Abstract
Antibiotic resistance is the major reason for Helicobacter pylori treatment failure, and the increasing frequency of antibiotic resistance is a challenge for clinicians. Resistance to clarithromycin and metronidazole is a particular problem. The standard triple therapy (proton pump inhibitor, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin) is no longer appropriate as the first-line treatment in most areas. Recent guidelines for the treatment of H. pylori infection recommend a quadruple regimen (bismuth or non-bismuth) as the first-line therapy. This treatment strategy is effective for areas with high resistance to clarithromycin or metronidazole, but the resistance rate inevitably increases as a result of prolonged therapy with multiple antibiotics. Novel potassium-competitive acid blocker-based therapy may be effective, but the data are limited. Tailored therapy based on antimicrobial susceptibility test results is ideal. This review discussed the current important regimens for H. pylori treatment and the optimum H. pylori eradication strategy.
1. Introduction
Helicobacter pylori is a Gram-negative, flagellated, spiral-shaped bacterium that penetrates the mucosal layer of the upper gastrointestinal tract [1,2]. It is responsible for peptic ulcers, gastric cancer, and other gastric diseases [3,4] and represents 25% of all infection-related malignancies; it is also associated with increased risk for gastrointestinal cancer [5]. Eradicating H. pylori relieves peptic ulcer disease and reduces the risk of gastric cancer [6,7]. Globally, the guidelines for the treatment of H. pylori are gradually changing, and the indications are expanding [4,8,9,10]. In addition, with the economic development of many developing countries and the increase in the aging population, the number of people receiving H. pylori eradication is increasing.
In the 1990s, triple therapy, consisting of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), clarithromycin, and amoxicillin, was introduced for the eradication of H. pylori infection and is now the standard worldwide [11,12]. Since then, the eradication rate of triple therapy has markedly decreased in many regions [13,14]. The reasons for this decline include bacterial factors, reinfection, genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C19, and patient compliance [15]. Antibiotic resistance is the most important cause of failure of H. pylori treatment [13,16]. Resistance to clarithromycin of H. pylori is particularly serious; clarithromycin-containing regimens are no longer appropriate because of the <80% eradication rate [14,17]. The rate of resistance to metronidazole and quinolones (which are chiefly used as second- or third-line regimens) is >15% worldwide [14,16]. Because the antibiotics suitable for H. pylori eradication are limited (clarithromycin, amoxicillin, metronidazole, levofloxacin, tetracycline, and rifabutin), an increase in antibiotic resistance is a major problem. Therefore, the exclusion of clarithromycin is not enough to prevent antibiotic resistance of H. pylori.
Current guidelines emphasize the importance of the local prevalence of antibiotic resistance when selecting a suitable H. pylori treatment regimen [4,9,10]. In areas with a high rate of resistance to certain antibiotics, treatment success can be improved by avoiding the use of such antibiotics. However, although a new combination of antibiotics may have an improved eradication rate, it may trigger resistance. The Taiwanese Government has restricted antimicrobial usage, resulting in a low rate of primary resistance to clarithromycin and metronidazole in H. pylori [18]. However, the rate of primary levofloxacin resistance increased from 4.9% in 2000–2007 to 13.4% in 2011–2012 [18]. In addition, the use of several antibiotics increases the rate of complications [4]. Therefore, it is important to determine the optimum H. pylori eradication strategy according to the results of antibacterial susceptibility testing (AST). However, the possibility of false negatives and applicability in all medical institutions are problems [19,20]. We reviewed the most important anti-H. pylori regimens, which overcome antibiotic resistance and strategies that can be applied in practice.
2. H. Pylori Treatment Based on AST Results
Bacterial culture is typically performed before selecting an antibiotic, but H. pylori culture is intricate and time-consuming. Examination of the clarithromycin sensitivity of H. pylori improves the eradication rate [21,22]. Gerrits et al. showed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) that the A2142G and A2143G mutations in 23S rRNA were associated with antibiotic resistance [22]. PCR is comparatively simple and cost-effective [21]. Therefore, for H. pylori treatment based on AST, such as a diagnostic test for clarithromycin resistance is useful. However, in some cases, the eradication rate is < 100%. This is because the point mutations other than A2142G or A2143G lead to unreliable results, e.g., A2142C, A2115G, G2142T, A2142T, and T2182C [23,24]. In addition, the distribution of mutations differs geographically. The A2142C mutation has an incidence of <10% in the United States and Europe but has not been reported in Japan [25,26,27,28]. In Hong Kong, the frequency of the A2144G mutation is higher than in other regions [29]. The different distributions of these mutations likely affect the eradication rate.
H. pylori therapy based on AST results significantly improves the eradication rate. However, unlike other regimens, few studies have evaluated AST-based first-line regimens. The intention-to-treat (ITT) eradication rate for a first-line regimen is >90% [30,31,32]. In South Korea, a PCR-based first-line tailored therapy is superior to the standard triple therapy (STT; amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and PPI) [30,31]. In a Greek study, genotypic resistance-guided triple therapy (clarithromycin and levofloxacin susceptibility testing by GenoType HelicoDR assay) has achieved a high H. pylori eradication rate (90.2% by ITT and 97.8% by per-protocol (PP) analyses) [32]. In addition, AST-guided first-line triple regimens result in a >90% eradication rate in patients with H. pylori resistant to two antibiotics [33]. Because the rate of multidrug-resistant H. pylori is increasing, this is an encouraging finding. Culture-based H. pylori first-line eradication regimens show an excellent therapeutic effect, even in regions with a high rate of antimicrobial resistance [34]. The overall resistance rates to amoxicillin, clarithromycin, metronidazole, and moxifloxacin are 6.7%, 31.0%, 41.8%, and 39.2%, respectively. However, the eradication rate is 93.1% (ITT) and 100.0% (PP) [34]. Chen et al. reported that a susceptibility-guided first-line modified bismuth quadruple regimen for H. pylori in a region with a high rate of antimicrobial resistance had a high eradication rate [35].
The success rate of AST-guided second-line/rescue regimens is lower than that of first-line regimens. The eradication rate is poor (68%) despite susceptibility testing for salvage treatment [36]. Likewise, in the United States, culture-guided therapy has shown a 60% success rate for patients who had failed at least three treatments [37]. Even if the culture identifies a clarithromycin-sensitive, rerunning clarithromycin after treatment failure is not recommended [38]. Therefore, AST-guided therapy alone cannot reach the required eradication rate. Liou et al. showed that genotypic tailored therapy was not significantly more effective than empirical therapy for rescue therapy strategy (78.0% vs. 72.2%, p = 0.170) [39]. Therefore, appropriate empiric therapy is an alternative to genotypic tailored therapy for refractory H. pylori infection.
