Abstract
Different lipid phase ratios (12, 14, and 16% w/w) were assessed for their ability to affect the technological and sensory properties of O/W emulsions in which bemotrizinol (BMTZ), a broad-spectrum sunscreen agent, was incorporated free or loaded into nanostructured lipid nanocarriers (NLC) to reduce its release from the vehicle and, hence, its skin permeation. The following technological properties were evaluated in vitro: spreadability, viscosity, pH, occlusion factor, BMTZ release, and sun protection factor (SPF). Sensory attributes were assessed by panelists in three different phases: before/during pick-up, rub-in, and after application. Raising the lipid phase ratio led to an increase in viscosity (from 8017 ± 143 cPs to 16,444 ± 770 cPs) and to a corresponding decrease in spreadability (from 9.35 ± 0.21 cm to 7.50 ± 0.10 cm), while the incorporation of BMTZ-loaded NLC determined a decrease in the occlusion factor (from 47.75 ± 1.16 to 25.91 ± 1.57) and an increase in SPF (from 6% for formulations containing 12% lipid phase to 15% for formulations containing 16% lipid phase). No BMTZ release was observed from all emulsions. Sensory attributes were mainly affected by the lipid phase ratio. These results suggest that the lipid phase ratio and BMTZ incorporation into NLC could contribute to determining the technological and sensory properties of O/W emulsions.
Keywords:
bemotrizinol; emulsions; sensory evaluation; UV filters; lipid nanoparticles; in vitro SPF 1. Introduction
Emulsions are the most common formulations used in the manufacture of cosmetics because of their moisturizing effect, their ability to maintain the proper water–lipid balance of the cutaneous barrier, and their ability to deliver active ingredients into the deeper skin layers, thus improving the effectiveness of skincare products [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. The main raw materials of these biphasic systems are water, lipids, viscosity-modifying agents, sensory agents (emollients and humectants), and emulsifiers [6,7,8,9]. The choice of the type and amount of such raw materials may play a key role in determining the safety and efficacy of the resulting emulsions, as skin permeation of the incorporated active ingredients could be strongly affected by vehicle composition [10,11,12]. As far as sunscreen agents are concerned, skin permeation should be avoided, or at least minimized, to improve both the safety and efficacy of sunscreen formulations [13,14]. In the last two decades, UV-filter incorporation into lipid nanoparticles has been proposed as a promising strategy to develop formulations containing lower amounts of organic UV filters without reducing the sun protection factor (SPF), due to the ability of these nanocarriers to act as physical sunscreens [15,16,17,18,19,20]. The first generation of lipid nanoparticles, namely, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN), consisted of a solid lipid core stabilized by surfactants in aqueous media [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. Due to their drawbacks, such as poor stability and loading capacity, a second generation of lipid nanoparticles (nanostructured lipid carriers, NLC), whose core was made up of mixtures of liquid and solid lipids, was developed [29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. SLN and NLC have been extensively studied as carriers for drugs and cosmetic active ingredients owing to their many advantages, including high biocompatibility, good tolerability, improved bioavailability, low cost of production, and easy scale-up. In addition, several studies have highlighted the ability of SLN and NLC to incorporate organic UV filters, thus supporting the feasibility of using these nanocarriers to develop sunscreen formulations [36,37,38,39]. In particular, due to the presence of solid lipids in their core, SLN and NLC could act as physical sunscreens, mostly reflecting UV radiation. Therefore, SLN and NLC could act in synergy with organic UV filters to improve SPF values of sunscreen products [36,37,38,39]. The increasing awareness of the harmful effects of both UV-A and UV-B radiation has drawn a great deal of attention to the search for broad-spectrum UV filters that could effectively protect the skin from UV solar radiation after their topical application. In this context, bemotrizinol (BMTZ), a triazine derivative (bis-ethylhexyloxyphenol methoxyphenyl triazine), has been designed to absorb UV radiation in the range of 280–380 nm and launched in the market as a broad-spectrum sunscreen [40,41,42,43,44].
In a previous work of ours, BMTZ was incorporated into various types of NLC, and the technological properties of O/W emulsions containing different percentages of optimized BMTZ-loaded NLC were evaluated [45]. BMTZ was chosen as a broad-spectrum UV filter because of its photostability, safety, and ability to absorb both UV-B and UV-A rays, converting the absorbed UV energy into less harmful forms [40,41,42,43,44]. In addition to absorbing UV radiation, BMTZ could form a thin film on the skin surface because of its poor ability to penetrate the skin. Such film would be able to reflect UV rays, thus providing an additional physical barrier that prevents UV radiation from reaching the deeper skin layers. Formulations, containing the same percentage of lipid phase and different percentages of optimized BMTZ-loaded NLC, showed interesting technological characteristics, such as low BMTZ release from the vehicle, good stability, and about a 20% increase of in vitro SPF values, in comparison with formulations containing the same percentage of free BMTZ.
As emulsion lipid content could affect both the in vitro release and skin permeation of incorporated active ingredients, in this work we investigated the effects of using different percentages of lipid phase with the same composition on the technological properties (viscosity, spreadability, occlusion factor, stability, in vitro release, and SPF value) of O/W emulsions, in which BMTZ-loaded NLC were incorporated. To the best of our knowledge, the effects of different lipid phase ratios on the technological properties of O/W emulsions used as vehicles for UV-filter-loaded lipid nanoparticles have not been fully explored.
In addition to technological properties, formulations’ sensory attributes, which are involved in consumer acceptance of cosmetic products, could be influenced by the emulsion lipid content [46,47]. Therefore, a sensory evaluation was performed on the emulsions under investigation to assess different parameters in the following steps: before and during product pick- up (glossiness, firmness, color, adhesiveness, and elasticity), during product “rub-in” (stickiness, spreadability, absorbency, and oiliness), and after emulsion application (“after feel”, glossiness, stickiness, and oiliness).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Isopropyl myristate (IPM), disodium EDTA (EDTA), imidazolidinyl urea (Kemipur 100®), C12-15 alkyl benzoate (Acemoll TN®), beeswax, and benzyl alcohol were supplied by Galeno (Carmignano, Prato, Italy). Almond oil and glycine soja oil were purchased from Farmalabor (Canosa di Puglia, Bari, Italy). Cetearyl alcohol and cetearyl glucoside (Montanov 68®) were supplied by Polichimica Srl (Bologna, Italy). Cetyl palmitate (Cutina CP®, CP), bis-ethylhexyloxyphenol methoxyphenyl triazine (bemotrizinol, Tinosorb S®, BMTZ), cetearyl isononanoate (Cetiol SN®), and glyceryl stearate (Cutina MD®) were a kind gift from BASF (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Oleth-20 (Brij 98®) was bought from Sigma-Aldrich (Milan, Italy). Glyceryl oleate (Tegin O®, GO) was obtained from A.C.E.F. S.p.A. (Fiorenzuola D’Arda, Piacenza, Italy). Regenerated cellulose membranes (Spectra/Por CE; Mol. Wt. Cut off 3000) were bought from Spectrum (Los Angeles, CA, USA).
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Bemotrizinol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)
NLC were prepared using the phase inversion temperature (PIT) method, using cetyl palmitate as a solid lipid (4% w/w), isopropyl myristate as a liquid lipid (3% w/w), and bemotrizinol (8% w/w), oleth-20 (8.7% w/w), and glyceryl oleate (4.4% w/w) as surfactant and co-surfactant, respectively [45]. The aqueous phase consisted of deionized water, containing Kemipur 100® 0.35% w/w as a preservative. After separately heating both the oil and aqueous phase at 90 °C, the aqueous phase was added slowly to the oil phase under vigorous stirring (700 rpm), leading to a colloidal suspension that was allowed to cool down to room temperature under continuous stirring. Then, the samples were stored in airtight jars at room temperature in the dark until used. Morphological analysis was performed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) using a transmission electron microscope (model JEM 2010, Jeol, Peabody, MA, USA) operating at an acceleration voltage of 200 KV. Samples were prepared by placing 5 μL of colloidal suspension on a Formvar (200-mesh) copper grid (TAAB Laboratories Equipment, Berks, UK). The excess of sample was removed by filter paper, and a drop of 2% (w/w) aqueous solution of uranyl acetate was added. The sample was analyzed after drying at room temperature. The mean particle size and size distribution (polydispersity index, PDI) of bemotrizinol-loaded NLC were determined by dynamic light scattering (Zetasizer Nano ZS90, Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK), using a 4 mW laser diode at 670 nm and scattering light at 90°. Before the analysis, the sample was diluted (1:5, sample/distilled water) and left to settle down to 25 °C for 2 min. The same Zetasizer was used to assess ζ-potential by laser Doppler velocimetry after diluting the samples in KCl 1 mM (pH 7.0).
2.3. Preparation of O/W Emulsions
The composition of O/W emulsions prepared using different percentages of oil phase is reported in Table 1. After separately heating phases A and B to 70 °C, the water phase was poured into the oil phase under stirring for 90 s at 5000 rpm (Turbomixer Silverson SL2, Silverson Machines Inc., East Longmeadow, MA, USA). The resulting emulsion was cooled to 40 °C under slight stirring, and then preservatives (phase C) were added. Afterwards, for samples A12NLC, A14NLC, and A16NLC, the same amount (30.0% w/w) of BMTZ-loaded NLC colloidal suspension was added under gentle mixing. Then, the emulsion was cooled to room temperature under continuous and gentle stirring. All samples were stored in airtight glass jars at room temperature and in the dark until used. Then, 48 h after emulsion preparation, pH measurements were performed using a Crison pH-meter model Basic 20 (Crison Instruments, Barcelona, Spain) after diluting the sample with distilled water to one-tenth of its original concentration, as previously reported [47].

