Abstract
The use of sunscreen is the most effective way to minimize sun damage to the skin. Excessive UV exposure is linked to an increased risk of melanoma and accelerated skin aging. Currently, approved UV filters fall into two categories: chemical- or mineral-based filters. Besides approved filters, there are numerous SPF-boosting additives that can be added to sunscreen products to enhance their efficacy. This manuscript shows the potential application of the novel SPF booster, Bacillus Lysate, developed from Bacillus pumilus PTA-126909, which was derived from research aboard the International Space Station. The addition of the 3.5%, 7%, or 10% Bacillus Lysate resulted in a 33%, 29%, and 22% boost in the SPF values of an SPF 30 sunscreen, respectively. The potential use of extremophiles and their byproducts, like the Bacillus Lysate presented here, may be a promising alternative SPF booster for the sunscreen industry.
1. Introduction
Skin cancer is the most diagnosed cancer in the world, and the incidence continues to increase year over year [1]. Sun exposure is generally highest for individuals under 21 years of age, with 25–50% of a person’s ultraviolet (UV) exposure occurring during childhood [2]. It is estimated that children receive three times the amount of annual UV exposure than adults [2]. Though the incidence of melanoma in childhood is rare, extended UV exposure during adolescence can lead to undesirable consequences later in life [3]. Therefore, it is imperative that sunscreen be used to minimize the acute and long-term effects of chronic UV exposure.
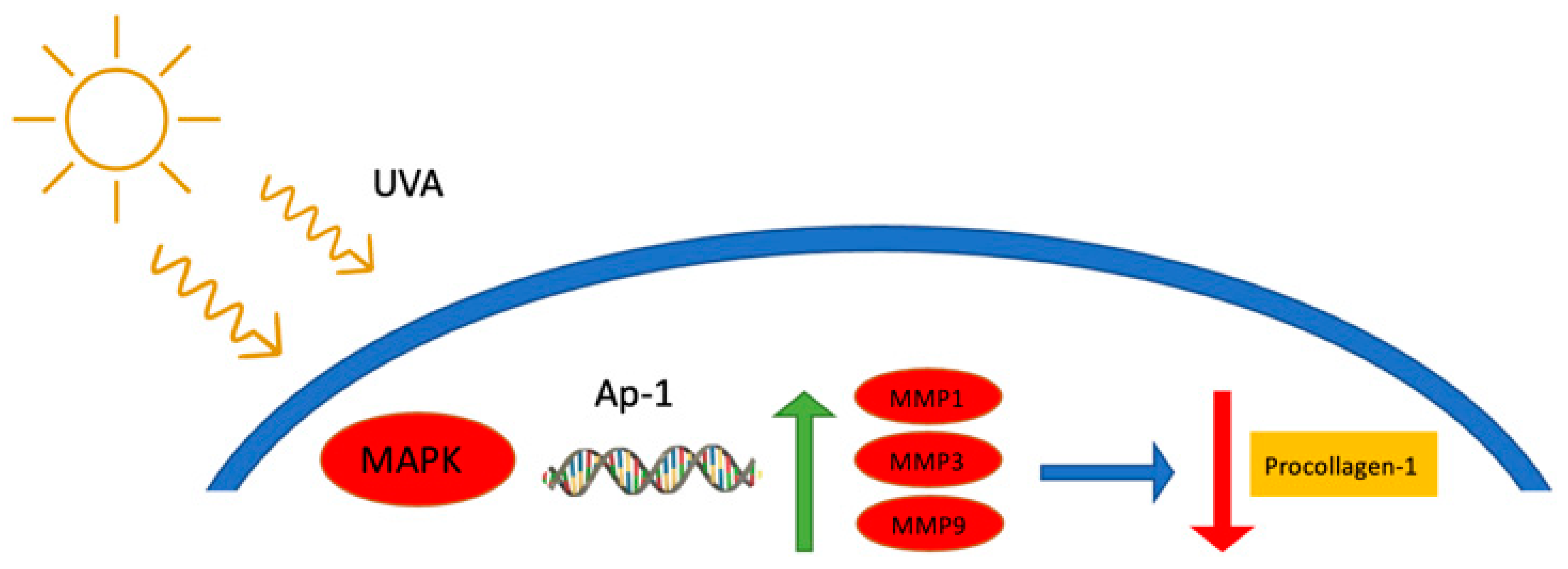
Sun exposure is necessary for the internal synthesis of Vitamin D; however, long-term non-shielded exposure can lead to premature aging, hyperpigmentation, accelerated wrinkle formation, chronic lesions, and melanoma [4,5,6,7]. There are three types of UV radiation experienced on Earth: UVC, UVB, and UVA. UVC radiation has a wavelength range between 100 and 280 nm and is considered shortwave UV radiation. This form of UV radiation is fully dispersed by the Earth’s ozone layer and does not make it down to the surface. It should be noted that this form of UV radiation is generated by germicidal lamps for surface and object decontamination [8]. Unlike UVC, both UVA and UVB wavelengths pass though the ozone layer and contact our skin. The medium wavelengths (280–320 nm) of UVB penetrate the epidermis of the skin and results in a series of adverse effects such as DNA damage, erythema, hypersensitization, sun burn, and increasing the risk of skin cancer [9,10,11]. The long wavelengths (320–400 nm) of UVA radiation penetrate much deeper than UVB. These wavelengths penetrate both the epidermis and dermis layers and are linked to accelerated skin aging [12,13]. These wavelengths generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) within the skin layers, which leads to accelerated wrinkle development and skin sagging [14,15]. One such mechanism, as seen in Figure 1, is by simultaneously cross-linking dermal collagen and inhibiting the synthesis of procollagen-1 by up-regulating metalloproteases (MMP) 1, 3, and 9 [14]. These proteases break down and suppress procollagen-1, leading to deleterious effects on skin elasticity and firmness [14,16]. High exposure to UVA has also been shown to promote skin cancer [17].