3. Bismuth Quadruple Therapy
Bismuth quadruple therapy (BQT) consists of bismuth, a PPI, metronidazole, and tetracycline. It is recommended as the first-line regimen by the Toronto Consensus, Maastricht V/Florence Consensus, and the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) guidelines [4,9,10]. The BQT regimen is not affected by clarithromycin resistance. According to a network meta-analysis, BQT for 10 or 14 days is superior to STT for 7 days [40]. Moreover, BQT is highly effective as an empirical first-line regimen (PP and ITT eradication rates are 98.8% and 92.7%, respectively) [41]. A randomized controlled trial (RCT) in Taiwan yielded a 96.0% eradication rate in patients who received BQT, although the rate of adverse events was 47.7% [42]. BQT was highly effective as the first-line regimen for H. pylori eradication in a prospective study in Spain (94.4% (ITT) and 96.2% (PP)) [43]. BQT has an excellent H. pylori eradication rate, but patient compliance may be reduced because of the large number of drugs. In addition, BQT is administered four times daily, which may also reduce patient compliance. To overcome this, twice daily BQT regimens have been introduced, and studies in South Korea have demonstrated their effectiveness [44,45]. Kim et al. demonstrated that twice daily BQT for 1 week was as effective and safe as the conventional four times daily BQT (93.9% vs. 92.9%) [45]. In addition, most patients show good compliance, and the eradication rate of the twice-daily BQT is high (88.2% (ITT) and 98.4% (PP)) [44]. A single capsule containing bismuth, metronidazole, and tetracycline has been developed. Xie et al. showed that single-capsule BQT therapy was effective for H. pylori eradication and well-tolerated (86.5% (ITT) and 94.6% (PP)) [46]. In an Italian study, single-capsule BQT therapy achieved eradication rates of 91% (ITT) and 97% (PP) [47]. In a meta-analysis, first- and second-line single-capsule BQT therapy achieved an eradication rate approaching 90%. Even this applies, regardless of the type and dose of the PPI, in patients with antibiotic resistance strain and in those formerly treated with clarithromycin [48]. A 7-day BQT second-line regimen exhibits an eradication rate of 93.6% (PP). The eradication rate of 7-day BQT is significantly higher than that of 14-day moxifloxacin containing triple regimen (93.6% vs. 73.8% (PP), p < 0.001) [49].
Whether the eradication rate improves when the treatment period is extended from 7 to 14 days is unclear. The Maastricht V/Florence Consensus recommends administration for at least 10 days [10]. The rate of resistance to tetracycline is reportedly low worldwide [50,51]. Therefore, resistance to metronidazole is the primary determinant of the success of H. pylori eradication. Resistance to metronidazole can be overcome by increasing the frequency, amount, and duration of administration, so treatment for ≥10 days is recommended in areas with a high rate of metronidazole resistance [52].
BQT has been reported to have excellent results in various studies, and the scope of its application is gradually expanding. In addition, BQT can be used relatively safely in patients with penicillin allergy [4]. BQT reportedly has a higher rate of adverse events than STT but a similar rate of patient compliance [53,54]. However, as the indication of BQT expands as a first-line treatment, there are also concerns. The number of second-line regimens that can be applied is greatly reduced when eradication with BQT as the first line fails. In addition, the rate of resistance to tetracycline, which is at present relatively low, may increase in the future. Various studies are needed to overcome this problem in the future.
4. Concomitant Therapy
Concomitant therapy, three antibiotics (clarithromycin, metronidazole or nitroimidazole, and amoxicillin) and PPI administered concomitantly, is recommended for 10 to 14 days [4,9,10]. Several meta-analyses have shown that concomitant therapy is superior to STT [55,56,57]. In addition, a recent meta-analysis demonstrated that concomitant therapy for 5 or 10 days was superior to STT for 5, 7, or 10 days [58]. A Spanish study demonstrated that concomitant therapy was significantly better than triple therapy (92% vs. 70% (ITT), p = 0.02 and 92% vs. 74% (PP), p = 0.05), and the eradication rate of concomitant therapy was superior to that of sequential therapy for antibiotic-resistant strains [59]. In addition, concomitant therapy and BQT as first-line regimens have shown similar H. pylori eradication rates in PP (97.7% vs. 96.2%, p = 0.605) and ITT (98.0% vs. 94.4%, p = 0.346) analyses [43]. Moreover, network meta-analyses have shown that concomitant therapy has superior efficacy to several other regimens [40,60].
Concomitant therapy is preferred over sequential therapy (a PPI and amoxicillin for 5 days, followed by a PPI, clarithromycin, and tinidazole for another 5 days) because it is simpler. There is controversy over whether concomitant therapy is superior to sequential therapy [61,62,63,64,65]. In a Spanish RCT, concomitant therapy was non-significantly superior (~ 5%) to sequential therapy (87% vs. 81% (ITT), p = 0.15; 91% vs. 86% (PP), p = 0.131) [65]. In addition, two meta-analyses reported no significant difference in eradication rate between concomitant therapy and sequential therapy [66,67].
The Maastricht V/Florence consensus does not recommend sequential therapy, unlike previous guidelines [10]. This is because sequential therapy has a lower eradication rate than concomitant therapy in cases of clarithromycin-resistant and metronidazole-susceptible H. pylori strains. Conversely, when H. pylori is susceptible to clarithromycin and resistant to metronidazole, sequential therapy shows a lower eradication rate than STT [10]. Increasing the dose or duration of metronidazole treatment may lead to the eradication of metronidazole-resistant H. pylori. The eradication rate of sequential therapy is low because the period of metronidazole administration is only 5 days.
Concomitant therapy has several limitations, such as a higher rate of adverse events than sequential therapy [68]. An increased frequency of complications may affect compliance with H. pylori treatment [69,70]. Although the frequency of adverse events is relatively high, the treatment period is <2 weeks, so the majority of patients complete the treatment course. In addition, there is concern that antibiotic resistance may be increased by excessive exposure to unnecessary antibiotics [71]. Finally, the effects of concomitant therapy are lower in H. pylori, resistant to both clarithromycin and metronidazole [72].