Table 1.
Composition (% w/w) of O/W emulsions containing free bemotrizinol (BMTZ) and BMTZ-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). q.s. = quantum sufficit to 100% w/w.
2.4. Stability Tests on O/W Emulsions
Accelerated stability tests were performed by centrifuging emulsion samples at 3000 rpm for 20 min using a centrifuge MiniSpin Plus (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). After centrifugation, the appearance, pH, and viscosity of the samples were evaluated.
Samples of the emulsions under investigation were stored in airtight glass jars at room temperature and at 37 °C for three months, sheltered from light. At various intervals (one week, two weeks, one month, two months, and three months), samples were analyzed to determine their appearance, pH, and viscosity.
2.5. Spreadability
Spreadability was determined by the parallel-plate method [47,48] using two glass plates (diameter 9 cm). Here, 1 g of sample was placed between the plates and a 50 g weight was put on the upper plate. After 1 min, the weight was removed, and the spreading diameter (expressed in centimeters) was measured. Each measurement was carried out in triplicate.
2.6. Occlusion Factor
The occlusion factor was assessed according to a method previously reported [49,50]. Beakers (100 mL) containing 50 mL of distilled water were covered with filter paper (cellulose acetate filter, perfecte 2, 90 mm, cutoff size: 4–7 µm, Cartiera Cordenons, Pordenone, Italy), sealed, and 200 mg of emulsion was spread on the filter surface (18.8 cm2; applied amount: 10.6 mg/cm2). After weighting the sample accurately, incubation was performed at 32 °C (skin surface temperature) for 48 h (50–55% RH) in an incubator (Incubator IN 30, Memmert GmbH, Schwabach, Germany). Then, samples were weighted to determine water evaporation. Beakers covered with filter paper free of sample formulation were used as a reference.
The occlusion factor (F) was calculated according to the following Equation (1):
where A is the water loss without sample (reference) and B is the water loss with sample. Each experiment was performed in triplicate.
F = 100 × [(A − B)/A]
2.7. Viscosity
Viscosity measurements [51,52] were performed 48 h after emulsion preparation to allow the sample to settle down. The viscosity of the formulations under investigation was determined by a Brookfield DV-II+Pro EXTRA rotation viscosimeter (Brookfield Engineering Laboratories, Inc., Middleboro, MA, USA) using spindle number 6. The instrument was calibrated as described in the operating instructions of the instrument manual, using silicone oil as a standard fluid. Each formulation (25 mL) was placed in a glass vial and left to settle down for 1 h prior to performing the measurement. Then, viscosity was monitored for 30 s at 6 rpm and room temperature. Each measurement was carried out in triplicate with a time interval of 5 min, and the results were expressed in cPs.
2.8. In Vitro Release of Bemotrizinol
Franz-type diffusion cells (LGA, Berkeley, CA, USA) were used to assess BMTZ release from the emulsions under investigation [53,54,55,56]. Experiments were performed using cellulose membranes previously moistened by immersion in distilled water for 1 h at room temperature. This methodology to assess in vitro drug release from topical formulations has been reported to be suitable to obtain reliable results [57]. After placing the membrane between the donor and the receptor compartment, the surface area available for diffusion was 0.75 cm2. As BMTZ is a poorly water-soluble compound, a mixture consisting of water/ethanol (50/50 v/v) was used as the receiving phase to ensure pseudo-sink conditions by increasing BMTZ’s solubility in the receiving phase. The use of receptor fluids containing solvents or surfactants to increase drug solubility has already been reported by others [58]. The receiving phase (4.5 mL, pH 6.5) was stirred (700 rpm) and thermostated at 35 °C to maintain the membrane surface at 32 °C throughout the experiment. After placing the sample (2 mg/cm2) in the donor compartment, 500 μL of the receiving solution was withdrawn at various intervals (0, 30, 60, 90, 120, and 240 min) and replaced with an equal volume of receptor fluid pre-thermostated to 35 °C. The amount of BMTZ in such samples was determined spectrophotometrically (UV-VIS Spectrophotometer Shimadzu model UV-1601, Shimadzu Italia, Milan, Italy) at 340 nm. A calibration curve was constructed in the range of 0.1–1 μg/mL by dissolving BMTZ in water/ethanol (50/50 v/v; limit of detection 0.01 μg/mL, and limit of quantification 0.05 μg/mL). Each experiment was performed in triplicate and results were expressed as mean ± S.D.
2.9. Determination of In Vitro Sun Protection Factor (SPF)
To evaluate the in vitro sun protection factor (SPF) values [59,60,61,62,63] of the formulations under investigation, the method described by Dutra et al. [64] was applied, with minor modifications. Each emulsion sample was properly diluted in deionized water (final concentration: 200 μg/mL) and analyzed spectrophotometrically (UV-VIS Spectrophotometer Shimadzu model UV-1601, Shimadzu Italia, Milan, Italy). Absorption data were acquired every 5 nm in the range of 290–320 nm. SPF values were calculated according to Equation (2):
where CF is the correction factor (=10), EE(λ) is the erythemal effect of the radiation with wavelength λ, I(λ) is the solar intensity of radiation with wavelength λ, and Abs(λ) is the absorbance of the sunscreen product at wavelength λ.
SPFspectrophotometric = CF × Σ EE(λ) × I (λ) × Abs (λ)
The values of EE(λ) × I(λ) at each wavelength in the range of 290–320 nm were constant, as determined by Sayre et al. [65], and were used to calculate the SPF values.
2.10. Sensory Evaluation
A descriptive sensory evaluation was performed by ten female panelists (aged 38 ± 8 years). Due to the nature of the study, the local Ethical Committee declared that no approval was required. After explaining the general concept of the study, detailed explanations of the test and on the use of the sensory descriptors were provided to all participants [47,66]. All participants provided their written informed consent to be enrolled in the study. Prior to performing the sensory evaluation on the investigated formulations, the panelists were trained by assessing three commercial O/W creams on the same attributes involved in the present study. In addition, panelists were instructed to apply about 2 mg of product over the back of the left hand.
The study was carried out under controlled temperature and relative humidity, and adequate light conditions. Panelists were asked to provide their assessment in three different steps: (1) before and during product pick-up, (2) during product rub-in, and (3) after product application on the skin. Each attribute was graded using pre-defined descriptive terms, to which a numeric value was assigned, as reported in Table 2.

Table 2.
Description of attributes used for sensory evaluation.
Freshly prepared samples were placed in containers labeled with four-digit code numbers and provided to the panelists along with an analysis form, reporting, for each step, the descriptive term and grading of the sensory attributes under evaluation. For each attribute in each phase, the sum of the scores (from 1 to 5) assigned by each panelist was performed and reported in radar charts (Excel for Windows version 11, Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA), in which each axis indicates the scores assigned by panelists for a given parameter. For each parameter, the minimum score was 10 and the maximum was 50. The participants were also asked to indicate their preferred formulation.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
Results were expressed as mean values ± standard deviation (S.D.) of three replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test, and values were considered statistically different when p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
Pharmaceutical and cosmetic emulsions are complex systems in which several components may affect the safety, efficacy, and consumer acceptance of the final product. Otto et al. [67], reviewing the effects of emulsion composition on dermal and transdermal delivery of active ingredients, outlined the importance of the proper choice of emulsion constituents, such as emollients and emulsifiers, to optimize the skin penetration of an active ingredient. In particular, the composition and amount of lipid phase could affect the performance of cosmetic emulsions. Generally, the lipid phase content in cosmetic O/W emulsions ranges between 10% w/w and 50% w/w, with 75% w/w being the maximum theoretical value. In this work, different lipid phase ratios (12–16% w/w) were assessed for their ability to modify the technological and sensory properties of O/W emulsions incorporating free BMTZ and BMTZ-loaded NLC.
In a previous work [45], the feasibility of incorporating BMTZ in NLC with different oil compositions was investigated. Using 3% w/w of isopropyl myristate and 4% of cetyl palmitate as components of the NLC core, stable colloidal suspensions with a maximum loading capacity of 8% w/w BMTZ were obtained. In the present work, such BMTZ-loaded NLC were incorporated in O/W emulsions prepared using different lipid phase ratios (12, 14, and 16% w/w). These nanoparticles were roughly spherical, with no sign of aggregation, and showed mean size (193.2 ± 8.8 nm), PDI (0.151 ± 0.012), and ζ-potential values (−11.1 ± 1.5 mV) suitable for incorporation into topical formulations. Generally, ζ-potential values greater than 30 mV, as the absolute value, are regarded as suitable to obtain stable colloidal suspensions. Despite ζ-potential values lower than 30 mV, BMTZ-loaded NLC showed good stability after storage for two months at room temperature. Such good stability was attributed to the presence of long polyoxyethylene chains of the surfactant oleth-20 on the nanoparticle surface, which could provide a steric stabilization [45].