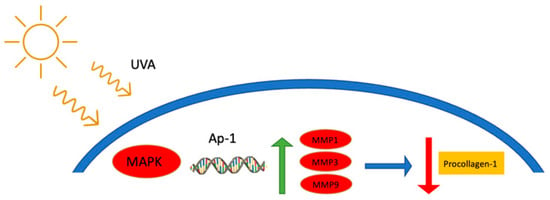
Figure 1.
The suppression/degradation mechanism of procollagen-1 from UVA exposure [14]. Briefly, UVA exposure activates mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), which leads to the activation of the MMP promoter, nuclear transcription factor AP-1. This upregulates the expressions of MMP 1, 3, and 9 which in turn break down and inhabit collagen production within the skin matrix.
Various UV filters and sunscreen formulations have been developed to help shield our skin from harmful UV ray exposure. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) first began regulating UV filter regulations in 1978, with the adoption of the Advanced Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, which approved the use of 21 UV filters for use in the United States. [18]. More recently, in February, the FDA recognized 22 UV filters as either Generally Recognized As Safe and Effective (GRASE, Category 1), Non-GRASE (Category 2), or Needs Further Evaluation (Category 3) [19]. Furthermore, an additional 20 filters were listed as Category 3 compounds and need to be submitted through the New Drug Application (NDA) process [18,19]. Unlike in Europe, UV filters are classified as drugs in the United States and therefore must undergo the same scrutiny as traditional drug therapies. Unfortunately, this has limited the amount of research and development for new UV filters for use in the United States since the time and cost for developing new drugs is substantial and highly regulated. The “race-to-the-bottom” price point for consumer care products, in both the supply side and consumer side, does not support the need for further innovation.
As a result, the industry has turned to UV filter boosters to enhance the sun protection factor (SPF) and differentiate their products on the marketplace. Boosters do not fall under the same guidelines as UV filters since they are not the main active ingredient responsible for UV protection. They generally fall under the same guidelines as traditional cosmetic ingredients, requiring safety and efficacy testing prior to International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) and Chemical Abstract Service (CAS) number registration. Boosters have been created from a variety of sources, such as plants, algae, bacteria, fungi, lichens, fruits, and biomass [20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Generally, the SPF-boosting capability comes from the production of pigments or phenolic compounds that can either block or absorb the sun’s UV energy. These compounds can either be innate to the organism or upregulated due to exposure to conditions that demand production from UV radiation, free-radicals, or environmental toxins [27,28,29,30,31,32].
Recently, a novel SPF booster has been derived from a strain of the extremely UV-resistant organism Bacillus pumilus SAFR-32. Originally isolated from an ultraclean spacecraft assembly facility, this organism’s spores were found to survive normally harmful UVC radiation exposure [33]. The organism was then sent to the International Space Station as part of a NASA Research Announcement Research Opportunities in Space and Earth Sciences (NRA ROSES) EXPOSE grant where the organism was placed outside of the International Space Station and exposed to various forms of space radiation for 18 months aboard the EXPOSE module [34,35,36,37]. When brought back down to Earth, the Bacillus pumilus SAFR-32 strain exhibited enhanced UV resistance. Through selective isolation, a specific strain of the organism, designated PTA-126909, was identified, and an extract of this organism was tested for its SPF-boosting capabilities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
Stock cultures of Bacillus pumilus ATCC PTA-126909 were stored at −80 °C in tryptic soy broth (TSB; BD Diagnostic Systems, Cat# DF0064-07-6) containing 25% (v/v) glycerol (ThermoScientific, Cat# 17904). Monthly, frozen stock cultures were transferred to working cultures through plating on tryptic soy agar (TSA; BD Diagnostic Systems, Cat# DF0370-075) slants/plates and incubating at 37 °C for 24 h.
Periodically, working cultures were streaked to ensure purity. Cultures were incubated overnight in TSB at 37 °C on a rotary shaker set at 150 RPM. All cultures were diluted with TSB to the desired cell numbers.
2.2. Production of Bacillus Lysate
Working cultures were made by transferring 10 μL of Bacillus pumilus PTA-126909 stock culture to a test tube containing 9 mL of TSB. The inoculated tube was allowed to incubate at 37 °C for 18 h on a rotary shaker set to 150 RPM. Overnight growth (1 mL) was transferred to multiple Erlenmeyer flasks, each containing 200 mL of TSB. The flasks were incubated at 37 °C for 18 h on a rotary shaker set to 100 RPM. Following incubation, the flasks were autoclaved at 121 °C at 16 psi for 45 min. Once sterile, the contents from each flask were transferred to sterile 500 mL Oakridge centrifuge bottles (Corning, Cat# 13-701-109) and centrifuged (Sorvall Lynx 4000 Superspeed; F12-6x500LEX rotor) for 15 min at 6861 RPM (8000× g). The supernatant was decanted, and each pellet resuspended in 4 mL of sterile deionized water. The suspended pellets were pooled together and aliquoted (25 mL) into sterile 50 mL conical tubes (Falcon 352070, Cat# 14-432-22). Each conical tube was sonicated (FisherBrand Ultra Sonicator; Model FB120) with a CL-18 probe for 10 min with a pulse cycle time of 30 s at 80% amplitude setting. The sonicated samples were then pooled together and sterilized a second time with a 45 min autoclave cycle at 121 °C at 16 psi. The sterilized product was designated as Bacillus Lysate. The total protein concentration of the Bacillus Lysate was determined using the Pierce™ Coomassie Plus (Bradford) Assay Kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA, Cat# 23236) following the manufacturer’s provided instructions. The Pierce™ Bovine Serum Albumin Standard Kit (Thermo Scientific, Cat# 23209) was used as the protein sample to generate the standard curve.
