Submarine Slides and Their Influence on Gas Hydrate and Shallow Gas in the Pearl River Mouth Basin
Abstract
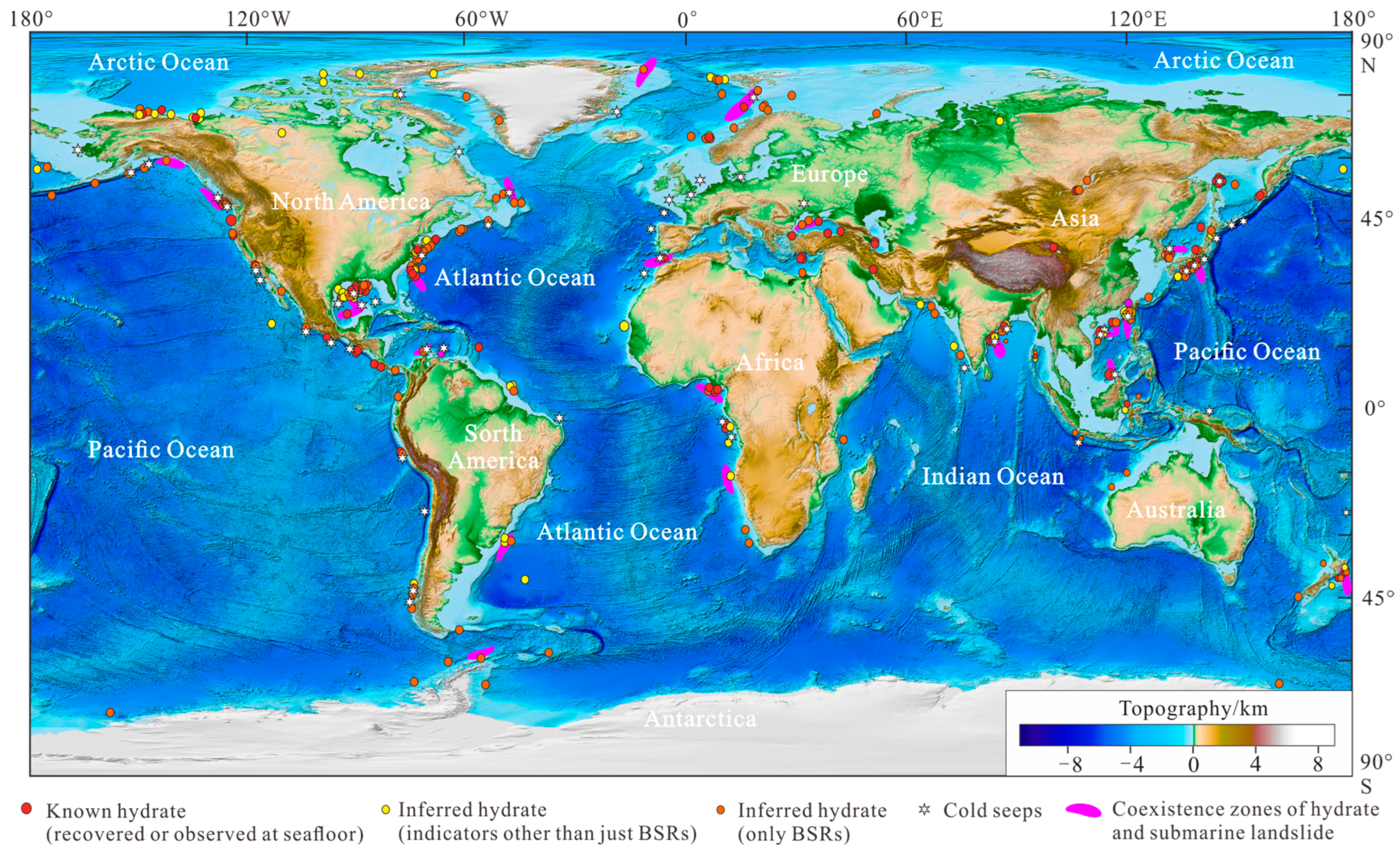
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting and Previous Research
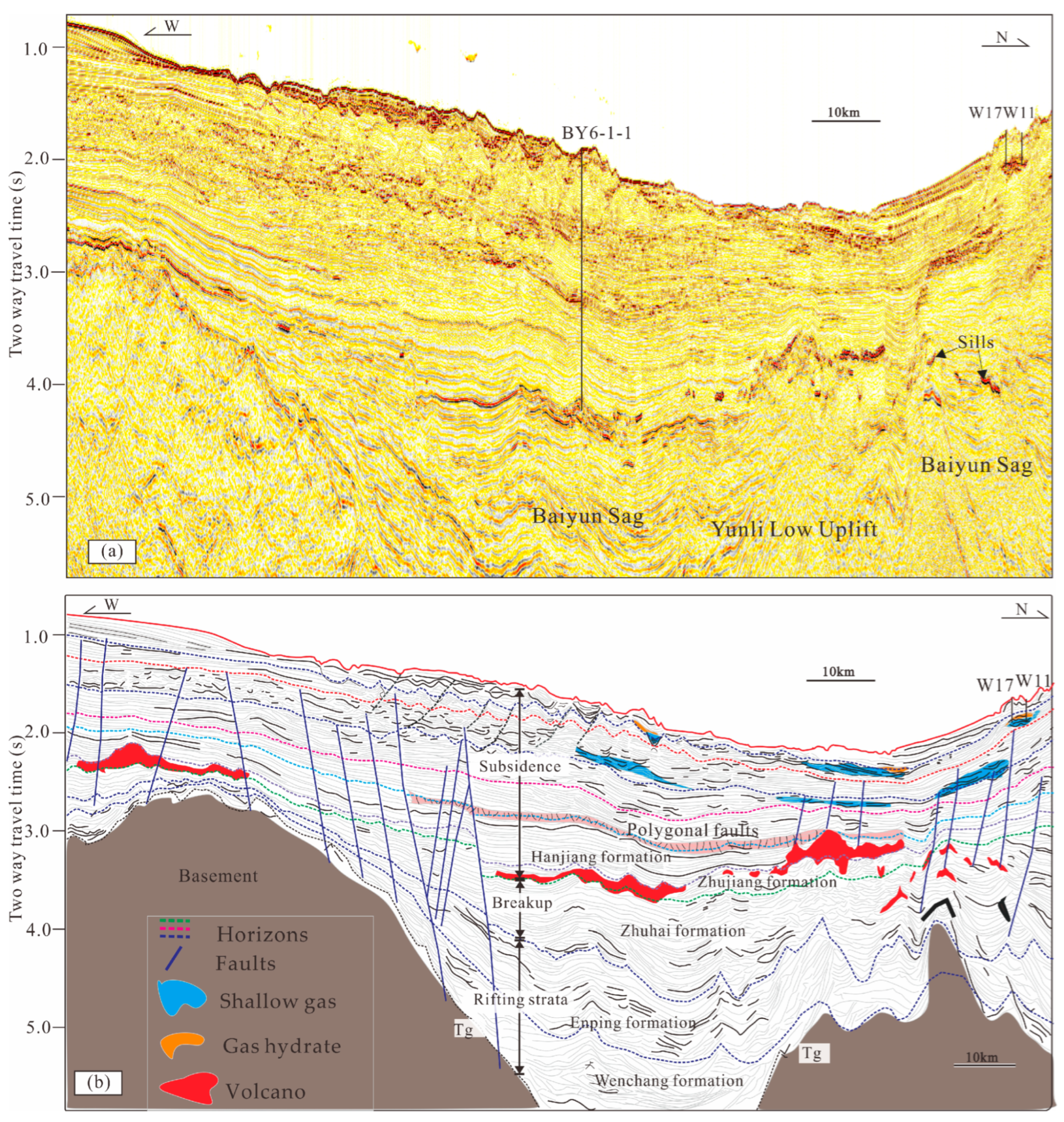
2.1. Regional Geological Background of the Pearl River Mouth Basin
2.2. Geohazards, Gas Hydrates and Shallow Gas in the PRMB
3. Data and Method
4. Results
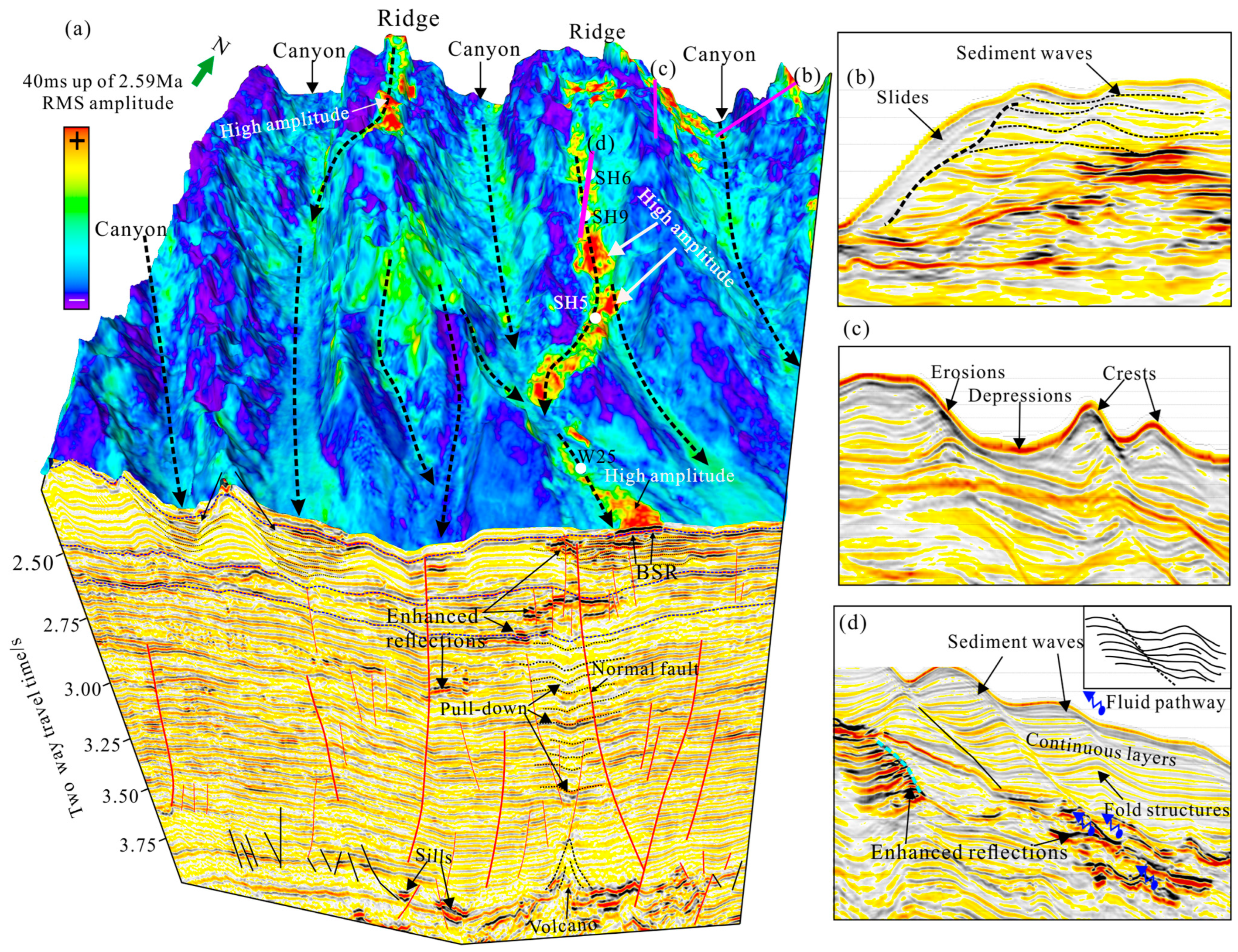
4.1. Distributions of Amplitude Anomalies Related to Gas Hydrate and Shallow Gas
4.1.1. Seismic Reflection Characteristics of Gas Hydrate and Shallow Gas
4.1.2. The Spatial Distributions of Gas Hydrates and Shallow Gas
4.2. Submarine Landslides and Their Relationships with Gas Hydrate Shallow Gas
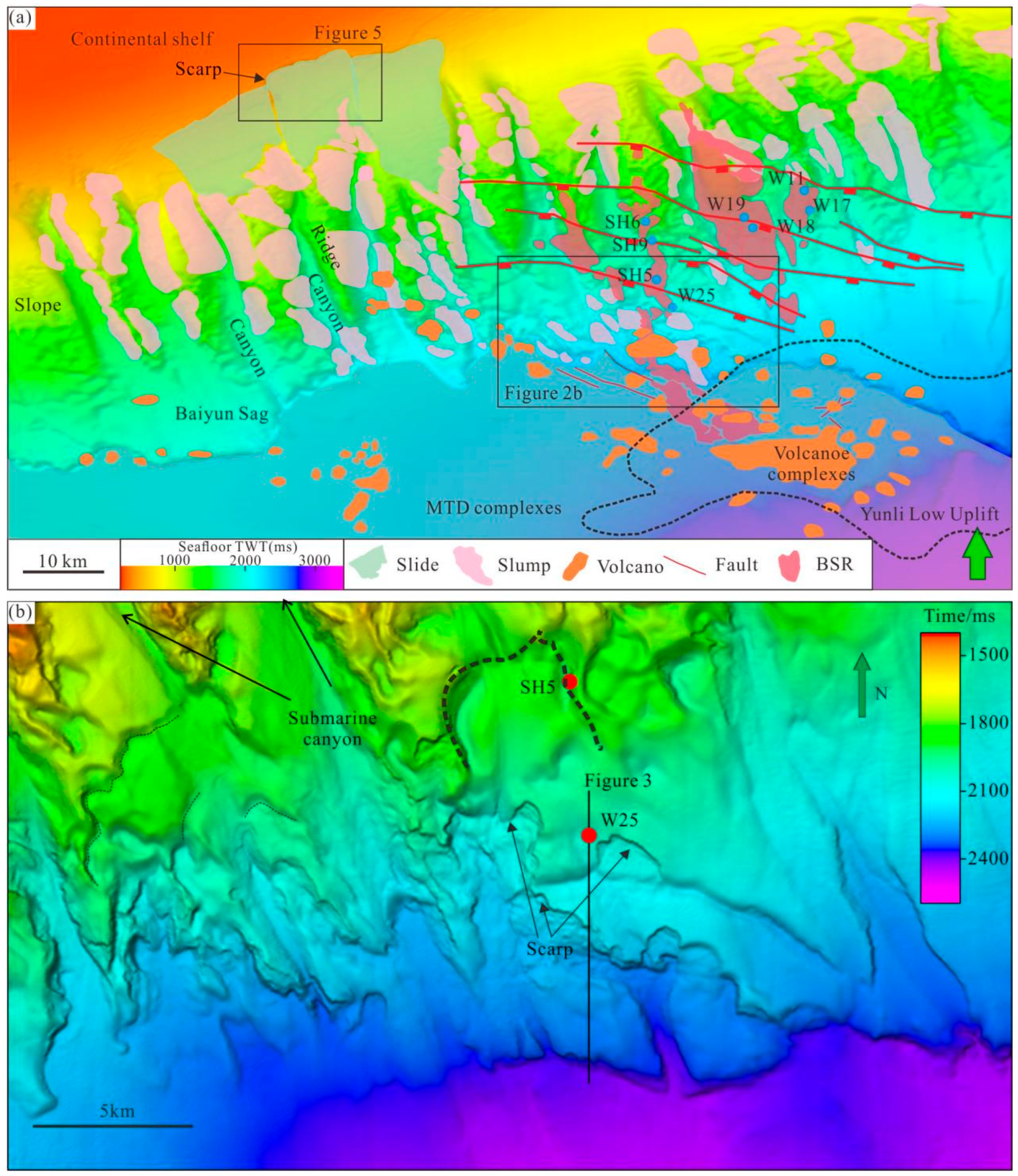
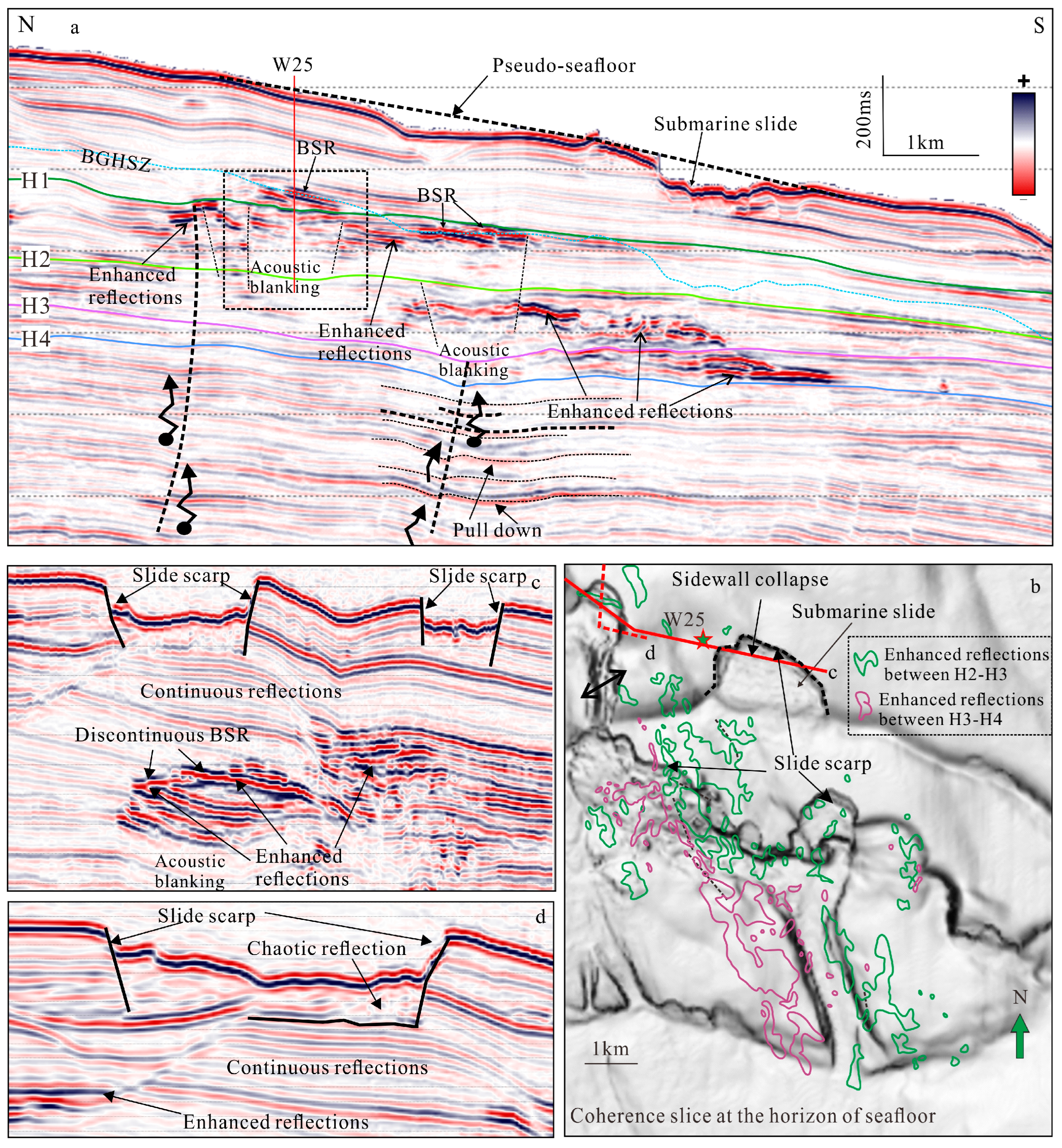
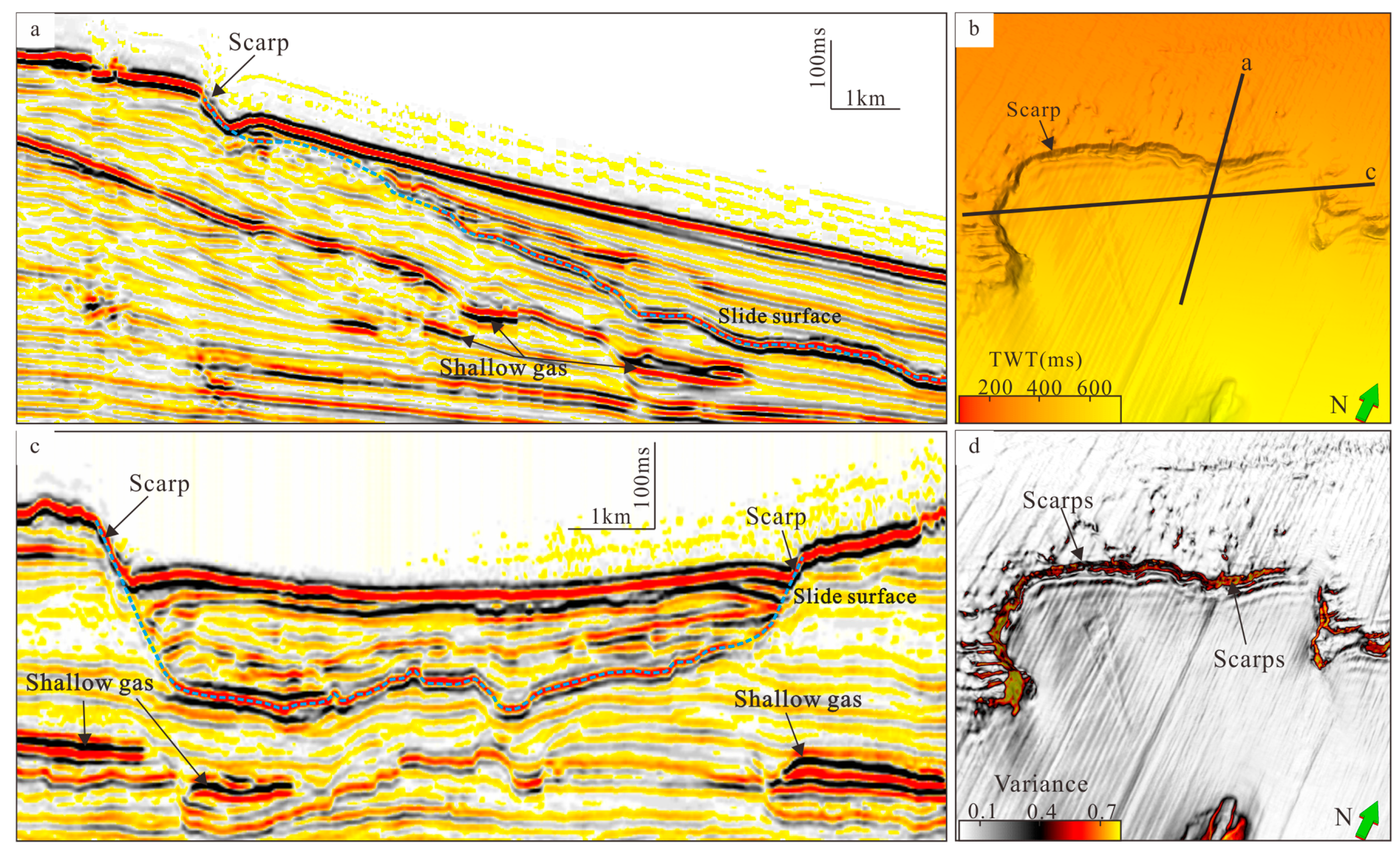
4.2.1. Characteristics of Submarine Slides
4.2.2. Characteristics of Reservoirs and Fluid Migration
4.3. Submarine Volcanic Complex
5. Discussion
5.1. Types and Distribution of Submarine Geohazards
5.2. Submarine Geohazards Related to the Distribution of Gas Hydrates
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sultan, N.; Foucher, J.; Cochonat, P.; Tonnerre, T.; Bourillet, J.; Ondreas, H.; Cauquil, E.; Grauls, D. Dynamics of gas hydrate: Case of the Congo continental slope. Mar. Geol. 2004, 206, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünz, S.; Mienert, J.; Vanneste, M.; Andreassen, K. Gas hydrates at the Storegga Slide: Constraints from an analysis of multicomponent, wide-angle seismic data. Geophysics 2005, 70, B19–B34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mienert, J.; Vanneste, M.; Bünz, S.; Andreassen, K.; Haflidason, H.; Sejrup, H.P. Ocean warming and gas hydrate stability on the mid-Norwegian margin at the Storegga Slide. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2005, 22, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, M.V.; Hassanpouryouzband, A.; Yang, J.; Tohidi, B. Insights into the climate-driven evolution of gas hydrate-bearing permafrost sediments: Implications for prediction of environmental impacts and security of energy in cold regions. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 14334–14346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigle, H.; Cook, A.; Fang, Y.; Bihani, A.; Song, W.; Flemings, P.B. Gas-driven tensile fracturing in shallow marine sediments. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2020JB020835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karstens, J.; Haflidason, H.; Berndt, C.; Crutchley, G.J. Revised Storegga Slide reconstruction reveals two major submarine landslides 12,000 years apart. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppel, C.D.; Kessler, J.D. The interaction of climate change and methane hydrates. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 126–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, L.L.; Van Dover, C.L.; German, C.R.; Kaiser, C.L.; Yoerger, D.R.; Ruppel, C.D.; Lobecker, E.; Skarke, A.D.; Wagner, J.K.S. Evidence for extensive methane venting on the southeastern US Atlantic margin. Geology 2013, 41, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.J.; Yang, J.; Li, A.; Mathias, S.; Hobbs, R. An irregular feather-edge and potential outcrop of marine gas hydrate along the Mauritanian margin. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 423, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skarke, A.; Ruppel, C.; Kodis, M.; Brothers, D.; Lobecker, E. Widespread methane leakage from the sea floor on the northern US Atlantic margin. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, C.; Feseker, T.; Treude, T.; Krastel, S.; Liebetrau, V.; Niemann, H.; Bertics, V.J.; Dumke, I.; Dünnbier, K.; Ferré, B.; et al. Temporal constraints on hydrate-controlled methane seepage off Svalbard. Science 2014, 343, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elger, J.; Berndt, C.; Rüpke, L.; Krastel, S.; Gross, F.; Geissler, W.H. Submarine slope failures due to pipe structure formation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.J.; Thatcher, K.E.; Mathias, S.A.; Yang, J. Deepwater canyons: An escape route for methane sealed by methane hydrate. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 323–324, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Bangs, N.L.; Hornbach, M.J.; Pecher, I.A.; Tobin, H.J.; Silver, E.A. The many double BSRs across the northern Hikurangi margin and their implications for subduction processes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 558, 116743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, B.; Flemings, P.B. Overpressure and fluid flow in the New Jersey continental slope: Implications for slope failure and cold seeps. Science 2000, 289, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugan, B.; Flemings, P.B.; Olgaard, D.L.; Gooch, M. Consolidation, effective stress, and fluid pressure of sediments from ODP Site 1073, US mid-Atlantic continental slope. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 215, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Collett, T.S.; Lee, M.W.