To evaluate the effects of BMTZ encapsulation into NLC, O/W emulsions containing the corresponding amount of free BMTZ (2.4% w/w) were prepared, as shown in Table 1. Preliminary investigations were carried out by comparing the technological properties (pH, viscosity, occlusion factor, and spreadability) of the O/W emulsions containing 2.4% w/w of free BMTZ with those of O/W emulsions having the same lipid and aqueous phase composition but prepared without BMTZ. The results of these experiments showed no significant differences between emulsions without BMTZ and emulsions containing 2.4% w/w of BMTZ for all assessed parameters
Prior to evaluating the technological properties, the emulsions under investigation were assessed for their stability. Accelerated stability tests performed by centrifugation did not show any sign of emulsion separation or alteration. Storing emulsions at room temperature and 37 °C for three months did not lead to any significant change in the pH, viscosity, and appearance of the samples, thus suggesting a good stability of all formulations.
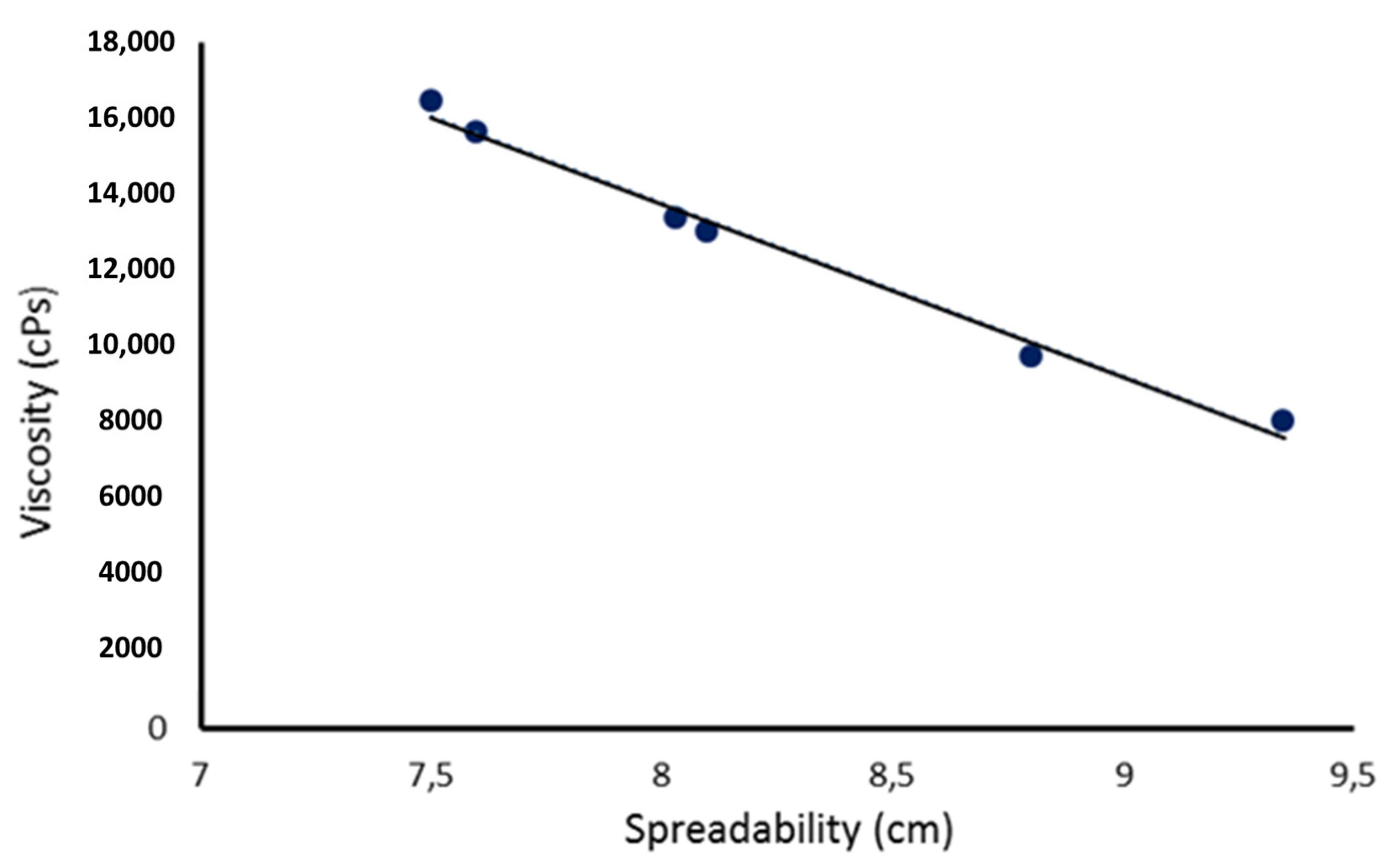
The technological properties of O/W emulsions containing free BMTZ and BMTZ-loaded NLC are summarized in Table 3. For all investigated emulsions, pH values were similar and ranged from 6.3 to 6.5. Although these values were greater than the skin surface pH value (5–5.5), they were within the physiological value and could be regarded as safe. Increasing the lipid phase ratio led to a greater viscosity of the resulting emulsions and to a decrease in spreadability. The incorporation of BMTZ-loaded NLC determined a decrease in viscosity of emulsions containing 12% w/w of oil phase, while no significant difference was observed for emulsions prepared using 14 and 16% w/w of lipid phase. A corresponding but inverse trend was observed when analyzing spreadability data. As shown in Figure 1, a good relationship (r2 = 0.9883) was observed between viscosity and spreadability values. These results support previous observations about the possibility of predicting the spreadability of topical formulations by measuring their viscosity [68,69].

Table 3.
Emulsion technological properties: pH, occlusion factor (F), spreadability (S), viscosity, and cumulative amount of bemotrizinol released after 4 h from the vehicle. N.D. = not detectable.
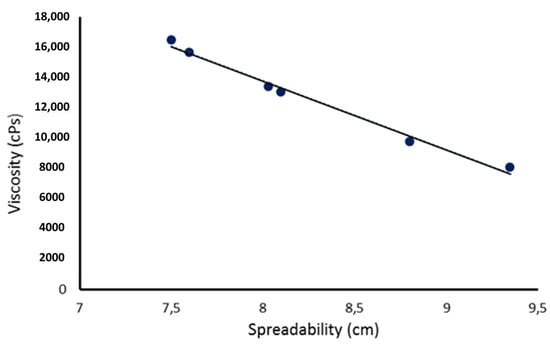
Figure 1.
Relationship between viscosity and spreadability of formulations A12, A12NLC, A14, A14NLC, A16, and A16NLC. S.D. was omitted for clarity.
Results of experiments performed to evaluate the occlusion factor (F) of the emulsions under investigation showed that an increase in lipid phase content from 12 to 14% w/w led to greater F values, but a further increase from 14 to 16% w/w did not result in an additional increase. These results support the hypothesis that the occlusive properties of O/W emulsions could be affected by the amounts of oils used for their preparation [70]. When BMTZ-loaded NLC were incorporated into the emulsions, F values decreased regardless of the lipid phase ratio, suggesting that BMTZ-loaded NLC could alter the emulsion structure, making it more permeable to water. Previous differential scanning calorimetry studies [45] pointed out that BMTZ-loaded NLC had low crystallinity, which was attributed to their high percentage of liquid lipids. As reported in the literature [49,71], lipid nanoparticles with low crystallinity could not be expected to provide a significant enhancement of the occlusion factor.
Early studies on skin permeation highlighted the key role of drug release from the vehicle in the percutaneous absorption process [72]. Indeed, for a drug to be able to permeate through the skin, its release from the formulation is an essential requisite. In the present work, BMTZ in vitro release from the emulsions under investigation was evaluated in experiments lasting 4 h because sunscreen formulations are not expected to remain on the skin surface for longer periods. As shown in Table 3, no BMTZ could be detected in the receiving phase, thus showing that the sunscreen agent was not released from the vehicle. These results suggest that no BMTZ skin permeation could be expected to occur after topical application of the investigated formulations.
The sun protection factor (SPF) is a fundamental parameter to assess the efficacy of sunscreen formulations. In 2006, the European Cosmetic and Perfumery Association (COLIPA) developed an in vivo method to determine SPF in humans [73], which has been used to draw up ISO 24444:2019 [74], the currently-in-use standardized in vivo SPF test. With in vivo methods being quite expensive and time-consuming, several alternative in vitro tests have been developed to obtain affordable, fast, and reliable results [75,76,77,78]. In this work, the method based on the Mansur equation was used to determine in vitro SPF values, as this type of test has already been applied in the evaluation of skin photo-protection of an active ingredient incorporated into lipid nanoparticles [79]. However, the reliability of this spectrophotometric method has been questioned because of the poor predictability of in vivo results, mainly due to an improper application of the method, such as incorrect dilution of the sample [80,81]. Recently, Hermund et al. [82], to evaluate the reliability of the Mansur method, tested three commercial sunscreen formulations using this in vitro method and compared the obtained results with the SPF values reported by the manufacturers. The authors found a good agreement between claimed SPF values and SPF values determined using the Mansur equation, highlighting the advantages of this in vitro method (use of conventional equipment and inexpensive solvent) and its usefulness to screen products during the development step. Recent examples of SPF determination using the parameters reported by Sayre et al. [65] include the evaluation of the in vitro photoprotective effect of the curcumin-loaded emulsion [83] and the UV-B-protection performance of proanthocyanidin-rich extracts obtained from Cinnamomum camphora leaves [84].