2.3. UV Absorption Profile
The UV absorption profile was obtained using a Molecular Devices SpectraMax Plus 384 microtiter plate reader equipped with SoftMax Pro analytical software (Molecular Devices, Version 5.46). Briefly, varying dilutions of the Bacillus Lysate (150 μL) were transferred to a NuncTM 96-well UV flat bottom microtiter plate (ThermoFisher Ref#8404) and scanned between 190 and 700 nm. Plots of the UV absorption profile were generated using GraphPad Prism Version 9.5.1 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA).
2.4. Formulation and Testing of Bacillus-Lysate-Formulated Chemical UV Filter Sunscreen
To determine the SPF boosting capability of the Bacillus Lysate, various percentages (3%, 7%, and 10%) were added to a SPF 30 sunscreen formulation. The sunscreen formulation and production process can be found in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4. In vivo SPF determination for each formulation was carried out following the International Standard—ISO 24444:2019 protocol [38]. The intrascapular area of the back to the right and left of the midline were used as test sites for SPF validation. Each test site was cleaned using a dry cotton pad and a 30 cm2 area was delineated using a gentian violet surgical marker. Care was taken to ensure that each site had uniform pigmentation, skin tone, and texture as well as the absence of warts, moles, nevi, scars, blemishes, and dermal lesions.

Table 1.
SPF 30 sunscreen formulation.

Table 2.
SPF 30 sunscreen formulation containing 3% Bacillus Lysate.

Table 3.
SPF 30 sunscreen formulation containing 7% Bacillus Lysate.

Table 4.
SPF 30 sunscreen formulation containing 10% Bacillus Lysate.
The complete protocol is described with the Internal Standard ISO 24444:2019 (Second edition 2019-12): Cosmetic–Sun Protection Test Methods—In vivo Determination of Sun Protection Factor (SPF). One unprotected site was used to determine a subject’s Minimal Erythemal Dose (MED), which was noted as the lowest erythemal effective radiant exposure that produced the first perceptible unambiguous erythema with defined borders appearing over >50% of the exposed site 16 to 24 h after UV exposure. A minimum of five progressive UV light doses were administered within each test site.
