Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Rate of ZnAg3 as a Novel Bioabsorbable Material for Osteosynthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tensile Testing
2.2. Shear Testing
2.2.1. Fatigue Testing
2.2.2. Quasi-Static Testing
2.3. Electrochemical Testing
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Tensile Testing
3.2. Shear Testing
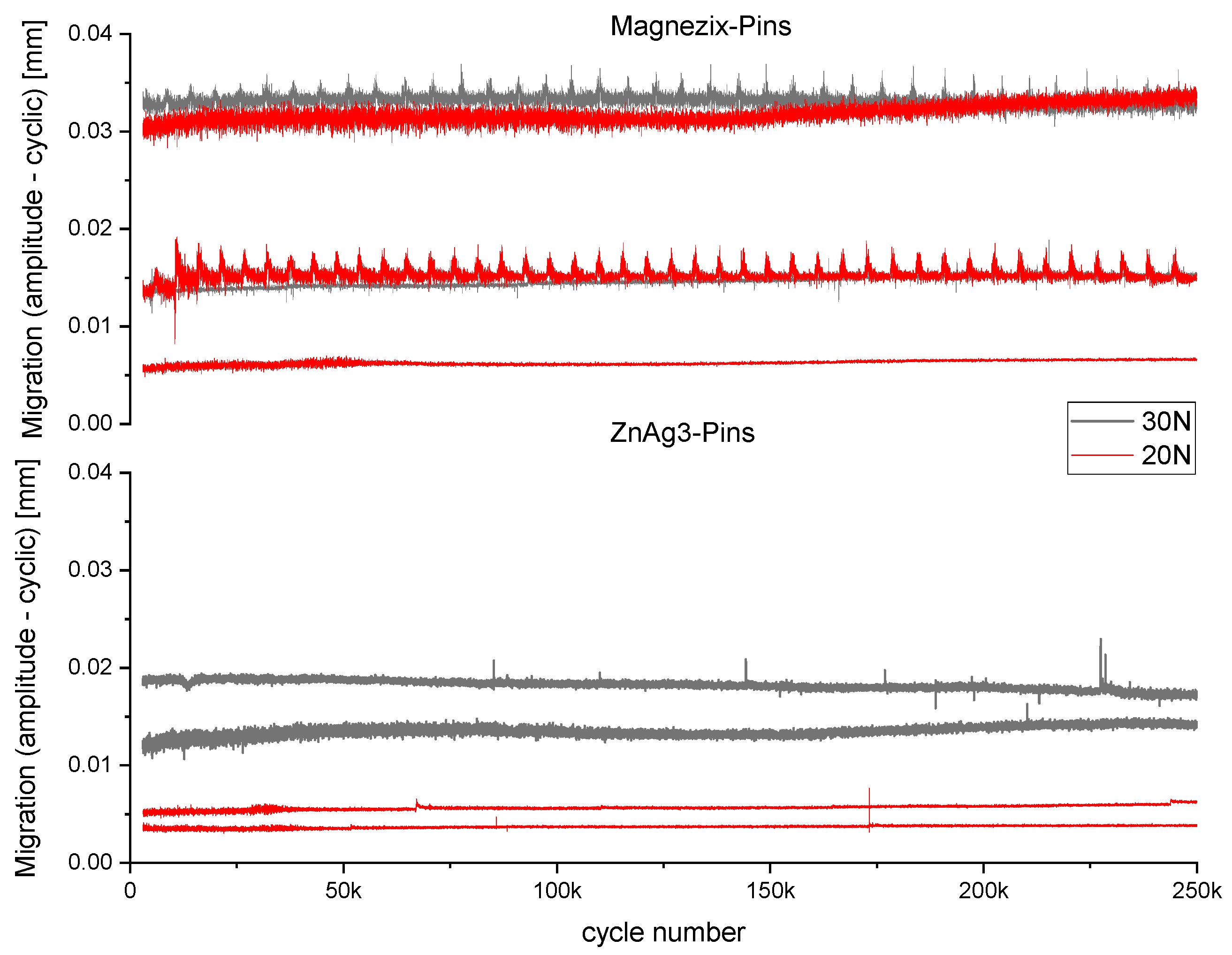
3.2.1. Fatigue Testing
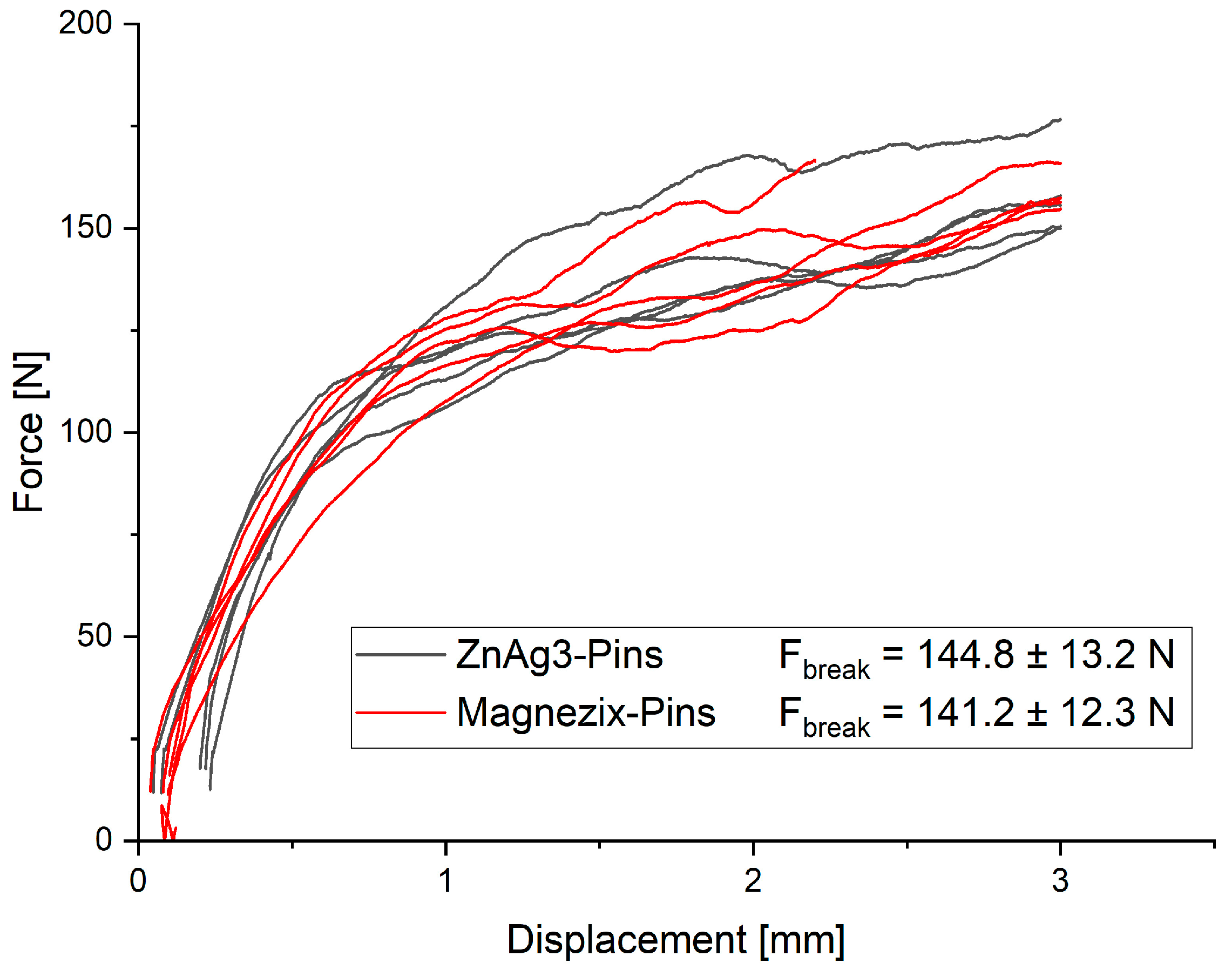
3.2.2. Quasi-Static Testing
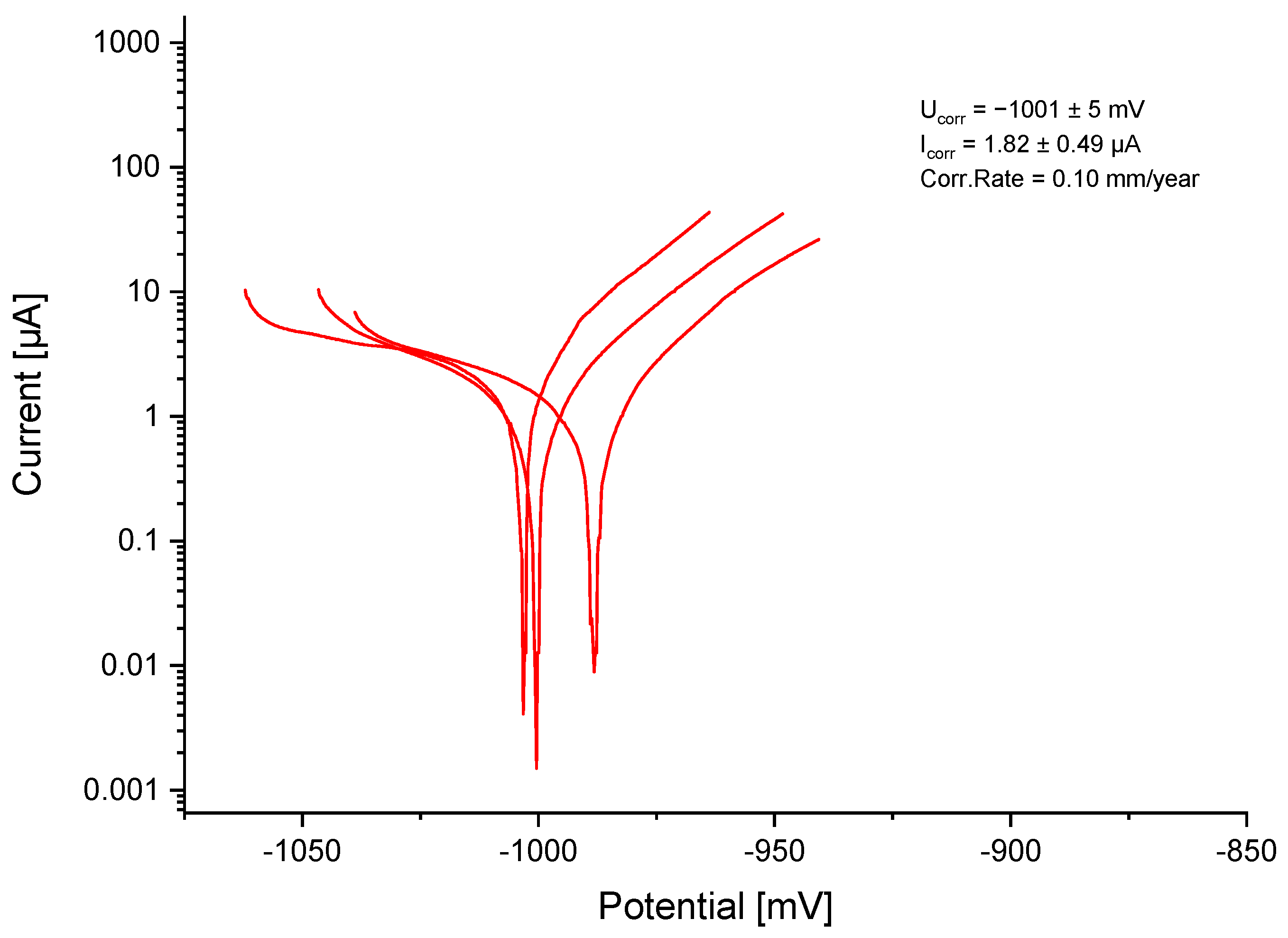
3.3. Electrochemical Testing
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanical Measurements
4.2. Electrochemical Measurements
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eliaz, N. Corrosion of metallic biomaterials: A review. Materials 2019, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressan, E.; Ferroni, L.; Gardin, C.; Bellin, G.; Sbricoli, L.; Sivolella, S.; Brunello, G.; Schwartz-Arad, D.; Mijiritsky, E.; Penarrocha, M.; et al. Metal nanoparticles released from dental implant surfaces: Potential contribution to chronic inflammation and peri-implant bone loss. Materials 2019, 12, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huiskes, R.; Weinans, H.; van Rietbergen, B. The relationship between stress shielding and bone resorption around total hip stems and the effects of flexible materials. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 274, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, S.W.; Cho, S.W.; Byun, S.H.; Yang, B.E. Bioabsorbable osteofixation materials for maxillofacial bone surgery: A review on polymers and magnesium-based materials. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walley, K.C.; Hofmann, K.J.; Velasco, B.T.; Kwon, J.Y. Removal of hardware after syndesmotic screw fixation: A systematic literature review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2016, 10, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, B.K.; Gamble, J.G.; Kha, S.T.; Hecht, G.G.; Vorhies, J.S.; Lucas, J.F. Indications for and risks associated with implant removal after pediatric trauma. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surgeons. Glob. Res. Rev. 2022, 6, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareb, B.; Roossien, C.C.; van Bakelen, N.B.; Verkerke, G.J.; Vissink, A.; Bos, R.R.M.; van Minnen, B. Comparison of the mechanical properties of biodegradable and titanium osteosynthesis systems used in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsma, E.J.; Rozema, F.R.; Bos, R.R.; de Bruijn, W.C. Foreign body reactions to resorbable poly(l-lactide) bone plates and screws used for the fixation of unstable zygomatic fractures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1993, 51, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallela, I.; Iizuka, T.; Salo, A.; Lindqvist, C. Lag-screw fixation of anterior mandibular fractures using biodegradable polylactide screws: A preliminary report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 57, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turvey, T.A.; Proffit, W.P.; Phillips, C. Biodegradable fixation for craniomaxillofacial surgery: A 10-year experience involving 761 operations and 745 patients. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.R.; Gohil, P. A review on biomaterials: Scope, applications & human anatomy significance. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2012, 2, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Staiger, M.P.; Pietak, A.M.; Huadmai, J.; Dias, G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: A review. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.; Michiardi, A.; Castaño, O.; Planell, J.A. Biomaterials in orthopaedics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 1137–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, F.; Kaese, V.; Haferkamp, H.; Switzer, E.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Wirth, C.J.; Windhagen, H. In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3557–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaass, C.; Ettinger, S.; Sonnow, L.; Koenneker, S.; Noll, Y.; Weizbauer, A.; Reifenrath, J.; Claassen, L.; Daniilidis, K.; Stukenborg-Colsman, C.; et al. Early results using a biodegradable magnesium screw for modified chevron osteotomies. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2016, 34, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.-l.; Atrens, A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 1999, 1, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtěch, D. Comparative mechanical and corrosion studies on magnesium, zinc and iron alloys as biodegradable metals. Mater. Teh. 2015, 49, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezuela, J.; Dargusch, M.S. The influence of alloying and fabrication techniques on the mechanical properties, biodegradability and biocompatibility of zinc: A comprehensive review. Acta Biomater. 2019, 87, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtěch, D.; Kubásek, J.; Šerák, J.; Novák, P. Mechanical and corrosion properties of newly developed biodegradable zn-based alloys for bone fixation. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3515–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, E.; Shao, J.; Ge, S. Advances on biodegradable zinc-silver-based alloys for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2021, 19, 22808000211062407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, A.A.; Guillory, R.J., II; Flom, K.L.; Morath, L.M.; Kolesar, T.M.; Mostaed, E.; Sikora-Jasinska, M.; Drelich, J.W.; Goldman, J. Analysis of vascular inflammation against bioresorbable zn–ag-based alloys. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 6779–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Heydari, Z.; Lami, G.H.; Saberi, A.; Baltatu, M.S.; Vizureanu, P. A comprehensive review of the current research status of biodegradable zinc alloys and composites for biomedical applications. Materials 2023, 16, 4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Hamzah, E.; Low, H.T.; Kasiri-Asgarani, M.; Farahany, S.; Akbari, E.; Cho, M.H. Fabrication of biodegradable zn-al-mg alloy: Mechanical properties, corrosion behavior, cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yang, F.; Ling, M.; Fan, Y. Association between bone trace elements and osteoporosis in older adults: A cross-sectional study. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720x221125984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M. Role of nutritional zinc in the prevention of osteoporosis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 338, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Su, Y.; Young, M.; Ma, J.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, L. Biological responses and mechanisms of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to zn and mg biomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27453–27461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, D. Bioabsorbable zinc ion induced biphasic cellular responses in vascular smooth muscle cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, P.K.; Shearier, E.R.; Zhao, S.; Guillory, R.J., 2nd; Zhao, F.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.W. Biodegradable metals for cardiovascular stents: From clinical concerns to recent zn-alloys. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.-H.; Yang, J.-A.; Zhu, D.; Ruan, L.; Takashima, K. Challenges in the use of zinc and its alloys as biodegradable metals: Perspective from biomechanical compatibility. Acta Biomater. 2019, 97, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora-Jasinska, M.; Mostaed, E.; Mostaed, A.; Beanland, R.; Mantovani, D.; Vedani, M. Fabrication, mechanical properties and in vitro degradation behavior of newly developed znag alloys for degradable implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierold, A.A. Reaction of bone to various metals. Arch. Surg. 1924, 9, 365–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, D.; Feyerabend, F.; Müller, W.D.; Schade, R.; Liefeith, K.; Kainer, K.U.; Willumeit, R. Antibacterial biodegradable mg-ag alloys. Eur. Cell Mater. 