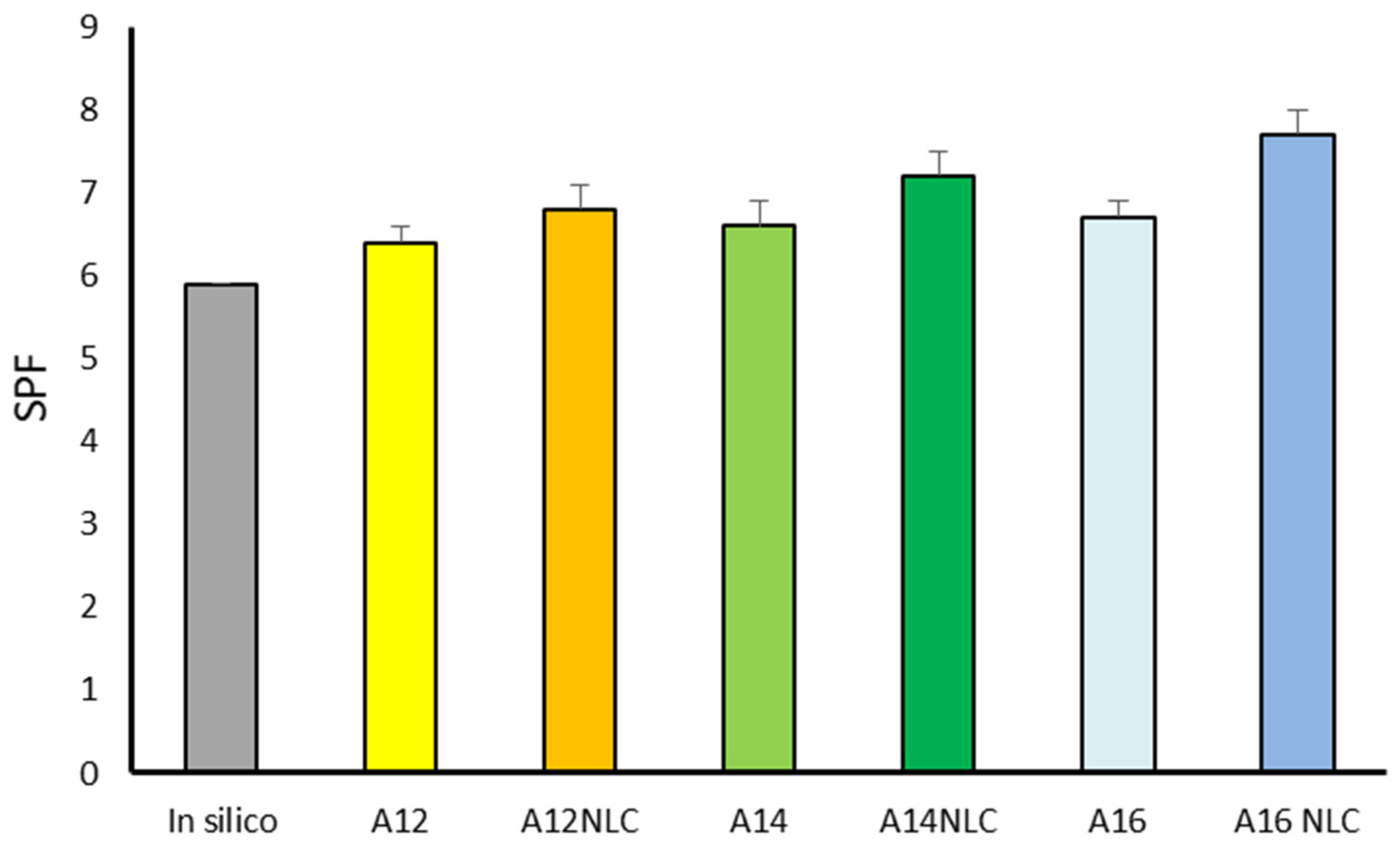
In this work, to assess the reliability of SPF values obtained by applying the Mansur equation, results were compared to those obtained in silico by the BASF sunscreen simulator (www.basf.com/sunscreen-simulator, accessed on 2 February 2024). This software is based on the concept that, according to Sayre et al. [65], SPF can be conceptualized as the ratio of areas under the transmittance vs. the wavelength plot, taking into account the erythemal weighted UV of solar radiation, which has been defined as a function of the wavelength, the irradiance, and the erythemal weighting function. As shown in Figure 2, the BASF sunscreen simulator predicted an SPF value of 5.9 for a formulation containing 2.4% w/w BMTZ. It is important to underline that this software was not able to account for vehicle effects and UV-filter incorporation into nanocarriers. Therefore, preliminarily, emulsions prepared using 12, 14, and 16% w/w of lipid phase free of BMTZ were tested to determine their SPF, providing very low values (0.95, 0.97, and 1.10, respectively).
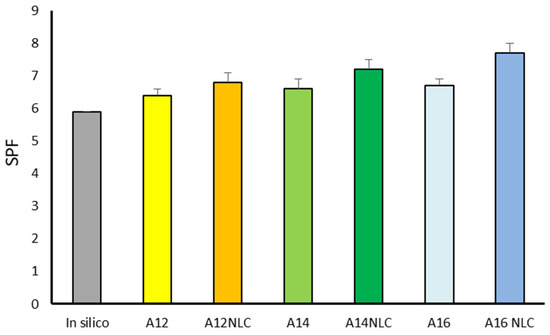
Figure 2.
Sun protection factor (SPF) calculated by the BAF sunscreen simulator for 2.4% w/w bemotrizinol (in silico) and in vitro for formulations A12, A12 NLC, A14, A14NLC, A16, and A16NLC. S.D. was not reported for in silico data because these data were generated by a software.
A slight increase, although not statistically significant, of SPF values was observed by raising the percentage of lipid phase. These results suggest that, regardless of its composition, the content of lipid phase could affect the photo-protective activity of O/W emulsions.
Formulations A12, A14, and A16, containing 2.4% of free BMTZ, showed SPF values in good agreement with the predicted in silico values (6.4, 6.6, and 6.7, respectively). The slightly higher SPF values obtained by the Mansur method could be attributed to the contribution to SPF provided by the vehicle that was not accounted for when SPF was estimated in silico. The results reported in Figure 2 pointed out that the incorporation of BMTZ into NLC led to an improvement of SPF, in comparison with the corresponding O/W emulsion containing the same percentage of free BMTZ. The SPF increase was in the range of 6% (formulation A12 NLC) to 15% (formulation A16NLC). As all data showed standard deviation values lower than 5%, the differences in SPF values between formulations containing free BMTZ and BMTZ-loaded NLC were statistically significant when compared using Student’s t-test. An increase in the SPF value as a result of UV-filter incorporation into lipid nanoparticles has already been reported in the literature. An early work by Wissing and Muller [85] reported about a 20% increase in SPF by encapsulating the UV-filter 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone into SLN. Similarly, the entrapment of silymarin, a flavonoid with antioxidant activity, into NLC incorporated in O/W emulsions provided about a 20% increase in SPF, in comparison with the same formulations containing free silymarin [79]. Recently, de Araújo et al. [86] reported an increased photo-protection due to UV-filter incorporation into NLC, despite a 10% reduction in filter content. The results of the present study are in good agreement with literature data, supporting a synergetic effect between UV-radiation absorption due to the organic filter and light scattering promoted by NLC, which could act as physical sunscreens because of their core structure, consisting mainly of solid lipids. In particular, in this work, lipid nanoparticles were prepared using cetyl palmitate as a solid lipid. According to Wissing and Muller [85], when cetyl palmitate is used as a solid lipid to prepare lipid nanocarriers, the crystalline nature of this lipid provides the resulting nanocarriers with the capacity of reflecting and scattering UV radiation on their own. Further studies have been planned to evaluate the in vivo SPF of the investigated formulations to assess the reliability of in vitro data.
In addition to suitable SPF values, consumers require that sunscreen emulsions show proper sensory attributes, such as good spreadability, low oiliness and stickiness, and a lack of residues on the skin. Among these properties, spreadability plays a key role, as sunscreen formulations are supposed to be applied in a thin and even layer on large area of the skin surface. Calvo et al. [8] summarized the most relevant sensory attributes that affect consumer acceptance of skincare products, highlighting the role of rheology and product formulation in determining the textural properties of cosmetic emulsions. A study performed on O/W emulsions containing different percentages of xanthan gum and oil phase showed the dependence on the percentage of such emulsion components of specific sensory attributes [87]. In particular, an increase in oil phase led to enhanced oiliness, consistency, and stickiness of the formulations, while different percentages of xanthan gum mainly affected the integrity of the shape, penetration force, wetness, spreadability, and glossiness.
