wang, Y.; Gou, W. Effect of air bubble size on cavitation erosion reduction. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2017, 60, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Wu, S.Z.; Liu, K.; Jiang, M.Z.; Wang, Z.L. Experimental Study on Effect of Inclination Angle on Bubble Collapse near Attached Air Bubble. China Ocean Eng. 2023, 37, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Liu, K.; Yuan, S.J.; Jiang, M.Z.; Wang, Z.L. Dynamics of the passive pulsation of a surface-attached air bubble subjected to a nearby oscillating spark-generated bubble. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 067101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Chen, Z.P.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, T.R.; Corbett, C. Experimental studies of bubble dynamics inside a corner. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 64, 104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh BH, T.; Ohl, S.W.; Klaseboer, E.; Khoo, B.C. Jet orientation of a collapsing bubble near a solid wall with an attached air bubble. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Zong, Z.; Dong, J. Some dynamical characteristics of a non-spherical bubble in proximity to a free surface. Acta Mech. 2012, 223, 2331–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, A.M.; Han, R.; Cui, P. Experimental and numerical study of two underwater explosion bubbles: Coalescence, fragmentation and shock wave emission. Ocean Eng. 2019, 190, 106414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



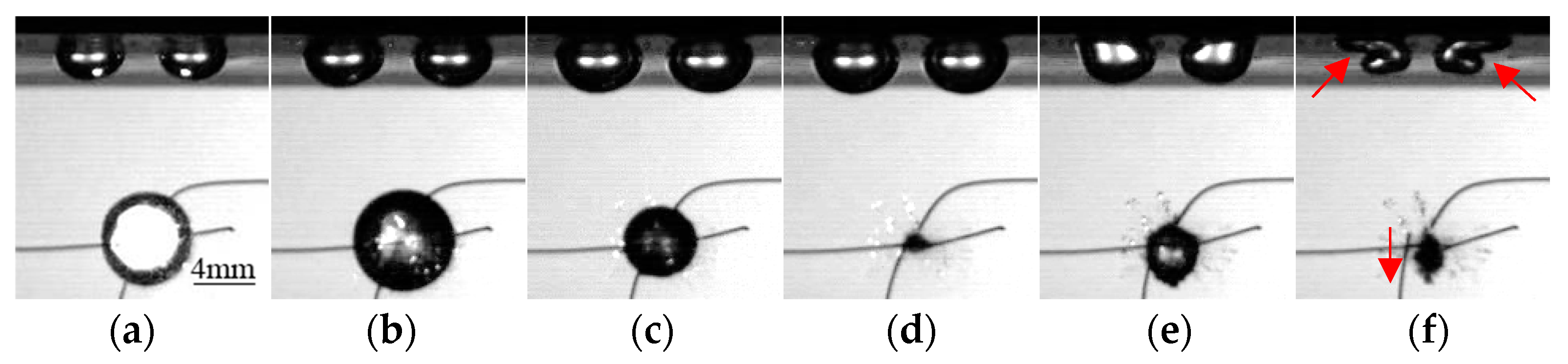

| γs | Re1 (mm) | Re2 (mm) | Rm (mm) | V′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.99 | 2.77 | 2.77 | 3.67 | 4.66 |
| 3.61 | 2.71 | 2.69 | 3.48 | 4.30 |
| γL | Re1 (mm) | Re2 (mm) | Rm (mm) | V′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.32 | 2.74 | 2.68 | 4.90 | 11.82 |
| 0.42 | 2.71 | 2.72 | 5.01 | 12.64 |
| γs | Re1 (mm) | Re2 (mm) | Rm (mm) | V′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.24 | 2.74 | 2.74 | 5.10 | 12.98 |
| 2.23 | 2.72 | 2.60 | 5.05 | 13.70 |
| γL | Re1 (mm) | Re2 (mm) | Rm (mm) | V′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.39 | 2.80 | 2.63 | 5.07 | 12.93 |
| 0.59 | 2.64 | 2.68 | 4.60 | 10.32 |
| Layout | γs | γL | Re1 (mm) | Re2 (mm) | Rm (mm) | V′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 2.15 | 0.42 | 2.71 | 2.72 | 5.01 | 12.64 |
| II | 2.23 | 0.42 | 2.72 | 2.60 | 5.05 | 13.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, M.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wu, S. Exploration of the Pulsation Characteristics of a Bubble Adjacent to the Structure with Multiple Air Bubble Adhesions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12091631
Jiang M, Liu K, Wang J, Zhao X, Wu S. Exploration of the Pulsation Characteristics of a Bubble Adjacent to the Structure with Multiple Air Bubble Adhesions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(9):1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12091631
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Mingzuo, Kun Liu, Jiaxia Wang, Xiaojie Zhao, and Shizeng Wu. 2024. "Exploration of the Pulsation Characteristics of a Bubble Adjacent to the Structure with Multiple Air Bubble Adhesions" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 9: 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12091631
APA StyleJiang, M., Liu, K., Wang, J., Zhao, X., & Wu, S. (2024). Exploration of the Pulsation Characteristics of a Bubble Adjacent to the Structure with Multiple Air Bubble Adhesions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(9), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12091631