Test material and SPF standards were swirled with a glass rod prior to use and evenly applied using a spatula to the rectangular test site areas using a minimum of 30 cm2 for a final concentration of 2.0 ± 0.05 mg/cm2. The test material and reference sunscreen test sites were randomly distributed on the back of each subject to reduce error arising from anatomical differences in skin. Evenness of application was verified through observation using a Wood’s Lamp, and the space between each test site was >1 cm.
Following application, the test sites were exposed to a series of progressive UV doses (minimum of five) based on the determined MED values for each subject. Lamp irradiance was monitored continuously during UV exposure. Post exposure (16–24 h), subjects were evaluated for delayed erythemal responses in a double-blind manner.
2.5. Determination of Protein Concentration
The protein concentration of Bacillus Lysate was determined using a Coomassie Plus (Bradford) assay kit (Thermo Scientific, Cat# 23236) following the protocol provided by the manufacturer. Albumin standards (Thermo Scientific, Cat# 23209) were used to generate standard curves and were used in accordance with the protocol provided by the manufacturer.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical comparisons of determined SPF values of sunscreen formulations containing various concentrations of Bacillus Lysate were performed using an unpaired two-tail t test with a 95% confidence interval. All analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism version 10.0.1 for Apple (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. UV Absorption Profile and Protein Concentration of Bacillus Lysate
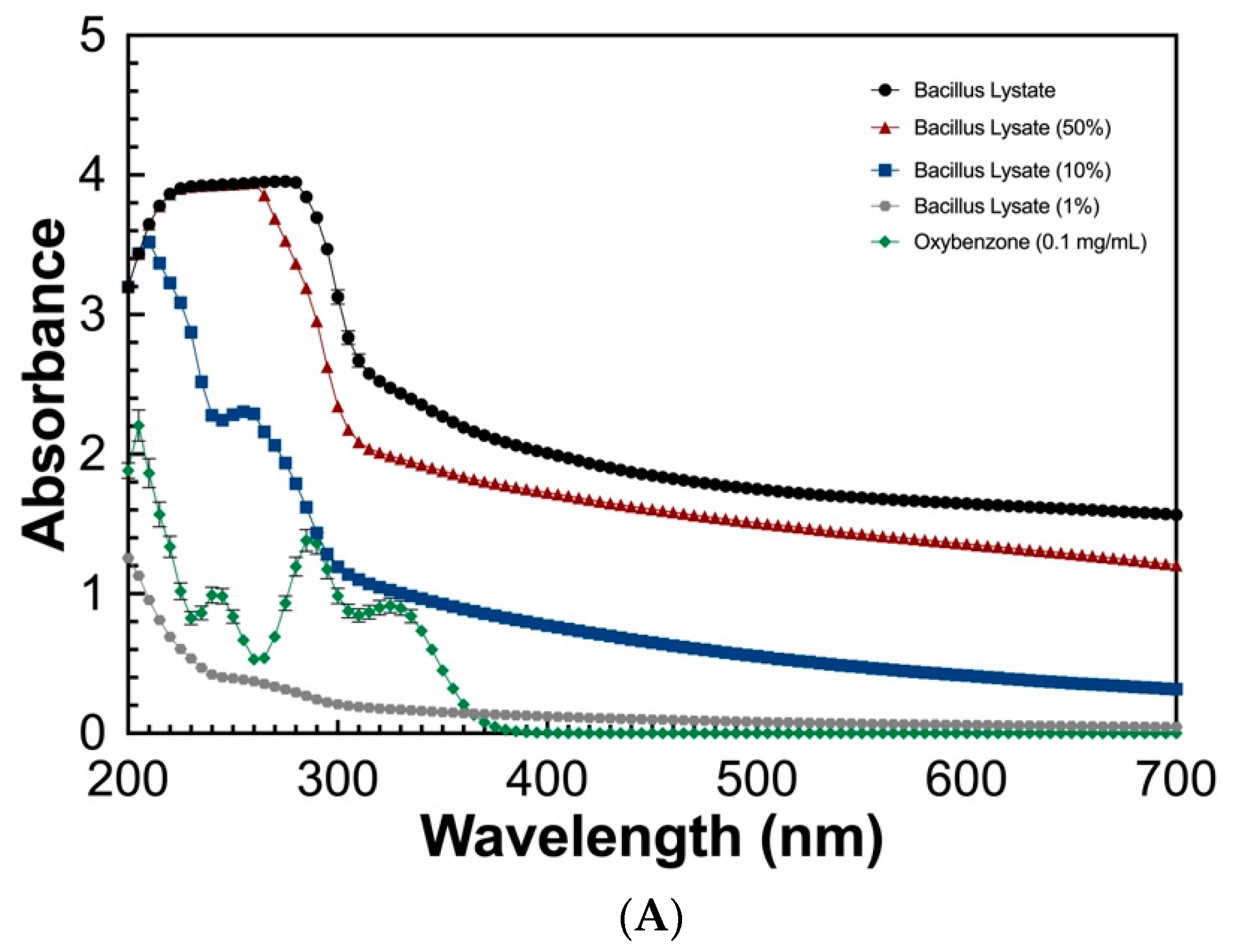
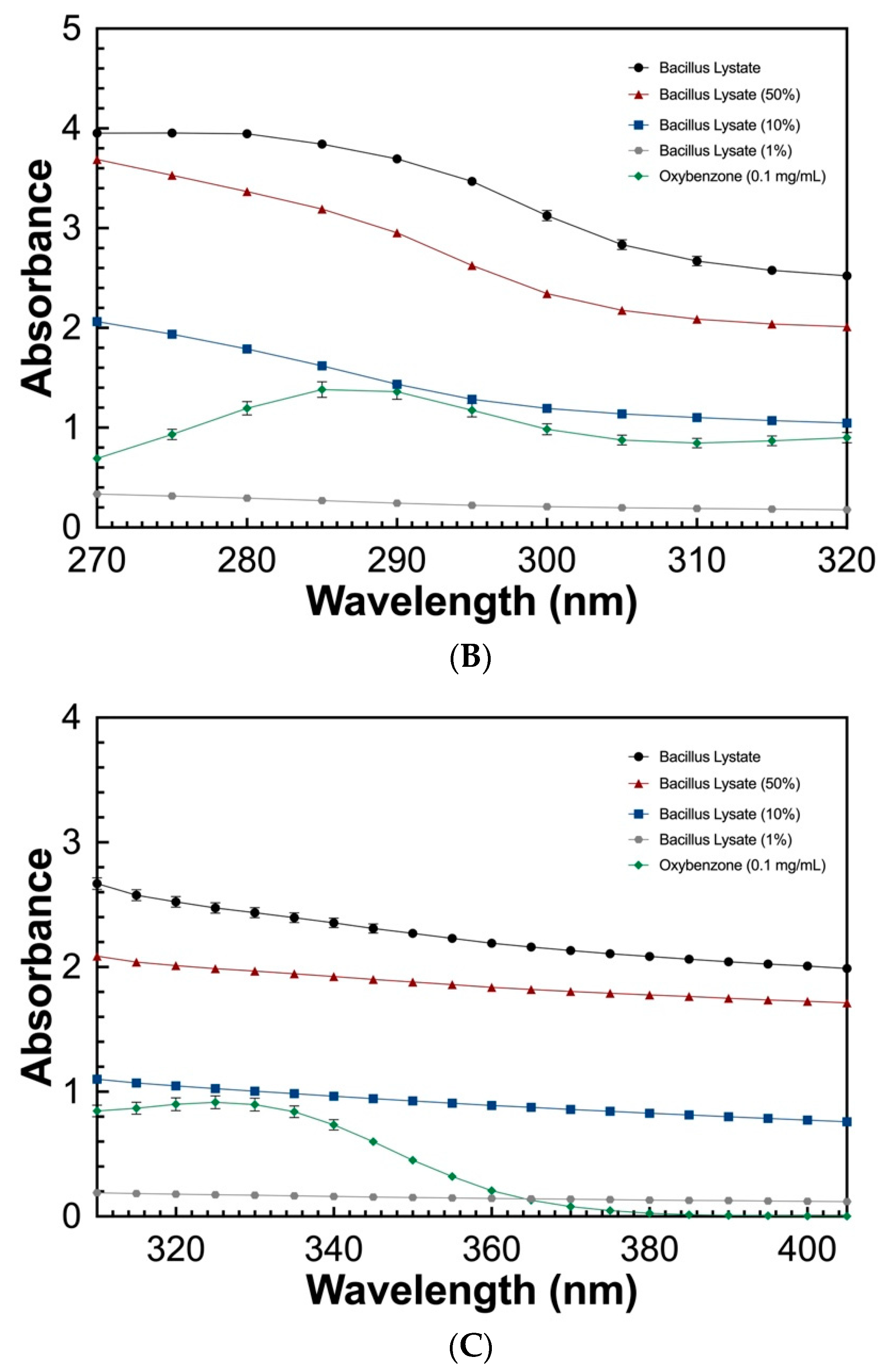
To determine the UV absorbing potential of the Bacillus Lysate, a spectral scan (280–700 nm) at varying concentrations (100%, 50%, 10%, and 1%) was measured and compared to that of oxybenzone (0.1 mg/mL). As seen in Figure 2, the Bacillus Lysate had significant absorbing properties between 200 and 400 nm for all concentrations ≥10%. The lysate outperformed oxybenzone in UVC, UVB, and UVA wavelength ranges at concentrations >1%, where 1% Bacillus Lysate had similar a UVB profile (Figure 2B) and an extended UVA profile (Figure 2C). The protein concentration of all samples can be found in Table 5.