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Wu, S. Geological controls on the occurrence of gas hydrate from core, downhole log, and seismic data in the Shenhu area, South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2014, 357, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Alves, T.M.; Li, W.; Wu, S. Recurrent slope failure enhancing source rock burial depth and seal unit competence in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, offshore South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2015, 643, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Völker, D.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Li, C.; Qin, Z.; et al. Three dimensional seismic studies of deep-water hazard-related features on the northern slope of South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 1125–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Alves, T.; Xie, X.; He, J.; Li, W.; Ni, X. Free gas accumulations in basal shear zones of mass-transport deposits (Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea): An important geohazard on continental slope basins. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 81, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Alves, T.M.; Lu, X.; Chen, C.; Xie, X. True volumes of slope failure estimated from a quaternary mass-transport deposit in the northern South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 2642–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Cartwright, J.; Xie, X.; Lu, X.; Yuan, S.; Chen, C. Reconstruction of repeated Quaternary slope failures in the northern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2018, 401, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Jackson, C.A.L.; Magee, C.; Xie, X. Deeply buried ancient volcanoes control hydrocarbon migration in the South China Sea. Basin Res. 2020, 32, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R. Late Jurassic–Cenozoic reconstructions of the Indonesian region and the Indian Ocean. Tectonophysics 2012, 570–571, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lin, J.; Qiu, N.; Jian, Z.; Wang, P.; Pang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, B. The role of magmatism in the thinning and breakup of the South China Sea continental margin: Special Topic: The South China Sea Ocean Drilling. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, B.; Hayes, D.E. Origin and History of the South China Sea Basin. Geophys. Union Geophys. Monogr. 1983, 27, 23–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lester, R.; McIntosh, K.; Van Avendonk, H.J.; Lavier, L.; Liu, C.-S.; Wang, T. Crustal accretion in the Manila trench accretionary wedge at the transition from subduction to mountain-building in Taiwan. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 375, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Replumaz, A.; Lacassin, R.; Tapponnier, P.; Leloup, P.H. Large river offsets and Plio-Quaternary dextral slip rate on the Red River fault (Yunnan, China). J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhong, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, S. Experimental evidence for the dynamics of the formation of the Yinggehai basin, NW South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2003, 372, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Zhao, D.; Xu, Y. Azimuthal Anisotropy Tomography of the Southeast Asia Subduction System. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2021JB022854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. New insights into marine basin opening. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, H.C.; Mohn, G.; Nirrengarten, M.; Sun, Z.; Stock, J.; Jian, Z.; Klaus, A.; Alvarez-Zarikian, C.A.; Boaga, J.; Bowden, S.A.; et al. Rapid transition from continental breakup to igneous oceanic crust in the South China Sea. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Mei, L.; Pang, X.; Gernigon, L.; Paton, D.; Zheng, J.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhong, Y. Rifted margin with localized detachment and polyphase magmatism: A new model of the northern South China Sea. GSA Bull. 2022, 135, 1667–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, Z.; Manatschal, G.; Pang, X.; Qiu, N.; Su, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Syn-rift magmatic characteristics and evolution at a sediment-rich margin: Insights from high-resolution seismic data from the South China Sea. Gondwana Res. 2021, 91, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Li, J. Propagated rifting in the Southwest Sub-basin, South China Sea: Insights from analogue modeling. J. Geodyn. 2016, 100, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Sun, Z.; Mohn, G.; Nirrengarten, M.; Tugend, J.; Manatschal, G.; Li, J. Lateral evolution of the rift-to-drift transition in the South China Sea: Evidence from multi-channel seismic data and IODP Expeditions 367&368 drilling results. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 531, 115932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gussinyé, M.; Collier, J.S.; Armitage, J.J.; Hopper, J.R.; Sun, Z.; Ranero, C.R. Towards a process-based understanding of rifted continental margins. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhong, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Shen, X.; Wu, Z.; Huang, K. Rapid post-rift tectonic subsidence events in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea margin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 147, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Peng, X.; Wu, S.; Lüdmann, T.; McIntosh, K.; Ma, B.; Xu, Z. Different expressions of the crustal structure across the Dongsha Rise along the northeastern margin of the South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 171, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, X.; Lin, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Kulhanek, D.K.; Wang, J.; et al. Ages and magnetic structures of the South China Sea constrained by deep tow magnetic surveys and IODP Expedition 349. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 4958–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xu, Z.; Sun, L.; Pang, X.; Yan, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C. The mechanism of post-rift fault activities in Baiyun sag, Pearl River Mouth basin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 89, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Wu, S.; Zhang, G.; Yuan, S. Rifting process and formation mechanisms of syn-rift stage prolongation in the deepwater basin, northern South China Sea. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 3715–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Chen, C.; Shao, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, M.; He, M.; Shen, J.; Lian, S.; Wu, X. Baiyun Movement, a Great Tectonic Event on the Oligocene-Miocene Boundary in the Northern South China Sea and Its Implications. Geol. Rev. 2007, 53, 145–151, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Graham, S.; Pang, X.; McHargue, T. Characteristics of migrating submarine canyons from the middle Miocene to present: Implications for paleoceanographic circulation, northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 27, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Su, M.; Zhuo, H.; Chen, H.; Jin, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z. Depositional architecture and evolution of Quaternary submarine canyon-fan system in the Baiyun Sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 170, 107167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qian, J.; Collett, T.S.; Shi, H.; Yang, S.; Yan, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, D. Characterization of gas hydrate distribution using conventional 3D seismic data in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Interpretation 2016, 4, SA25–SA37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, L.; Liu, J.; Jin, J.; Kuang, Z.; Zhou, J. The geophysical characteristics and identification of the coexistence of gas hydrate and free gas. Earth Sci. Front. 