5. Hybrid Therapy
Hybrid therapy is a combination of sequential and concomitant therapy. Hybrid therapy comprises a PPI and amoxicillin for 7 days, followed by a PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole for 7 days [4]. Although the Toronto Consensus and Maastricht V/Florence Consensus do not recommend hybrid therapy, the ACG clinical guidelines recommend its use as a first-line treatment in patients without prior macrolide exposure in regions with a low rate of clarithromycin resistance. Several meta-analyses have reported the efficacy and tolerability of hybrid therapy [40,67,73]. Wang et al. demonstrated that hybrid therapy was an alternative to concomitant or sequential therapy (ITT eradication rates of hybrid, concomitant, and sequential therapy were 88.6%, 86.3%, and 84.7%, respectively; PP eradication rates were 92.1%, 92.5%, and 87.5%) [73]. In addition, there are no significant differences in tolerability or compliance between hybrid therapy and STT, sequential, or concomitant regimens [40,67,73].
In a prospective multicenter study, hybrid therapy cured >90% of patients with H. pylori infection in areas with high rates of clarithromycin and metronidazole resistance; this is similar to the eradication rate of concomitant therapy [74]. In addition, compliance with hybrid therapy is superior to that of concomitant therapy (98.8% vs. 95.2%, p = 0.05). However, the eradication rate of hybrid therapy is significantly lower for dual-resistant H. pylori. In a prospective study, the eradication rate in patients with dual antibiotic resistance (clarithromycin and metronidazole) was noticeably decreased (50%) compared to those with only clarithromycin resistance (91.4%) or metronidazole (90.5%) resistance [75].
6. Levofloxacin-Based Therapy
Levofloxacin is active on a large spectrum of various bacteria, and some studies use levofloxacin as the first-line treatment of H. pylori infection [15]. A prospective study in China showed that cefuroxime, levofloxacin, a PPI, and bismuth as first-line therapy achieved an H. pylori eradication rate of 97.2% of levofloxacin-susceptible cases and 84.0% of levofloxacin-resistant cases [76]. However, the eradication rate has been 0% in cases of resistance to both cefuroxime and levofloxacin. Once-daily 14- and 7-day levofloxacin dosing regimens (levofloxacin, clarithromycin, rabeprazole, and bismuth) have shown eradication rates of 94% and 84%, respectively [77]. Gan et al. compared the efficacy of different dosages of levofloxacin for the eradication of H. pylori [78]. The eradication rates in the once- and twice-daily groups were 77.5% and 79.5% (ITT) and 82.9% and 86.4% (PP), respectively [78]. There are no significant differences in the eradication or compliance rate. Bovine lactoferrin enhances the efficacy of levofloxacin-based first-line regimens for H. pylori infection [79]. The eradication success rate is 96.1% for esomeprazole/amoxicillin/levofloxacin/bovine lactoferrin and 75% for esomeprazole/amoxicillin/levofloxacin [79]. The LOAD (levofloxacin, omeprazole, nitazoxanide, and doxycycline) regimen has been introduced recently [71]. Basu et al. reported that LOAD had an eradication rate of 89.4% compared to 73.3% for STT (p < 0.05) [80].
Levofloxacin is a quinolone and is widely used worldwide for, for instance, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, tuberculosis, and H. pylori. Therefore, many patients have a history of exposure to levofloxacin. Most guidelines recommend that levofloxacin-based regimens be applied as a rescue rather than a first-line therapy [81]. The ACG clinical guidelines weakly recommend levofloxacin-based triple (amoxicillin, levofloxacin, and PPI), sequential (5 to 7 days of a PPI and amoxicillin, followed by 5 to 7 days of a PPI, nitroimidazole, and levofloxacin), or quadruple (a PPI, levofloxacin, doxycycline, and nitazoxanide for 7 or 10 days) first-line regimens [4].
Sitafloxacin is a fourth-generation fluoroquinolone and has potent activity against gyrA mutation-positive H. pylori strains [82]. Sitafloxacin is mainly used with amoxicillin or metronidazole as a rescue rather than first-line therapy. Sitafloxacin-containing third-line regimens are reportedly effective for H. pylori eradication (75.8% (ITT) and 83.3% (PP)) [83]. Fourth-generation fluoroquinolones, such as sitafloxacin and garenoxacin, may overcome the quinolone resistance of H. pylori [84,85]. Among 100 strains with high rates of resistance to clarithromycin, metronidazole, and levofloxacin, >95% are susceptible to sitafloxacin [86]. The efficacy of sitafloxacin or garenoxacin-containing regimens against gyrA mutation-positive H. pylori should be evaluated.
7. Rifabutin-Based Therapy
Rifabutin is a rifamycin derivative and structurally similar to rifampicin (anti-tuberculosis drug). It is mainly used for atypical tuberculosis, such as Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare and M. tuberculosis resistant to rifampicin [87]. Rifabutin suppresses protein synthesis by inhibiting the beta-subunit of the Helicobacter DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which is encoded by rpoB. Therefore, mutation of rpoB confers resistance to rifabutin [88]. All extant guidelines suggest that rifabutin-based regimens be considered only as rescue therapies for H. pylori eradication [81]. According to a meta-analysis, the cure rates of the second-, third-, and fourth/fifth-line rifabutin-based therapies are 79%, 66%, and 70%, respectively [87]. In an Italian study, rifabutin-based triple therapy (rifabutin, amoxicillin, and PPI) for 14 days achieved an eradication rate of 72.7% (PP) and 71.5% (ITT) in patients in whom H. pylori eradication failed following treatment with conventional antibiotics [89]. Rifabutin does not share antibiotic resistance with clarithromycin and amoxicillin and is fat-soluble and readily absorbed after oral intake [88,90]. In addition, rifabutin is stable at a wide range of pH values and is not degraded by gastric acid, and the rate of resistance in H. pylori is low because it is rarely used clinically [87,91]. Therefore, rifabutin-based regimens are important for rescue therapy. However, another study demonstrated that the eradication rate of rifabutin-based rescue therapy was not good, with 50.0% in ITT analysis and 54.5% in PP analysis [92]. As there are some parts that do not achieve a stable eradication rate as rescue therapy, it may be considered that related studies are needed.
To date, most studies on rifabutin-based regimens have focused on rescue therapy. Recently Graham et al. showed that a rifabutin-based triple regimen (amoxicillin, rifabutin, and a PPI) had a higher eradication rate than amoxicillin plus a PPI as the first-line empirical treatment of H. pylori (83.8% vs. 57.7%, p < 0.001) [93]. This suggests that rifabutin is a breakthrough first-line treatment in the era of antibiotic resistance. However, it is more expensive than other antibiotics. In addition, it may induce resistance to the regimen of tuberculosis treatment [94]. Moreover, because the use of rifampicin promotes point mutation of rpoB and increases the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of rifabutin, previous rifampicin treatment must be determined before administering rifabutin [95]. Finally, rifabutin has a small risk for myelotoxicity [87].