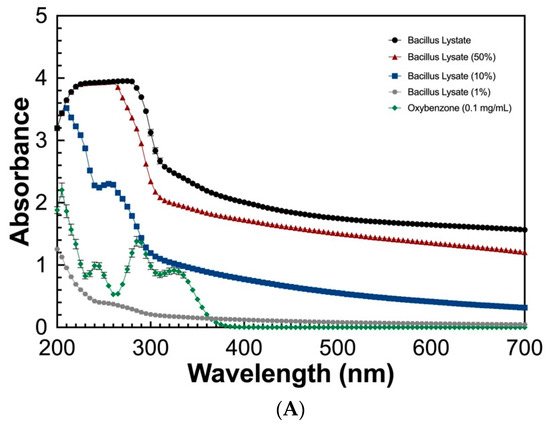
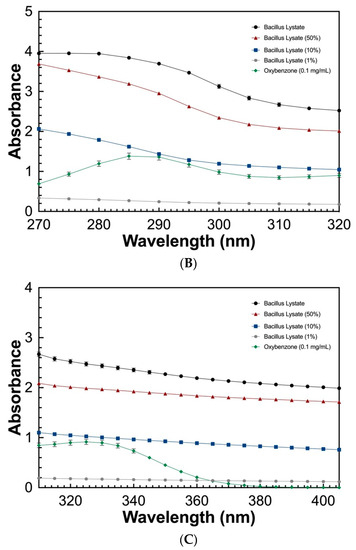
Figure 2.
The UV absorbing profile of Bacillus Lysate between 200 and 700 nm (A) and highlight of UVB (B) and UVA (C) wavelength ranges. All plots were generated using triplicate technical replicates of averages of triplicate samples.

Table 5.
Protein concentration of Bacillus Lysate samples as determined via the Bradford Assay.
3.2. SPF-Boosting Capability of Bacillus Lysate
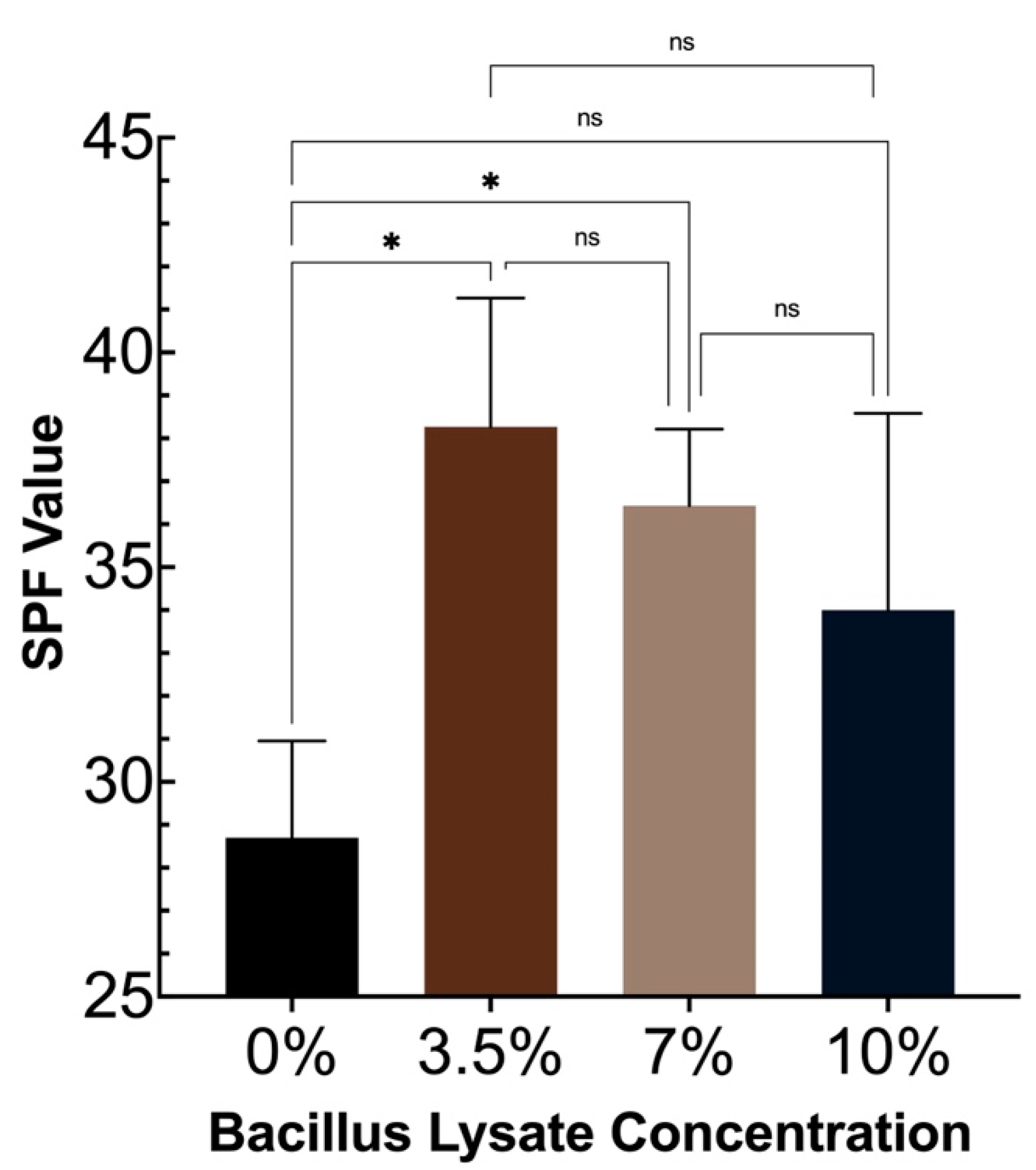
The SPF-boosting capability of the Bacillus Lysate was determined by adding 3.5%, 7%, or 10% Bacillus Lysate to a base SPF 30 sunscreen formulation and testing the SPF of each formulation using a 3-person panel ISO 24444:2019 testing protocol. The results from the study can be found in Figure 3. The addition of 3.5% Bacillus Lysate significantly boosted the SPF value of the formulation by 33%, where the addition of 7% or 10% increased the SPF value by 29% and 22%, respectively. There was no significant difference in SPF boosting between the various Bacillus Lysate concentrations. It should be noted that one sample in the 7% and 10% Bacillus Lysate ISO24444:2019 assay was determined to have an SPF value of <19.8. This was deemed not valid, and that data point was not included, as denoted in Figure 3.