2025, 32, 1–16, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qian, J.; Sun, L. Geological controls on the occurrence of recently formed highly concentrated gas hydrate accumulations in the Shenhu area, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 116, 104294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-G.; Sun, Q.L.; Wu, T.-Y.; Yuan, S.Q.; Ma, Y.B.; Yao, G.S. Polygonal fault and oil-gas accumulation in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin. Acta Pet. Scinca 2009, 30, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.-X.; Zhang, M.; Liang, J.-Q.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Holland, M.; Schultheiss, P.; Fu, S.; Sha, Z.; the GMGS3 Science Team. Preliminary results of China’s third gas hydrate drilling expedition: A critical step from discovery to development in the South China Sea. Fire Ice Newsl. 2015, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Jiang, T.; Kuang, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Tian, D.; Xiong, P. Characteristics of gas chimneys and their implications on gas hydrate accumulation in the Shenhu area, northern south China sea. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 84, 103629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collett, T.-S.; Johnson, A.; Knapp, C.; Boswell, R. (Eds.) Natural gas hydrates: A review. In Natural Gas Hydrates–Energy Resource Potential and Associated Geologic Hazards; AAPG Memoir: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; Volume 89, pp. 146–219. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Wang, X.; Collett, T.S.; Guo, Y.; Kang, D.; Jin, J. Downhole log evidence for the coexistence of structure II gas hydrate and free gas below the bottom simulating reflector in the South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, J.; Kuang, Z.; Lu, C.; Kou, B.; Lu, Q.; Wang, J. Fine-grained gas hydrate reservoir properties estimated from well logs and lab measurements at the Shenhu gas hydrate production test site, the northern slope of the South China sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 122, 104676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Kang, D.; Lu, H.; Lu, J. Characterization of coexistence of gas hydrate and free gas using sonic logging data in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 101, 104540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, E.D., Jr.; Koh, C.A. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Jin, J.; Song, H.; Su, B.; Qian, J.; Zhang, G. The influence of submarine landslides on the distribution and enrichment of gas hydrate and free gas. Chin. J. Geophys. 