8. Potassium-Competitive Acid Blocker-Based Therapy
Potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB) is an inhibitor of gastric acid secretion, with a faster onset and longer-acting acid suppression, and is more potent than a PPI [96,97]. In addition, P-CAB does not require activation by stomach acid, so it can be taken irrespective of the timing of meals. In the treatment of H. pylori, gastric pH must be maintained above a certain level to enable antibiotic activity [98]. P-CAB inhibits H+ and K+-ATPase-mediated gastric acid secretion and is acid-stable and less impaired by the CYP2C19 system than PPIs [71,99]. Because PPIs have a short duration of action and their efficacy is influenced by various subtypes of cytochrome P450 (PPIs are mainly metabolized by CYP2C19 and CYP3A4), a new anti-H. pylori regimen containing PCAB has attracted attention [99,100]. Vonoprazan is currently marketed in Japan, promoting research on P-CAB for H. pylori treatment.
According to a multicenter RCT in Japan, the first-line eradication rate of vonoprazan-based triple therapy (vonoprazan, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin) was 92.6% vs. 75.9% for STT (p < 0.0001) [101]. A meta-analysis of Japanese studies involving 1599 patients demonstrated that vonoprazan-based triple therapy was significantly superior to STT for patients with clarithromycin-resistant strains (82.0% vs. 40.0%, p < 0.0001) [102]. By contrast, the eradication rate of clarithromycin-susceptible strains is not significantly different. If the organism is resistant to clarithromycin, the STT is slipped to the dual therapy (PPI + amoxicillin), and dual therapy is important to maintain gastric pH at ≥6. In this regard, it is thought that vonoprazan has strengths. In addition, a vonoprazan-based triple regimen is as effective as susceptibility-guided PPI-based STT for H. pylori eradication (97.4% vs. 95.7%) [103]. In a study of the efficacy of 7-day vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin dual therapy as a first-line H. pylori treatment, the eradication rates of dual (vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin) and triple therapies (vonoprazan, low-does amoxicillin, and clarithromycin) were 84.5% and 89.2% (p = 0.203) by ITT analysis, respectively, and 87.1% and 90.2% (p = 0.372) by PP analysis, respectively [104]. In the reality of increasing antimicrobial resistance, it can be said that the decrease in the total amount of antibiotics using vonoprazan shows a positive aspect in the future treatment of H. pylori.
In Japan, P-CAB-based regimens are licensed as first- and second-line treatment for H. pylori eradication. Murakami et al. demonstrated the efficacy of a P-CAB-based second-line triple regimen (success rate of 98.0%) [101]. Another RCT showed that vonoprazan-based triple therapy (vonoprazan, amoxicillin, and sitafloxacin) was more effective when PPI was used with those antibiotics as a third-line treatment regimen for H. pylori (83.3% vs. 57.1% (PP), p = 0.043) [83]. Therefore, P-CAB-based therapy may be a viable alternative first- and second-line regimen for H. pylori eradication.
9. Treatments When Primary Therapy Fails
All guidelines recommend avoiding antibiotics taken by a patient previously [4,8,9,10]. In particular, reuse of clarithromycin and levofloxacin must be avoided because of the high rates of resistance. They also recommend a BQT- or levofloxacin-based triple second-line treatment regimen for H. pylori [81]. Susceptibility testing for appropriate rescue therapy should be considered if the first- or second-line therapy fails [10,81].
According to the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus, after the failure of BQT as first-line treatment, a quinolone-containing triple or quadruple therapy is recommended [10]. After the failure of a first-line non-bismuth quadruple regimen, a BQT- or quinolone-containing triple or quadruple regimen is recommended [10]. BQT, non-bismuth quadruple therapy, and quinolone-containing triple therapy can be used in a non-overlapping manner with the second- or third-line treatment regimen [10].
The Toronto Consensus and the ACG guidelines, like the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus, emphasize the importance of BQT and levofloxacin-containing regimens as second-line [4,9]. An important difference from the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus is the opposition to the use of non-bismuth quadruple second-line regimen because this is less efficacious than other therapies [9]. In addition, rifabutin-based regimens should be reserved for patients with at least three previous treatment failures [9]. The ACG guidelines state that the second-line regimen should be selected based on previous exposure to antibiotics and local antibiotic resistance data [4].
10. Conclusions
Table 1 summarizes important regimens for the treatment of H. pylori. H. pylori treatment is an important global issue because it has been directly implicated as a cause of several gastrointestinal diseases. There is clear concern about increased rates of resistance over time, highlighting the necessity for suitable antibiotic use going forward to minimize further growth of antibiotic resistance. AST-based tailored therapy showed a good eradication rate when applied first-line. Because the rate of antibiotic resistance of H. pylori is increasing, the role of tailored therapies should be expanded. However, if tailored therapy cannot be applied to all patients due to realistic problems, using a locally highly effective empiric regimen is a reasonable alternative. In addition, when using such an empiric regimen, a simple and efficient H. pylori treatment strategy is needed. Therefore, we suggest BQT as first-line therapy when AST or regional resistance data are not available (Figure 1). If BQT is unavailable, we suggest empiric concomitant therapy. P-CAB may be an alternative, but data are sparse and restricted to East Asia.

Table 1.
Regimens for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection.
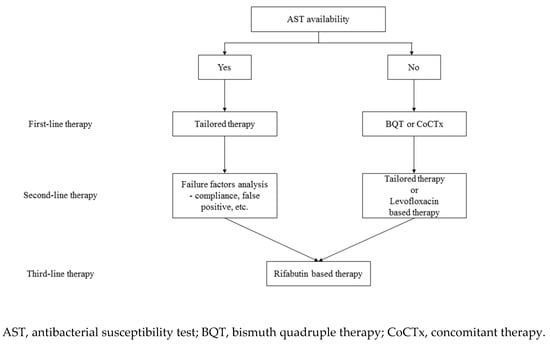
Figure 1.
Simplified H. pylori treatment strategy.
Tailored therapy, according to the AST results, promotes H. pylori treatment without increasing antibiotic resistance, so susceptibility testing should be emphasized. There are also additional considerations; for example, how to set the duration of treatment if susceptible to clarithromycin and how to choose a regimen (BQT or amoxicillin-metronidazole-PPI) if resistance to clarithromycin has not been studied. Further work should focus on maximizing the therapeutic effects of tailored therapies based on the results of AST.