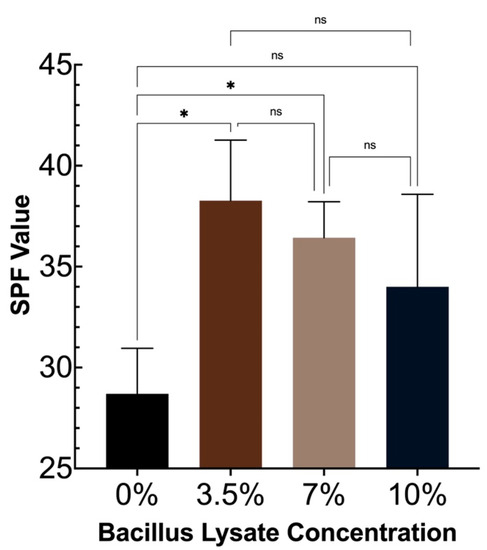
Figure 3.
The SPF-boosting capability of the Bacillus Lysate at various concentrations using a 3-person ISO 24444:2019 testing protocol. Statistical analysis of the SPF values compared to the control was performed using an unpaired two-tailed t test with a 95% confidence interval. Statistical analysis between sunscreen samples was performed using a one-way ANOVA with a 95% confidence interval; *, a significant difference between samples; and ns, no significant difference between samples.
4. Discussion
Researchers have been studying extreme or adaptable microorganisms for functional components for decades, and their implementation for commercial, industrial, and medical applications is commonplace [39,40,41,42]. Small molecules, enzymes, and polymers are just a few examples of products that are often isolated from extremophiles [43,44,45,46]. A few extremophiles, such as Tardigrades and Deinococcus radiodurans, have been studied for UV-resistant genes and compounds [47,48,49,50]. The UV filter industry in the United States is a double-edged sword; the development of new UV filters is needed, but the pathway to get there is long and expensive. In the United States, sunscreens and UV filters are regulated as pharmaceuticals whereas in most other countries they are considered cosmetics. This strict regulation has stunted most UV filter innovation in the United States, which is evident by the limited number of approved UV filters on the market. The development and use of SPF boosters is a methodology used to enhance the efficacy of sunscreens without requiring FDA submissions. There are numerous boosters on the market that are well accepted by the sunscreen industry. These are often developed from plants and algae, giving companies and formulators options for new products. However, SPF boosters cannot be the main source of UV protection within a product, which is why they are added to synergistically work with approved UV filters. The Bacillus Lysate presented here is a promising alternative SPF booster for the sunscreen industry. A 3% addition of the lysate to an SPF 30 sunscreen significantly boosted the SPF value by 33%. The benefits from this can be seen in two ways: (1) the addition of the lysate increased the efficacy of the sunscreen without the addition of more UV filters, and (2) the addition of the lysate helps ensure that the SPF value of the sunscreen stays true to the advertised claims, with both views being beneficial for the consumer. A significant boost was also achieved with the addition of 7% Bacillus Lysate, but the boosting effect was less than the 3.5% Bacillus Lysate sample. The addition of 10% Bacillus Lysate did not result in a statistically significant boost in SPF value. Since the lysate is a complex mixture of organic material, high concentrations may result in unwanted interactions with the UV filters and/or formulation, resulting in decreased performance. There was no significant difference in performance between all tested Bacillus Lysate concentrations, suggesting that maximum performance can be achieved at the lowest concentration tested under these conditions.
Limitations of the current SPF testing protocols, including the ISO 24444:2019 testing protocol, should be highlighted. The current testing methods have performed well over the years for providing a relative sun protection factor value. However, discrepancies in testing results are known within the industry. The discrepancies are hard to correct since they are often linked to technique variation and artificial solar simulators. For example, erythema resulting from UV exposure is visually graded by laboratory technicians, which allows interpretation differences between technicians and between testing facilities [50,51]. The application of sunscreens to the backs of clinical subjects is another area where technician skill is important. If the application of sunscreen is inconsistent, the observed SPF values can shift dramatically [52]. This discrepancy was observed during this study as well. Testing of the 7% and 10% Bacillus Lysate yielded one test sample with a perceived SPF value < 19.8. Due to the inability to accurately quantify the value, the data points were deemed inadequate and were not included.