2022, 65, 3674–3689, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J.; Liu, E.; Song, P.; Yan, D.; Luo, W.; Zhan, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Uysal, I.T.; Yang, P. Influencing Factors and Model of Shallow Gas Enrichment in the Quaternary Sediments of the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-G.; Wu, K.-Q.; Pei, J.-X.; Hu, L. Enrichment mechanisms and accumulation model of ultra-deep water and ultra-shallow gas: A case study of Lingshui 36-1 gas field in Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 1–13, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Collett, T.S.; Li, S.; Kuang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Deng, W.; Yan, W.; Qian, J.; Jin, J. Characterization of a complex sand-rich gas hydrate reservoir system in the Indian marine continental margin with downhole log and seismic data. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 155, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Shi, H.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Identification and accumulation control factors of natural gas hydrate and shallow gas in Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. China Offshore Oil Gas 2018, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; He, M.; Magee, C.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Luan, Z.; Zhang, G.; et al. Shallow gas and gas hydrate accumulations influenced by magmatic complexes in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2022, 453, 106928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Alves, T.M.; Wu, S.; Zhao, M.; Xie, X. Early Miocene magmatism in the Baiyun Sag (South China Sea): A view to the origin of intense post-rift magmatism. Gondwana Res. 2023, 120, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, S.; Cartwright, J.; Huuse, M. A subsurface evacuation model for submarine slope failure. Basin Res. 2009, 21, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, E.L.; Talling, P.J.; Carter, L. Which earthquakes trigger damaging submarine mass movements: Insights from a global record of submarine cable breaks? Mar. Geol. 2017, 384, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Chen, K.; He, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, F.; Yu, S. Recurrent mass transport deposits and their triggering mechanisms in the kaiping sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 73, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phrampus, B.J.; Hornbach, M.J. Recent changes to the Gulf Stream causing widespread gas hydrate destabilization. Nature 2012, 490, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboulot, V.; Ker, S.; Sultan, N.; Thomas, Y.; Marsset, B.; Scalabrin, C.; Ruffine, L.; Boulart, C.; Ion, G. Freshwater lake to salt-water sea causing widespread hydrate dissociation in the Black Sea. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Davies, R.J.; Yang, J. Gas trapped below hydrate as a primer for submarine slope failures. Mar. Geol. 2016, 380, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wei, J.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Zhang, W. Complex gas hydrate system in a gas chimney, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 104, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horozal, S.; Bahk, J.-J.; Urgeles, R.; Kim, G.Y.; Cukur, D.; Kim, S.-P.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, B.-J.; Kim, J.-H. Mapping gas hydrate and fluid flow indicators and modeling gas hydrate stability zone (GHSZ) in the Ulleung Basin, East (Japan) Sea: Potential linkage between the occurrence of mass failures and gas hydrate dissociation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 80, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, B. Petrophysical and consolidation behavior of mass transport deposits from the northern Gulf of Mexico, IODP Expedition 308. Mar. Geol. 2012, 315–318, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, M.; Moore, G.F.; Kimura, G. Slumping and mass transport deposition in the Nankai forearc: Evidence from IODP drilling and 3-D reflection seismic data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2011, 12, Q0AD13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, J.; Hu, J.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, W. Submarine Slides and Their Influence on Gas Hydrate and Shallow Gas in the Pearl River Mouth Basin. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13020308
Jin J, Hu J, Li L, Li J, Zhu Z, Wang X, Zhou J, Wang W. Submarine Slides and Their Influence on Gas Hydrate and Shallow Gas in the Pearl River Mouth Basin. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(2):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13020308
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Jiapeng, Jinzi Hu, Lixia Li, Jie Li, Zhenyu Zhu, Xiujuan Wang, Jilin Zhou, and Wenlong Wang. 2025. "Submarine Slides and Their Influence on Gas Hydrate and Shallow Gas in the Pearl River Mouth Basin" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 2: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13020308
APA StyleJin, J., Hu, J., Li, L., Li, J., Zhu, Z., Wang, X., Zhou, J., & Wang, W. (2025). Submarine Slides and Their Influence on Gas Hydrate and Shallow Gas in the Pearl River Mouth Basin. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(2), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13020308