Author Contributions
S.Y.K. wrote the manuscript, and J.-W.C. contributed to the study concept and design. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (grant number: 2020R1I1A306686511) and the Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (grant number: 2020R1F1A1076839).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kandulski, A.; Selgrad, M.; Malfertheiner, P. Helicobacter pylori infection: A clinical overview. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2008, 40, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McColl, K.E. Clinical practice. Helicobacter pylori infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, M.; Franceschi, S.; Vignat, J.; Forman, D.; de Martel, C. Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Howden, C.W.; Moss, S.F. ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 212–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testerman, T.L.; Morris, J. Beyond the stomach: An updated view of Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12781–12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chiang, T.H.; Chou, C.K.; Tu, Y.K.; Liao, W.C.; Wu, M.S.; Graham, D.Y. Association Between Helicobacter pylori Eradication and Gastric Cancer Incidence: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Hibi, T. Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. Future. Microbiol. 2010, 5, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Jung, H.K.; Lee, H.L.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.G.; Shin, W.G.; Shin, E.S.; Lee, Y.C. Korean College of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 62, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallone, C.A.; Chiba, N.; van Zanten, S.V.; Fischbach, L.; Gisbert, J.P.; Hunt, R.H.; Jones, N.L.; Render, C.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Moayyedi, P.; et al. The Toronto Consensus for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Adults. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Gonzalez, L.; Calvet, X.; Garcia, N.; Lopez, T.; Roque, M.; Gabriel, R.; Pajares, J.M. Proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin and either amoxycillin or nitroimidazole: A meta-analysis of eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Current European concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection The Maastricht Consensus Report. European Helicobacter pylori Study Group. Gut 1997, 41, 8–13. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y.; Fischbach, L. Helicobacter pylori treatment in the era of increasing antibiotic resistance. Gut 2010, 59, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoldi, A.; Carrara, E.; Graham, D.Y.; Conti, M.; Tacconelli, E. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance in Helicobacter pylori: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis in World Health Organization Regions. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Choi, D.J.; Chung, J.W. Antibiotic treatment for Helicobacter pylori: Is the end coming? World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 6, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thung, I.; Aramin, H.; Vavinskaya, V.; Gupta, S.; Park, J.Y.; Crowe, S.E.; Valasek, M.A. Review article: The global emergence of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 514–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.Y.; Park, D.I.; Park, H.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, Y.J. Dual-priming oligonucleotide-based multiplex PCR for the detection of Helicobacter pylori and determination of clarithromycin resistance with gastric biopsy specimens. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.M.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, M.J.; Chen, C.C.; Fang, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Wu, J.; Luo, J.; Liou, T.; Chang, W.; et al. The Primary Resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Taiwan after the National Policy to Restrict Antibiotic Consumption and Its Relation to Virulence Factors-A Nationwide Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Park, K.S. Optimal First-Line Treatment for Helicobacter pylori Infection: Recent Strategies. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 9086581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, C.; Blanco, A.; Alarcon, T. Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 30, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.J.; Kim, N.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, B.H.; Nam, R.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, M.K.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, D.H.; Jung, H.C.; et al. Change in antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori strains and the effect of A2143G point mutation of 23S rRNA on the eradication of H. pylori in a single center of Korea. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrits, M.M.; van Vliet, A.H.; Kuipers, E.J.; Kusters, J.G. Helicobacter pylori and antimicrobial resistance: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megraud, F. H pylori antibiotic resistance: Prevalence, importance, and advances in testing. Gut 2004, 53, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulten, K.; Gibreel, A.; Skold, O.; Engstrand, L. Macrolide resistance in Helicobacter pylori: Mechanism and stability in strains from clarithromycin-treated patients. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 1997, 41, 2550–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, G.G.; Shortridge, D.; Versalovic, J.; Beyer, J.; Flamm, R.K.; Graham, D.Y.; Ghoneim, A.T.; Tanaka, S.K. A PCR-oligonucleotide ligation assay to determine the prevalence of 23S rRNA gene mutations in clarithromycin-resistant Helicobacter pylori. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, T.; Domingo, D.; Prieto, N.; Lopez-Brea, M. Clarithromycin resistance stability in Helicobacter pylori: Influence of the MIC and type of mutation in the 23S rRNA. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorn, L.J.; Glupczynski, Y.; Kusters, J.G.; Megraud, F.; Midolo, P.; Maggi-Solca, N.; Queiroz, D.M.; Nouhan, N.; Stet, E.; Quint, W.G. Accurate prediction of macrolide resistance in Helicobacter pylori by a PCR line probe assay for detection of mutations in the 23S rRNA gene: Multicenter validation study. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Fujimura, S.; Udagawa, H.; Shimizu, T.; Maisawa, S.; Ozawa, K.; Iinuma, K. Antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori strains in Japanese children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Wong, B.C.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Berg, D.E.; Cho, C.H.; Lai, K.C.; Hu, W.H.; Fung, F.M.; Hui, W.M.; Lam, S.K. High prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection with dual resistance to metronidazole and clarithromycin in Hong Kong. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.I.; Cheung, D.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Jun, E.J.; Oh, J.H.; Chung, W.C.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.S.; Park, S.; et al. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori according to 23S ribosomal RNA point mutations associated with clarithromycin resistance. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Jeon, S.R.; Kim, H.G.; Jin, S.Y.; Park, S. Cost-effectiveness of a tailored Helicobacter pylori eradication strategy based on the presence of a 23S ribosomal RNA point mutation that causes clarithromycin resistance in Korean patients. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papastergiou, V.; Mathou, N.; Licousi, S.; Evgenidi, A.; Paraskeva, K.D.; Giannakopoulos, A.; Stavrou, P.; Platsouka, E.; Karagiannis, J.A. Seven-day genotypic resistance-guided triple Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy can be highly effective. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosme, A.; Montes, M.; Ibarra, B.; Tamayo, E.; Alonso, H.; Mendarte, U.; Lizasoan, J.; Herreros-Villanueva, M.; Bujanda, L. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing before first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with dual or triple antibiotic resistance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, N.; Nam, R.H.; Lee, S.M.; Kwon, Y.H.; Sohn, S.D.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, D.H.; Jung, H.C. Favorable outcomes of culture-based Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in a region with high antimicrobial resistance. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Long, X.; Ji, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, D.; Gao, H.; Xu, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y. Randomised controlled trial: Susceptibility-guided therapy versus empiric bismuth quadruple therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori treatment. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumel, B.; Goelz, H.; Kist, M.; Glocker, E.O. Retrospective study on outcome of salvage Helicobacter pylori eradication therapies based on molecular genetic susceptibility testing. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakta, D.; Graham, D.Y.; Chan, J.; El-Serag, H.B. Lessons From Using Culture-Guided Treatment After Referral for Multiple Treatment Failures for Helicobacter pylori Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1531–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylina, M.; Munoz, N.; Sanchez-Delgado, J.; Lopez-Gongora, S.; Calvet, X.; Puig, I. Systematic review: Would susceptibility-guided treatment achieve acceptable cure rates for second-line Helicobacter pylori therapy as currently practiced? Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.M.; Chen, P.Y.; Luo, J.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Fang, Y.J.; Yang, T.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Bair, M.J.; Chenet, M.J.; et al. Efficacies of Genotypic Resistance-Guided vs Empirical Therapy for Refractory Helicobacter pylori Infection. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Z.; Threapleton, D.E.; Wang, J.Y.; Xu, J.M.; Yuan, J.Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Ye, Q.L.; Guo, B.; Mao, C.; et al. Comparative effectiveness and tolerance of treatments for Helicobacter pylori: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2015, 351, h4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Hung, I.F.; Seto, W.K.; Tong, T.; Hsu, A.S.; Lam, F.Y.; But, D.Y.K.; Wong, S.Y.; Leung, W.K. Ten day sequential versus 10 day modified bismuth quadruple therapy as empirical firstline and secondline treatment for Helicobacter pylori in Chinese patients: An open label, randomised, crossover trial. Gut 2014, 63, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.I.; Tsay, F.W.; Graham, D.Y.; Tsai, T.J.; Tsai, K.W.; Kao, J.Y.; Peng, N.J.; Kuo, C.H.; Kao, S.S.; Wang, H.M.; et al. Equivalent Efficacies of Reverse Hybrid and Bismuth Quadruple Therapies in Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias-Garcia, F.; Baston-Rey, I.; de la Iglesia-Garcia, D.; Calvino-Suarez, C.; Nieto-Garcia, L.; Dominguez-Munoz, J.E. Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy versus concomitant quadruple therapy as first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection in an area of high resistance to clarithromycin: A prospective, cross-sectional, comparative, open trial. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Chung, J.W.; Woo, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.O.; Kwon, K.A.; Park, D.K. Two-week bismuth-containing quadruple therapy and concomitant therapy are effective first-line treatments for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A prospective open-label randomized trial. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6790–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Sung, I.K.; Park, H.S. Efficacy and safety of twice a day, bismuth-containing quadruple therapy using high-dose tetracycline and metronidazole for second-line Helicobacter pylori eradication. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; et al. New single capsule of bismuth, metronidazole and tetracycline given with omeprazole versus quadruple therapy consisting of bismuth, omeprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in duodenal ulcer patients: A Chinese prospective, randomized, multicentre trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorini, G.; Zullo, A.; Saracino, I.M.; Gatta, L.; Pavoni, M.; Vaira, D. Pylera and sequential therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication: A culture-based study in real clinical practice. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, O.P.; McNicholl, A.G.; Gisbert, J.P. Meta-analysis of three-in-one single capsule bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Roh, J.H.; Park, M.I.; Park, S.J.; Moon, W.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, K.; Heo, J.J. Effect of 7-day Bismuth Quadruple Therapy versus 14-day Moxifloxacin Triple Therapy for Second-line Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy. Korean. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 73, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyanova, L.; Mitov, I. Geographic map and evolution of primary Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibacterial agents. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2010, 8, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megraud, F.; Coenen, S.; Versporten, A.; Kist, M.; Lopez-Brea, M.; Hirschl, A.M.; Andersen, L.P.; Goossens, H.; Glupczynski, Y.; Study Group participants. Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics in Europe and its relationship to antibiotic consumption. Gut 2013, 62, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbach, L.; Evans, E.L. Meta-analysis: The effect of antibiotic resistance status on the efficacy of triple and quadruple first-line therapies for Helicobacter pylori. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venerito, M.; Krieger, T.; Ecker, T.; Leandro, G.; Malfertheiner, P. Meta-analysis of bismuth quadruple therapy versus clarithromycin triple therapy for empiric primary treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Digestion 2013, 88, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzaris, G.J.; Petraki, K.; Archavlis, E.; Amberiadis, P.; Christoforidis, P.; Kourtessas, D.; Chiotakakou, E.; Triantafyllou, G. Omeprazole triple therapy versus omeprazole quadruple therapy for healing duodenal ulcer and eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection: A 24-month follow-up study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 14, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Calvet, X. Review article: Non-bismuth quadruple (concomitant) therapy for eradication of Helicobater pylori. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, A.S.; Kramer, J.R.; Graham, D.Y.; Treiber, G. Meta-analysis: Four-drug, three-antibiotic, non-bismuth-containing “concomitant therapy” versus triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Calvet, X. Update on non-bismuth quadruple (concomitant) therapy for eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2012, 5, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.J.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, Y.N.; Chen, C.C.; Fang, Y.J.; Lin, J.T.; Wu, M.S.; Liou, J.M.; Taiwan Gastrointestinal Disease Helicobacter Consortium. Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis: Concomitant Therapy vs. Triple Therapy for the First-Line Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1444–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Pazos-Pacheco, C.; Vinagre-Rodriguez, G.; Perez-Gallardo, B.; Duenas-Sadornil, C.; Hernandez-Alonso, M.; Gonzalez-Garcia, G.; Mateos-Rodriguez, J.M.; Fernandez-Bermejo, M.; Gisbert, J.P. Nonbismuth quadruple (concomitant) therapy: Empirical and tailored efficacy versus standard triple therapy for clarithromycin-susceptible Helicobacter pylori and versus sequential therapy for clarithromycin-resistant strains. Helicobacter 2012, 17, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.S.; Park, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Nam, E.; Lee, H.L. Efficacy of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapies in Korea: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.W.; Han, J.P.; Kim, K.O.; Kim, S.Y.