In this work, the effects of different oil phase ratios on the sensory attributes of O/W emulsions containing NLC-loaded BMTZ as a sunscreen agent were evaluated. As NLC consist of solid and liquid lipids, their incorporation into O/W emulsions could affect the consumer perception of several parameters, such as oiliness, spreadability, stickiness, and glossiness. A statistical analysis (ANOVA, analysis of variance) of panelists’ ability to provide reliable opinions was performed in the training phase, showing that between-repetition and between-assessor variations were not significant (p > 0.05).
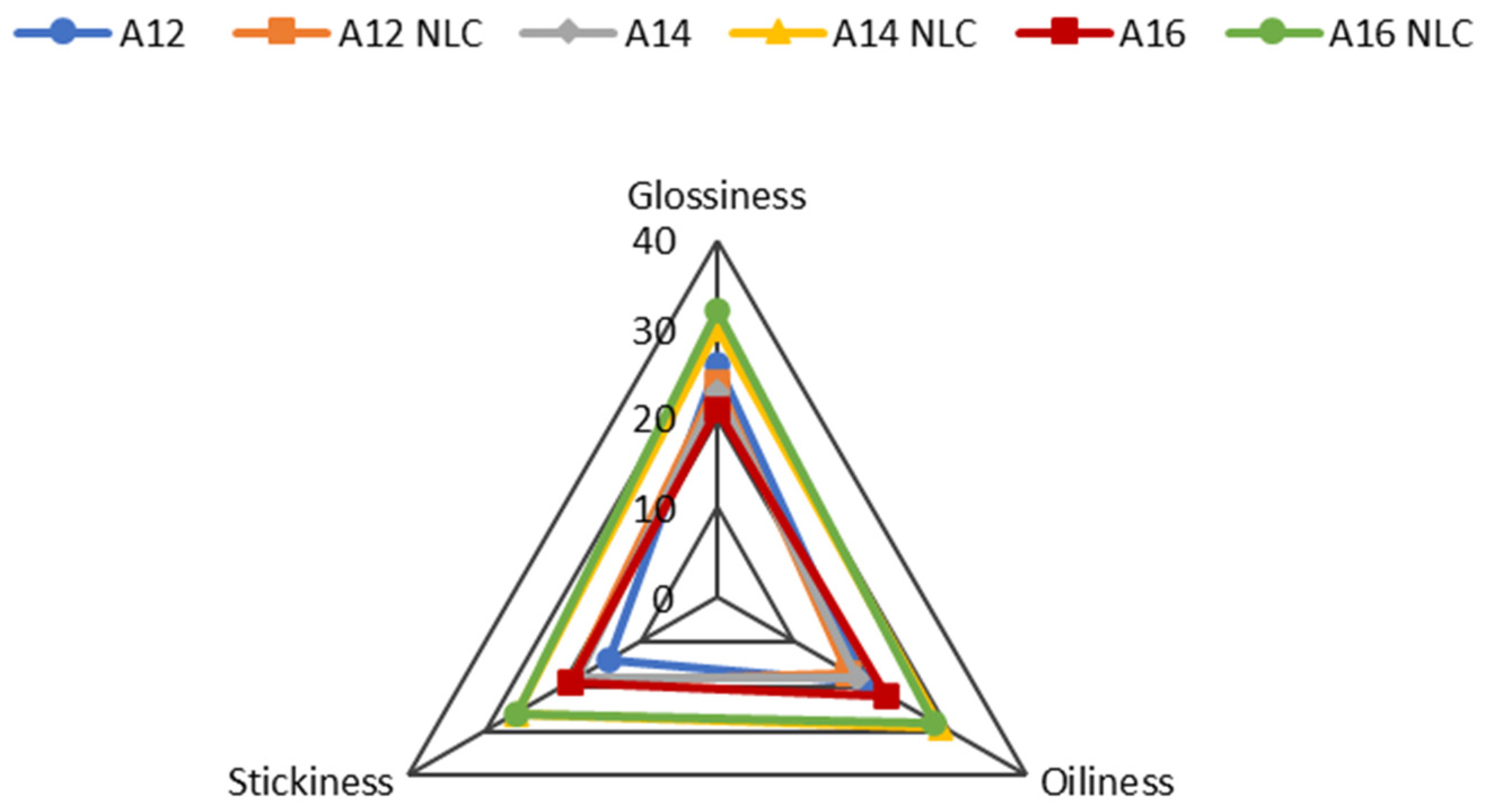
The results of the sensory evaluation performed before and during product pick-up, during rub-in, and after product application (after feel) are shown in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5.
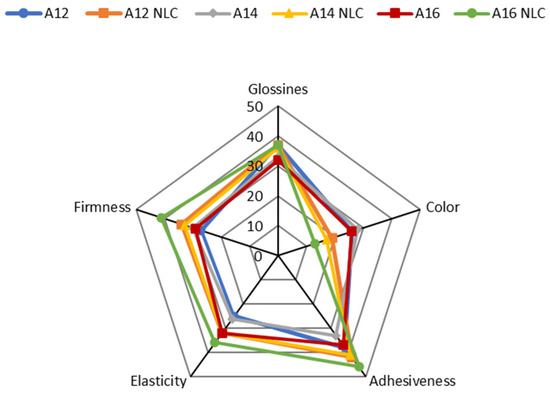
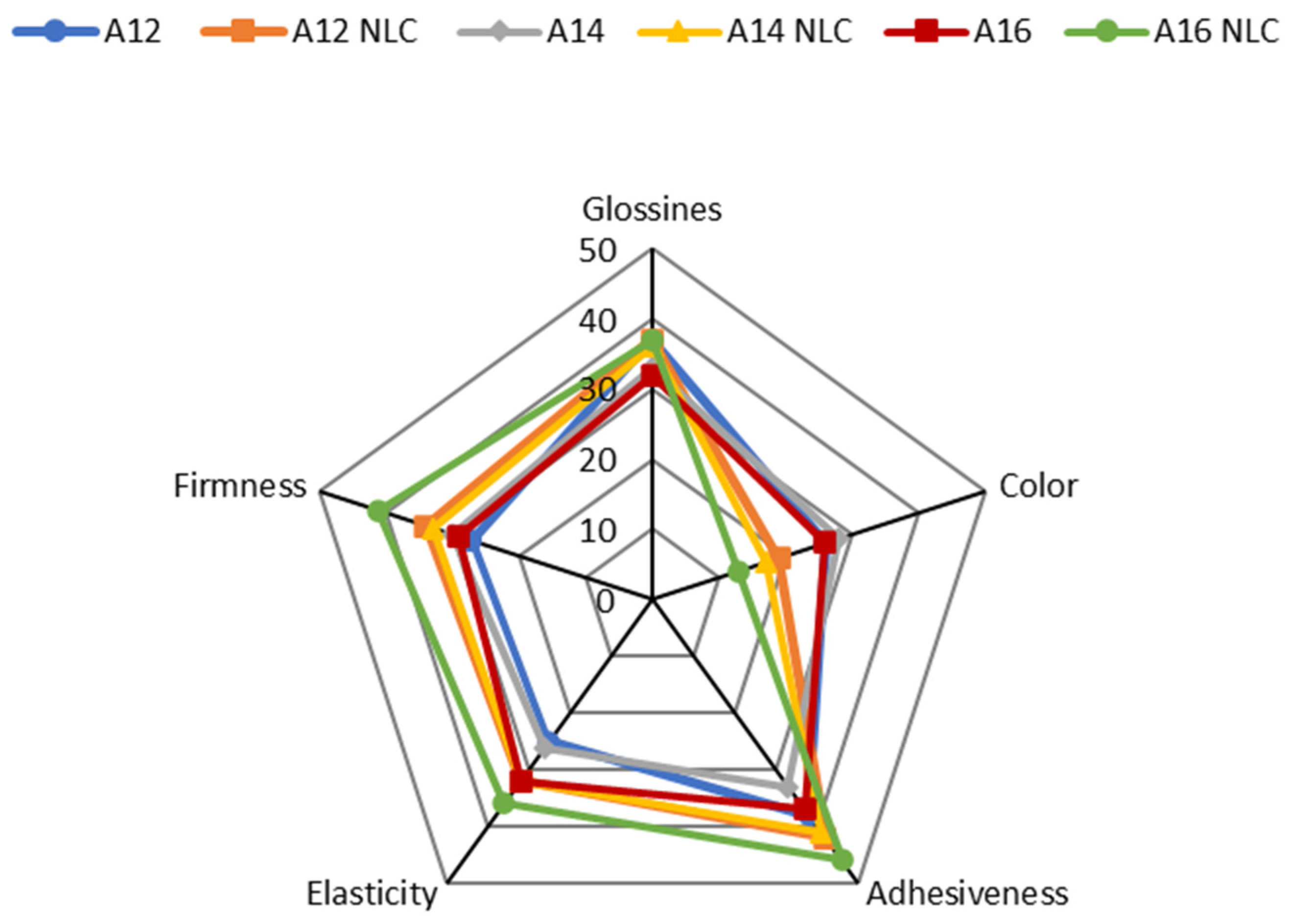
Figure 3.
Sensory evaluation of formulations A12, A12NLC, A14, A14NLC, A16, and A16NLC before and during pick-up from the container. Each axis indicates the scores assigned by panelists for a given parameter. Data were reported as the sum of all scores that panelists assigned to a given parameter.
