Inhibitory Effect of 2-Aza-8-oxohypoxanthine on Tyrosinase Activity and Melanin Production
Abstract
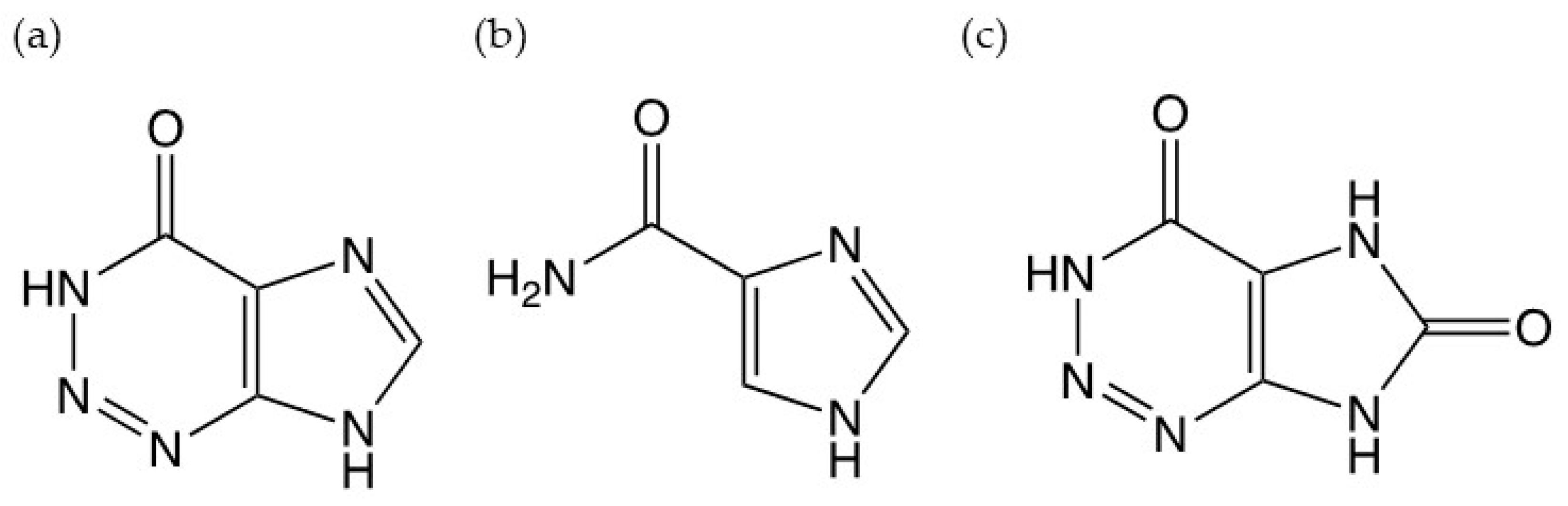
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Cell Culture and Tyrosinase Activity Assay
2.4. Cell Culture and Measurement of Melanin
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability after AOH Treatment in B164A5 Cells
3.2. AOH Inhibits Tyrosinase Activity
3.3. AOH Inhibits Melanin Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchinson, A. Fairy chemicals. Nature 2014, 505, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsbottom, J. Rate of growth of fungus rings. Nature 1926, 117, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantz, H.L.; Piemeisel, R.L. Fungus fairy rings in Eastern Colorado and their effect on vegetation. J. Agric. Res. 1917, 11, 191–245. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.D. Fungi and turf diseases. 7: Fairy rings. J. Sports Turf Res. Inst. 1957, 10, 324–352. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.H.; Ohnishi, T.; Yamakawa, Y.; Takeda, S.; Sekiguchi, S.; Maruyama, W.; Yamashita, K.; Suzuki, T.; Morita, A.; Ikka, T.; et al. The source of “fairy rings”: 2-azahypoxanthine and its metabolite found in a novel purine metabolic pathway in plants. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1552–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Kikuchi, A.; Pumkaeo, P.; Hirai, H.; Tokuyama, S.; Kawagishi, H. Bioconversion of AHX to AOH by resting cells of Burkholderia contaminans CH-1. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, H. Fairy chemicals—A candidate for a new family of plant hormones and possibility of practical use in agriculture. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, H. Are fairy chemicals a new family of plant hormones? Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2019, 95, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, H.; Hyodo, S.; Ibuki, R.; Wu, J.; Choi, J.H.; Kawagishi, H. Safety evaluation of 2-aza-8-oxohypoxanthine based on in vitro and human patch tests. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 7, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Ibuki, R.; Kawagishi, H. Safety evaluation of 2-aza-8-oxohypoxanthine by in vitro skin sensitization and human tests. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 8, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, H.; Ito, M.; Ibuki, R.; Kawagishi, H. The potential of 2-aza-8-oxohypoxanthine as a cosmetic ingredient. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooksey, C.J.; Garratt, P.J.; Land, E.J.; Pavel, S.; Ramsden, C.A.; Riley, P.A.; Smit, N.P. Evidence of the indirect formation of the catecholic intermediate substrate responsible for the autoactivation kinetics of tyrosinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26226–26235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.D.; Peles, D.; Wakamatsu, K.; Ito, S. Current challenges in understanding melanogenesis: Bridging chemistry, biological control, morphology, and function. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009, 22, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, C.; Solano, F. New insights into the active site structure and catalytic mechanism of tyrosinase and its related proteins. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009, 22, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, D.L.; Stefania, R.; Aime, S.; Oraevsky, A. Melanin-Based Contrast Agents for Biomedical Optoacoustic Imaging and Theranostic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, H.; Kondoh, H.; Ichihashi, M.; Hearing, V.J. Approaches to identify inhibitors of melanin biosynthesis via the quality control of tyrosinase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Namasivayam, V. Skin whitening agents: Medicinal chemistry perspective of tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, H.; Ito, M.; Ibuki, R.; Kawagishi, H. Clinical evaluation of topical lotion containing 2-aza-8-oxohypoxanthine on skin barrier function against water loss. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, H.; Ito, S.; Ibuki, R.; Kawagishi, H. Potential of fairy chemicals as functional cosmetic ingredients: Effect of 2-aza-8-oxohypoxanthine on skin lightness. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2022, 24, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeuchi, K.; Fujii, R.; Sugiyama, S.; Asakawa, T.; Inai, M.; Hamashima, Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Suzuki, T.; Kawagishi, H.; Kan, T. Practical synthesis of natural plant-growth regulator 2-azahypoxanthine, its derivatives, and biotin-labeled probes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 3813–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, Y.-C. Arbutin as a Skin Depigmenting Agent with Antimelanogenic and Antioxidant Properties. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Fukuda, M. In vitro effectiveness of several whitening cosmetic components in human melanocytes. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1991, 42, 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Akiu, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Asahara, T.; Fujinuma, Y.; Fukuda, M. Inhibitory effect of arbutin on melanogenesis-biochemical study using cultured B16 melanoma cells. Nippon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi 1991, 101, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.J.; Lee, E.H.; Kang, T.H.; Ha, S.K.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, T.J.; Kang, C.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.Y. Inhibitory effects of arbutin on melanin biosynthesis of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone-induced hyperpigmentation in cultured brownish guinea pig skin tissues. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosdahl, I.; Szabo, G. Mitotic activity of epidermal melanocytes in UV-irradiated mouse skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1978, 70, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iozumi, K.; Hoganson, G.E.; Pennella, R.; Mark, A.; Everett, M.A.; Fuller, B.B. Role of Tyrosinase as the Determinant of Pigmentation in Cultured Human Melanocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 100, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G.; Mishima, Y. Loss of melanogenic properties in tyrosinases induced by glucosylation inhibitors within malignant melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 1994–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mishima, Y.; Imokawa, G. Selective Aberration and Pigment Loss in Melanosomes of Malignant Melanoma Cells in Vitro by Glycosylation Inhibitors: Premelanosomes as Glycoprotein. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1983, 81, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K.; Uzuka, M.; Morikawa, F.; Toda, K.; Seiji, M. Transfer mechanism of melanosomes in epidermal cell culture. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1976, 67, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.P. Melanogenesis and Melanoma. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, B. Role of PGE2 and other inflammatory mediators in skin aging and their inhibition by topical natural anti-inflammatories. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, R.-M.; Hann, S.-K.; Oh, H.S. siRNA-mediated knock-down of COX-2 in melanocytes suppresses melanogenesis. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochiai, Y.; Kaburagi, S.; Obayashi, K.; Ujiie, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Okano, Y.; Masaki, H.; Ichihashi, M.; Sakurai, H. A new lipophilic pro-vitamin C, tetra-isopalmitoyl ascorbic acid (VC-IP), prevents UV-induced skin pigmentation through its anti-oxidative properties. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2006, 44, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, Y.; Iwamoto, M.; Masuda, T.; Tagami, H. Stimulatory effect of prostaglandin E2 on the configuration of normal human melanocytes in vitro. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1987, 89, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Safety Test | Guideline | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Ames test | OECD TG471 | No mutagenicity (max 5000 μg/mL) |
| In vitro skin irritation | OECD TG439 | No irritation |
| In vitro eye irritation (SkinethicTM HCE) | OECD TG492 | No irritation |
| In vitro phototoxicity (Skinethic skin irritation) | OECD TG432 | No phototoxicity |
| In vitro skin sensitization (DPRA) | OECD TG442C | No sensitization |
| In vitro skin sensitization (KeratinoSens) | OECD TG442D | No sensitization |
| In vitro skin sensitization (h-CLAT) | OECD TG442E | No sensitization |
| Human skin patch test * | - | Negative (skin irritation index: 3.7) |
| Human phototoxicity and photosensitization test * | - | Negative |
| Repeated insult patch test (RIPT) * | - | Negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aoshima, H.; Mizuno, R.; Iwatsu, Y.; Onishi, S.; Hyodo, S.; Ibuki, R.; Kawagishi, H.; Saitoh, Y. Inhibitory Effect of 2-Aza-8-oxohypoxanthine on Tyrosinase Activity and Melanin Production. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11020043
Aoshima H, Mizuno R, Iwatsu Y, Onishi S, Hyodo S, Ibuki R, Kawagishi H, Saitoh Y. Inhibitory Effect of 2-Aza-8-oxohypoxanthine on Tyrosinase Activity and Melanin Production. Cosmetics. 2024; 11(2):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11020043
Chicago/Turabian StyleAoshima, Hisae, Ruka Mizuno, Yuho Iwatsu, Shiori Onishi, Sayuri Hyodo, Rinta Ibuki, Hirokazu Kawagishi, and Yasukazu Saitoh. 2024. "Inhibitory Effect of 2-Aza-8-oxohypoxanthine on Tyrosinase Activity and Melanin Production" Cosmetics 11, no. 2: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11020043
APA StyleAoshima, H., Mizuno, R., Iwatsu, Y., Onishi, S., Hyodo, S., Ibuki, R., Kawagishi, H., & Saitoh, Y. (2024). Inhibitory Effect of 2-Aza-8-oxohypoxanthine on Tyrosinase Activity and Melanin Production. Cosmetics, 11(2), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11020043