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, C.W.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, B.W.; Bang, B.W.; et al. Ten-day empirical sequential or concomitant therapy is more effective than triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A multicenter, prospective study. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2016, 48, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, B.W.; Ji, J.S.; Choi, H. Randomized clinical trial comparing 10- or 14-day sequential therapy and 10- or 14-day concomitant therapy for the first line empirical treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Choe, J.W.; Jung, S.W.; Hyun, J.J.; Jung, Y.K.; Koo, J.S.; Yim, H.J. Helicobacter pylori eradication rates of concomitant and sequential therapies in Korea. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, T.L.; Fock, K.M.; Song, M.; Ang, D.; Kwek, A.B.; Ong, J.; Tan, J.; Teo, E.K.; Dhamodaran, S. Ten-day triple therapy versus sequential therapy versus concomitant therapy as first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicholl, A.G.; Marin, A.C.; Molina-Infante, J.; Castro, M.; Barrio, J.; Ducons, J.; Calvet, X.; Coba, C.; Montoro, M.; Bory, F.; et al. Randomised clinical trial comparing sequential and concomitant therapies for Helicobacter pylori eradication in routine clinical practice. Gut 2014, 63, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatta, L.; Vakil, N.; Vaira, D.; Scarpignato, C. Global eradication rates for Helicobacter pylori infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis of sequential therapy. BMJ 2013, 347, f4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Deng, T.; Luo, H. Meta-analysis of sequential, concomitant and hybrid therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zullo, A.; Scaccianoce, G.; De Francesco, V.; Ruggiero, V.; D’Ambrosio, P.; Castorani, L.; Bonfrate, L.; Vannella, L.; Hassan, C.; Portincasa, P. Concomitant, sequential, and hybrid therapy for H. pylori eradication: A pilot study. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2013, 37, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Hyun, J.J.; Jung, S.W.; Koo, J.S.; Yim, H.J.; Park, J.J.; Chun, H.J.; Choi, J.H. Comparative study of Helicobacter pylori eradication rates with 5-day quadruple “concomitant” therapy and 7-day standard triple therapy. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Choi, C.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, N.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Clinical outcomes of two-week sequential and concomitant therapies for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized pilot study. Helicobacter 2013, 18, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, B.; Cogdill, A.G. Helicobacter pylori: A Review of Current Diagnostic and Management Strategies. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1917–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Wu, M.S. Rational Helicobacter pylori therapy: Evidence-based medicine rather than medicine-based evidence. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Lv, Z.F.; Xiong, H.F.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Y. Review: Efficacy and safety of hybrid therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2015, 20, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Romano, M.; Fernandez-Bermejo, M.; Federico, A.; Gravina, A.G.; Pozzati, L.; Garcia-Abadia, E.; Vinagre-Rodriguez, G.; Martinez-Alcala, C.; Hernandez-Alonso, M.; et al. Optimized nonbismuth quadruple therapies cure most patients with Helicobacter pylori infection in populations with high rates of antibiotic resistance. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulos, S.D.; Papastergiou, V.; Martinez-Gonzalez, B.; Xirouchakis, E.; Familias, I.; Sgouras, D.; Mentis, A.; Karatapanis, S. Hybrid therapy as first-line regimen for Helicobacter pylori eradication in a high clarithromycin resistance area: A prospective open-label trial. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Fu, W.; Zhou, L. Cefuroxime, levofloxacin, esomeprazole, and bismuth as first-line therapy for eradicating Helicobacter pylori in patients allergic to penicillin. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auttajaroon, J.; Vilaichone, R.K.; Chotivitayatarakorn, P.; Mahachai, V. Once-daily rabeprazole, levofloxacin, clarithromycin-MR, and bismuth for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized study of 7 or 14 days (ONCE study). Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.Y.; Peng, T.L.; Huang, Y.M.; Su, K.H.; Zhao, L.L.; Yao, L.Y.; Yang, R.J. Efficacy of two different dosages of levofloxacin in curing Helicobacter pylori infection: A Prospective, Single-Center, randomized clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccaglione, A.F.; Di Giulio, M.; Di Lodovico, S.; Di Campli, E.; Cellini, L.; Marzio, L. Bovine lactoferrin enhances the efficacy of levofloxacin-based triple therapy as first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: An in vitro and in vivo study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P.P.; Rayapudi, K.; Pacana, T.; Shah, N.J.; Krishnaswamy, N.; Flynn, M. A randomized study comparing levofloxacin, omeprazole, nitazoxanide, and doxycycline versus triple therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1970–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallone, C.A.; Moss, S.F.; Malfertheiner, P. Reconciliation of Recent Helicobacter pylori Treatment Guidelines in a Time of Increasing Resistance to Antibiotics. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, H.; Suzuki, H. Update on quinolone-containing rescue therapies for Helicobacter pylori infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sue, S.; Shibata, W.; Sasaki, T.; Kaneko, H.; Irie, K.; Kondo, M.; Maeda, S. Randomized trial of vonoprazan-based versus proton-pump inhibitor-based third-line triple therapy with sitafloxacin for Helicobacter pylori. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Muraoka, H.; Hibi, T. Sitafloxacin and garenoxacin may overcome the antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori with gyrA mutation. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2009, 53, 1720–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Waskito, L.A.; Syam, A.F.; Nusi, I.A.; Siregar, G.; Richardo, M.; Bakry, A.F.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Wibawa, I.D.N.; Yamaoka, Y. Alternative eradication regimens for Helicobacter pylori infection in Indonesian regions with high metronidazole and levofloxacin resistance. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2019, 12, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Aftab, H.; Shrestha, P.K.; Sharma, R.P.; Subsomwong, P.; Waskito, L.A.; Doohan, D.; Fauzia, K.A.; Yamaoka, Y. Effective therapeutic regimens in two South Asian countries with high resistance to major Helicobacter pylori antibiotics. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Calvet, X. Review article: Rifabutin in the treatment of refractory Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heep, M.; Beck, D.; Bayerdorffer, E.; Lehn, N. Rifampin and rifabutin resistance mechanism in Helicobacter pylori. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 1999, 43, 1497–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribaldone, D.G.; Fagoonee, S.; Astegiano, M.; Durazzo, M.; Morgando, A.; Sprujevnik, T.; Giordanino, C.; Baronio, M.; Angelis, C.D.; Saracco, G.M.; et al. Rifabutin-Based Rescue Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Long-Term Prospective Study in a Large Cohort of Difficult-to-Treat Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akada, J.K.; Shirai, M.; Fujii, K.; Okita, K.; Nakazawa, T. In vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori activities of new rifamycin derivatives, KRM-1648 and KRM-1657. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 1999, 43, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunin, C.M. Antimicrobial activity of rifabutin. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22 (Suppl. 1:S3-13), 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.; Kim, N.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, Y.J.; Kwon, S.; Na, G.; Choi, J.Y.; Kang, J.B.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, J.W.; et al. Rifabutin-based Fourth and Fifth-line Rescue Therapy in Patients with for Helicobacter pylori Eradication Failure. Korean. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 69, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y.; Canaan, Y.; Maher, J.; Wiener, G.; Hulten, K.G.; Kalfus, I.N. Rifabutin-Based Triple Therapy (RHB-105) for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, H.; Koop, H.; Lehn, N.; Heep, M. Rifabutin-based triple therapy after failure of Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment: Preliminary experience. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2000, 31, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Suzuki, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Kaneko, F.; Ootani, S.; Muraoka, H.; Saito, Y.; Kobayashi, I.; Hibi, T. Past rifampicin dosing determines rifabutin resistance of Helicobacter pylori. Digestion 2009, 79, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.Y.; Munson, K.B.; Marcus, E.A.; Lambrecht, N.W.; Sachs, G. The binding selectivity of vonoprazan (TAK-438) to the gastric H+, K+ -ATPase. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.G. [New Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapies]. Korean. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 72, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sachs, G.; Scott, D.R.; Wen, Y. Gastric infection by Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2011, 13, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y.; Dore, M.P. Update on the Use of Vonoprazan: A Competitive Acid Blocker. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.J.; Pu, Q.H.; Zhong, X.F.; Zhang, J. Efficacy and Safety of Vonoprazan-Based versus Proton Pump Inhibitor-Based Triple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Shiino, M.; Funao, N.; Nishimura, A.; Asaka, M. Vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, as a component of first-line and second-line triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A phase III, randomised, double-blind study. Gut 2016, 65, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Oshima, T.; Horikawa, T.; Tozawa, K.; Tomita, T.; Fukui, H.; Watari, J.; Miwa, H. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Vonoprazan, a potent acid blocker, is superior to proton-pump inhibitors for eradication of clarithromycin-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, H.; Yoshino, K.; Ando, K.; Nomura, Y.; Ohta, K.; Satoh, K.; Ichiishi, E.; Ishizuka, A.; Otake, T.; Kohgo, Y.; et al. Vonoprazan-based triple therapy is non-inferior to susceptibility-guided proton pump inhibitor-based triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Ann. Clin. Microbiol Antimicrob. 2018, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Gotoda, T.; Kusano, C.; Ikehara, H.; Ichijima, R.; Ohyauchi, M.; Ito, H.; Kawamura, M.; Ogata, Y.; Ohtaka, M.; et al. Seven-day vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin dual therapy as first-line Helicobacter pylori treatment: A multicentre randomised trial in Japan. Gut 2020, 69, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Lee, H.; Lee, Y.C.; Jeon, S.W.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, H.S.; Sung, J.K.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.U.; Park, M.I.; et al. Ten-Day Concomitant, 10-Day Sequential, and 7-Day Triple Therapy as First-Line Treatment for Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Nationwide Randomized Trial in Korea. Gut. Liver. 2019, 13, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y. Comparison of four different regimens against Helicobacter pylori as a first-line treatment: A prospective, cross-sectional, comparative, open trial in Chinese children. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, C.S.; Lim, H.; Jeong, H.M.; Shin, W.G.; Choi, J.H.; Soh, J.S.; Kang, H.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Hong, J.T.; Shin, S.P.; et al. Amoxicillin or tetracycline in bismuth-containing quadruple therapy as first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.; Gravina, A.G.; Nardone, G.; Federico, A.; Dallio, M.; Martorano, M.; Mucherino, C.; Romiti, A.; Avallone, L.; Granata, L.; et al. Non-bismuth and bismuth quadruple therapies based on previous clarithromycin exposure are as effective and safe in an area of high clarithromycin resistance: A real-life study. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.C.; Liang, C.M.; Bi, K.W.; Kuo, C.M.; Lu, L.S.; Wu, C.K.; Yang, S.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Lee, C.H.; Huang, C.F.; et al. A comparison between dexlansoprazole modified release-based and lansoprazole-based nonbismuth quadruple (concomitant) therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication: A prospective randomized trial. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2019, 12, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.I.; Tsay, F.W.; Kao, J.Y.; Peng, N.J.; Tsai, K.W.; Tsai, T.J.; Kuo, C.H.; Kao, S.S.; Wang, H.M.; Chen, Y.H.; et al. Equivalent efficacies of reverse hybrid and concomitant therapies in first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, N.; Zaw, T.T.; Sain, K.; Waiyan, S.; Danta, M.; Cooper, D.; Aung, N.M.; Kyi, M.M.; Hanson, J. Sequential Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in Myanmar; a randomized clinical trial of efficacy and tolerability. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zullo, A.; Fiorini, G.; Scaccianoce, G.; Portincasa, P.; De Francesco, V.; Vassallo, R.; Urban, F.; Monica, F.; Mogavero, G.; Amato, A.; et al. Sequential therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication: 10- or 14-day regimen? J. Gastrointestin. Liver. Dis. 2019, 28, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, F.W.; Wu, D.C.; Yu, H.C.; Kao, S.S.; Lin, K.H.; Cheng, J.S.; Wang, H.M.; Chen, W.C.; Sun, W.C.; Tsai, K.W.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial Shows that both 14-Day Hybrid and Bismuth Quadruple Therapies Cure Most Patients with Helicobacter pylori Infection in Populations with Moderate Antibiotic Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2017, 61, e00140-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, T.; Tsujii, Y.; Okamoto, A.; Tomita, R.; Higaki, Y.; Osugi, N.; Sugimoto, A.; Takahashi, K.; Mukai, K.; Nakamatsu, D.; et al. A Triple-Drug Blister-Packaged Drug with Vonoprazan Improves First-Line Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in Elderly Patients: A Retrospective Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study. Digestion 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Huang, Y.; Liang, X.; Ji, Y.; Yu, L.; Lu, H. Susceptibility-guided therapy for Helicobacter pylori-infected penicillin-allergic patients: A prospective clinical trial of first-line and rescue therapies. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Jung, H.K.; Lee, H.L.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.G.; Shin, W.G.; Shin, E.S.; Lee, Y.C.; Korean College of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in Korea, 2013 revised edition. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Ota, H.; Okuda, M.; Kikuchi, S.; Satoh, K.; Shimoyama, T.; Suzuki, H.; Handa, O.; Furuta, T.; Mabe, K.; et al. Guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan: 2016 Revised Edition. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).