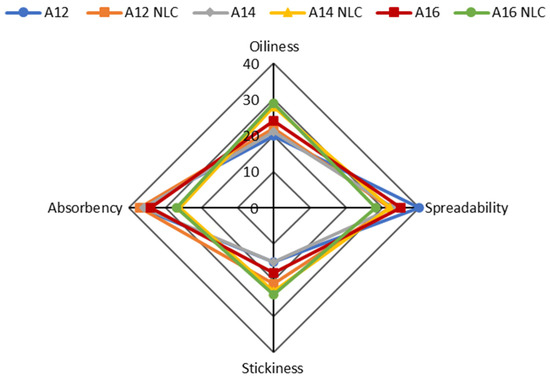
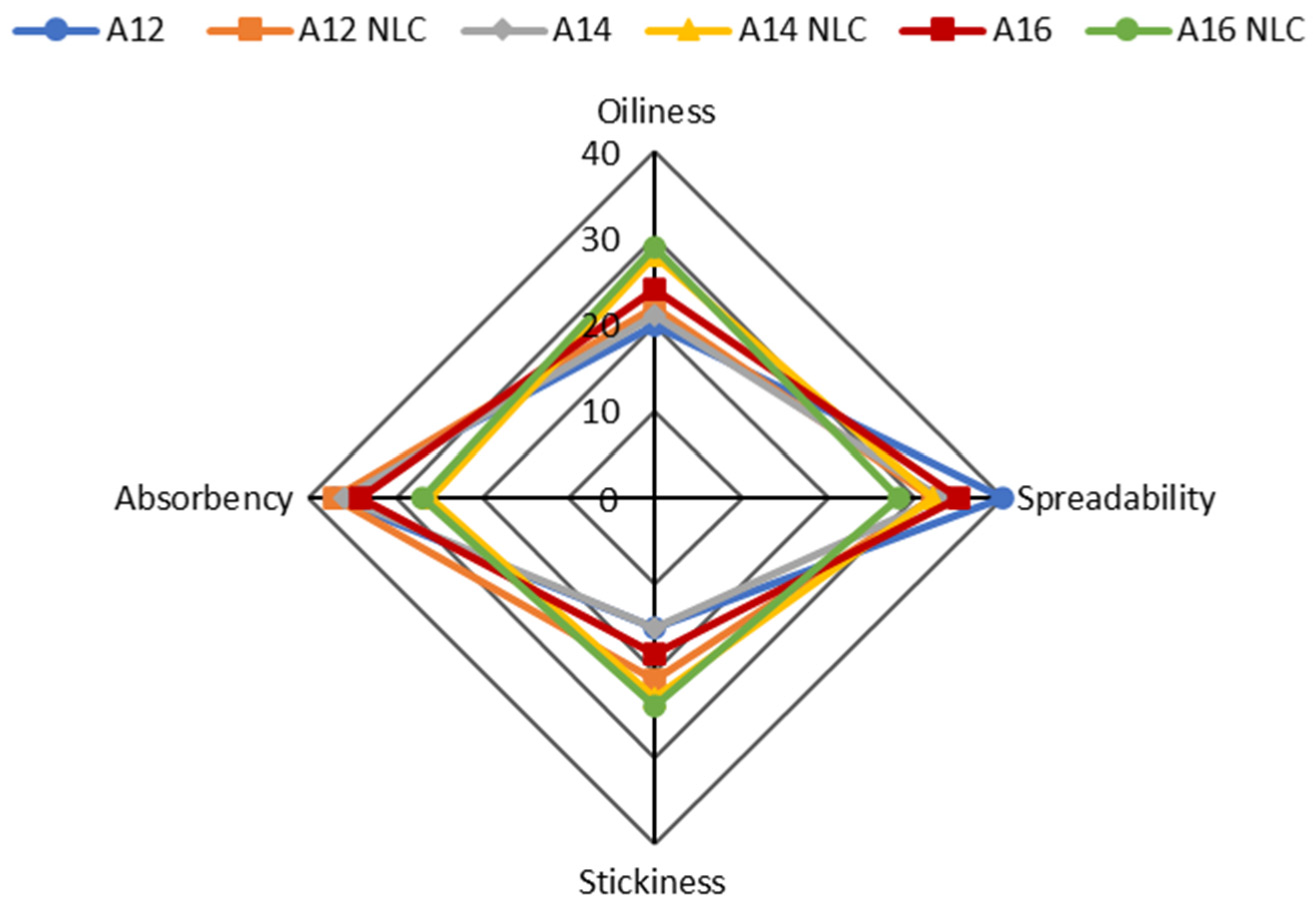
Figure 4.
Sensory evaluation of formulations A12, A12NLC, A14, A14NLC, A16, and A16NLC during rub-in on the skin surface. Each axis indicates the scores assigned by panelists for a given parameter. Data were reported as the sum of all scores that panelists assigned to a given parameter.
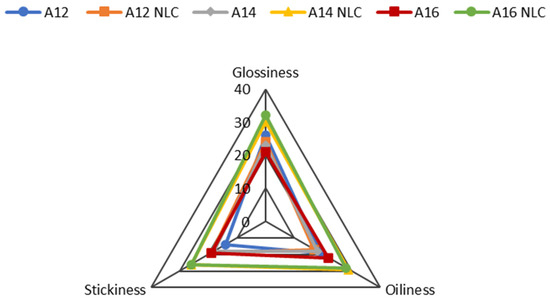
Figure 5.
Sensory evaluation of formulations A12, A12NLC, A14, A14NLC, A16, and A16NLC after application on the skin surface (after feel). Each axis indicates the scores assigned by panelists for a given parameter. Data were reported as the sum of all scores that panelists assigned to a given parameter.
When the product was in the container, the incorporation of NLC in the cream mainly affected color perception. Emulsions containing free BMTZ were perceived as yellowish or pale yellow, while formulations incorporating BMTZ loaded into NLC were assessed as whitish or white. BMTZ is a light-yellow powder whose addition to a cream makes the formulation a yellowish color. BMTZ incorporation into NLC seemed to almost completely mask the color of this UV filter, leading to whitish or white formulations. In addition, it is interesting to note that the increase in lipid phase content for emulsions containing BMTZ-loaded NLC seemed to move the perception of color toward white. This observation requires further investigations to confirm these results using a large number of panelists and to provide a rational explanation of such finding. The emulsion (A16NLC) containing the highest percentage of lipid phase was considered the most elastic, adhesive, and firm when BMTZ-loaded NLC were incorporated (Figure 3). As expected, during rub-in, the formulation that was scored as the most spreadable was formulation A12, which showed the lowest viscosity. A close relationship between formulation viscosity and spreadability during application onto the skin surface has been reported in previous studies [88,89]. However, an increase in the oil phase ratio from 12 to 14% w/w reduced the perceived ease of spreading, but a further increase to 16% w/w did not alter this perception. These results could be attributed to the close viscosity values of emulsions A14 and A16, which did not allow the panelists to discriminate between these formulations. The incorporation of BMTZ-loaded NLC resulted in a decrease in spreadability, in comparison to the corresponding emulsion containing free BMTZ. As shown in Figure 4, oiliness increased by raising the ratio of oil phase, and this effect was enhanced by the incorporation of BMTZ-loaded NLC. Reduced absorbency and increased stickiness of the products under evaluation were reported as a result of both higher oil phase content and BMTZ-loaded NLC incorporation. Sensations of oiliness and stickiness due to product application on the skin surface are regarded as important parameters in determining the answers provided by the panelists and the resulting hedonic response [90,91].
In the last phase (Figure 5), the panelists were asked to express their opinion about the residue remaining on the skin after application of the product (after feel). The incorporation of BMTZ-loaded NLC markedly increased the sensations of oiliness, glossiness, and stickiness in formulations containing 14% and 16% of oil phase. A different trend was observed for formulations prepared with the lowest lipid ratio (12% w/w), in which the addition of BMTZ-loaded NLC resulted in lower glossiness and oiliness but greater stickiness.
At the end of the descriptive sensory evaluation, the panelists were asked to choose the cream that, in their opinion, had the best performance. Three panelists stated their preference as formulation A12, and three panelists preferred formulation A12NLC. The remaining four formulations received one preference each. These results suggest that the lipid phase content had a stronger influence on the sensory attributes than BMTZ incorporation into NLC.