2013, 25, 284–298, discussion 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lee, P.; Lui, V.C.H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Lok, C.N.; To, M.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Wong, K.K.Y. Silver nanoparticles promote osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells and improve bone fracture healing in osteogenesis mechanism mouse model. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1949–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Schille, C.; Schweizer, E.; Rupp, F.; Heiss, A.; Legner, C.; Klotz, U.E.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Scheideler, L. Mechanical characteristics, in vitro degradation, cytotoxicity, and antibacterial evaluation of zn-4.0ag alloy as a biodegradable material. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and its application in dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehl, R.; Brunetto, P.S.; Woischnig, A.K.; Varisco, M.; Rajacic, Z.; Vosbeck, J.; Terracciano, L.; Fromm, K.M.; Khanna, N. Preventing implant-associated infections by silver coating. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquart, S.; Girod-Fullana, S.; Brouillet, F.; Pigasse, C.; Siadous, R.; Fatnassi, M.; Grimoud, J.; Rey, C.; Roques, C.; Combes, C. Injectable bone cement containing carboxymethyl cellulose microparticles as a silver delivery system able to reduce implant-associated infection risk. Acta Biomater. 2022, 145, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagelstein, S.; Zankovic, S.; Kovacs, A.; Barkhoff, R.; Seidenstuecker, M. Mechanical analysis and corrosion analysis of zinc alloys for bioabsorbable implants for osteosynthesis. Materials 2022, 15, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Escobar, D.; Champagne, S.; Yilmazer, H.; Dikici, B.; Boehlert, C.J.; Hermawan, H. Current status and perspectives of zinc-based absorbable alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2019, 97, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Märdian, S.; Seemann, R.; Schmidt-Bleek, K.; Heyland, M.; Duda, G. Biologie und biomechanik der frakturheilung und osteosynthese. Orthopädie Unfallchirurgie Up2date 2019, 14, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, H.; Munir, K.; Wen, C.; Li, Y. Recent research and progress of biodegradable zinc alloys and composites for biomedical applications: Biomechanical and biocorrosion perspectives. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 836–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Xie, C.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Research on an mg-zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törne, K.; Larsson, M.; Norlin, A.; Weissenrieder, J. Degradation of zinc in saline solutions, plasma, and whole blood. J. Biomed. Mater. Research. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 104, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törne, K.B.; Ashraf, K.F.; Andreas, Ö.; Jonas, W. Zn–mg and zn–ag degradation mechanism under biologically relevant conditions. Surf. Innov. 2018, 6, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Fitzpatrick, V.; Ibrahim, A.; Zwierstra, M.J.; Hanna, P.; Lechtig, A.; Nazarian, A.; Lin, S.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Design of biodegradable, implantable devices towards clinical translation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesner, M.; Zankovic, S.; Kovacs, A.; Benner, M.; Barkhoff, R.; Seidenstuecker, M. Biocompatibility assessment of zinc alloys as a new potential material for bioabsorbable implants for osteosynthesis. Materials 2023, 16, 5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, J.I.; Sammarco, V.J.; Boucher, H.R.; Parks, B.G.; Schon, L.C.; Myerson, M.S. Mechanical comparison of cyclic loading in five different first metatarsal shaft osteotomies. Foot Ankle Int. 2002, 23, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DIN En ISO 6892-1:2020-06; Metallic Materials-Tensile Testing Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature (ISO 6892-1:2019). Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2020.
- Kılıç, B.; Çalışkan, M.; Agar, A.; Uzun, B.; Ertem, F.; Gülabi, D.; Ertürk, C. Comparison of two different screw trajectories in the treatment of oblique scaphoid fractures: A mechanical study on composite bone models. Jt. Dis. Relat. Surg. 2021, 32, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clyde, J.; Kosmopoulos, V.; Carpenter, B. A biomechanical investigation of a knotless tension band in medial malleolar fracture models in composite sawbones®. J. Foot Ankle Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Foot Ankle Surg. 2013, 52, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faradaysches gesetz. Faust Metalltechnik Enzyklopädie; Engineering und Spezifikationsschreiben; Faust Metalltechnik GmbH: Laufach, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mostaed, E.; Sikora-Jasinska, M.; Drelich, J.W.; Vedani, M. Zinc-based alloys for degradable vascular stent applications. Acta Biomater. 2018, 71, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Mostaed, E.; Cao, X.; Huang, G.; Fabrizi, A.; Bonollo, F.; Chi, C.; Vedani, M. Effects of texture and grain size on mechanical properties of az80 magnesium alloys at lower temperatures. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaed, E.; Vedani, M.; Hashempour, M.; Bestetti, M. Influence of ecap process on mechanical and corrosion properties of pure mg and zk60 magnesium alloy for biodegradable stent applications. Biomatter 2014, 4, e28283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostaed, E.; Ge, Q.; Vedani, M.; Botelho, P.; Zanella, C.; Deflorian, F. Investigation on the influence of grain size on strength, ductility, and corrosion properties in mg and mg-zn based alloys for biodegradable stents. Eur. Cells Mater. 2013, 26, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Wang, K.; Strich, R.; Zhou, J.G. In vitro biodegradation behavior, mechanical properties, and cytotoxicity of biodegradable zn-mg alloy. J. Biomed. Mater. Research. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syntellix, A.G. Innovation verstehen-die besonderen eigenschaft von magnezix®. In Syn Broschuere; Special Report DE Druck; Syntellix AG: Hannover, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Jia, B.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, X.; Li, G.; Lin, W.; Zhu, D.; Dai, K.; Zheng, Y. Alloying design of biodegradable zinc as promising bone implants for load-bearing applications. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, P.K.; Drelich, J.; Goldman, J. Zinc exhibits ideal physiological corrosion behavior for bioabsorbable stents. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2577–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, H.; Alamdari, H.; Mantovani, D.; Dubé, D. Iron-manganese: New class of degradable metallic biomaterials prepared by powder metallurgy. Powder Metall. 2008, 51, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinhammer, M.; Hänzi, A.C.; Löffler, J.F.; Uggowitzer, P.J. Design strategy for biodegradable fe-based alloys for medical applications. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Hata, Y.; Watanabe, F. Implant fracture under dynamic fatigue loading: Influence of embedded angle and depth of implant. Odontology 2016, 104, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnka, H.J.; Parks, B.G.; Ivanic, G.; Chu, I.T.; Easley, M.E.; Schon, L.C.; Myerson, M.S. Six first metatarsal shaft osteotomies: Mechanical and immobilization comparisons. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2000, 381, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagelstein, S.; Seidenstuecker, M.; Kovacs, A.; Barkhoff, R.; Zankovic, S. Fixation performance of bioabsorbable zn-6ag pins for osteosynthesis. Materials 2022, 15, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Xie, X.H.; Zheng, Y.F.; Cong, Y.; Zhou, F.Y.; Qiu, K.J.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.H.; Huang, L.; Tian, L.; et al. Development of biodegradable zn-1x binary alloys with nutrient alloying elements mg, ca and sr. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törne, K.; Örnberg, A.; Weissenrieder, J. Influence of strain on the corrosion of magnesium alloys and zinc in physiological environments. Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindel, M. Bone mineral density of the metatarsal bones and the first ray in male sportsmen. Anat. (Int. J. Exp. Clin. Anat.) 2010, 4, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebeck, J.; Goldhahn, J.; Städele, H.; Messmer, P.; Morlock, M.M.; Schneider, E. Effect of cortical thickness and cancellous bone density on the holding strength of internal fixator screws. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2004, 22, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.R.; Harrington, R.M.; Lee, K.M.; Anderson, P.A.; Tencer, A.F.; Kowalski, D. Factors affecting the pullout strength of cancellous bone screws. J. Biomech. Eng. 1996, 118, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhou, W.; Xiong, P.; Wang, P.; Yuan, W.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Y. In vitro degradation and biocompatibility evaluation of typical biodegradable metals (mg/zn/fe) for the application of tracheobronchial stenosis. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahshoor, M.; Guo, Y. Biodegradable orthopedic magnesium-calcium (mgca) alloys, processing, and corrosion performance. Materials 2012, 5, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roesner, M.; Zankovic, S.; Kovacs, A.; Benner, M.; Barkhoff, R.; Seidenstuecker, M. Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Rate of ZnAg3 as a Novel Bioabsorbable Material for Osteosynthesis. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15020028
Roesner M, Zankovic S, Kovacs A, Benner M, Barkhoff R, Seidenstuecker M. Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Rate of ZnAg3 as a Novel Bioabsorbable Material for Osteosynthesis. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2024; 15(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoesner, Maria, Sergej Zankovic, Adalbert Kovacs, Moritz Benner, Roland Barkhoff, and Michael Seidenstuecker. 2024. "Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Rate of ZnAg3 as a Novel Bioabsorbable Material for Osteosynthesis" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 15, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15020028
APA StyleRoesner, M., Zankovic, S., Kovacs, A., Benner, M., Barkhoff, R., & Seidenstuecker, M. (2024). Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Rate of ZnAg3 as a Novel Bioabsorbable Material for Osteosynthesis. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 15(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15020028