To further complicate things, there are concerns around the use of traditional UV filter chemistries. These concerns range from hormone disruption in children to bleaching of the coral reefs [53,54,55,56]. Using a booster like Bacillus Lysate may help limit the number of traditional chemistries needed for SPF performance and bring a certain ease of mind to consumers. Secondly, by ensuring the advertised SPF values of a sunscreen are at or above the claimed SPF value, Bacillus Lysate may help bring creditability and security to brands. Overall, any innovation that can enhance protection from UV exposure would be welcomed by the industry and consumers alike.
Author Contributions
K.S.L.: lead/first and corresponding author; manuscript writing and editing. E.Y.: second author; data generation and manuscript editing. T.S.A.: third author; research and manuscript writing and editing. J.G.: fourth author; manuscript editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Advanced Laboratories, Inc. IRB 00013226 9 November 2021.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the scientific and administrative staff of EdenRoc Sciences LLC for allowing us to continue our research. We would also like to personally thank Edward Schulak and the advisory board for their continued support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Patel, A.R.; Zaslow, T.L.; Wren, T.A.; Daoud, A.K.; Campbell, K.; Nagle, K.; Coel, R.A. A characterization of sun protection attitudes and behaviors among children and adolescents in the United States. Prev. Med. Rep. 2019, 16, 100988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Marcelino, G.; Wang, R.; Gultekin, S.; Humphreys, L.; Smit, A.K.; Sharman, A.R.; St Laurent, A.G.; Evaquarta, R.; Dobbinson, S.J.; Cust, A.E. School-based interventions to improve sun-safe knowledge, attitudes and behaviors in childhood and adolescence: A systematic review. Prev. Med. 2021, 146, 106459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, B.A.; Lin, T.; Chang, L.C.; Okada, A.; Wong, W.K.; Glanz, K.; Bastani, R. Sun protection practices and sun exposure among children with a parental history of melanoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammeyer, A.; Luiten, R. Oxidation events and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 21, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.; Bae, S.; An, S.; Choe, Y.B.; Ahn, K.J.; An, I.S. Effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin and skin cell signaling pathways. Korean J. Aesthet. Cosmetol. 2013, 11, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison, E.; Yoseph, R.; Wainman, H. Skin of colour: Essentials for the non-dermatologist. Clin. Med. 2023, 23, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seite, S.; Colige, A.; Piquemal-Vivenot, P.; Montastier, C.; Fourtanier, A.; Lapiere, C.; Nusgens, B. A full-UV spectrum absorbing daily use cream protects human skin against biological changes occurring in photoaging. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2000, 16, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.L.; Linnes, J.; Luongo, J. Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation: Future directions for air disinfection and building applications. Photochem. Photobiol. 2013, 89, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budden, T.; Bowden, N.A. The role of altered nucleotide excision repair and UVB-induced DNA damage in melanomagenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1132–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas-Ahner, J.M.; Wulff, B.C.; Tober, K.L.; Kusewitt, D.F.; Riggenbach, J.A.; Oberyszyn, T.M. Gender differences in UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis, inflammation, and DNA damage. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3468–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustorff, B.; Sycha, T.; Lieba-Samal, D.; Rolke, R.; Treede, R.-D.; Magerl, W. The pattern and time course of somatosensory changes in the human UVB sunburn model reveal the presence of peripheral and central sensitization. Pain 2013, 154, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krutmann, J. The role of UVA rays in skin aging. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2001, 11, 170–171. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, C.-C.E.; Hung, Y.-T.; Fang, A.-H.; Ching-Shuang, W. Effects of irradiance on UVA-induced skin aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 94, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.J.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Wan, Y.; Datta, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Mechanisms of photoaging and chronological skin aging. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gruijl, F.R. Photocarcinogenesis: UVA vs. UVB radiation. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 15, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, E.; Steinbauer, J.; Landthaler, M.; Szeimies, R.M. Skin ageing. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beani, J.-C. Ultraviolet A-induced DNA damage: Role in skin cancer. Bull. De L’academie Natl. De Med. 2014, 198, 273–295. [Google Scholar]
- Sabzevari, N.; Qiblawi, S.; Norton, S.A.; Fivenson, D. Sunscreens: UV filters to protect us: Part 1: Changing regulations and choices for optimal sun protection. Int. J. Women’s Dermatol. 2021, 7, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, T.F.; Lim, H.W. The important role of dermatologists in public education on sunscreens. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.; Bharadwaj, A.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Yoo, C.G.; Kim, T.H. A Review of Biomass-Derived UV-Shielding Materials for Bio-Composites. Energies 2023, 16, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalekar, M.R.; Padher, S.; Ladkat, S.; Paranjape, P. Evaluation of carboxymethyl xyloglucan as SPF booster in Oxybenzone cream. IJAR 2017, 3, 813–816. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Garg, G.; Garg, V.K.; Sharma, P. Review on herbal plants having sunscreen and antioxidant activity. Pharmacologyonline 2009, 3, 244–267. [Google Scholar]
- Yarovaya, L.; Khunkitti, W. Effect of grape seed extract as a sunscreen booster. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 41, 708–715. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Shin, S.; Ryu, D.; Cho, E.; Yoo, J.; Park, D.; Jung, E. Evaluating the Sun Protection Factor of Cosmetic Formulations Containing Afzelin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, R.J.; Casadevall, A. Functions of fungal melanin beyond virulence. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2017, 31, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanuja, S.; Iswarya, S.; Sridevi, J.; Gnanamani, A. Exploring the UVB-protective efficacy of melanin precursor extracted from marine imperfect fungus: Featuring characterization and application studies under in vitro conditions. Int. Microbiol. 2018, 21, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allam, N.G.; Abd El-Zaher, E.H. Protective role of Aspergillus fumigatus melanin against ultraviolet (UV) irradiation and Bjerkandera adusta melanin as a candidate vaccine against systemic candidiasis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 6566–6577. [Google Scholar]