4. Conclusions
Effectiveness, safety, and sensory attributes of cosmetic emulsions are strongly affected by their constituents. As far as sunscreen emulsions are concerned, UV-filter skin permeation should be avoided, or at least kept as low as possible, to obtain safe and effective formulations. Different strategies have been proposed to achieve this goal, among which reducing the UV-filter content and modifying the emulsion composition are regarded as very promising. In this context, the results of the present work highlighted the strong impact of the lipid phase ratio and encapsulation of UV filters into NLC on the technological and sensory properties of the resulting O/W emulsions. In addition, UV-filter release from the investigated formulations was not detectable during 4 h, thus suggesting that a proper choice of emulsion components could allow for improving the safety and efficacy of sunscreen formulations while obtaining products with a good consumer acceptance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M.; methodology, L.M. and C.P.; validation, L.M. and C.P.; formal analysis, L.M. and D.S.; investigation, D.S.; resources, L.M. and C.P.; data curation, L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, L.M.; writing—review and editing, L.M., C.P. and D.S.; visualization, D.S.; supervision, L.M. and C.P.; project administration, L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Due to the nature of the study, the local Ethical Committee declared that no approval was required.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sikora, E. Cosmetic Emulsions; Wydawnictwo PK: Kraków, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, M.H.; Nestor, M.S. A Supersaturated Oxygen Emulsion for Wound Care and Skin Rejuvenation. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2020, 19, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanholi, K.d.S.S.; da Silva, J.B.; Batistela, V.R.; Gonçalves, R.S.; Said dos Santos, R.; Balbinot, R.B.; Lazarin-Bidóia, D.; Bruschi, M.L.; Nakamura, T.U.; Nakamura, C.V.; et al. Design and Optimization of Stimuli-Responsive Emulsion-Filled Gel for Topical Delivery of Copaiba Oil-Resin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Shang, Y.; Zeng, X. Study on the Development of Wax Emulsion with Liquid Crystal Structure and Its Moisturizing and Frictional Interactions with Skin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyja, R.; Jankowski, A. The Effect of Additives on Release and in Vitro Skin Retention of Flavonoids from Emulsion and Gel Semisolid Formulations. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zou, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, S. Salt of Organosilicon Framework as a Novel Emulsifier for Various Water–Oil Biphasic Systems and a Catalyst for Dibromination of Olefins in an Aqueous Medium. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 33693–33703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Q.; Li, X.; Ma, C. Systematic Comparison of Structural and Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-water and Water-in-oil Biphasic Emulgels: Effect of Emulsion Type, Oil-phase Composition, and Oil Fraction. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 4200–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, F.; Gómez, J.M.; Ricardez-Sandoval, L.; Alvarez, O. Integrated Design of Emulsified Cosmetic Products: A Review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 161, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, C.; Ng, K.M. Product-oriented Process Synthesis and Development: Creams and Pastes. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 2746–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, T.M.; Mijaljica, D.; Townley, J.P.; Spada, F.; Harrison, I.P. Vehicles for Drug Delivery and Cosmetic Moisturizers: Review and Comparison. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Jung, E.-C.; Zhu, H.; Zou, Y.; Hui, X.; Maibach, H. Vehicle Effects on Human Stratum Corneum Absorption and Skin Penetration. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadzovska, D.; Brooks, J.D.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Riviere, J.E. Predicting Skin Permeability from Complex Vehicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohynek, G.J.; Schaefer, H. Benefit and Risk of Organic Ultraviolet Filters. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 33, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, L.; Turnaturi, R.; Parenti, C.; Pasquinucci, L. In Vitro Evaluation of Sunscreen Safety: Effects of the Vehicle and Repeated Applications on Skin Permeation from Topical Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, S.; Keck, C.M.; Anselmi, C.; Müller, R.H. Skin Photoprotection Improvement: Synergistic Interaction between Lipid Nanoparticles and Organic UV Filters. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 414, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissing, S. Cosmetic Applications for Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN). Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 254, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Jäger, E.; Jäger, A.; Štěpánek, P.; Cano, A.; Viseras, C.; de Melo Barbosa, R.; Chorilli, M.; Zielińska, A.; Severino, P.; et al. Lipid Nanomaterials for Targeted Delivery of Dermocosmetic Ingredients: Advances in Photoprotection and Skin Anti-Aging. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.A.; Contri, R.V.; Beck, R.C.R.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Improving Drug Biological Effects by Encapsulation into Polymeric Nanocapsules. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, J.-P.; Lim, S.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, C.-K. Stabilization of All-Trans Retinol by Loading Lipophilic Antioxidants in Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Nanostructured Lipid Matrices for Improved Microencapsulation of Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Novel Drug Delivery Systems: Applications, Advantages and Disadvantages. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) for Controlled Drug Delivery- a Review of the State of the Art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglia, C.; Santonocito, D.; Bonaccorso, A.; Musumeci, T.; Ruozi, B.; Pignatello, R.; Carbone, C.; Parenti, C.; Chiechio, S. Lipid Nanoparticle Inclusion Prevents Capsaicin-Induced TRPV1 Defunctionalization. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santonocito, D.; Raciti, G.; Campisi, A.; Sposito, G.; Panico, A.; Siciliano, E.A.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Damiani, E.; Puglia, C. Astaxanthin-Loaded Stealth Lipid Nanoparticles (AST-SSLN) as Potential Carriers for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Formulation Development and Optimization. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, C.; Sinani, G.; Ulker, Z. Current State of Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN and NLC) for Skin Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2023, 29, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samee, A.; Usman, F.; Wani, T.A.; Farooq, M.; Shah, H.S.; Javed, I.; Ahmad, H.; Khan, R.; Zargar, S.; Kausar, S. Sulconazole-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhanced Antifungal Activity: In Vitro and In Vivo Approach. Molecules 2023, 28, 7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassano, R.; Serini, S.; Curcio, F.; Trombino, S.; Calviello, G. Preparation and Study of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Based on Curcumin, Resveratrol and Capsaicin Containing Linolenic Acid. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohaib, M.; Shah, S.U.; Shah, K.U.; Shah, K.U.; Khan, N.R.; Irfan, M.M.; Niazi, Z.R.; Alqahtani, A.A.; Alasiri, A.; Walbi, I.A.; et al. Physicochemical Characterization of Chitosan-Decorated Finasteride Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Skin Drug Delivery. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7792180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shidhaye, S.; Vaidya, R.; Sutar, S.; Patwardhan, A.; Kadam, V. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers – Innovative Generations of Solid Lipid Carriers. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordillo-Galeano, A.; Mora-Huertas, C. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: A review emphasizing on particle structure and drug release. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 133, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Klang, V.; Stojcic, T.; Fuchs, C.; Wolzt, M.; Valenta, C. NLC versus Nanoemulsions: Effect on Physiological Skin Parameters during Regular in Vivo Application and Impact on Drug Penetration. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglia, C.; Blasi, P.; Ostacolo, C.; Sommella, E.; Bucolo, C.; Platania, C.B.M.; Romano, G.L.; Geraci, F.; Drago, F.; Santonocito, D.; et al. Innovative Nanoparticles Enhance N-Palmitoylethanolamide Intraocular Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, C.; Patrício, A.B.; Prata, J.M.; Nadhman, A.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Fonte, P. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles vs. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Comparative Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katari, O.; Jain, S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carrier-Based Nanotherapeutics for the Treatment of Psoriasis. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 1857–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.B.; Baldim, I.; Oliveira, W.P.; Rao, R.; Yadav, N.; Gama, F.M.; Mahant, S. SLN and NLC for Topical, Dermal, and Transdermal Drug Delivery. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, L.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Ottimo, S.; Puglisi, G.; Castelli, F. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Studies on Sunscreen Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Prepared by the Phase Inversion Temperature Method. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissing, S.A.; Müller, R.H. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carrier for Sunscreens: In Vitro Release and in Vivo Skin Penetration. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglia, C.; Damiani, E.; Offerta, A.; Rizza, L.; Tirendi, G.G.; Tarico, M.S.; Curreri, S.; Bonina, F.; Perrotta, R.E. Evaluation of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) and Nanoemulsions as Carriers for UV-Filters: Characterization, in Vitro Penetration and Photostability Studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 51, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacatusu, I.; Badea, N.; Murariu, A.; Bojin, D.; Meghea, A. Effect of UV Sunscreens Loaded in Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: A Combinated SPF Assay and Photostability. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 523, 247/[819]–259/[831]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelain, E.; Gabard, B. Photostabilization of Butyl Methoxydibenzoylmethane (Avobenzone) and Ethylhexyl Methoxycinnamate by Bis-Ethylhexyloxyphenol Methoxyphenyl Triazine (Tinosorb S), a New UV Broadband Filter. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 74, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benevenuto, C.G.; Guerra, L.O.; Gaspar, L.R. Combination of Retinyl Palmitate and UV-Filters: Phototoxic Risk Assessment Based on Photostability and in Vitro and in Vivo Phototoxicity Assays. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 68, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, T.S.; Moreira, L.M.C.C.; Oliveira, T.M.T.; Melo, D.F.; Azevedo, E.P.; Gadelha, A.E.G.; Fook, M.V.L.; Oshiro-Júnior, J.A.; Damasceno, B.P.G.L. Bemotrizinol-Loaded Carnauba Wax-Based Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Sunscreen: Optimization, Characterization, and In Vitro Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira Gomes, J.V.; Cherem Peixoto da Silva, A.; Lamim Bello, M.; Rangel Rodrigues, C.; Aloise Maneira Corrêa Santos, B. Molecular Modeling as a Design Tool for Sunscreen Candidates: A Case Study of Bemotrizinol. J. Mol. Model. 