- Krastanov, A.; Alexieva, Z.; Yemendzhiev, H. Microbial degradation of phenol and phenolic derivatives. Eng. Life Sci. 2013, 13, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, S.C.; Logan, B.A. Energy dissipation and radical scavenging by the plant phenylpropanoid pathway. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimi, H.; Cillard, J.; Cillard, P.; Rahmani, M. Peroxyl and hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of some natural phenolic antioxidants. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1991, 68, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favas, R.; Morone, J.; Martins, R.; Vasconcelos, V.; Lopes, G. Cyanobacteria secondary metabolites as biotechnological ingredients in natural anti-aging cosmetics: Potential to overcome hyperpigmentation, loss of skin density and UV radiation-deleterious effects. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.-H.; Chollet-Krugler, M.; Gouault, N.; Tomasi, S. UV-protectant metabolites from lichens and their symbiotic partners. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 1490–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, L.; Sawyer, J.; Venkateswaran, K.; Nicholson, W. Extreme spore UV resistance of Bacillus pumilus isolates obtained from an ultraclean spacecraft assembly facility. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 47, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.J.; Malli Mohan, G.B.; Singh, N.K.; Vaishampayan, P.A.; Kalkum, M.; Venkateswaran, K. Alteration of proteomes in first-generation cultures of Bacillus pumilus spores exposed to outer space. Msystems 2019, 4, e00195-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, S.M.; Ledford, S.M.; Wacker, A.; Verma, S.; Serda, B.; McKaig, J.; Varelas, J.; Nicoll, P.M.; Venkateswaran, K.; Smith, D.J. Long-read sequencing reveals increased occurrence of genomic variants and adenosine methylation in Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032 after long-duration flight exposure onboard the International Space Station. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2021, 20, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuerger, A.C.; Richards, J.T.; Newcombe, D.A.; Venkateswaran, K. Rapid inactivation of seven Bacillus spp. under simulated Mars UV irradiation. Icarus 2006, 181, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishampayan, P.A.; Fox, G.E.; Venkateswaran, K. Survival of Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032 in simulated Mars atmosphere in real space conditions. In Proceedings of the Instruments, Methods, and Missions for Astrobiology XIII, San Diego, CA, USA, 1–5 August 2010; pp. 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 24444:2019; Cosmetics—Sun Protection Test Methods—In Vivo Determination of the Sun Protection Factor (SPF). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Niehaus, F.; Bertoldo, C.; Kähler, M.; Antranikian, G. Extremophiles as a source of novel enzymes for industrial application. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 51, 711–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, A.; Schäfers, C.; Schröder, C.; Antranikian, G. Towards a sustainable biobased industry–highlighting the impact of extremophiles. New Biotechnol. 2018, 40, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Capalash, N.; Sharma, P. Communication mechanisms in extremophiles: Exploring their existence and industrial applications. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 221, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, K.S.; Morey, J.M.; Bharat, B.; Haney, N.M.; Panesar, S.S. Biofilms-Impacts on Human Health and Its Relevance to Space Travel. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, K.S.; Levin, R.E. Purification and characterization of iso-ribonucleases from a novel thermophilic fungus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, K.S.; Levin, R.E. Characterization of a recently purified thermophilic DNase from a novel thermophilic fungus. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaus, B.; Kambourova, M.; Oner, E.T. Exopolysaccharides from extremophiles: From fundamentals to biotechnology. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, L.-A.; Newman, D.J.; Giddings, L.-A.; Newman, D.J. Bioactive compounds from extremophiles. In Bioactive Compounds from Extremophiles: Genomic Studies, Biosynthetic Gene Clusters, and New Dereplication Methods; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa, D.D.; Cumbers, J.; Sakakibara, I.; Rogoff, D.; Leuko, S.; Harnoto, R.; Arakawa, K.; Katayama, T.; Kunieda, T.; Toyoda, A. Analysis of DNA repair and protection in the Tardigrade Ramazzottius varieornatus and Hypsibius dujardini after exposure to UVC radiation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, C.; Riolo, G.; Marzocchi, C.; Brunetti, J.; Pini, A.; Cantara, S. The tardigrade damage suppressor protein modulates transcription factor and DNA repair genes in human cells treated with hydroxyl radicals and UV-C. Biology 2021, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Narumi, I.; Funayama, T.; Kikuchi, M.; Watanabe, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Nikaido, O.; Yamamoto, K. Characterization of pathways dependent on the uvsE, uvrA1, or uvrA2 gene product for UV resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3693–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y. The radioresistant and survival mechanisms of Deinococcus radiodurans. Radiat. Med. Prot. 2023, 4, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miksa, S.; Lutz, D.; Guy, C.; Delamour, E. Sunscreen sun protection factor claim based on in vivo interlaboratory variability. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2016, 38, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaberry, Y.S.; Svarc, F.E. Sun protection, progress, myths, and inconsistencies (a proposal for the democratization of ISO 24443). Photochem. Photobiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, R.B.; Pergolizzi, J.V., Jr.; Taylor, R., Jr.; Kitzen, J.M.; NEMA Research Group. Sunscreen bans: Coral reefs and skin cancer. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2019, 44, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, M.; Pawlowski, S.; Petersen-Thiery, M.; Miller, I.B.; Nietzer, S.; Heisel-Sure, Y.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Schupp, P.J. Challenges in current coral reef protection–possible impacts of UV filters used in sunscreens, a critical review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 665548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.P. Ensuring the safety of sunscreens, and their efficacy in preventing skin cancers: Challenges and controversies for clinicians, formulators, and regulators. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, M.E.; Wang, S.Q. Current sunscreen controversies: A critical review. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2011, 27, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).