2019, 25, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ruiz, C.D.; Plautz, J.R.; Schuetz, R.; Sanabria, C.; Hammonds, J.; Erato, C.; Klock, J.; Vollhardt, J.; Mesaros, S. Preliminary Clinical Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Bemotrizinol - A New Sunscreen Active Ingredient Being Considered for Inclusion under FDA’s over-the-Counter (OTC) Sunscreen Monograph. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 139, 105344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, L.; Santonocito, D.; Castelli, F.; Russo, R.; Puglia, C.; Sarpietro, M.G. Bemotrizinol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for the Development of Sunscreen Emulsions. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2024. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Lukic, M.; Jaksic, I.; Krstonosic, V.; Cekic, N.; Savic, S. A Combined Approach in Characterization of an Effective w/o Hand Cream: The Influence of Emollient on Textural, Sensorial and in Vivo Skin Performance. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2012, 34, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, L.; Rapisarda, L.; Ministeri, C.; Puglisi, G. Effects of Lipids and Emulsifiers on the Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Cosmetic Emulsions Containing Vitamin E. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, B.; Verma, S. Preparation and Evaluation of Novel In Situ Gels Containing Acyclovir for the Treatment of Oral Herpes Simplex Virus Infections. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 280928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.; Lippacher, A.; Müller, R. Investigations on the Occlusive Properties of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN). J. Cosmet. Sci. 2001, 52, 313–324. [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro, L.; Santagati, L. Use of Vegetable Oils to Improve the Sun Protection Factor of Sunscreen Formulations. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamustafa, F.; Çelebi, N. Development of an Oral Microemulsion Formulation of Alendronate: Effects of Oil and Co-Surfactant Type on Phase Behaviour. J. Microencapsul. 2008, 25, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufahrt, A.; Förster, F.J.; Heine, H.; Schaeg, G.; Leonhardi, G. Long-Term Tissue Culture of Epithelial-like Cells from Human Skin (NCTC Strain 2544). Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1976, 256, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglia, C.; Tropea, S.; Rizza, L.; Santagati, N.A.; Bonina, F. In Vitro Percutaneous Absorption Studies and in Vivo Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Essential Fatty Acids (EFA) from Fish Oil Extracts. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 299, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.R.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Cabral, C.; Garcia, M.L.; Souto, E.B. Release Kinetics and Cell Viability of Ibuprofen Nanocrystals Produced by Melt-Emulsification. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 166, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Madsen, F.B.; Eriksen, S.H.; Andersen, A.J.C.; Skov, A.L. A Reliable Quantitative Method for Determining CBD Content and Release from Transdermal Patches in Franz Cells. Phytochem. Anal. 2022, 33, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, R.D.; Akanji, T.; Li, H.; Shen, J.; Allababidi, S.; Seeram, N.P.; Bertin, M.J.; Ma, H. Evaluations of Skin Permeability of Cannabidiol and Its Topical Formulations by Skin Membrane-Based Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay and Franz Cell Diffusion Assay. Med. Cannabis Cannabinoids 2022, 5, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.P.; Elkins, J.; Lam, S.-Y.; Skelly, J.P. Determination of in Vitro Drug Release from Hydrocortisone Creams. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 53, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, D.R. In Vitro Skin Permeation Techniques. J. Control. Release 1992, 18, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Colantonio, S.; Dawson, A.; Lin, X.; Beecker, J. Sunscreen Application, Safety, and Sun Protection: The Evidence. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2019, 23, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Shin, S.; Ryu, D.; Cho, E.; Yoo, J.; Park, D.; Jung, E. Evaluating the Sun Protection Factor of Cosmetic Formulations Containing Afzelin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, c21-00398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breneman, A. Sun Protection Factor Testing: A Call for an In Vitro Method. Cutis 2022, 110, E15–E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageon, L.; Moyal, D.; Coutet, J.; Candau, D. Importance of Sunscreen Products Spreading Protocol and Substrate Roughness for in Vitro Sun Protection Factor Assessment. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardeike, J.; Hommoss, A.; Müller, R.H. Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN, NLC) in Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Dermal Products. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 366, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, E.A.; Oliveira, D.A.G.d.C.; Kedor-Hackmann, E.R.M.; Santoro, M.I.R.M. Determination of Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of Sunscreens by Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry. Rev. Bras. De. Ciências Farm. 2004, 40, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayre, R.M.; Agin, P.P.; LeVee, G.J.; Marlowe, E. A Comparison of In Vivo and In Vitro Testing of Sunscreening Formulas. Photochem. Photobiol. 1979, 29, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallica, F.; Leonardi, C.; Toscano, V.; Santonocito, D.; Leonardi, P.; Puglia, C. Assessment of Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizers for Long-Term Use, Formulated with Addition of Natural Ingredients in Comparison to Who Formulation 1. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, A.; Du Plessis, J.; Wiechers, J.W. Formulation Effects of Topical Emulsions on Transdermal and Dermal Delivery. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardy, F.; Vennat, B.; Pouget, M.P.; Pourrat, A. Functionalization of Hydrocolloids: Principal Component Analysis Applied to the Study of Correlations Between Parameters Describing the Consistency of Hydrogels. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2000, 26, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Aggarwal, D.; Garg, S.; Singla, A.K. Spreading of Semisolid Formulations: An Update. Pharm. Technol. 2002, 26, 84–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, L.; Parenti, C.; Turnaturi, R.; Pasquinucci, L. Resveratrol-Loaded Lipid Nanocarriers: Correlation between In Vitro Occlusion Factor and In Vivo Skin Hydrating Effect. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.A.; Müller, R.H. The Influence of the Crystallinity of Lipid Nanoparticles on Their Occlusive Properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, R.C.; Maibach, H.I. Cutaneous Pharmacokinetics: 10 Steps to Percutaneous Absorption. Drug Metab. Rev. 1983, 14, 169–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Sun protection factor (SPF) Test Method. COLIPA Guidelines 2006. Available online: https://downloads.regulations.gov›attachment_65 (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- ISO 24444:2019(E); Cosmetics—Sun Protection Test Methods—In Vivo Determination of the Sun Protection Factor (SPF). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:24444:ed-2:v1:en (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Sheu, M.-T.; Lin, C.-W.; Huang, M.-C.; Shen, C.-H.; Ho, H.-O. Correlation of in Vivo and in Vitro Measurements of Sun Protection Factor. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pissavini, M.; Tricaud, C.; Wiener, G.; Lauer, A.; Contier, M.; Kolbe, L.; Trullás Cabanas, C.; Boyer, F.; Meredith, E.; de Lapuente, J.; et al. Validation of a New in Vitro Sun Protection Factor Method to Include a Wide Range of Sunscreen Product Emulsion Types. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2020, 42, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, E.P.; Freitas, Z.M.; Souza, K.R.; Garcia, S.; Vergnanini, A. In Vitro and In Vivo Determinations of Sun Protection Factors of Sunscreen Lotions with Octylmethoxycinnamate. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 1999, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraf, S.; Kaur, C. In Vitro Sun Protection Factor Determination of Herbal Oils Used in Cosmetics. Pharmacogn. Res. 2010, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netto MPharm, G.; Jose, J. Development, Characterization, and Evaluation of Sunscreen Cream Containing Solid Lipid Nanoparticles of Silymarin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ácsová, A.; Hojerová, J.; Janotková, L.; Bendová, H.; Jedličková, L.; Hamranová, V.; Martiniaková, S. The Real UVB Photoprotective Efficacy of Vegetable Oils: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2021, 20, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.I.; Liu, S.; Brooks, G.J.; Lanctot, Y.; Gruber, J. V Reliable and Simple Spectrophotometric Determination of Sun Protection Factor: A Case Study Using Organic UV Filter-based Sunscreen Products. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermund, D.B.; Torsteinsen, H.; Vega, J.; Figueroa, F.L.; Jacobsen, C. Screening for New Cosmeceuticals from Brown Algae Fucus Vesiculosus with Antioxidant and Photo-Protecting Properties. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.G.; Bagora, N.; Nayak, M.; Ajish, J.K.; Gupta, N.; Kunwar, A. The Preparation of Curcumin-Loaded Pickering Emulsion Using Gelatin–Chitosan Colloidal Particles as Emulsifier for Possible Application as a Bio-Inspired Cosmetic Formulation. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liao, H.; Dai, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zou, Z. Characterization and Anti-Ultraviolet Radiation Activity of Proanthocyanidin-Rich Extracts from Cinnamomum camphora by Ultrasonic-Assisted Method. Molecules 2024, 29, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissing, S.A.; Müller, R.H. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN)-a Novel Carrier for UV Blockers. Pharmazie 2001, 56, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Araújo, M.M.; Schneid, A.C.; Oliveira, M.S.; Mussi, S.V.; de Freitas, M.N.; Carvalho, F.C.; Bernes Junior, E.A.; Faro, R.; Azevedo, H. NLC-Based Sunscreen Formulations with Optimized Proportion of Encapsulated and Free Filters Exhibit Enhanced UVA and UVB Photoprotection. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubuisson, P.; Picard, C.; Grisel, M.; Savary, G. How Does Composition Influence the Texture of Cosmetic Emulsions? Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 536, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc-Musioł, B.; Siemiradzka, W.; Dolińska, B. Formulation and Evaluation of Hydrogels Based on Sodium Alginate and Cellulose Derivatives with Quercetin for Topical Application. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, E.; Picard, C.; Savary, G. Spreading Behavior of Cosmetic Emulsions: Impact of the Oil Phase. Biotribology 2018, 16, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, G.M.S.; Srebernich, S.M.; de Macedo Souza, J.A. Stability and Sensory Assessment of Emulsions Containing Propolis Extract and/or Tocopheryl Acetate. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 47, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcast, D.; Clegg, S. Sensory Perception of Creaminess and Its Relationship with Food Structure. Food Qual. Prefer. 2002, 13, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).